Development of an Innovative Dual Construct for Targeted Drug Delivery in the Oral Cavity
Abstract
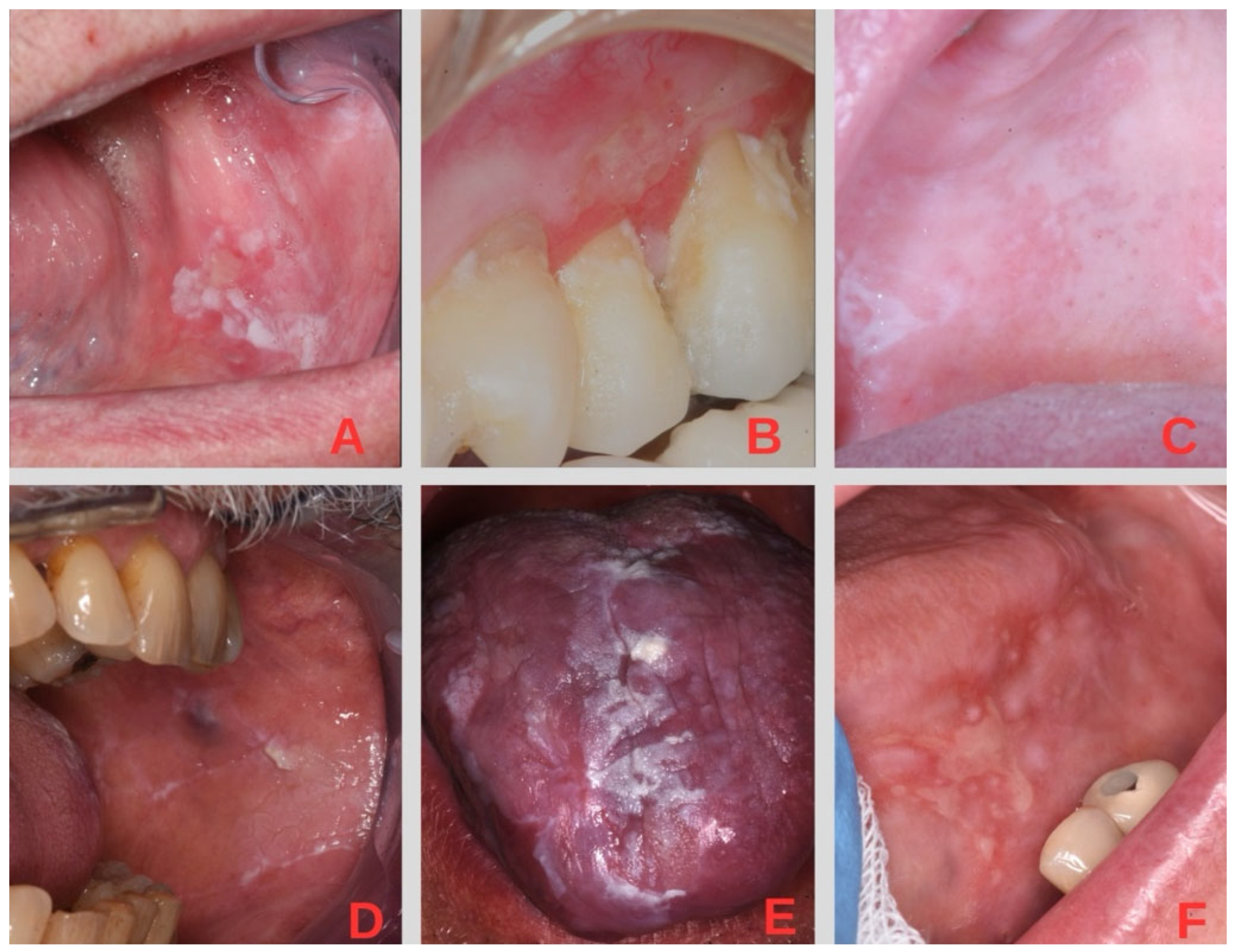
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Human Fibroblast Isolation and Cell Cultures
2.2.2. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity Induced by DEX Without a Carrier (DEX-f)
2.2.3. HPLC Analysis
2.2.4. Preparation and Characterization of Polylactic Acid and Chitosan–Polylactic Acid-Based Fibers (PLA-FBs and CS-PLA-FBs)
2.2.5. Preparation and Characterization of DEX-Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) Nanoparticles (DEX-PLGA-NPs)
2.2.6. Cellular Uptake of 6-Coumarin-Loaded PLGA-NPs
2.2.7. Effect of CS-PLA-FBs and DEX-PLGA-NPs on Cell Viability
2.2.8. In Vitro Release Studies of DEX from PLGA-NPs and Determination of Intracellular Concentrations
2.2.9. Mucin–CS-PLA-FB Interaction
2.2.10. PLGA-NP Integration into PLA-FBs and Cellular Uptake
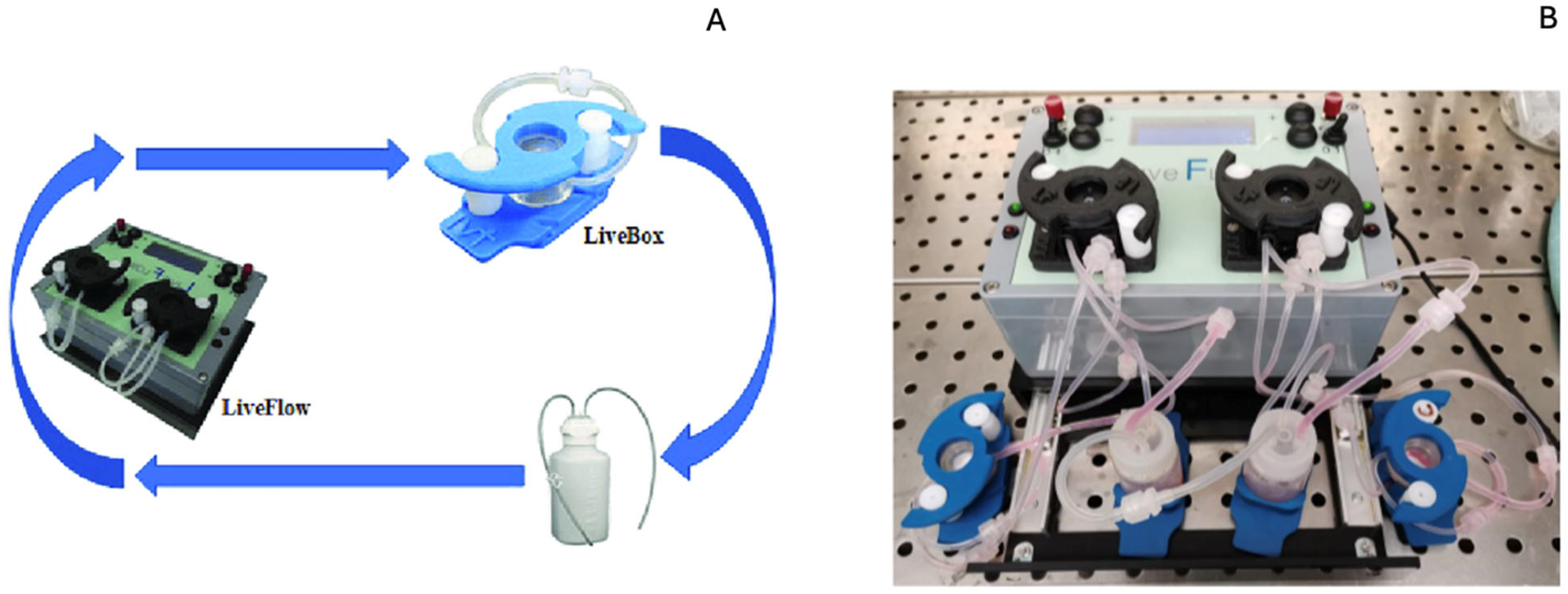
2.2.11. Test in Bioreactor
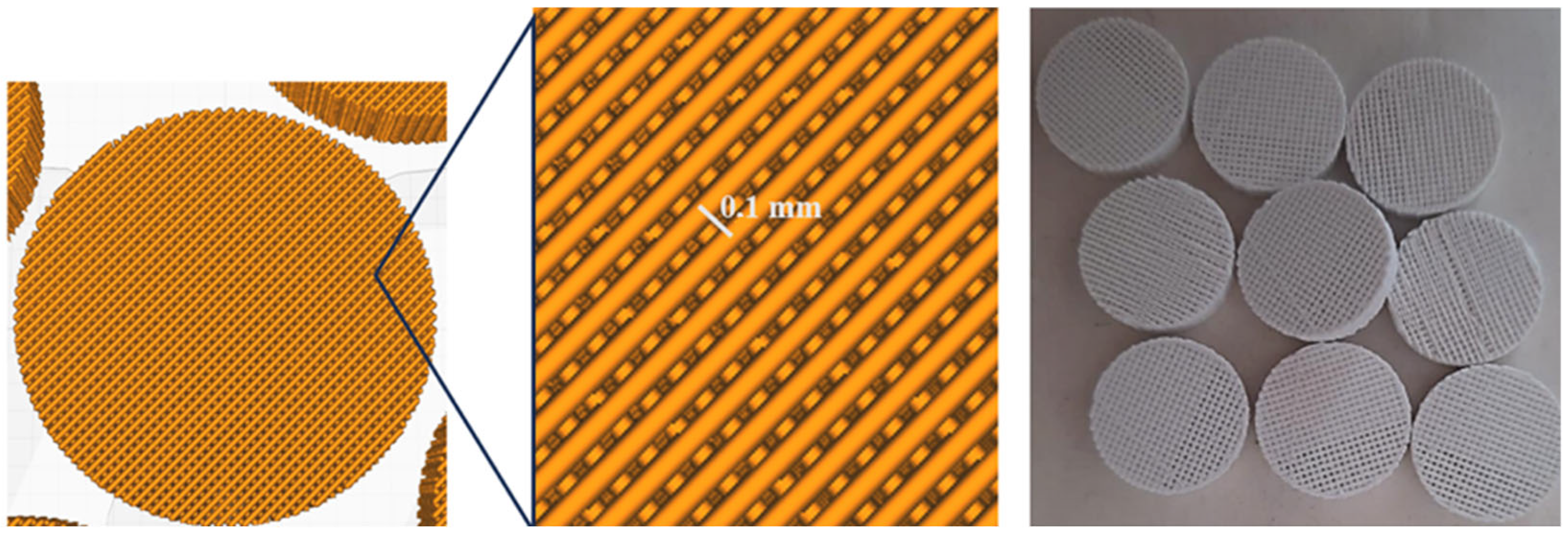
2.2.12. Production of 3D PLA Scaffolds
2.2.13. Cell Proliferation on PLA Scaffolds
2.2.14. DEX Releasing Test and Quantification of Intracellular Concentration
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity Induced by DEX-f
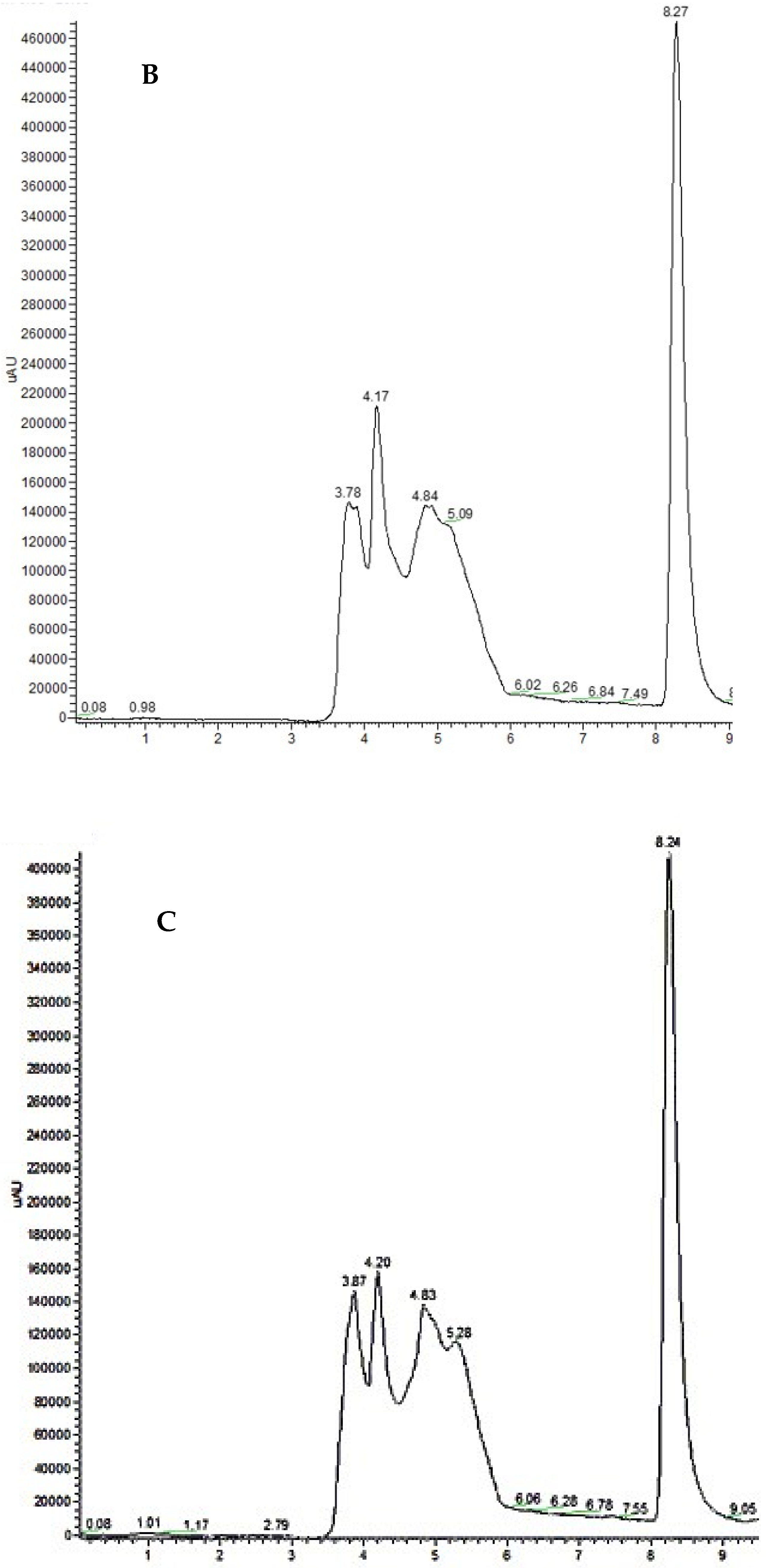
3.2. HPLC Analysis and Recovery Efficiency
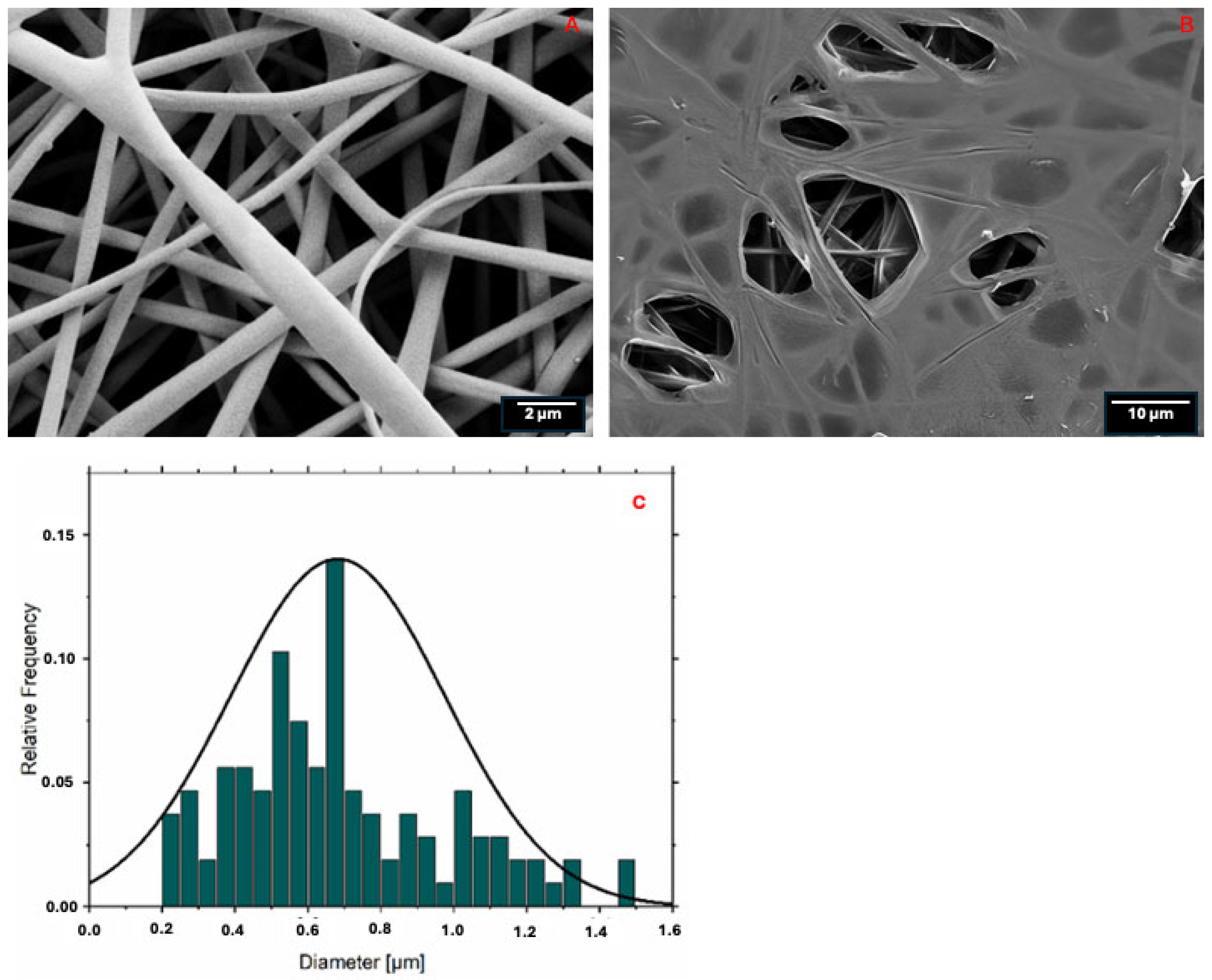
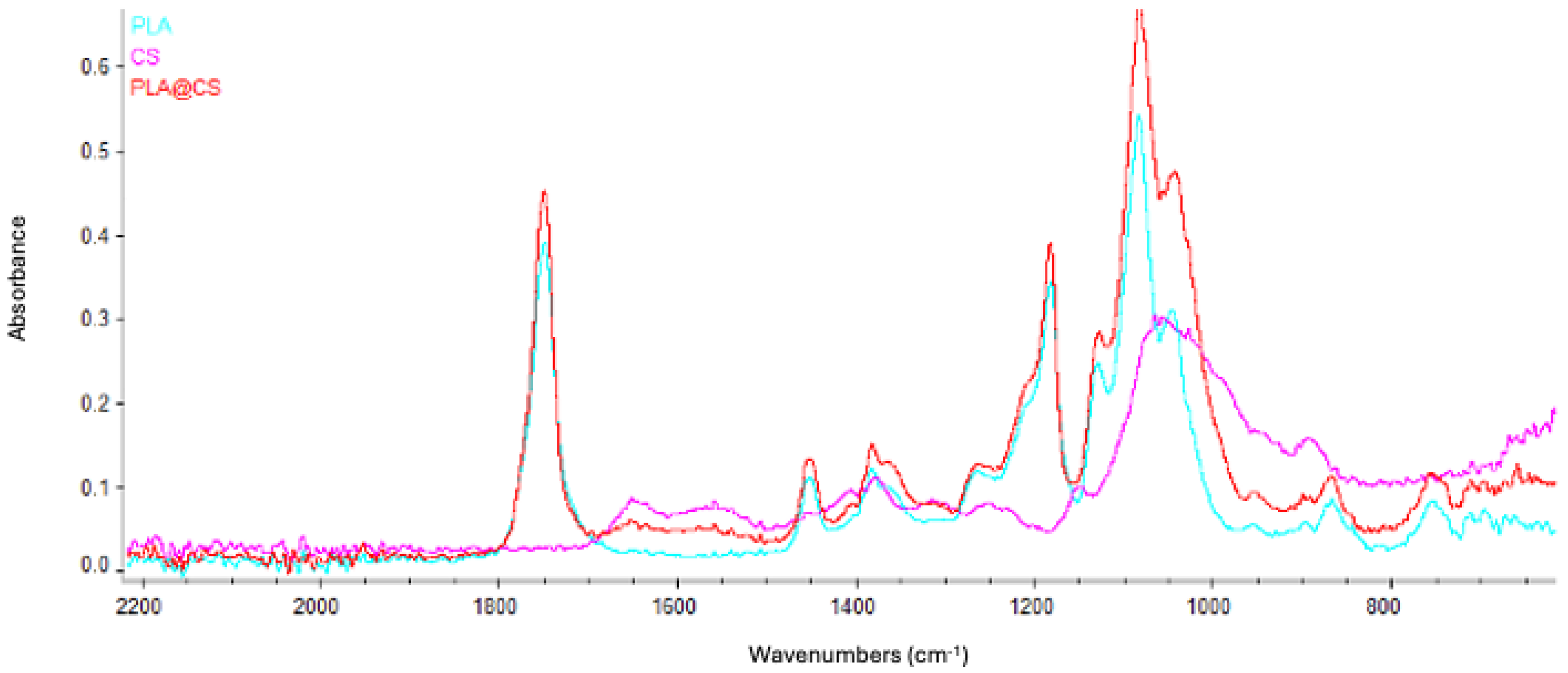
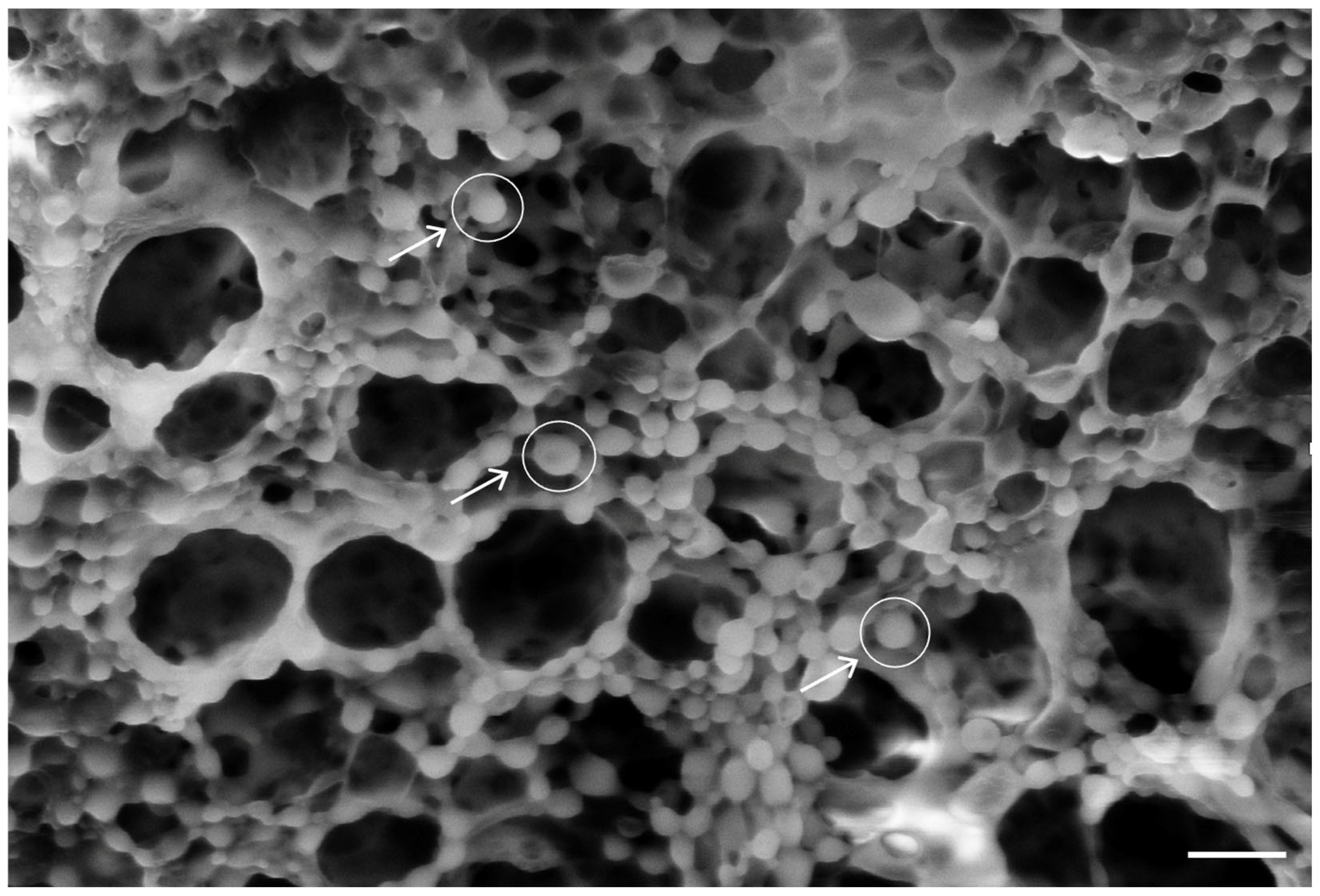
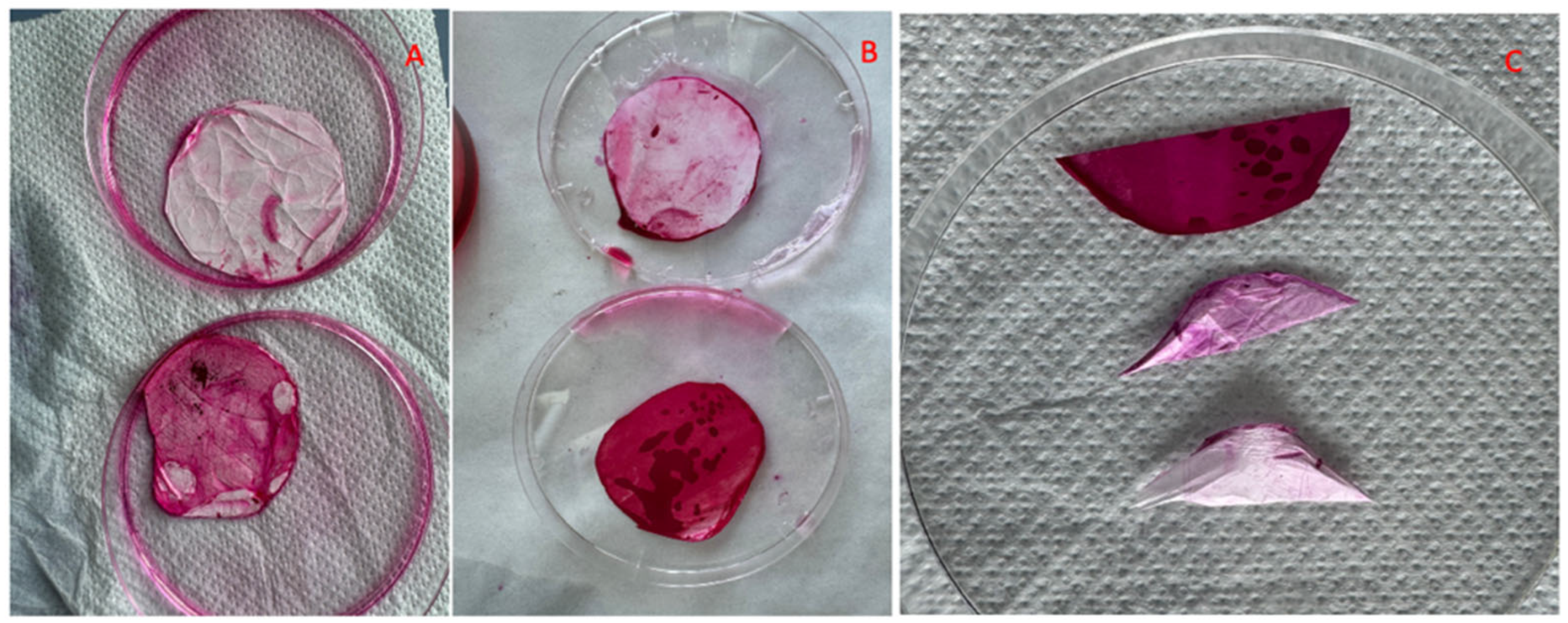
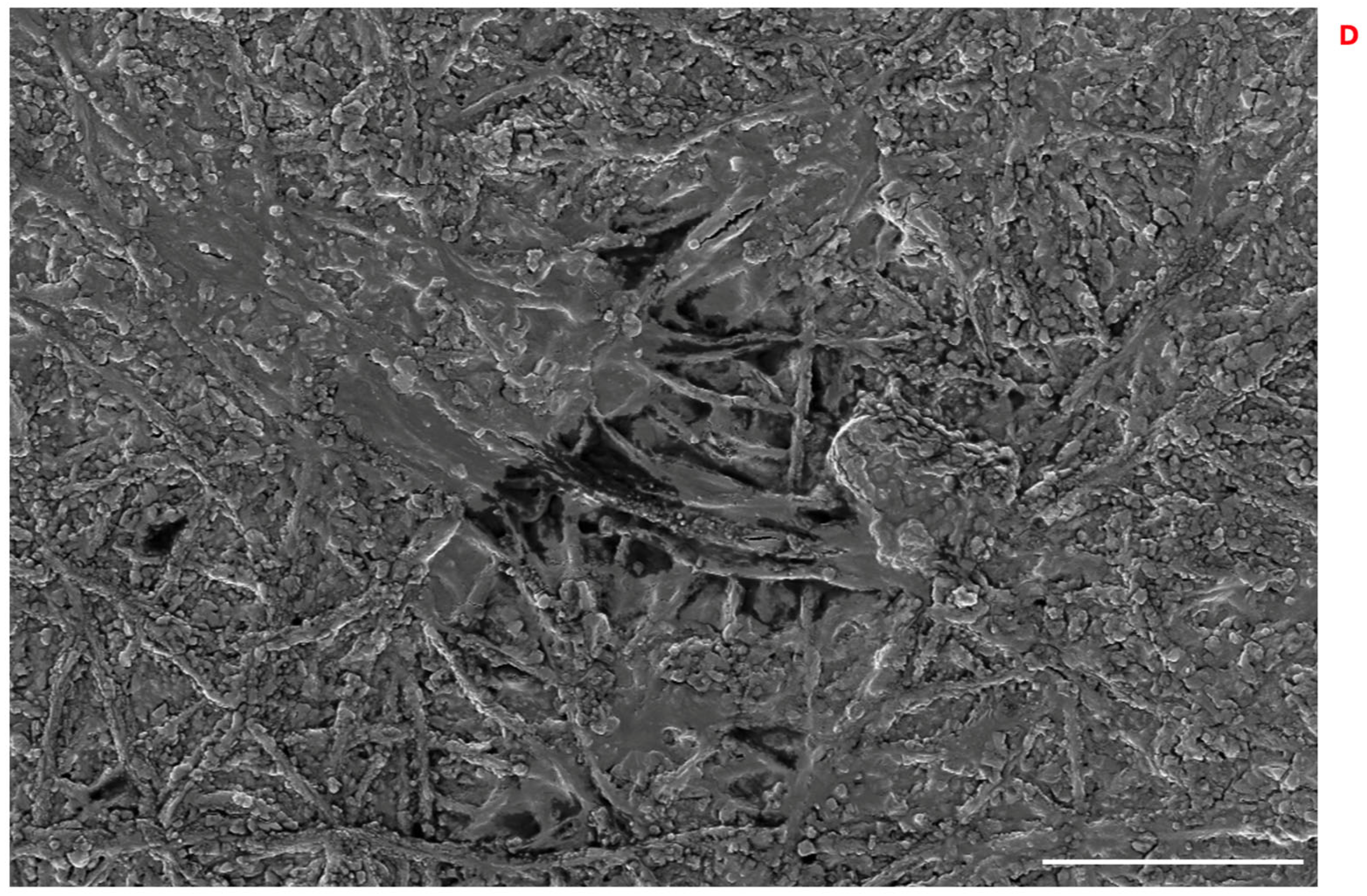
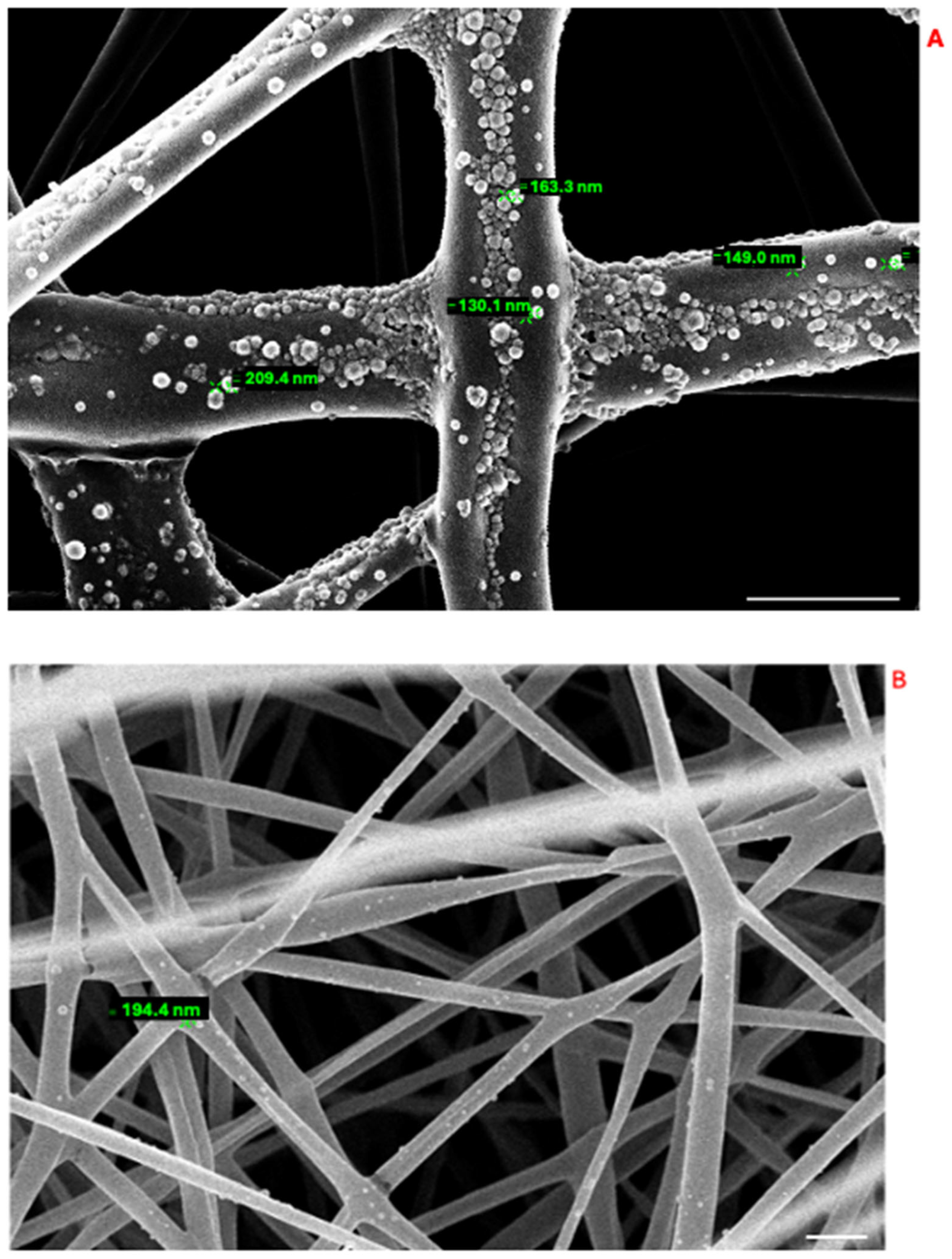
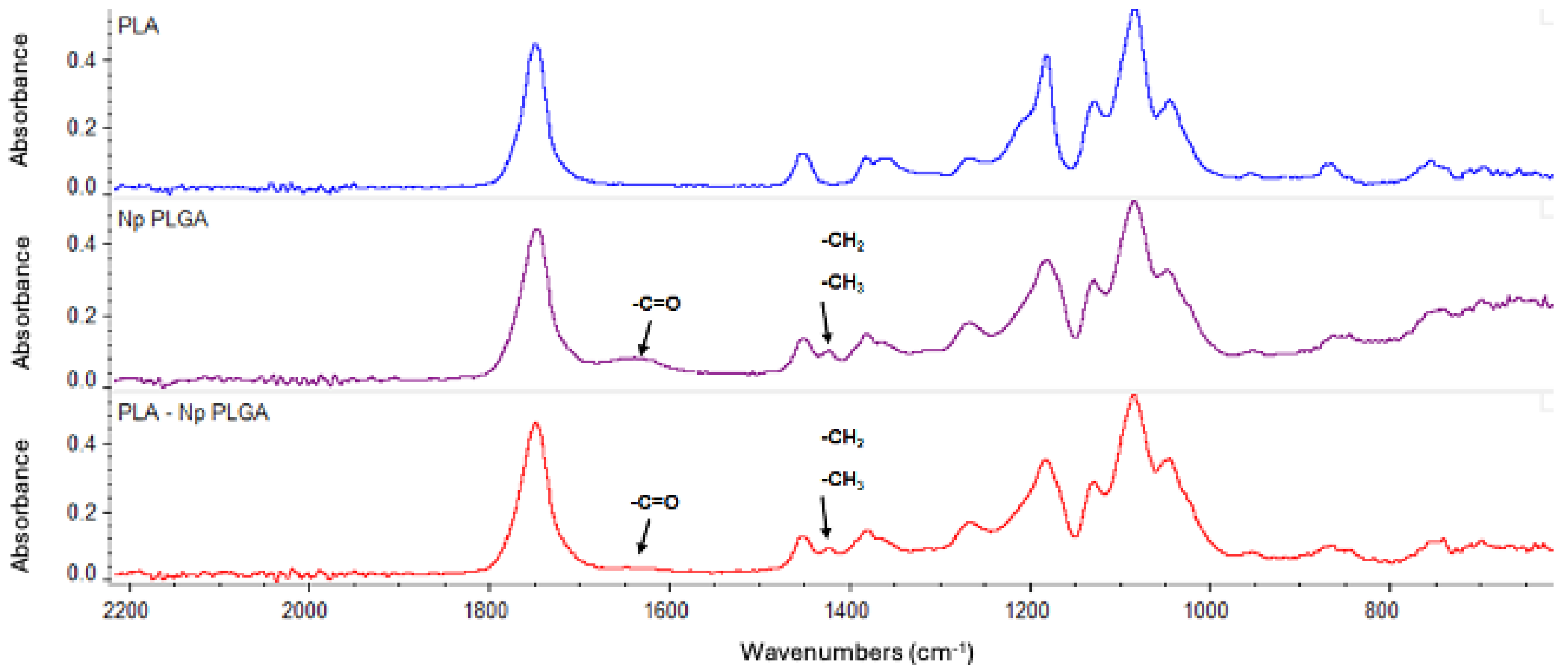
3.3. PLA-FB, CS-PLA-FB, and PLGA-NP Characterization
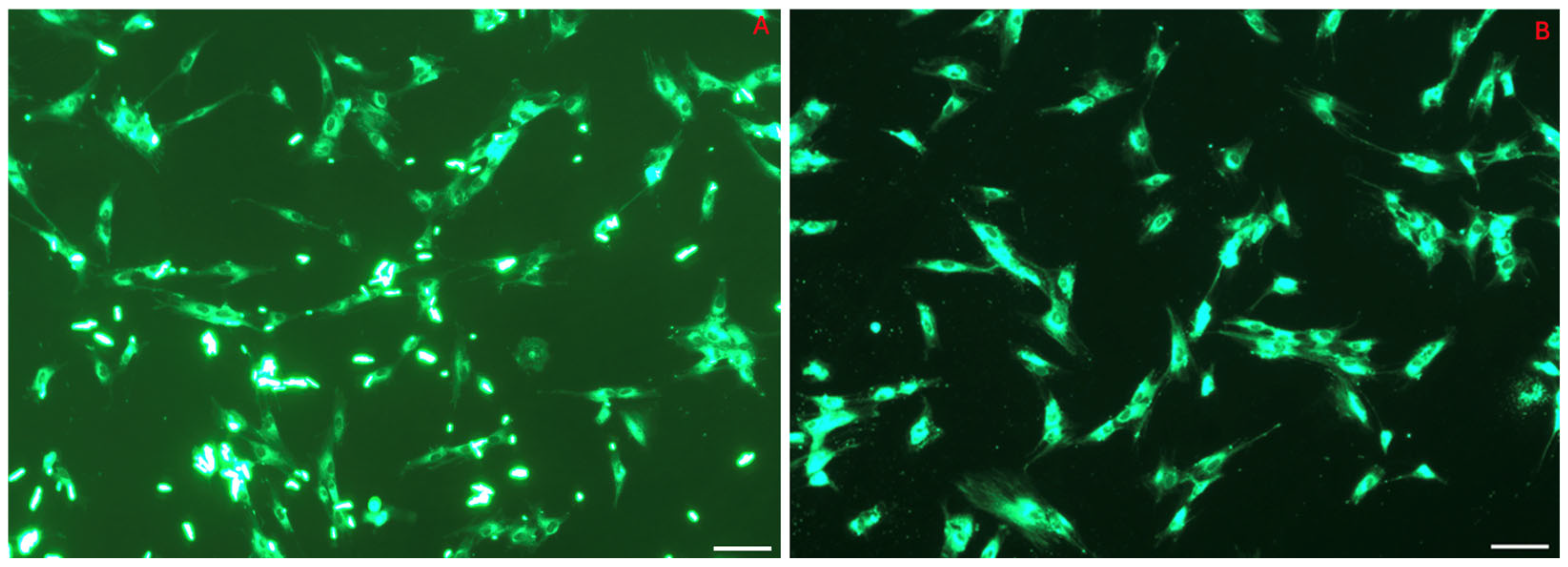
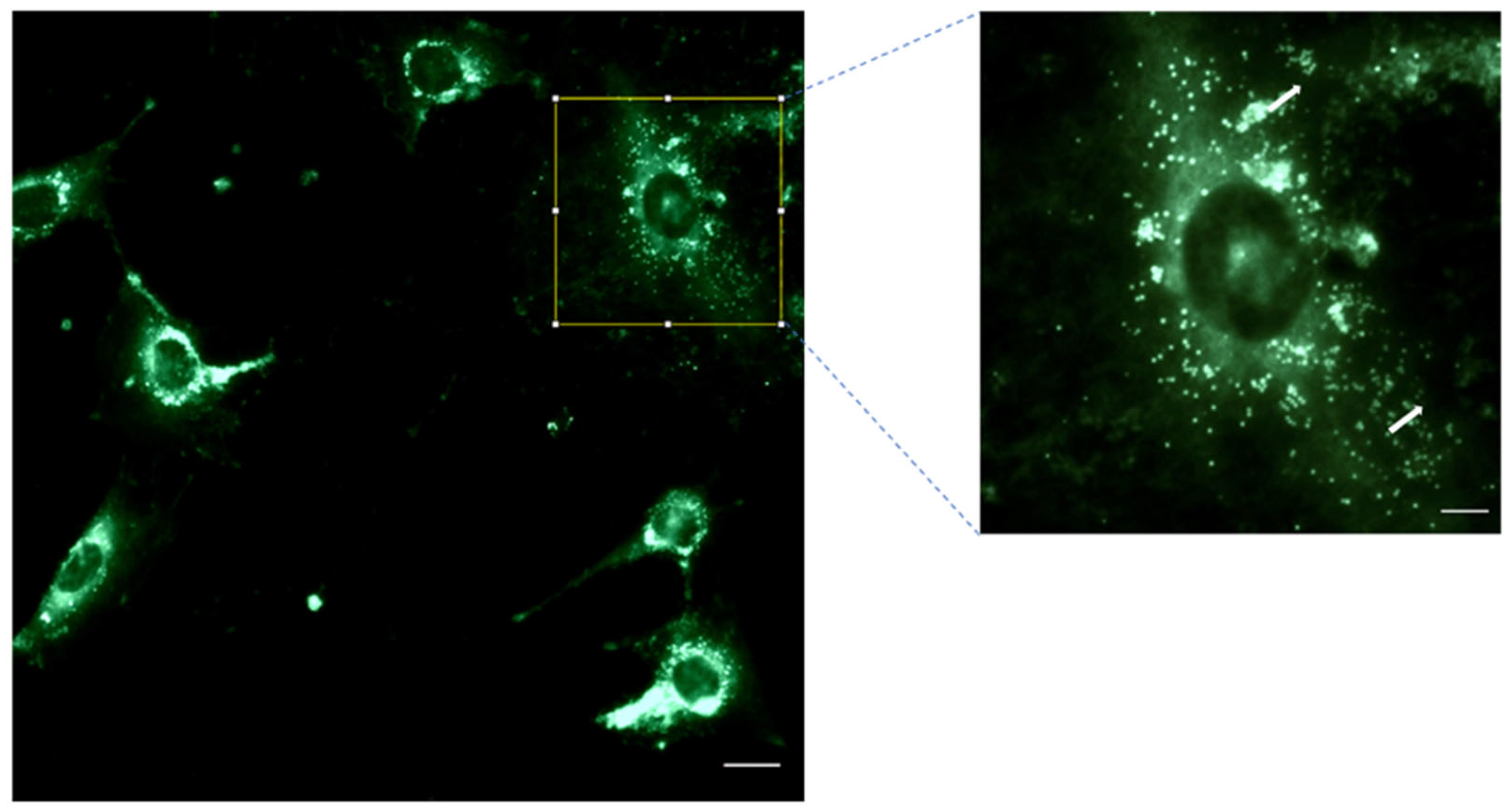
3.4. NP Cell Uptake: Internalization of 6-Coumarin
3.5. Effect of CS-PLA-FBs and DEX-PLGA-NPs on Cell Viability
3.6. Intracellular Concentrations of DEX from PLGA-NPs
3.7. Mucin–CS-PLA-FB Interaction
3.8. PLGA-NP Integration into PLA-FBs and Release in DMEM
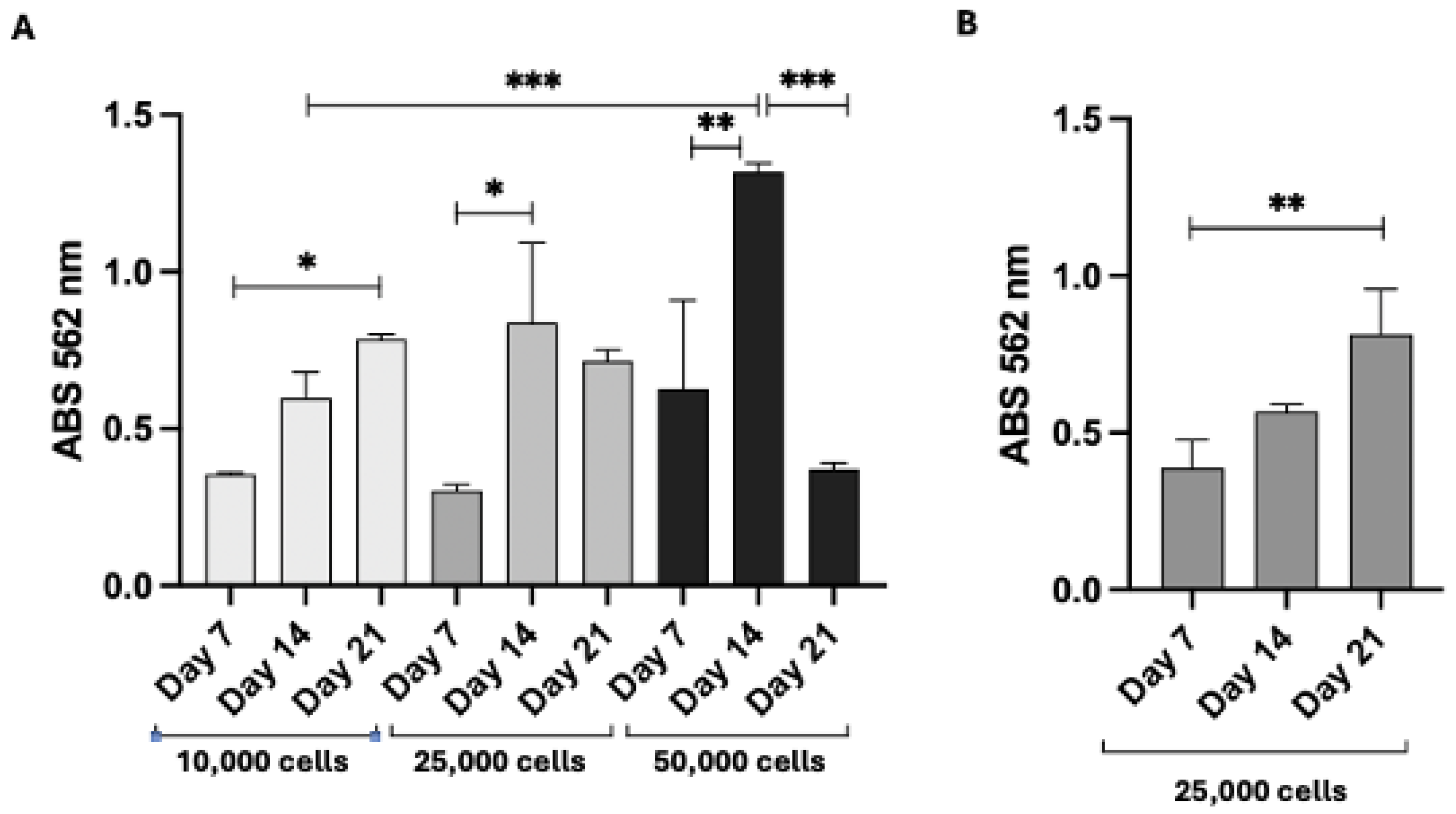
