Preparation and Optimization of MiR-375 Nano-Vector Using Two Novel Chitosan-Coated Nano-Structured Lipid Carriers as Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Generation of Stable miR-375 Expression Construct
2.3. Preparation and Optimization of Chitosan-Coated NSLCs
2.4. Nano-Formulation of miR-375
2.5. Evaluation of Physicochemical Characteristics
2.5.1. Particle Size (PS), Zeta Potential (ZP), and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
2.5.2. Morphological Evaluations
2.5.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometry(FT-IR)
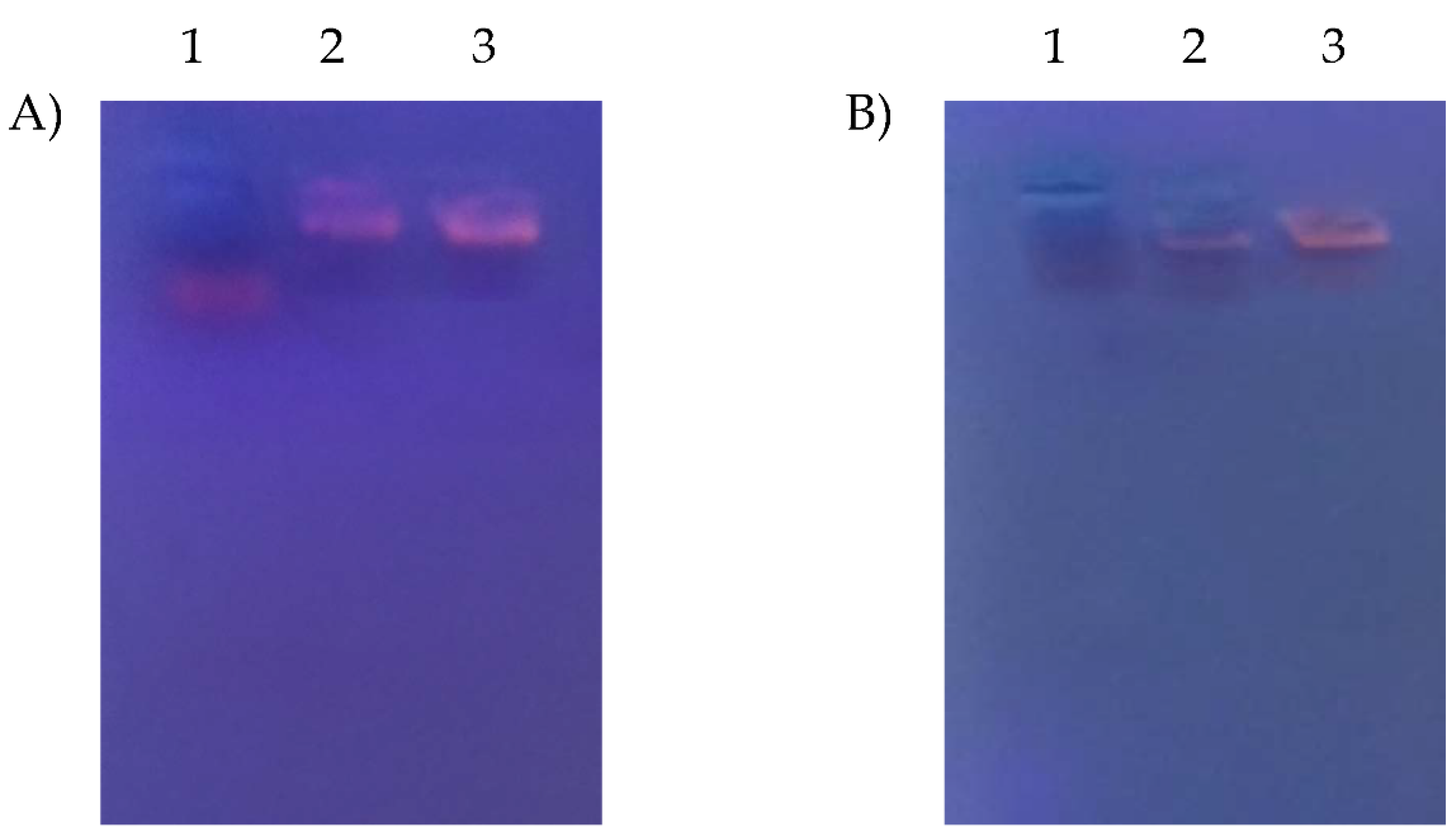
2.6. Gel Retardation Assay
2.7. MiR-375 Loading Efficiency
2.8. Lyophilization Study
2.9. Stability Studies
2.9.1. Storage (Physical) Stability Study
2.9.2. Serum Stability Study
2.10. HCC Cell Culture
2.11. Transfection Efficiency and Cellular Uptake
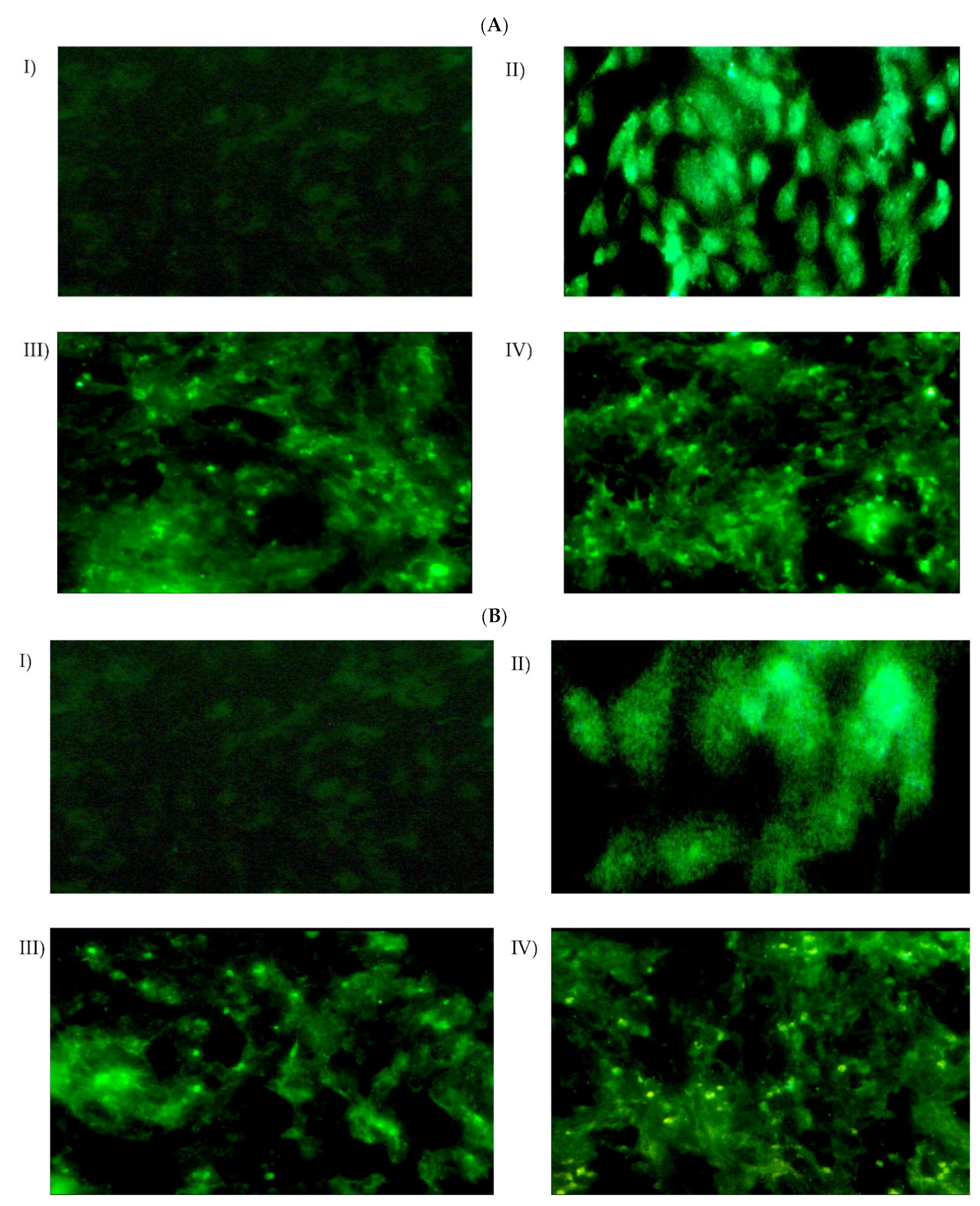
2.11.1. Qualitative Assessment by Fluorescence Microscopy
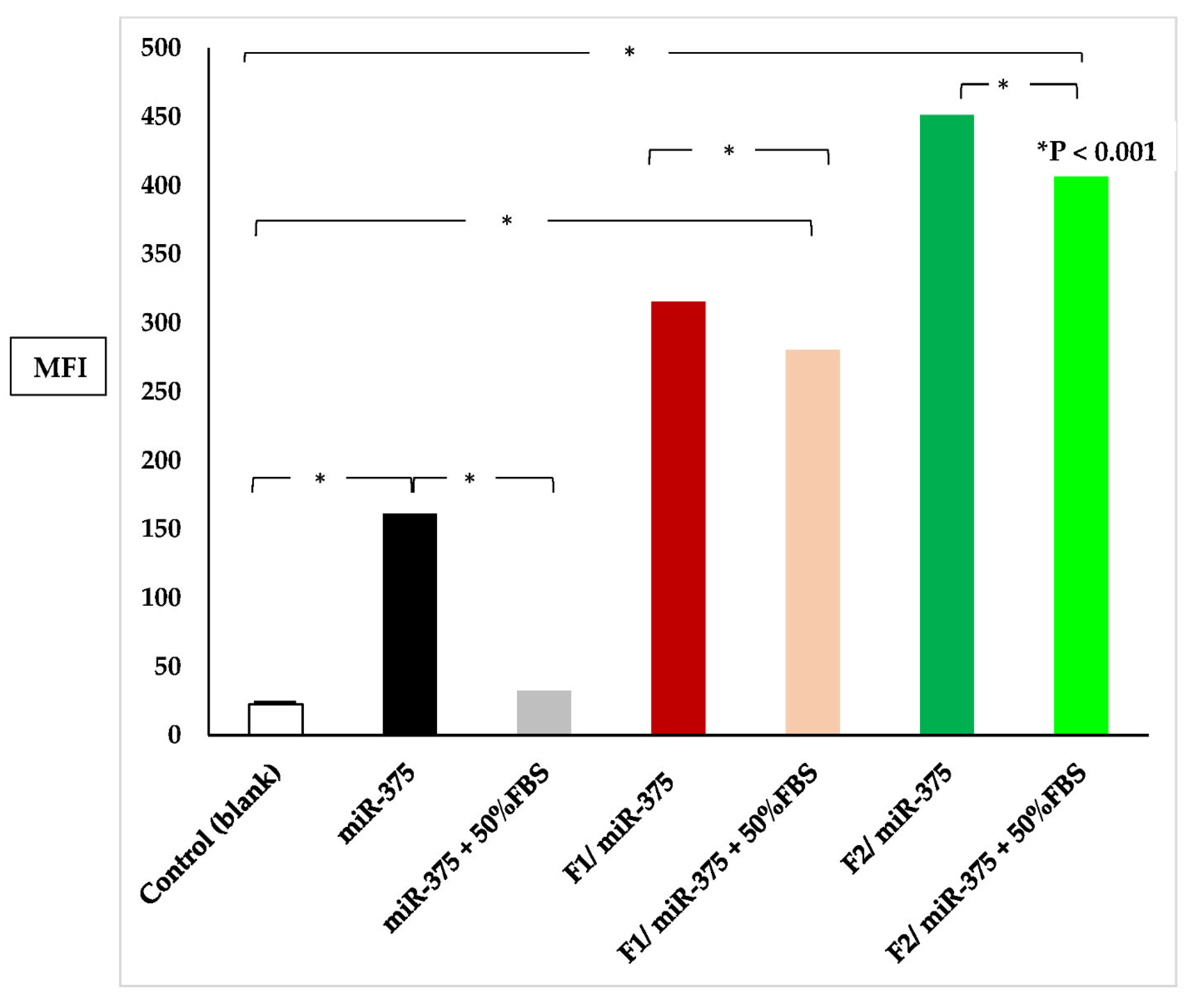
2.11.2. Quantitative Assessment by Flow Cytometry
2.12. Cytotoxicity Assessment
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
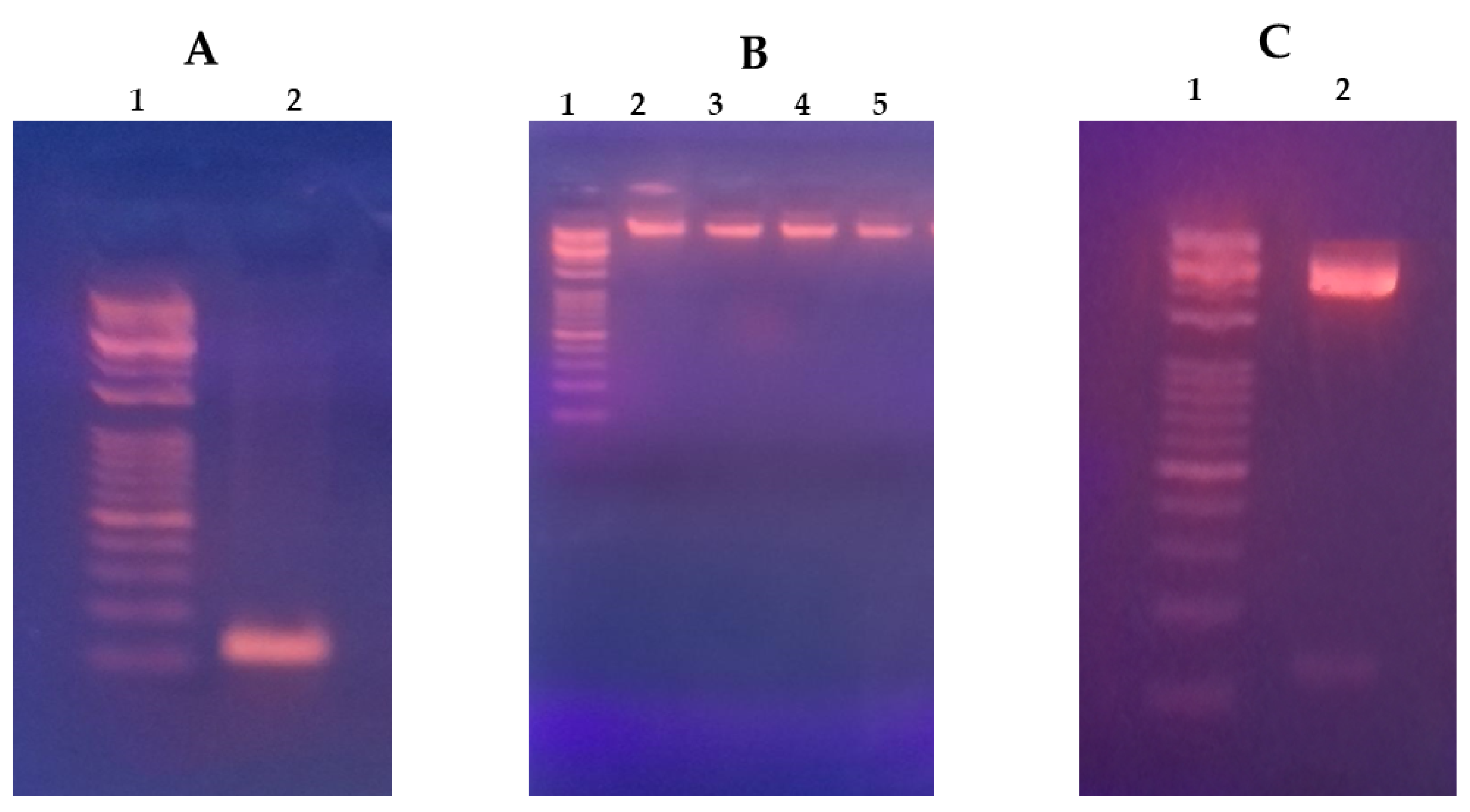
3.1. HCC Suppressor miR-375 Expression Construct
3.2. Factors That Influence PS, ZP, and PDI of the Nano-Formulations
3.3. Nano-Formulation of miR-375
3.4. Results of Physicochemical Characterization
3.4.1. DLS Results
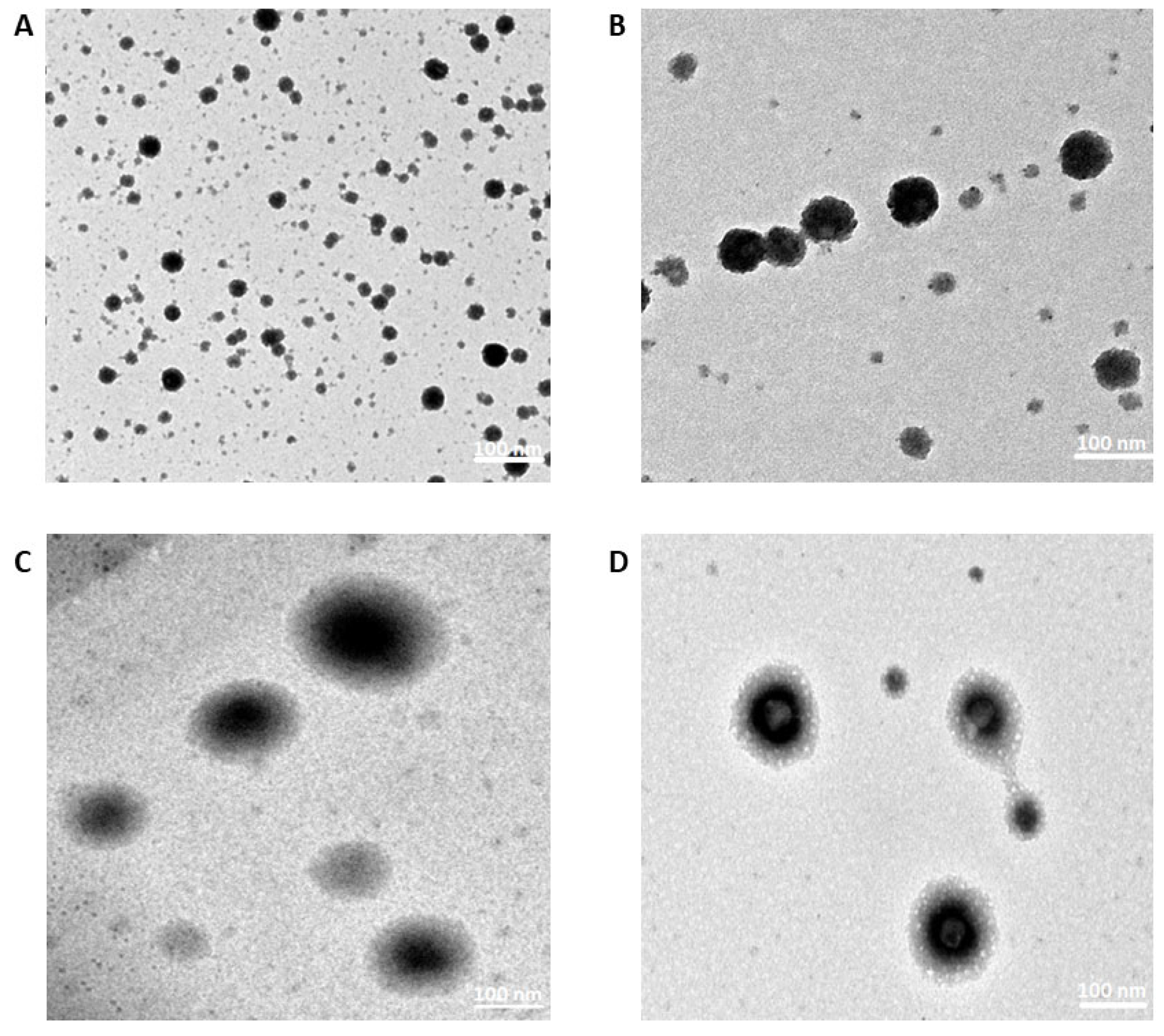
3.4.2. TEM Results
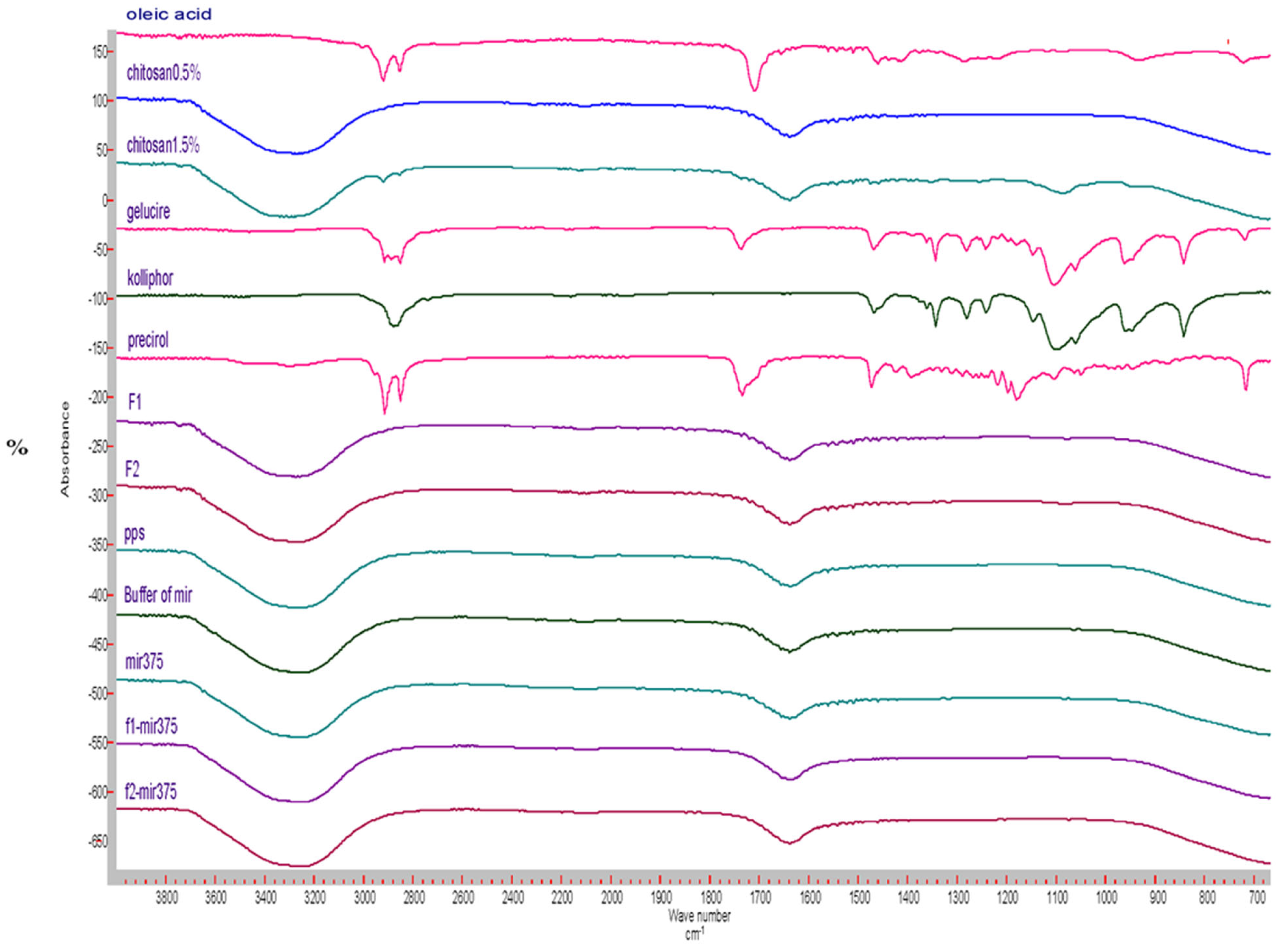
3.4.3. FT-IR Results
3.5. Optimization of miR-375 Loaded into the CS-Coated NSLCs
3.6. MiR-375 Conjugation Efficiency
3.7. Lyophilization Study
3.8. Stability Studies
3.8.1. Storage Stability Study
3.8.2. Serum Stability Study
3.9. Transfection Efficiency
3.9.1. Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Localization
3.9.2. Quantitation of Cellular Uptake
3.10. In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Asafo-Agyei, K.O.; Samant, H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Eddie, K.; Abdalla, M.; Facskeith, E.; Stuart, M.D.; Amit, G.; Singal, M.D. Overview of treatment approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. 2022. Available online: https://medilib.ir/uptodate/show/2489 (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Wen, N.; Cai, Y.; Li, F.; Ye, H.; Tang, W.; Song, P.; Cheng, N. The clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma worldwide: A concise review and comparison of current guidelines: 2022 update. Biosci. Trends 2022, 16, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Association. Liver Cancer Survival Rates. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/liver-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Reda El Sayed, S.; Cristante, J.; Guyon, L.; Denis, J.; Chabre, O.; Cherradi, N. MicroRNA Therapeutics in Cancer: Current Advances and Challenges. Cancers 2021, 13, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.; Shah, J. Recent trends in targeting miRNAs for cancer therapy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1732–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otmani, K.; Lewalle, P. Tumor Suppressor miRNA in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanism of Deregulation and Clinical Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 708765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, K.; Rouas, R.; Lewalle, P. OncomiRs as noncoding RNAs having functions in cancer: Their role in immune suppression and clinical implications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 913951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, R.; Baghaei, K.; Amani, D.; Piccin, A.; Hashemi, S.M.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Zali, M.R. Exosome-mediated delivery of functionally active miRNA-375-3p mimic regulate epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) of colon cancer cells. Life Sci. 2021, 269, 119035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; He, S.; Pan, H.; Liu, X.; Yuan, B.; Ding, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-375: Potential cancer suppressor and therapeutic drug. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.W.; Lin, J.S.; He, X.X. The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, J. MiR-375 gene therapy attenuates drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting cell autophagy. Res. Sq. 2020, 70, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhefnawi, M.; Salah, Z.; Soliman, B. The Promise of miRNA Replacement Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Gene Ther. 2019, 19, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElHefnawi, M.; Soliman, B.; Abu-Shahba, N.; Amer, M. An Integrative Meta-analysis of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2013, 11, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, B.; Salem, A.; Ghazy, M.; Abu-Shahba, N.; El Hefnawi, M. Bioinformatics functional analysis of let-7a, miR-34a, and miR-199a/b reveals novel insights into immune system pathways and cancer hallmarks for hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour. Biol. 2018, 40, 1010428318773675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, Z.; Abd El Azeem, E.M.; Youssef, H.F.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; Farrag, A.R.; El-Meliegy, E.; Soliman, B.; Elhefnawi, M. Effect of Tumor Suppressor MiR-34a Loaded on ZSM-5 Nanozeolite in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Approach. Curr. Gene Ther. 2019, 19, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfiky, A.M.; Mohamed, R.H.; Abd El-Hakam, F.E.; Yassin, M.A.; ElHefnawi, M. Targeted delivery of miR-218 via decorated hyperbranched polyamidoamine for liver cancer regression. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, M.; Elhefnawi, M.; El-Ahwany, E.; Awad, A.F.; Gawad, N.A.; Zada, S.; Tawab, F.M. Hsa-miR-195 targets PCMT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma that increases tumor life span. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 11301–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cai, W.; Wu, L.; Zhao, P.; Liu, X.G. Aberrant expression of two miRNAs promotes proliferation, hepatitis B virus amplification, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells: Evidence from bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.X.; Kuang, S.Z.; Liao, J.Z.; Xu, C.R.; Chang, Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Gong, J.; Tian, D.A.; Guo, A.Y.; Lin, J.S. The regulation of microRNA expression by DNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.F.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, H.; Liao, J.Z.; Lin, J.S.; Xia, C.; Chang, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, A.Y.; He, X.X. The ASH1-miR-375-YWHAZ Signaling Axis Regulates Tumor Properties in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jia, L.; Ding, Y. Upregulation of miR-375 inhibits human liver cancer cell growth by modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis via targeting ErbB2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3319–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.M.; Poon, R.T.P.; Luk, J.M. MicroRNA-375 targets Hippo-signaling effector YAP in liver cancer and inhibits tumor properties. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, T.; Sun, F.F.; Feng, J.Q.; Peng, J.J.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Y.D.; et al. MicroRNA-375 represses tumor angiogenesis and reverses resistance to sorafenib in hepatocarcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumortier, O.; Fabris, G.; Pisani, D.F.; Casamento, V.; Gautier, N.; Hinault, C.; Lebrun, P.; Duranton, C.; Tauc, M.; Dalle, S.; et al. microRNA-375 regulates glucose metabolism-related signaling for insulin secretion. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 244, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yan, W.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Nace, G.; Geller, D.A.; Lin, J.; Tsung, A. miR-375 inhibits autophagy and reduces viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 177–187.e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Jin, H.; Li, H. MicroRNA-375 Targets ATG14 to Inhibit Autophagy and Sensitize Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3557–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Li, H.; Jiang, Z.; Hsu, H.-J.; Hsu, H.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. miR-375/Yes-associated protein axis regulates IL-6 and TGF-β expression, which is involved in the cisplatin-induced resistance of liver cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, D.Y.; Huang, L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: Challenges and strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, M.; Slack, F.J. Challenges identifying efficacious miRNA therapeutics for cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z. Recent progress in microRNA-based delivery systems for the treatment of human disease. ExRNA 2019, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, I.; Chatterjee, A. Recent Advances in miRNA Delivery Systems. Methods Protoc. 2021, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Xing, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Wu, W.; Guo, J.; Mitragotri, S. Nanocarrier-Mediated Cytosolic Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatut, A.E.; Mattheolabakis, G. Non-viral based miR delivery and recent developments. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holjencin, C.J.A. Delivery Platforms for miRNA-Based Cancer Therapeutics. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/26363 (accessed on 19 July 2023).
