Cyclodextrins as Multi-Functional Ingredients in Dentistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cyclodextrins in Oral Hygiene Compositions
2.1. Toothpastes
2.2. Toothpaste Additives
2.3. Mouthwashes
3. Cyclodextrins in Dental Repair
3.1. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds with Anesthetics
3.2. Cyclodextrins in Dental Materials—Fillings, Pastes and Cements
3.2.1. Materials with α-Cyclodextrin
3.2.2. Materials with β-Cyclodextrin or Its Derivatives
3.3. Cyclodextrin-Based Systems in Osteogenesis
3.3.1. Hydroxyapatite/Cyclodextrin Composite Nanoparticles
3.3.2. Cyclodextrin–Bisphosphonate Conjugates
3.4. Cyclodextrin-Based Strategies for the Management of Periodontal Disease
3.4.1. Materials Containing Cyclodextrins as Drug Carriers
3.4.2. Cyclodextrins as Building Blocks for Innovative Materials with Sustained Release
4. Outlook and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willis, J.R.; Gabaldón, T. The human oral microbiome in health and disease: From sequences to ecosystems. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeles, S.R.; Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Ly, M.; Lum, A.G.; Salzman, J.; Boehm, T.K.; Pride, D.T. Human oral viruses are personal, persistent and gender-consistent. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulloa, P.C.; van der Veen, M.H.; Krom, B.P. Review: Modulation of the oral microbiome by the host to promote ecological balance. Odontology 2019, 107, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melissari, A.; Alexopoulos, A.; Mantzourani, I.; Plessas, S.; Voidarou, C.; Tsigalou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Investigating nutritional behavior and oral health habits among adults and children in Nοrth-Eastern Greece. Oral 2021, 1, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral Care Market Is Expected to Reach $54.9 Billion. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2023/05/18/2672001/0/en/Oral-Care-Market-is-Expected-to-Reach-54-9-billion-MarketsandMarkets.html (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Dhillon, G.S.; Kaur, S.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.K.; Clédon, M.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Triclosan: Current status, occurrence, environmental risks and bioaccumulation potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5657–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, S.-E.; Pyo, Y.-C.; Tran, P.; Park, J.-S. Solubility enhancement and application of cyclodextrins in local drug delivery. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, M.; Stańczak, A.; Kołodziejczyk, M. Characteristic of Cyclodextrins: Their role and use in the pharmaceutical technology. Curr. Drug Targ. 2020, 21, 1495–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caira, M.R. Cyclodextrin inclusion of medicinal compounds for enhancement of their physicochemical and biopharmaceutical properties. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2357–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.-Q.; Wen, H. Applications of Complexation in the Formulation of Insoluble Compounds. In Water-Insoluble Drug Formulation, 2nd ed.; Liu, R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; Chapter 8; pp. 133–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, G.; Caridi, F.; Venuti, V.; Paolino, D.; Ventura, C.A. Chitosan/cyclodextrin nanospheres for potential nose-to-brain targeting of idebenone. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matencio, A.; Hoti, G.; Monfared, Y.K.; Rezayat, A.; Pedrazzo, A.R.; Caldera, F.; Trotta, F. Cyclodextrin monomers and polymers for drug activity enhancement. Polymers 2021, 13, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaetano, F.; Cristiano, M.C.; Paolino, D.; Celesti, C.; Iannazzo, D.; Pistarà, V.; Iraci, N.; Ventura, C.A. Bicalutamide anticancer activity enhancement by formulation of soluble inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szejtli, J.; Szente, L. Elimination of bitter, disgusting tastes of drugs and foods by cyclodextrins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 61, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arima, H.; Higashi, T.; Motoyama, K. Improvement of the bitter taste of drugs by complexation with cyclodextrins: Applications, evaluations and mechanisms. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szente, L.; Szejtli, J. Cyclodextrins as food ingredients. Trends Food Sci. 2004, 15, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puskás, I.; Szente, L.; Szőcs, L.; Fenyvesi, E. Recent list of cyclodextrin-containing drug products. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2023, 67, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Zöller, T. Cyclodextrine–Wundertüten in Pharmazie und Alltag. Pharm. Ztg. 2008, 28, 6177. Available online: http://www.pharmazeutische-zeitung.de/index.php?id=6177 (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Background Review for Cyclodextrins Used as Excipients; EMA: London, UK, 2014. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Report/2014/12/WC500177936.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Buschmann, H.-J.; Schollmeyer, E. Applications of cyclodextrins in cosmetic products: A review. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2002, 53, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, S.S.; Pais, J. Getting under the skin: Cyclodextrin inclusion for the controlled delivery of active substances to the dermis. In Design of Nanostructures for Versatile Therapeutic Applications, 1st ed.; Grumezescu, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 10; pp. 407–449. [Google Scholar]
- Yaz. Available online: https://www.bayer.com/sites/default/files/2020-11/yaz-pm-en.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Bocanegra, M.; Seijas, A.; Yibirín, M.G. Efficacy and tolerability of conventional nimesulide versus beta-cyclodextrin nimesulide in patients with pain after surgical dental extraction: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy study. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2003, 64, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boczar, D.; Michalska, K. Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes with antibiotics and antibacterial agents as drug-delivery systems—A pharmaceutical perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.B.; Braga, S.S. Cyclodextrin Inclusion of Nutraceuticals, from the Bench to your Table. In Cyclodextrins: Synthesis, Chemical Applications and Role in Drug Delivery, 1st ed.; Ramirez, F.G., Ed.; NovaSience: Hauppage, NY, USA, 2015; Chapter 6; pp. 195–224. [Google Scholar]
- Szente, L.; Singhal, A.; Domokos, A.; Song, B. Cyclodextrins: Assessing the impact of cavity size, occupancy, and substitutions on cytotoxicity and cholesterol homeostasis. Molecules 2018, 23, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Fenyvesi, F.; Bácskay, I.; Váradi, J.; Fenyvesi, É.; Iványi, R.; Szente, L.; Tósaki, Á.; Vecsernyé, M. Evaluation of the cytotoxicity of β-cyclodextrin derivatives: Evidence for the role of cholesterol extraction. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulmedarat, L.; Bochot, A.; Lesieur, S.; Fattal, E. Evaluation of buccal methyl-β-cyclodextrin toxicity on human oral epithelial cell culture model. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Leeves, N.; Bjornsdottir, B.; Duffy, L.; Masson, M. Effect of cyclodextrins and polymers on triclosan availability and substantivity in toothpastes in vivo. J. Pharm Sci. 1999, 88, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triclosan Bexident Gums Toothpaste. Available online: https://www.salutemshop.com/en/care-for-dental-health-pastes-mouthwashes-toothbrushes/160-gums-toothpaste-bexident-triclosan-anticaries-antibacterial-protects-gums-8470003638388.html (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- GUM (Quasi-Drug) Well Plus Periodontal Disease Prevention Toothpaste, Dental Paste, Herb Mint, High Fluorine Concentration 1.450 ppm. Available online: https://www.amazon.co.jp/-/en/Quasi-Drug-Periodontal-Prevention-Toothpaste-Concentration/dp/B084ZD72FR?th=1 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- BlanX Pro Pure White. Available online: http://www.blanx.com/pure-white-en (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- BlanX Pro Pure White Toothpaste 75 mL. Available online: https://www.i-health.ae/products/blanx-pro-pure-white-blue-75ml (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Nature’s Gate Organics Whitening Toothpaste. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Natures-Gate-Whitening-Toothpaste-Raspberry/dp/B000OYNBBC (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Watsons Dentiste Toothpaste Set. Available online: https://watsonsworld.com/product/dentiste-toothpaste-set/ (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Abiru, M.; Sato, T.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Sato, K.; GC Corporation. Antimicrobial Dental Composition. Patent DE602005006329T2, 16 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Babbush, C.A. The efficacy of perfect smile toothpaste containing coenzyme Q10-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex in reducing mild to moderate gingivitis. Nat. Med. J. 2006, 6, 16–20. Available online: https://www.naturalmedicinejournal.com/journal/efficacy-perfect-smile-toothpaste-containing-coenzyme-q10-b-cyclodextrin-inclusion (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- AP+ Whitening Powder. Available online: https://eu.hismileteeth.com/products/whitening-powder (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Nelson, D.G.A.; Sheehan, C.J.; Johnson and Johnson Consumer, Inc. Cyclodextrins in Dental Products. Patent US5945087A, 31 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- GUM® HaliControl® Mouthwash. Available online: https://professional.sunstargum.com/en-en/products/mouthwashes/gum-halicontrol-mouthwash.html (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Curaprox Perioplus+ Regenerate. Available online: https://curaprox.co.uk/shop/oral-rinses-and-gels/oral-rinses/perioplus-regenerate (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- SPLAT Professional Bio-Active Mouthwash White Plus. Available online: https://www.splatoralcare.uk/products/mouthwash-white-plus (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Malic, S.; Emanuel, C.; Lewis, M.A.O.; Williams, D.W. Antimicrobial activity of novel mouthrinses against planktonic cells and biofilms of pathogenic microorganisms. Microbiol. Discov. 