Preparation and Evaluation of Auxiliary Permeable Microneedle Patch Composed of Polyvinyl Alcohol and Eudragit NM30D Aqueous Dispersion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of AP-MNs
2.3. Formulation Optimization of PVA and Eudragit NM30D
2.4. Determination of Matrix Solution Addition
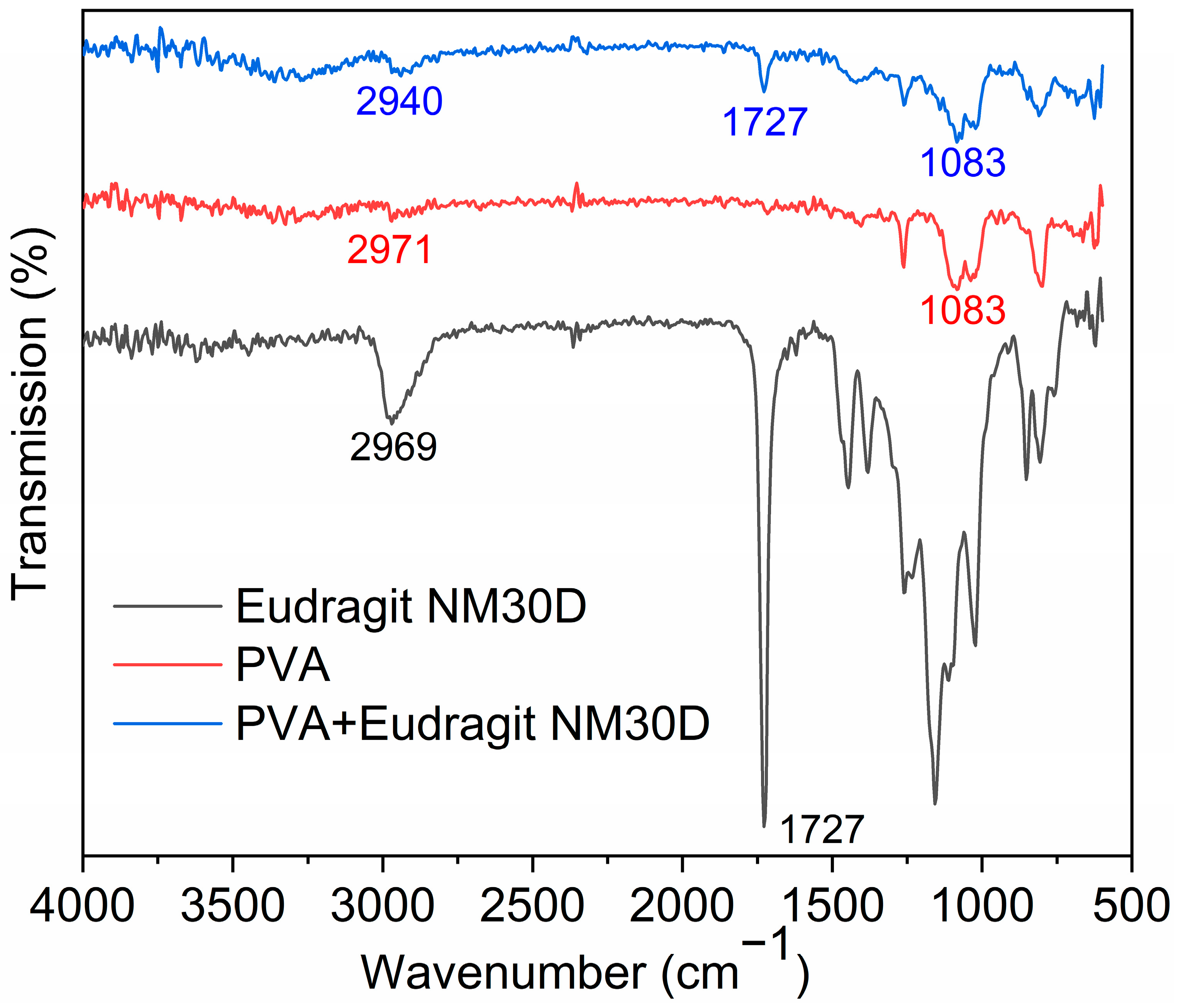
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.6. Morphological Characterization
2.7. Skin Permeability
2.8. Cell Activity and Biocompatibility
2.9. In Vitro Swelling Properties
2.10. In Vitro Percutaneous Permeability Test for Acidic and Alkaline Drugs of AP-MNs
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
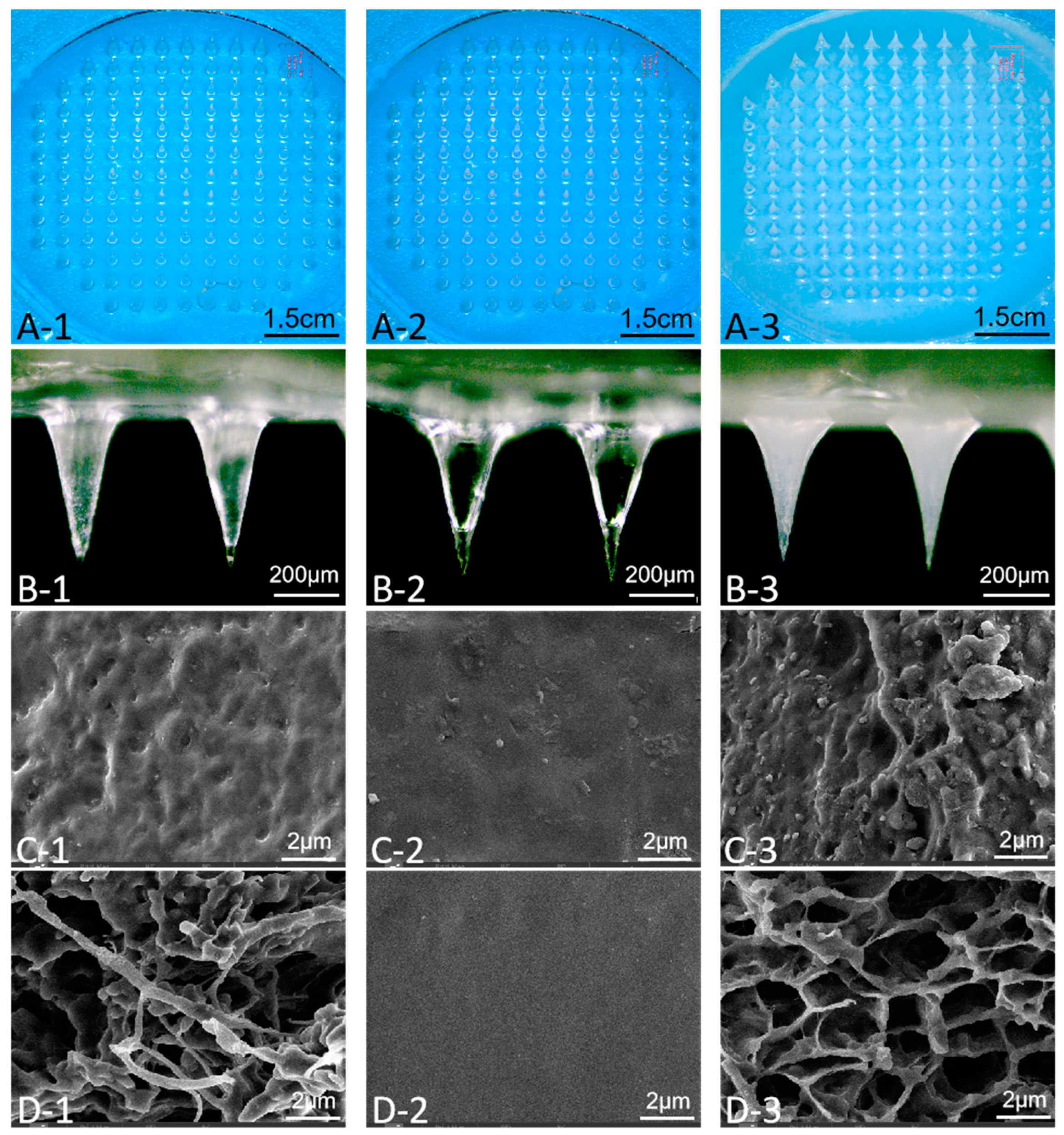
3.1. Determination of AP-MN Formulation
3.2. Determination of Addition Amount of MN Solution
3.3. Three-Dimensional Network Structure Characterization of AP-MNs
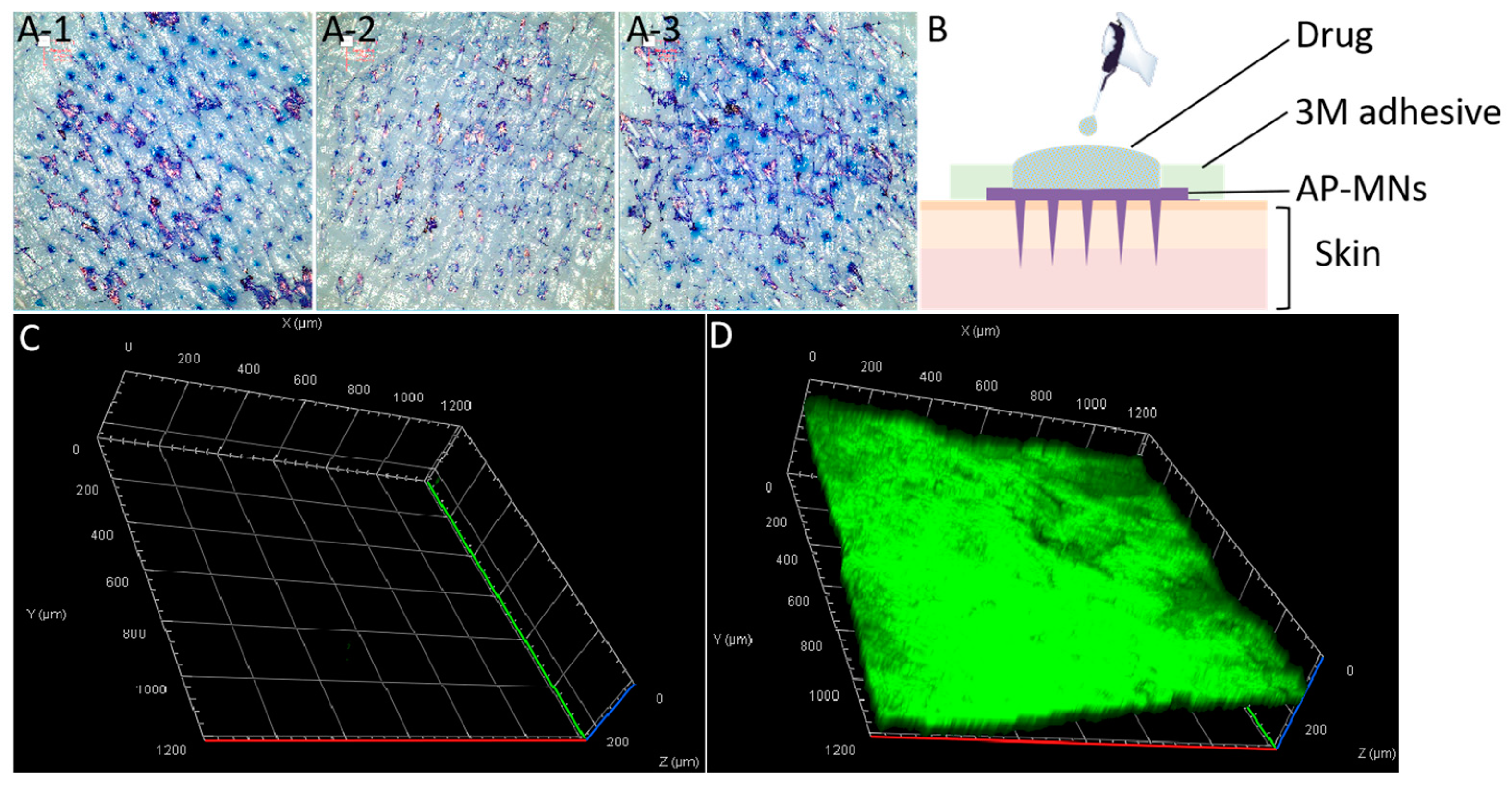
3.4. Permeability and Safety of AP-MNs
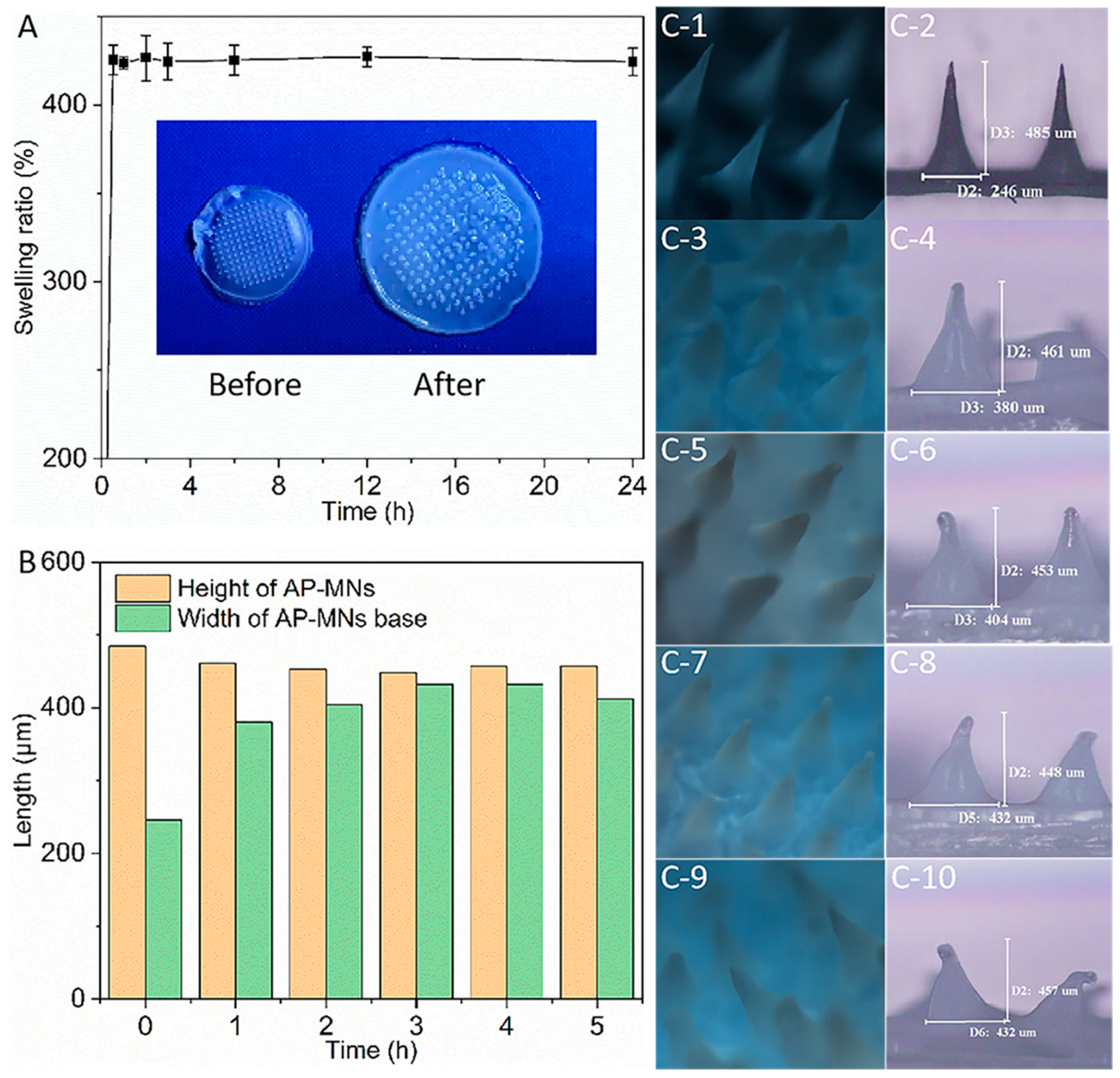
3.5. Swelling Characterization of AP-MNs
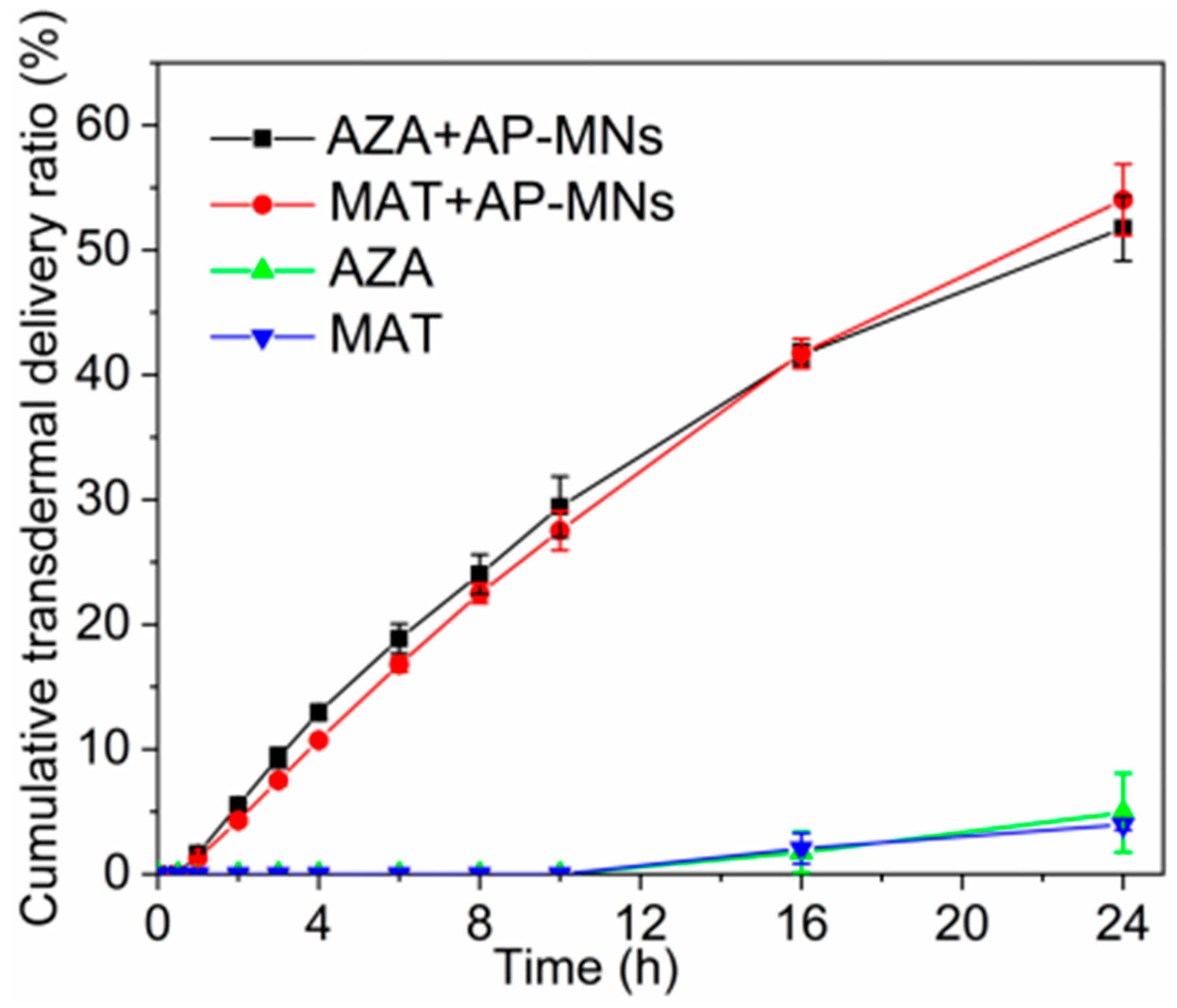
3.6. In Vitro Transdermal Permeation Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkilani, A.Z.; Nasereddin, J.; Hamed, R.; Nimrawi, S.; Hussein, G.; Abo-Zour, H.; Donnelly, R.F. Beneath the Skin: A Review of Current Trends and Future Prospects of Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, B.R.; Xing, M.Z.; Meng, F.D.; Zhang, S.H.; Yang, G.Z.; Cheng, A.G.; Yan, C.X.; Xu, B.; Gao, Y.H. Thermal stability of exenatide encapsulated in stratified dissolving microneedles during storage. