Eculizumab in C3 Glomerulopathy: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
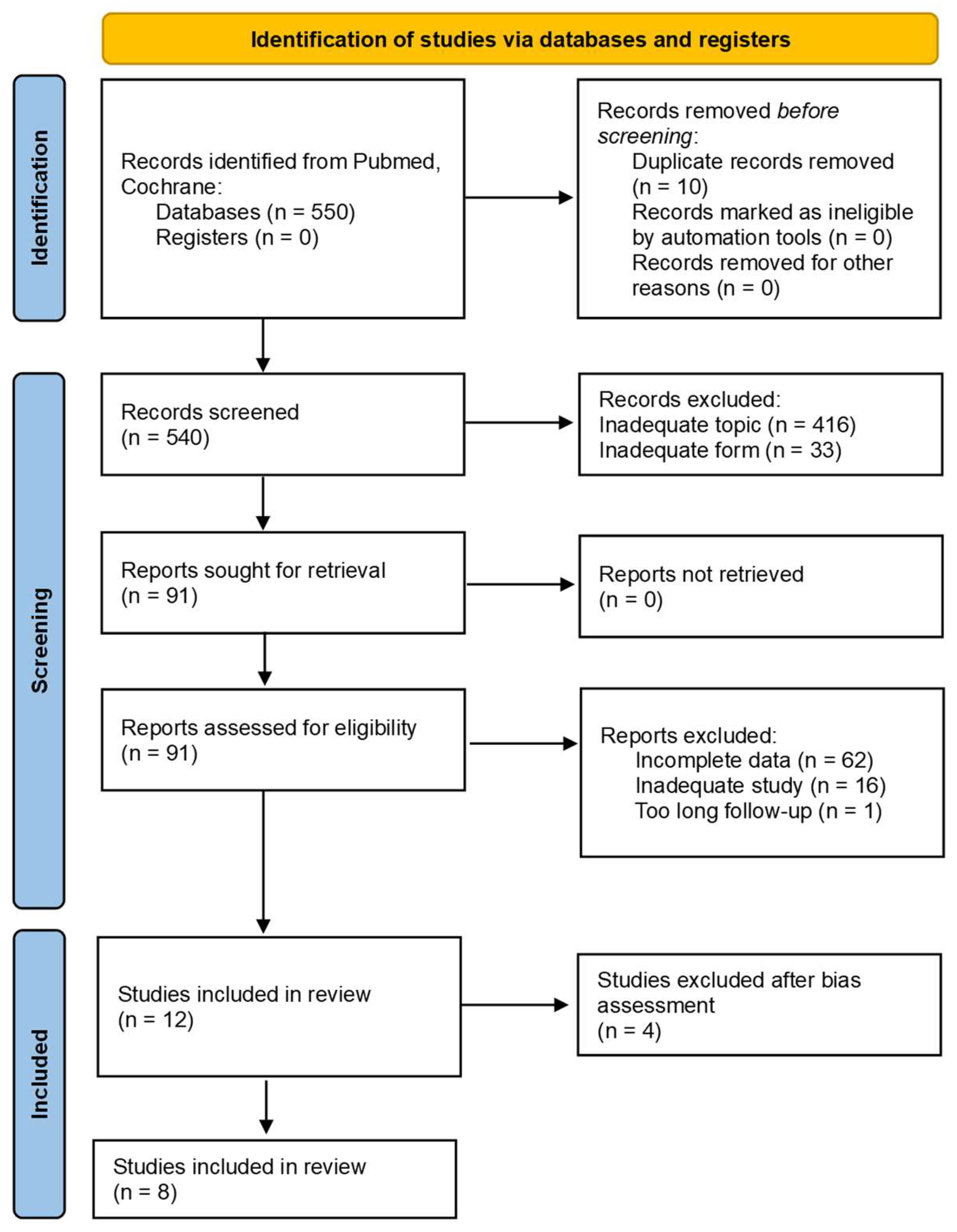
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Collection Process
2.5. Bias Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Studies
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.3. Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, R.J.H.; Appel, G.B.; Blom, A.M.; Cook, H.T.; D’Agati, V.D.; Fakhouri, F.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Józsi, M.; Kazatchkine, M.; Kavanagh, D.; et al. C3 Glomerulopathy—Understanding a Rare Complement-Driven Renal Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.B.; Bomback, A.S. C3 Glomerulopathy: Pathogenesis and Treatment. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020, 27, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, K.; Goel, D.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Mao, M.A.; Herrmann, S.M. C3 Glomerulopathy: A Kidney Disease Mediated by Alternative Pathway Deregulation. Front. Nephrol. 2024, 4, 1460146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C.; Chen, Q.; Wiech, T.; Goodship, T.; Johnson, S.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Nester, C.; Dragon-Durey, M.A.; Mache, C.; et al. The Role of Complement in C3 Glomerulopathy. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petr, V.; Thurman, J.M. The Role of Complement in Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, T.; Sato, S.; Okazaki, H.; Nangaku, M.; Mayadas, T.N. Expansion of Anticomplement Therapy Indications from Rare Genetic Disorders to Common Kidney Diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2024, 75, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, M.; Donadelli, R.; Remuzzi, G. Autoimmune Abnormalities of the Alternative Complement Pathway in Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis and C3 Glomerulopathy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.E.; Stitzel, A.E.; Tsokos, G. On the origin of C3 nephritic factor (antibody to the alternative pathway C3 convertase): Evidence for the Adam and Eve concept of autoantibody production. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1992, 64, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvillo, F.; López-Trascasa, M. Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy and C3 Glomerulopathy: Dysregulation of the Complement System as a Common Pathogenic Mechanism. Nefrologia 2018, 38, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuleman, M.S.; Vieira-Martins, P.; El Sissy, C.; Audard, V.; Baudouin, V.; Bertrand, D.; Bridoux, F.; Louillet, F.; Dossier, C.; Esnault, V.; et al. Rare Variants in Complement Genes in C3 Glomerulopathy and Immunoglobulin-Mediated Membranoproliferative GN. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Wiech, T.; Rudnick, R.; Afonso, S.; Person, F.; Skerka, C. CFHR Gene Variations Provide Insights in the Pathogenesis of the Kidney Diseases Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3 Glomerulopathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuleman, M.S.; Petitprez, F.; Pickering, M.C.; Le Quintrec, M.; Artero, M.R.; Duval, A.; Rabant, M.; Gilmore, A.; Boyer, O.; Hogan, J.; et al. Complement Terminal Pathway Activation and Intrarenal Immune Response in C3 Glomerulopathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 35, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, R.A.; Young, N.S.; Antonioli, E.; Risitano, A.M.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Schubert, J.; Gaya, A.; Coyle, L.; de Castro, C.; Fu, C.L.; et al. Multicenter Phase 3 Study of the Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab for the Treatment of Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Blood 2008, 111, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, C.M.; Licht, C.; Muus, P.