Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Lurasidone Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
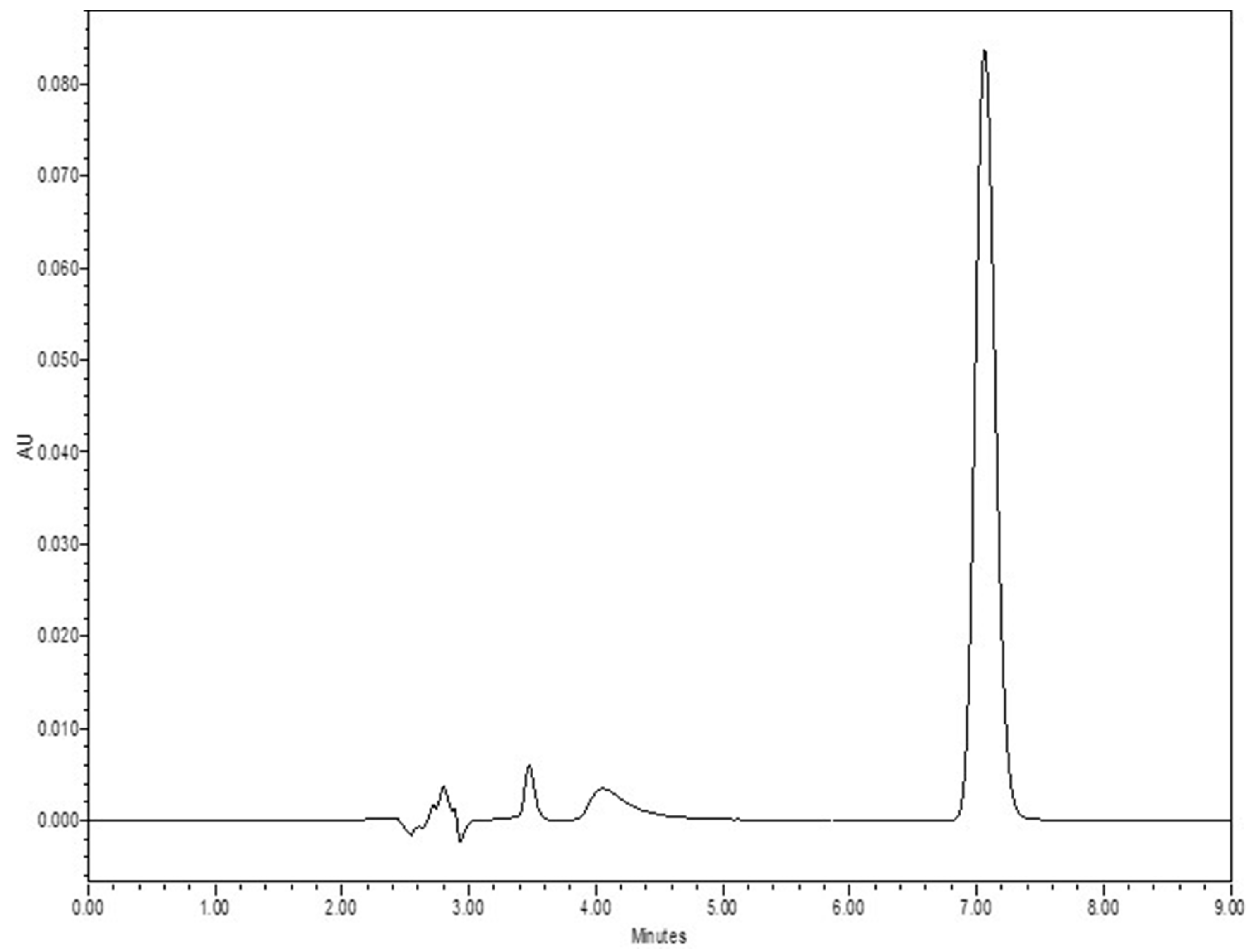
2.2.1. Quantitative Analysis
2.2.2. In Vitro Permeation Test (IVPT) Study
Skin Integrity and Resistance Measurement
Lurasidone Detection in Receptor Fluid and Skin
2.2.3. Passive Delivery and Effect of Chemical Enhancers
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.2.5. Preparation of PLGA Nanoparticles
2.2.6. Characterizations of Nanoparticles
Nanoparticle Size
Entrapment Efficacy
2.2.7. Release Studies
2.2.8. Microneedle Treatment Dr. PenTM Ultima A6
2.2.9. Poly Dimethyl Siloxane (PDMS) Molds
2.2.10. Microneedle Preparation
Fabrication of Tip-Loaded Effervescent Microneedle Patch
Effervescence for Backing Part
2.2.11. Microneedle Characterization
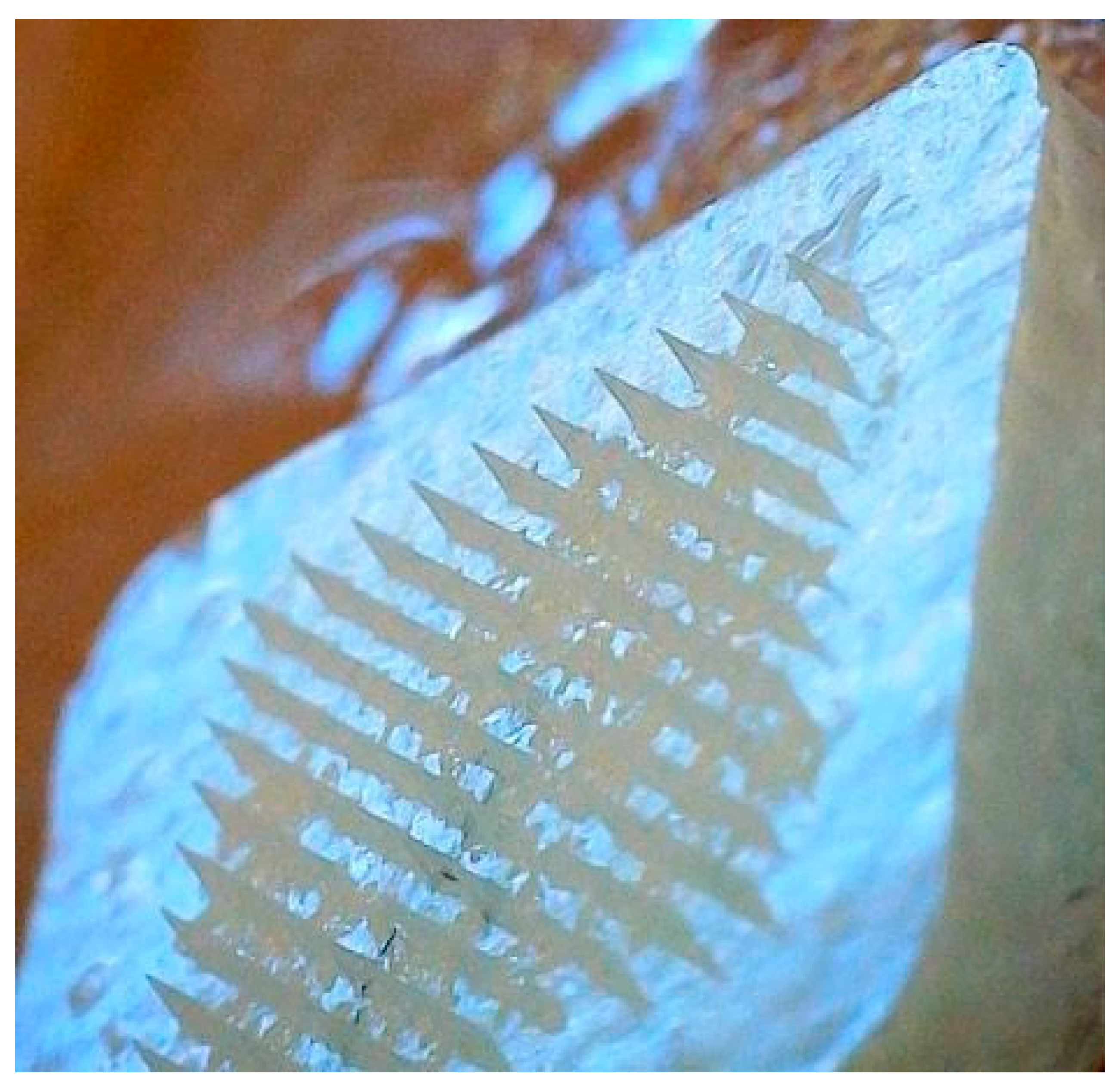
Parafilm M® Microneedle Insertion Analysis
Drug Analysis in Microneedle Tips
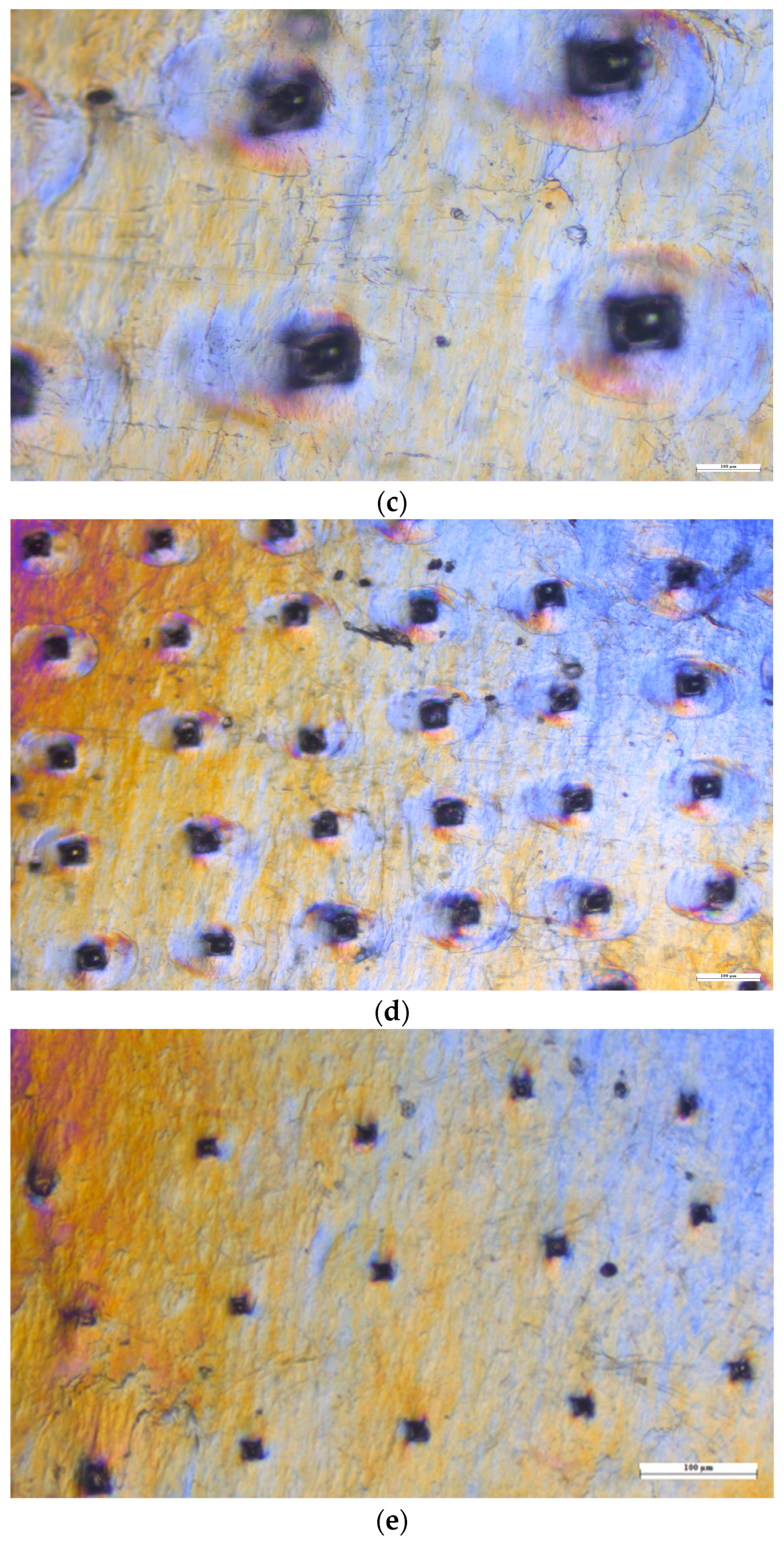
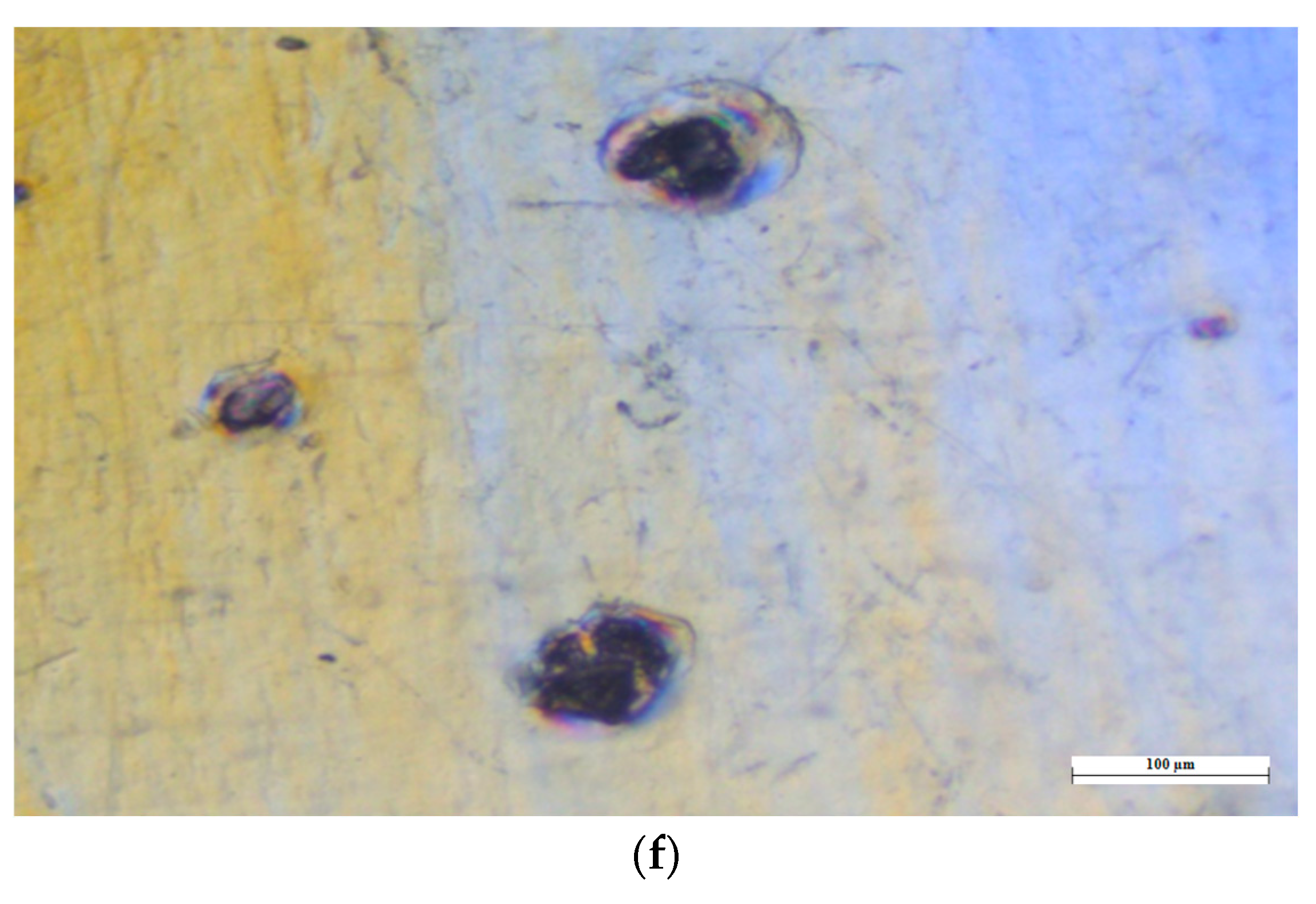
Microneedle Insertion on the Skin
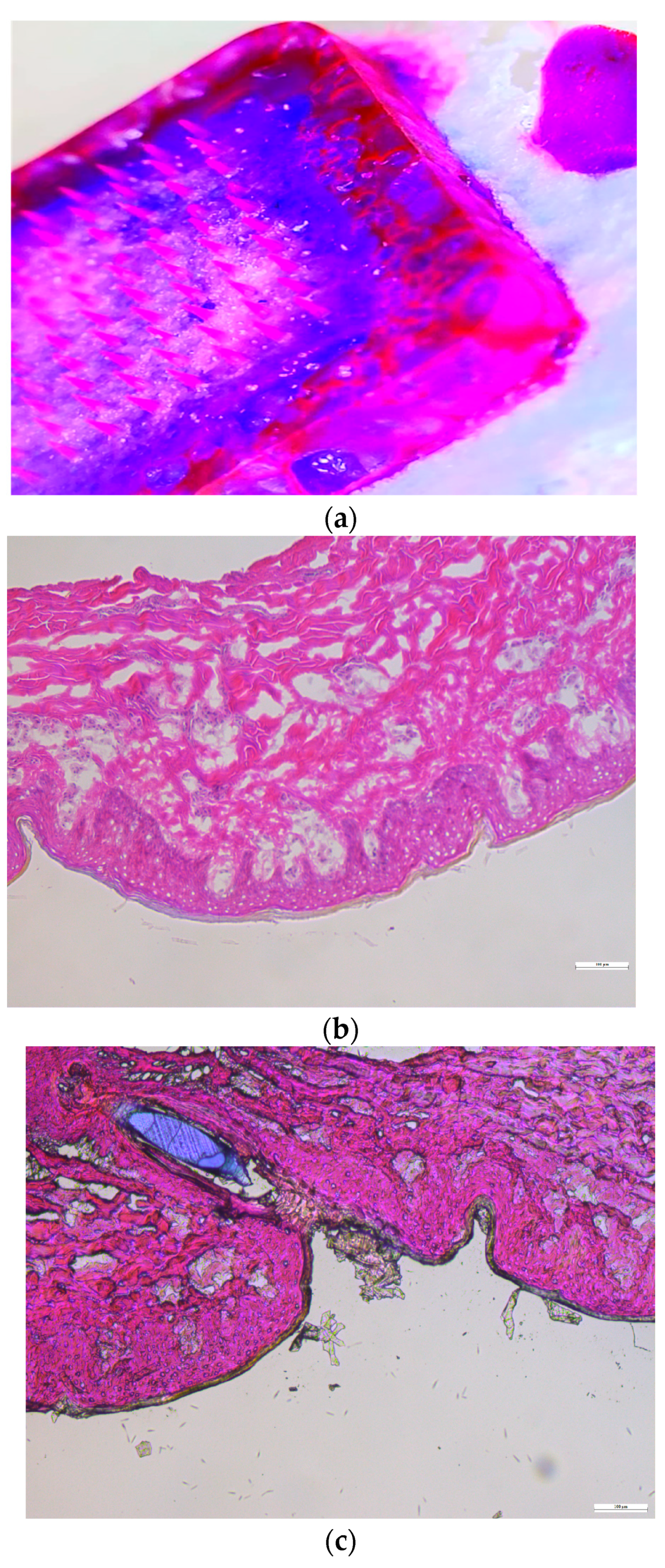
Histology Study
Mechanical Strength of Microneedles
2.2.12. SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) Analysis
2.2.13. IVPT Study with Microneedles
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Analysis
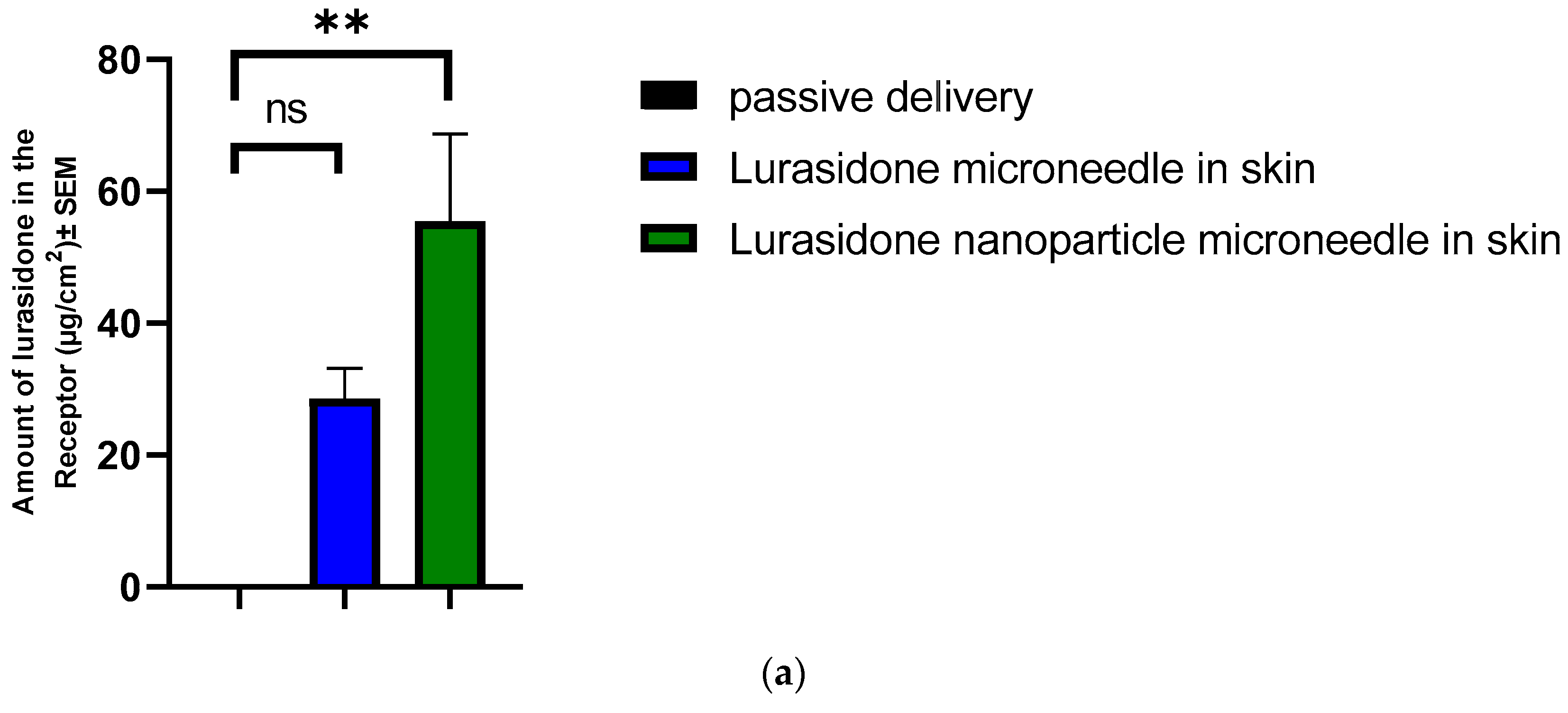
3.2. In Vitro Permeation Test (IVPT) Study
3.3. Passive Testing
3.4. Delivery with Chemical Enhancers
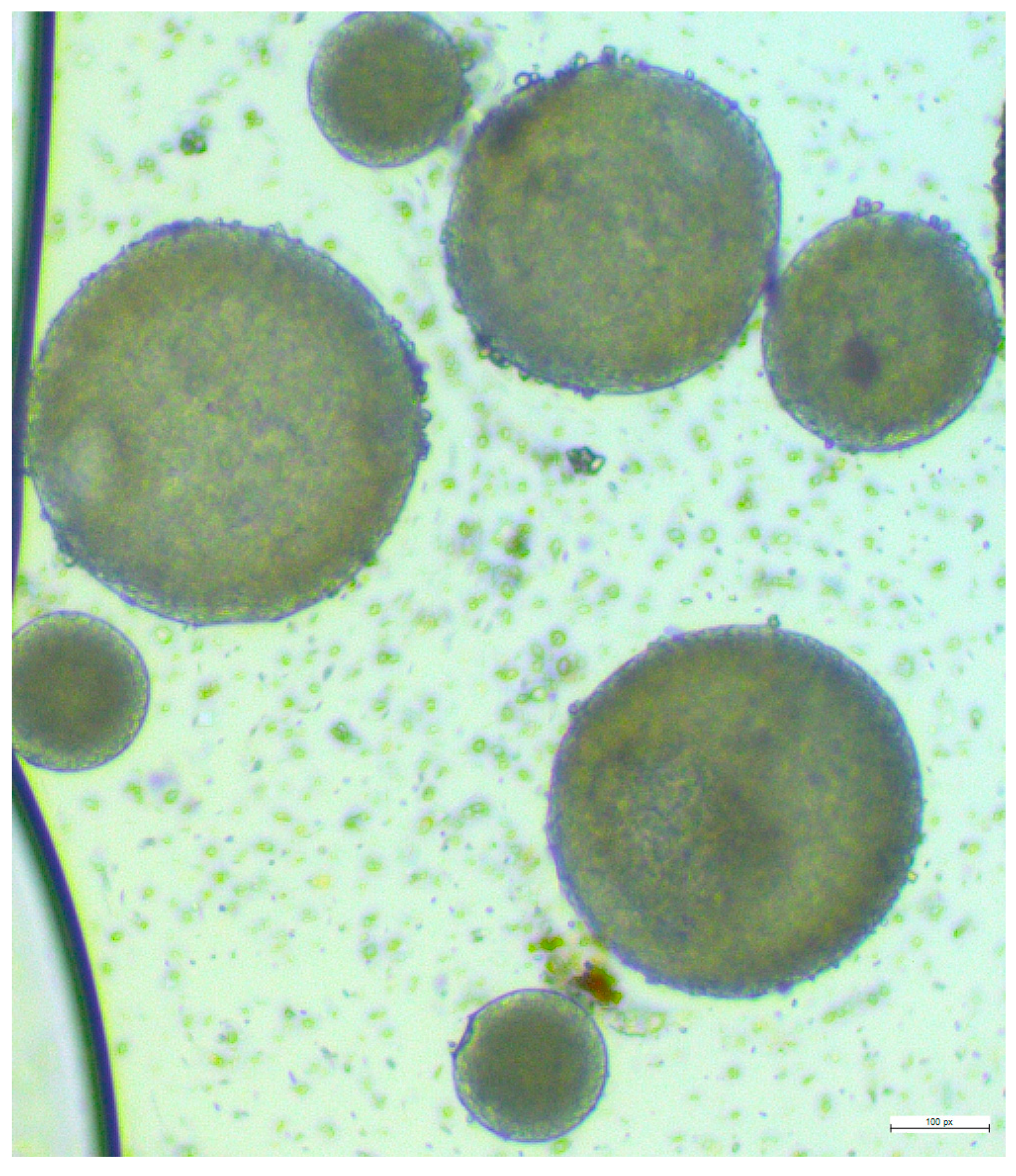
3.5. Fabrication of Lurasidone Nanoparticles
3.6. Release Study
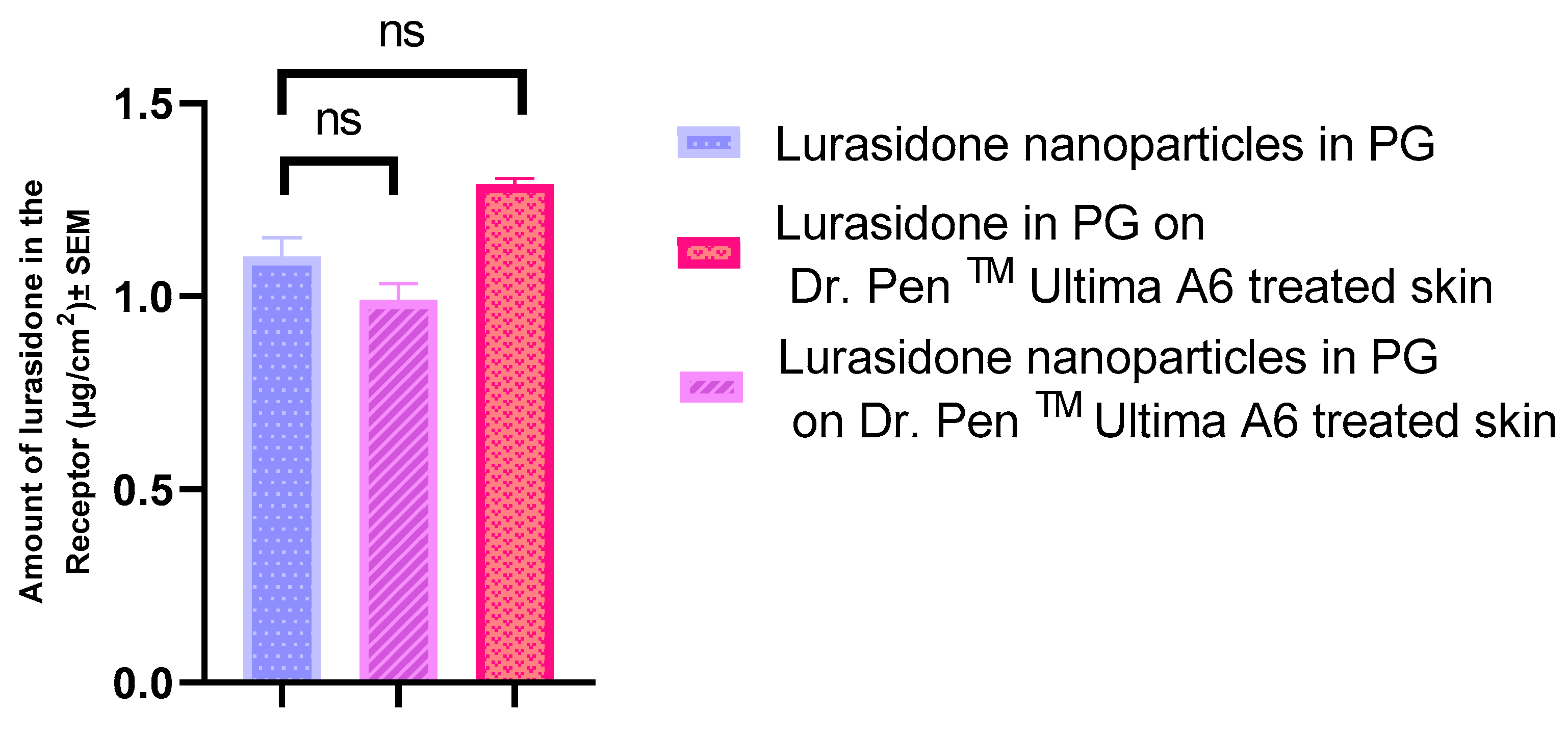
3.7. IVPT with Dr. PenTM Ultima A6
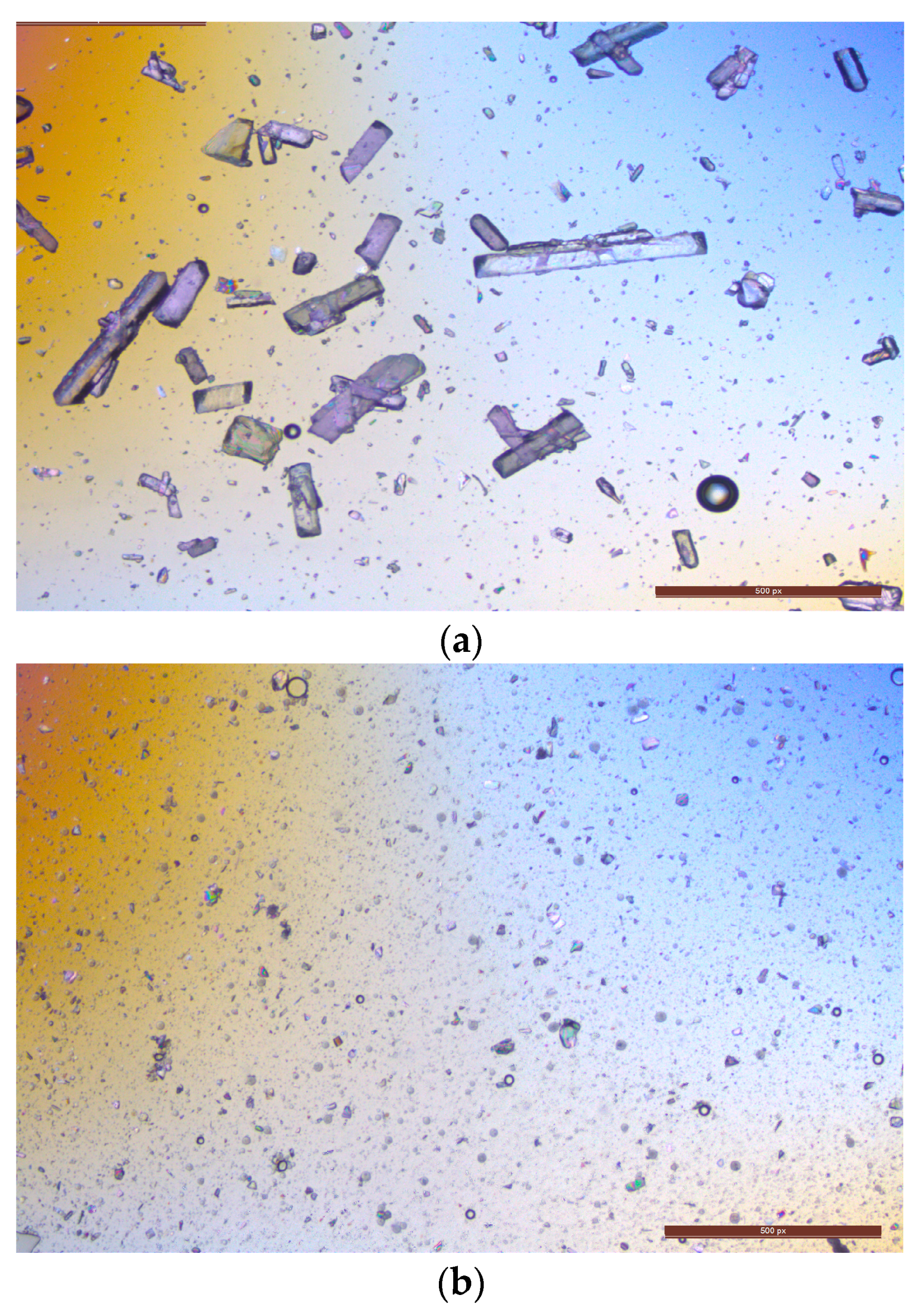
3.8. Volume of Microneedle Tips
3.9. Preparation of Microneedles