- Kanvinde, S.; Kulkarni, T.; Deodhar, S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Dasgupta, A. Non-Viral Vectors for Delivery of Nucleic Acid Therapies for Cancer. BioTech 2022, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, M.; Pemmada, R.; Madhavan, M.; Shailaja, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kandiyil, S.P.; Donahue, J.M.; Thomas, V. Encapsulation of miRNA and siRNA into Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Turkeshi, A.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Progress in systemic co-delivery of microRNAs and chemotherapeutics for cancer treatment by using lipid-based nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloribi-Djefaflia, S.; Vasseur, S.; Guillaumond, F. Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.M.; Perone, Y.; Dehairs, J.; Lupien, L.E.; de Laat, V.; Talebi, A.; Loda, M.; Kinlaw, W.B.; Swinnen, J.V. Lipids and cancer: Emerging roles in pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic intervention. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 245–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Jia, L.; Chu, F.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; Guo, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, L. Nanostructured lipid carriers for MicroRNA delivery in tumor gene therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Han, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X. Dual drugs (microRNA-34a and paclitaxel)-loaded functional solid lipid nanoparticles for synergistic cancer cell suppression. J. Control. Release 2014, 194, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, R.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.E.; Moon, J.J.; Schwendeman, A. High-Density Lipoproteins: Nature’s Multifunctional Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3015–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Antonellis, P.; Liguori, L.; Falanga, A.; Carotenuto, M.; Ferrucci, V.; Andolfo, I.; Marinaro, F.; Scognamiglio, I.; Virgilio, A.; De Rosa, G.; et al. MicroRNA 199b-5p delivery through stable nucleic acid lipid particles (SNALPs) in tumorigenic cell lines. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2013, 386, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Song, K.; Lu, X.; Feng, W.; Di, W. Liposomal Delivery of MicroRNA-7 Targeting EGFR to Inhibit the Growth, Invasion, and Migration of Ovarian Cancer. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11669–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, I.; Yasir, M.; Verma, M.; Singh, A.P. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.; Abdin, S.M.; Kamal, L.; Orive, G. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Delivery of Chemotherapeutics: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, V.A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Maeng, H.J. Preparation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Drug Delivery and the Effects of Preparation Parameters of Solvent Injection Method. Molecules 2020, 25, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayón-Cordero, L.; Alkorta, I.; Arana, L. Application of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Improve the Efficiency of Anticancer Drugs. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Velmurugan, R. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A potential drug carrier for cancer chemotherapy. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwanullah, M.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Garg, A.; Ahmad, J. Advancement in design of nanostructured lipid carriers for cancer targeting and theranostic application. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.H.; Ye, Q.F.; Miao, X.Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, S.Q.; Xiong, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, Z.J. Current status of sorafenib nanoparticle delivery systems in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5464–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, C.P.; Patrício, A.B.; Prata, J.M.; Nadhman, A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Fonte, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles vs. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Comparative Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, W.; Gu, D.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Pan, H. Chondroitin sulfate and L-Cysteine conjugate modified cationic nanostructured lipid carriers: Pre-corneal retention, permeability, and related studies for dry eye treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, S.L.; Francis, D.M.; Kholmatov, P.; Kidambi, S. Targeted Delivery of MicroRNA125a-5p by Engineered Lipid Nanoparticles for the Treatment of HER2 Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Peng, F.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ye, P.; Lu, M.; Yang, G.; Gai, Y.; Yang, T.; et al. Targeted delivery of chemically modified anti-miR-221 to hepatocellular carcinoma with negatively charged liposomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4825–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Huang, L. Nanoparticles modified with tumor-targeting scFv deliver siRNA and miRNA for cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Mohammed, K.A.; Kaye, F.; Sharma, P.; Moudgil, B.M.; Clapp, W.L.; Nasreen, N. Targeted delivery of let-7a microRNA encapsulated ephrin-A1 conjugated liposomal nanoparticles inhibit tumor growth in lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4481–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Cardoso, A.L.; Custódia, C.; Cunha, P.; Pereira de Almeida, L.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C. MiRNA-21 silencing mediated by tumor-targeted nanoparticles combined with sunitinib: A new multimodal gene therapy approach for glioblastoma. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafernik, K.; Ładniak, A.; Blicharska, E.; Czarnek, K.; Ekiert, H.; Wiącek, A.E.; Szopa, A. Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles as Effective Drug Delivery Systems—A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, S.; Behera, A.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Chapter 6—Uses of chitosan in drug delivery. In Chitosan in Biomedical Applications; Hasnain, M.S., Beg, S., Nayak, A.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genedy, H.H.; Delair, T.; Montembault, A. Chitosan Based MicroRNA Nanocarriers. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forterre, A.; Komuro, H.; Aminova, S.; Harada, M. A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiei, M.; Kashanian, S.; Lucia, L.A.; Khazaei, M. Intrinsic parameters for the synthesis and tuned properties of amphiphilic chitosan drug delivery nanocarriers. .J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Ali, A.A.; Eid, H.M. Chitosan on the surface of nanoparticles for enhanced drug delivery: A comprehensive review. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnaloja, F.; Jacchetti, E.; Soncini, M.; Raimondi, M.T. Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Bone Scaffolds Optimization. Polymers 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Kumar Annamareddy, S.H.; Abanti, S.; Kumar Rath, P. Physicochemical properties and characterization of chitosan synthesized from fish scales, crab and shrimp shells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannavà, C.; De Gaetano, F.; Stancanelli, R.; Venuti, V.; Paladini, G.; Caridi, F.; Ghica, C.; Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Ferlazzo, G.; et al. Chitosan-Hyaluronan Nanoparticles for Vinblastine Sulfate Delivery: Characterization and Internalization Studies on K-562 Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisa, U.; Astuti, I.; Martien, R.; Maulana, D.R.; Ysrafil. Chitosan Nanoparticle as a Delivery System of miRNA 217 for Suppressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progressivity by Targeting AEG-1/P53. In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia JIMC; SciTePress: Setúbal, Portugal, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 131–138. ISBN 978-989-758-499-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Q.; Liu, Y.