Towards a Less Invasive Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer: Initial Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.4. Animals
2.5. Methods
2.5.1. Preparation of AuNPs
2.5.2. Physicochemical Characterization
Mean Size, Polydispersity Index (PdI), and Surface Charge
Morphology Assessment
Absorbance Spectrum Determination
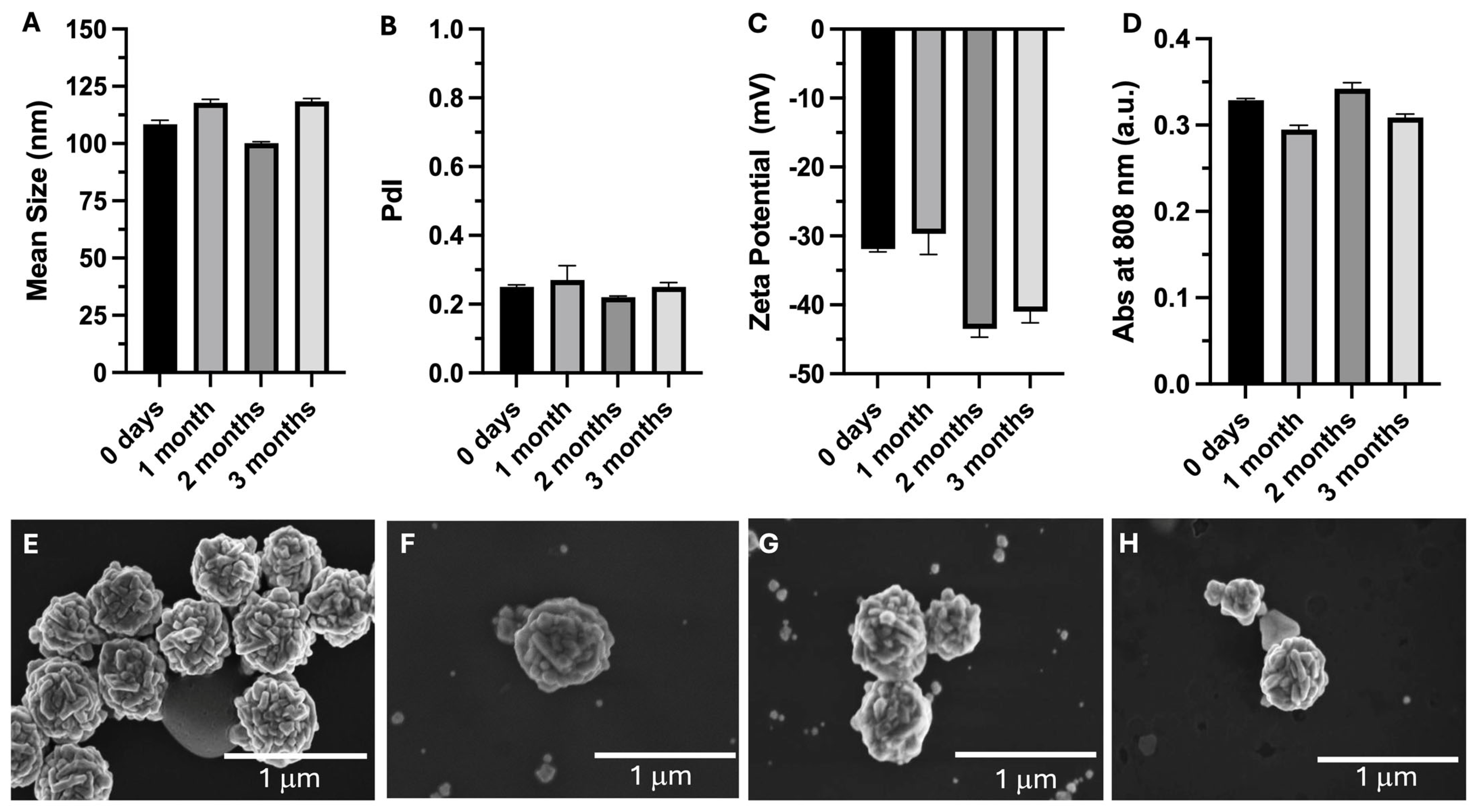
2.5.3. Stability Assessment over 3 Months
2.5.4. Sterility Assessment
Sterility Assessment by Direct Inoculation
Sterility Assessment by Membrane Filtration
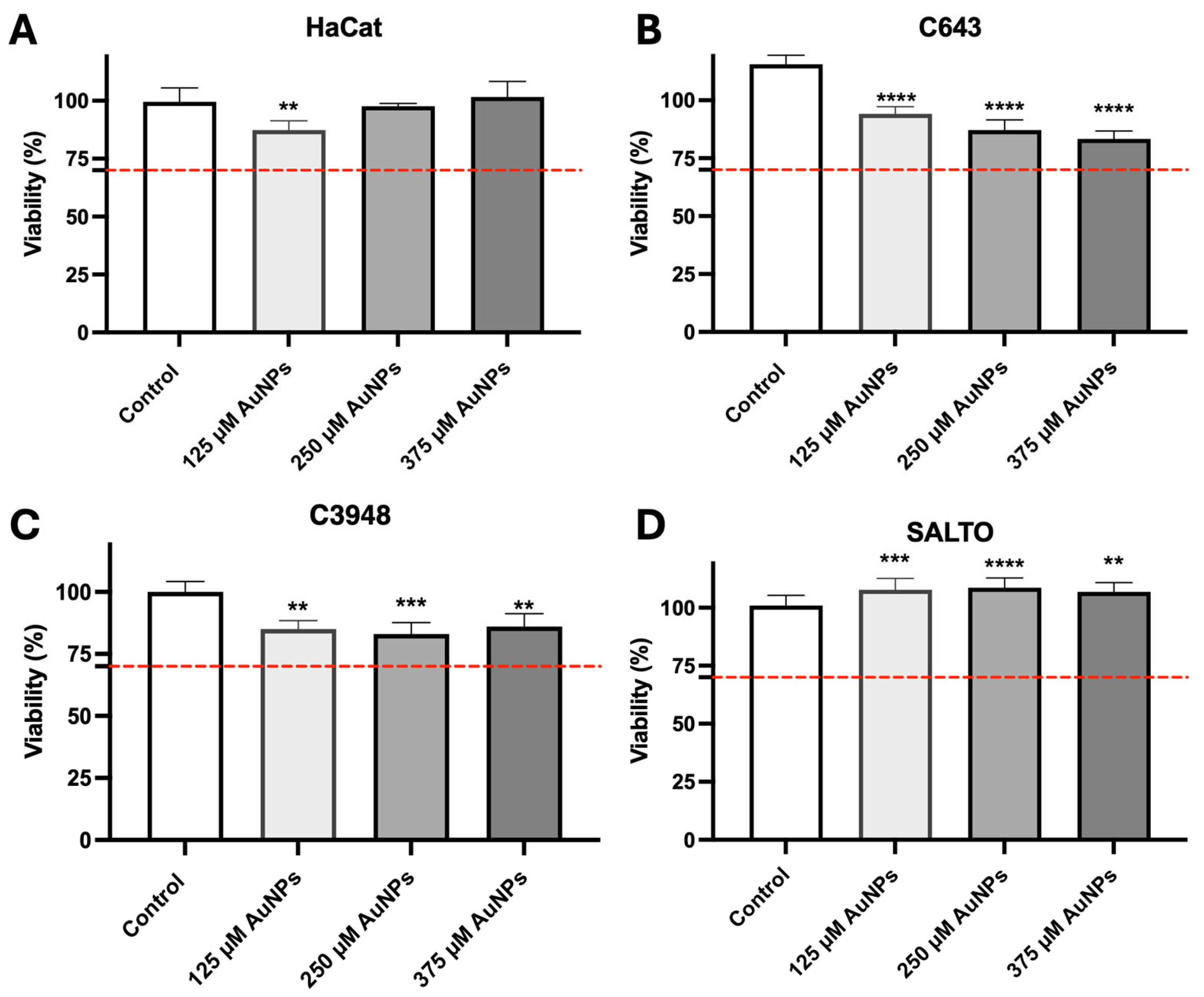
2.5.5. In Vitro Safety Assessment in Immortalized Cell Lines
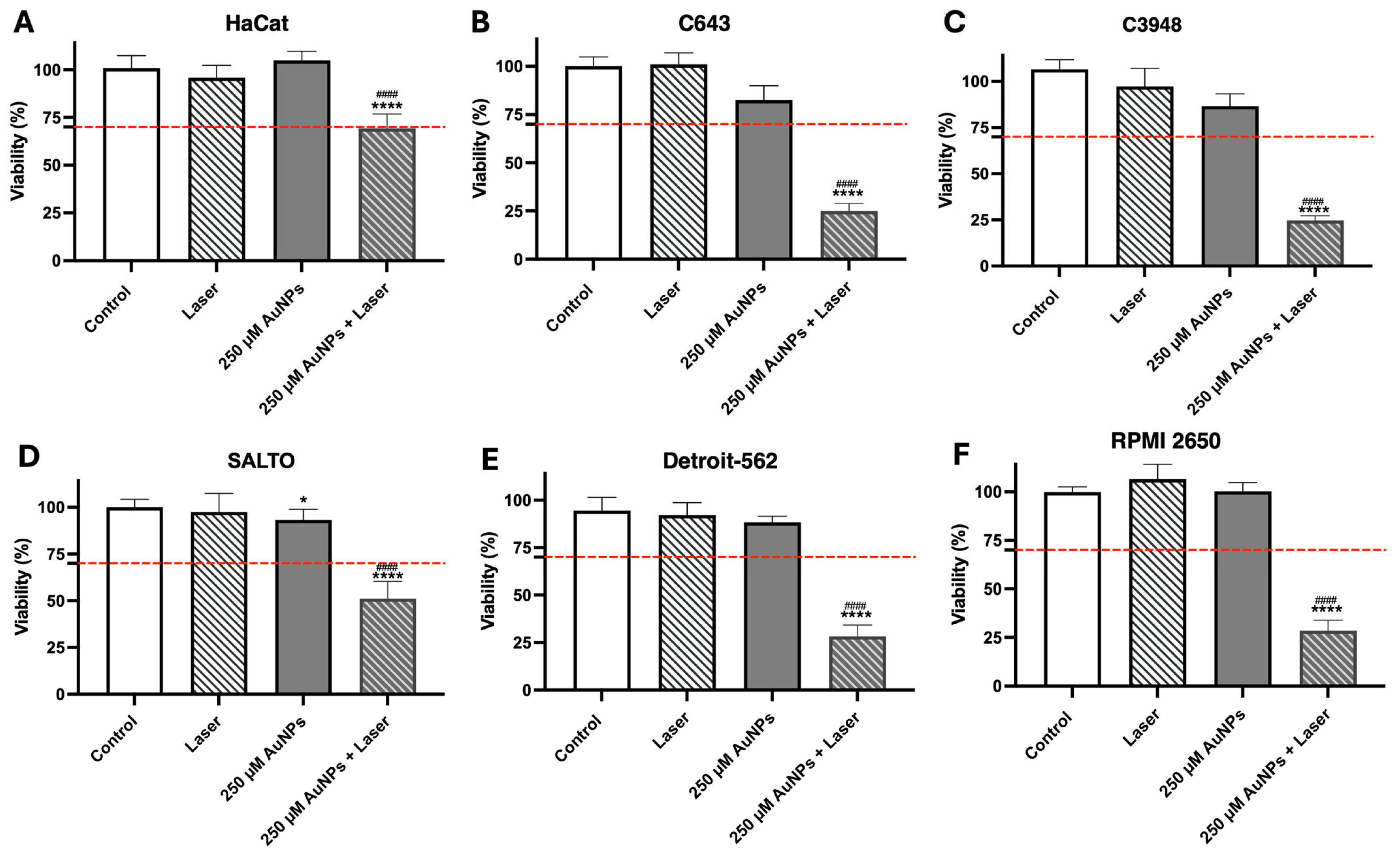
2.5.6. Efficacy in HNC Cell Lines
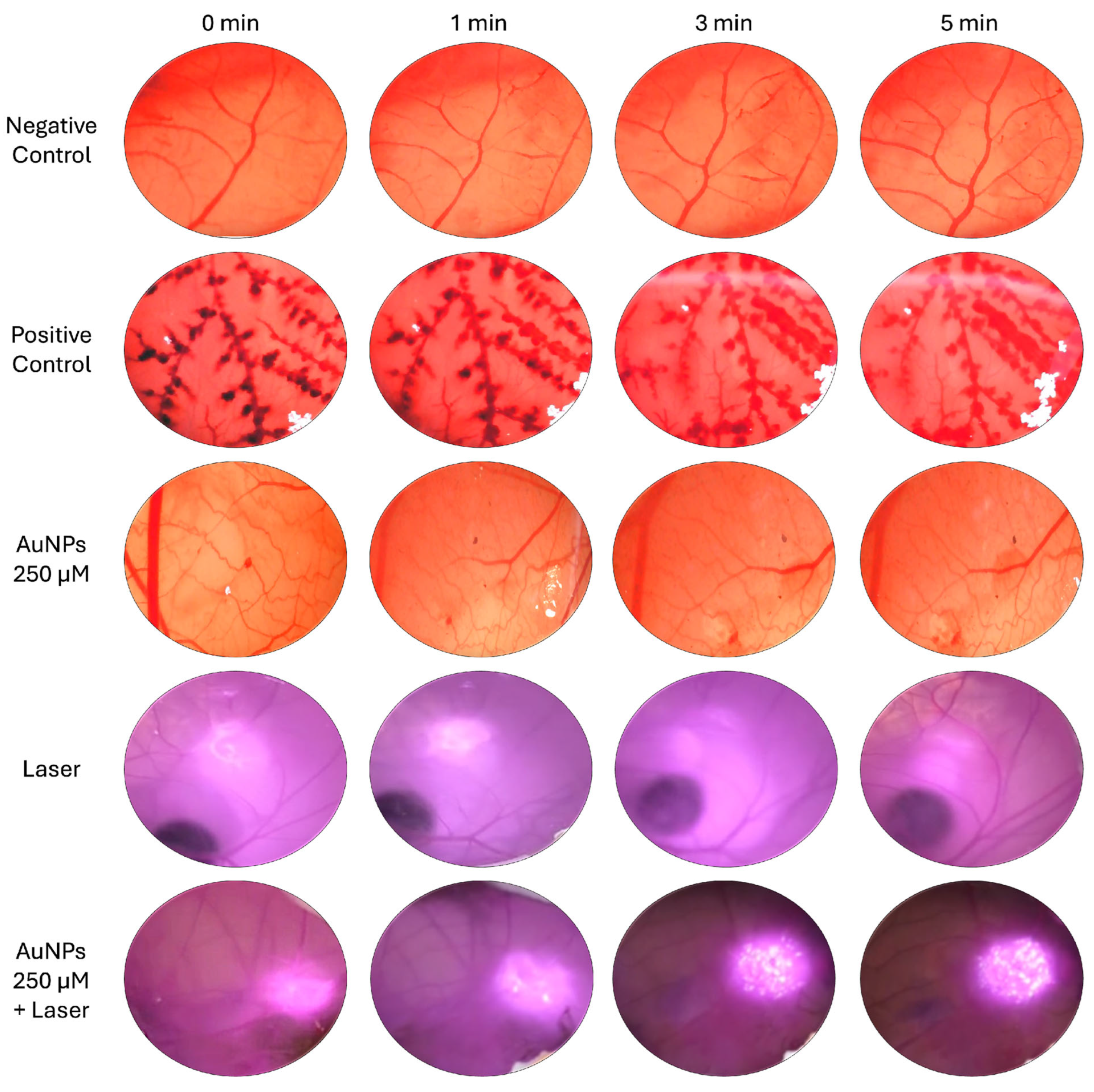
2.5.7. Hen’s Egg Test on the Chorioallantoic Membrane
2.5.8. In Vivo Biodistribution and Safety Assessment
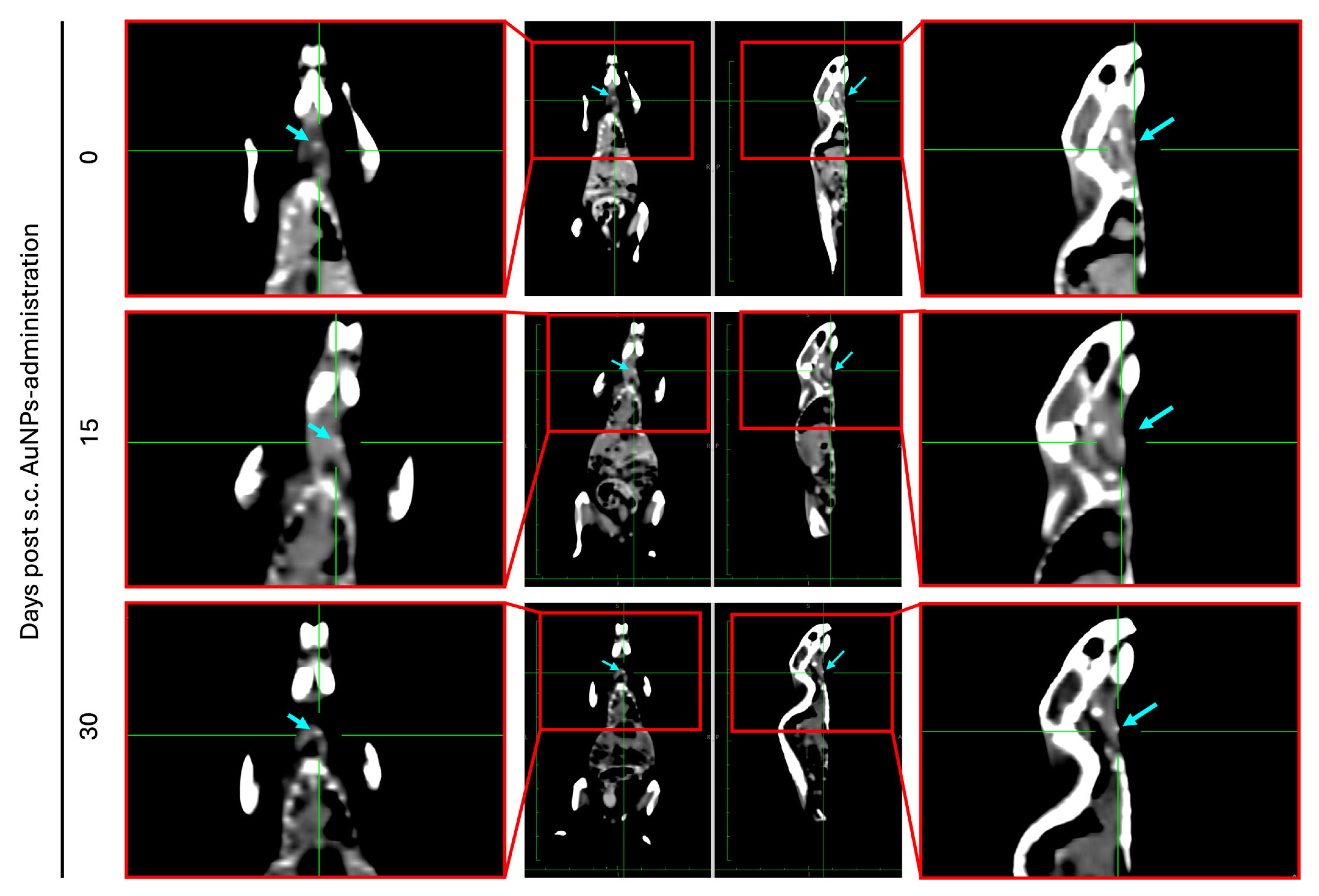
2.5.9. CT Scan to Measure Local Retention of AuNPs in Vivo
2.5.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
3.2. Stability Assessment over 3 Months
3.3. Sterility Assessment
3.4. In Vitro Safety Assessment
3.5. In Vitro Efficacy
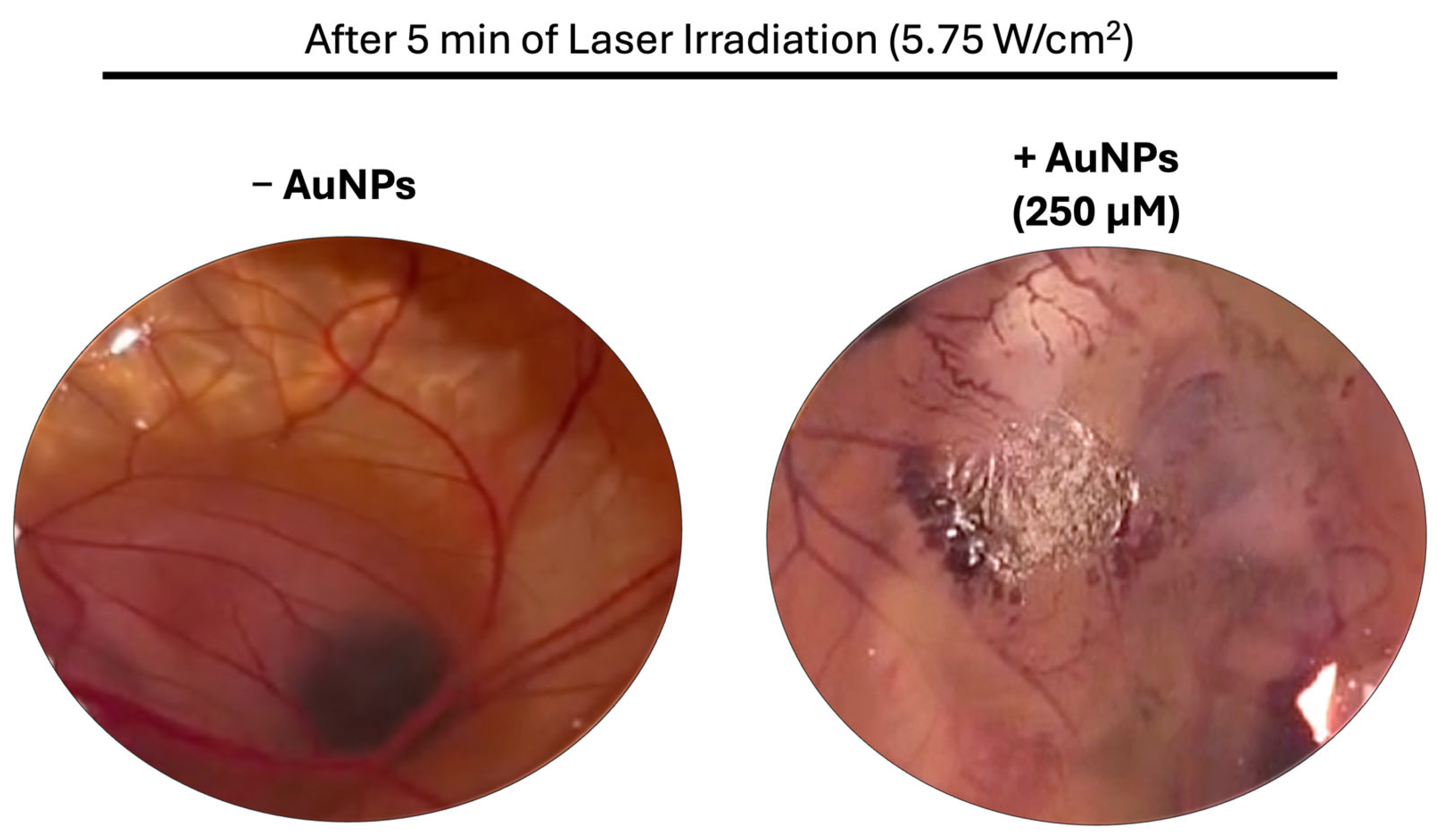
3.6. Hen’s Egg Test on the Chorioallantoic Membrane
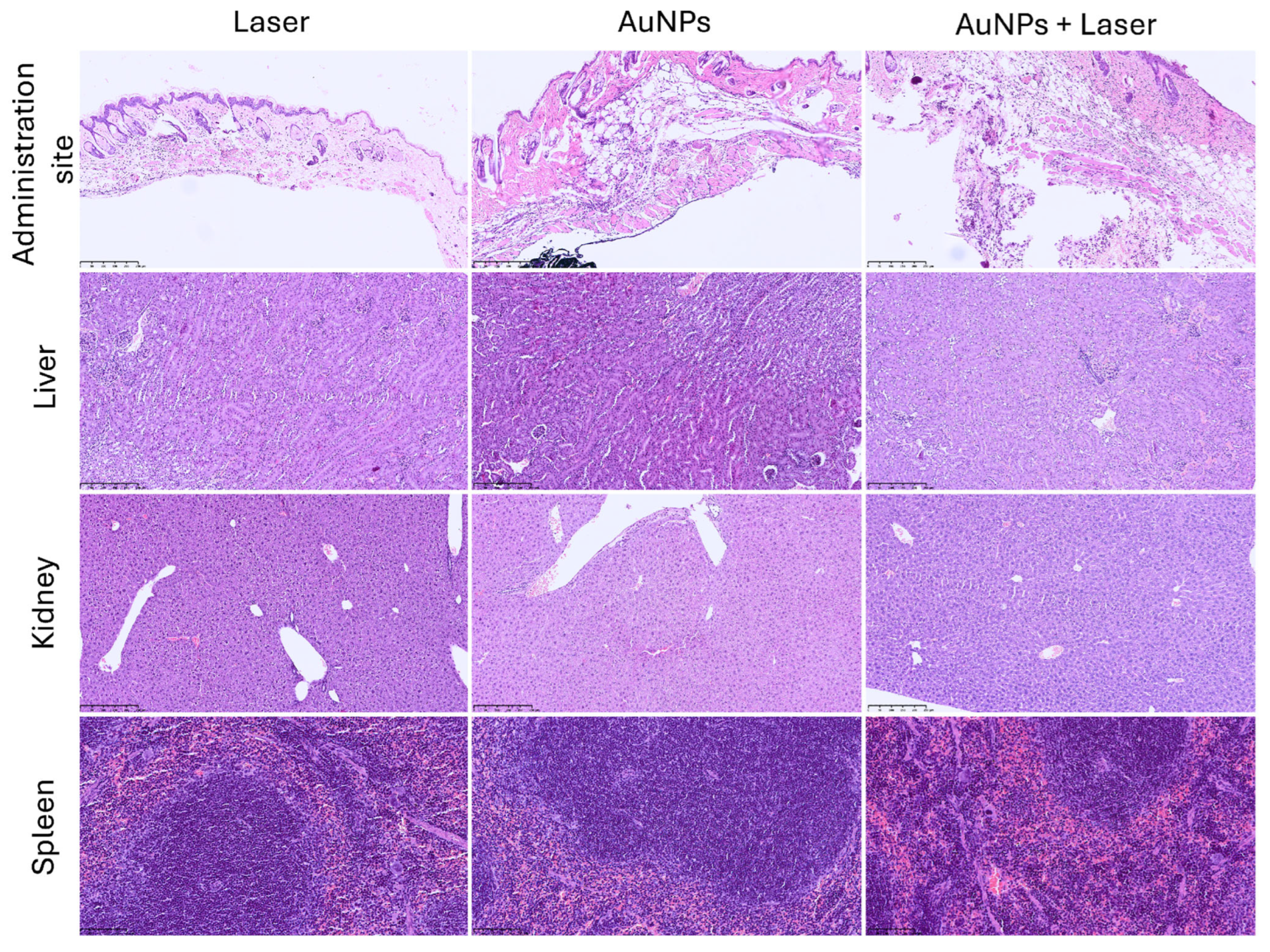
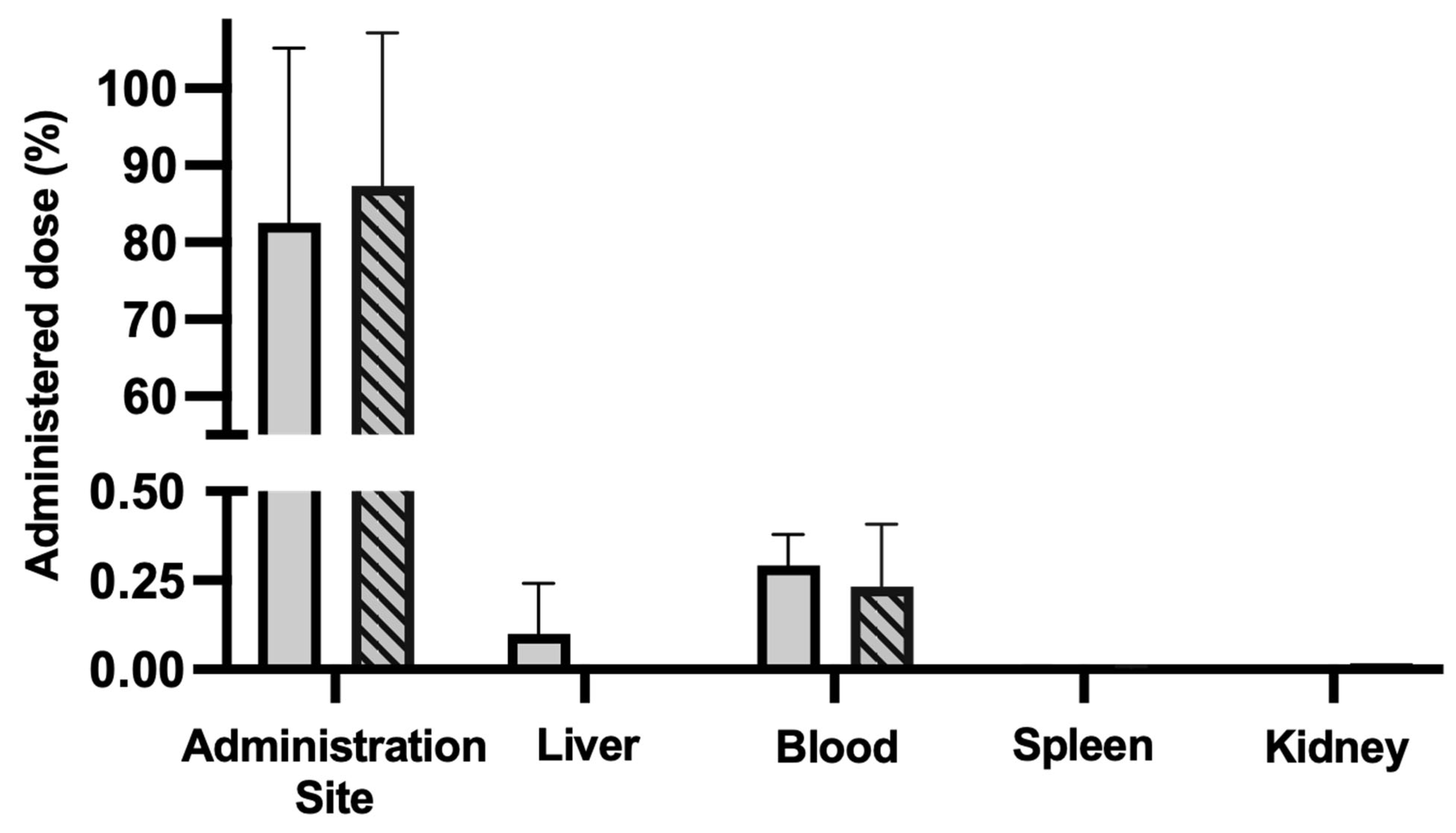
3.7. Acute Biodistribution and Safety
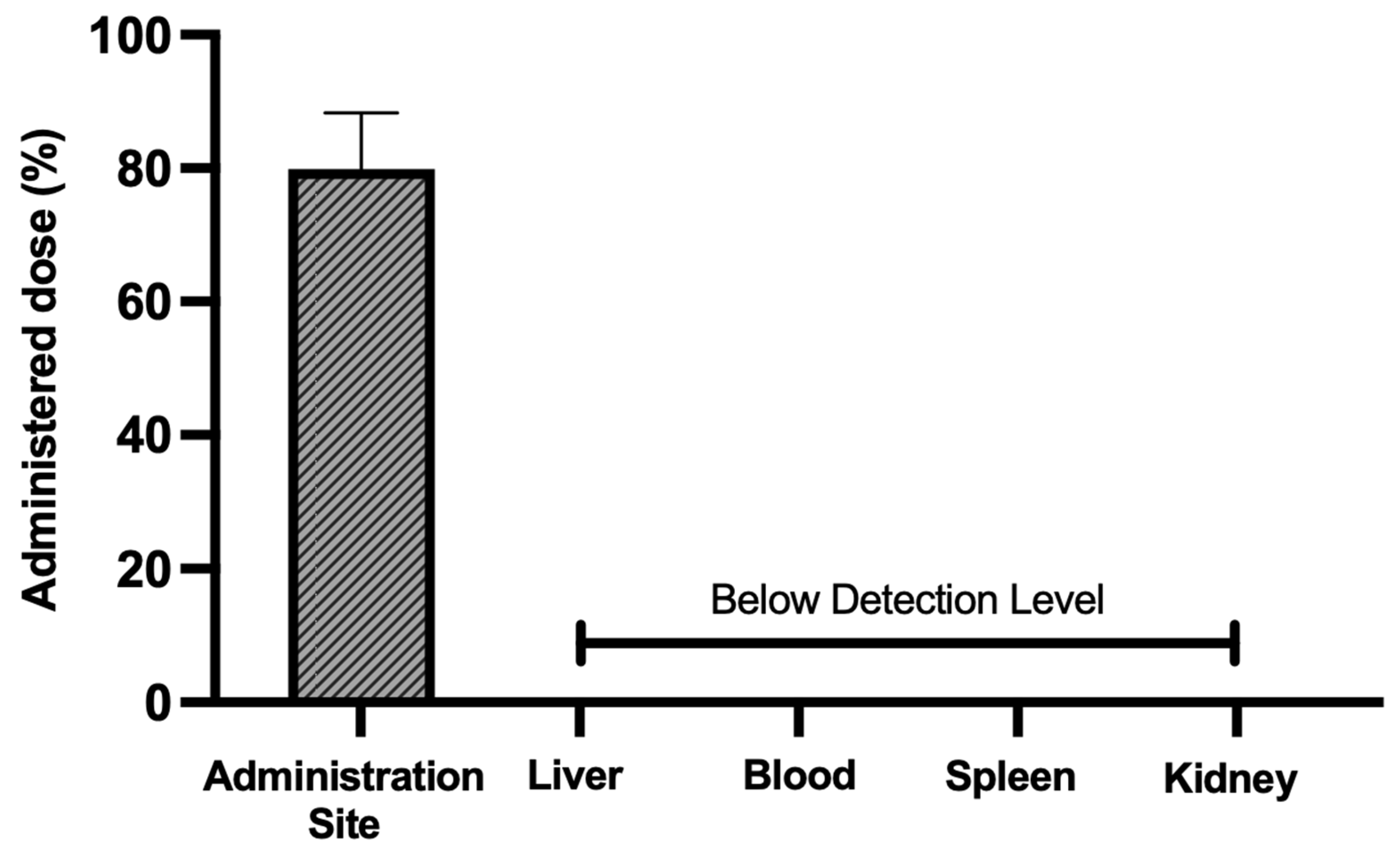
3.8. Biodistribution and Safety After 30 Days
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hieawy, A.; Liu, H.; Ma, J. Advances in Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers: A Review. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 25, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zheng, M.; Ren, X.; Tang, Y.; Liang, X. Local Hyperthermia in Head and Neck Cancer: Mechanism, Application and Advance. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57367–57378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shao, C.; Duan, Y.; Zheng, G.; Cai, Y.; Ge, M.; Xu, J. Recent Advances of Photodiagnosis and Treatment for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Neoplasia 2025, 60, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wen, Y.; Wen, J. Head and Neck Cancer: Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapy. MedComm 2024, 5, e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, T.; Adorno, M.; Mendonca, E.; Leles, C. Factors Associated with the Quality of Life of Subjects with