Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) as a Carrier for Kaempferol Delivery to Protect Against Gamma Radiation-Induced Mortality and Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell and Animals
2.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analytical Methods
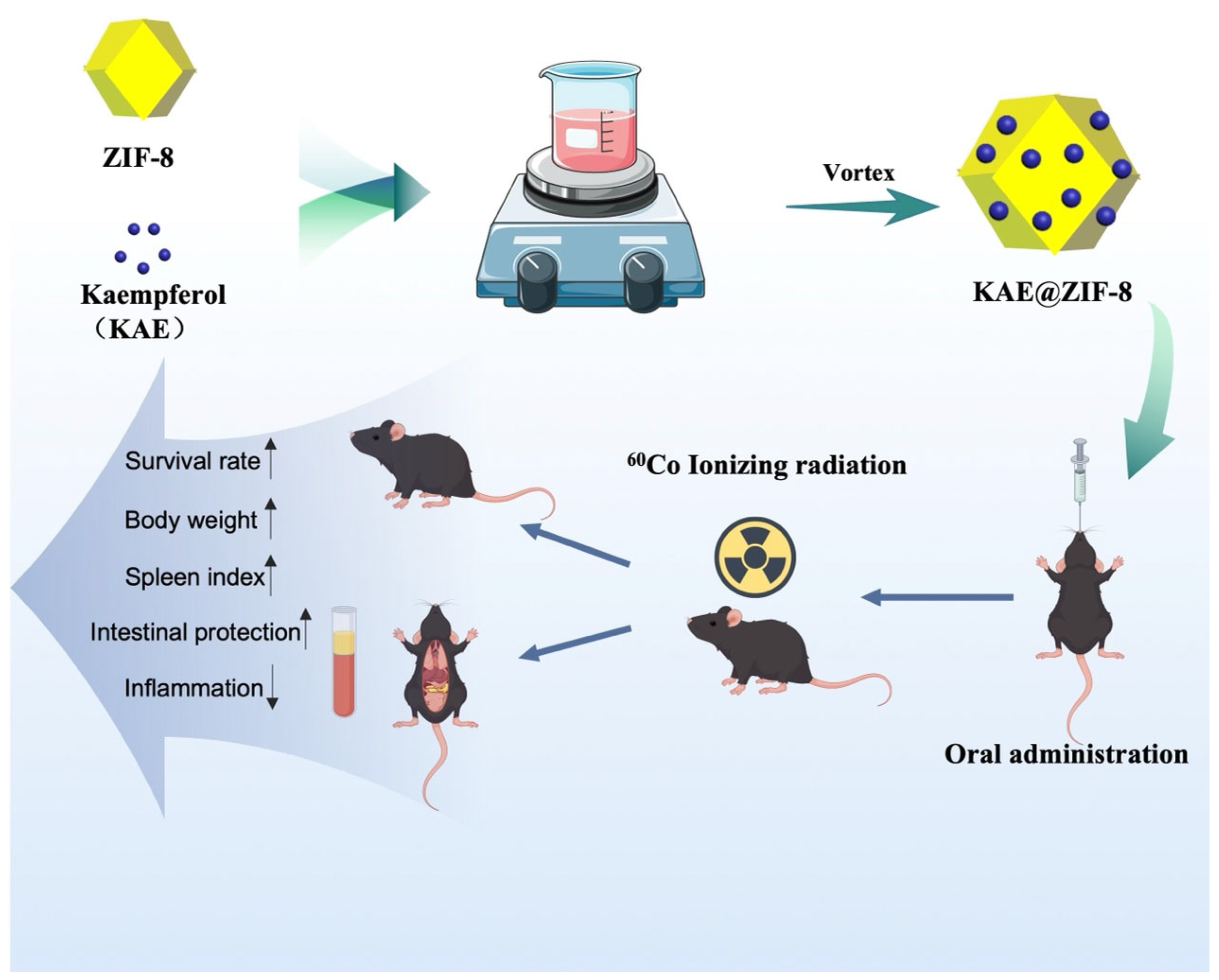
2.4. KAE@ ZIF-8
2.4.1. Preparation of KAE@ ZIF-8
