Assessment of Infant Exposure to Antidepressants through Breastfeeding: A Literature Review of Currently Available Approaches
Abstract
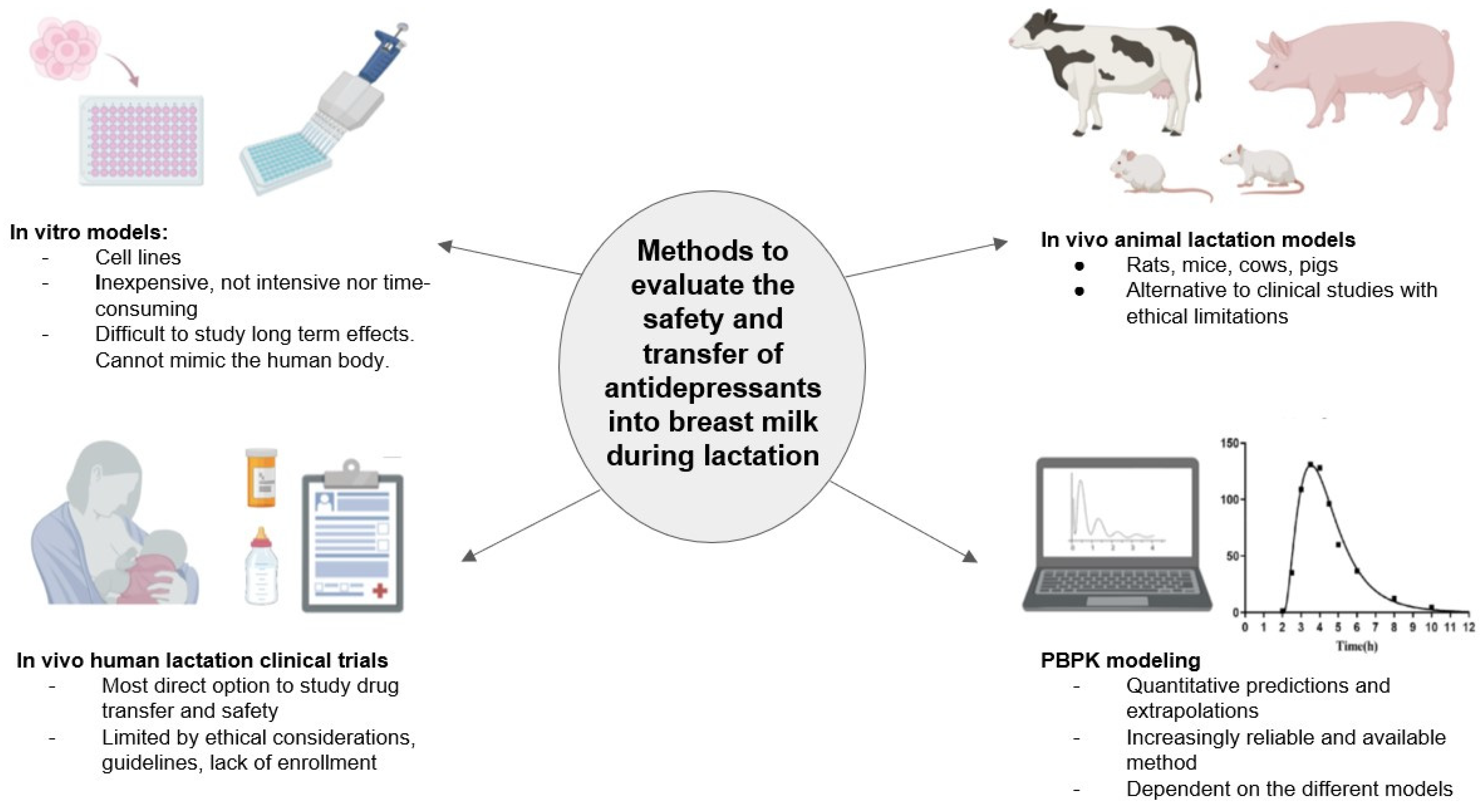
1. Introduction
2. In Vitro Models to Predict Drug Excretion into Breast Milk
3. Animal Models for Lactation Study
4. Rodents
5. Other Animals
6. Human Studies and Reports of Antidepressant Use during Lactation
| Drug | Drug Class # | First-Line/Second-Line Treatment | Study Type | Study Size | Obs. M/P Ratio | RID | Observed Adverse Effects in Infants | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amitriptyline | Tricyclic | Second line | Cohort study | 2 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 0.9 | 1% | One infant tested in the low normal range for development and was slightly hypotonic | Yoshida et al., 1997 [46] |
| Bupropion | NDRI | First line | Cohort study | 10 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 2.8 | 0.2% | No adverse effects reported | Kaplan et al., 2004 [47] |
| Citalopram | SSRI | First line | Cohort study | 7 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 1.8 | 3.2–3.7% | No adverse effects reported | Kristensen et al., 2000 [48] |
| Clomipramine | Tricyclic | Second line | Cohort study | 2 mother–infant pairs | 0.4–3.0 | 1.3% | No adverse effects reported | Smith et al., 1997 [46] |
| Desipramine | Tricyclic | Second line | Case report | 1 mother and her infant | Mean: 1.45 | N/A | No adverse effects reported | Reed et al., 1986 [49] |
| Desvenlafaxine | SNRI | First line | Cohort Study | 10 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 2.24 | 6.8% | 7 infants were at a lower growth percentile but all 10 infants had normal development | Teoh et al., 2010 [50] |
| Dothiepin | Tricyclic | Not available in the U.S. | Cohort study | 8 mothers with plasma samples taken from 5 infants | Mean range: 0.78–1.59 | 0.58% | No adverse effects reported | Lebedevs et al., 1992 [51] |
| Doxepin | Tricyclic | Second line | Case report | 1 mother-infant pair | Mean: 1.66 | 2.2% | No adverse effects reported | Ilett et al., 1985 [52] |
| Duloxetine | SNRI | First line | Open label study | 6 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 0.25 | 0.14% | No adverse effects reported | Loghin et al., 2008 [53] |
| Escitalopram | SSRI | First line | Cohort study | 8 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 2.2 | 3.9% | No adverse effects reported | Hackett et al., 2006 [54] |
| Fluoxetine | SSRI | First line | Cohort study | 23 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 0.62 | 0.54% | No adverse effects reported | Riggs et al., 2006 [55] |
| Fluvoxamine | SSRI | First line | Meta-analysis | 6 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 0.9 | 0.98% | No adverse effects reported | Levy et al., 2004 [4] |
| Imipramine | Tricyclic | Second line | Cohort study | 4 mother–infant pairs | Range: 0.9–1.5 | 2.9% | No adverse effects reported | Smith et al., 1997 [46] |
| Mianserin | Tetracyclic | Not available in the U.S. | Case reports | 2 mother–infant pairs | 3.6, 0.8 | 1.4%, 0.5% | No adverse effects reported | Norman et al., 1993 [56] |
| Mirtazapine | Tetracyclic | First line | Cohort study | 8 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 1.1 | 1.5% | No adverse effects reported | Ilett et al. 2007 [57] |
| Moclobemide | MAOI | Not available in the U.S. | Cohort study | 6 mother–infant pairs | 0.7 | 1% | No adverse effects reported | Schoerlin et al. 1990 [58] |
| Nortriptyline | Tricyclic | Second line | Case reports | 1 mother–infant pair | Mean: 1.6 | 1.3% | No adverse effects reported | Skjaeraasen et al., 1988 [59] |
| Paroxetine | SSRI | First line | Cohort study | 9 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 0.6 | 2% | No adverse effects reported | Touw et al., 2024 [60] |
| Reboxetine | NRI | Not available in the U.S. | Open-label study | 4 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 0.06 | 2% | No adverse effects reported | Ilett et al. 2006 [61] |
| Sertraline | SSRI | First line | Cohort study | 15 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 2.3 | 1% | No adverse effects reported | Touw et al., 2024 [60] |
| Trazodone | SARI | Second line | Clinical trial | 6 mother–infant pairs | Mean: 0.14 | 0.65% | No adverse effects reported | Ross et al., 1986 [62] |