3.9.1. Lurasidone Concentration in Microneedle Solution
3.9.2. Effervescent Backing Membrane
3.10. Microneedle Characterization
3.10.1. Histology Study
3.10.2. Mechanical Strength of Microneedles
3.10.3. Mechanical Uniformity of Microneedles
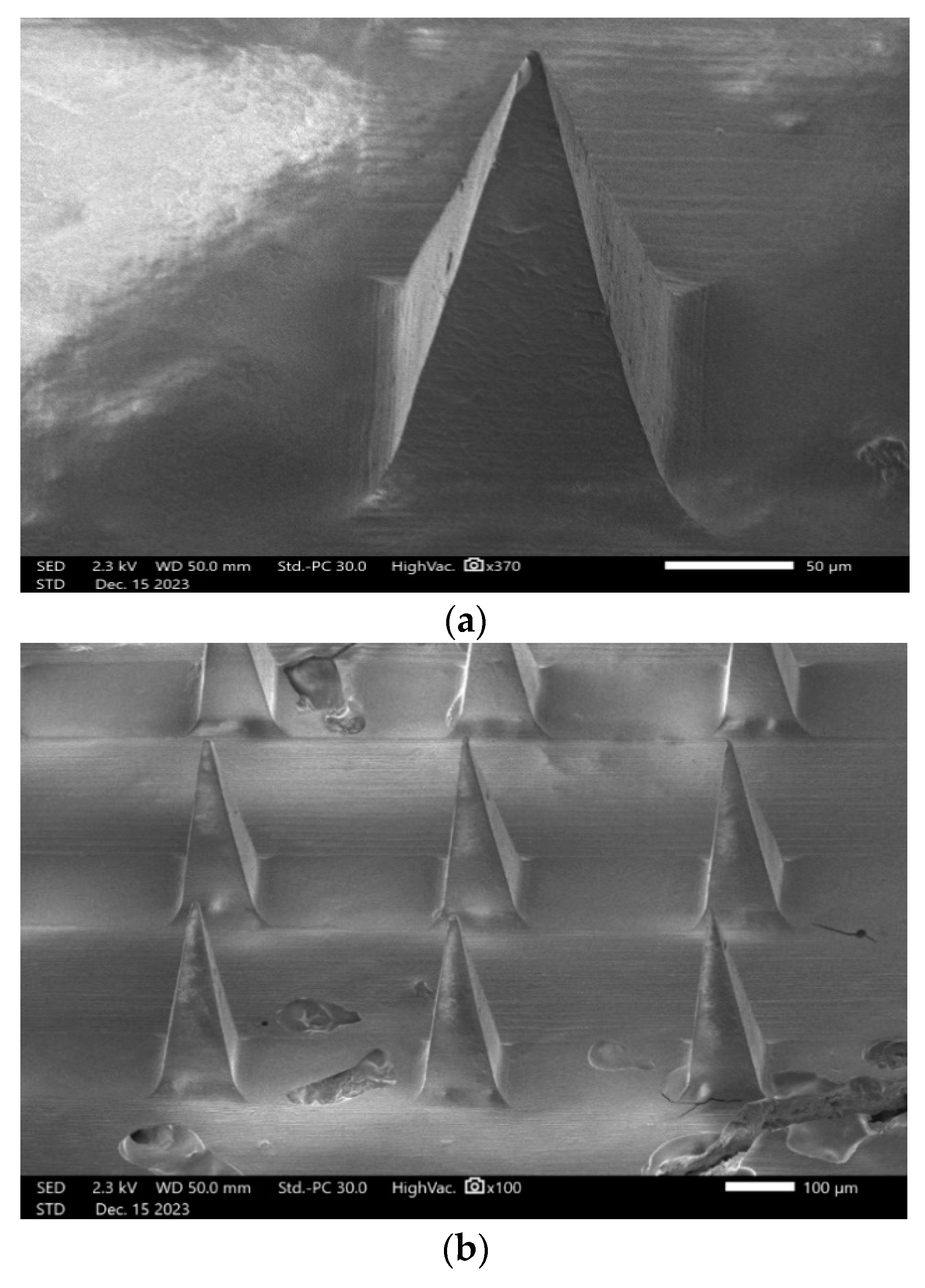
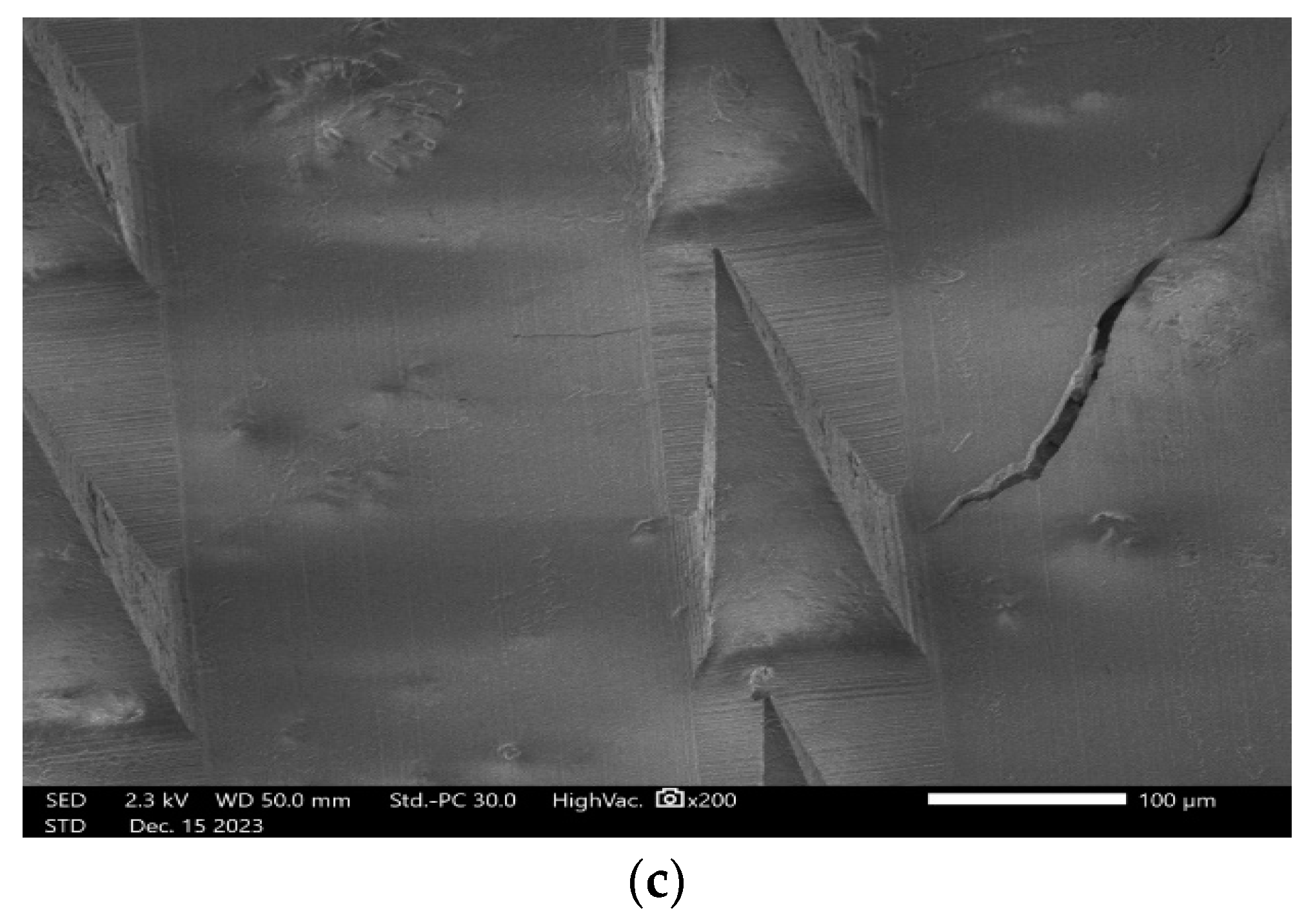
3.10.4. SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) Analysis
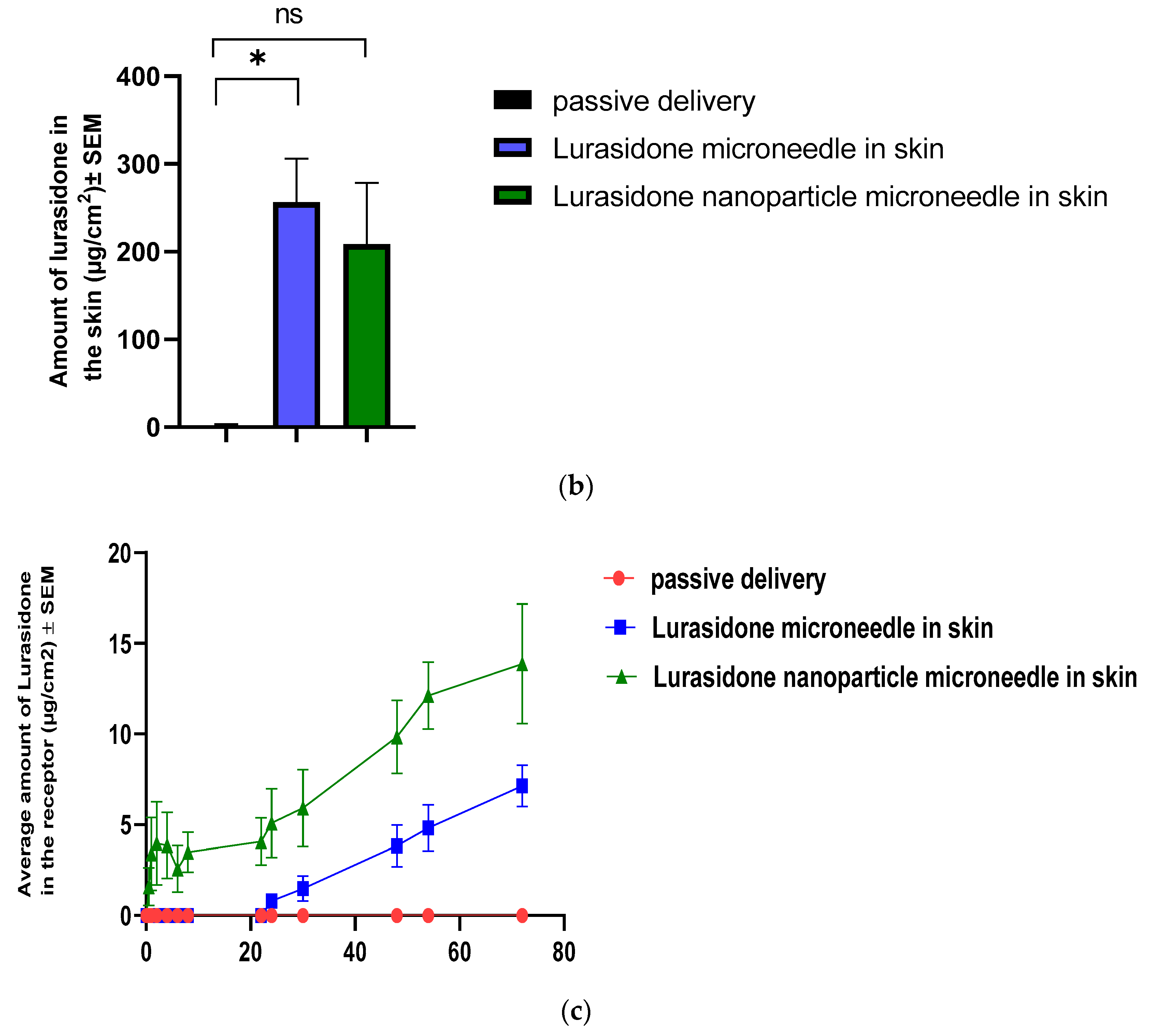
3.11. IVPT Study with Microneedles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiorillo, A.; Cuomo, A.; Sampogna, G.; Albert, U.; Calò, P.; Cerveri, G.; De Filippis, S.; Masi, G.; Pompili, M.; Serafini, G.; et al. Lurasidone in adolescents and adults with schizophrenia: From clinical trials to real-world clinical practice. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 1801–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boydell, J.; Dean, K.; Dutta, R.; Giouroukou, E.; Fearon, P.; Murray, R. A comparison of symptoms and family history in schizophrenia with and without prior cannabis use: Implications for the concept of cannabis psychosis. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 93, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, J. Insight in schizophrenia: A review. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępnicki, P.; Kondej, M.; Kaczor, A.A. Current concepts and treatments of schizophrenia. Molecules 2018, 23, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.M. Lurasidone: A Clinical Overview. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 72 (Suppl. 1), 24–28. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22217440/ (accessed on 24 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawa, R.; Scarff, J.R. Lurasidone: A New Treatment Option for Bipolar Depression. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 12, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azhar, Y.; Shaban, K. Pharma-Kritik [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022; Volume 36, pp. 169–177. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541057/ (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Pompili, M.; Verzura, C.; Trovini, G.; Buscajoni, A.; Falcone, G.; Naim, S.; Nardella, A.; Sorice, S.; Baldessarini, R.J.; Girardi, P. Lurasidone: Efficacy and Safety in the Treatment of Psychotic and Mood Disorders. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2017, 17, 197–205. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14740338.2017.1379989 (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoellhammer, C.M.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Skin permeabilization for transdermal drug delivery: Recent advances and future prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, M.; Kipping, T.; Banga, A.K. Modulated delivery of donepezil using a combination of skin microporation and iontophoresis. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, H.; Banga, A.K. Formation and Closure of Microchannels in Skin Following Microporation. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Morris, A. Performance of transdermal therapeutic systems: Effects of biological factors. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2011, 1, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Bozorg, B.D.; Kim, Y.; Wieber, A.; Birk, G.; Lubda, D.; Banga, A.K. Poly (vinyl alcohol) microneedles: Fabrication, characterization, and application for transdermal drug delivery of doxorubicin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 129, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, L.K.; Moffatt, K.; Tekko, I.A.; Paredes, A.J.; Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Mishra, D.; Peng, K.