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 636, 122863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.B.; Li, L.; Wu, S.S.; Yuan, X.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, X.; Guo, M.L. 3D-printed microneedle arrays for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 350, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, K.; Singh, T.; Dang, S. Advances in microneedle-based transdermal delivery for drugs and peptides. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Chew, S.W.T.; Zheng, M.J.; Lio, D.C.S.; Wiraja, C.; Mei, Y.; Ning, X.Y.; Cui, M.Y.; Than, A.; Shi, P.; et al. Cryomicroneedles for transdermal cell delivery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, D.D.; Chen, B.Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Guo, X.D. Insulin delivery systems combined with microneedle technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pireddu, R.; Schlich, M.; Marceddu, S.; Valenti, D.; Pini, E.; Fadda, A.M.; Lai, F.; Sinico, C. Nanosuspensions and Microneedles Roller as a Combined Approach to Enhance Diclofenac Topical Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbaan, F.J.; Bal, S.M.; van den Berg, D.J.; Dijksman, J.A.; van Hecke, M.; Verpoorten, H.; van den Berg, A.; Luttge, R.; Bouwstra, J.A. Improved piercing of microneedle arrays in dermatomed human skin by an impact insertion method. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.E.; Li, Y.S.; Pang, W.L.; Xue, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Jiang, C.P.; Shen, C.Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L. Preparation, characterisation and comparison of glabridin-loaded hydrogel-forming microneedles by chemical and physical cross-linking. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 617, 121612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ita, K. Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles-Potential and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjani, Q.K.; Permana, A.D.; Carcamo-Martinez, A.; Dominguez-Robles, J.; Tekko, I.A.; Larraneta, E.; Vora, L.K.; Ramadon, D.; Donnelly, R.F. Versatility of hydrogel-forming microneedles in in vitro transdermal delivery of tuberculosis drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 158, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Xing, M.Z.; Zhang, S.H.; Yang, G.Z.; Gao, Y.H. Process optimization of Ca2+ cross-linked alginate-based swellable microneedles for enhanced transdermal permeability: More applicable to acidic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 618, 121669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; White, L.R.; Estrela, P.; Leese, H.S. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles: Current Advancements and Future Trends. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2000307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, A.; Banga, A.K. Novel in situ forming hydrogel microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Garland, M.J.; Migalska, K.; Majithiya, R.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kole, P.L.; Mahmood, T.M.T.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Alkilani, A.Z.; Larraneta, E.; McAlister, E.; Courtenay, A.J.; Kearney, M.C.; Singh, T.R.R.; McCarthy, H.O.; Kett, V.L.; et al. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles Prepared from “Super Swelling” Polymers Combined with Lyophilised Wafers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, S.A.H.; Anjani, Q.K.; Utomo, E.; Ripolin, A.; Donnelly, R.F. Development and characterization of a dry reservoir-hydrogel-forming microneedles composite for minimally invasive delivery of cefazolin. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 617, 121593. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, A.Y.R.; Hasir, N.A.; Imran, N.B.P.; Hamdan, M.F.; Mahfufah, U.; Wafiah, N.; Arjuna, A.; Utami, R.N.; Permana, A.D. Development of hydrogel-forming microneedles for transdermal delivery of albendazole from liquid reservoir. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2022, 34, 1101–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.N.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Patrojanasophon, P.; Pamornpathomkul, B.; Opanasopit, P. Fabrication, characterization and comparison of alpha-arbutin loaded dissolving and hydrogel forming microneedles. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elim, D.; Fitri, A.M.N.; Mahfud, M.A.S.b.; Afika, N.; Sultan, N.A.F.; Hijrah; Asri, R.M.; Permana, A.D. Hydrogel forming microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of sildenafil citrate from polyethylene glycol reservoir: An ex vivo proof of concept study. Colloids Surf. B 2023, 222, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Z.; He, M.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Wu, M.; Gao, Y.H. An acryl resin-based swellable microneedles for controlled release intradermal delivery of granisetron. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, S.; Szeimies, R.M.; Lee, G. Self-adhesive thin films for topical delivery of 5-aminolevulinic acid. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 53, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.Q.; Yao, J.