| Venlafaxine | SNRI | First line | Clinical trial | 6 mothers and 7 infants | Mean: 2.5 | 6.4% | All infants had normal development but 2 had decreased weight gain | Kristensen et al., 2002 [63] |
7. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
8. Citalopram
9. Fluoxetine
10. Paroxetine
11. Sertraline
12. PBPK Models to Facilitate the Estimation of Drug Secretion into Breast Milk
13. Other Approaches
14. Challenges
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuehner, C. Why is depression more common among women than among men? Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaynes, B.N.; Gavin, N.; Meltzer-Brody, S.; Lohr, K.N.; Swinson, T.; Gartlehner, G.; Brody, S.; Miller, W.C. Perinatal depression: Prevalence, screening accuracy, and screening outcomes. AHRQ Evid. Rep. Summ. 2005, 119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubovicky, M.; Belovicova, K.; Csatlosova, K.; Bogi, E. Risks of using SSRI/SNRI antidepressants during pregnancy and lactation. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2017, 10, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, A.M.; Levy, B.T.; Hartz, A.J.; Bentler, S.; Donohue, M.; Ellingrod, V.L.; Wisner, K.L. Pooled Analysis of Antidepressant Levels in Lactating Mothers, Breast Milk, and Nursing Infants. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berle, J.O.; Spigset, O. Antidepressant Use during Breastfeeding. Curr. Women’s Health Rev. 2011, 7, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chad, L.; Pupco, A.; Bozzo, P.; Koren, G. Update on antidepressant use during breastfeeding. Can. Fam. Physician 2013, 59, 633–634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misri, S.; Sivertz, K. Tricyclic Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation: A Preliminary Report. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 1991, 21, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmorstein, N.R.; Malone, S.M.; Iacono, W.G. Psychiatric Disorders Among Offspring of Depressed Mothers: Associations With Paternal Psychopathology. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, J.L.; Meltzer-Brody, S. Antidepressant Use During Pregnancy: Current Controversies and Treatment Strategies. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 52, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, M.C.; Wisner, K.L.; Pinto-Foltz, M.D. The Impact of Postpartum Depression on Mothering. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2006, 35, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, H.C.; Frattarelli, D.A.C.; Galinkin, J.L.; Green, T.P.; Johnson, T.; Neville, K.; Paul, I.M.; Anker, J.V.D.; Committee on Drugs. The Transfer of Drugs and Therapeutics Into Human Breast Milk: An Update on Selected Topics. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e796–e809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Johnson, T.; Sahin, L.; Tassinari, M.S.; Anderson, P.O.; Baker, T.E.; Bucci-Rechtweg, C.; Burckart, G.J.; Chambers, C.D.; Hale, T.W.; et al. Evaluation of the Safety of Drugs and Biological Products Used During Lactation: Workshop Summary. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 101, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xue, I.; Gu, Q.; Zou, P.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y.; Fisher, J.; Tran, D. Developing an In Vitro to In Vivo Extrapolation (IVIVE) Model to Predict Human Milk-to-Plasma Drug Concentration Ratios. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.O. Drugs in Lactation. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutritional Status during Pregnancy and Lactation. Nutrition during Lactation; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 5. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK235589/ (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- DI Scalea, T.L.; Wisner, K.L. Antidepressant medication use during breastfeeding. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 52, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuebe, A. The risks of not breastfeeding for mothers and infants. Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 2, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldman, A.S.; Hopkinson, J.M.; Rassin, D.K. Benefits and Risks of Breastfeeding. Adv. Pediatr. 