Facial Disfigurement Due to Surgical Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cirugía Bucal 2018, 23, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tie, Y.; Alu, A.; Ma, X.; Shi, H. Targeted Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer: Signaling Pathways and Clinical Studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.M.; Weaver, A.N.; Acosta, P.; Harris, L.; Bowles, D.W. Review of Current and Future Medical Treatments in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, N.; Qu, N. New Advances in the Therapeutic Strategy of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Review of Latest Therapies and Cutting-Edge Research. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2025, 1880, 189230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Singh, R.; Mehndiratta, S.; Dadhich, M. The Impact of Facial Disfigurement and Self-Image Anxiety on the Quality of Life of Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Oral Oncol. Rep. 2024, 10, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contrera, K.J.; Reddy, P.D.; Helou, V.; Myers, J.N.; Skinner, H.D.; Ferrarotto, R.; Myers, E.N. The Evolution of Multidisciplinary Head and Neck Cancer Treatment. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, M.N.; Faísca, P.; Ferreira, H.A.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Current Insights and Progress in the Clinical Management of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.-H.; Ryu, N.-E.; Lim, D.-J.; Park, H. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Paik, J.; Kim, H. Effect of Gold Nanoparticles Distribution Radius on Photothermal Therapy Efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Diez, J.; Foti, A.; Casanova-Carvajal, Ó.; Marrodán, L.; Granado, N.; Satriano, C.; Martínez-Murillo, R.; Serrano-Olmedo, J.-J.; Ramos-Gómez, M. Effect of Photothermal Therapy Using Gold Nanoparticles Conjugated with Hyaluronic Acid in an Intracranial Murine Glioblastoma Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 9327–9346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessel, C.M.; Pattani, V.P.; Rasch, M.; Panthani, M.G.; Koo, B.; Tunnell, J.W.; Korgel, B.A. Copper Selenide Nanocrystals for Photothermal Therapy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wang, C.; Hu, L.; Guo, P. Nanostructures as Photothermal Agents in Tumor Treatment. Molecules 2022, 28, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M. Research