Revisiting the Metabolism of Donepezil in Rats Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Molecular Networking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animal Experiment
2.3. Sample Preparations
2.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
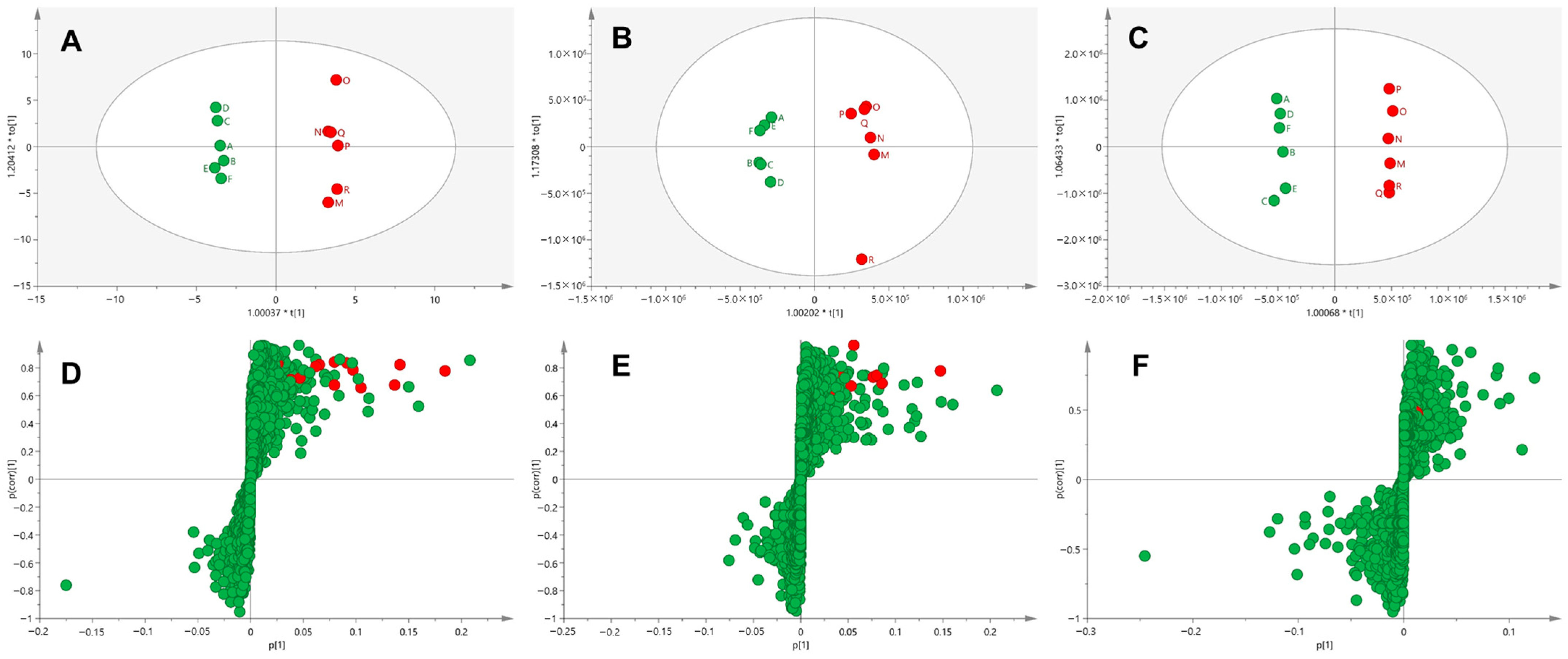
2.5. Multivariate Analysis
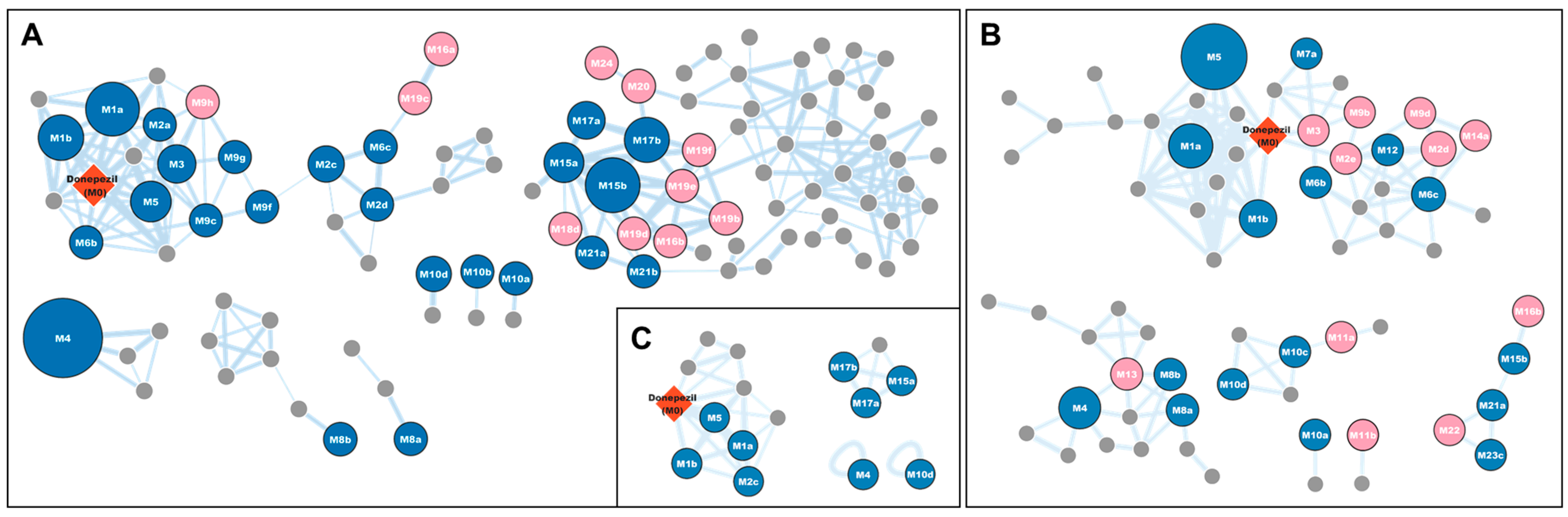
2.6. Molecular Networking
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Profiling of Donepezil Metabolites Using Metabolomic and Molecular Networking Approaches
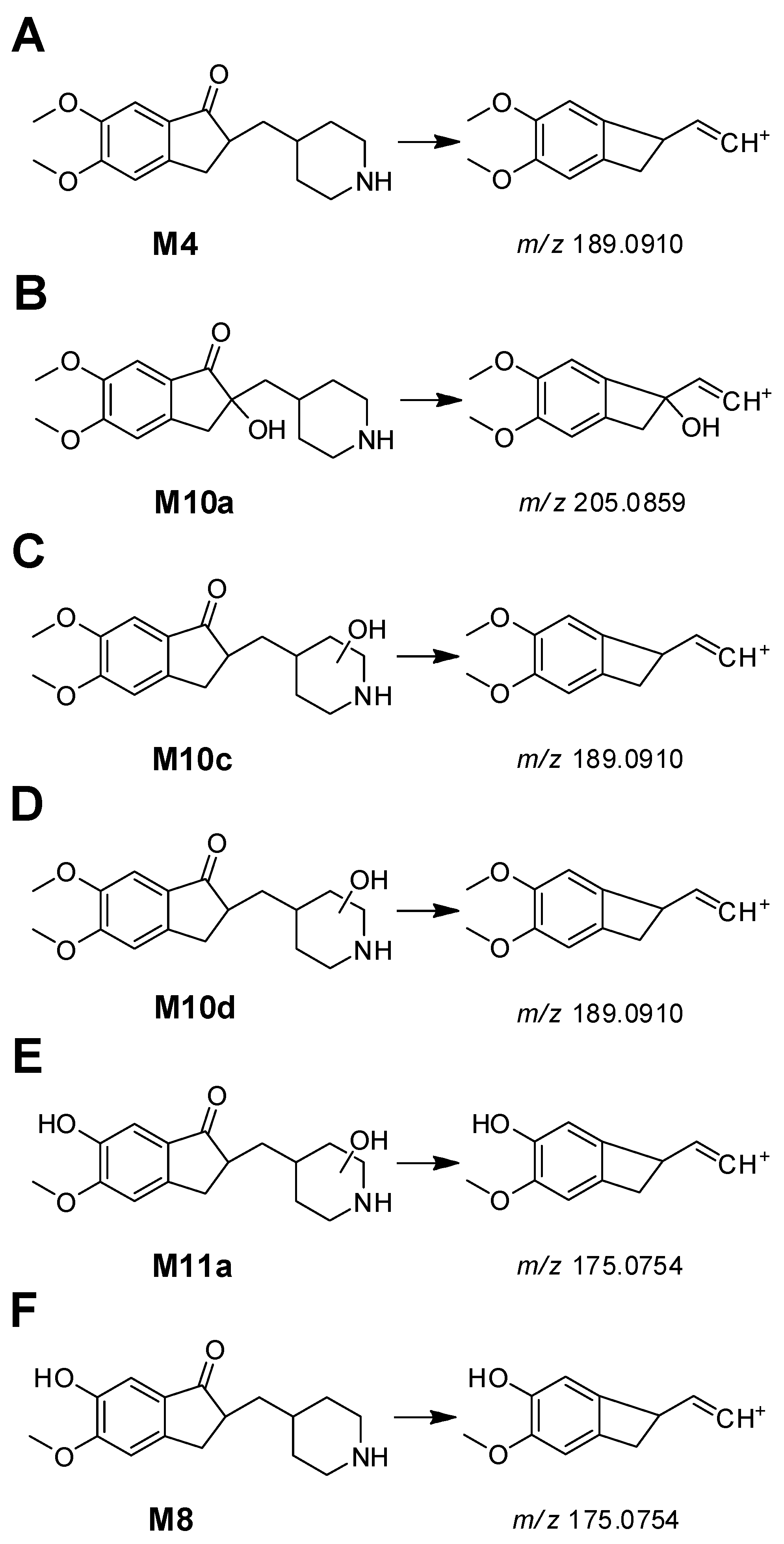
3.2. Phase I Metabolites Structure Identification
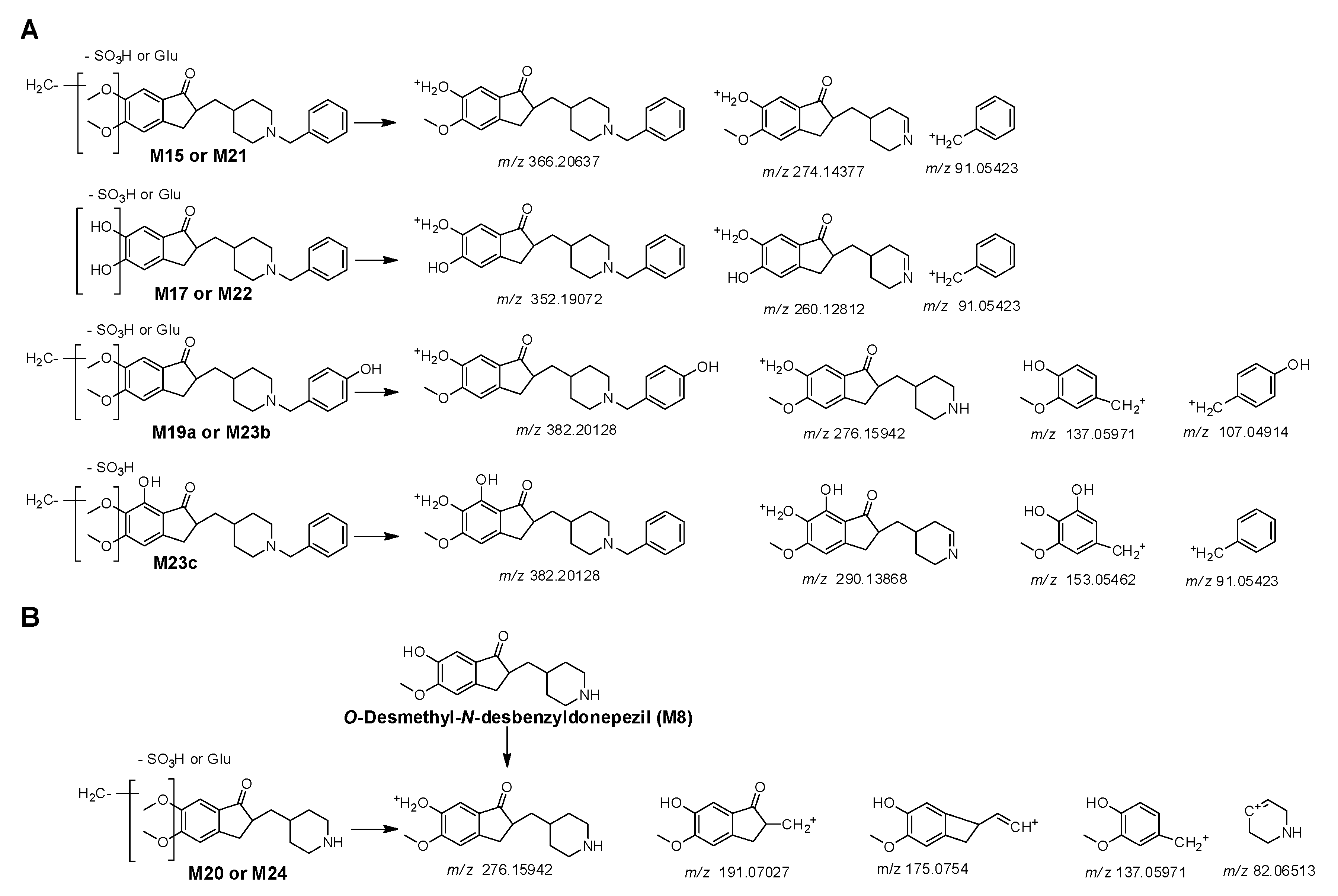
3.3. Phase II Metabolites Structure Identification
3.4. Distribution of Donepezil Metabolites in Urine, Feces, and Liver Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Chen, B.Z.; Zhang, X.P.; Zheng, H.; Guo, X.D. An Update on the Routes for the Delivery of Donepezil. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagawa, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ueno, A.; Maeda, T.; Obi, T. Impact of CYP2D6, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 Polymorphisms on Plasma Concentrations of Donepezil and Its Metabolite in Patients with Alzheimer Disease. Ther. Drug Monit. 2021, 43, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coin, A.; Pamio, M.V.; Alexopoulos, C.; Granziera, S.; Groppa, F.; de Rosa, G.; Girardi, A.; Sergi, G.; Manzato, E.; Padrini, R. Donepezil plasma concentrations, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 phenotypes, and cognitive outcome in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.E.; Seo, H.J.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, G.M.; Ji, S.B.; Park, S.Y.; Wu, Z.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Liu, K.H. In Vitro Metabolism of Donepezil in Liver Microsomes Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiseo, P.J.; Perdomo, C.A.; Friedhoff, L.T. Metabolism and elimination of 14C-donepezil in healthy volunteers: A single-dose study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 46 (Suppl. S1), 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Mishima, M.; Nagai, Y.; Yuzuriha, T.; Yoshimura, T. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of donepezil (Aricept) after a single oral administration to Rat. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1999, 27, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.S.; Kim, G.; Yim, D.; Moon, K.S.; Lee, S.J.; Shin, J.G.; Kim, D.H. Identification and characterization of amiodarone metabolites in rats using UPLC-ESI-QTOFMS-based untargeted metabolomics approach. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2018, 81, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, W.G.; Moon, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.S. Metabolomics-assisted metabolite profiling of itraconazole in human liver preparations. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1083, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jo, J.H.; Seo, K.A.; Hwang, H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S. Nontargeted metabolomics-guided sildenafil metabolism study in human liver microsomes. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1072, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Nothias, L.F.; Wang, M.; Kim, D.H.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Kang, K.B.; Yoo, H.H. Tandem Mass Spectrometry Molecular Networking as a Powerful and Efficient Tool for Drug Metabolism Studies. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.A.; Nothias, L.F.; Vining, O.; Meehan, M.; Esquenazi, E.; Dorrestein, P.C. Molecular Networking as a Drug Discovery, Drug Metabolism, and Precision Medicine Strategy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, Y.B.; Seo, J.I.; Yoo, H.H. Exploring Metabolic Pathways of Anamorelin, a Selective Agonist of the Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor, via Molecular Networking. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Kim, G.J.; Park, S.Y.; Shon, J.C.; Liu, K.H.; Choi, H. In Vitro Metabolism Study of Seongsanamide A in Human Liver Microsomes Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Feature-Based Molecular Networking. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.S.; Seo, H.; Kim, G.B.; Hong, J.; Yoo, H.H. MS-Based Molecular Networking of Designer Drugs as an Approach for the Detection of Unknown Derivatives for Forensic and Doping Applications: A Case of NBOMe Derivatives. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5483–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Davis, S.R.; Meng, M.; Yuan, W.; Diehl, L.; Arjmand, F.M.; Lucke, R.M.; Huang, B.; Wen, J.; Shudo, J.; Nagata, T. Dried blood spot analysis of donepezil in support of a GLP 3-month dose-range finding study in rats. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Kind, T.; Yoon, Y.R.; Fiehn, O.; Liu, K.H. Comparative evaluation of extraction methods for simultaneous mass-spectrometric analysis of complex lipids and primary metabolites from human blood plasma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7275–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.A.; Abdine, H.H.; Al-Quadeb, B.T.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Nakashima, K. Stereoselective HPLC assay of donepezil enantiomers with UV detection and its application to pharmacokinetics in rats. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2006, 830, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Davis, S.R.; Murgasova, R.; Toole, C.; Arjmand, F.M.; Diehl, L.; Cayme, B.; Wen, J.; Shudo, J.; Nagata, T. Comparison of Metabolism of Donepezil in Rat, Mini-Pig and Human, Following Oral and Transdermal Administration, and in an In Vitro Model of Human Epidermis. J. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L. Sample normalization methods in quantitative metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1430, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, S.; Johansson, E.; Sjostrom, L.; Mellerowicz, E.J.; Edlund, U.; Shockcor, J.P.; Gottfries, J.; Moritz, T.; Trygg, J. Visualization of GC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using OPLS class models. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron, A.T.; Gentry, E.C.; McPhail, K.L.; Nothias, L.F.; Nothias-Esposito, M.; Bouslimani, A.; Petras, D.; Gauglitz, J.M.; Sikora, N.; Vargas, F.; et al. Reproducible molecular networking of untargeted mass spectrometry data using GNPS. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1954–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrack, B.M.; Hnatyshyn, S.; Ott, K.H.; Reily, M.D.; Sanders, M.; Zhang, H.; Drexler, D.M. Normalization strategies for metabonomic analysis of urine samples. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, H.F.; Chua, E.W.L.; Mir, S.A.; Burla, B.; Bendt, A.K.; Wenk, M.R. Evaluation of Normalization Approaches for Quantitative Analysis of Bile Acids in Human Feces. Metabolites 2022, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoi, M.; Percival, M.; Nemr, C.; Li, A.; Gibala, M.