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle array systems for long-acting drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 159, 44–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Bhattaccharjee, S.A.; Beck-Broichsitter, M.; Banga, A.K. Fabrication and characterization of hyaluronic acid microneedles to enhance delivery of magnesium ascorbyl phosphate into skin. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.F.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, C.; Li, W. Advances in microneedle patches for long-acting contraception. Acta Mater. Med. 2023, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Almotairy, A.R.Z.; Henidi, H.; Alshehri, O.Y.; Aldughaim, M.S. Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of the Implication of Nanoparticles’ Physicochemical Properties on Responses in Biological Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-C.; Li, T.S.; Su, H.L.; Lee, P.C.; Wang, H.-M.D. Transdermal Delivery Systems of Natural Products Applied to Skin Therapy and Care. Molecules 2020, 25, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Hou, X.; Fan, W.; Ding, B.; Wu, X.; et al. Penetration and distribution of PLGA nanoparticles in the human skin treated with microneedles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 402, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy and Its Role in Overcoming Drug Resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; Nimrawi, S.; Al-Nemrawi, N.K.; Nasereddin, J. Microneedle-assisted transdermal delivery of amlodipine besylate loaded nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2022, 48, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Quan, G.; Sun, Y.; Yang, D.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Nanoparticles-encapsulated polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Jiang, G.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z. Fabrication of Rapidly Separable Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Metformin on Diabetic Rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 3004–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, A.; Fattahi, F. Formulation, characterization and physicochemical evaluation of potassium citrate effervescent tablets. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tang, J.; Terry, R.N.; Li, S.; Brunie, A.; Callahan, R.L.; Noel, R.K.; Rodríguez, C.A.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Long-acting reversible contraception by effervescent microneedle patch. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, J.Y.; Terry, R.N.; Tang, J.; Romanyuk, A.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Core-shell microneedle patch for six-month controlled-release contraceptive delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 347, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, D.; Banga, A.K. Development and evaluation of a drug-in-adhesive transdermal delivery system for delivery of olanzapine. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Vora, L.K.; Tekko, I.A.; Permana, A.D.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Ramadon, D.; Chambers, P.; McCarthy, H.O.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Dissolving microneedle patches loaded with amphotericin B microparticles for localised and sustained intradermal delivery: Potential for enhanced treatment of cutaneous fungal infections. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattaccharjee, S.; Beck-Broichsitter, M.; Banga, A.K. In Situ Gel Formation in Microporated Skin for Enhanced Topical Delivery of Niacinamide. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, S.M.; Kipping, T.; Banga, A.K. Fabrication of Polymeric Microneedles using Novel Vacuum Compression Molding Technique for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 3004–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.I.; Walsh, S.P.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. A review of polyvinyl alcohol and its uses in cartilage and orthopedic applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadreza, M.; Iraji, P.; Mahmoudi, Z.; Rahiman, N.; Akhgari, A. Design and physico-mechanical evaluation of fast-dissolving valsartan polymeric drug delivery system by electrospinning method. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, A.J.; Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Permana, A.D.; Murphy, A.J.; Picco, C.J.; Vora, L.K.; Coulter, J.A.; Donnelly, R.F. Novel tip-loaded dissolving and implantable microneedle array patches for sustained release of finasteride. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio-Sancho, S.; Serna-Jiménez, C.E.; Calatayud-Pascual, M.A.; Balaguer-Fernández, C.; Femenía-Font, A.; Merino, V.; López-Castellano, A. Transdermal absorption of memantine—Effect of chemical enhancers, iontophoresis, and role of enhancer lipophilicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, L.K.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larrañeta, E.; González-Vázquez, P.; Thakur RR, S.; Vavia, P.R. Novel bilayer dissolving microneedle arrays with concentrated PLGA nano-microparticles for targeted intradermal delivery: Proof of concept. J. Control. Release 