Progress on Carbon Materials in Tumor Photothermal Therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Xiao, Z.; Ling, J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, T. Exploring the Application of Metal-Based Photothermal Agents in Photothermal Therapy Combined with Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1553158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, R.; Gao, X.; Li, B.; Xu, H.; Shan, L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L. Significant Effect on the Photo Conversion Performance of Non-Stoichiometric Tungsten Oxide with Various Reaction Solvents. J. Lumin. 2022, 252, 119388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hanyu, M.; Yang, Z.; Nagatsu, K.; Suzuki, H.; Ouyang, J.; Ji, X.; Wei, J.; et al. Marriage of Black Phosphorus and Cu2+ as Effective Photothermal Agents for PET-Guided Combination Cancer Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, T.; Ming, J. Photothermal Therapy of Copper Incorporated Nanomaterials for Biomedicine. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.; Li, Z.; Luo, W.; Chen, H.; Deng, T.; Gong, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Li, B.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. A Copper-Based Photothermal-Responsive Nanoplatform Reprograms Tumor Immunogenicity via Self-Amplified Cuproptosis for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2500652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, M.; Mosca, S.; Gardner, B.; Palombo, F.; Matousek, P.; Stone, N. Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy Limitation in Clinical Applications Regarding Pain Management. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Miao, Y.; Du, H.; et al. Nanomaterials for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 14443–14460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, L.-C.; Chung, F.F.-L.; Tan, Y.-F.; Leong, C.-O. Toxicity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-M.; Pan, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.-T.; Luo, T.; Li, W.-W. Biogenic Copper Selenide Nanoparticles for Near-Infrared Photothermal Therapy Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 27638–27646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, K.J.; Buzzá, H.H.; Bagnato, V.S.; Romero, M.P. Carbon-Based Materials in Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapies Applied to Tumor Destruction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawdon, A.; Weydemeyer, E.; Peng, C.