Injectable Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Polypeptide Hydrogels as Drug Depots for Antitumor Chemo-Immunotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(L-Glutamic Acid) Functionalized with Dibenzocyclooctyne (PLG-DBCO)
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of the Hydrogel
2.4. Degradation Behavior of the Hydrogel
2.5. Drug Release
2.5.1. In Vitro Release of OXA
2.5.2. In Vitro Release of Cy3-IgG
2.5.3. In Vivo Release of Cy5-IgG
2.6. Material Cytotoxicity
2.7. Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD) Induction
2.7.1. Exposure of Calreticulin (CRT)
2.7.2. Release of HMGB-1
2.8. B16F10 Unilateral Tumor Model
2.9. Immune Cell Analysis of the B16F10 Unilateral Tumor Model
2.10. Bilateral-Tumor Model
2.11. Animal Procedure
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
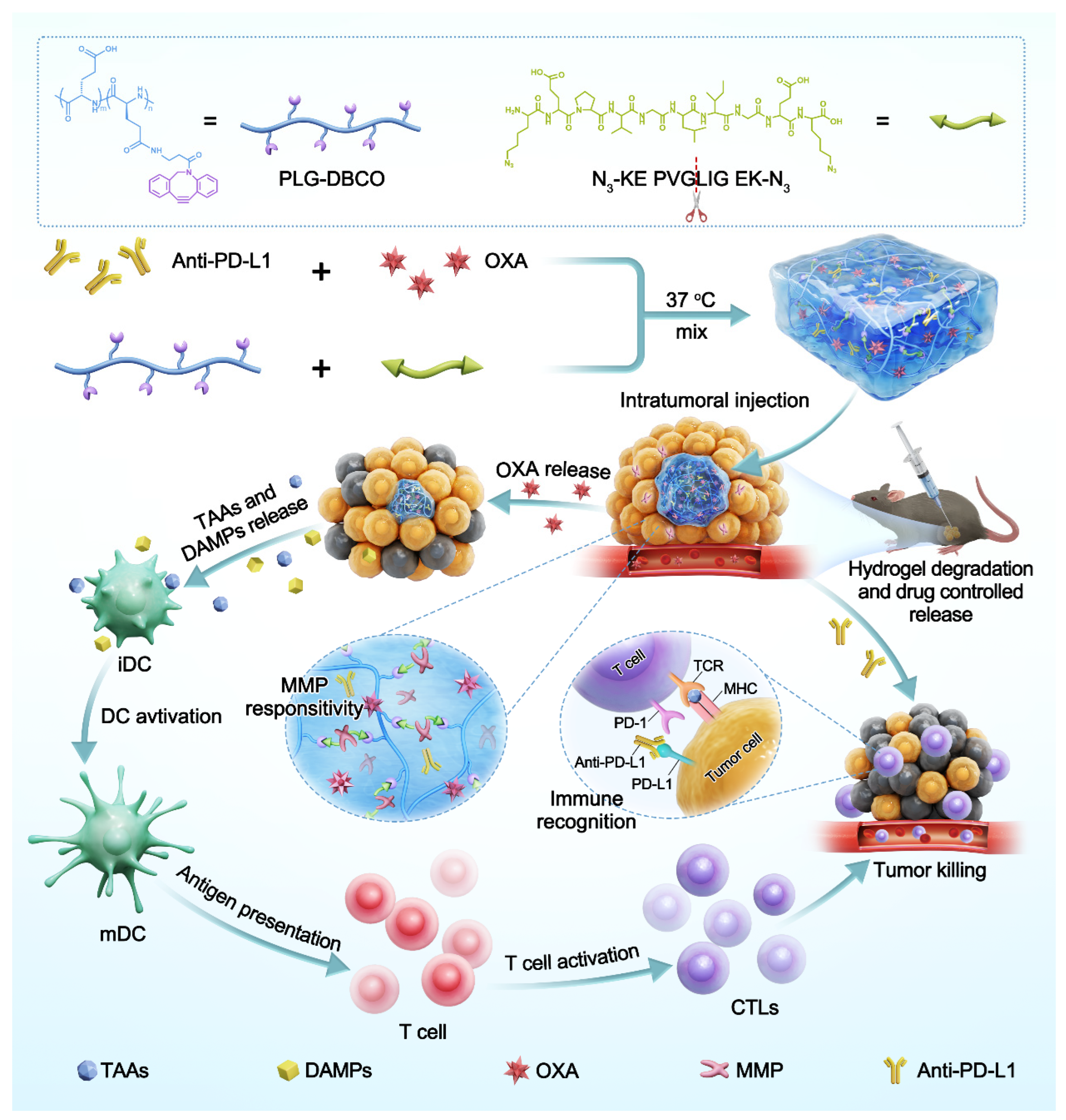
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrogels
3.2. The Responsive Degradation of Hydrogels
3.3. The Responsive Drug Release of Hydrogels
3.4. Induction of Immunogenic Cell Death
3.5. Tumor Inhibition Efficacy of OXA and Anti-PD-L1 Co-Loaded Hydrogels in the Unilateral B16F10 Melanoma Model
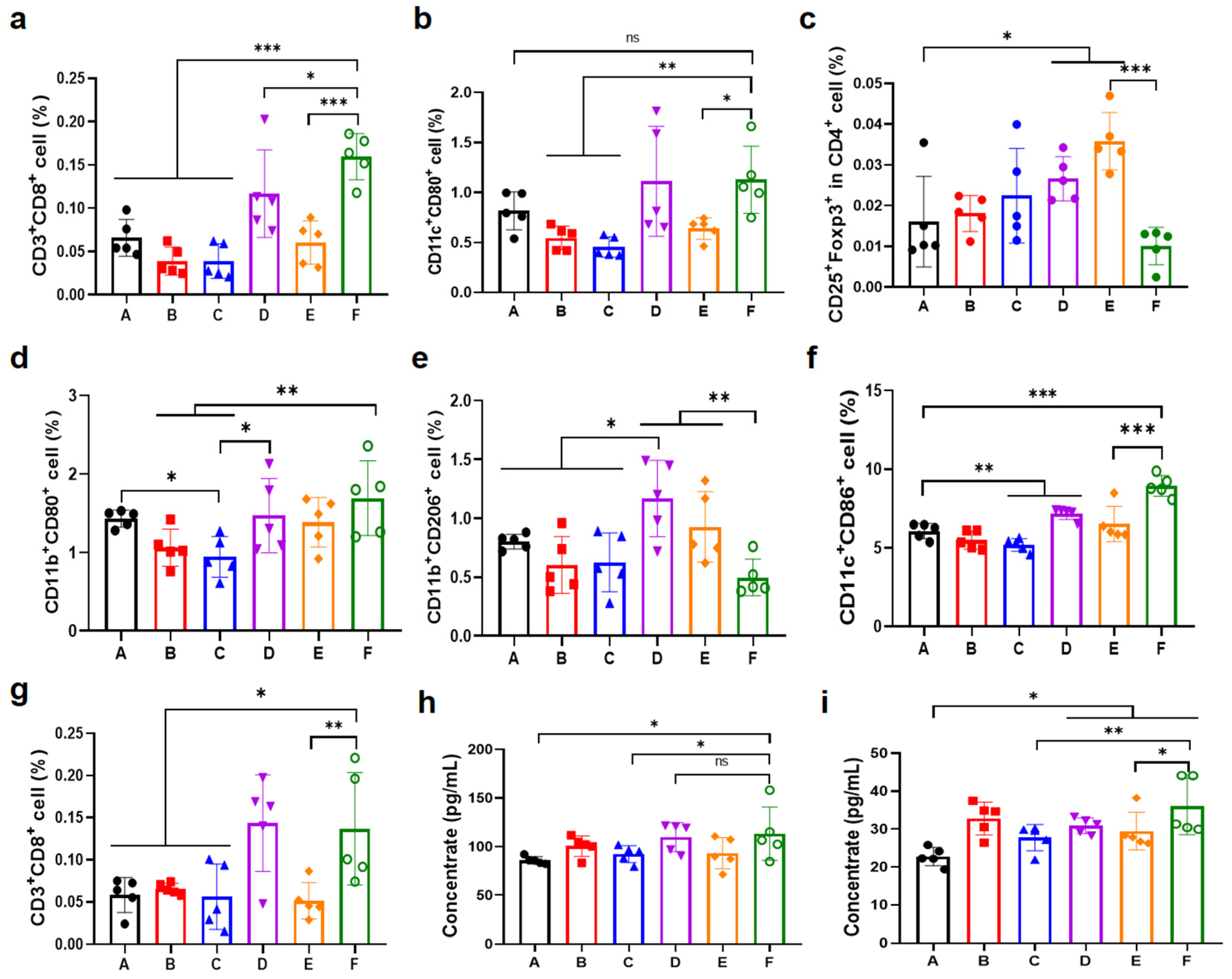
3.6. Antitumor Immune Response in the Unilateral B16F10 Melanoma Model
3.7. Chemo-Immunotherapy in a Bilateral-Tumor Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Tan, L.; Siu, K.T.H.; Guan, X.-Y. Exploring treatment options in cancer: Tumor treatment strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Dey, A.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Sanyal, R.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, D.K.; De Falco, V.; Upadhyay, A.; Kandimalla, R.; Chaudhary, A.; et al. Cancer chemotherapy and beyond: Current status, drug candidates, associated risks and progress in targeted therapeutics. Genes Dis. 2023, 10, 1367–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: Understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiam-Galvez, K.J.; Allen, B.M.; Spitzer, M.H. Systemic immunity in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xu, C. Immune checkpoint signaling and cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.C.; Zappasodi, R. A decade of checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in melanoma: Understanding the molecular basis for immune sensitivity and resistance. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Han, Z.; Ma, D. Immune checkpoint therapy for solid tumours: Clinical dilemmas and future trends. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syn, N.L.; Teng, M.W.L.; Mok, T.S.K.; Soo, R.A. De-novo and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint targeting. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e731–e741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Liang, C.; Tao, H.; Du, Y.; Wu, D.; Dong, Z.; Jin, Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, J.; Xiao, Z.; et al. Localized cocktail chemoimmunotherapy after in situ gelation to trigger robust systemic antitumor immune responses. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroemer, G.; Galassi, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Galluzzi, L. Immunogenic cell stress and death. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Cai, J.; Yuan, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, C.; et al. Immunogenic cell death inducers: Current advances and future perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 542, 216846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinhuis, K.M.; Ros, W.; Kok, M.; Steeghs, N.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. Enhancing antitumor response by combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with chemotherapy in solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shim, M.K.; Moon, Y.; Kim, J.; Cho, H.; Yun, W.S.; Shim, N.; Seong, J.-K.; Lee, Y.; Lim, D.-K.; et al. Cancer cell-specific and pro-apoptotic SMAC peptide-doxorubicin conjugated prodrug encapsulated aposomes for synergistic cancer immunotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Hao, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, L.; Miao, L.; Liu, Z. Liposomal oxaliplatin prodrugs loaded with metformin potentiate immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. J. Control. Release 2022, 350, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Xiong, N.; Cheng, S.-C.; Barry, W.T.; Penson, R.T.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Hoffman, M.A.; Horowitz, N.; Dizon, D.S.; Stover, E.H.; et al. Combined pembrolizumab and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in platinum resistant ovarian cancer: A phase 2 clinical trial. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Minashi, K.; Sakai, D.; Nishina, T.; Omuro, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Iwagami, S.; Kawakami, H.; Esaki, T.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. Phase IIb study of pembrolizumab combined with S-1 + oxaliplatin or S-1 + cisplatin as first-line chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 2814–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, A.; Diaz, A.E.; Doyle, P.S. Hydrogel-enabled, local administration and combinatorial delivery of immunotherapies for cancer treatment. Mater. Today 2023, 65, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Chen, X. Designing hydrogels for immunomodulation in cancer therapy and regenerative medicine. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2308894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Du, C.; Huang, W.; Lei, Y. Injectable smart stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Pioneering advancements in biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 12, 8–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, T.