-F.; Ye, P.-J.; Gao, P.; Li, Z.-P.; Tang, S.-Y.; He, D.-X.; Tang, S.-S.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.-Y. Delivery of Liver-Specific miRNA-122 Using a Targeted Macromolecular Prodrug toward Synergistic Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10578–10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaban, K.; Salva, E.; Akbuga, J. The effects of chitosan/miR-200c nanoplexes on different stages of cancers in breast cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 95, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaban, K.; Salva, E.; Akbuga, J. In Vitro Dose Studies on Chitosan Nanoplexes for microRNA Delivery in Breast Cancer Cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Malichewe, C.; Shi, Z.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z.; Guo, X. Chitosan nanoparticle mediated upregulation of microRNA34a expression to suppress the proliferation, migration, invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Wen, Y.; Song, J.H.; Parikh, N.U.; Mangala, L.S.; Blessing, A.M.; Ivan, C.; Wu, S.Y.; Varkaris, A.; Shi, Y.; et al. Chitosan nanoparticle-mediated delivery of miRNA-34a decreases prostate tumor growth in the bone and its expression induces non-canonical autophagy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29161–29177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamies, E.T.H.N.; Ramírez, J.A.M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Mateo, M.; Guisán, J.M.; Arráez, J.L.R. Concentration effects in the determination of the hydrodynamic radius of gold nanoparticles by dynamic light scattering: A comparison of relative pre-processing methods. Talanta 2013, 116, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosco, D.; Cilurzo, F.; Maiuolo, J.; Federico, C.; Di Martino, M.T.; Cristiano, M.C.; Tassone, P.; Fresta, M.; Paolino, D. Delivery of miR-34a by chitosan/PLGA nanoplexes for the anticancer treatment of multiple myeloma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yan, B.; Wang, Y. Cryoprotectant choice and analyses of freeze-drying drug suspension of nanoparticles with functional stabilisers. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amis, T.M.; Renukuntla, J.; Bolla, P.K.; Clark, B.A. Selection of Cryoprotectant in Lyophilization of Progesterone-Loaded Stearic Acid Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalitha, L.J.; Sales, T.J.; Clarance, P.P.; Agastian, P.; Kim, Y.-O.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Mohamed, S.E.; Tack, J.C.; Na, S.W.; Kim, H.-J. In-vitro phytopharmacological and anticancer activity of Loranthus Longiflorus Desv. Var. Falcatuskurz against the human lung cancer cells. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2020, 32, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.A.; Sharaky, M.; Faid, A.H. Ionic Gelation Synthesis, Characterization and Cytotoxic Evaluation of Chitosan Nanoparticles on Different Types of Human Cancer Cell Models. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, H.C.; Mattsson, J.; Murray, B.J. Sucrose diffusion in aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 19207–19216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almalik, A.; Alradwan, I.; Kalam, M.A.; Alshamsan, A. Effect of cryoprotection on particle size stability and preservation of chitosan nanoparticles with and without hyaluronate or alginate coating. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.C.; Yañez, O.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Morales, J.O. Development of a Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC) by a Low-Energy Method, Comparison of Release Kinetics and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouco, H.; Diaz-Rodriguez, P.; Guillin, A.; Remuñán-López, C.; Landin, M. A Traffic Light System to Maximize Carbohydrate Cryoprotectants’ Effectivity in Nanostructured Lipid Carriers’ Lyophilization. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, J.; Eskandari, S.; Tabbakhian, M. Freeze-drying of nanostructure lipid carriers by different carbohydrate polymers used as cryoprotectants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Weng, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, Q.; Guo, F.; Wu, D.; Song, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, G. Characteristics, Cryoprotection Evaluation and In Vitro Release of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veilleux, D.; Nelea, M.; Biniecki, K.; Lavertu, M.; Buschmann, M.D. Preparation of Concentrated Chitosan/DNA Nanoparticle Formulations by Lyophlization for Gene Delivery at Clinically Relevant Dosages. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 10, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, A.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Fujita, K.; Tani, J.; Masaki, T. MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Hayat, M.K.; Ren, J.; Nasir, S.; Fawad, M.; Bai, Q. The Key Role of microRNAs in Initiation and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 950374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oura, K.; Morishita, A.; Masaki, T. Molecular and Functional Roles of MicroRNAs in the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Liao, J.Z.; Lin, J.S.; Li, B.; Yuan, W.G.; Lee, R.J.; Li, L.; Xu, C.R.; He, X.X. Gold nanoparticles delivered miR-375 for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86675–86686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.T.; Ramlan, T.A.; Jamaluddin, N.N.; Zamri, N.; Salfi, R.; Khan, A.; Sami, F.; Majeed, S.; Hasnain, M.S. Lipid-based Nanocarriers for Cancer and Tumor Treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4272–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondì, M.L.; Botto, C.; Amore, E.; Emma, M.R.; Augello, G.; Craparo, E.F.; Cervello, M. Lipid nanocarriers containing sorafenib inhibit colonies formation in human hepatocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 493, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, G.; Park, J.W.; Yoon, I.-S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs): Recent advances in drug delivery. J. Pharm. Investig. 2013, 43, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.N.; Li, Y.L.; Yan, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Hu, F.Q.; Yuan, H. Ternary nanoparticles composed of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles, protamine, and DNA for gene delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2859–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Cázares, M.B.; Saavedra-Leos, M.Z.; Jordan-Alejandre, E.; Nuñez-Olvera, S.I.; Cómpean-Martínez, I.; López-Camarillo, C. Lipid-based nanoparticles for the therapeutic delivery of non-coding RNAs in breast cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, J.; Amin, S.; Rahman, M.; Rub, R.A.; Singhal, M.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Rahman, Z.; Addo, R.T.; Ahmad, F.J.; Mushtaq, G.; et al. Solid Matrix Based Lipidic Nanoparticles in Oral Cancer Chemotherapy: Applications and Pharmacokinetics. Curr. Drug Metab. 2015, 16, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwanullah, M.; Ahmad, J.; Amin, S. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Novel Platform for Chemotherapeutics. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpoot, K. Lipid-based Nanoplatforms in Cancer Therapy: Recent Advances and Applications. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2020, 20, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapeinos, C.; Battaglini, M.; Ciofani, G. Advances in the design of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for targeting brain diseases. J. Control. Release 2017, 264, 306–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, P.; Rong, Z.; Li, B.; Xue, H.; You, J.; He, C.; Li, W.; He, X.; Lee, R.J.; et al. Anti-tumor Efficiency of Lipid-coated Cisplatin Nanoparticles Co-loaded with MicroRNA-375. Theranostics 2016, 6, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Yang, T.; You, J.; He, X.; Lee, R.J.; Li, L.; Xu, C. Delivery of miR-375 and doxorubicin hydrochloride by lipid-coated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles to overcome multiple drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5271–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; You, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; He, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Lu, Y.; et al. MiR-375 delivered by lipid-coated doxorubicin-calcium carbonate nanoparticles overcomes chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Lu, Y.; You, J.; Lee, R.J.; et al. Enhancing anti-tumor efficiency in hepatocellular carcinoma through the autophagy inhibition by miR-375/sorafenib in lipid-coated calcium carbonate nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.P.; Liao, J.Z.; Lu, Y.Q.; Tian, D.A.; Ye, F.; Zhao, P.X.; Xiang, G.Y.; Tang, W.X.; He, X.X. MiR-375 and Doxorubicin Co-delivered by Liposomes for Combination Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Huang, M.; Guo, W.W.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, L.Z.; Jiang, G. Nano-based delivery of RNAi in cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshosaz, J.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Sadeghi, H.; Khadem, M. Galactosylated nanostructured lipid carriers for delivery of 5-FU to hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Liposome Res. 2012, 22, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfoddin, A.; Al-Kassas, R. Development of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for improving ocular delivery of acyclovir. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, A.; Savic, S.; Vuleta, G.; Müller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Polyhydroxy surfactants for the formulation of lipid nanoparticles (SLN and NLC): Effects on size, physical stability and particle matrix structure. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 406, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puluhulawa, L.; Joni, I.M.; Elamin, K.; Mohammed, A.; Muchtaridi, M.; Wathoni, N. Chitosan–Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Active Targeting in Cancer Therapy. Polymers 2022, 14, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhi, S.; Behera, A.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Chapter 7—Chitosan-based drug delivery systems in cancer therapeutics. In Chitosan in Drug Delivery; Hasnain, M.S., Beg, S., Nayak, A.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Winnicka, K. Stability of chitosan-a challenge for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1819–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmuganathan, R.; Edison, T.; LewisOscar, F.; Kumar, P.; Shanmugam, S.; Pugazhendhi, A. Chitosan nanopolymers: An overview of drug delivery against cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Maestri, M.; Giunchedi, P. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Therapy and Theranostics of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver-Targeting. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1819–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Peppas, N.A.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Zeta potential and solubility of chitosan with different molecular weights and degrees of deacetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kamat, V.; Bodas, D.; Paknikar, K. Chitosan nanoparticles synthesis caught in action using microdroplet reactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.J.D.C.M.; Souza, E.F.; Oliveira, A.S.; Teixeira, J.A. Influence of chitosan concentration on the properties of chitosan films and the release of a model drug. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Barzegari Firouzabadi, F.; Oryan, S.H.; Sheikhha, M.H.; Kalantar, S.M.; Javed, A. Preparation and Evaluation of A Novel Liposomal Nano-Formulation in Metastatic Cancer Treatment Studies. Cell J. 2019, 21, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthiah, M.; Park, I.-K.; Cho, C.-S. Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of therapeutic genes: Focus on miRNA therapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Huang, Z.-R.; Fang, J.-Y. Effects of lipophilic emulsifiers on the oral administration of lovastatin from nanostructured lipid carriers: Physicochemical characterization and pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Affram, K.; Nottingham, E.L.; Han, B.; Amissah, F.; Krishnan, S.; Trevino, J.; Agyare, E. Application of smart solid lipid nanoparticles to enhance the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, C.; Sánchez-Hernández, N.; García-Montoya, E.; Pérez-Lozano, P.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Ticó, J.R.; Suñé, C.; Miñarro, M. DNA delivery via cationic solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Delgado, D.; Solinís, M.A.; Pedraz, J.L.; Echevarría, E.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Gascón, A.R. Solid lipid nanoparticles as potential tools for gene therapy: In vivo protein expression after intravenous administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaolaza, P.S.; Delgado, D.; del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Gascón, A.R.; Solinís, M. A novel gene therapy vector based on hyaluronic acid and solid lipid nanoparticles for ocular diseases. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, D.; del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Angeles Solinís, M.; Bartkowiak, A.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A. New gene delivery system based on oligochitosan and solid lipid nanoparticles: ‘in vitro’ and ‘in vivo’ evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, B.; Ren, W.; Mo, X.; Zhou, C.; He, H.; Jia, H.; Wang, L.; Jacob, S.T.; Lee, R.J.; et al. Enhanced hepatic delivery of siRNA and microRNA using oleic acid based lipid nanoparticle formulations. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, H.; Lam, K.; Bajusz, C.; Laczkó, D.; Karikó, K.; Schreiner, P.; Martin, A.; Lutwyche, P.; Heyes, J.; Pardi, N. Lyophilization provides long-term stability for a lipid nanoparticle-formulated, nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, F.; Guo, Y.B.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, Z.W.; Yang, Y.M.; Mao, Q.S. Asialoglycoprotein receptor-magnetic dual targeting nanoparticles for delivery of RASSF1A to hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.L.; Paoletti, C.; Campisi, M.; Osaki, T.; Adriani, G.; Kamm, R.D.; Mattu, C.; Chiono, V. MicroRNA delivery through nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2019, 313, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Cui, S.; Yan, J. Toxicity of cationic lipids and cationic polymers in gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezgel, Ö.; Szarpak-Jankowska, A.; Arnould, A.; Auzély-Velty, R.; Texier, I. Chitosan-lipid nanoparticles (CS-LNPs): Application to siRNA delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 510, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Meng, T.; Yuan, M.; Wen, L.; Cheng, B.; Liu, N.; Huang, X.; Hong, Y.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F. MicroRNA-200c delivered by solid lipid nanoparticles enhances the effect of paclitaxel on breast cancer stem cell. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6713–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucak-Smajić, A.; Ruseska, I.; Letofsky-Papst, I.; Vranić, E.; Zimmer, A. Development and Characterization of Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Drug Delivery Systems for miRNA-27a. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutschner, T.; Diederichs, S. The hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, M.A.; Arzumanyan, A.; Kulathinal, R.J.; Blain, S.W.; Holcombe, R.F.; Mahajna, J.; Marino, M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Nawroth, R.; Sanchez-Garcia, I.; et al. Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S25–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.X.; Chang, Y.; Meng, F.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Xie, Q.H.; Tang, F.; Li, P.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Lin, J.S. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: Improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Feron, O.; Préat, V. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Passive and active tumor targeting of nanocarriers for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Rizwanullah, M.; Ahmad, J.; Alasmary, M.Y.; Akhter, M.H.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Warsi, M.H.; Haque, A. Progress in nanomedicine-based drug delivery in designing of chitosan nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 602–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwanullah, M.; Amin, S.; Mir, S.R.; Fakhri, K.U.; Rizvi, M.M.A. Phytochemical based nanomedicines against cancer: Current status and future prospects. J. Drug Target 2018, 26, 731–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jnaidi, R.; Almeida, A.J.; Gonçalves, L.M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Smart Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannon-Peppas, L.; Blanchette, J.O. Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Lipid (mg) | Surfctant (mg) | Water (mL) | Chitosan (%) | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Studied Factors | Solid | Liquid | |||||
| Precirol ATO-5 | Oleic Acid | Gelucire 50/13 | Kolliphore P188 | ||||
| Effect of solid: liquid lipid ratio | 100 | 300 | 70 | 130 | 10 | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| 134 | 266 | ||||||
| 200 | 200 | ||||||
| 266 | 134 | ||||||
| 300 | 100 | ||||||
| 320 | 80 | ||||||
| Effect of surfactant concentration | 275 | 275 | 17 | 33 | 10 | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| 247 | 247 | 35 | 71 | ||||
| 194 | 194 | 71 | 129 | ||||
| 141 | 141 | 106 | 212 | ||||
| Effect of chitosan concentration | 141 | 141 | 106 | 212 | 10 | 0.5 | 4.0 |
| 1.0 | |||||||
| 1.5 | |||||||
| 2.0 | |||||||
| Effect of pH of chitosan solution | 141 | 141 | 106 | 212 | 10 | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| 4.5 | |||||||
| 5.0 | |||||||
| 5.5 | |||||||
| Factors | Ratio (Solid: Liquid Lipid) | Formulation Code | PS Z-Average (nm) | ZP (mV) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of Precirol: Oelic acid ratio | 1:3 | A | 243.22 ± 10.86 | 50.46 ± 3.33 | 0.48 |
| 1:2 | B | 157.81 ± 5.16 | 38.72 ± 6.80 | 0.45 | |
| 1:1 | C | 116.72 ± 3.10 | 43.25 ± 4.71 | 0.42 | |
| 2:1 | D | 199.43 ± 8.14 | 31.33 ± 2.40 | 0.17 | |
| 3:1 | E | 246.06 ± 11.72 | 52.17 ± 5.34 | 0.55 | |
| 4:1 | F | 137.84± 8.03 | 59.41 ± 6.61 | 0.43 | |
| Effect of Gelucire/Kalliphore concentration (w/w) | 0.5% | G | 138.92 ± 9.67 | 46.72 ± 3.33 | 0.35 |
| 1.0% | H | 130.53 ± 5.02 | 46.56 ± 4.80 | 0.46 | |
| 2.0% | I | 116.76 ± 3.10 | 43.28 ± 4.71 | 0.42 | |
| 3.0% | J | 101.03 ± 6.14 | 43.71 ± 3.40 | 0.23 | |
| Effect of chitosan concentration (w/w) | 0.5% | K | 89.45 ± 9.67 | 45.91 ± 4.03 | 0.31 |
| 1.0% | L | 101.02 ± 6.14 | 43.75 ± 3.40 | 0.23 | |
| 1.5% | M | 100.27 ± 3.10 | 61.83 ± 2.74 | 0.40 | |
| 2.0% | N | 103.23 ± 5.24 | 48.34 ± 5.01 | 0.41 | |
| Effect of Chitosan solution pH | 4.0 | O | 98.17 ± 8.65 | 28.03 ± 2.33 | 0.43 |
| 4.5 | P | 65.24 ± 6.02 | 32.54 ± 3.86 | 0.25 | |
| 5.0 | Q | 68.22 ± 2.13 | 16.57 ± 3.04 | 0.22 | |
| 5.5 | R | 77.62 ± 6.01 | 9.28 ± 4.12 | 0.19 |
| Characterization | PS (nm) | ZP (mV) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (blank) | 65.2 ± 6.02 | 32.5 ± 3.86 | 0.25 |
| F1/miR375 * | 207.33 ± 8.08 | 7.7 ± 1.02 | 0.37 |
| F2 (blank) | 100.2 ± 3.10 | 61.8 ± 2.74 | 0.40 |
| F2/miR375 ** | 243.12 ± 9.33 | 5.8 ± 1.34 | 0.31 |
| F1/miR-375 | Conjugation (%) | F2/miR-375 | Conjugation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 70.39 | 1:1 | 92.50 |
| 20:1 | 75.22 | 20:1 | 98.13 |
| 50:1 | 80.16 | 50:1 | 100 |
| 80:1 | 85.57 | 80:1 | 100 |
| 100:1 | 90.60 | 100:1 | 100 |
| 150:1 | 93.79 | 150:1 | 100 |
| 200:1 | 95.90 | 200:1 | 100 |
| 230:1 | 97.0 | 230:1 | 100 |
| 250:1 | 100 | 250:1 | 100 |
| 300:1 | 100 | 300:1 | 100 |
| 350:1 | 100 | 350:1 | 100 |
| Cryoprotectants | Freeze-Drying Time (h) | PS (nm) | PDI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1/miR-375 | F2/miR-375 | F1/miR-375 | F2/miR-375 | ||
| Avicel | 6 | 2320.31 ± 1103.20 | 2656.22 ± 1066.04 | 0.42 | 0.46 |
| Mannitol | 6 | 872.27 ± 103.14 | 629.25 ± 81.53 | 0.58 | 0.53 |
| Lactose | 6 | 445.72 ± 110.03 | 574.74 ± 104.81 | 0.44 | 0.57 |
| Trehalose | 5.5 | 303.31 ± 79.13 | 330.50 ± 103.71 | 0.17 | 0.49 |
| Sucrose | 3.5 | 219.15 ± 9.85 | 283.22 ± 7.06 | 0.40 | 0.41 |
| Freeze at −20 °C | - | 251.34 ± 3.38 | 264.65 ± 7.46 | 0.43 | 0.56 |
| Freshly prepared colloid; CS-coated NSLCs/miR-375 | - | 207.33 ± 8.08 | 243.12 ± 9.33 | 0.37 | 0.31 |
| Duration | PS (nm) | ZP (mV) | PDI | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | |||||||
| A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | |
| Fresh NSLC /miR375 Colloid | 207.33 ± 8.08 | 243.12 ± 9.33 | 5.8 ± 1.34 | 7.7 ± 1.02 | 0.36 | 0.31 | ||||||
| Day 7 | 248.66 ± 6.35 | 281.25 ± 2.31 | 279.15 ± 8.95 | 289.47 ± 9.51 | 4.33 ± 6.01 | 7.36 ± 2.03 | 5.36 ± 3.02 | 5.34 ± 2.50 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.51 |
| 1 month | 270.05 ± 5.56 | 269.36 ± 5.87 | 286.44 ± 4.36 | 300.89 ± 5.68 | 3.24 ± 3.02 | 5.22 ± 6.01 | 4.51 ± 4.11 | 4.97 ± 1.57 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.51 | 0.45 |
| 2 month | 258.36 ± 7.26 | 274.32 ± 3.02 | 300.57 ± 3.65 | 302.27 ± 4.53 | 0.36 ± 2.03 | 4.03 ± 4.23 | 2.34 ± 1.98 | 5.03 ± 1.11 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| 3 month | 280.05 ± 8.32 | 285.61 ± 5.03 | 305.78 ± 2.98 | 310.39 ± 4.56 | −4.56 ± 3.01 | 4.39 ± 0.42 | −2.09 ± 1.22 | 3.85 ± 2.22 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.66 | 0.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soliman, B.; Wen, M.M.; Kandil, E.; El-Agamy, B.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; ElHefnawi, M. Preparation and Optimization of MiR-375 Nano-Vector Using Two Novel Chitosan-Coated Nano-Structured Lipid Carriers as Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040494
Soliman B, Wen MM, Kandil E, El-Agamy B, Gamal-Eldeen AM, ElHefnawi M. Preparation and Optimization of MiR-375 Nano-Vector Using Two Novel Chitosan-Coated Nano-Structured Lipid Carriers as Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(4):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040494
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoliman, Bangly, Ming Ming Wen, Eman Kandil, Basma El-Agamy, Amira M. Gamal-Eldeen, and Mahmoud ElHefnawi. 2024. "Preparation and Optimization of MiR-375 Nano-Vector Using Two Novel Chitosan-Coated Nano-Structured Lipid Carriers as Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 4: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040494
APA StyleSoliman, B., Wen, M. M., Kandil, E., El-Agamy, B., Gamal-Eldeen, A. M., & ElHefnawi, M. (2024). Preparation and Optimization of MiR-375 Nano-Vector Using Two Novel Chitosan-Coated Nano-Structured Lipid Carriers as Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics, 16(4), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040494