-A. Tumor Photothermolysis: Using Carbon Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy. Eur. J. Nanomed. 2013, 5, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Qi, J.; Lin, X.; Xiong, Y.; He, F.; Deng, W.; Liu, G. Biomimetic Black Phosphorus Nanosheet-Based Drug Delivery System for Targeted Photothermal-Chemo Cancer Therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 707208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.S.; Day, E.S. Gold Nanoparticle-mediated Photothermal Therapy: Applications and Opportunities for Multimodal Cancer Treatment. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, M.N.; Nunes, D.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Rodrigues, C.; Faísca, P.; Ferreira, H.A.; Coelho, J.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy—Influence of Experimental Conditions on the Properties of Resulting AuNPs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 101, 106215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.L.; Wilson, R.E.; Amrhein, K.D.; Huang, X. Gold Nanorod-Assisted Photothermal Therapy and Improvement Strategies. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Gonçalves, T.; Gaspar, M.M.; Coelho, J.M.P.; Marques, V.; Viana, A.S.; Ascensão, L.; Carvalho, L.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Ferreira, H.A.; Ferreira, D.; et al. The Role of Rosmarinic Acid on the Bioproduction of Gold Nanoparticles as Part of a Photothermal Approach for Breast Cancer Treatment. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.; Ferreira-Gonçalves, T.; Ascensão, L.; Viana, A.S.; Carvalho, L.; Catarino, J.; Faísca, P.; Oliva, A.; de Barros, D.P.C.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; et al. Safety of Gold Nanoparticles: From In Vitro to In Vivo Testing Array Checklist. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Gonçalves, T.; Nunes, D.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; de Almeida, A.P.; Carvalho, L.; Ferreira, D.; Catarino, J.; Faísca, P.; Ferreira, H.A.; et al. Rational Approach to Design Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy: The Effect of Gold Salt on Physico-Chemical, Optical and Biological Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 650, 123659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.; Charmier, A.J.; Afonso, R.A.; Catarino, J.; Faísca, P.; Carvalho, L.; Ascensão, L.; Coelho, J.