2013, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, S.J.; Lewis, M.A.O.; Wilson, M.J.; Williams, D.W. Antimicrobial activity of Citrox® (Flavobac™) bioflavonoid preparations against oral microorganisms. Br. Dent. J. 2010, 210, E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrouel, F.; Valette, M.; Gadea, E.; Esparcieux, A.; Illes, G.; Langlois, M.E.; Perrier, H.; Claude Dussart, C.; Tramini, P.; Ribaud, M.; et al. Use of an antiviral mouthwash as a barrier measure in the SARS-CoV-2 transmission in adults with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind controlled trial. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, T.; Citrox Biosciences Ltd. Bioflavonoid Compositions and Their Use for Water Purification and Food Preservation. Patent GB2578146A, 22 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, T.; Citrox Biosciences Ltd. Bioflavonoid Impregnated Materials. Patent EP2888398B1, 30 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Burga-Sánchez, J.; Ferreira, L.E.N.; Volpato, M.C.; Cabeça, L.F.; Braga, M.; Fraceto, L.F.; de Paula, E.; Groppo, F.C. Physicochemical characterization and cytotoxicity of articaine-2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréville, J.C.; Dollo, G.; Le Corre, P.; Chevanne, F.; Le Verge, R. Controlled systemic absorption and increased anesthetic effect of bupivacaine following epidural administration of bupivacaine-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin complex. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, D.R.; Tsuneda, S.S.; Cereda, C.M.; Carvalho, F.G.F.; Preté, P.S.C.; Fernandes, S.A.; Yokaichiya, F.; Franco, M.K.K.D.; Mazzaro, I.; Fraceto, L.F.; et al. Development and pharmacological evaluation of ropivacaine-2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 33, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco de Lima, R.A.; de Jesus, M.B.; Cereda, C.M.; Tofoli, G.R.; Cabeça, L.F.; Mazzaro, I.; Fraceto, L.F.; de Paula, E. Improvement of tetracaine antinociceptive effect by inclusion in cyclodextrins. J. Drug Target 2012, 20, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpe, L.; Franz-Montan, M.; dos Santos, C.P.; da Silva, C.B.; Nolasco, F.P.; Caldas, C.S.; Volpato, M.C.; de Paula, E.; Groppo, F.C. Anaesthetic efficacy of bupivacaine2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin for dental anaesthesia after inferior alveolar nerve block in rats. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 52, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staněk, J.; Azar, B.E.; Fichtel, T. Cement-based materials in dentistry. In Reinforced Concrete Structures; Saleh, H.M., Mhadhbi, M., Hassan, A.I., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.H.; Lozano, M.A.M.; Vila, J.C.; Escribano, A.B.; Galve, P.F. Composite resins. A review of the materials and clinical indications. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2006, 11, E215–E220. Available online: https://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/medicorpa/v11n2/en_23.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Chen, X.; Taguchi, T. Bonding a titanium plate and soft tissue interface by using an adhesive bone paste composed of α-tricalcium phosphate and α-cyclodextrin/nonanyl group-modified poly(vinyl alcohol) inclusion complex. Colloids Surf. B 2021, 203, 111757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
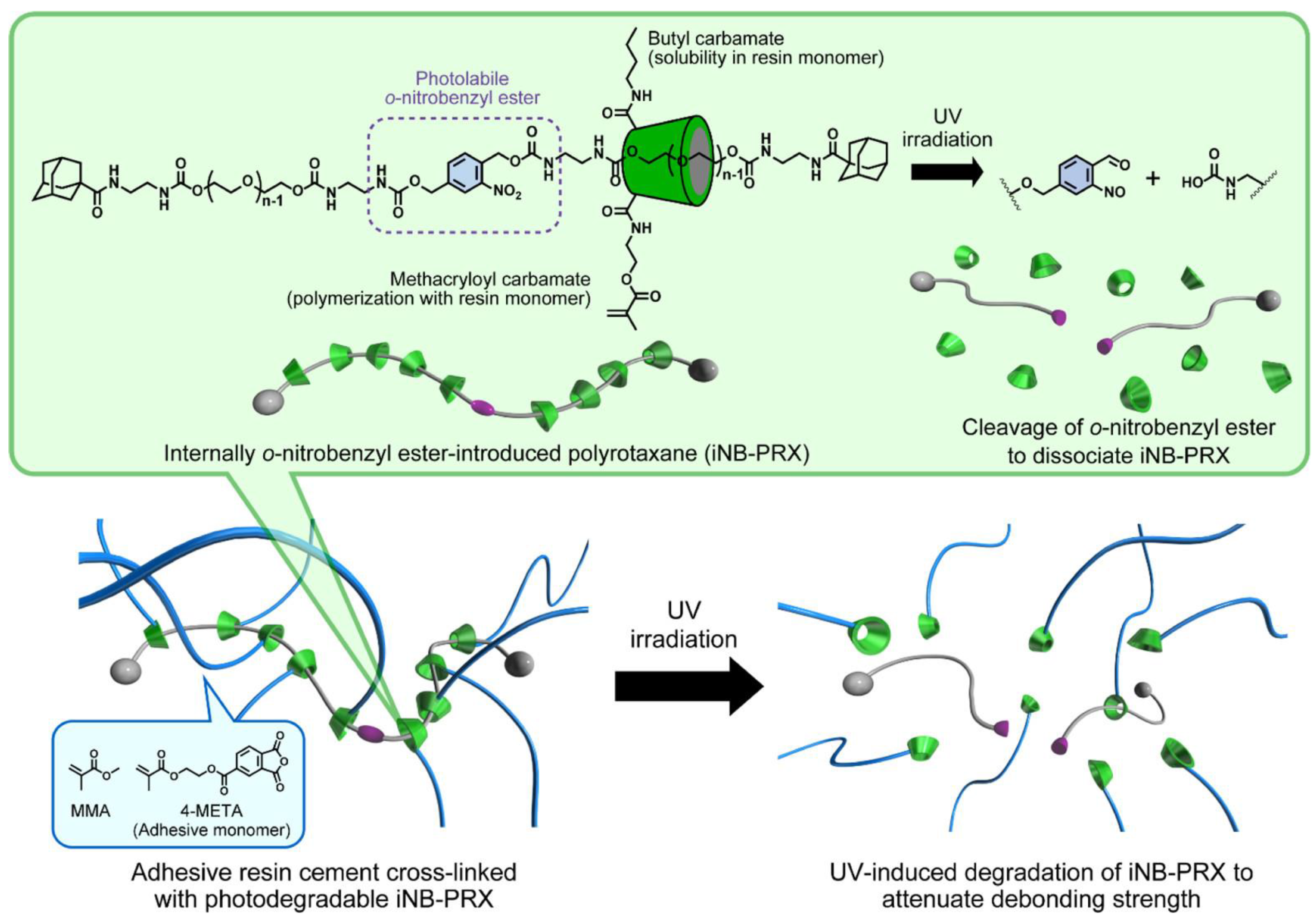
- Matsunaga, S.; Tamura, A.; Fushimi, M.; Santa, H.; Arisaka, Y.; Nikaido, T.; Tagami, J.; Yui, N. Light-embrittled dental resin cements containing photodegradable polyrotaxane cross-linkers for attenuating debonding strength. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5756–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, L.A.; Dickens, S.H.; Bowen, R.L. Effects of polymerization initiator complexation in methacrylated beta-cyclodextrin formulations. Dent. Mater. 2004, 20, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, L.A.; Dickens, S.H.; Bowen, R.L. Properties of eight methacrylated beta-cyclodextrin composite formulations. Dent. Mater. 2005, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghrery, A.; Aytac, Z.; Dubey, N.; Mei, L.; Schwendeman, A.; Bottino, M.C. Electrospinning of dexamethasone/cyclodextrin inclusion complex polymer fibers for dental pulp therapy. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 191, 111011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-G.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, J.-M.; Suh, J.-Y. The effects of dexamethasone on the apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013, 43, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.D.; Kim, Y.J. Morphological structure and characteristics of hydroxyapatite/β-cyclodextrin composite nanoparticles synthesized at different conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.S.; Paz, F.A.A.; Braga, S.S. Bisphosphonates, old friends of bones and new trends in clinics. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1260–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Lee, H.T.; Reinhardt, R.A.; Marky, L.A.; Wang, D. Novel biomineral-binding cyclodextrins for controlled drug delivery in the oral cavity. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Wiswall, A.T.; Rutledge, J.E.; Akhter, M.P.; Cullen, D.M.; Reinhardt, R.A.; Wang, D. Osteotropic β-cyclodextrin for local bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajano, V.C.C.; Brasileiro, C.B.; Henriques, J.A.S.; Cota, L.M.; Lanza, C.M.; Cortés, M.E. Doxycycline encapsulated in β-cyclodextrin for periodontitis: A clinical trial. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 33, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, B.S.; Streit, S.; Schneider, A.L.S.; Meier, M.M. Bioactive bacterial cellulose membrane with prolonged release of chlorhexidine for dental medical application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, S.S.; Paz, F.A.A. The emerging role of cyclodextrin metal–organic frameworks in ostheotherapeutics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
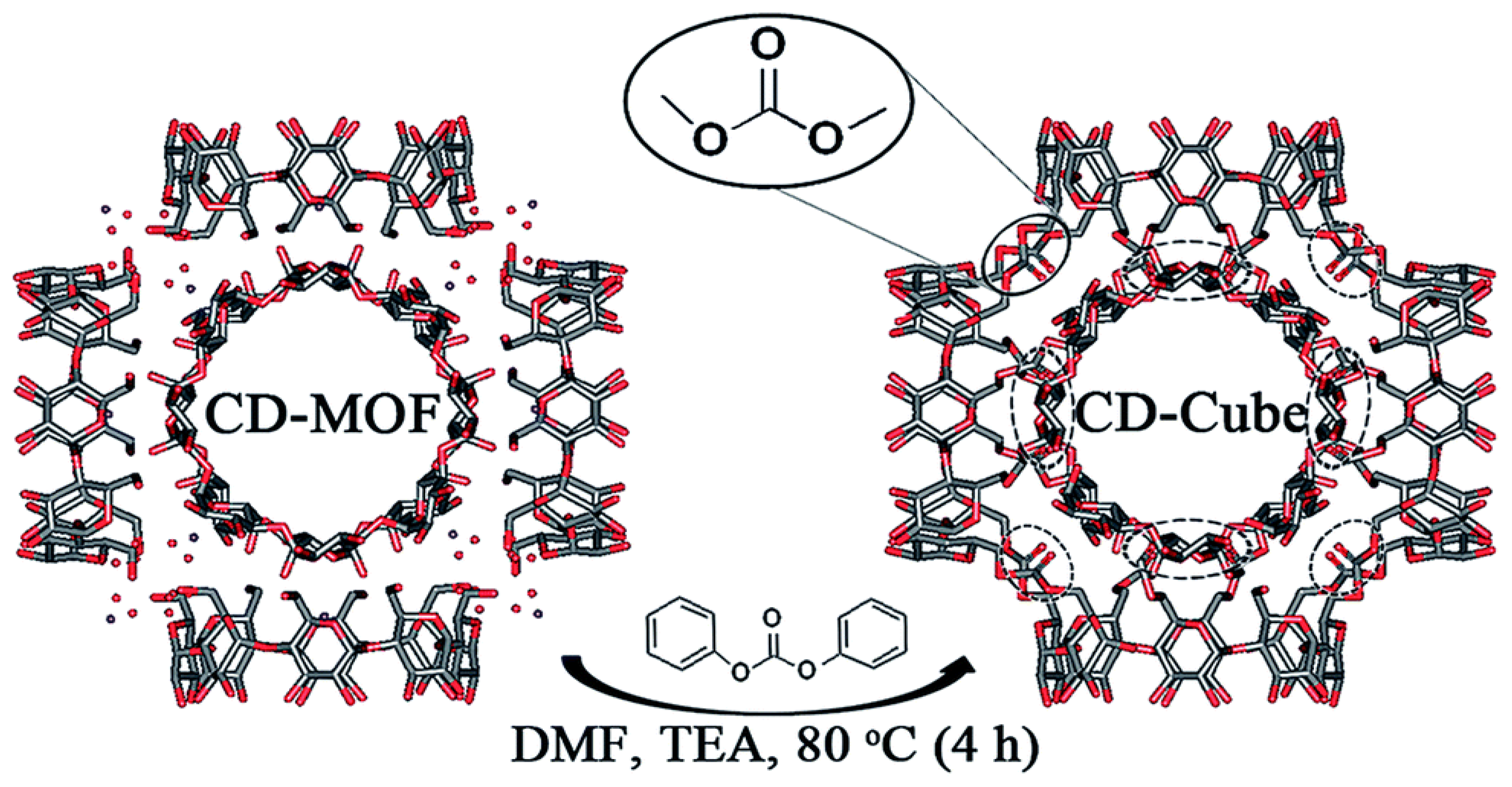
- Singh, V.; Guo, T.; Wu, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Gref, R.; Zhang, J. Template-directed synthesis of a cubic cyclodextrin polymer with aligned channels and enhanced drug payload. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 20789–20794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ren, X.; Guo, T.; Cao, Z.; Sun, H.; Huang, C.; Huang, F.; Shu, Z.; Hao, J.; Gui, S.; et al. Controlled release of iodine from cross-linked cyclodextrin metal-organic frameworks for prolonged periodontal pocket therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
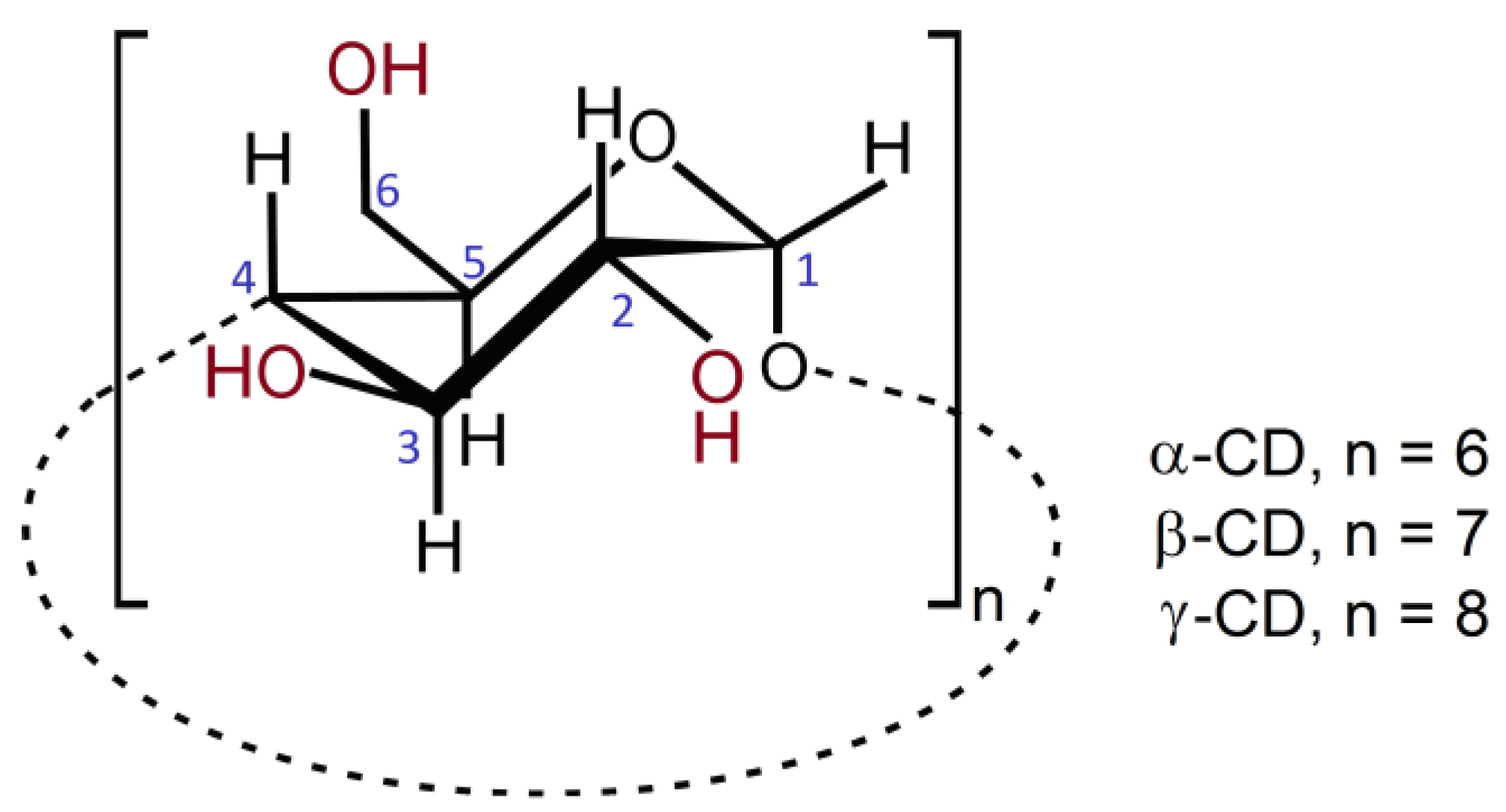


| Cyclodextrin | Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Nasal | Ocular | Dermal | Parenteral | |
| α-CD | — | — | — | — | ✓ |
| β-CD | ✓ | — | ✓ | ✓ | not allowed |
| γ-CD | ✓ | — | — | ✓ | — |
| HPβCD | ✓ | — | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RAMEB | not allowed | ✓ | ✓ | not allowed | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braga, S.S. Cyclodextrins as Multi-Functional Ingredients in Dentistry. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092251
Braga SS. Cyclodextrins as Multi-Functional Ingredients in Dentistry. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(9):2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092251
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraga, Susana Santos. 2023. "Cyclodextrins as Multi-Functional Ingredients in Dentistry" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 9: 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092251
APA StyleBraga, S. S. (2023). Cyclodextrins as Multi-Functional Ingredients in Dentistry. Pharmaceutics, 15(9), 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092251