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.; Bingham, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, N.; Polimera, H.V.; Arora, P.; Agraharkar, M.; Gajulapalli, R. Continued Anticomplement Therapy: A Lifeline for Post-Renal-Transplant Patients with Complement-Mediated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Therapeutics 2024, 1, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Kienle, G.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Sox, H.; Riley, D.; the CARE Group. The CARE Guidelines: Consensus-Based Clinical Case Reporting Guideline Development. Headache 2013, 53, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quintrec, M.; Lionet, A.; Kandel, C.; Bourdon, F.; Gnemmi, V.; Colombat, M.; Fakhouri, F. Eculizumab for Treatment of Rapidly Progressive C3 Glomerulopathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Moreno, A.; de la Cerda, F.; Cabrera, R.; García, E.; Blasco, M.; Gallego, N.; Praga, M. Eculizumab in Dense-Deposit Disease after Renal Transplantation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 2055–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkan, S.; Fyfe, B.; Weiss, L.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Smith, R.J.H. Eculizumab and Recurrent C3 Glomerulonephritis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkaya, O.; Akman, S.; Korkmaz, E.; Bayrakci, U.S.; Topaloglu, R.; Bakkaloglu, A. Eculizumab Therapy in a Patient with Dense-Deposit Disease Associated with Partial Lipodystrophy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Eden, G.; Hilger, T.; Knaup, S.; Wiech, T.; Zipfel, P.F.; Heeringa, P.; Höhne, M.; Józsi, M. An Interdisciplinary Diagnostic Approach to Guide Therapy in C3 Glomerulopathy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 826513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, K.; Kamei, K.; Sato, M.; Honda, M. Eculizumab for Pediatric Dense Deposit Disease: A Case Report and Literature Review. Clin. Nephrol. Case Stud. 2020, 8, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersnik Levart, T.; Furlan, P.; Kenig, A.; Vizjak, A. Severe Active C3 Glomerulonephritis Triggered by Immune Complexes and Inactivated after Eculizumab Therapy. Diagn. Pathol. 2016, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jandal, A.; Zhong, W.; Gopal, D.; Horner, V.; Frater-Rubsam, L.; Djamali, A.; Bhutani, G. What Lies In-Between: C3 Glomerulopathy with Non-Hemolytic Renal Microangiopathy and an Ultra-Rare C3 Variant. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 365, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besbas, N.; Gulhan, B.; Gucer, S.; Korkmaz, E.; Ozaltin, F. A Novel CFHR5 Mutation Associated with C3 Glomerulonephritis in a Turkish Girl. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, A.P.; Ramos, N.; Perurena-Prieto, J.; Manrique-Rodríguez, S.; Climente, M.; Quintanilla, L.G.; Escolano, Á.; Miarons, M. Pharmacokinetics of Eculizumab in Adult and Pediatric Patients with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3 Glomerulopathy. Farm. Hosp. 2024, 48, T16–T22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomback, A.S.; Smith, R.J.H.; Barile, G.R.; Zhang, Y.; Heher, E.C.; Herlitz, L.C.; Stokes, M.B.