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, F.; Rong, Y.; Chen, X.; He, C. Chiral polypeptide hydrogels regulating local immune microenvironment and anti-tumor immune response. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Ding, J.; Li, Z.; Rong, Y.; He, C.; Chen, X. ROS-responsive thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogels for localized drug delivery and improved tumor chemoimmunotherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Chen, X. Bioactive polypeptide hydrogels modified with RGD and N-cadherin mimetic peptide promote chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; di Marco, G.; Iudin, D.; Viola, M.; van Nostrum, C.F.; van Ravensteijn, B.G.P.; Vermonden, T. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels: The dynamic smart biomaterials of tomorrow. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 8377–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Kou, L.; Tu, Y.; Zhu, L. MMP-responsive ‘smart’ drug delivery and tumor targeting. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordeleau, F.; Mason, B.N.; Lollis, E.M.; Mazzola, M.; Zanotelli, M.R.; Somasegar, S.; Califano, J.P.; Montague, C.; LaValley, D.J.; Huynh, J.; et al. Matrix stiffening promotes a tumor vasculature phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Fingleton, B.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer—Trials and tribulations. Science 2002, 295, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Jang, N.H.; Lee, H.J. Natural products as regulators against matrix metalloproteinases for the treatment of cancer. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, K.J.; Jensen, M.M.; Subrahmanyam, N.B.; Ghandehari, H. Matrix-metalloproteinases as targets for controlled delivery in cancer: An analysis of upregulation and expression. J. Control. Release 2017, 259, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, B.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Feng, Y. Enzyme-responsive strategy as a prospective cue to construct intelligent biomaterials for disease diagnosis and therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 1883–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.I.; Magalhães, M.V.; Bidarra, S.J.; Moroni, L.; Barrias, C.C. Versatile click alginate hydrogels with protease-sensitive domains as cell responsive/instructive 3D microenvironments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakroun, R.W.; Sneider, A.; Anderson, C.F.; Wang, F.; Wu, P.H.; Wirtz, D.; Cui, H. Supramolecular design of unsymmetric reverse bolaamphiphiles for cell-sensitive hydrogel degradation and drug release. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4434–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Su, H.; Xu, D.; Monroe, M.K.; Anderson, C.F.; Zhang, W.; Oh, R.