Gold-Doped Hybrid Nanoparticles: A Versatile Tool for Multimodal Imaging of Cell Trafficking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Gold-Doped NPs
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of NPs
2.4. In Vitro Characterization of NPs
2.5. Fluorescence-Free High-Resolution Imaging
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Gold-Doping on the Physicochemical Properties of NPs
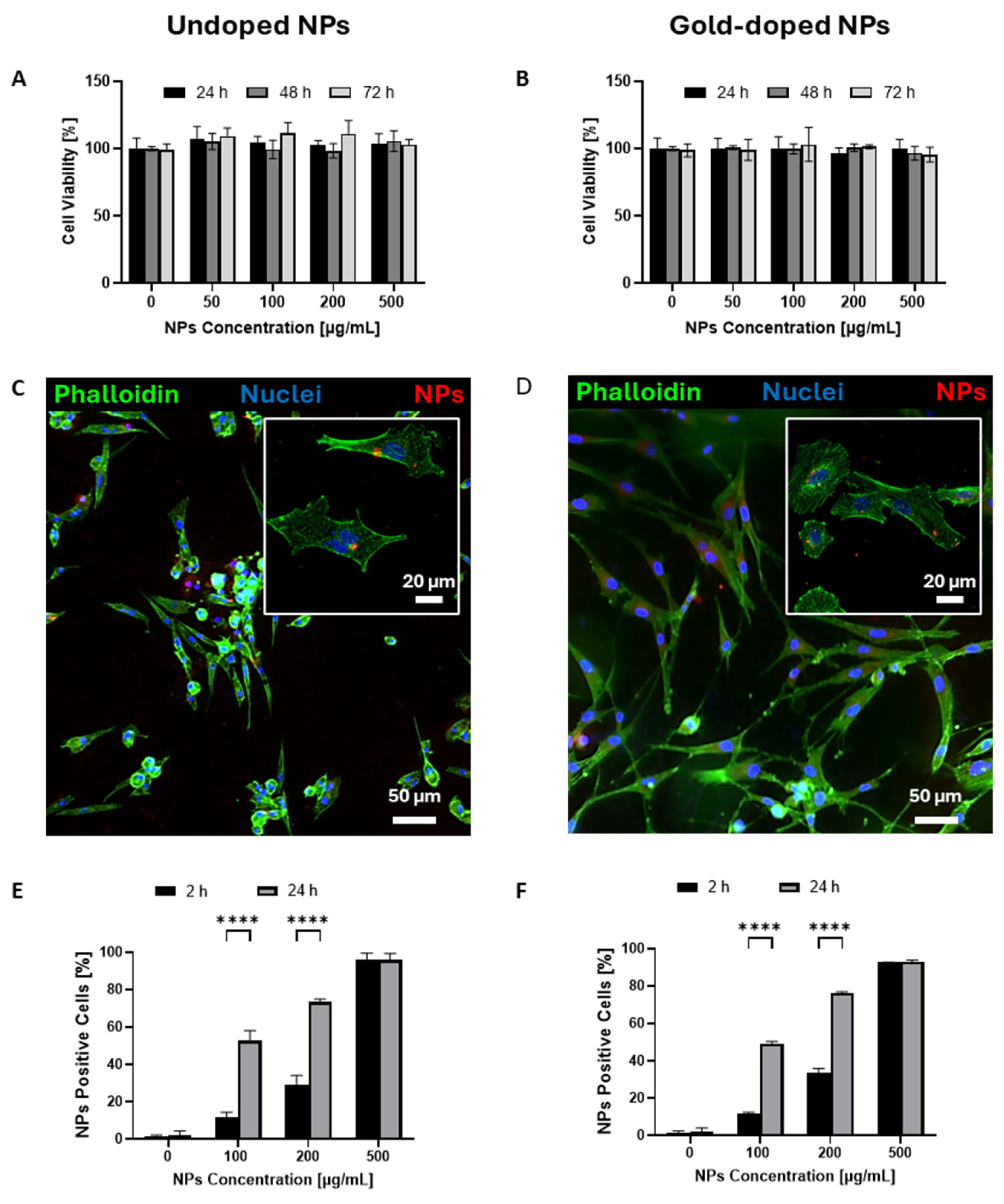
3.2. Impact of Gold-Doping on the Biological Properties of NPs
3.3. Effect of Gold Doping on the Optical Properties of NPs
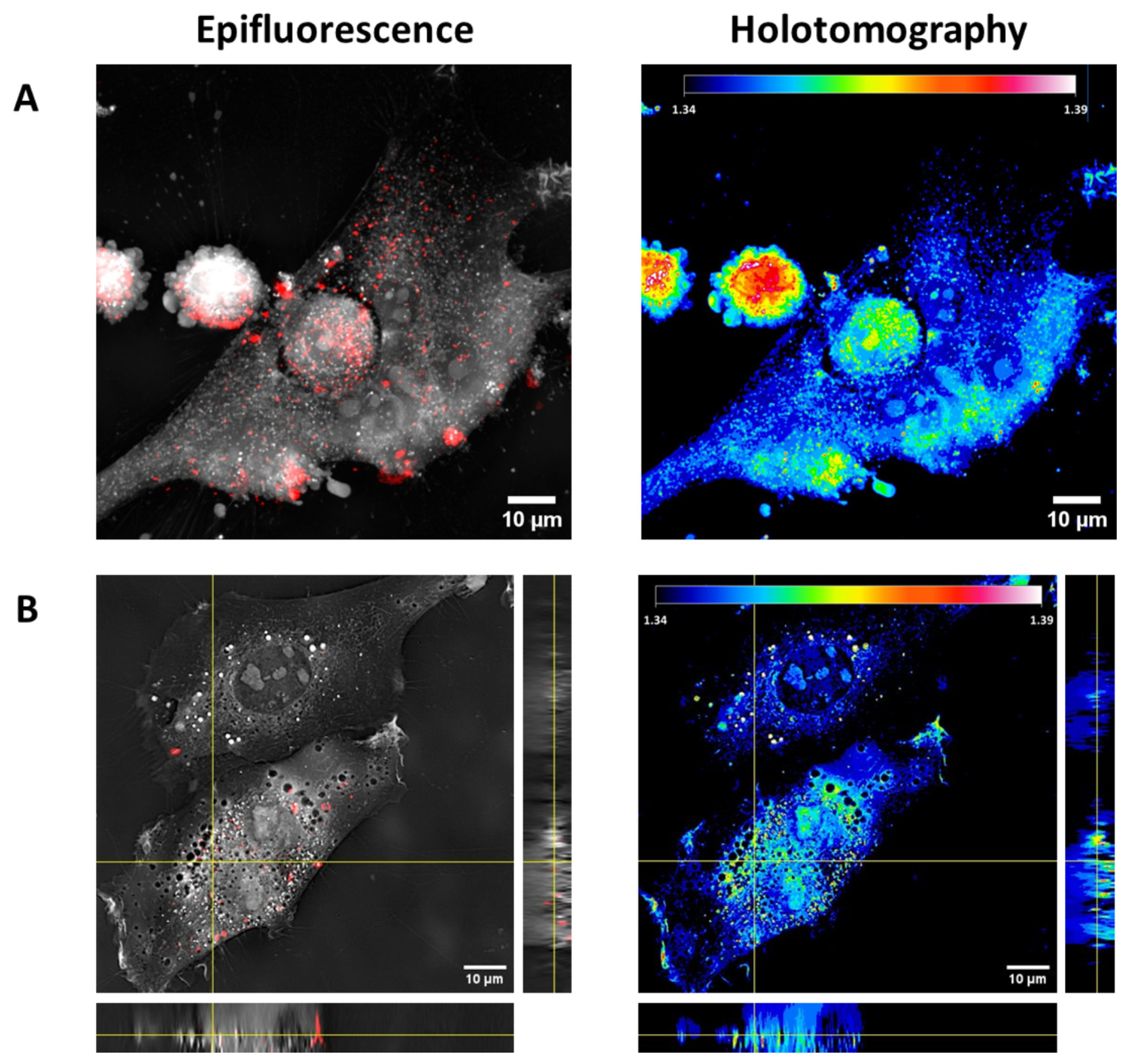
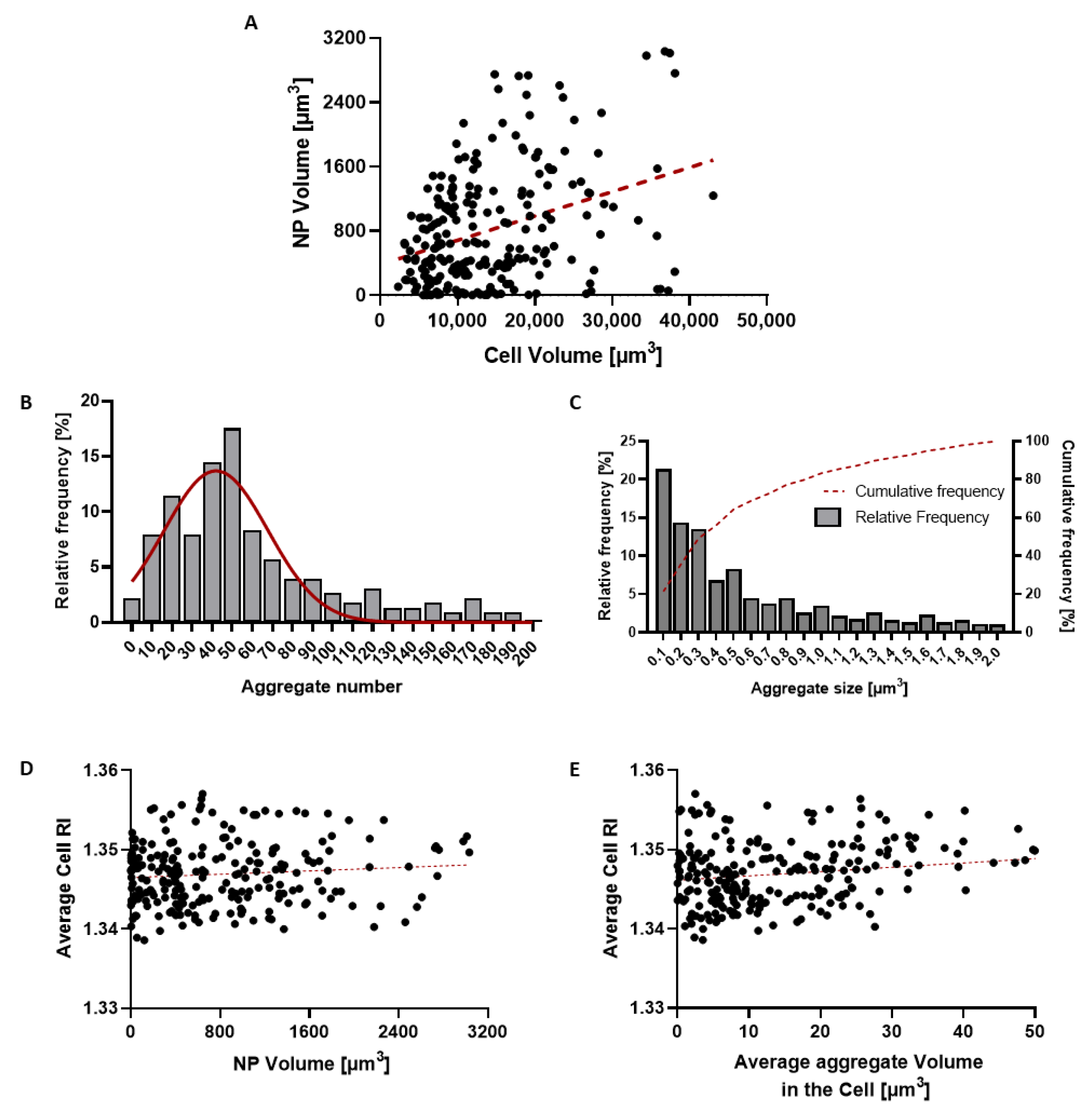
3.4. Fluorescence-Free High-Resolution Imaging of Cell Trafficking of Gold-Doped NPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy |
| RI | Refractive Index |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PCL | Poly(Ε-Caprolactone) |
| EGG-PG | L-A-Phosphatidylglycerol (Egg, Chicken) (Sodium Salt) |
| DSPE-PEG | 1,2-Dioleoyl-Sn-Glycero-3-Phosphoethanolamine-N-[Methoxy(Polyethylene Glycol)-2000] (Ammonium Salt) |
| Egg-Liss-Rhod PE | L-A-Phosphatidylethanolamine-N- (Lissamine Rhodamine B Sulfonyl) Ammonium Salt |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| NTA | Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis |
| LE | Loading Efficiency |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dihydrochloride |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SPR | Surface Plasmonic Resonance |
| dSTORM | Direct Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy |
| EPR | Enhanced Permeability and Retention |
| CLEM | Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy |
| sp ICP-MS | Single-Particle ICP-MS |
| sc ICP-MS | Single-Cell ICP-MS |
References
- Jia, Y.; Jiang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J.; Magar, K.T.; Boucetta, H.; Teng, C.; He, W. Approved Nanomedicine against Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Song, R.; Li, R.; Liu, M.; Ba, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fan, K. Nanomaterials for Refining Tumor Microenvironment and Enhancing Therapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Review. Oncol. Transl. Med. 2024, 10, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubicondo, M.; Ciardelli, G.; Mattu, C.; Tuszynski, J.A. Recent Advancements in Colchicine Derivatives: Exploring Synthesis, Activities, and Nanoformulations for Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy. Drug Discov. Today 2025, 30, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Santos, A.; Evdokiou, A.; Losic, D. An Overview of Nanotoxicity and Nanomedicine Research: Principles, Progress and Implications for Cancer Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7153–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering Precision Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of Nanoparticle Design for Overcoming Biological Barriers to Drug Delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, H.; Jangde, R.K. Current Updated Review on Preparation of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Next Nanotechnol. 2023, 2, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, B.; Khlebtsov, N. Drug Delivery Using Gold Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2025, 216, 115481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.D.; Fernandes, D.E.M.; Amorim, C.O.; Amaral, V.S.; Coutinho, P.J.G.; Rodrigues, A.R.O.; Castanheira, E.M.S. Magnetoliposomes with Calcium-Doped Magnesium Ferrites Anchored in the Lipid Surface for Enhanced DOX Release. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, R.; Luciani, P. Liposomes: Bridging the Gap from Lab to Pharmaceuticals. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2025, 75, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, T.R.; Raj, A.; Tseng, T.H.; Xiao, H.; Nguyen, R.; Mohammed, F.S.; Halder, S.; Xu, M.; Wu, M.J.; Bao, S.; et al. Biocompatibility of Nanomaterials and Their Immunological Properties. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 042005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, B.L.; Fattahi, P.; Brown, J.L. Polymeric Nanoparticles: The Future of Nanomedicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 271–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattu, C.; Brachi, G.; Menichetti, L.; Flori, A.; Armanetti, P.; Ranzato, E.; Martinotti, S.; Nizzero, S.; Ferrari, M.; Ciardelli, G. Alternating Block Copolymer-Based Nanoparticles as Tools to Modulate the Loading of Multiple Chemotherapeutics and Imaging Probes. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, A.; Obidiro, O.; Elesho, R.; Agbaje, K.; Kochakzade, M.; Karla, P.K. Recent Advances and FDA Approvals in Nanoformulations for Drug Delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 2025, 27, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano Based Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiot, E.D.; Sokolov, A.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Schiöth, H.B. Nanoparticles in Clinical Trials: Analysis of Clinical Trials, FDA Approvals and Use for COVID-19 Vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhecke, D.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Clift, M.J.D.; Blank, F.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Quantification of Nanoparticles at The Single-Cell Level: An Overview About State-of-the-Art Techniques and Their Limitations. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1885–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantra, R.; Knight, A. Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Fate of Engineered Nanoparticles: A Review on the Application of Imaging Techniques. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, P.; Fitzpatrick, L.W.; Simpson, J.C.; Dawson, K.A. High-Speed Imaging of Rab Family Small GTpases Reveals Rare Events in Nanoparticle Trafficking in Living Cells. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed-Cox, A.; Pandzic, E.; Johnston, S.T.; Heu, C.; McGhee, J.; Mansfeld, F.M.; Crampin, E.J.; Davis, T.P.; Whan, R.M.; Kavallaris, M. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Nanoparticles in Live Tumor Spheroids Impacted by Cell Origin and Density. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, A.; Nelissen, I.; Haase, A.; Åberg, C.; Moya, S.; Jacobs, A.; Alnasser, F.; Bewersdorff, T.; Deville, S.; Luch, A.; et al. Quantitative Measurement of Nanoparticle Uptake by Flow Cytometry Illustrated by an Interlaboratory Comparison of the Uptake of Labelled Polystyrene Nanoparticles. NanoImpact 2018, 9, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.R.; Kwak, M.; Lee, T.G.; Lee, J.Y. Quantifying the Level of Nanoparticle Uptake in Mammalian Cells Using Flow Cytometry. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 15743–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammertink, B.H.A.; Deckers, R.; Derieppe, M.; De Cock, I.; Lentacker, I.; Storm, G.; Moonen, C.T.W.; Bos, C. Dynamic Fluorescence Microscopy of Cellular Uptake of Intercalating Model Drugs by Ultrasound-Activated Microbubbles. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shibata, A.; Destache, C.J. Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy: An Ultra-Sensitive Tool Used to Evaluate Intracellular Antiretroviral Nano-Drug Delivery in HeLa Cells. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 084803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, A.; Nordmeyer, D.; Boreham, A.; Holzhausen, C.; Mundhenk, L.; Graf, C.; Meinke, M.C.; Vogt, A.; Hadam, S.; Lademann, J.; et al. Overview about the Localization of Nanoparticles in Tissue and Cellular Context by Different Imaging Techniques. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saptarshi, S.R.; Duschl, A.; Lopata, A.L. Interaction of Nanoparticles with Proteins: Relation to Bio-Reactivity of the Nanoparticle. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, A.M.; Haeni, L.; Hirschi, L.A.; Vanni, S.; Campomanes-Ramos, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Petri-Fink, A. The Choice of Nanoparticle Surface-Coupled Fluorescent Dyes Impacts Cellular Interaction. ChemNanoMat 2022, 8, e202100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehemann, K.; Schneider, S.W.; Luger, T.A.; Godin, B.; Ferrari, M.; Fuchs, H. Nanomedicine—Challenge and Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, Q.; Li, W.; Cai, X.; Mao, L.; Li, R. Approaches to Nanoparticle Labeling: A Review of Fluorescent, Radiological, and Metallic Techniques. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.J.; Burgers, T.C.Q.; Vlijm, R.; Roos, W.H.; Åberg, C. Rapid Internalization of Nanoparticles by Human Cells at the Single Particle Level. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 16517–16529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavaloiu, R.-D.; Sha’At, F.; Sha’At, M.; Nechifor, G. Intracellular Uptake Study of Polymeric Nanoparticles Loaded with Cardiovascular Drugs Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Chem. Proc. 2020, 3, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Frickenstein, A.N.; Wilhelm, S. High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis of Nanoparticle-Cell Interactions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166, 117172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Koh, D.; Gwak, E.; Srambickal, C.V.; Seo, D.; Widengren, J.; Lee, J.C. Pushing the Resolution Limit of Stimulated Emission Depletion Optical Nanoscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, A.D. Confocal Microscopy: Principles and Modern Practices. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2020, 92, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatesta, M. Transmission Electron Microscopy as a Powerful Tool to Investigate the Interaction of Nanoparticles with Subcellular Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzendruber, D.C.; Burnett, I.H.; Wertz, P.W.; Madison, K.C.; Squier, C.A. Osmium Tetroxide and Ruthenium Tetroxide Are Complementary Reagents for the Preparation of Epidermal Samples for Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshelev, V.; Mukhamadiyarov, R.; Kutikhin, A. Reduced Osmium-Tetroxide-Osmium, Lanthanides, and Phosphotungstic Acid Allow Whole-Specimen, Organelle-Resolution Analysis of Epoxy Resin-Embedded Cardiovascular Tissues. Atherosclerosis 2024, 395, 117716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, D.; La Spina, R.; Ponti, J.; Bianchi, I.; Gilliland, D. Inorganic Species-Doped Polypropylene Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusta, M.F.; Ernst, L.M.; Moriones, O.H.; Piella, J.; Valeri, M.; Bastus, N.G.; Puntes, V. Long-Term Intracellular Tracking of Label-Free Nanoparticles in Live Cells and Tissues with Confocal Microscopy. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2301713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Qian, W.; Shao, X.; Xie, Z.; Cheng, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, X. Label-Free Imaging of Gold Nanoparticles in Single Live Cells by Photoacoustic Microscopy. In Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing 2016; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9708, pp. 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Yoon, J.; Park, Y. Simultaneous 3D Visualization and Position Tracking of Optically Trapped Particles Using Optical Diffraction Tomography. Optica 2015, 2, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotte, Y.; Toy, F.; Jourdain, P.; Pavillon, N.; Boss, D.; Magistretti, P.; Marquet, P.; Depeursinge, C. Marker-Free Phase Nanoscopy. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.P.P.; Mahajan, R. Gold Polymer Nanomaterials: A Promising Approach for Enhanced Biomolecular Imaging. Nanotheranostics 2024, 8, 64–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.; Oh, J.; Yang, S.A.; Park, Y.K. Holotomography: Refractive Index as an Intrinsic Imaging Contrast for 3-D Label-Free Live Cell Imaging. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 1310, pp. 211–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Oh, N.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Pack, C.G.; Park, J.H.; Park, Y.K. Label-Free High-Resolution 3-D Imaging of Gold Nanoparticles inside Live Cells Using Optical Diffraction Tomography. Methods 2018, 136, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanemann, T.; Boehm, J.; Müller, C.; Ritzhaupt-Kleissl, E. Refractive Index Modification of Polymers Using Nanosized Dopants. In Proceedings of the Micro-Optics SPIE Photonics Europe 2008, Strasbourg, France, 7–11 April 2008; Volume 6992, pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Lin, B.; Lv, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Yi, Y. Au Nanoparticles-Doped Polymer All-Optical Switches Based on Photothermal Effects. Polymers 2020, 12, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, S.; Achanta, V.G.; Mahendru, N.; Prabhu, S.S.; Falconieri, M.; Sharma, G. High Refractive Index Gold Nanoparticle Doped Bi2O3-B2O3 Glasses for THz Frequencies. Opt. Mater. 