3.9. Proliferation of 3T3 Swiss Fibroblasts and HFs on PLA Scaffolds and DEX Intracellular Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: A Comprehensive Review on Clinical Aspects and Management. Oral Oncol. 2020, 102, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Lodi, G. Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: Proceedings from an Expert Symposium. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1859–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, M.; Troiano, G.; Cordaro, M.; Corsalini, M.; Gioco, G.; Lo Muzio, L.; Pignatelli, P.; Lajolo, C. Rate of Malignant Transformation of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, J.; Patel, D.; Campbell, J.H. Oral Lichen Planus. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 25, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moles, M.Á.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; González-Ruiz, I.; González-Ruiz, L.; Ayén, Á.; Lenouvel, D.; Ruiz-Ávila, I.; Ramos-García, P. Worldwide Prevalence of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moles, M.Á.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; González-Ruiz, I.; González-Ruiz, L.; Ayén, Á.; Lenouvel, D.; Ruiz-Ávila, I.; Ramos-García, P. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Characteristics of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Arising in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and a Comprehensive Meta-Analysis. Oral Oncol. 2020, 106, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Moles, M.A.; Scully, C.; Gil-Montoya, J.A. Oral Lichen Planus: Controversies Surrounding Malignant Transformation. Oral Dis. 2008, 14, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerame, D.; Sossi, D.; De Biasi, M.; Tommasin, E.; Castaldo, A.; Marigo, L.; Castagnola, R.; Somma, F. Trattamenti Endodontici Semplificati Di Lesioni Periapicali: Valutazione Del Risultato Clinico Con Digital Subtraction Radiography. G. Ital. Endod. 2013, 27, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrozzo, M.; Porter, S.; Mercadante, V.; Fedele, S. Oral Lichen Planus: A Disease or a Spectrum of Tissue Reactions? Types, Causes, Diagnostic Algorhythms, Prognosis, Management Strategies. Periodontology 2000 2019, 80, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbari, S.M.H.; Abushouk, A.I.; Attia, A.; Elmaraezy, A.; Menshawy, A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Elsaadany, B.A.; Ahmed, E.M. Malignant Transformation of Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Lichenoid Lesions: A Meta-Analysis of 20095 Patient Data. Oral Oncol. 