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D.; Canetta, P.A.; et al. Eculizumab for Dense Deposit Disease and C3 Glomerulonephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Fuentes, M.C.; Caba-Molina, M.; Polo-Moyano, A.; Palomares-Bayo, M.; Galindo-Sacristan, P.; De Gracia-Guindo, C. A 78-Year-Old Man with Chronic Kidney Disease and Monoclonal Gammopathy Who Developed Post-Transplant C3 Glomerulopathy—Recurrence or De Novo? A Case Report and Literature Review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2023, 24, e939726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggenenti, P.; Daina, E.; Gennarini, A. C5 Convertase Blockade in Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis: A Single Arm Clinical Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, T.; Arnold, F.; Kappes, J.; Seidl, M.; Häffner, K.; Bergmann, C.; Walz, G.; Neumann-Haefelin, E. Treating C3 Glomerulopathy with Eculizumab. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, D.; Sabapathy, V.; Chauss, D. Role of Local Complement Activation in Kidney Fibrosis and Repair. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e188345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisinger, M.J.; Goebeler, V.; Lu, Z.; Meixner, S.C.; Myles, T.; Pryzdial, E.L.G.; Conway, E.M. Thrombin Generates Previously Unidentified C5 Products that Support the Terminal Complement Activation Pathway. Blood 2012, 120, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedemann, N.C.; Habel, M.; Ziereisen, J.; Hermann, M.; Schneider, C.; Wehling, C.; Kirschfink, M.; Kentouche, K.; Guo, R. Controlling the Anaphylatoxin C5a in Diseases Requires a Specifically Targeted Inhibition. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 180, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshikawa, N.; Hasegawa, S.; Nagashima, Y.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Tsubota, Y.; Miyata, S.; Miyagi, Y.; Yasumitsu, H.; Miyazaki, K. Expression of trypsin by epithelial cells of various tissues, leukocytes, and neurons in human and mouse. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, W. Cleavage of the fifth component of complement and generation of a functionally active C5b6-like complex by human leukocyte elastase. Immunobiology 2000, 201, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayashi, S.; Ohyashiki, K.; Ando, K.; Brodsky, A.L.; Noji, H.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Genetic Variants in C5 and Poor Response to Eculizumab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, A.; Noël, L.H.; Roumenina, L.T.; Le Quintrec, M.; Ngo, S.; Dragon-Durey, M.A.; Macher, M.A.; Zuber, J.; Karras, A.; Provot, F.; et al. Acquired and Genetic Complement Abnormalities Play a Critical Role in Dense Deposit Disease and Other C3 Glomerulopathies. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, S.H.; Valeri, A.M.; Appel, G.B.; Sherwinter, J.; Stokes, M.B.; Said, S.M.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D. Dense Deposit Disease: Clinicopathologic Study of 32 Pediatric and Adult Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisch, N.M.; Pezzillo, K.K. HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors for the Prevention of Nephropathy. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, M. Rituximab for Treatment of Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis and C3 Glomerulopathies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2180508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaca-Fontán, F.; Díaz-Encarnación, M.M.; Lucientes, L.; Cavero, T.; Cabello, V.; Ariceta, G.; Quintana, L.F.; Marco, H.; Barros, X.; Ramos, N.; et al. Mycophenolate Mofetil in C3 Glomerulopathy and Pathogenic Drivers of the Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabasco, C.; Cavero, T.; Román, E.; Rojas-Rivera, J.; Olea, T.; Espinosa, M.; Cabello, V.; Fernández-Juarez, G.; González, F.; Ávila, A.; et al. Effectiveness of Mycophenolate Mofetil in C3 Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avasare, R.S.; Canetta, P.A.; Bomback, A.S.