2017, 72, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, R.P.; Schreiber, E.; Tietze, R.; Yang, H.; Pilarsky, C.; Alexiou, C. Intracellular Quantification and Localization of Label-Free Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Holotomographic Microscopy. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2020, 13, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattu, C.; Boffito, M.; Sartori, S.; Ranzato, E.; Bernardi, E.; Sassi, M.P.; Di Rienzo, A.M.; Ciardelli, G. Therapeutic Nanoparticles from Novel Multiblock Engineered Polyesterurethanes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachi, G.; Ruiz-Ramírez, J.; Dogra, P.; Wang, Z.; Cristini, V.; Ciardelli, G.; Rostomily, R.C.; Ferrari, M.; Mikheev, A.M.; Blanco, E.; et al. Intratumoral Injection of Hydrogel-Embedded Nanoparticles Enhances Retention in Glioblastoma. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 23838–23850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabari, R.M.; Mattu, C.; Partheeban, S.; Almarhoon, A.; Boffito, M.; Ciardelli, G.; Ramtoola, Z. Novel Polyurethane-Based Nanoparticles of Infliximab to Reduce Inflammation in an in-Vitro Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.L.; Campisi, M.; Osaki, T.; Possenti, L.; Mattu, C.; Adriani, G.; Kamm, R.D.; Chiono, V. Modeling Nanocarrier Transport across a 3D In Vitro Human Blood-Brain–Barrier Microvasculature. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, C.; Cervadoro, A.; Palange, A.L.; Key, J.; Aryal, S.; Ramirez, M.R.; Mattu, C.; Ciardelli, G.; O’Neill, B.E.; Decuzzi, P. Enhancing Photothermal Cancer Therapy by Clustering Gold Nanoparticles into Spherical Polymeric Nanoconstructs. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 76, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, A.; Cao, C.; Cui, D. Toxicity of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs): A Review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Bucher, G.; Passos, M.S.P.d.; Modesto, V.; Serra, M.Á.; Gilliland, D.; Riccardi, N.; Ponti, J. Exploring Nanoplastics Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Organisms: A Study Using Gold-Doped Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garms, B.C.; Poli, H.; Baggley, D.; Han, F.Y.; Whittaker, A.K.; Anitha, A.; Grøndahl, L. Evaluating the Effect of Synthesis, Isolation, and Characterisation Variables on Reported Particle Size and Dispersity of Drug Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 5657–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, T.; Torrano, A.A.; Houel-Renault, L.; Machelart, A.; Brodin, P.; Gref, R. An Original Methodology to Study Polymeric Nanoparticle-Macrophage Interactions: Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis in Cell Culture Media and Quantification of the Internalized Objects. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancani, E.; Menendez-Miranda, M.; Pastor, A.; Brisset, F.; Bernet-Camard, M.F.; Desmaële, D.; Gref, R. Nanoparticles with High Payloads of Pipemidic Acid, a Poorly Soluble Crystalline Drug: Drug-Initiated Polymerization and Self-Assembly Approach. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Abulateefeh, S.R.; Murphy, C.J. Facile Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with PLGA Polymer Brushes and Efficient Encapsulation into PLGA Nanoparticles: Toward Spatially Precise Bioimaging of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2019, 36, 1800414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmady, Z.S.; Donno, R.; Gennari, A.; Prestat, E.; Marotta, R.; Mironov, A.; Newman, L.; Lawrence, M.J.; Tirelli, N.; Ashford, M.; et al. Enhanced Intraliposomal Metallic Nanoparticle Payload Capacity Using Microfluidic-Assisted Self-Assembly. Langmuir 2019, 35, 13318–13331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, S.; Deng, R.; Wang, J.; Nie, Z.; Zhu, J. A Simple Route to Improve Inorganic Nanoparticles Loading Efficiency in Block Copolymer Micelles. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 2282–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Burkhard, P. Encapsulation of Gold Nanoparticles into Self-Assembling Protein Nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringhieri, P.; Iannitti, R.; Nardon, C.; Palumbo, R.; Fregona, D.; Morelli, G.; Accardo, A. Target Selective Micelles for Bombesin Receptors Incorporating Au(III)-Dithiocarbamato Complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardon, C.; Boscutti, G.; Dalla Via, L.; Ringhieri, P.; Di Noto, V.; Morelli, G.; Accardo, A.; Fregona, D. CCK8 Peptide-Labeled Pluronic® F127 Micelles as a Targeted Vehicle of Gold-Based Anticancer Chemotherapeutics. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochard, I.; Boisvert, J.P.; Persello, J.; Foissy, A. Surface Charge, Effective Charge and Dispersion/Aggregation Properties of Nanoparticles. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.R.; Wei, X.Q.; Song, X.; Hao, L.Y.; Cai, X.X.; Zhang, Z.R.; Peng, Q.; Lin, Y.F. Independent Effect of Polymeric Nanoparticle Zeta Potential/Surface Charge, on Their Cytotoxicity and Affinity to Cells. Cell Prolif. 2015, 48, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovskaya, Y.; Melnikov, P.; Baklaushev, V.; Gabashvili, A.; Osipova, N.; Mantrov, S.; Ermolenko, Y.; Maksimenko, O.; Gorshkova, M.; Balabanyan, V.; et al. Delivery of Doxorubicin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles into U87 Human Glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.C.; Lin, W.J. Improve BBB Penetration and Cytotoxicity of Palbociclib in U87-MG Glioblastoma Cells Delivered by Dual Peptide Functionalized Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya, G.; Tiwary, R.; Mudassir, M.; Singh, N.; Saha, S.; Chosdol, K.; Sinha, S.; Chattopadhyay, P. Passive Internalization and Active Extrusion Determines PLGA-Nanoparticle Concentration in Cancer Cell Lines. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, N.; Li, J.; Weng, Y.; Yuan, B.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y. Influence of Surface Chemistry on Particle Internalization into Giant Unilamellar Vesicles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8039–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, E.K.; Abedi-Gaballu, F.; Hosseini, T.F.M.; Mohammadi, A.; Mansoori, B.; Dehghan, G.; Baradaran, B.; Sheibani, N. Glimpse into the Cellular Internalization and Intracellular Trafficking of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles in Cancer Cells. Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 22, 1897–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, M.H.; Salerno, M.; Abdelrasoul, G.N.; Liakos, I.; Scarpellini, A.; Marras, S.; Diaspro, A. Effect of Anderson Localization on Light Emission from Gold Nanoparticle Aggregates. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.K.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Ultrafast Electron Relaxation Dynamics in Coupled Metal Nanoparticles in Aggregates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 110, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Michel, E.; Larrea, A.; Lahuerta, C.; Sebastian, V.; Imbuluzqueta, E.; Arruebo, M.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J.; Santamaría, J. A Simple Approach to Obtain Hybrid Au-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles with a Tunable Metal Load. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 6495–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apyari, V.V.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Arkhipova, V.V.; Atnagulov, A.G.; Gorbunova, M.V.; Zolotov, Y.A. Label-Free Gold Nanoparticles for the Determination of Neomycin. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallontzi, S.; Fabris, L.; Jitianu, M.; Hernandez, A.; Jitianu, A.; Klein, L.C. Gold Nanoparticles in Melting Gels. J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, H.; Nasir, S.M. Gold Nanoparticles Embedded on the Surface of Polyvinyl Alcohol Layer. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2008, 4, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovinszky, K.; Szalóki, M.; Csarnovics, I.; Bonyár, A.; Petrik, P.; Kalas, B.; Daróczi, L.; Kéki, S.; Kökényesi, S.; Hegedűs, C. Optimization of Plasmonic Gold Nanoparticle Concentration in Green LED Light Active Dental Photopolymer. Polymers 2021, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, A.Y. Synthesized Polymeric Nanocomposites with Enhanced Optical and Electrical Properties Based on Gold Nanoparticles for Optoelectronic Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Yoon, J.; Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Yang, S.