Stability of Ternary Drug–Drug–Drug Coamorphous Systems Obtained Through Mechanochemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Samples Preparation
Mixture Composition and Experimental Design
Neat Grinding (NG) Experiments
Physical Mixtures’ Preparation
2.2.2. Samples Characterization
Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
True Density Determinations
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
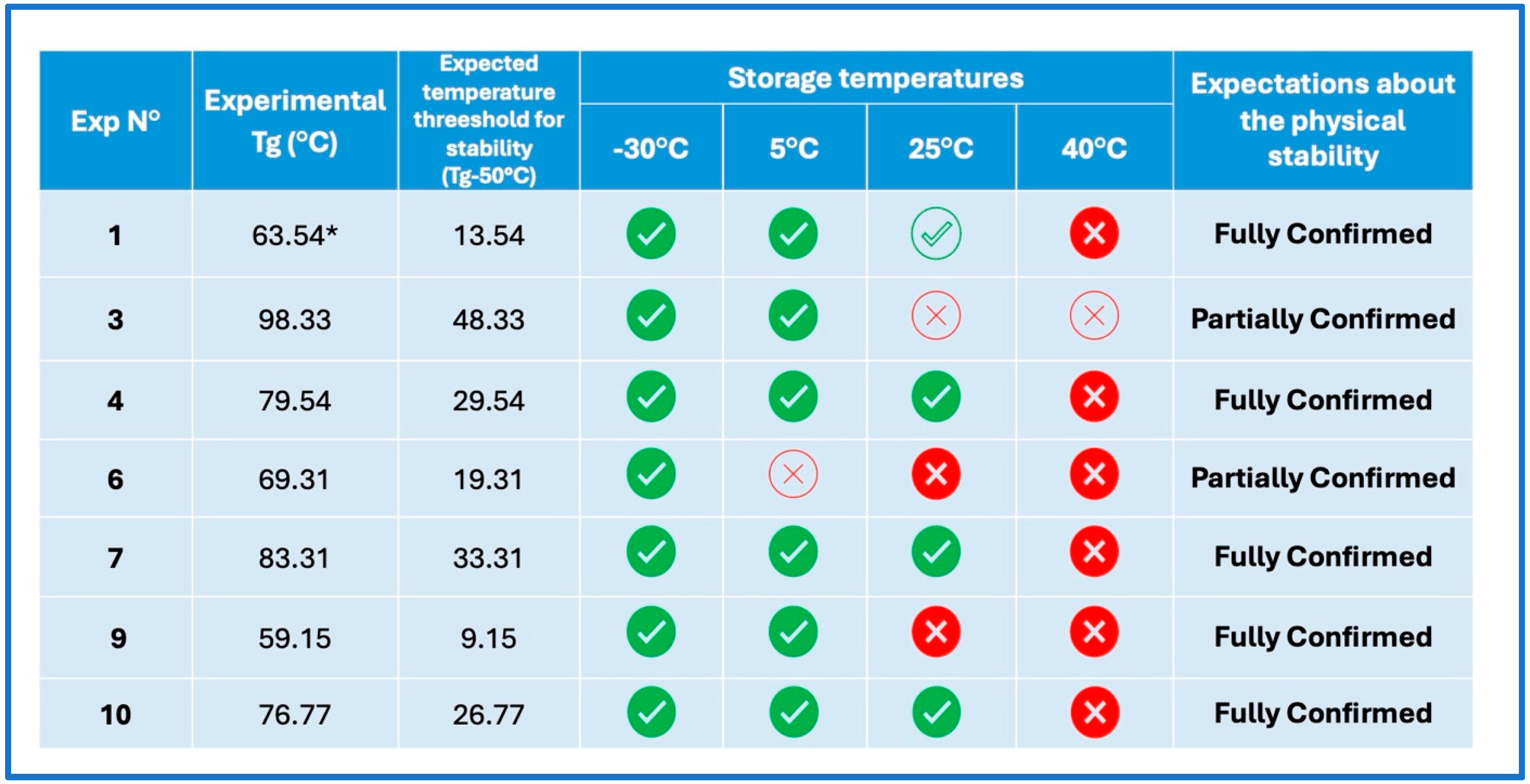
Stability Studies According to “Tg—50 °C” Rule
Drug Recovery
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babu, N.J.; Nangia, A. Solubility Advantage of Amorphous Drugs and Pharmaceutical Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 2662–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Moinuddin, S.M.; Cai, T. Advances in Coamorphous Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagianni, A.; Kachrimanis, K.; Nikolakakis, I. Co-Amorphous Solid Dispersions for Solubility and Absorption Improvement of Drugs: Composition, Preparation, Characterization and Formulations for Oral Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.; Knipp, G.; Zografi, G. Assessing the Performance of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1355–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Emerging Trends in the Stabilization of Amorphous Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, E.; Adrjanowicz, K.; Zakowiecki, D.; Milanowski, B.; Tarnacka, M.; Hawelek, L.; Dulski, M.; Pilch, J.; Smolka, W.; Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak, I.; et al. Enhancement of the Physical Stability of Amorphous Indomethacin by Mixing It with Octaacetylmaltose. Inter and Intra Molecular Studies. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 2887–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Duggirala, N.K.; Kumar, N.S.K.; Su, Y.; Suryanarayanan, R. Design of Ternary Amorphous Solid Dispersions for Enhanced Dissolution of Drug Combinations. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, N.; Aaltonen, J.; Saville, D.; Rades, T. Physical Characterization and Stability of Amorphous Indomethacin and Ranitidine Hydrochloride Binary Systems Prepared by Mechanical Activation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, W.; Song, Y.; Luo, M.; Hu, E.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Y.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qian, S. Mechanistic Insights into the Crystallization of Coamorphous Drug Systems. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodagekar, A.; Chavan, R.B.; Mannava, M.K.C.; Yadav, B.; Chella, N.; Nangia, A.K.; Shastri, N.R. Co Amorphous Valsartan Nifedipine System: Preparation, Characterization, in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 139, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Yin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, G.; Wu, W. Dissolution Changes in Drug-Amino Acid/Biotin Co-Amorphous Systems: Decreased/Increased Dissolution during Storage without Recrystallization. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 188, 106526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, A.; Grohganz, H.; Löbmann, K.; Rades, T.; Leopold, C.S. Influence of the Cooling Rate and the Blend Ratio on the Physical Stability of Co-Amorphous Naproxen/Indomethacin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’angelo, A.; Edgar, B.; Hurt, A.P.; Antonijević, M.D. Physico-Chemical Characterisation of Three-Component Co-Amorphous Systems Generated by a Melt-Quench Method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narala, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Srinivasan, P.; Mandati, P.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M.A. Pharmaceutical Co-Crystals, Salts, and Co-Amorphous Systems: A Novel Opportunity of Hot-Melt Extrusion. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, R.; Priemel, P.A.; Surwase, S.; Graeser, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Theoretical Considerations in Developing Amorphous Solid Dispersions. In Amorphous Solid Dispersions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 35–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, R.B.; Thipparaboina, R.; Kumar, D.; Shastri, N.R. Co Amorphous Systems: A Product Development Perspective. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Amorphous Pharmaceutical Solids: Preparation, Characterization and Stabilization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.F.C.; Rosado, M.T.S.; Maria, T.M.R.; Pereira Silva, P.S.; Silva, M.R.; Eusébio, M.E.S. Introduction to Pharmaceutical Co-Amorphous Systems Using a Green Co-Milling Technique. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, P.F.M.; Willart, J.-F.; Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F.; Descamps, M. Using Milling To Explore Physical States: The Amorphous and Polymorphic Forms of Dexamethasone. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasa, D.; Jones, W. Screening for New Pharmaceutical Solid Forms Using Mechanochemistry: A Practical Guide. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 117, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PRALEN Gocce per Gatti, Cani Cuccioli e Di Piccola Taglia | UPD. Available online: https://medicines.health.europa.eu/veterinary/it/600000094039 (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Lindenberg, M.; Kopp, S.; Dressman, J.B. Classification of Orally Administered Drugs on the World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines According to the Biopharmaceutics Classification System. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Crystallogr. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Trastullo, R.; Keiser, J.; Zanolla, D.; Zingone, G.; Voinovich, D.; Albertini, B. An Explorative Analysis of Process and Formulation Variables Affecting Comilling in a Vibrational Mill: The Case of Praziquantel. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, E.J.; Andrade, M.A.B.; Gubitoso, M.R.; Bezzon, V.D.N.; Smith, P.A.; Byrn, S.R.; Bou-Chacra, N.A.; Carvalho, F.M.S.; de Araujo, G.L.B. Acoustic Levitation and High-Resolution Synchrotron X-Ray Powder Diffraction: A Fast Screening Approach of Niclosamide Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Abbrunzo, I.; Bianco, E.; Gigli, L.; Demitri, N.; Birolo, R.; Chierotti, M.R.; Škoríc, I.; Keiser, J.; Häberli, C.; Voinovich, D.; et al. Praziquantel Meets Niclosamide: A Dual-Drug Antiparasitic Cocrystal. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 644, 123315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-M.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wu, C.-B.; Li, S.; Lu, T.-B. Crystal Engineering Approach to Improve the Solubility of Mebendazole. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinovich, D.; Campisi, B.; Phan-Tan-Luu, R. Experimental Design for Mixture Studies. Compr. Chemom. 2020, 1, 391–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qui Sommes-Nous ?|NemrodW. Available online: https://www.nemrodw.com/fr/whoweare#intro%20 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Chierotti, M.R.; Hasa, D.; Voinovich, D.; Gigli, L.; Demitri, N.; Geremia, S.; Keiser, J.; et al. A New Soluble and Bioactive Polymorph of Praziquantel. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Vioglio, P.C.; Chierotti, M.R.; Gigli, L.; Demitri, N.; Passerini, N.; Albertini, B.; Franceschinis, E.; Keiser, J.; et al. Exploring Mechanochemical Parameters Using a DoE Approach: Crystal Structure Solution from Synchrotron XRPD and Characterization of a New Praziquantel Polymorph. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 140, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, B.J.; Ponichtera, K. Physiology, Boyle’s Law; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.-P.; Yeh, C.-F. Phase Behavior of Ternary Blends of Tactic Poly(Methyl Methacrylate)s and Poly(Styrene-Co-Acrylonitrile). Polym. J. 1999, 31, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tobyn, M.; Brown, J.; Dennis, A.B.; Fakes, M.; Gao, Q.; Gamble, J.; Khimyak, Y.Z.; Mcgeorge, G.; Patel, C.; Sinclair, W.; et al. Amorphous Drug-PVP Dispersions: Application of Theoretical, Thermal and Spectroscopic Analytical Techniques to the Study of a Molecule With Intermolecular Bonds in Both the Crystalline and Pure Amorphous State. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 3456–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrdla, P.J.; Floyd, P.D.; Dell’Orco, P.C. Predicting the Solubility Enhancement of Amorphous Drugs and Related Phenomena Using Basic Thermodynamic Principles and Semi-Empirical Kinetic Models. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of Temperature and Moisture on the Physical Stability of Binary and Ternary Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Celecoxib. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, N.S.; Minor, H. General Procedure for Evaluating Amorphous Scattering and Crystallinity from X-Ray Diffraction Scans of Semicrystalline Polymers. Polymer 1990, 31, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatema, K.; Sajeeb, B.; Sikdar, K.Y.K.; Al Hossain, A.M.; Bachar, S.C. Evaluation of the Formulation of Combined Dosage Form of Albendazole and Mebendazole through In Vitro Physicochemical and Anthelmintic Study. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 21, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Dubey, P.; Kumar, S.U.; Sachdev, A.; Matai, I.; Gopinath, P. Bionanotherapeutics: Niclosamide Encapsulated Albumin Nanoparticles as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12078–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yao, Y. Octenylsuccinate Hydroxypropyl Phytoglycogen Enhances the Solubility and In-Vitro Antitumor Efficacy of Niclosamide. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Hernández-Laguna, A.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Molecular Modeling and Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy of the Crystal Structure of the Chiral Antiparasitic Drug Praziquantel. J. Mol. Model. 2017, 23, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Lara, J.C.; Guzman-Villanueva, D.; Arenas-García, J.I.; Herrera-Ruiz, D.; Rivera-Islas, J.; Román-Bravo, P.; Morales-Rojas, H.; Höpfl, H. Cocrystals of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients-Praziquantel in Combination with Oxalic, Malonic, Succinic, Maleic, Fumaric, Glutaric, Adipic, and Pimelic Acids. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbuio, A.Q.P.; Hanashiro, T.; Markman, B.E.O.; Fonseca, F.L.A. Evaluation and Study of Mebendazole Polymorphs Present in Raw Materials and Tablets Available in the Brazilian Pharmaceutical Market. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrdla, P.J.; Floyd, P.D.; Dell’Orco, P.C. The Amorphous State: First-Principles Derivation of the Gordon–Taylor Equation for Direct Prediction of the Glass Transition Temperature of Mixtures; Estimation of the Crossover Temperature of Fragile Glass Formers; Physical Basis of the “Rule of 2/3”. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 20523–20532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzghoul, A.; Alhalaweh, A.; Mahlin, D.; Bergström, C.A.S. Experimental and Computational Prediction of Glass Transition Temperature of Drugs. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasten, G.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Co-Former Selection for Co-Amorphous Drug-Amino Acid Formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 557, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Invernizzi, S.; Voinovich, D.; Bertoni, S.; Melegari, C.; Millotti, G.; Albertini, B. Milling and Comilling Praziquantel at Cryogenic and Room Temperatures: Assessment of the Process-Induced Effects on Drug Properties. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 153, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Zografi, G. Phase Behavior of Binary and Ternary Amorphous Mixtures Containing Indomethacin, Citric Acid and PVP. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajber, L.; Corrigan, O.I.; Healy, A.M. Physicochemical Evaluation of PVP–Thiazide Diuretic Interactions in Co-Spray-Dried Composites—Analysis of Glass Transition Composition Relationships. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Bates, S.; Carvajal, M.T. Toward Understanding the Evolution of Griseofulvin Crystal Structure to a Mesophase after Cryogenic Milling. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 367, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, B.C.; Shamblin, S.L.; Zografi, G. Molecular Mobility of Amorphous Pharmaceutical Solids Below Their Glass Transition Temperatures. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Mooter, G. The Use of Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Formulation Strategy to Overcome Poor Solubility and Dissolution Rate. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2012, 9, e79–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, M.; Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Crystallization of Indomethacin from the Amorphous State below and above Its Glass Transition Temperature. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheokand, S.; Modi, S.R.; Bansal, A.K. Dynamic Vapor Sorption as a Tool for Characterization and Quantification of Amorphous Content in Predominantly Crystalline Materials. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3364–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanolla, D.; Hasa, D.; Arhangelskis, M.; Schneider-Rauber, G.; Chierotti, M.R.; Keiser, J.; Voinovich, D.; Jones, W.; Perissutti, B. Mechanochemical Formation of Racemic Praziquantel Hemihydrate with Improved Biopharmaceutical Properties. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedeker, D.; Gossmann, R.; Langer, K.; Brunklaus, G. Crystal Engineering of Pharmaceutical Co-Crystals: “NMR Crystallography” of Niclosamide Co-Crystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3087–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengale, S.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Löbmann, K. Recent Advances in Co-Amorphous Drug Formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šagud, I.; Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Škorić, I. Identification of Degradation Products of Praziquantel during the Mechanochemical Activation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH Q1A (R2) Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Drug Products-Scientific Guideline | European Medicines Agency (EMA). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q1a-r2-stability-testing-new-drug-substances-drug-products-scientific-guideline (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Transformations between Co-Amorphous and Co-Crystal Systems and Their Influence on the Formation and Physical Stability of Co-Amorphous Systems. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovago, I.; Wang, W.; Qiu, D.; Raijada, D.; Rantanen, J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Bond, A.; Löbmann, K. Properties of the Sodium Naproxen-Lactose-Tetrahydrate Co-Crystal upon Processing and Storage. Molecules 2016, 21, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpeläinen, T.; Pajula, K.; Ervasti, T.; Uurasjärvi, E.; Koistinen, A.; Korhonen, O. Raman Imaging of Amorphous-Amorphous Phase Separation in Small Molecule Co-Amorphous Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 155, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalaweh, A.; Alzghoul, A.; Mahlin, D.; Bergström, C.A.S. Physical Stability of Drugs after Storage above and below the Glass Transition Temperature: Relationship to Glass-Forming Ability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