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Gold-Based Nanoplataform for the Treatment of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: A Step Forward. Cancers 2021, 13, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, S.; Ferreira-Gonçalves, T.; Lopes, J.; Amaral, M.N.; Viana, A.S.; Coelho, J.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. A Step Forward for the Treatment of Localized Prostate Cancer Using Gold Nanoparticles Combined with Laser Irradiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Godinho-Santos, A.; Coelho, J.M.P.; Cabaço, L.C.; Barral, D.C.; Faísca, P.; Catarino, J.; Nunes, D.; Fortunato, E.; et al. Combination of Gold Nanoparticles with Near-Infrared Light as an Alternative Approach for Melanoma Management. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 668, 124952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, M.N.; Kumar, P.; Faísca, P.; Ferreira, H.A.; Coelho, J.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy: Expanding the Frontiers of Cancer Treatment and Theragnostics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 190, 118399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.T.; Pojo, M.; Simões-Pereira, J.; Roque, R.; Saramago, A.; Roque, L.; Martins, C.; André, S.; Cabeçadas, J.; Leite, V.; et al. Establishment and Characterization of a New Patient-Derived Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Line (C3948), Obtained through Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology. Endocrine 2019, 66, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannellini, T.; Spadaro, M.; Di Carlo, E.; Ambrosino, E.; Iezzi, M.; Amici, A.; Lollini, P.L.; Forni, G.; Cavallo, F.; Musiani, P. Timely DNA Vaccine Combined with Systemic IL-12 Prevents Parotid Carcinomas before a Dominant-Negative P53 Makes Their Growth Independent of HER-2/Neu Expression. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7695–7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.; Martins, A.S.; Catarino, J.; Faísca, P.; Kumar, P.; Pinto, J.F.; Pinto, R.; Correia, I.; Ascensão, L.; Afonso, R.A.; et al. How Can Biomolecules Improve Mucoadhesion of Oral Insulin? A Comprehensive Insight Using Ex-Vivo, In Silico, and In Vivo Models. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Mejuto, A.; Raptopoulos, G.; Malandain, N.; Neves Amaral, M.; Ardao, I.; Finšgar, M.; Laromaine, A.; Roig, A.; Pinto Reis, C.; García-González, C.A.; et al. 3D-Printed Cellulose Aerogels Minimally Cross-Linked with Polyurea: A Robust Strategy for Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 34444–34457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Rao, J.