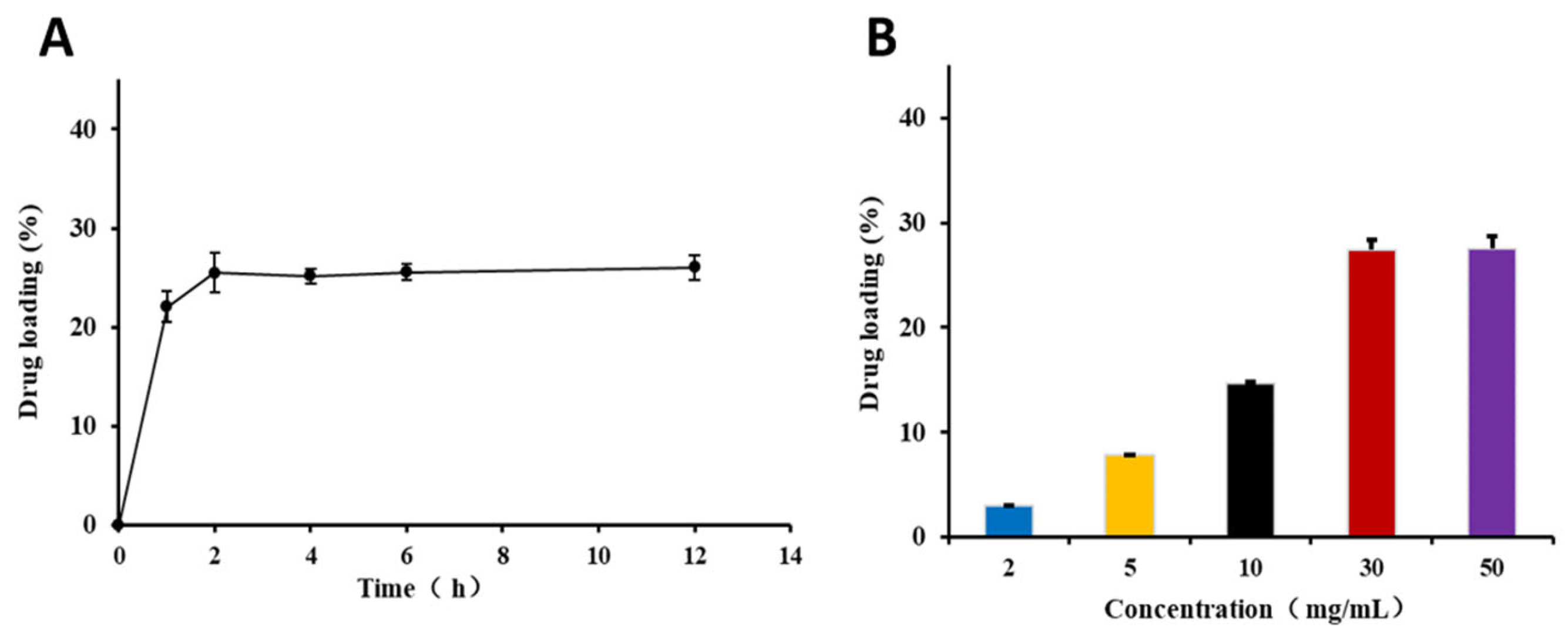
2.4.2. Drug Loading Time
2.4.3. Drug Loading Concentration
2.4.4. Drug Loading
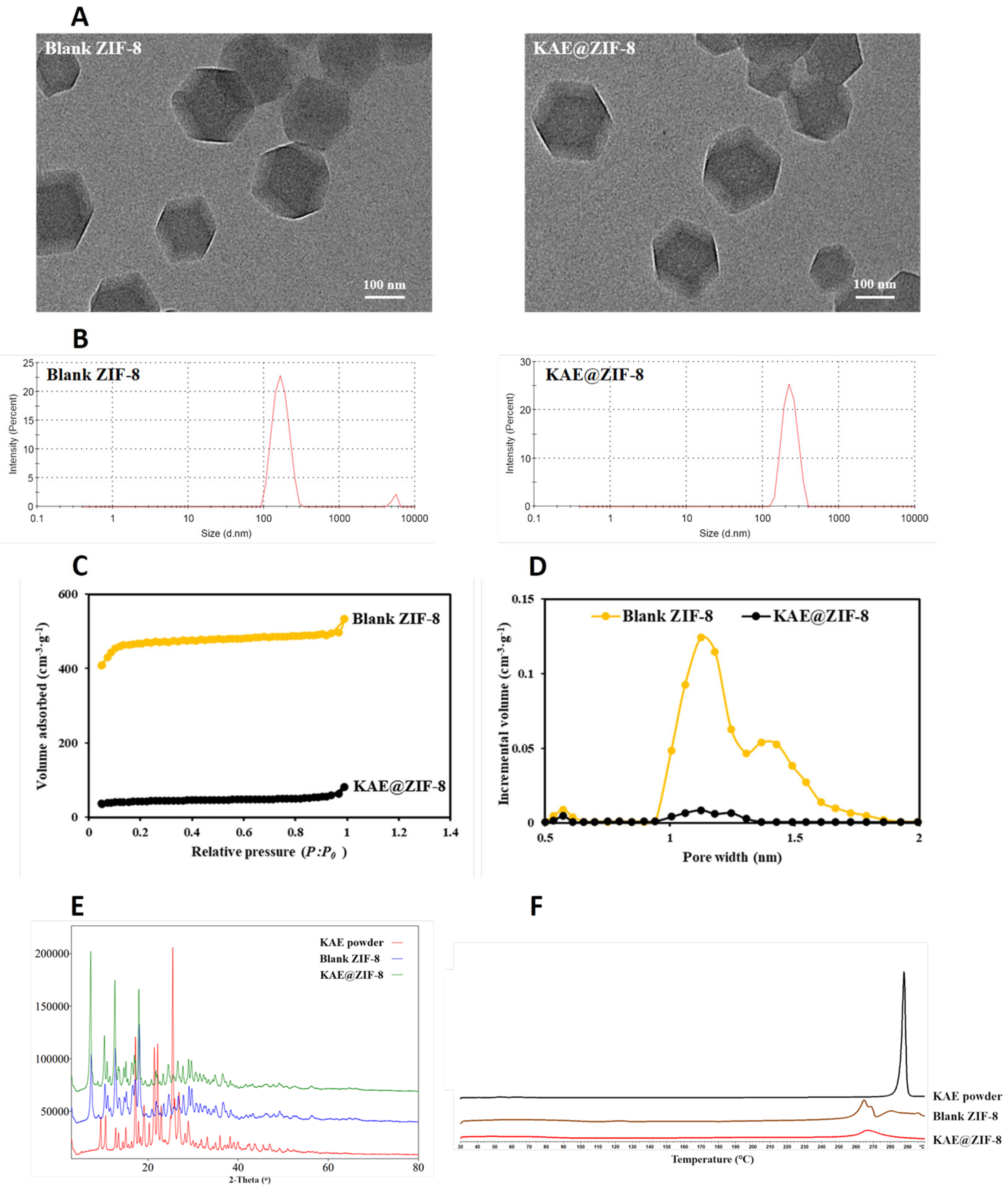
2.5. Sample Characterization
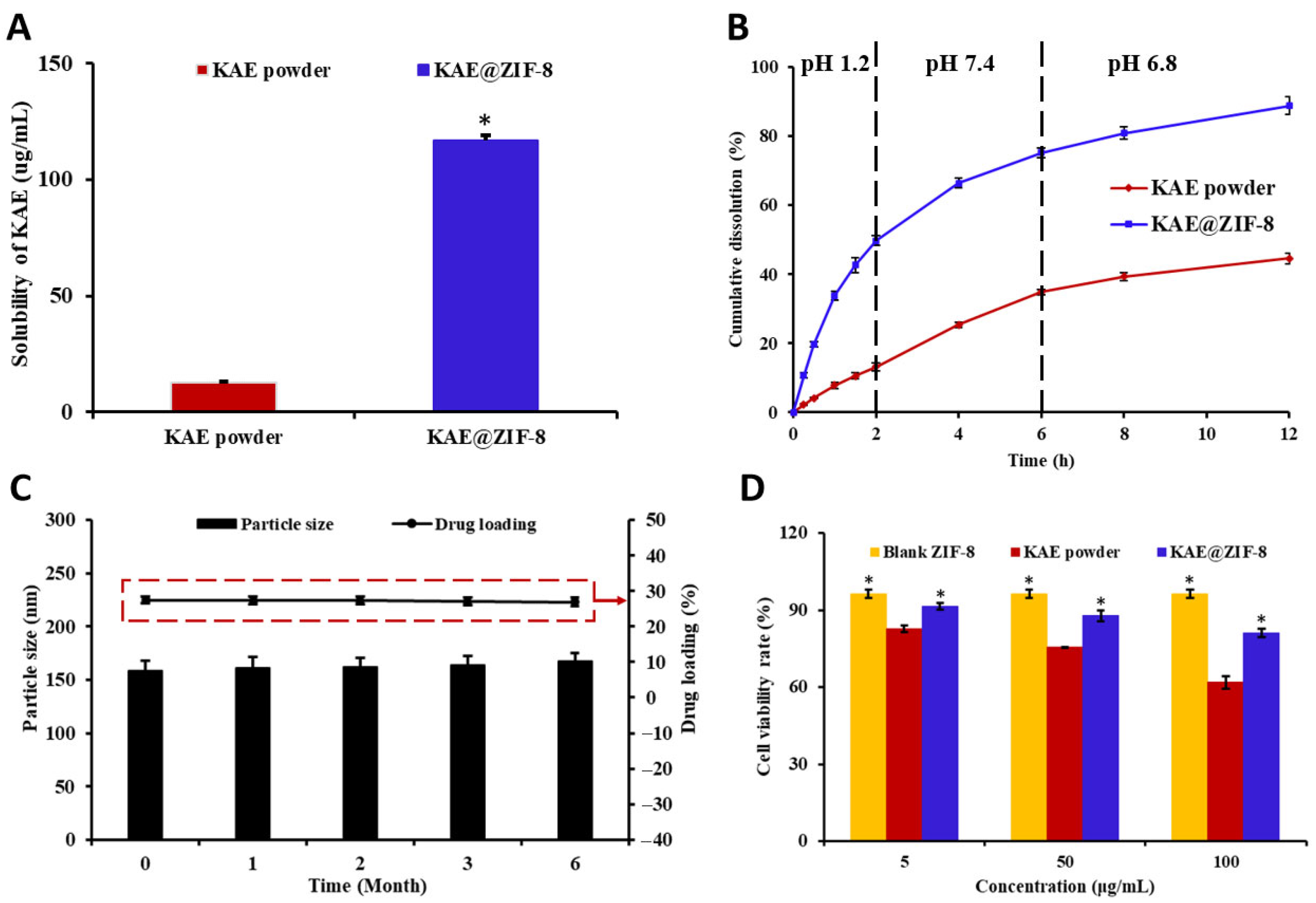
2.6. Equilibrium Solubility and In Vitro Release
2.7. Stability
2.8. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic
2.9. Cytotoxicity
2.10. Protective Effects of Ionizing Radiation
2.10.1. Gamma Radiation and KAE@ZIF-8 Treatment
- (A)
- Control group: 9 mice and 5 mice, respectively, intragastrically administered saline, continuously dosed for 7 d before radiation with 0 Gy TBI.
- (B)
- 9 Gy radiation group: 9 mice, intragastrically administered saline, continuous dosing for 7 d before radiation with 9 Gy TBI.