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Appel, G.B. Mycophenolate Mofetil in Combination with Steroids for Treatment of C3 Glomerulopathy: A Case Series. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, K.A.; Schlueter, A.J. Management of Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis Type II with Plasmapheresis. J. Clin. Apher. 2002, 17, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häffner, K.; Michelfelder, S.; Pohl, M. Successful Therapy of C3Nef-Positive C3 Glomerulopathy with Plasma Therapy and Immunosuppression. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zand, L.; Lorenz, E.C.; Cosio, F.G.; Fervenza, F.C.; Nasr, S.H.; Gandhi, M.J.; Smith, R.J.H.; Sethi, S. Clinical Findings, Pathology, and Outcomes of C3GN after Kidney Transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, G.; Dello Strologo, A.; Grandaliano, G.; Pesce, F. Updates on C3 Glomerulopathy in Kidney Transplantation: Pathogenesis and Treatment Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.P.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Huang, L.; Rajan, S.; Ke, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. Clinical Safety and Efficacy of Pegcetacoplan in a Phase 2 Study of Patients with C3 Glomerulopathy and Other Complement-Mediated Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; Nester, C.; Cavero, T.; Karras, A.; Le Quintrec, M.; Lightstone, L.; Eisenberger, U.; Soler, M.J.; Kavanagh, D.; Daina, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Iptacopan in Patients with C3 Glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 2754–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podos, S.D.; Trachtman, H.; Appel, G.B.; Bomback, A.S.; Dixon, B.P.; Wetzels, J.F.; Cook, H.T.; Parikh, S.V.; Pickering, M.C.; Tumlin, J.; et al. Baseline Clinical Characteristics and Complement Biomarkers of Patients with C3 Glomerulopathy Enrolled in Two Phase 2 Studies Investigating the Factor D Inhibitor Danicopan. Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomback, A.S.; Herlitz, L.C.; Yue, H.; Kedia, P.P.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P. Effect of Avacopan, a Selective C5a Receptor Inhibitor, on Complement 3 Glomerulopathy Histologic Index of Disease Chronicity. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7 (Suppl. 2), S47–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomback, A.S.; Herlitz, L.C.; Kedia, P.P.; Petersen, J.; Yue, H.; Lafayette, R.A. Safety and Efficacy of Avacopan in Patients with Complement 3 Glomerulopathy: Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2025, 36, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, T.; Scully, M.; Ariceta, G.; Cataland, S.; Garlo, K.; Heyne, N.; Luque, Y.; Menne, J.; Miyakawa, Y.; Yoon, S.-S.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of the Long-Acting Complement C5 Inhibitor Ravulizumab for the Treatment of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in Adults. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
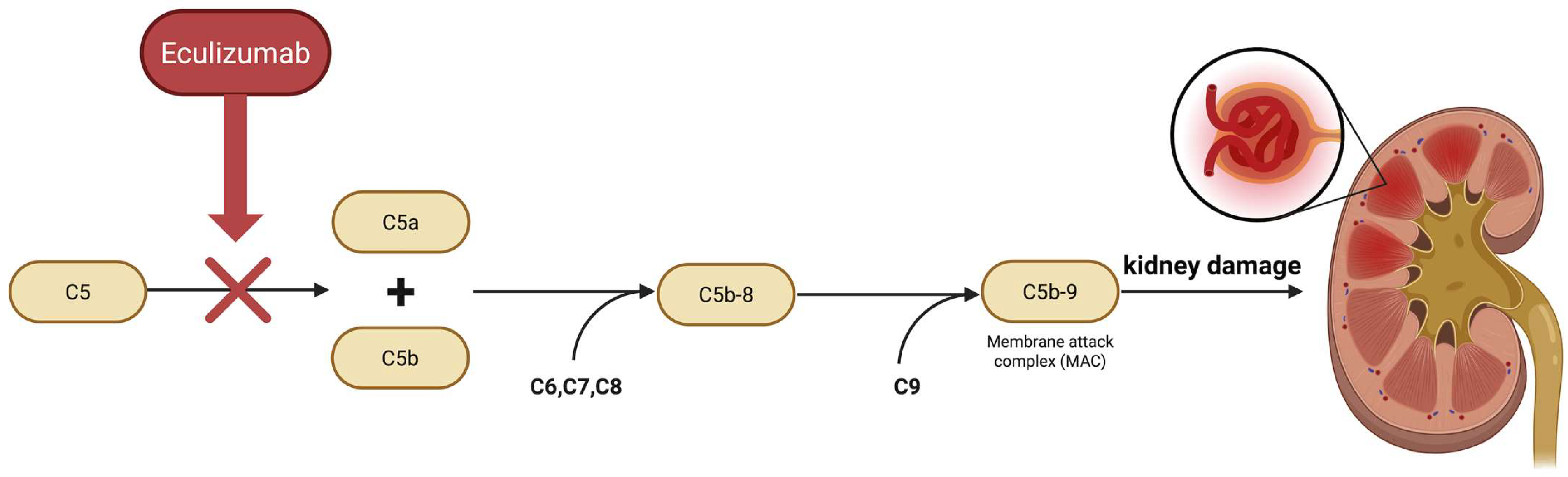
| Study | Illness | Initial GFR | Final GFR | Initial Creatinine (mg/dL) | Final Creatinine (mg/dL) | Observation Time (Months) | Initial UPCr (g/g) | Final UPCr (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Le Quintrec et al. [17] | C3G | 8.87 | 33.01 | 6 | 2 | 19 | 12.55 | 0.71 |
| C3G | 23.17 | 67.31 | 2.2 | 0.9 | 32 | 1.41 | 0.8 | |
| C3G | 16.43 | 47.64 | 4.1 | 1.7 | 6 | 11.49 | 6.9 | |
| Ozkaya et al. [20] | DDD | 184.28 | 180.03 | 0.49 | 0.5 | 7 | - | - |
| Sanchez-Moreno et al. [18] | DDD | 72.47 | 101.86 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 30 | 1 | 0.1 |
