The Intra-Articular Delivery of a Low-Dose Adeno-Associated Virus-IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Vector Alleviates the Progress of Arthritis in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Viral Vector Production
2.3. Animals
2.4. In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging
2.5. Rat OA Model
2.6. X-Ray Clinical Score
- 0: A normal state, with no observed narrowing of the joint space and the absence of reactive bone changes on the X-ray;
- I: There is a possibility of mild narrowing of the joint space and initial, minor osteophyte formation;
- II: The definite presence of small osteophytes and potential narrowing of the joint space, as evidenced on the X-ray;
- III: Characterized by multiple, moderate-sized osteophytes, definitive narrowing of the joint space, some degree of subchondral bone sclerosis, and a likelihood of bony deformity within the joint;
- IV: A severe state with numerous large osteophytes, marked narrowing of the joint space, pronounced subchondral bone sclerosis, and overt bony deformity of the joint.
2.7. Micro-CT Examination
2.8. ELISA Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
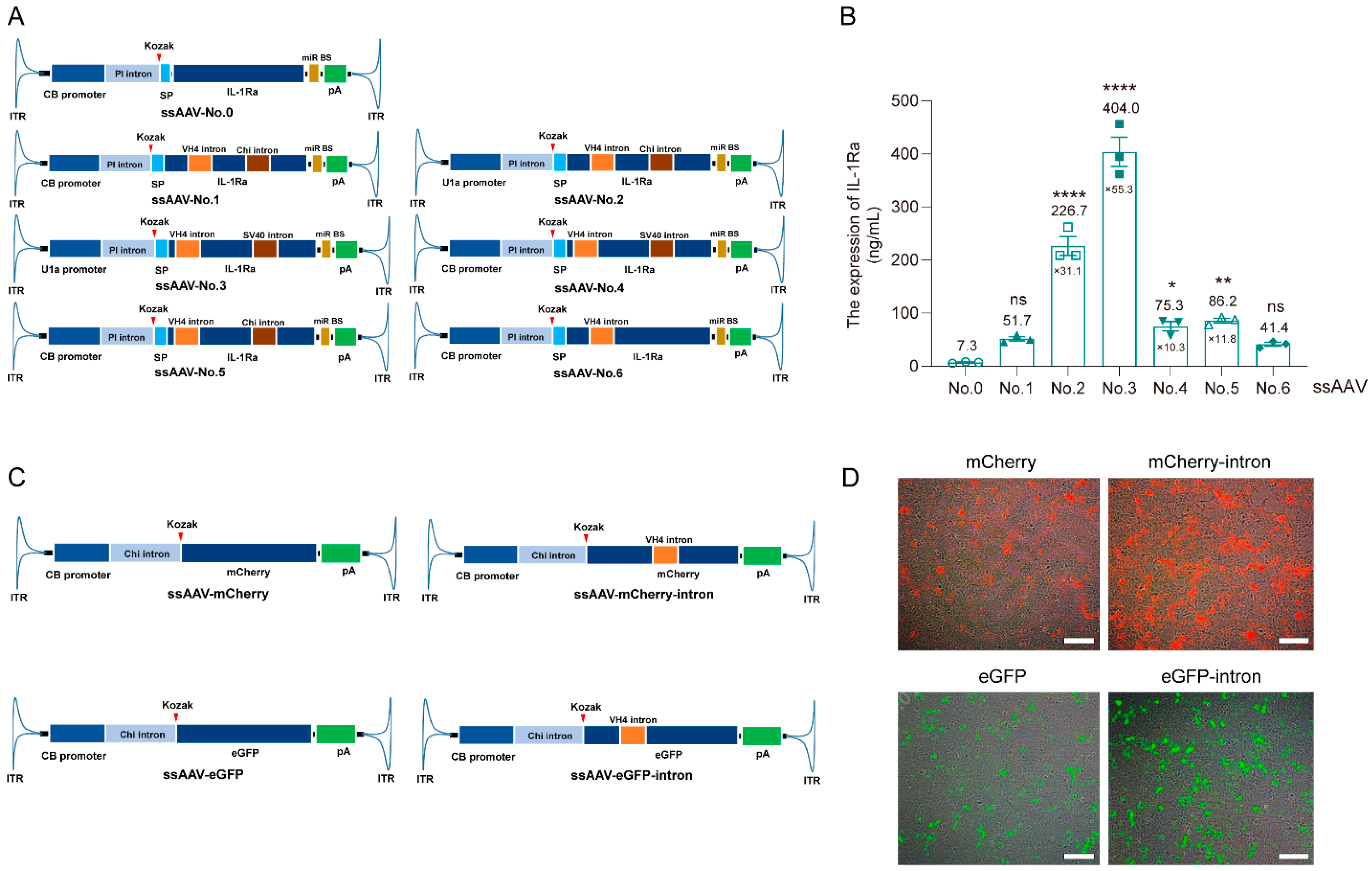
3.1. Optimize the Expression Cassette of IL-1Ra Plasmid Using Intron Insertion into CDS Technology
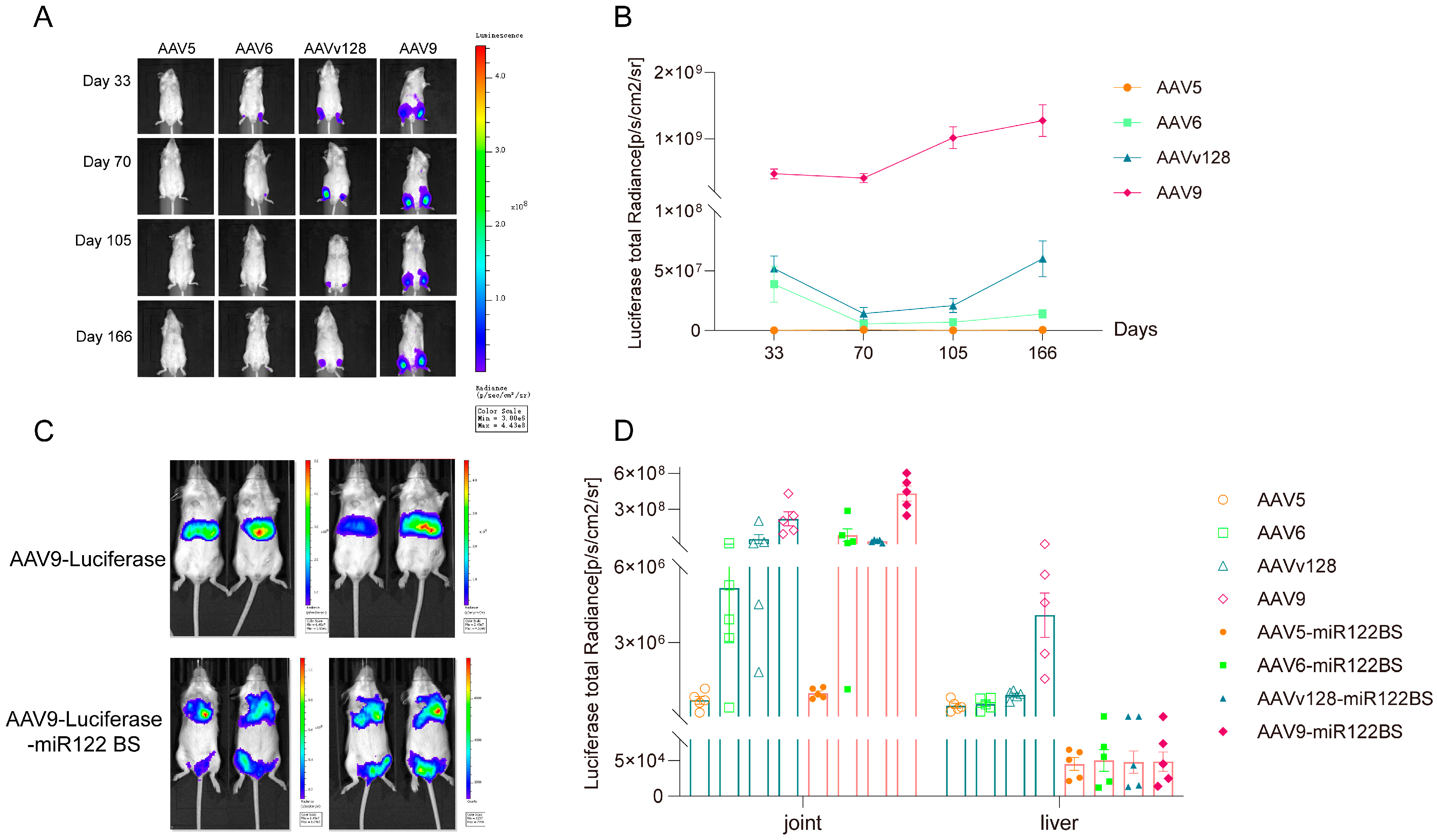
3.2. Intra-Articular Injection of AAV9-Luciferase-miR122 BS Vector Significantly Reduces the Expression Level in Liver
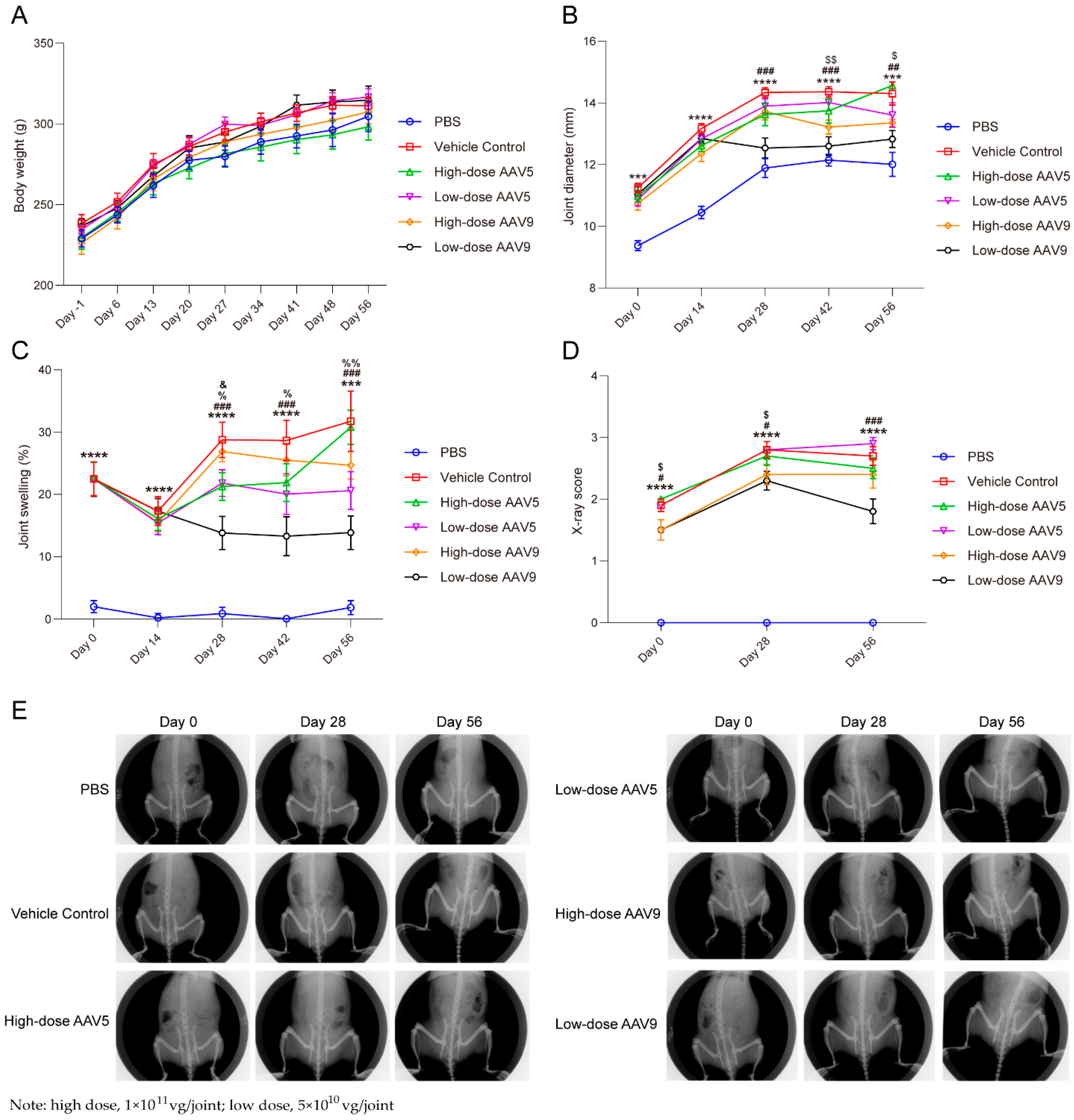
3.3. Low-Dose AAV Has Good Efficacy on OA Model in Rats, While High-Dose AAV Has Poor Therapeutic Effect
3.4. AAV-IL-1Ra Gene Therapy Substantially Protects Trabecular Bone-Related Indicators in Animal Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.-I.; Kim, T.-K. Regenerative Therapy for Osteoarthritis: A Perspective. Int. J. Stem Cells 2020, 13, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grässel, S.; Muschter, D. Recent advances in the treatment of osteoarthritis. F1000Research 2020, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.; Kang, D.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.-B.; Kim, J.-H. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: Current status and future directions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Barr, A.J.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Cooper, C.; Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R.; Jones, G.; Teichtahl, A.J.; Pelletier, J.-P. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, H.; Little, C.B. The role of fat and inflammation in the pathogenesis and management of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, iv10–iv21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arend, W.P.; Malyak, M.; Guthridge, C.J.; Gabay, C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: Role in biology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, X.; Goupille, P.; Beaulieu, A.D.; Burch, F.X.; Bensen, W.G.; Conrozier, T.; Loeuille, D.; Kivitz, A.J.; Silver, D.; Appleton, B.E. Intraarticular injection of anakinra in osteoarthritis of the knee: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.H.; Kraus, V.B.; Setton, L.A. Progress in intra-articular therapy. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 10, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Samulski, R.J. Engineering adeno-associated virus vectors for gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, Q.; Zheng, Q. Preclinical evaluation of KH631, a novel rAAV8 gene therapy product for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 3308–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levings, R.S.W.; Smith, A.D.; Broome, T.A.; Rice, B.L.; Gibbs, E.P.; Myara, D.A.; Hyddmark, E.V.; Nasri, E.; Zarezadeh, A.; Levings, P.P.; et al. Self-Complementary Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Gene Delivery for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: Test of Efficacy in an Equine Model. Hum. Gene Ther. Clin. Dev. 2018, 29, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Liu, S.; Ou, L. rAAV immunogenicity, toxicity, and durability in 255 clinical trials: A meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1001263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, C.; Yuan, Z.; Li, J.; He, B.; Zheng, H.; Mayer, C.; Xiao, X. Liver-specific microRNA-122 target sequences incorporated in AAV vectors efficiently inhibits transgene expression in the liver. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Guo, C.; Ji, X.; Cui, Q.; Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Zheng, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-122-Mediated Liver Detargeting Enhances the Tissue Specificity of Cardiac Genome Editing. Circulation 2024, 149, 1778–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Sha, S.; Hong, M.S.; Maloney, A.J.; Barone, P.W.; Neufeld, C.; Wolfrum, J.; Springs, S.L.; Sinskey, A.J.; Braatz, R.D. Mechanistic model for production of recombinant adeno-associated virus via triple transfection of HEK293 cells. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 21, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, D.D.; Latham, K.A.; Rosloniec, E.F. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Mazzon, E.; Dugo, L.; Serraino, I.; Britti, D.; De Maio, M.; Caputi, A.P. Absence of endogeneous interleukin-10 enhances the evolution of murine type-II collagen-induced arthritis. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2001, 12, 568–580. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Xie, Q.; Luo, S.