- (C)
- 9 Gy KAE 10 mg/kg group: 9 mice, 10 mg/kg/day intragastrically administered KAE diluted with saline, continuous KAE dosing for 7 d before radiation with 9 Gy TBI.
- (D)
- 9 Gy Blank ZIF-8 group: 9 mice, 36.4 mg/kg/day intragastrically administered ZIF-8 diluted with saline, continuous ZIF-8 dosing for 7 d before radiation with 9 Gy TBI.
- (E)
- 9 Gy KAE@ZIF-8 group: 9 mice, 36.4 mg/kg/day intragastrically administered KAE@ZIF-8 diluted with saline, continuous KAE@ZIF-8 dosing for 7 d before radiation with 9 Gy TBI.
- (F)
- 7 Gy radiation group: 5 mice, intragastrically administered saline, continuous dosing for 7 d before radiation with 7 Gy TBI.
- (G)
- 7 Gy KAE 10 mg/kg group: 5 mice, 10 mg/kg/day intragastrically administered KAE diluted with saline, continuous KAE dosing for 7 d before radiation with 7 Gy TBI.
- (H)
- 7 Gy KAE@ZIF-8 group: 5 mice, 36.4 mg/kg/day intragastrically administered KAE@ZIF-8 diluted with saline, continuous KAE@ZIF-8 dosing for 7 d before radiation with 7 Gy TBI.
2.10.2. Organ Index
2.10.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10.4. Morphological Examination, Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated d-UTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) and Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin (α-SMA) Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of Standard Curves
3.2. Preparation of KAE@ZIF-8
3.3. Characterization of KAE@ZIF-8
3.4. Solubility, Stability and Cytotoxicity of KAE@ZIF-8
3.5. Pharmacokinetics Study
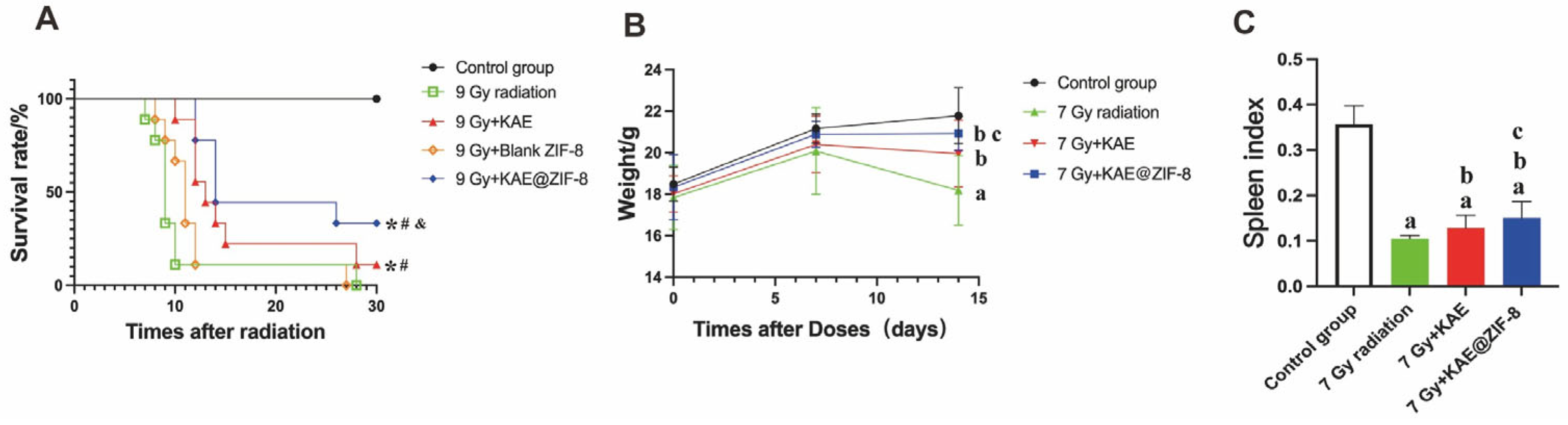
3.6. KAE@ZIF-8 Protects Mice Against Radiation-Induced Motility and Weight Reduction
3.7. KAE@ZIF-8 Reduces Ionizing Radiation-Induced Spleen Injury in Mice
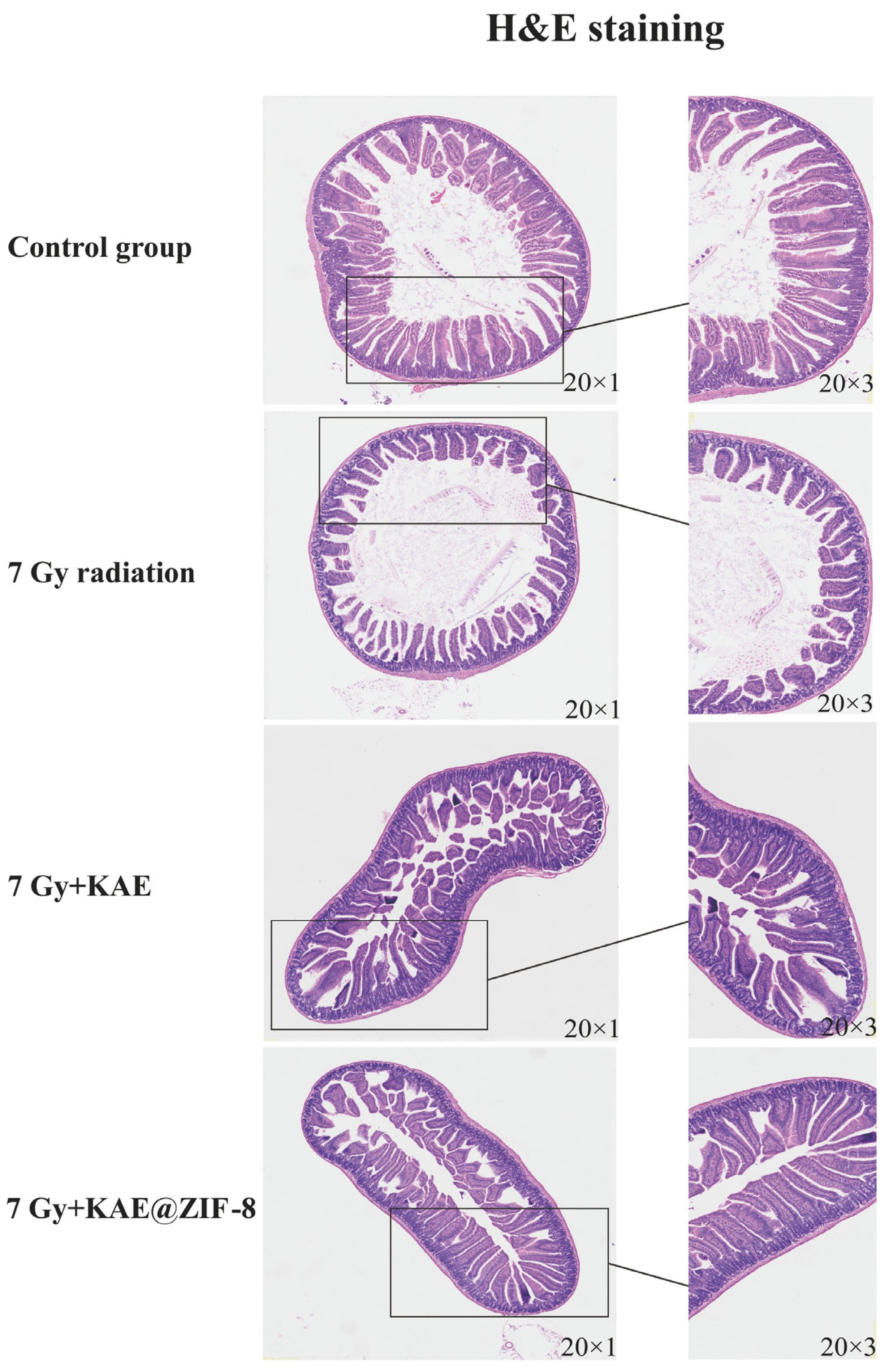
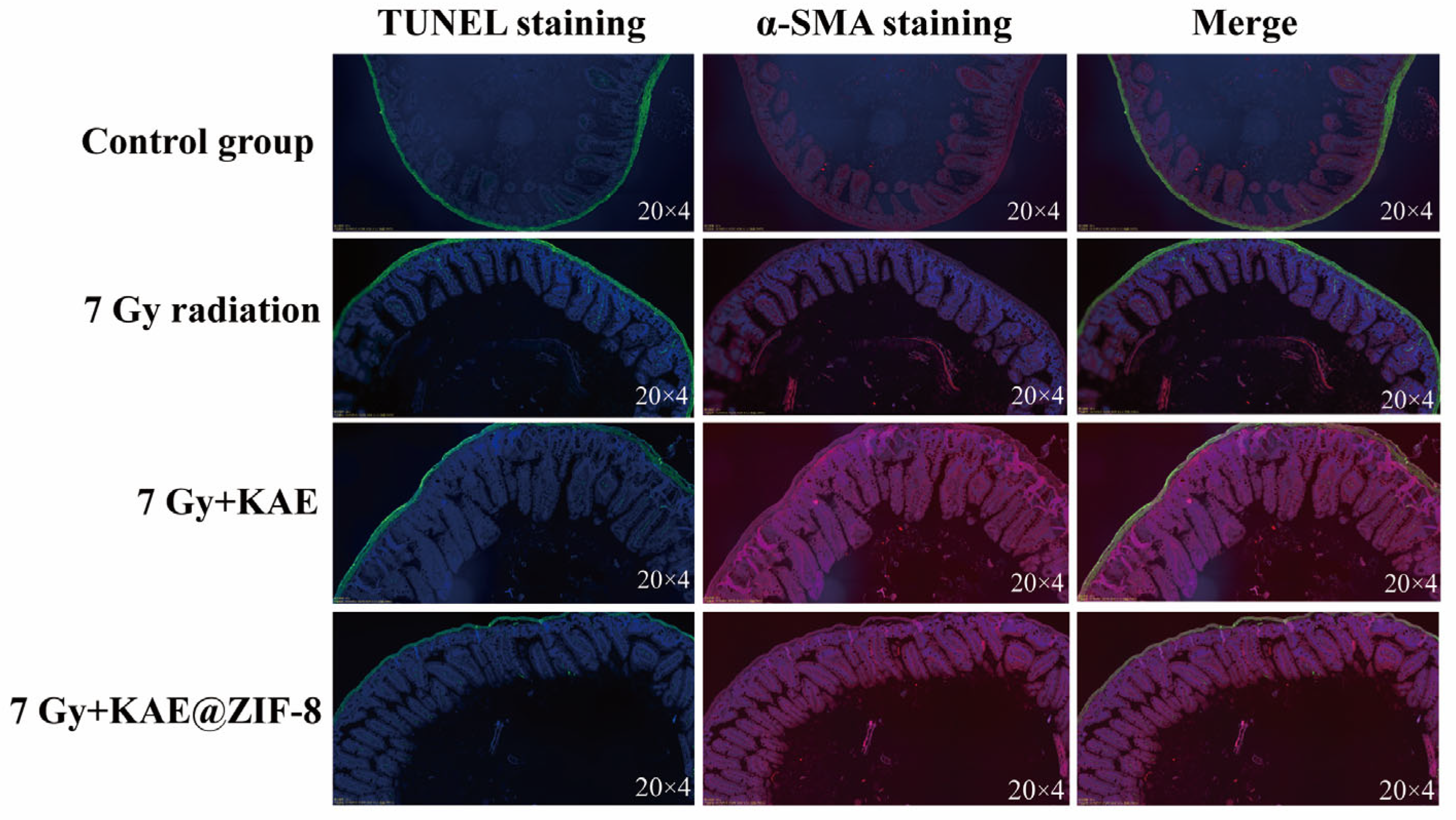
3.8. KAE@ZIF-8 Attenuates Ionizing Radiation-Induced Small Intestinal Tissue Damage in Mice
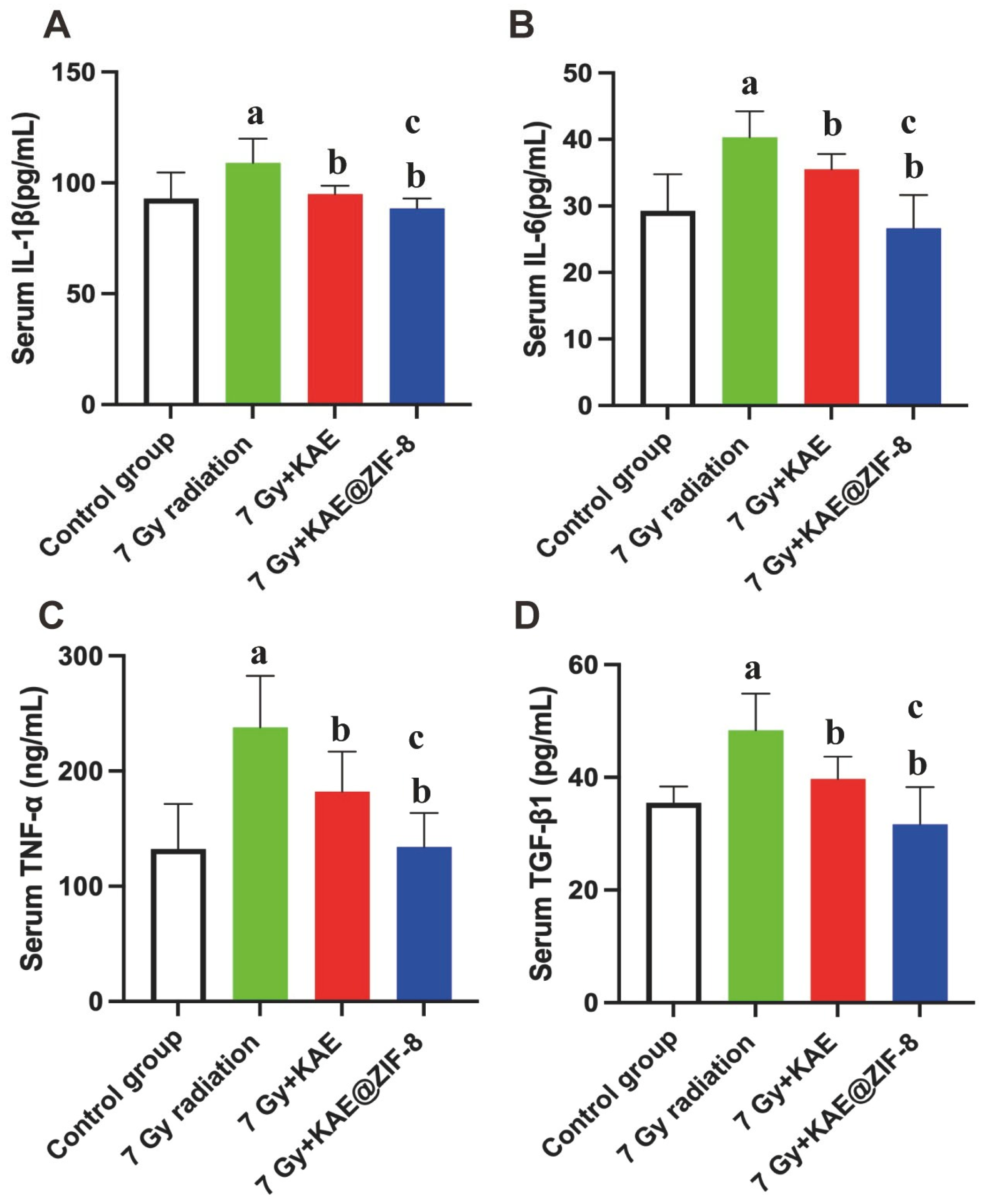
3.9. KAE@ZIF-8 Attenuates Ionizing Radiation-Induced Inflammation in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lumniczky, K.; Impens, N.; Armengol, G.; Candéias, S.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Hornhardt, S.; Martin, O.A.; Rödel, F.; Schaue, D. Low dose ionizing radiation effects on the immune system. Environ. Int. 2021, 149, 106212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, S.; Little, M.P.; Kaiser, J.C.; Impens, N.; Hamada, N.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Simar, D.; Salomaa, S. Ionizing radiation-induced circulatory and metabolic diseases. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meador, J.A.; Morris, R.J.; Balajee, A.S. Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Damage Response in Primary Melanocytes and Keratinocytes of Human Skin. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2022, 162, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenova, V.; Mladenov, E.; Stuschke, M.; Iliakis, G. DNA Damage Clustering after Ionizing Radiation and Consequences in the Processing of Chromatin Breaks. Molecules 2022, 27, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuszkiewicz, J.; Woźniak, A.; Szewczyk-Golec, K. Ionizing Radiation as a Source of Oxidative Stress—The Protective Role of Melatonin and Vitamin, D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelonek, K.; Pietrowska, M.; Widlak, P. Systemic effects of ionizing radiation at the proteome and metabolome levels in the blood of cancer patients treated with radiotherapy: The influence of inflammation and radiation toxicity. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadgholi, M.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Induced by Ionizing Radiation in Healthy and Cancerous Cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 2751–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, A.; Liang, H.; Li, L.; Yang, B.; Whittaker, A.K. Reactive Oxygen Species Amplifier for Apoptosis-Ferroptosis Mediated High-Efficiency Radiosensitization of Tumors. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 10288–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnautou, P.; Garnier, G.; Maillot, J.; Konopacki, J.; Brachet, M.; Bonnin, A.; Amabile, J.C.; Malfuson, J.V. Management of acute radiation syndrome. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2024, 31, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathy, P.; Kaginelli, S.B. Quality assurance of lead aprons for radiation protection. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2023, 199, 2491–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, V.; Murugan, A.; Shameem, A.; Thangarasu, S.; Bahadur, S.A. A Simple Synthesis Method of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) Nanocrystals as Superior Electrode Material for Energy Storage Systems. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 4707–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanuma Kumar, G.E.N.; Kumar, S.S.; Balaji, M.; Maurya, D.K.; Kesavulu, M. Pterocarpus santalinus L. extract mitigates gamma radiation-inflicted derangements in BALB/c mice by Nrf2 upregulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Hsiao, L.D.; Wang, C.Y.; Lin, W.N.; Shih, Y.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Cho, R.L.; Tseng, H.C.; Yang, C.M. HO-1 Upregulation by Kaempferol via ROS-Dependent Nrf2-ARE Cascade Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Intercellular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Expression in Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Antioxidant 2022, 11, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Improvement strategies for the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble flavonoids: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabeek, W.M.; Marra, M.V. Dietary Quercetin and Kaempferol: Bioavailability and Potential Cardiovascular-Related Bio-activity in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouhar, E.; Adibifar, A.; Salimi, M.; Karami, Z.; Shadmani, N.; Rostamizadeh, K. Novel pH-responsive alginate-stabilized curcumin-selenium-ZIF-8 nanocomposites for synergistic breast cancer therapy. J. Drug Target. 