Development of Practical Low-Volume Screening Method and Pharmacokinetic Simulation of Levofloxacin-Loaded Nanofiber Inserts for Sustained Ocular Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Precursor Solution Preparation for the Electrospinning Process
2.3. Preparation of Nanofibers
2.4. Small-Volume Dissolution Study
- Dissolution Vessel: A square-shaped borosilicate glass container (8 cm × 8 cm base, 6 cm height) was used as the dissolution bath. It was filled with water and maintained at the desired temperature throughout the experiments. To minimize evaporation of the dissolution medium, a custom-designed lid was 3D-printed using polylactic acid (PLA) filament (basic black PLA, SNAPMAKER HK LIMITED, Hong Kong, China). The lid was fabricated with a Snapmaker 2.0 Modular 3-in-1 3D Printer A350T (SNAPMAKER HK LIMITED, Hong Kong, China).
- Magnetic Stirrer with Heating Function: An IKA RCT Basic safety control stirrer (IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG, Staufen im Breisgau, Germany) served as the base. The device featured two control knobs for independent regulation of temperature and stirring speed. The heating plate ensured homogeneous thermal distribution throughout the medium.
- 3D printed custom cylindrical cage: The predetermined size and weight nanofibrous sheets were screwed on a magnetic stirring bar (diameter: 2 mm and length: 7 mm) and it was placed into a 3D printed custom cylindrical cage (inner diameter: 0.5 cm, length: 1 cm), which ensured that the nanofibrous sample was immersed into the dissolution medium.
- Automatic Pipette Assembly: The pipette was vertically mounted onto an external retort stand, aligned with the center of the vessel for reproducible sample withdrawal. In this model, 200 µL aliquots were withdrawn at predetermined intervals.
- Temperature Sensor: A digital probe was affixed to a vertical rod via a clamp. The probe extended through the designated port on the vessel lid to monitor the temperature within the dissolution vessel (water bath), ensuring consistent thermal control of the medium (±0.2 °C).
Data Analysis and Limitations
- y = cumulative percentage of drug released (%),
- A = asymptotic maximum dissolution (%),
- x = time (sec),
- xc = lag time (sec),
- d = shape factor (controls the release kinetics),
- k = scale parameter (related to the time required for drug release).
- Rt is the percentage of drug released at time t from the reference (40 mL);
- Tt is the percentage of drug released at time t from the test sample (2 mL)
- n is the number of time points.
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Model
2.5.1. Key Parameters and Assumptions
Eye Drop Model
- Drug concentration and dosing: 5 mg/mL, applied in every 2 h.
- Dose per drop: 0.25 mg per application (0.05 mL volume/drop).
- Dosing: 12 doses per day over 24 h.
- Determination of clearance rate for eyedrops:
Nanofibrous Insert Model
- Insert Weight: 10 mg, levofloxacin at 10% (w/w).
- Drug Content per Insert: 1 mg.
- Drug Release Rate Constant (krelease).
- Ocular Clearance rate:
- Hydration-triggered in situ gelation,
- Mucoadhesion of the nanofiber matrix,
- Reduced exposure to nasolacrimal drainage.
- Dosing: Both once-daily and twice-daily applications were simulated to determine their efficacy.
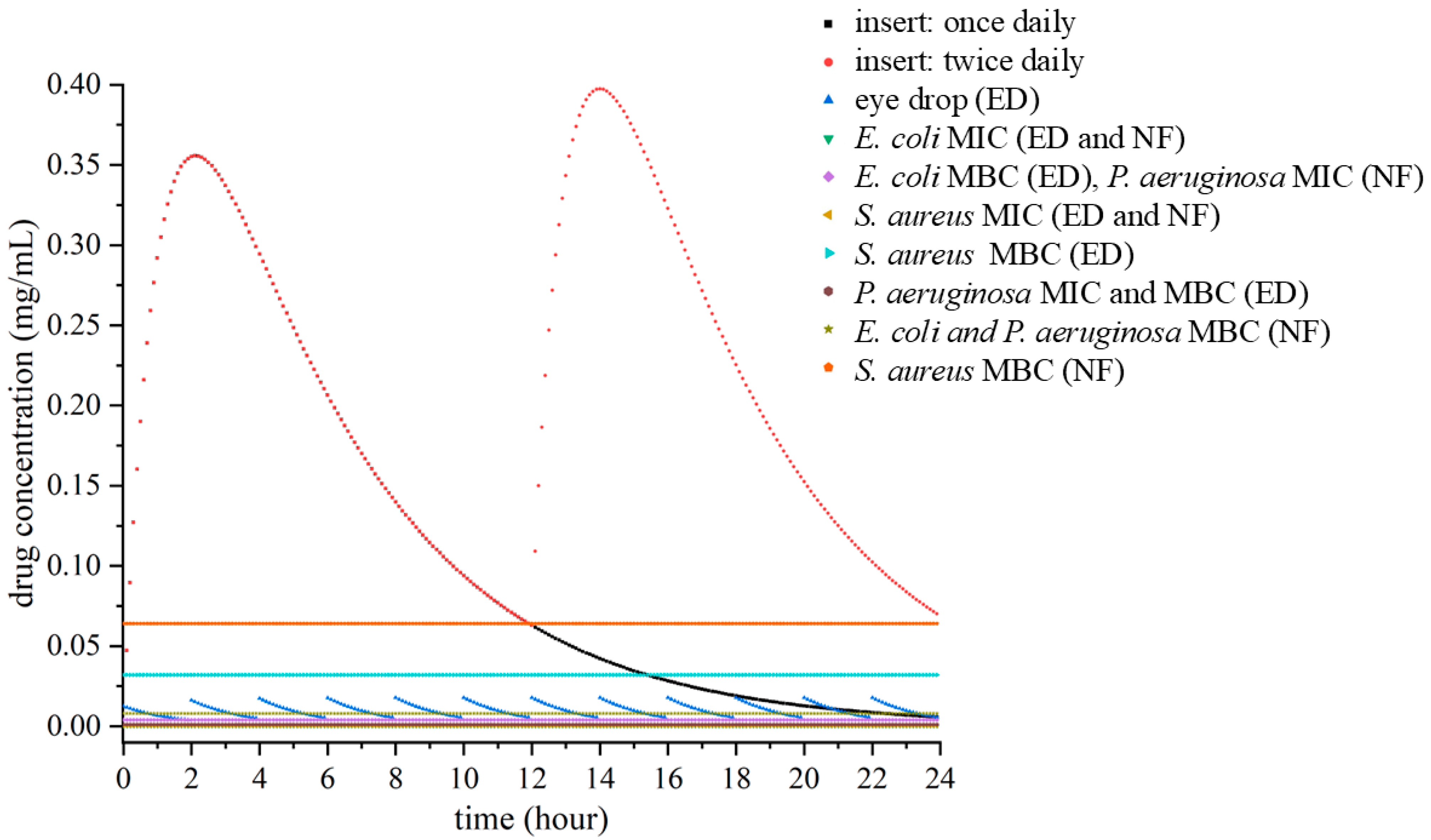
Pathogen-Specific Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Thresholds