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Characterization of the Human Skeletal Muscle Metabolome for Elucidating the Mechanisms of Bicarbonate Ingestion on Strenuous Interval Exercise. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Wu, Z.; Lee, B.; Shon, J.C.; Lee, T.; Lee, I.K.; Sim, T.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, N.D.; Kim, S.H.; et al. In vitro metabolism of an estrogen-related receptor gamma modulator, GSK5182, by human liver microsomes and recombinant cytochrome P450s. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2015, 36, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.A.; Bae, S.K.; Choi, Y.K.; Choi, C.S.; Liu, K.H.; Shin, J.G. Metabolism of 1’- and 4-hydroxymidazolam by glucuronide conjugation is largely mediated by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases 1A4, 2B4, and 2B7. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Lee, D.; Wu, Z.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, B.M.; Huh, T.L.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, T.W.; et al. In vitro metabolism of obovatol and its effect on cytochrome P450 enzyme activities in human liver microsomes. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2013, 34, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, S.Y.; Park, E.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Song, I.S.; Liu, K.H. Evaluation of the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Saxagliptin through Reactive Metabolite Identification in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, W.G.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.S. Revisiting the Metabolism and Bioactivation of Ketoconazole in Human and Mouse Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

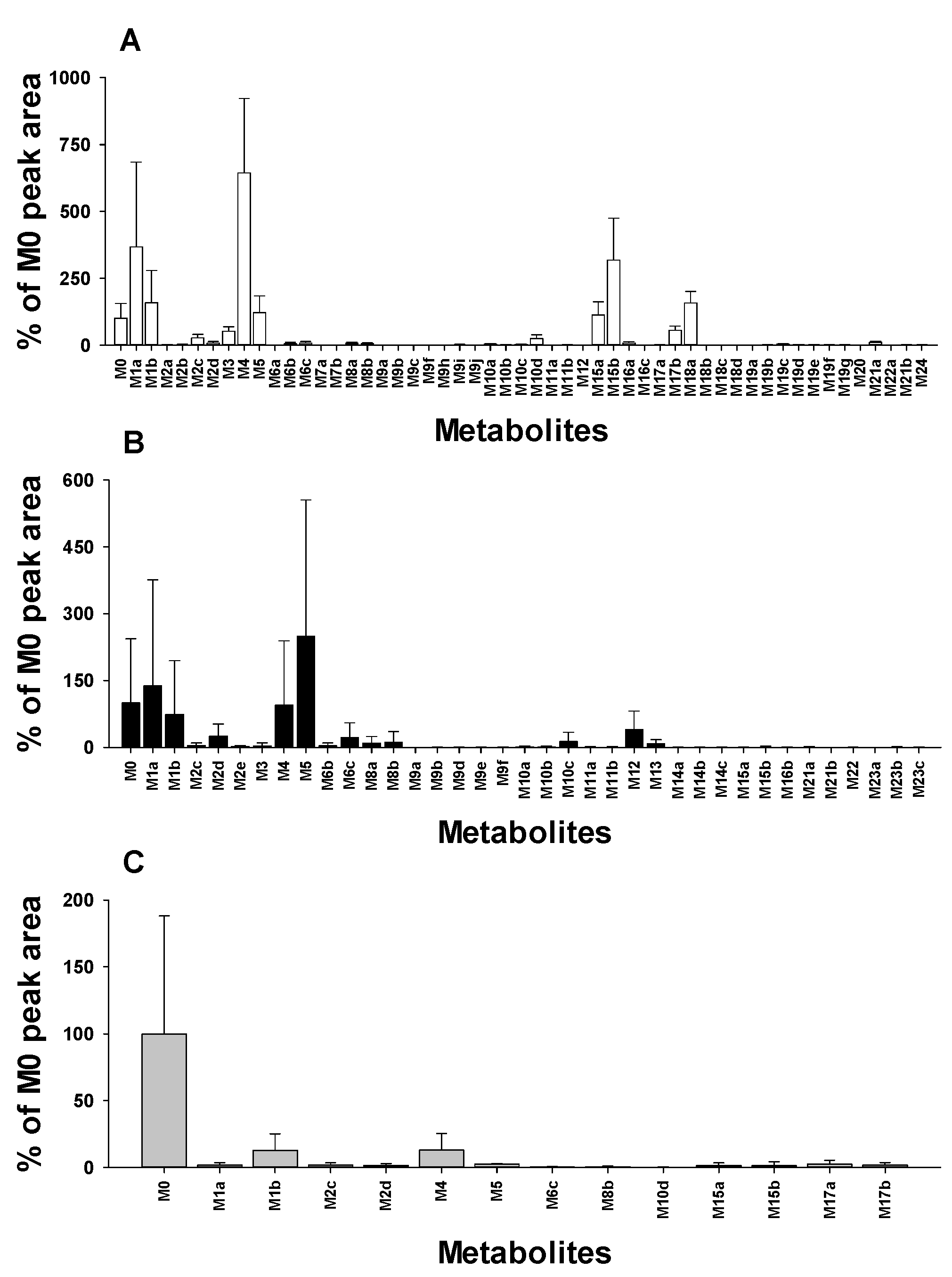
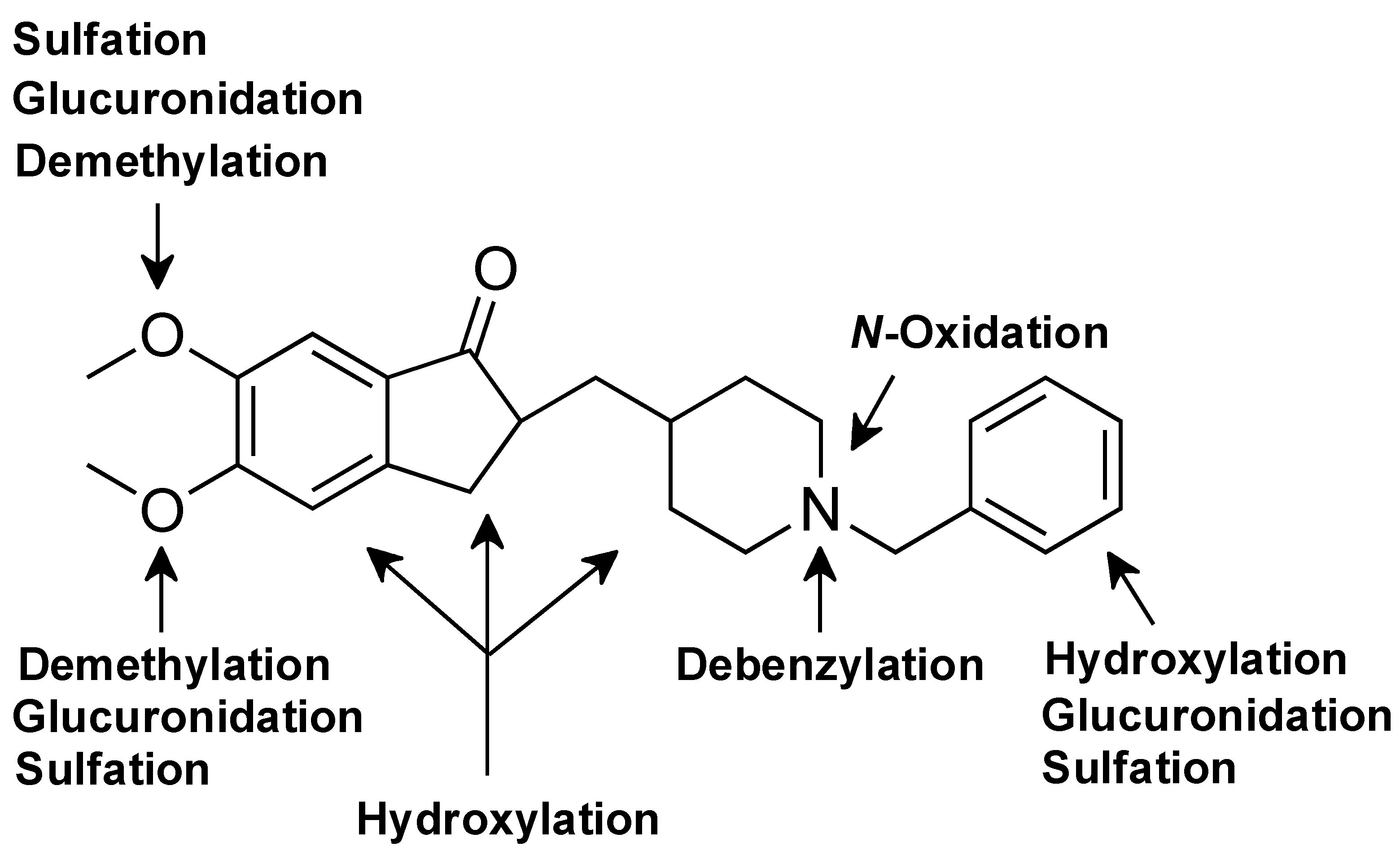

| Metabolites | tR (min) | [M+H]+ | Error (ppm) | Formula (Neutral) | Reaction Type | Urine | Feces | Liver | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured | Theoretical | MB a | FBMN | MB | FBMN | MB | FBMN | |||||
| Donepezil | 10.22 | 380.2213 | 380.2220 | −1.84 | C24H29NO3 | - | ||||||