2024, 32, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xie, L.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L. Dexamethasone-loaded zeolitic imidazolate frameworks nanocomposite hydrogel with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects for periodontitis treatment. Mater. Today Bio. 2022, 16, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sudlow, G.; Wang, Z.; Cao, S.; Jiang, Q.; Neiner, A.; Morrissey, J.J.; Kharasch, E.D.; Achilefu, S.; Singamaneni, S. Metal-Organic Framework Encapsulation Preserves the Bioactivity of Protein Therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, T.; Singh, C.; Gupta, G.D. Novel metal organic frameworks improves solubility and oral absorption of mebendazole: Physicochemical characterization and in vitro-in vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, S.; Prasetija, K.A.; Yuliana, M.; Wijaya, C.J.; Bundjaja, V.; Angkawijaya, A.E.; Jiang, Y.F.; Putro, J.N.; Hartono, S.B.; Ayucitra, A.; et al. pH-responsive hollow core zeolitic-imidazolate framework-8 as an effective drug carrier of 5-fluorouracil. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 27, 101277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Hu, M.; Dong, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhan, X.; Chang, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, X. Folic acid decorated zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) loaded with baicalin as a nano-drug delivery system for breast cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 8337–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; You, Y.; Zha, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J.; Kwan, H.Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Biotin decorated celastrol-loaded ZIF-8 nano-drug delivery system targeted epithelial ovarian cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangar, S.P.; Chaudhary, V.; Sharma, N.; Bansal, V.; Ozogul, F.; Lorenzo, J.M. Kaempferol: A flavonoid with wider biological activities and its applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 9580–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rofeal, M.; El-Malek, F.A.; Qi, X. In vitro assessment of green polyhydroxybutyrate/chitosan blend loaded with kaempferol nanocrystals as a potential dressing for infected wounds. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 375102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periferakis, A.; Periferaki, K.; Badarau, I.A.; Petran, E.M.; Popa, D.C.; Caruntu, A.; Costache, R.S.; Scheeau, C.; Caruntu, C.; Costache, D.O. Kaempferol: Antimicrobial Properties, Sources, Clinical, and Traditional Applications. Int. J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiak, N.; Tykarska, E.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. The Study of Amorphous Kaempferol Dispersions Involving FT-IR Spectroscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, B.; de Morais, L.A.; Viana, M.C.; Carneiro, G. Promising strategies for improving oral bioavailability of poor water-soluble drugs. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2023, 18, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhai, S.; Qin, Y.; Hao, M.; Su, S.; Li, S.; Tang, X. Competitive coordination assembly of light-degradable gold nanocluster-intercalated metal organic frameworks for photoresponsive drug release. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2024, 12, 4018–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C.; Daniel, A.R.; Driver, L.M.; Lee, C.L.; Kirsch, D.G. Histological assessment of intestinal injury by ionizing radiation. Methods Cell Biol. 2023, 180, 147–175. [Google Scholar]
- Santivasi, W.L.; Xia, F. Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapko, J.; Talapko, D.; Katalinić, D.; Kotris, I.; Erić, I.; Belić, D.; Vasilj Mihaljević, M.; Vasilj, A.; Erić, S.; Flam, J.; et al. Health Effects of Ionizing Radiation on the Human Body. Medicina 2024, 60, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Status. DNA Cell Biol. 2024, 43, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Du, C.; Wang, J.; Liao, W. Insights into ionizing radiation-induced bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasoul, Y.; Dheyauldeen, S.; Mohsen, C.; Ahmed, E.M.; Bagher, F.; Abolhasan, R.; Peyman, A.; Hengameh, F.; Masoud, N. Radiation Protection and Mitigation by Natural Antioxidants and Flavonoids: Implications to Radiotherapy and Radiation Disasters. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, T.; Feng, J.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, Y. Kaempferol protects against gamma radiation-induced mortality and damage via inhibiting oxidative stress and modulating apoptotic molecules in vivo and vitro. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 60, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mao, J.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Wu, B.; Yuan, Y. Kaempferol Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Through Intervening Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress Induced Apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, E.; Cao, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; You, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Feng, Y. The mitochondria-targeted Kaempferol nanoparticle ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Xing, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lin, L.; Yu, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, X. Tannic acid and zinc ion coordination of nanase for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease by promoting mucosal repair and removing reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Acta Biomater. 2024, 177, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, R.; Han, G.G.; Luong, H.; Vaishnava, S. Intestinal epithelial cell intrinsic zinc home-ostasis is critical for host-microbiome symbiosis. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; Handy, R.D.; Upton, M.; Besinis, A. Review of Antimicrobial nanocoatings in Medicine and Dentistry: Mechanisms of Action, Biocompatibility Performance, Safety, and benefits compared to antibiotics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 7064–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Fan, T.; Jia, M.; Yin, R.; Xue, J.; Xian, L.; Fan, P.; Zhan, M. Biomimetic ZIF-8 Nanoparticles: A Novel Approach for Biomimetic Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 5523–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIF-8) for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 7023–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Kong, D.; Guo, W.; Xia, X.; Li, D.; Zhou, D. Metal-organic-framework-based sitagliptin-release platform for multieffective radiation-induced intestinal injury targeting therapy and intestinal flora protective capabilities. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantara, C.; Moya, S.M.; Houchen, C.W.; Umar, S.; Ullrich, R.L.; Singh, P.; Carney, D.H. Novel regenerative peptide TP508 mitigates radiation-induced gastrointestinal damage by activating stem cells and preserving crypt integrity. Lab. Invest. 2015, 95, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Ryoo, S.B.; Heo, K.; Kim, J.G.; Son, T.G.; Moon, C.; Yang, K. Attenuating effects of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) in radiation induced intestinal injury in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formulation of KAE | Tmax (h) | Cmax (μg/mL) | AUC0-∞ (μg/mL·h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KAE powder | 1.65 ± 0.80 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 1.14 ± 0.03 |
| KAE@ZIF-8 | 0.96 ± 0.29 | 0.76 ± 0.10 ** | 2.54 ± 0.08 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Han, L.; Gong, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Y. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) as a Carrier for Kaempferol Delivery to Protect Against Gamma Radiation-Induced Mortality and Damage. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111489
Yang G, Wang J, Wang R, Han L, Gong C, Chen J, Chen M, Yuan Y. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) as a Carrier for Kaempferol Delivery to Protect Against Gamma Radiation-Induced Mortality and Damage. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111489
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Gang, Jing Wang, Rong Wang, Lu Han, Chunai Gong, Jiyuan Chen, Minyan Chen, and Yongfang Yuan. 2025. "Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) as a Carrier for Kaempferol Delivery to Protect Against Gamma Radiation-Induced Mortality and Damage" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111489
APA StyleYang, G., Wang, J., Wang, R., Han, L., Gong, C., Chen, J., Chen, M., & Yuan, Y. (2025). Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) as a Carrier for Kaempferol Delivery to Protect Against Gamma Radiation-Induced Mortality and Damage. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111489