2.5.2. Model Equations
Eye Drop Concentration Model
Nanofiber Insert Concentration Model for a Single Application
Nanofiber Insert Concentration Model for Twice-Daily Application
3. Results
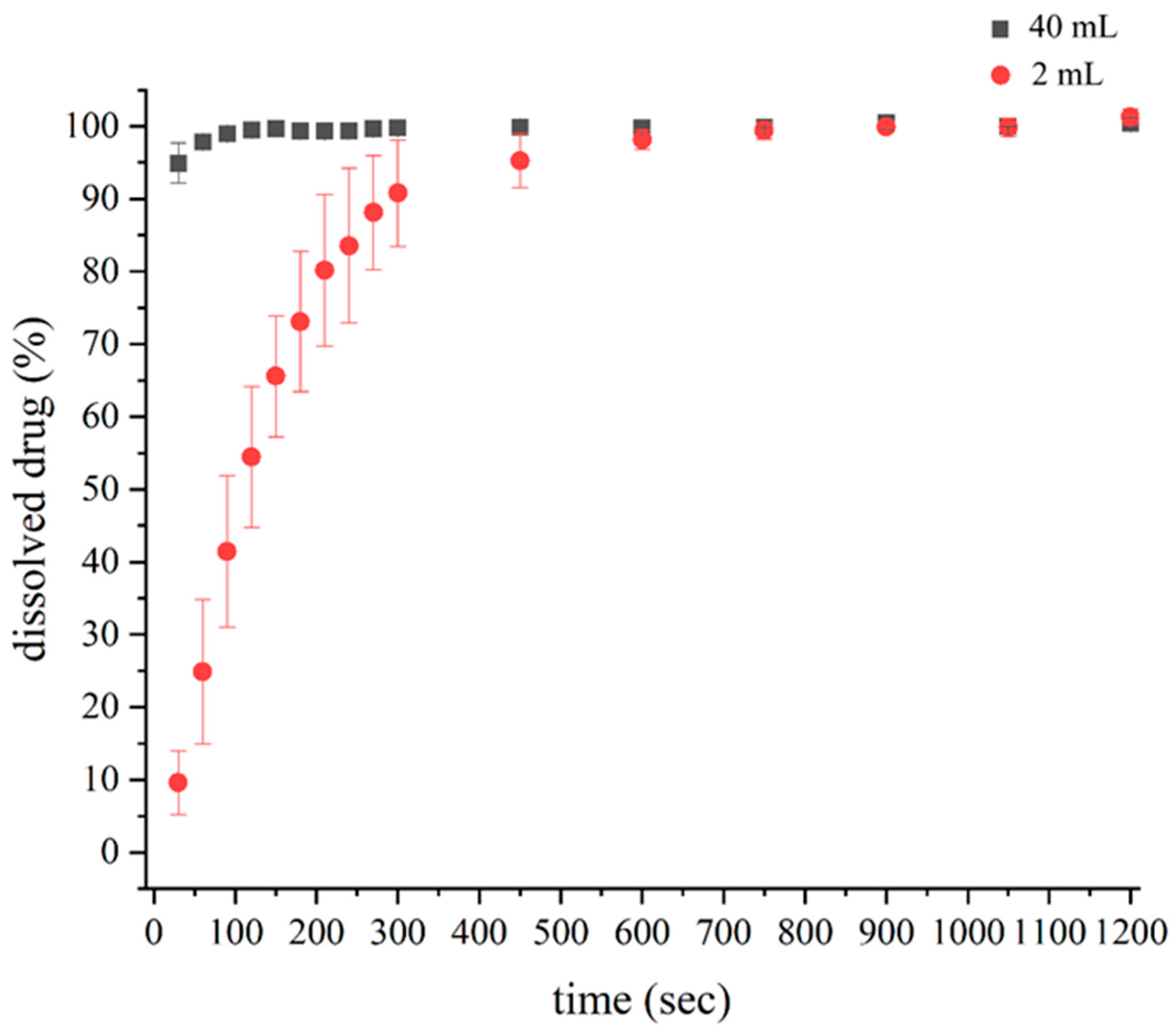
3.1. Small Volume Dissolution
3.2. Pharmacokinetic Simulation
- (i)
- a once-daily application of the nanofibrous insert,
- (ii)
- a twice-daily insert regimen, and
- (iii)
- conventional eye drops administered every two hours. The simulated profiles are shown in Figure 3.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leclercq, B.; Mejlachowicz, D.; Behar-Cohen, F. Ocular Barriers and Their Influence on Gene Therapy Products Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkouh, A.; Peter, F.; Czejka, M. Systemic side effects of eye drops: A pharmacokinetic perspective. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanier, O.L.; Manfre, M.G.; Bailey, C.; Liu, Z.; Sparks, Z.; Kulkarni, S.; Chauhan, A. Review of Approaches for Increasing Ophthalmic Bioavailability for Eye Drop Formulations. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Sabroso, C.; Alonso-González, M.; Fernández-Carballido, A.; Aparicio-Blanco, J.; Córdoba-Díaz, D.; Navarro-García, F.; Córdoba-Díaz, M.; Torres-Suárez, A.I. Limitations and Challenges in the Stability of Cysteamine Eye Drop Compounded Formulations. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jünemann, A.; Chorągiewicz, T.; Ozimek, M.; Grieb, P.; Rejdak, R. Drug bioavailability from topically applied ocular drops. Does drop size matter? Ophthalmol. J. 2016, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehuys, E.; Delaey, C.; Christiaens, T.; Van Bortel, L.; Van Tongelen, I.; Remon, J.-P.; Boussery, K. Eye drop technique and patient-reported problems in a real-world population of eye drop users. Eye 2020, 34, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, P.W.J.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Advances in Ophthalmic Drug Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 1297–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, L.V.; Kapadia, R.; Sawant, K.K. A novel nanoparticles impregnated ocular insert for enhanced bioavailability to posterior segment of eye: In vitro, in vivo and stability studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Garg, V.K.; Garg, G. Ocular inserts—Advancement in therapy of eye diseases. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, S.; Zelkó, R. A Systematic Review of Drug-Loaded Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Ophthalmic Inserts. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.A.; Ali, I.H.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Noninvasive Biodegradable Nanoparticles-in-Nanofibers Single-Dose Ocular Insert: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Evaluation. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, E.; Abboud, H.; Nagy, N.; Hofmeister, B.; Ostorházi, E.; Tóth, B.; Pinke, B.; Mészáros, L.; Zelkó, R.; Kazsoki, A. Formulation and Development of Nanofiber-Based Ophthalmic Insert for the Treatment of Bacterial Conjunctivitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghe, S.; Mirzaeei, S. Preservative-free electrospun nanofibrous inserts for sustained delivery of ceftazidime; design, characterization and pharmacokinetic investigation in rabbit’s eye. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 8, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, T.; Bhat, G.S.; Tock, R.W.; Parameswaran, S.; Ramkumar, S.S. Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Progress. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Concepts, Materials, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.J.; Chase, G.G.; Yarin, A.L.; Reneker, D.H. Effects of parameters on nanofiber diameter determined from electrospinning model. Polymer 2007, 48, 6913–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, A.; Mussa Farkhani, S. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibres. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 8, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Lin, Y.; Guo, X.; Ramasubramanian, B.; Wang, R.; Radacsi, N.; Jose, R.; Qin, X.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of nanofibres. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2024, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sahu, D.; Pradhan, D.; Halder, J.; Biswasroy, P.; Kar, B.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Design and optimization of gatifloxacin loaded polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber for the treatment of dry eye infection: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Yu, L.; Lv, Y. Voriconazole Composited Polyvinyl Alcohol/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Nanofibers for Ophthalmic Delivery. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Mishra, V.; Gharat, S.; Momin, M.; Omri, A. Cellulosic Polymers for Enhancing Drug Bioavailability in Ocular Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.R.; Lima, T.H.; Fernandes-Cunha, G.M.; Oréfice, R.L.; Da Silva-Cunha, A.; Zhao, M.; Behar-Cohen, F. Ocular biocompatibility of dexamethasone acetate loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeei, S.; Faryadras, F.B.; Mehrandish, S.; Rezaei, L.; Daneshgar, F.; Karami, A. Development and evaluation of polycaprolactone-based electrospun nanofibers containing timolol maleate as a sustained-release device for treatment of glaucoma: In vivo evaluation in equine eye. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeei, S.; Taghe, S.; Asare-Addo, K. Nokhodchi, APolyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Single-Layered and Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan/Eudragit RL100 Multi-layered Electrospun Nanofibers as an Ocular Matrix for the Controlled Release of Ofloxacin: An In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, R.S.; Das, A.; Alzhrani, R.M.; Kang, D.; Bhaduri, S.B.; Boddu, S.H.S. Comparison of electrospun and solvent cast polylactic acid (PLA)/poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) inserts as potential ocular drug delivery vehicles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrandish, S.; Ghobad, M.; Mirzaeei, S. Preparation and functional evaluation of electrospun polymeric nanofibers as a new system for sustained topical ocular delivery of itraconazole. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2022, 27, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikhi Shoushtari, F.; Naghshbandy, M.; Rezaei, L.; Mehrandish, S.; Mirzaeei, S. Fabrication of Anti-glaucoma Nanofibers as Controlled-Release Inserts for Ophthalmic Delivery of Brimonidine Tartrate: In Vivo Evaluation in Caprine Eye. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 14, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.P.; Smitha, R. Penetration Enhancers and Ocular Bioadhesives: Two New Avenues for Ophthalmic Drug Delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompella, U.B.; Kadam, R.S.; Lee, V.H. Recent Advances in Ophthalmic Drug Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Shin, K.-S.; Kim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-K. Stimulus-Responsive Contact Lens for IOP Measurement or Temperature-Triggered Drug Release. Transl. Vis. Vision. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezwada, P.; Clark, L.A.; Schneider, S. Intrinsic cytotoxic effects of fluoroquinolones on human corneal keratocytes and endothelial cells. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2008, 24, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Jog, R.; Shen, J.; Newman, B.; Wang, Y.; Choi, S.; Burgess, D.J. Physicochemical attributes and dissolution testing of ophthalmic ointments. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, S.; Nagy, N.; Pinke, B.; Mészáros, L.; Kazsoki, A.; Zelkó, R. Development and Evaluation of Different Electrospun Cysteamine-Loaded Nanofibrous Webs: A Promising Option for Treating a Rare Lysosomal Storage Disorder. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Bushetti, S.S.; Raju, S.A.; Ahmad, R.; Singh, M.; Ajmal, M. Polymeric ocular hydrogels and ophthalmic inserts for controlled release of timolol maleate. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, B.; Jójárt-Laczkovich, O.; Kovács, A.; Berkó, S.; Sipos, B.; Katona, G.; Budai-Szűcs, M. Comparative Study of Dexamethasone-Loaded Thermoresponsive In Situ Gels and Polymeric Micelles for Ocular Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksungur, P.; Demirbilek, M.; Denkbaş, E.B.; Vandervoort, J.; Ludwig, A.; Ünlü, N. Development and characterization of Cyclosporine A loaded nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery: Cellular toxicity, uptake, and kinetic studies. J. Control Release 2011, 151, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrianto, M.F.; Annuryanti, F.; Wilson, C.G.; Sheshala, R.; Thakur, R.R.S. In vitro dissolution testing models of ocular implants for posterior segment drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1355–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramaniam, J.; Srinatha, A.; Pandit, J.K. Studies on Indomethacin Intraocular Implants Using Different in vitro Release Methods. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudnason, K.; Solodova, S.; Vilardell, A.; Masson, M.; Sigurdsson, S.; Jonsdottir, F. Numerical simulation of Franz diffusion experiment: Application to drug loaded soft contact lenses. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, J.; Bajaj, T.; Goyal, A.; Rath, G. Development of Nanofibrous Ocular Insert for Retinal Delivery of Fluocinolone Acetonide. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 44, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Shen, J.; Jog, R.; Zhang, C.; Newman, B.; Wang, Y.; Choi, S.; Burgess, D.J. In vitro release testing method development for ophthalmic ointments. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, J.R.; Foureaux, G.; Fuscaldi, L.L.; Ribeiro, T.G.; Rodrigues, L.B.; Bravo, R.; Castilho, R.O.; Yoshida, M.I.; Cardoso, V.N.; Fernandes, S.O.; et al. Bimatoprost-Loaded Ocular Inserts as Sustained Release Drug Delivery Systems for Glaucoma Treatment: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievens-Figueroa, L.; Pandya, N.; Bhakay, A.; Keyvan, G.; Michniak-Kohn, B.; Bilgili, E.; Davé, R.N. Using USP I and USP IV for Discriminating Dissolution Rates of Nano- and Microparticle-Loaded Pharmaceutical Strip-Films. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenwald, R.D. Ocular Drug Delivery. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 18, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtti, A. Challenges and obstacles of ocular pharmacokinetics and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barar, J.; Asadi-Khiavi, M.; Mortazavi-Tabatabaei, S.; Omidi, Y. Ocular Drug Delivery; Impact of in vitro Cell Culture Models. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2009, 4, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raizman, M.B.; Rubin, J.M.; Graves, A.L.; Rinehart, M. Tear concentrations of levofloxacin following topical administration of a single dose of 0.5% levofloxacin ophthalmic solution in healthy volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2002, 24, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A. The use of mucoadhesive polymers in ocular drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1595–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacIsaac, K.D.; Wang, I.M.; Menetski, J.; Roberts, C. Genomic and systems approaches to translational biomarker discovery in immunological diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Yoo, H.; Hwang, T.; Park, T.-J.; Paik, D.-H.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, J. Fabrication of levofloxacin-loaded nanofibrous scaffolds using coaxial electrospinning. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 42, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pathogen | Nanofibrous Sample | Eye Drop | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (µg/mL) | MBC (µg/mL) | MIC (µg/mL) | MBC (µg/mL) | |
| E. coli | <0.125 | 8 | <0.125 | 4 |
| S. aureus | 0.25 | 64 | 0.25 | 32 |
| P. aeruginosa | 4 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| Parameter | 40 mL Dissolution Volume | 2 mL Dissolution Volume |
|---|---|---|
| A | 100.2234 | 101.0138 |
| xc | 23.4049 | 9.7956 |
| d | 0.1593 | 0.9147 |
| k | 0.0008 | 165.4082 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abboud, H.A.; Zelkó, R.; Kazsoki, A. Development of Practical Low-Volume Screening Method and Pharmacokinetic Simulation of Levofloxacin-Loaded Nanofiber Inserts for Sustained Ocular Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101343
Abboud HA, Zelkó R, Kazsoki A. Development of Practical Low-Volume Screening Method and Pharmacokinetic Simulation of Levofloxacin-Loaded Nanofiber Inserts for Sustained Ocular Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101343
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbboud, Houssam Aaref, Romána Zelkó, and Adrienn Kazsoki. 2025. "Development of Practical Low-Volume Screening Method and Pharmacokinetic Simulation of Levofloxacin-Loaded Nanofiber Inserts for Sustained Ocular Therapy" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101343
APA StyleAbboud, H. A., Zelkó, R., & Kazsoki, A. (2025). Development of Practical Low-Volume Screening Method and Pharmacokinetic Simulation of Levofloxacin-Loaded Nanofiber Inserts for Sustained Ocular Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101343