| M1a | 8.46 | 366.2057 | 366.2064 | −1.91 | C23H27NO3 | 6-O-demethylation | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| M1b | 8.72 | 366.2057 | 366.2064 | −1.91 | C23H27NO3 | 5-O-demethylation | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| M2a | 7.73 | 396.2159 | 396.2169 | −2.52 | C24H29NO4 | hydroxylation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M2b | 8.01 | 396.2162 | 396.2169 | −1.77 | C24H29NO4 | hydroxylation | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| M2c | 8.21 | 396.2163 | 396.2169 | −1.51 | C24H29NO4 | hydroxylation | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| M2d | 8.40 | 396.2159 | 396.2169 | −2.52 | C24H29NO4 | hydroxylation | - | + | + | - | - | - |
| M2e | 8.81 | 396.2161 | 396.2169 | −2.02 | C24H29NO4 | hydroxylation | - | - | + | + | - | - |
| M3 | 11.02 | 396.2163 | 396.2169 | −1.51 | C24H29NO4 | N-oxidation | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| M4 | 5.59 | 290.1743 | 290.1751 | −2.76 | C17H23NO3 | N-debenzylation | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| M5 | 7.12 | 352.1901 | 352.1907 | −1.70 | C22H25NO3 | didemethylation | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| M6a | 5.97 | 382.2006 | 382.2013 | −1.83 | C23H27NO4 | 6-O-demethylation + hydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M6b | 6.56 | 382.2003 | 382.2013 | −2.62 | C23H27NO4 | 5-O-demethylation + hydroxylation | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| M6c | 6.85 | 382.2003 | 382.2013 | −2.62 | C23H27NO4 | O-demethylation + hydroxylation | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| M7a | 9.28 | 382.2005 | 382.2013 | −2.09 | C23H27NO4 | 6-O-demethylation + N-oxidation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M7b | 9.57 | 382.2008 | 382.2013 | −1.31 | C23H27NO4 | 5-O-demethylation + N-oxidation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M8a | 3.75 | 276.1588 | 276.1594 | −2.17 | C16H21NO3 | 6-O-demethylation + N-debenzylation | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| M8b | 4.02 | 276.1588 | 276.1594 | −2.17 | C16H21NO3 | 5-O-demethylation + N-debenzylation | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| M9a | 5.79 | 412.2107 | 412.2118 | −2.67 | C24H29NO5 | dihydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M9b | 6.48 | 412.2108 | 412.2118 | −2.43 | C24H29NO5 | dihydroxylation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M9c | 6.85 | 412.2108 | 412.2118 | −2.43 | C24H29NO5 | dihydroxylation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M9d | 7.67 | 412.2108 | 412.2118 | −2.43 | C24H29NO5 | dihydroxylation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M9e | 8.06 | 412.2106 | 412.2118 | −2.91 | C24H29NO5 | dihydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M9f | 8.39 | 412.2112 | 412.2118 | −1.46 | C24H29NO5 | dihydroxylation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M9g | 8.65 | 412.2109 | 412.2118 | −2.18 | C24H29NO5 | dihydroxylation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M9h | 9.09 | 412.2108 | 412.2118 | −2.43 | C24H29NO5 | hydroxylation + N-oxidation | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| M9i | 9.53 | 412.2110 | 412.2118 | −1.94 | C24H29NO5 | hydroxylation + N-oxidation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M10a | 3.21 | 306.1692 | 306.1700 | −2.61 | C17H23NO4 | hydroxylation + N-debenzylation | - | + | + | + | - | - |
| M10b | 3.57 | 306.1692 | 306.1700 | −2.61 | C17H23NO4 | hydroxylation + N-debenzylation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M10c | 3.65 | 306.1693 | 306.1700 | −2.29 | C17H23NO4 | hydroxylation + N-debenzylation | - | - | + | + | - | - |
| M10d | 4.11 | 306.1694 | 306.1700 | −1.96 | C17H23NO4 | hydroxylation + N-debenzylation | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| M11a | 2.49 | 292.1536 | 292.1543 | −2.40 | C16H21NO4 | O-demethylation + N-debenzylation + hydroxylation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M11b | 3.21 | 292.1543 | 292.1543 | 0.00 | C16H21NO4 | O-demethylation + N-debenzylation + hydroxylation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M12 | 5.26 | 368.1851 | 368.1856 | −1.36 | C22C25NO4 | didemethylation + hydroxylation | - | - | + | + | - | - |
| M13 | 2.56 | 262.1433 | 262.1438 | −1.91 | C15H19NO3 | didemethylation + N-debenzylation | - | - | + | + | - | - |
| M14a | 5.69 | 398.1954 | 398.1962 | −2.01 | C23H27NO5 | O-demethylation + dihydroxylation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M14b | 6.10 | 398.1956 | 398.1962 | −1.51 | C23H27NO5 | O-demethylation + dihydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M14c | 6.66 | 398.1956 | 398.1962 | −1.51 | C23H27NO5 | O-demethylation + dihydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M15a | 5.85 | 542.2377 | 542.2385 | −1.48 | C29H35NO9 | 6-O-demethylation + glucuronidation | + | + | - | - | - | + |
| M15b | 6.10 | 542.2379 | 542.2385 | −1.11 | C29H35NO9 | 5-O-demethylation + glucuronidation | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| M16a | 6.35 | 572.2478 | 572.2490 | −2.10 | C30H37NO10 | hydroxylation+ glucuronidation | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| M16b | 7.33 | 572.2481 | 572.2490 | −1.57 | C30H37NO10 | hydroxylation+ glucuronidation | - | + | - | + | - | - |