| Kasahara et al. [22] | DDD | 80.27 | 107.76 | 1.02 | 0.78 | 12 | - | - |
| Levart et al. [23] | C3G | 65.82 | 53.03 | 1.54 | 1.82 | 24 | - | - |
| Jandal et al. [24] | C3G | 15.98 | 47.96 | 3.5 | 1.41 | 6 | 6.36 | 2.97 |
| Schmidt et al. [21] | C3G | 23.01 | 42.66 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 5 | - | - |
| Gurkan et al. [19] | C3G | 65.61 | 77.45 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 12 | 3 | 1.3 |
| Study | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sanchez Moreno et al. [18] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Le Quintrec et al. [17] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ozkaya et al. [20] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Gurkan et al. [19] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Besbas et al. [25] | Unclear | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Parra et al. [26] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Bomback et al. [27] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Ruiz-Fuentes et al. [28] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Schmidt et al. [21] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Jandal et al. [24] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Kasahara et al. [22] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Levart et al. [23] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Factor | Better/Worse Response to Treatment | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| C5b-9/MAC deposition on renal biopsy | Better response | Eculizumab blocks C5, therefore preventing formation of C5b-9. Cases with intrarenal C5b-9 showed clinical improvement after therapy [17,21] |
| Minimal fibrosis/sclerosis on renal biopsy | Better response | Eculizumab cannot reverse structural damage. Patients without chronic, irreversible changes more often show recovery [1,37] |
| Elevated soluble C5b-9 | Better response | Eculizumab reduces C5b-9 and C3a accordingly with clinical improvement [21] |
| Post-transplant recurrent disease | Better response | Several post-transplant patients with recurrent C3G/DDD improved after eculizumab treatment [18,19] |
| Presence of C3NeF | Worse response | When dominant pathogenic mechanism of complement activation is C3 deposition driven by C3NeF, there is smaller impact of blocking C5 [37] |
| Genetic C5 variants preventing eculizumab binding | Worse response | Certain C5 polymorphisms block eculizumab binding (e.g., p.Arg885His) [34] |
| Advanced chronic kidney disease | Worse response | Longstanding disease with following fibrosis or sclerosis gives limited chance for recovery [38] |
| Overlap syndromes | Worse response | Overlap syndromes may alter the mechanism of injury [24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewandowski, D.; Konieczny, M.; Chrzanowski, K.; Jakubowska, M.; Paryzek, Z.; Miedziaszczyk, M.; Idasiak-Piechocka, I. Eculizumab in C3 Glomerulopathy: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101284
Lewandowski D, Konieczny M, Chrzanowski K, Jakubowska M, Paryzek Z, Miedziaszczyk M, Idasiak-Piechocka I. Eculizumab in C3 Glomerulopathy: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewandowski, Dominik, Mateusz Konieczny, Krzysztof Chrzanowski, Marta Jakubowska, Zuzanna Paryzek, Miłosz Miedziaszczyk, and Ilona Idasiak-Piechocka. 2025. "Eculizumab in C3 Glomerulopathy: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101284
APA StyleLewandowski, D., Konieczny, M., Chrzanowski, K., Jakubowska, M., Paryzek, Z., Miedziaszczyk, M., & Idasiak-Piechocka, I. (2025). Eculizumab in C3 Glomerulopathy: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101284