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Therapeutic supramolecular tubustecan hydrogel combined with checkpoint inhibitor elicits immunity to combat cancer. Biomaterials 2021, 279, 121182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; He, C.; Xiao, C.; Li, G.; Chen, X. Injectable glycopolypeptide hydrogels as biomimetic scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Phuengkham, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Dinh, V.V.; Lee, I.; Shin, I.W.; Shin, H.S.; Jin, S.M.; Um, S.H.; Lee, H.; et al. Syringeable immunotherapeutic nanogel reshapes tumor microenvironment and prevents tumor metastasis and recurrence. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudazi, R.; Zowada, R.; Manas-Zloczower, I.; Feke, D.L. Porous hydrogels: Present challenges and future opportunities. Langmuir 2023, 39, 2092–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Feng, J.; Klocker, H.; Lee, C.; Zhang, J. Type IV collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9) in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2004, 7, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Shan, X.; Sun, X.; You, Q.; Gong, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Injectable supramolecular hydrogel co-loading abemaciclib/NLG919 for neoadjuvant immunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Mo, H.; Hu, X.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Niu, L.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; et al. Single-cell analyses reveal key immune cell subsets associated with response to PD-L1 blockade in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yong, T.; Bie, N.; Zhan, G.; Li, X.; Liang, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, G.; et al. Boosting anti-PD-1 therapy with metformin-loaded macrophage-derived microparticles. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, S.; Wang, T.; Ding, J.; Yang, J.; He, C.; Rong, Y. Injectable Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Polypeptide Hydrogels as Drug Depots for Antitumor Chemo-Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111453
Liang S, Wang T, Ding J, Yang J, He C, Rong Y. Injectable Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Polypeptide Hydrogels as Drug Depots for Antitumor Chemo-Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111453
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Shuang, Tianran Wang, Junfeng Ding, Jiaxuan Yang, Chaoliang He, and Yan Rong. 2025. "Injectable Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Polypeptide Hydrogels as Drug Depots for Antitumor Chemo-Immunotherapy" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111453
APA StyleLiang, S., Wang, T., Ding, J., Yang, J., He, C., & Rong, Y. (2025). Injectable Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Polypeptide Hydrogels as Drug Depots for Antitumor Chemo-Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111453