2017, 68, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, G.; Viviano, M.; Chisci, E.; Chisci, G.; Picciotti, M. A Comparative Immunohistochemical and Immunophenotypical Study on Lymphocytes Expression in Patients Affected by Oral Lichen Planus. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2013, 42, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chainani-Wu, N.; Silvermam, S.; Lozada-Nur, F.; Mayer, P.; Watson, J.J. Oral Lichen Planus: Patient Profile, Disease Progression and Treatment Responses. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2001, 132, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Johani, K.A.; Hegarty, A.M.; Porter, S.R.; Fedele, S. Calcineurin Inhibitors in Oral Medicine. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 61, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewska-Kuska, M.; Ślebioda, Z.; Dorocka-Bobkowska, B. The Effectiveness of Topical Forms of Dexamethasone in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus—A Systematic Review. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, G.; Rad, M.; Zarei, M.R.; Lotfi, S.; Sadeghi, M.; Ahmadi, Z. Efficacy of Tacrolimus and Clobetasol in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, C.; Eisen, D.; Carrozzo, M. Management of Oral Lichen Planus. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2000, 1, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, T.d.S.F.; de Fatima Correia Silva Alves, J.; Gomes, C.C.; Nascimento, A.R.d.; de Resende Stoianoff, M.A.; Gomez, R.S. Kinetics of Oral Colonization by Candida Spp. during Topical Corticotherapy for Oral Lichen Planus. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2014, 43, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzinelli, E.; Favuzzi, I.; Arcovito, A.; Castagnola, R.; Fratocchi, G.; Mordente, A.; Nocca, G. Oral Mucosa Models to Evaluate Drug Permeability. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümrü, B.; Akkitap, M.P. Oral Candidiasis as a Local Adverse Effect of Inhaled Corticosteroids: What the Dental Practitioner Should Know. Black Sea J. Health Sci. 2022, 5, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffleur, F. Mucoadhesive Polymers for Buccal Drug Delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat-Miller, N.; Chittchang, M.; Johnston, T.P. The Use of Mucoadhesive Polymers in Buccal Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1666–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotaru, D.; Chisnoiu, R.; Picos, A.; Picos, A.; Chisnoiu, A. Treatment Trends in Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Lichenoid Lesions (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamishehkar, H.; Nokhodchi, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Kouhsoltani, M. Triamcinolone Acetonide Oromucoadhesive Paste for Treatment of Aphthous Stomatitis. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Salmeron, R.; Toussaint, B.; Huang, N.; Bourgeois Ducournau, E.; Alviset, G.; Goulay Dufaÿ, S.; Hillaireau, H.; Dufaÿ Wojcicki, A.; Boudy, V. Mucoadhesive Poloxamer-Based Hydrogels for the Release of HP-β-CD-Complexed Dexamethasone in the Treatment of Buccal Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, S.; Nepal, P.; Ghimire, G.; Basnet, R.; Rawat, I.; Dahal, A.; Pandey, J.; Parajuli-Baral, K. Formulation and Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Buccal Tablets of Aceclofenac. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orekhova, A.; Palocci, C.; Chronopoulou, L.; De Angelis, G.; Badiali, C.; Petruccelli, V.; D’Angeli, S.; Pasqua, G.; Simonetti, G. Poly-(lactic-co-glycolic) Acid Nanoparticles Entrapping Pterostilbene for Targeting Aspergillus Section Nigri. Molecules 2022, 27, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Yamada, K.; Miyake, M.; Onoue, S. Recent Advancements in the Development of Nanocarriers for Mucosal Drug Delivery Systems to Control Oral Absorption. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ghahramani, Y.; Azhdari, R.; Yousefi, K.; Gholami, A.; Fallahi Nezhad, F.; Vijayakameswara Rao, N.; Omidifar, N.; Chiang, W.H. Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Effects of Graphene Oxide @AlFu MOF Based Saponin Natural Product on OSCC Line. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Bahrani, S.; Yousefi, K.; Behbudi, G.; Babapoor, A.; Omidifar, N.; Lai, C.W.