-D.; Guo, R.; Li, M.; He, Q. Size-Adjustable Nano-Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Tumor Retention and Penetration. Pharm. Front. 2021, 03, e98–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Tran, T.B.; Lin, E.; Hunt, S.; Haveman, R.; Castro, K.; Lu, J. Size-Transformable Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 834–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frickenstein, A.N.; Mukherjee, S.; Harcourt, T.; He, Y.; Sheth, V.; Wang, L.; Malik, Z.; Wilhelm, S. Quantification of Monodisperse and Biocompatible Gold Nanoparticles by Single-Particle ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 4353–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.E.F.; Pereira, A.C.; Resende, M.A.C.; Ferreira, L.F. Gold Nanoparticles: A Didactic Step-by-Step of the Synthesis Using the Turkevich Method, Mechanisms, and Characterizations. Analytica 2023, 4, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, K.; Kaplan, M.; Çalış, S. Effects of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Zeta Potential on Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourali, P.; Benada, O.; Pátek, M.; Neuhöferová, E.; Dzmitruk, V.; Benson, V. Response of Biological Gold Nanoparticles to Different PH Values: Is It Possible to Prepare Both Negatively and Positively Charged Nanoparticles? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Bage, N.; Dasgupta Ghosh, B.; Kar, P. Easy Synthesis of 4-Quinonimine Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles in Stable Aqueous Colloidal State. Part. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and Zeta Potential—What They Are and What They Are Not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, H.; Rahman, D.S.; Sengupta, M.; Ghosh, S.K. Gold Nanostars in Plasmonic Photothermal Therapy: The Role of Tip Heads in the Thermoplasmonic Landscape. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 13082–13094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Benz, F.; Wheeler, M.C.; Oram, J.; Baumberg, J.J.; Cespedes, O.; Christenson, H.K.; Coletta, P.L.; Jeuken, L.J.C.; Markham, A.F.; et al. One-Step Fabrication of Hollow-Channel Gold Nanoflowers with Excellent Catalytic Performance and Large Single-Particle SERS Activity. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14932–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.P.P.; Lim, D.-K. Photothermal Effect of Gold Nanoparticles as a Nanomedicine for Diagnosis and Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Chávez, S.A.; Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; Caballero-Florán, I.H.; Giraldo-Gomez, D.M.; Figueroa-Gonzalez, G.; Reyes-Hernandez, O.D.; González-Del Carmen, M.; González-Torres, M.; Cortés, H.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Insights into Terminal Sterilization Processes of Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pišlová, M.; Kolářová, K.; Vokatá, B.; Brož, A.; Ulbrich, P.; Bačáková, L.; Kolská, Z.; Švorčík, V. A New Way to Prepare Gold Nanoparticles by Sputtering—Sterilization, Stability and Other Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 115, 111087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, Á.; Pelaz, B.; Moros, M.; Sánchez-Espinel, C.; Hernández, A.; Fernández-López, C.; Grazú, V.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; et al. Sterilization Matters: Consequences of Different Sterilization Techniques on Gold Nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhr, C.R.; Wiesmann, N.; Tanner, R.C.; Brieger, J.; Eckrich, J. The Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay in Nanotoxicological Research—An Alternative for In Vivo Experimentation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista-Duharte, A.; Jorge Murillo, G.; Pérez, U.M.; Tur, E.N.; Portuondo, D.F.; Martínez, B.T.; Téllez-Martínez, D.; Betancourt, J.E.; Pérez, O. The Hen’s Egg Test on Chorioallantoic Membrane. Int. J. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.S.; Brinker, C.J.; Leong, H.S. Bridging the In Vitro to In Vivo Gap: Using the Chick Embryo Model to Accelerate Nanoparticle Validation and Qualification for In Vivo Studies. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19626–19650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldayel, A.M.; Hufnagel, S.; O’Mary, H.L.; Valdes, S.A.; Alzhrani, R.F.; Xu, H.; Cui, Z. Effect of Nanoparticle Size on Their Distribution and Retention in Chronic Inflammation Sites. Discov. Nano 2023, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Austin, L.A.; Mackey, M.A.