| M16c | 7.42 | 572.2483 | 572.2490 | −1.22 | C30H37NO10 | hydroxylation+ glucuronidation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M17a | 5.16 | 528.2222 | 528.2228 | −1.14 | C28H33NO9 | didemethylation + glucuronidation | + | + | - | - | + | + |
| M17b | 5.83 | 528.2222 | 528.2228 | −1.14 | C28H33NO9 | didemethylation + glucuronidation | + | + | - | - | - | + |
| M18a | 3.52 | 544.2169 | 544.2177 | −1.47 | C28H33NO10 | didemethylation + glucuronidation + hydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M18b | 4.19 | 544.2174 | 544.2177 | −0.55 | C28H33NO10 | didemethylation + glucuronidation + hydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M18c | 5.01 | 544.2173 | 544.2177 | −0.73 | C28H33NO10 | didemethylation + glucuronidation + hydroxylation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M18d | 6.05 | 544.2175 | 544.2177 | −0.37 | C28H33NO10 | didemethylation + glucuronidation + hydroxylation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M19a | 4.20 | 558.2324 | 558.2334 | −1.79 | C29H35NO10 | O-demethylation + hydroxylation + glucuronidation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M19b | 4.41 | 558.2324 | 558.2334 | −1.79 | C29H35NO10 | O-demethylation + hydroxylation + glucuronidation | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| M19c | 4.88 | 558.2322 | 558.2334 | −2.15 | C29H35NO10 | O-demethylation + hydroxylation + glucuronidation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M19d | 5.13 | 558.2323 | 558.2334 | −1.97 | C29H35NO10 | O-demethylation + hydroxylation + glucuronidation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M19e | 6.10 | 558.2324 | 558.2334 | −1.79 | C29H35NO10 | O-demethylation + N-oxidation + glucuronidation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M19f | 6.53 | 558.2324 | 558.2334 | −1.79 | C29H35NO10 | O-demethylation + N-oxidation + glucuronidation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M19g | 6.81 | 558.2321 | 558.2334 | −2.33 | C29H35NO10 | O-demethylation + N-oxidation + glucuronidation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M20 | 2.02 | 452.1906 | 452.1915 | −1.99 | C22H29NO9 | O-demethylation + N-debenzylation + glucuronidation | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| M21a | 8.14 | 446.1621 | 446.1632 | −2.47 | C23H27NO6S | 6-O-demethylation + sulfation | - | + | - | + | - | - |