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.H. Recent Advancements in Polythiophene-Based Materials and Their Biomedical, Geno Sensor and DNA Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Zare-Hoseinabadi, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ranjbar, S.; Amani, A.M. Emerging Frontiers in Drug Release Control by Core-Shell Nanofibers: A Review. Drug Metab. Rev. 2019, 51, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciotti, I.; Chronopoulou, L.; Palocci, C.; Amalfitano, A.; Cantiani, M.; Cordaro, M.; Lajolo, C.; Calla, C.; Boninsegna, A.; Lucchetti, D.; et al. Controlled Release of 18-β-Glycyrrhetic Acid by Nanodelivery Systems Increases Cytotoxicity on Oral Carcinoma Cell Line. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 285101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilbey, K. Optimization of Rutin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesized by Single-Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Di Vito, M.; Mazzinelli, E.; Favuzzi, I.; Torelli, R.; Cacaci, M.; Arcovito, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Garzoli, S.; Nocca, G.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde Loaded Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) Microparticles for Antifungal Delivery Application against Resistant Candida albicans and Candida glabrata. Plants 2023, 12, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radicioni, G.; Stringaro, A.; Molinari, A.; Nocca, G.; Longhi, R.; Pirolli, D.; Scarano, E.; Iavarone, F.; Manconi, B.; Cabras, T.; et al. Characterization of the Cell Penetrating Properties of a Human Salivary Proline-Rich Peptide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 2868–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 7405:2018; Dentistry—Evaluation of Biocompatibility of Medical Devices Used in Dentistry. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/71503.html (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Chronopoulou, L.; Cacciotti, I.; Amalfitano, A.; Di Nitto, A.; D’Arienzo, V.; Nocca, G.; Palocci, C. Biosynthesis of Innovative Calcium Phosphate/Hydrogel Composites: Physicochemical and Biological Characterisation. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 095102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sletten, G.B.G.; Dahl, J.E. Cytotoxic Effects of Extracts of Compomers. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1999, 57, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riswanto, F.D.O.; Virginia, D.M.; Putri, D.C.A.; Yuliani, S.H. Analytical Method Validation and Determination of Dexamethasone in Divided Powder Using Reverse Phase HPLC. Pharmaciana 2017, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocca, G.; Callà, C.; Santini, S.A.; Amalfitano, A.; Marigo, L.; Rossetti, D.V.; Spagnuolo, G.; Cordaro, M. Quantitative Determination of 18-β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid in HepG2 Cell Line by High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 2018, 5673186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Reyes, B.L.; Gómez-Muñoz, C.L.; Zaca-Morán, P.; Galindo-Ramírez, F.; Morales-Sánchez, M.A. Fabrication of a PLA/PVA-BIO-HA Polymeric Membrane by the Electrospinning Technique. Fibers 2024, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.F.; Akram, M.; Alshemary, A.; Hussain, R. Antibacterial Polylactic Acid/Chitosan Nanofibers Decorated with Bioactive Glass. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R.; Sovány, T.; Gácsi, A.; Ambrus, R.; Katona, G.; Imre, N.; Csóka, I. Synthesis and Statistical Optimization of Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Encapsulating GLP1 Analog Designed for Oral Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liao, Y.; Tong, X.; Yan, F. Novel Urea Derivative-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles to Inhibit Caries-Associated Streptococcus Mutans. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, X.; Hou, H. Chitosan Interaction with Stomach Mucin Layer to Enhances Gastric Retention and Mucoadhesive Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 121926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Kong, L. Chitosan-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles with Versatile Surface for Improved Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, D.; Robinson, J.R. Drug Delivery via the Mucous Membranes of the Oral Cavity. J. Pharm. Sci. 1992, 81, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junginger, H.E.; Hoogstraate, J.A.; Verhoef, J.C. Recent Advances in Buccal Drug Delivery and Absorption—In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. J. Control. Release 1999, 62, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moles, M.Á. The Use of Topical Corticoids in Oral Pathology. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2010, 15, e827–e831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolina Alves, R.; Perosa Fernandes, R.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Damiani Victorelli, F.; Chorilli, M. A Critical Review of the Properties and Analytical Methods for the Determination of Curcumin in Biological and Pharmaceutical Matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 49, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, R.; Rohani, B.; Golestannejad, Z.; Sadeghian, S.; Mirzaee, S. Comparison of Therapeutic Effect of Mucoadhesive Nano-Triamcinolone Gel and Conventional Triamcinolone Gel on Oral Lichen Planus. Dent. Res. J. 2019, 16, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiras, A.; Vieira, A.; Simoes, S.; Veiga, F. Mucoadhesive Buccal Systems as a Novel Strategy for Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Administration. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 10, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.D.; Sridhar, D.A.; Mallikarjuna, S.C. Drug Delivery from the Oral Cavity: A Focus on Mucoadhesive Buccal Drug Delivery Systems. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 466–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Khar, R.; Ahuja, A.; Kalra, R. Buccoadhesive Erodible Disk for Treatment of Oro-Dental Infections: Design and Characterisation. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 238, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, M.K.; Kwak, B.T.; Choi, H.K. Preparation of Buccal Patch Composed of Carbopol, Poloxamer and Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Hameed, M.M.; Mohamed Khan, S.A.P.; Thamer, B.M.; Rajkumar, N.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Newehy, M. Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications: Methods and Mechanism. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 34, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Maeki, M.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Tokeshi, M. Preparation of Size-Tunable Sub-200 Nm PLGA-Based Nanoparticles with a Wide Size Range Using a Microfluidic Platform. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
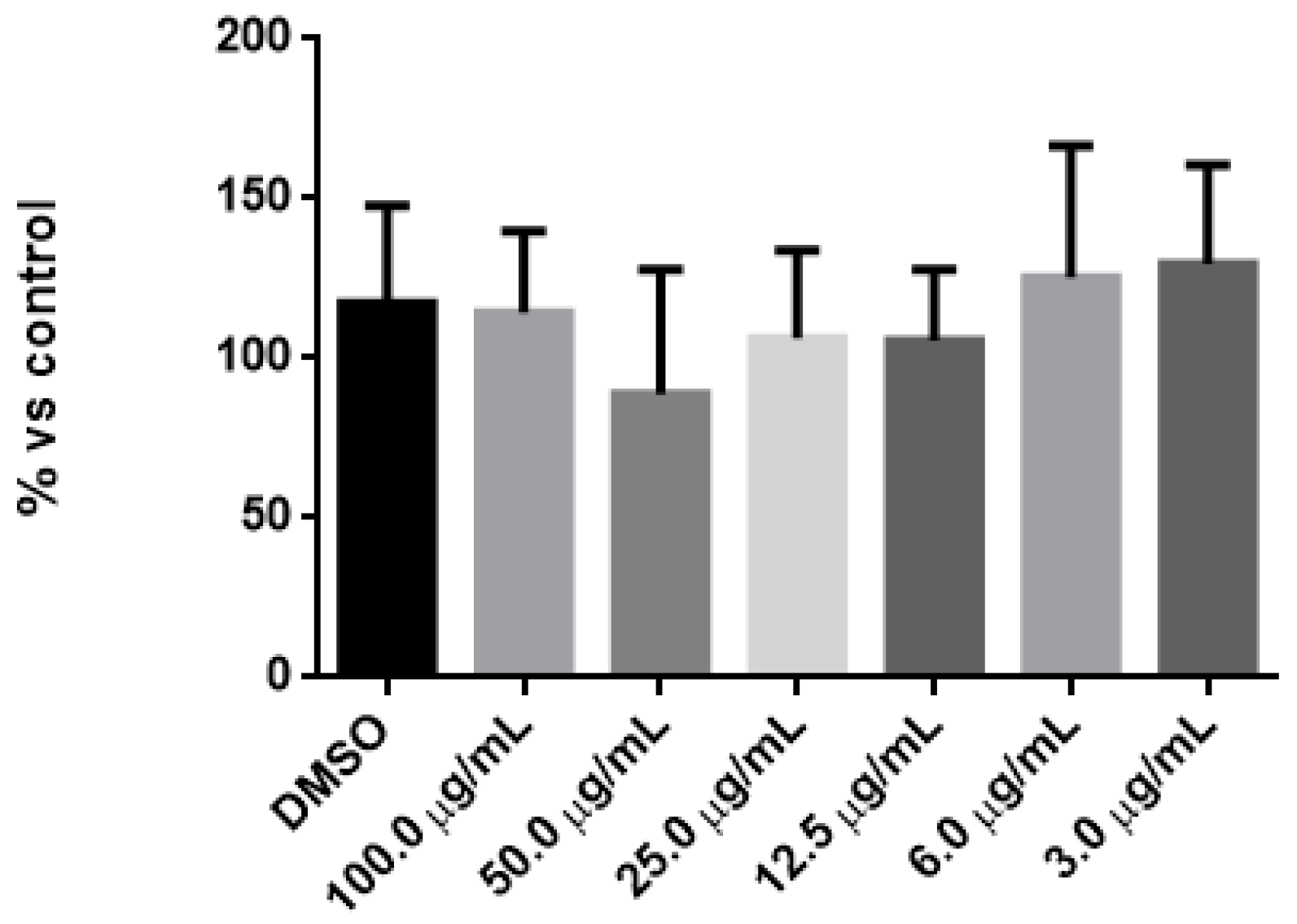



| Tukey’s Multiple Comparisons Test | p Value |
|---|---|