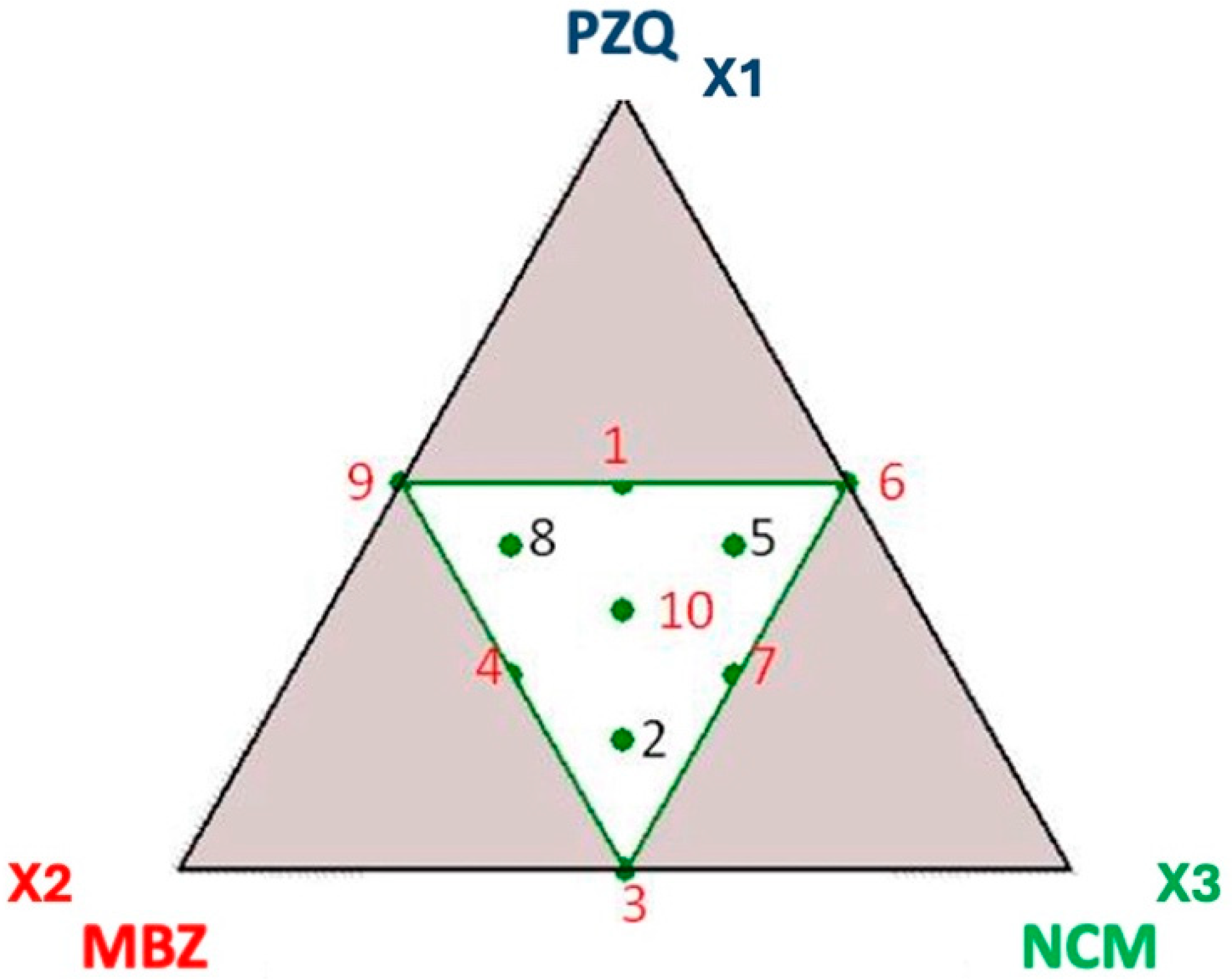







| Exp. N° | Molar Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PZQ X1 | MBZ X2 | NCM X3 | |
| 1 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 0.250 |
| 2 | 0.167 | 0.417 | 0.417 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.500 | 0.500 |
| 4 | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.250 |
| 5 | 0.417 | 0.167 | 0.417 |
| 6 | 0.500 | 0 | 0.500 |
| 7 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.500 |
| 8 | 0.417 | 0.417 | 0.167 |
| 9 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 |
| Sample/Exp. N° | Molar Ratio | Experimental Tg (°C) ± S.D. | Theoretical Tg According to G-T Equation (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PZQ | NCM | MBZ | |||
| PZQ | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40.94 * ± 0.90 | 28.56 § |
| NCM | 0 | 1 | 0 | 82.90 * ± 0.64 | 85.47 § |
| MBZ | 0 | 0 | 1 | 111.98 ± 0.73 | 142.95 § |
| 1 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 0.250 | / | 63.54 |
| 2 | 0.167 | 0.417 | 0.417 | / | 84.17 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 98.33 ± 0.34 | 96.95 |
| 4 | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 79.54 ± 0.59 | 75.40 |
| 5 | 0.417 | 0.167 | 0.417 | 74.02 ± 0.59 | 71.02 |
| 6 | 0.500 | 0 | 0.500 | 69.31 ± 0.87 | 68.67 |
| 7 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.500 | 83.31 ± 0.76 | 81.58 |
| 8 | 0.417 | 0.417 | 0.167 | 60.40 ± 0.13 | 65.40 |
| 9 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0 | 59.15 ± 0.95 | 57.87 |
| 10 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 76.77 ± 0.09 | 73.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Abbrunzo, I.; Venier, E.; Selmin, F.; Škorić, I.; Bernardo, E.; Procida, G.; Perissutti, B. Stability of Ternary Drug–Drug–Drug Coamorphous Systems Obtained Through Mechanochemistry. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010092
D’Abbrunzo I, Venier E, Selmin F, Škorić I, Bernardo E, Procida G, Perissutti B. Stability of Ternary Drug–Drug–Drug Coamorphous Systems Obtained Through Mechanochemistry. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Abbrunzo, Ilenia, Elisabetta Venier, Francesca Selmin, Irena Škorić, Enrico Bernardo, Giuseppe Procida, and Beatrice Perissutti. 2025. "Stability of Ternary Drug–Drug–Drug Coamorphous Systems Obtained Through Mechanochemistry" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010092
APA StyleD’Abbrunzo, I., Venier, E., Selmin, F., Škorić, I., Bernardo, E., Procida, G., & Perissutti, B. (2025). Stability of Ternary Drug–Drug–Drug Coamorphous Systems Obtained Through Mechanochemistry. Pharmaceutics, 17(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010092