2007, 54, 275–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljalil, K.; Pansari, A.; Ning, J.; Jamei, M. Prediction of drug concentrations in milk during breastfeeding, integrating predictive algorithms within a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2021, 10, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S. Mother and Child: Medication Use in Pregnancy and Lactation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 100, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, F. Excretion of drugs by milk. In Concepts in Biochemical Pharmacology; Brodie, B.B., Gilette, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Sychterz, C.; Chang, M.; Huang, L.; Schmidt, B.J.; Gaohua, L. A perspective on the current use of the phase distribution model for predicting milk-to-plasma drug concentration ratio. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2022, 11, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleishaker, J.C.; Desai, N.; McNamara, P.J. Factors Affecting the Milk-to-Plasma Drug Concentration Ratio in Lactating Women: Physical Interactions with Protein and Fat. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, H.; Begg, E.J. Prediction of Drug Distribution into Human Milk from Physicochemical Characteristics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 18, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, H.; Begg, E. Prediction of drug concentrations in human skim milk from plasma protein binding and acid-base characteristics. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1988, 25, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarianni, L.; Belk, D.; Aird, S.; Bennett, P. An in vitro technique for the rapid determination of drug entry into breast milk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 40, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athavale, M.A.; Maitra, A.; Patel, S.; Bhate, V.R.; Toddywalla, V.S. Development of an in vitro cell culture model to study milk to plasma ratios of therapeutic drugs. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2013, 45, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Applebee, Z.; Zou, P.; Wang, Z.; Diaz, E.S.; Li, Y. An in vitro human mammary epithelial cell permeability assay to assess drug secretion into breast milk. Int. J. Pharm. X 2022, 4, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventrella, D.; Forni, M.; Bacci, M.L.; Annaert, P. Non-clinical Models to Determine Drug Passage into Human Breast Milk. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventrella, D.; Ashkenazi, N.; Elmi, A.; Allegaert, K.; Aniballi, C.; DeLise, A.; Devine, P.J.; Smits, A.; Steiner, L.; Forni, M.; et al. Animal Models for In Vivo Lactation Studies: Anatomy, Physiology and Milk Compositions in the Most Used Non-Clinical Species: A Contribution from the ConcePTION Project. Animals 2021, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, K.M. A review of the hormone prolactin during lactation. Prog. Food Nutr. Sci. 1990, 14, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, P.E.; Owens, R.A.; Cox, D.B.; Kent, J.C. Breast development and control of milk synthesis. Food Nutr. Bull. 1996, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, D.T.; Kent, J.C.; Owens, R.A.; Hartmann, P.E. Ultrasound Imaging of Milk Ejection in the Breast of Lactating Women. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaus, M. Mother and infant: Early emotional ties. Pediatrics 1998, 102 (Suppl. 5), 1244–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak-Fiećko, R.; Kamelska-Sadowska, A.M. The Comparison of Nutritional Value of Human Milk with Other Mammals’ Milk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePeters, E.J.; Hovey, R.C. Methods for collecting milk from mice. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2009, 14, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhman, L.A. The effect of intranasal oxytocin on lactation. Obstet. Gynecol. 1963, 21, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suenderhauf, C.; Parrott, N. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of the minipig: Data compilation and model implementation. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. CHMP Assessment Report for Thymanax; European Medicine Agency: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, N.; Ito, K.; Koshimichi, H.; Hisaka, A.; Honma, M.; Igarashi, T.; Suzuki, H. Contribution of Protein Binding, Lipid Partitioning, and Asymmetrical Transport to Drug Transfer into Milk in Mouse Versus Human. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2410–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capello, C.F.; Bourke, C.H.; Ritchie, J.C.; Stowe, Z.N.; Newport, D.J.; Nemeroff, A.; Owens, M.J. Serotonin Transporter Occupancy in Rats Exposed to Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors In Utero or via Breast Milk. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 339, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrup-Jensen, A.; Bates, C.J.; Begg, E.J.; Edwards, C.L.; Matheson, I.; Mountford, P.J.; Neville, M.C.; Notarianni, L.J.; Prentiss, A.; Rane, A.; et al. Drugs and Human Lactation, 2nd ed.; Bennett, P.N., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Laskey, C. Antidepressant Use in Breastfeeding Patient. US Pharm. 2021, 46, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Laine, K.; Heikkinen, T.; Ekblad, U.; Kero, P. Effects of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors during pregnancy on serotonergic symptoms in newborns and cord blood monoamine and prolactin concentrations. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2003, 60, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, P.; Semmekrot, B.A.; van der Stappen, J. Neonatal effects of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors during pregnancy. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006, 91, F153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Smith, B.; Craggs, M.; Kumar, R.C. Investigation of pharmacokinetics and of possible adverse effects in infants exposed to tricyclic antidepressants in breast-milk. J. Affect. Disord. 1997, 43, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, J.S.; Kaplan, C.P.; Barenboim, D.; Jacob, P.; Benowitz, N.L. Bupropion in breast milk: An exposure assessment for potential treatment to prevent post-partum tobacco use. Tob. Control 2004, 13, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampono, J.; Kristensen, J.H.; Hackett, L.P.; Paech, M.; Kohan, R.; Ilett, K.F. Citalopram and demethylcitalopram in human milk; distribution, excretion and effects in breast fed infants. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 50, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancer, H.; Reed, K. Desipramine and 2-hydroxydesipramine in human breast milk and the nursing infant’s serum. Am. J. Psychiatry 1986, 143, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampono, J.; Teoh, S.; Hackett, L.P.; Kohan, R.; Ilett, K.F. Estimation of desvenlafaxine transfer into milk and infant exposure during its use in lactating women with postnatal depression. Arch. Women’s Ment. Health 2011, 14, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilett, K.; Lebedevs, T.; Wojnar-Horton, R.; Yapp, P.; Roberts, M.; Dusci, L.; Hackett, L. The excretion of dothiepin and its primary metabolites in breast milk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 33, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, J.; Ilett, K.; Booth, J.; Hackett, L. Excretion of doxepin and N-desmethyldoxepin in human milk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1985, 20, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, E.D.; Loghin, C.; Knadler, M.P.; Quinlan, T.; Zhang, L.; Chappell, J.; Lucas, R.; Bergstrom, R.F. Pharmacokinetics of Duloxetine in Breast Milk and Plasma of Healthy Postpartum Women. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 47, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampono, J.; Hackett, L.P.; Kristensen, J.H.; Kohan, R.; Page-Sharp, M.; Ilett, K.F. Transfer of escitalopram and its metabolite demethylescitalopram into breastmilk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Riggs, K.W.; Misri, S.; Kent, N.; Oberlander, T.F.; Grunau, R.E.; Fitzgerald, C.; Rurak, D.W. Stereoselective disposition of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 61, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buist, A.; Norman, T.; Dennerstein, L. Mianserin in breast milk [letter]. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1993, 36, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, J.H.; Ilett, K.F.; Rampono, J.; Kohan, R.; Hackett, L.P. Transfer of the antidepressant mirtazapine into breast milk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 63, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, G.; Schoerlin, M.; Tam, Y.; Moran, C.; Pfefen, J.; Francoual, C.; Pedarriosse, A.; Chavinie, J.; Olive, G. Moclobemide excretion in human breast milk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1990, 29, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, I.; Skjaeraasen, J. Milk concentrations of flupenthixol, nortriptyline and zuclopenthixol and between-breast differences in two patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1988, 35, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besten-Bertholee, D.D.; Touw, D.J.; Damer, E.A.; Mian, P.; Ter Horst, P.G.J. Sertraline, citalopram and paroxetine in lactation: Passage into breastmilk and infant exposure. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1414677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, L.P.; Ilett, K.F.; Rampono, J.; Kristensen, J.H.; Kohan, R. Transfer of reboxetine into breastmilk, its plasma concentrations and lack of adverse effects in the breastfed infant. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeeck, R.; Ross, S.; McKenna, E. Excretion of trazodone in breast milk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1986, 22, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilett, K.F.; Kristensen, J.H.; Hackett, L.P.; Paech, M.; Kohan, R.; Rampono, J. Distribution of venlafaxine and its O-desmethyl metabolite in human milk and their effects in breastfed infants. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, F.; Hadipour, A.L.; Battaglia, S.; Falzone, A.; Avenanti, A.; Vicario, C.M. The Role of Serotonin in Fear Learning and Memory: A Systematic Review of Human Studies. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.M. Use of antidepressants during pregnancy and lactation. Ment. Health Clin. 2013, 3, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, T.; Ekblad, U.; Kero, P.; Ekblad, S.; Laine, K. Citalopram in pregnancy and lactation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 72, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franssen, E.J.F.; Meijs, V.; Ettaher, F.; Valerio, P.G.; Keessen, M.; Lameijer, W. Citalopram Serum and Milk Levels in Mother and Infant During Lactation. Ther. Drug Monit. 2006, 28, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berle, J.; Steen, V.M.; Aamo, T.O.; Breilid, H.; Zahlsen, K.; Spigset, O. Breastfeeding during Maternal Antidepressant Treatment with Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2004, 65, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, Z.N.; Hostetter, A.L.; Owens, M.J.; Ritchie, J.C.; Sternberg, K.; Cohen, L.S.; Nemeroff, C.B. The pharmacokinetics of sertraline excretion into human breast milk: Determinants of infant serum concentrations. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2003, 64, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrick, V.; Smith, L.M.; Hwang, S.; Altshuler, L.L.; Haynes, D. Weight Gain in Breastfed Infants of Mothers Taking Antidepressant Medications. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2003, 64, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pansari, A.; Faisal, M.; Jamei, M.; Abduljalil, K. Prediction of basic drug exposure in milk using a lactation model algorithm integrated within a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2022, 43, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharaj, A.R.; Edginton, A.N. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation in Pediatric Drug Development. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2014, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, S.R.; Malik, P.R.V.; Stefan, C.; Edginton, A.N.; Colantonio, D.A.; Ito, S. Predicting Escitalopram Exposure to Breastfeeding Infants: Integrating Analytical and In Silico Techniques. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zou, P.; Fang, Y.; Li, Y. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to predict drug concentrations of breast cancer resistance protein substrates in milk. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2022, 43, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, G.G.; Samson, J.H.; Ambrose, P.J.; Schroeder, D.H. Excretion of Bupropion in Breast Milk. Ann. Pharmacother. 