| M21b | 8.45 | 446.1621 | 446.1632 | −2.47 | C23H27NO6S | 5-O-demethylation + sulfation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| M22 | 7.94 | 432.1463 | 432.1475 | −2.78 | C22H25NO6S | didemethylation + sulfation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M23a | 6.48 | 462.1571 | 462.1581 | −2.16 | C23H27NO7S | O-demethylation + hydroxylation + sulfation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M23b | 6.72 | 462.1572 | 462.1581 | −1.95 | C23H27NO7S | O-demethylation + hydroxylation + sulfation | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M23c | 8.60 | 462.1575 | 462.1581 | −1.30 | C23H27NO7S | O-demethylation + hydroxylation + sulfation | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| M24 | 3.70 | 356.1155 | 356.1162 | −1.97 | C16H21NO6S | O-demethylation + N-debenzylation + sulfation | - | + | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, E.-J.; Kim, E.-H.; Kim, K.-Y.; Jeon, J.-H.; Song, I.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Liu, K.-H. Revisiting the Metabolism of Donepezil in Rats Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Molecular Networking. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010115
Park E-J, Kim E-H, Kim K-Y, Jeon J-H, Song I-S, Park S-Y, Liu K-H. Revisiting the Metabolism of Donepezil in Rats Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Molecular Networking. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(1):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010115
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Eun-Ji, Eui-Hyeon Kim, Ki-Young Kim, Ji-Hyeon Jeon, Im-Sook Song, So-Young Park, and Kwang-Hyeon Liu. 2025. "Revisiting the Metabolism of Donepezil in Rats Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Molecular Networking" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 1: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010115
APA StylePark, E.-J., Kim, E.-H., Kim, K.-Y., Jeon, J.-H., Song, I.-S., Park, S.-Y., & Liu, K.-H. (2025). Revisiting the Metabolism of Donepezil in Rats Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Molecular Networking. Pharmaceutics, 17(1), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010115