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size Matters: Gold Nanoparticles in Targeted Cancer Drug Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Hagens, W.I.; Krystek, P.; Burger, M.C.; Sips, A.J.A.M.; Geertsma, R.E. Particle Size-Dependent Organ Distribution of Gold Nanoparticles after Intravenous Administration. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, M.B.; Wegierak, D.; Exner, A.A. Using Imaging Modalities to Predict Nanoparticle Distribution and Treatment Efficacy in Solid Tumors: The Growing Role of Ultrasound. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, e1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
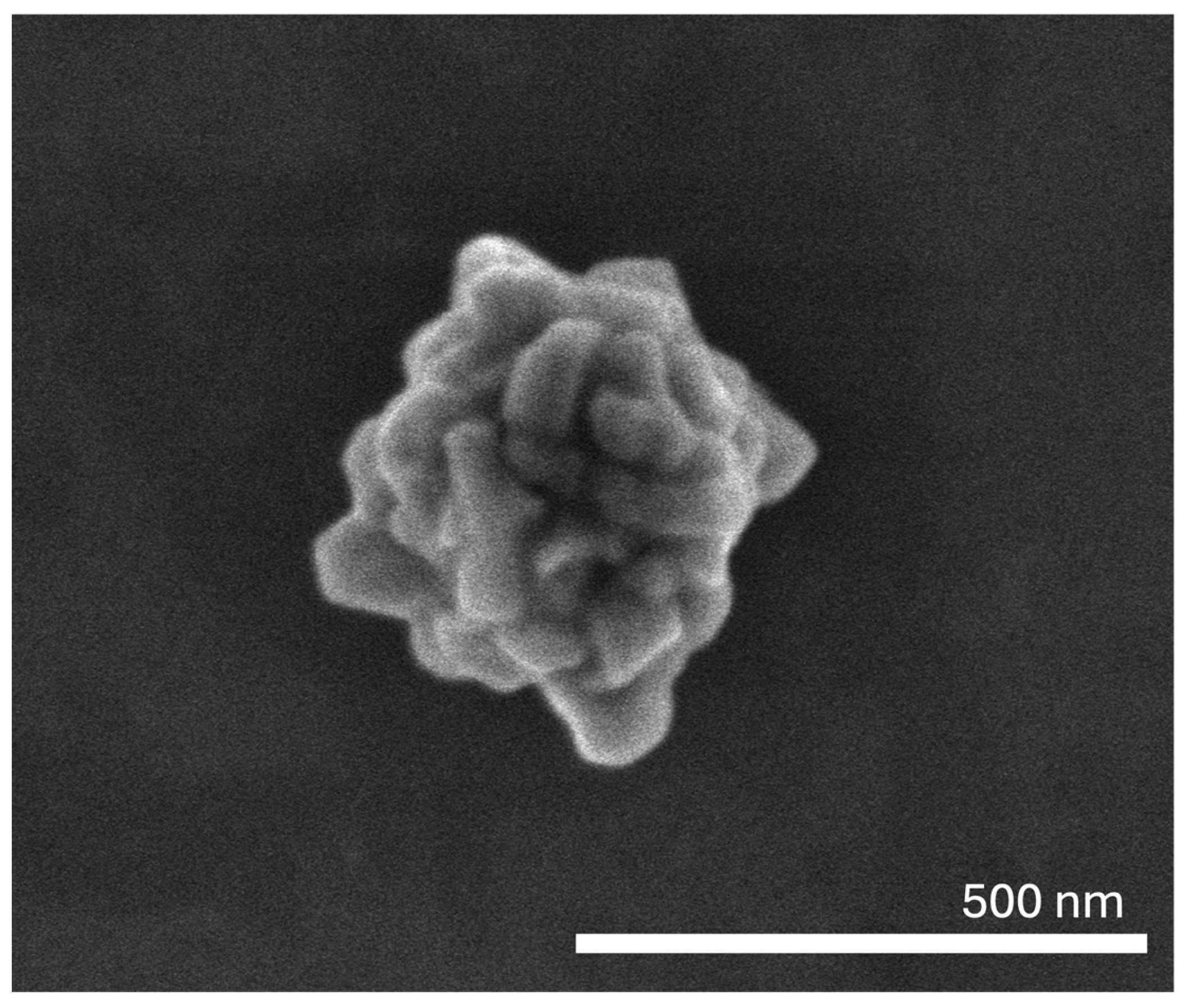


| Mean Size (nm) | PdI | Zeta Potential (mV) | Abs808nm (a.u.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNPs | 118.2 ± 7.1 | 0.27 ± 0.05 | −32.9 ± 0.4 | 0.342 ± 0.007 |
| Tissue Indexes (Mean ± SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney | Spleen | Liver | |
| Laser | 12.7 ± 0.4 | 6.1 ± 0.1 | 23.4 ± 0.5 |
| AuNPs | 12.4 ± 0.6 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 22.6 ± 0.7 |
| AuNPs + Laser | 12.9 ± 0.5 | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 22.5 ± 3.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, M.N.; Neto, Í.; Cabral, M.; Nunes, D.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Rodrigues, C.; de Almeida, A.P.; Catarino, J.; Faísca, P.; et al. Towards a Less Invasive Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer: Initial Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101283
Amaral MN, Neto Í, Cabral M, Nunes D, Fortunato E, Martins R, Rodrigues C, de Almeida AP, Catarino J, Faísca P, et al. Towards a Less Invasive Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer: Initial Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101283
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Mariana Neves, Íris Neto, Mitza Cabral, Daniela Nunes, Elvira Fortunato, Rodrigo Martins, Carla Rodrigues, António P. de Almeida, José Catarino, Pedro Faísca, and et al. 2025. "Towards a Less Invasive Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer: Initial Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101283
APA StyleAmaral, M. N., Neto, Í., Cabral, M., Nunes, D., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Rodrigues, C., de Almeida, A. P., Catarino, J., Faísca, P., Ferreira, H. A., Coelho, J. M. P., Gaspar, M. M., & Reis, C. P. (2025). Towards a Less Invasive Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer: Initial Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101283