-A.; Park, Y. Optical Diffraction Tomography Techniques for the Study of Cell Pathophysiology. J. Biomed. Photonics Eng. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, K.; Marzi, A.; Wiemann, M.; Rauen, U.; Kemper, B.; Schnekenburger, J. Morphological Alterations in Primary Hepatocytes upon Nanomaterial Incubation Assessed by Digital Holographic Microscopy and Holotomography. In Proceedings of the Quantitative Phase Imaging VIII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2022; Popescu, G., Park, Y., Liu, Y., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Srichana, T.; Thawithong, E.; Nakpheng, T.; Paul, P.K. Flow Cytometric Analysis, Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic, and Holotomographic Imaging Demonstrate Potentials of Levofloxacin Dry Powder Aerosols for TB Treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, J.; Uckermann, O.; Kirsche, K.; Schackert, G.; Koch, E.; Kirsch, M.; Galli, R. Correlation of Biomechanics and Cancer Cell Phenotype by Combined Brillouin and Raman Spectroscopy of U87-MG Glioblastoma Cells. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Geng, F.; Cheng, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Yong, W.H.; Chakravarti, A.; Guo, D. Lipid Droplets Maintain Energy Homeostasis and Glioblastoma Growth via Autophagic Release of Stored Fatty Acids. iScience 2020, 23, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J.; Heo, J.; Choi, C.; Park, Y. Three-Dimensional Label-Free Imaging and Quantification of Lipid Droplets in Live Hepatocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanina, I.Y.; Lazareva, E.N.; Tuchin, V.V. Refractive Index of Adipose Tissue and Lipid Droplet Measured in Wide Spectral and Temperature Ranges. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 4839–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ahn, J.W.; Jo, Y.; Kang, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Cheon, Y.; Kim, J.W.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Park, K. Label-Free Tomographic Imaging of Lipid Droplets in Foam Cells for Machine-Learning-Assisted Therapeutic Evaluation of Targeted Nanodrugs. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.; Turnbull, T.; Paterson, D.J.; Thierry, B.; Kempson, I. Cell Size as a Primary Determinant in Targeted Nanoparticle Uptake. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4222–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Arai, Y.; Hirai, H.; Ishimoto, R.; Nagano, K.; Higashisaka, K.; Nagai, T.; Tsutsumi, Y. Intracellular Trafficking of Particles inside Endosomal Vesicles Is Regulated by Particle Size. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Tang, T.; Pang, H.B. Cellular Internalization of Bystander Nanomaterial Induced by TAT-Nanoparticles and Regulated by Extracellular Cysteine. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleron, J.; Querbes, W.; Zeigerer, A.; Borodovsky, A.; Marsico, G.; Schubert, U.; Manygoats, K.; Seifert, S.; Andree, C.; Stöter, M.; et al. Image-Based Analysis of Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated SiRNA Delivery, Intracellular Trafficking and Endosomal Escape. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Kuhn, D.A.; Ali, Z.; Gasser, M.; Amin, F.; Parak, W.J.; Vanhecke, D.; Fink, A.; Gehr, P.; Brandenberger, C. Quantification of Gold Nanoparticle Cell Uptake under Controlled Biological Conditions and Adequate Resolution. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, A.S.M.; Salim, M.B. Probing the Intracellular Refractive Index and Molecular Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle in HeLa Cells Using Single Particle Spectroscopy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6019–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrian, T.; Muela, Y.; Delgado, L.; Albertazzi, L.; Pujals, S. A Super-Resolution and Transmission Electron Microscopy Correlative Approach to Study Intracellular Trafficking of Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 14615–14627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campardelli, R.; Della Porta, G.; Gomez, L.; Irusta, S.; Reverchon, E.; Santamaria, J. Au–PLA Nanocomposites for Photothermally Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 2, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Tagami, T.; Ozeki, T. Gold Nanoparticle-Coated Thermosensitive Liposomes for the Triggered Release of Doxorubicin, and Photothermal Therapy Using a near-Infrared Laser. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 626, 127038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichello, G.A.; Fukuda, T.; Maekawa, T.; Whitby, R.L.D.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Alavijeh, M.; Pannala, A.S.; Sarker, D.K. Preparation of Liposomes Containing Small Gold Nanoparticles Using Electrostatic Interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 105, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Mukherjee, B.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Paul, P.; Choudhury, R.; Kumar, A.; Mondal, L.; Hossain, C.M.; Maji, R. Colloidal Gold-Loaded, Biodegradable, Polymer-Based Stavudine Nanoparticle Uptake by Macrophages: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 6049–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, D.B.; Dunne, M.; Stewart, J.; Allen, C.; Jaffray, D.A. Cellular Uptake and Transport of Gold Nanoparticles Incorporated in a Liposomal Carrier. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzel, A.; Agiotis, L.; Baron, A.; Zhigaltsev, I.V.; Cullis, P.R.; Hasanzadeh Kafshgari, M.; Meunier, M. Single Pulse Nanosecond Laser-Stimulated Targeted Delivery of Anti-Cancer Drugs from Hybrid Lipid Nanoparticles Containing 5 Nm Gold Nanoparticles. Small 2023, 19, 2305591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, B.S.; Alamri, A.H.; McConville, C. Polymeric Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Malignant Gliomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo Choi, H.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J.P.; Itty Ipe, B.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Renal Clearance of Quantum Dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmire, M.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Clearance Properties of Nano-Sized Particles and Molecules as Imaging Agents: Considerations and Caveats. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Qian, H.; Liu, B.; Jiang, X. The Combined Effects of Size and Surface Chemistry on the Accumulation of Boronic Acid-Rich Protein Nanoparticles in Tumors. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloss, K.; Hamar, P. Augmentation of the EPR Effect by Mild Hyperthermia to Improve Nanoparticle Delivery to the Tumor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.F.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Möhwald, H. Enhanced Raman Imaging and Optical Spectra of Gold Nanoparticle Doped Microcapsules. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 3003–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wernersbach, I.; Harms, G.S.; Schäfer, M.K.E. Microglia Subtypes Show Substrate- and Time-Dependent Phagocytosis Preferences and Phenotype Plasticity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 945485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppstädter, J.; Seif, M.; Dembek, A.; Cavelius, C.; Huwer, H.; Kraegeloh, A.; Kiemer, A.K. M2 Polarization Enhances Silica Nanoparticle Uptake by Macrophages. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 129823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Pathak, J.L.; Carneiro, A.M.D.; Chung, C.Y. Differential Regulation of Adhesion and Phagocytosis of Resting and Activated Microglia by Dopamine. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Hugonnet, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Ha, J.; Lee, C.; Park, H.; Yoon, K.J.; Shin, Y.; et al. Holotomography. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2024, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bai, B.; Ryu, D.H.; Liu, T.; Lee, C.; Luo, Y.; Lee, M.J.; Huang, L.; Shin, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Quantitative Phase Imaging Methods for Life Sciences. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, N.J.; Khan, F.R.; Mitrano, D.M.; Boyle, D.; Thompson, R.C. Demonstrating the Translocation of Nanoplastics across the Fish Intestine Using Palladium-Doped Polystyrene in a Salmon Gut-Sac. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 106994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, D.; Bogni, A.; La Spina, R.; Gilliland, D.; Ponti, J. Investigating the Cellular Uptake of Model Nanoplastics by Single-Cell ICP-MS. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Romero, L.; Blanco-González, E.; Montes-Bayón, M. Single-Cell ICP-MS in Combination with Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting for Investigating the Effects of Nanotransported Cisplatin(IV) Prodrugs. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 11874–11878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theiner, S.; Loehr, K.; Koellensperger, G.; Mueller, L.; Jakubowski, N. Single-Cell Analysis by Use of ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1784–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte Rodríguez, M.; Álvarez-Fernández García, R.; Blanco, E.; Bettmer, J.; Montes-Bayón, M. Quantitative Evaluation of Cisplatin Uptake in Sensitive and Resistant Individual Cells by Single-Cell ICP-MS (SC-ICP-MS). Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11491–11497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, J.B.; Kromann, E.B. Pitfalls and Opportunities in Quantitative Fluorescence-Based Nanomedicine Studies—A Commentary. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottstein, C.; Wu, G.; Wong, B.J.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Precise Quantification of Nanoparticle Internalization. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titma, T.; Shimmo, R.; Siigur, J.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Antimony, Copper, Cobalt, Manganese, Titanium and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for the Alveolar and Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Cells in Vitro. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laib, I.; Gheraissa, N.; Benaissa, A.; Benkhira, L.; Azzi, M.; Benaissa, Y.; Abdelaziz, A.G.; Tian, F.; Walsh, M.; Bechelany, M.; et al. Tailoring Innovative Silver Nanoparticles for Modern Medicine: The Importance of Size and Shape Control and Functional Modifications. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 33, 102071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; McLeod, E.; Qi, H.; Wan, Z.; Sun, R.; Ozcan, A. On-Chip Cytometry Using Plasmonic Nanoparticle Enhanced Lensfree Holography. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.L.; Fu, Q.C.; Jiang, L.F.; Zheng, L.M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Diagnosing and Treating Degenerative Orthopaedic Diseases: A Review. Eur. Cells Mater. 2024, 48, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
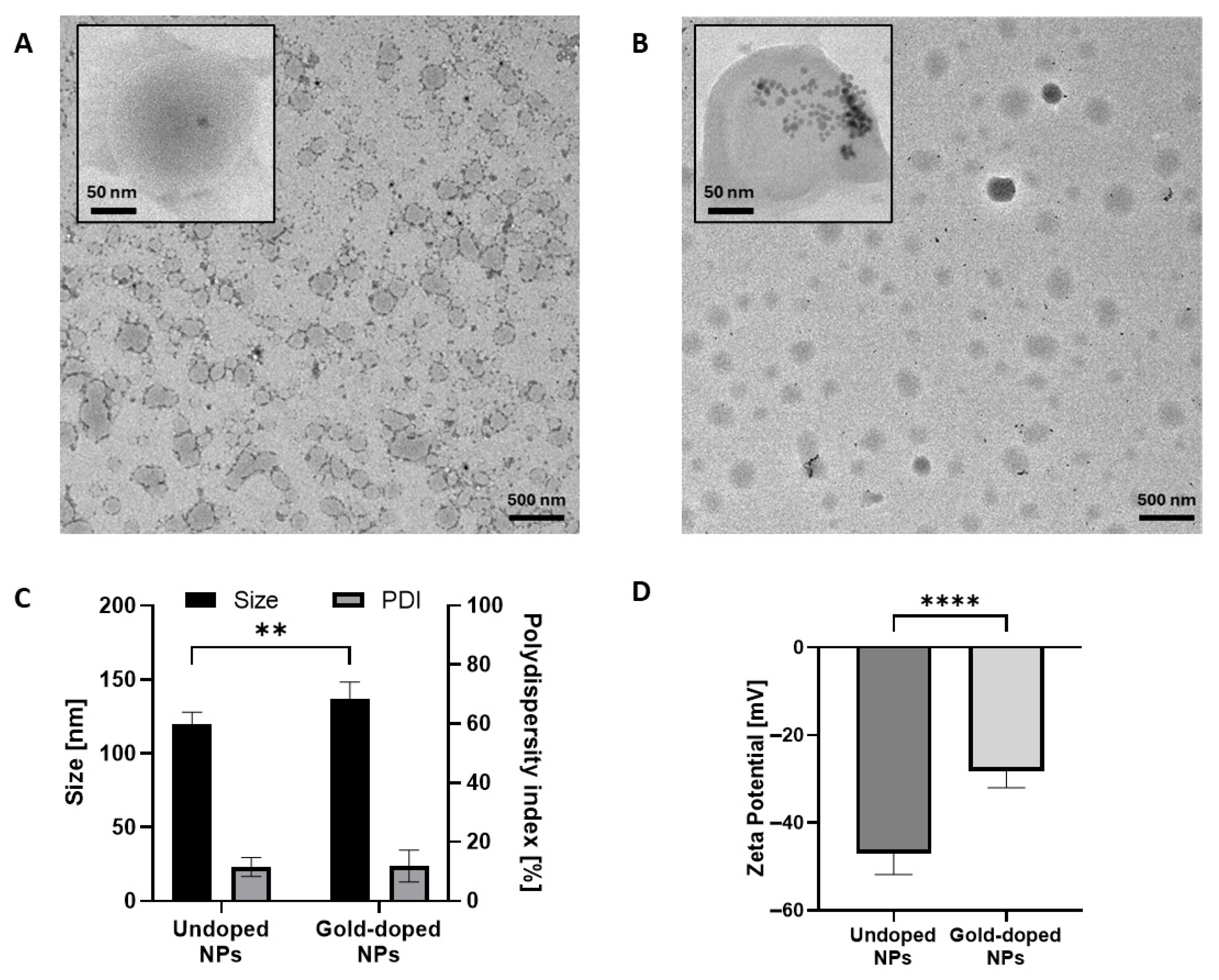






| Undoped NPs | Gold-Doped NPs | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) (DLS) | 120 ± 8 | 140 ± 13 | 0.006 (**) |
| Size (nm) (TEM) | 124 ± 43 | 141 ± 52.8 | <0.0001 (****) |
| Size (nm) (NTA) | 101 ± 2 | 124 ± 1 | 0.0004 (***) |
| PDI (%) | 12 ± 3 | 11 ± 6 | 0.9961 |
| Z potential (mV) | −47 ± 5 | −28 ± 4 | <0.0001 (****) |
| Density (NPs/mL) | 3.3 ± 0.1 × 1012 | 4.0 ± 0.2 × 1012 | 0.01 (*) |
| Gold-doping efficiency (%) | N/A | 56.3 ± 7.6% (indirect) | N/A |
| N/A | 47.7 ± 2.6% (direct) | N/A |
| Colocalization between fluorescent and high-RI voxels | 92 ± 3% |
| Average Aggregate Size | 0.55 ± 0.50 µm3 |
| Average volume (%) occupied by NPs | 6.7 ± 5.5% |
| Average number of aggregates per cell | 50 ± 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bezze, A.; Ponti, J.; Stanco, D.; Mattioda, C.; Mattu, C. Gold-Doped Hybrid Nanoparticles: A Versatile Tool for Multimodal Imaging of Cell Trafficking. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121612
Bezze A, Ponti J, Stanco D, Mattioda C, Mattu C. Gold-Doped Hybrid Nanoparticles: A Versatile Tool for Multimodal Imaging of Cell Trafficking. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(12):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121612
Chicago/Turabian StyleBezze, Andrea, Jessica Ponti, Deborah Stanco, Carlotta Mattioda, and Clara Mattu. 2025. "Gold-Doped Hybrid Nanoparticles: A Versatile Tool for Multimodal Imaging of Cell Trafficking" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 12: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121612
APA StyleBezze, A., Ponti, J., Stanco, D., Mattioda, C., & Mattu, C. (2025). Gold-Doped Hybrid Nanoparticles: A Versatile Tool for Multimodal Imaging of Cell Trafficking. Pharmaceutics, 17(12), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121612