2017, 265, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.W.; Musakhanian, J. Skin Penetration and Permeation Properties of Transcutol®—Neat or Diluted Mixtures. AAPS Pharmscitech 2018, 19, 3512–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Tomoda, K.; Koji, M.; Makino, K. Hydrophilic drug-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for transdermal delivery. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, A.; Bhattaccharjee, S.A.; Zhang, W.; Clark, M.; Singh, O.N.; Doncel, G.F.; Banga, A.K. Development of a Transdermal Delivery System for Tenofovir Alafenamide, a Prodrug of Tenofovir with Potent Antiviral Activity Against HIV and HBV. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Organic Phase | Aqueous Phase | Organic Phase/Aqueous Phase (PVA 1%) | Drug/Polymer Ratio | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THF | 1% | 2% | 3% | 1:15 | 1:20 | 1:30 | 1:35 | 1:5 | 2:5 | 3:5 | 1:3 | 2:3 | 1:1 |
| Acetone | 1% | 2% | 3% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| DCM | 1% | 2% | 3% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Wt. ratio of NP: PVP | 1.5:1 | 1:1 | 1:1.5 | 1:2 |
| NP solution | 1.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 20%,15%, and 10% PVP | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| Solvent | Solubility (mg/mL) n = 3 |
|---|---|
| PBS | 0 |
| PEG | 3975.1 ± 45 |
| propylene glycol | 954.55 ± 34 |
| Volpo 6% | 98.3 ± 12 |
| 80% PEG: 20% Volpo 6% | 494.6 ± 15 |
| 70% PEG: 30% Volpo 6% | 121.7 ± 17 |
| 10 mM citric acid buffer pH 3 | 15,067.4 ± 46 |
| 10 mM citric acid buffer pH 3.5 | 3603.4 ± 24 |
| 10 mM citric acid buffer pH 4 | 1048.2 ± 18 |
| 10 mM citric acid buffer pH 4.5 | 321.3 ± 16 |