| DMSO vs. 100.0 µg/mL | >0.05 |
| DMSO vs. 50.0 µg/mL | >0.05 |
| DMSO vs. 25.0 µg/mL | >0.05 |
| DMSO vs. 12.5 µg/mL | >0.05 |
| DMSO vs. 6.0 µg/mL | >0.05 |
| DMSO vs. 3.0 µg/mL | >0.05 |
| DEX | |
|---|---|
| Linear regression equation | Y = 3.29 × 106 X + 11,437 |
| DEX concentration range used for the calibration curve | From 0.625 to 5 µg/mL |
| R2 | 0.99 |
| LOD | 0.3 µg/mL |
| LOQ | 0.92 µg/mL |
| Drug Added to Cell Lysates (µg/mL) | Drug Recovery from Cell Lysates (µg/mL) | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEX | 1.85 | 1.79 | 96.7 |
| DEX | 1.72 | 1.68 | 97.7 |
| Intracellular DEX | µg DEX | % of DEX vs. Total DEX |
|---|---|---|
| NPs 4 h | 14.70 ± 2.87 | 2.1 ± 0.41 |
| DEX-f 4 h | 15.75 ± 5.46 | 2.25 ± 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazzinelli, E.; Favuzzi, I.; Messina, M.; Fratocchi, G.; Vincenzoni, F.; Santo Stefano, E.; Cecconi, F.; Lajolo, C.; Basco, A.; Castagnola, R.; et al. Development of an Innovative Dual Construct for Targeted Drug Delivery in the Oral Cavity. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020272
Mazzinelli E, Favuzzi I, Messina M, Fratocchi G, Vincenzoni F, Santo Stefano E, Cecconi F, Lajolo C, Basco A, Castagnola R, et al. Development of an Innovative Dual Construct for Targeted Drug Delivery in the Oral Cavity. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(2):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020272
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazzinelli, Elena, Ilaria Favuzzi, Marianna Messina, Giorgia Fratocchi, Federica Vincenzoni, Eleonora Santo Stefano, Francesco Cecconi, Carlo Lajolo, Alessia Basco, Raffaella Castagnola, and et al. 2025. "Development of an Innovative Dual Construct for Targeted Drug Delivery in the Oral Cavity" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 2: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020272
APA StyleMazzinelli, E., Favuzzi, I., Messina, M., Fratocchi, G., Vincenzoni, F., Santo Stefano, E., Cecconi, F., Lajolo, C., Basco, A., Castagnola, R., Cordaro, M., Scilla, F., Papa, V., Arcovito, A., Cacciotti, I., & Nocca, G. (2025). Development of an Innovative Dual Construct for Targeted Drug Delivery in the Oral Cavity. Pharmaceutics, 17(2), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020272