1993, 27, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauwelaerts, N.; Macente, J.; Deferm, N.; Bonan, R.H.; Huang, M.-C.; Van Neste, M.; Bibi, D.; Badee, J.; Martins, F.S.; Smits, A.; et al. Generic Workflow to Predict Medicine Concentrations in Human Milk Using Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modelling—A Contribution from the ConcePTION Project. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Dobchev, D.A.; Hür, E.; Fara, D.C.; Karelson, M. QSAR treatment of drugs transfer into human breast milk. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeshima, T.; Yoshida, S.; Watanabe, M.; Itagaki, F. Prediction model for milk transfer of drugs by primarily evaluating the area under the curve using QSAR/QSPR. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.; Trabjerg, B.B.; Sun, Y.; Dreier, J.W. Association of Maternal Antidepressant Prescription during Pregnancy with Standardized Test Scores of Danish School-aged Children. JAMA 2021, 326, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, D.; Chateau, D.; Struck, S.; Lee, J.B.; Dahl, M.; Derksen, S.; Katz, L.Y.; Ruth, C.; Hanlon-Dearman, A.; Brownell, M. In Utero Antidepressants and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Kindergarteners. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20191157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernia, S.; DeMaagd, G. The New Pregnancy and Lactation Labeling Rule. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 713–715. [Google Scholar]
| Drug | Drug Class | Animal Species | M/P Ratio | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agomelatine | Melatonergic and serotonergic agonist # | Rat | 0.348–1.128 | EMA, 2008 [39] |
| Moclobemide | MAOI | Mouse | 1.41 | Ito et al., 2013 [40] |
| Trazadone | SARI | Mouse | 0.20 | Ito et al., 2013 [40] |
| Escitalopram | SSRI | Rat | <0.15 * | Bourke et al., 2011 [41] |
| Paroxetine | SSRI | Rat | <0.028 * | Bourke et al., 2011 [41] |
| Fluoxetine | SSRI | Rat | <0.028 * | Bourke et al., 2011 [41] |
| Venlafaxine | SNRI | Rat | <0.057 * | Bourke et al., 2011 [41] |
| Drug | Drug Class # | First-Line/Second-Line Treatment | Lactation Adverse Events (If Reported) | Year Drug Approved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agomelatine | Melatonergic and serotonergic agonist | Not available in the U.S. | Possible drowsiness and developmental concerns in one infant out of sixteen infants | Not approved in the U.S. |
| Isocarboxazid | MAOI | Second line | Unknown | 1959 |
| Levomilnacipran | SNRI | First line | Unknown | 2013 |
| Lofepramine | Tricyclic | Not available in the U.S. | Unknown | Not approved in the U.S. |
| Phenelzine | MAOI | Second line | Unknown | 1961 |
| Tranylcypromine | MAOI | Second line | Abdominal distention and feeding intolerance in one infant | 1961 |
| Trimipramine | Tricyclic | Available in the U.S. but not clinically used | Unknown | 1982 |
| Vilazodone | SPARI | First line | Unknown | 2011 |
| Vortioxetine | SPARI | First line | No adverse effects reported | 2013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arbitman, L.; Chen, S.; Kim, B.; Lee, M.; Zou, P.; Doughty, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T. Assessment of Infant Exposure to Antidepressants through Breastfeeding: A Literature Review of Currently Available Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070847
Arbitman L, Chen S, Kim B, Lee M, Zou P, Doughty B, Li Y, Zhang T. Assessment of Infant Exposure to Antidepressants through Breastfeeding: A Literature Review of Currently Available Approaches. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(7):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070847
Chicago/Turabian StyleArbitman, Leah, Shirley Chen, Brian Kim, Melinda Lee, Peng Zou, Bennett Doughty, Yanyan Li, and Tao Zhang. 2024. "Assessment of Infant Exposure to Antidepressants through Breastfeeding: A Literature Review of Currently Available Approaches" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 7: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070847
APA StyleArbitman, L., Chen, S., Kim, B., Lee, M., Zou, P., Doughty, B., Li, Y., & Zhang, T. (2024). Assessment of Infant Exposure to Antidepressants through Breastfeeding: A Literature Review of Currently Available Approaches. Pharmaceutics, 16(7), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070847