| Preparation Method | Nanoparticle Size | Polydispersity Index | % of Drug Encapsulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetone and homogenization | 325.3 nm | 0.295 Mw/Mn | %28.3 |
| Acetone and syringe pump | 284.8 nm | 0.163 Mw/Mn | %40.2 |
| THF and homogenization | 335.8 nm | 0.432 Mw/Mn | %31.8 |
| THF and syringe pump | 409.2 nm | 0.462 Mw/Mn | %57.3 |
| PLGA/Drug | Nanoparticle Size | Polydispersity Index | % of Drug Encapsulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5:1 | 332.7 nm | 0.227 Mw/Mn | %50.1 |
| 5:2 | 367.9 nm | 0.159 Mw/Mn | %49.0 |
| 5:3 | 877.0 nm | 0.592 Mw/Mn | %36.7 |
| 3:1 | 316.1 nm | 0.298 Mw/Mn | %54.3 |
| 3:2 | 635.2 nm | 0.383 Mw/Mn | %25.3 |
| 1:1 | 643.6 nm | 0.449 Mw/Mn | %42.2 |
| Solution | µg of Drug Quantity in 75 µL |
|---|---|
| Just PVA | 61.412 |
| 5% w/v PVP | 54.916 |
| 10% w/v PVP | 35.988 |
| 20% w/v PVP | 19.137 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radmard, A.; Banga, A.K. Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Lurasidone Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030308
Radmard A, Banga AK. Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Lurasidone Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(3):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030308
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadmard, Ariana, and Ajay K. Banga. 2024. "Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Lurasidone Nanoparticles" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 3: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030308
APA StyleRadmard, A., & Banga, A. K. (2024). Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Lurasidone Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics, 16(3), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030308