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Intra-Articular Delivery of an AAV-Anti-TNF-α Vector Alleviates the Progress of Arthritis in a RA Mouse Model. Hum. Gene Ther. 2024, 35, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, Q.; Qin, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; et al. An adeno-associated virus variant enabling efficient ocular-directed gene delivery across species. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaul, O. How introns enhance gene expression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 91, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy-Hulbert, A.; Thomas, R.; Li, X.-P.; E Lilley, C.; Coffin, R.S.; Roes, J. Interruption of coding sequences by heterologous introns can enhance the functional expression of recombinant genes. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, T.; Jacobebbinghaus, N.; Einhaus, A.; Lauersen, K.J.; Kruse, O. Introns mediate post-transcriptional enhancement of nuclear gene expression in the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.B.; Carter, A.; Korf, I.; Kojima, N. Intron sequences that stimulate gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 92, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, L.; Hoffman, H.M. IL-1 and autoinflammatory disease: Biology, pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, W.; Grosshans, H. The liver-specific microRNA miR-122: Biology and therapeutic potential. Prog. Drug Res. 2011, 67, 221–238. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, M.; Jacquemin, E.; Munnich, A.; Lyonnet, S.; Henrion-Caude, A. miR-122, a paradigm for the role of microRNAs in the liver. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopling, C. Liver-specific microRNA-122: Biogenesis and function. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdmanis, P.N.; Kim, H.K.; Chu, K.; Zhang, F.; Xu, J.; Munding, E.M.; Shen, J.; Kay, M.A. miR-122 removal in the liver activates imprinted microRNAs and enables more effective microRNA-mediated gene repression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Qu, G.; Yang, X.; Xu, R.; Xiao, W. Systemic elimination of de novo capsid protein synthesis from replication-competent AAV contamination in the liver. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 22, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Baumert, T.F.; Zeisel, M.B. miR-122—A key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Mou, H.; Ibraheim, R.; Liang, S.-Q.; Liu, P.; Xue, W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Tissue-restricted genome editing in vivo specified by microRNA-repressible anti-CRISPR proteins. RNA 2019, 25, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.; Ma, H.; Xie, J.; Kaplan, F.S.; Gao, G.; Shim, J.-H. AAV-Mediated Targeting of the Activin A-ACVR1(R206H) Signaling in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Keeler, G.D.; Zhang, Y.; Hoffman, B.E.; Ling, C.; Qing, K.; Srivastava, A. AAV3-miRNA vectors for growth suppression of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and human liver tumors in a murine xenograft model in vivo. Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Burt, D.R.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus-mediated microRNA delivery and therapeutics. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dismuke, D.J.; Tenenbaum, L.; Samulski, R.J. Biosafety of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors. Curr. Gene Ther. 2014, 13, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Herstine, J.A.; Bradbury, A.; Gray, S.J. AAV-based in vivo gene therapy for neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Avery, R.; Brown, D.M.; Heier, J.S.; Ho, A.C.; Huddleston, S.M.; Jaffe, G.J.; Khanani, A.M.; Pakola, S.; Pieramici, D.J.; et al. Gene therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration by subretinal delivery of RGX-314: A phase 1/2a dose-escalation study. Lancet 2024, 403, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.; Gessler, D.J.; Zhan, W.; Gallagher, T.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus as a delivery vector for gene therapy of human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwin, N.; Bendele, A.; Glasson, S.; Carlson, C. The OARSI histopathology initiative—Recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18 (Suppl. S3), S24–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thysen, S.; Luyten, F.P.; Lories, R.J.U. Targets, models and challenges in osteoarthritis research. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; He, C.; Bai, S.; He, P.; Jiang, M.; et al. Single-shot AAV-vectored vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 with fast and long-lasting immunity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 13, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, I.; Zeng, A.; Greer-Short, A.; Aycinena, J.A.; Tefera, A.E.; Shenwai, R.; Farshidfar, F.; Van Pell, M.; Xu, E.; Reid, C.; et al. AAV9:PKP2 improves heart function and survival in a Pkp2-deficient mouse model of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Levy, D.; Petropoulos, C.J.; Bashirians, G.; Winburn, I.; Mahn, M.; Somanathan, S.; Cheng, S.H.; Byrne, B.J. Binding and neutralizing anti-AAV antibodies: Detection and implications for rAAV-mediated gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Evans, C.H.; Benson, J.M.; Hutt, J.A.; Seagrave, J.; Wilder, J.A.; Grieger, J.C.; Samulski, R.J.; Terse, P.S. Safety and biodistribution assessment of sc-rAAV2.5IL-1Ra administered via intra-articular injection in a mono-iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis rat model. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 15052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levings, R.S.W.; Broome, T.A.; Smith, A.D.; Rice, B.L.; Gibbs, E.P.; Myara, D.A.; Hyddmark, E.V.; Nasri, E.; Zarezadeh, A.; Levings, P.P.; et al. Gene Therapy for Osteoarthritis: Pharmacokinetics of Intra-Articular Self-Complementary Adeno-Associated Virus Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Delivery in an Equine Model. Hum. Gene Ther. Clin. Dev. 2018, 29, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, X. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Transection-Induced Cellular and Extracellular Events in Menisci: Implications for Osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, A.T.; Suzuki, M.; Markusic, D.M.; Zolotukhin, I.; Ryals, R.C.; Moghimi, B.; Ertl, H.C.J.; Muruve, D.A.; Lee, B.; Herzog, R.W. The genome of self-complementary adeno-associated viral vectors increases Toll-like receptor 9-dependent innate immune responses in the liver. Blood 2011, 117, 6459–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, S.N.; Somanathan, S.; Giles, A.R.; Wilson, J.M. TLR9 signaling mediates adaptive immunity following systemic AAV gene therapy. Cell Immunol. 2019, 346, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y. The TLR9-MyD88 pathway is critical for adaptive immune responses to adeno-associated virus gene therapy vectors in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2388–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhuri, M.; Zhan, W.; Maeda, Y.; Li, J.; Lotun, A.; Chen, J.; Sylvia, K.; Dasgupta, I.; Arjomandnejad, M.; Nixon, T.; et al. Novel Combinatorial MicroRNA-Binding Sites in AAV Vectors Synergistically Diminish Antigen Presentation and Transgene Immunity for Efficient and Stable Transduction. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 674242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Muhuri, M.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Xu, G.; Luo, L.; Li, J.; Letizia, A.J.; Wang, S.K.; Chan, Y.K.; et al. Circumventing cellular immunity by miR142-mediated regulation sufficiently supports rAAV-delivered OVA expression without activating humoral immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 4, 99052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertl, H.C.J. T Cell-Mediated Immune Responses to AAV and AAV Vectors. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 666666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, H.C.J. Immunogenicity and toxicity of AAV gene therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 975803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, D.H.; Zaidman, C.; Arya, K.; Millner, R.; Farrar, M.A.; Mackie, F.E.; Goedeker, N.L.; Dharnidharka, V.R.; Dandamudi, R.; Reyna, S.P. Thrombotic Microangiopathy Following Onasemnogene Abeparvovec for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Case Series. J. Pediatr. 2021, 231, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. Gene therapy community grapples with toxicity issues, as pipeline matures. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 804–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; Guermazi, A.; Roemer, F.; Zhang, Y.; Neogi, T. Structural correlates of pain in joints with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafeber, F.P.; van Spil, W.E. Osteoarthritis year 2013 in review: Biomarkers; reflecting before moving forward, one step at a time. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, L.; Deng, Z.; Huang, Z. New treatment for osteoarthritis: Gene therapy. Precis. Clin. Med. 2023, 6, pbad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, Z.; Yu, C. Suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by gene transfer of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-10. J. Orthop. Res. 2004, 22, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, A.; Grol, M.W.; Ruan, M.Z.C.; Dawson, B.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, M.-M.; Song, I.-W.; Jayaram, P.; Cela, R.; Gannon, F.; et al. Combinatorial Prg4 and Il-1ra Gene Therapy Protects Against Hyperalgesia and Cartilage Degeneration in Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuppal, R. Current concepts in the articular cartilage repair and regeneration. J. Orthop. 2017, 14, A1–A3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Yu, X.; Xu, X.; Xie, Q.; Ke, X.; Zheng, Q. The Intra-Articular Delivery of a Low-Dose Adeno-Associated Virus-IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Vector Alleviates the Progress of Arthritis in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121518
Luo S, Jiang H, Li Q, Yang S, Yu X, Xu X, Xie Q, Ke X, Zheng Q. The Intra-Articular Delivery of a Low-Dose Adeno-Associated Virus-IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Vector Alleviates the Progress of Arthritis in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(12):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121518
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Shuang, Hao Jiang, Qingwei Li, Shiping Yang, Xuemei Yu, Xiongliang Xu, Qing Xie, Xiao Ke, and Qiang Zheng. 2024. "The Intra-Articular Delivery of a Low-Dose Adeno-Associated Virus-IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Vector Alleviates the Progress of Arthritis in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 12: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121518
APA StyleLuo, S., Jiang, H., Li, Q., Yang, S., Yu, X., Xu, X., Xie, Q., Ke, X., & Zheng, Q. (2024). The Intra-Articular Delivery of a Low-Dose Adeno-Associated Virus-IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Vector Alleviates the Progress of Arthritis in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Pharmaceutics, 16(12), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121518