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Huang, S.P. Research Progress in Pharmaceutical Acrylic Acid Resin Film-coating Materials. Mater. Rev. 2007, 21, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Mooranian, A.; Ionescu, C.M.; Walker, D.; Jones, M.; Wagle, S.R.; Kovacevic, B.; Chester, J.; Foster, T.; Johnston, E.; Kuthubutheen, J.; et al. Single-Cellular Biological Effects of Cholesterol-Catabolic Bile Acid-Based Nano/Micro Capsules as Anti-Inflammatory Cell Protective Systems. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fang, H.H.; Gui, S.Y.; Huang, Y.Z. Solid dispersion-based pellet for colon delivery of tacrolimus through time- and pH-dependent layer coating: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo studies. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 55, e17309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitri, A.M.N.; Elim, D.; Mahfud, M.A.S.; Sultan, N.A.F.; Saputra, M.D.; Afika, N.; Friandini, R.A.; Djide, N.J.N.; Permana, A.D. Polymeric hydrogel forming microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of sildenafil citrate from direct-compressed tablet reservoir for potential improvement of pulmonary hypertension therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekko, I.A.; Chen, G.Y.; Dominguez-Robles, J.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Hamdan, I.M.N.; Vora, L.; Larraneta, E.; McElnay, J.C.; McCarthy, H.O.; Rooney, M.; et al. Development and characterisation of novel poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)-based hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays for enhanced and sustained transdermal delivery of methotrexate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.X.; Wu, F.; Liu, J.G.; Fan, G.R.; Welsh, W.; Zhu, H.; Jin, T. Phase-Transition Microneedle Patches for Efficient and Accurate Transdermal Delivery of Insulin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4633–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Wang, B.B.; Li, W.X.; Fei, W.M.; Cui, Y.; Guo, X.D. In vivo safety assessment, biodistribution and toxicology of polyvinyl alcohol microneedles with 160-day uninterruptedly applications in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 160, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, B.L.; Chen, B.Z.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Fei, W.M.; Cui, Y.; Guo, X.D. Dissolving microneedle rollers for rapid transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.Z.; Yang, G.Z.; Zhang, S.H.; Gao, Y.H. Acid-base combination principles for preparation of anti-acne dissolving microneedles loaded with azelaic acid and matrine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 165, 105935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.Z.; Zhang, S.H.; Ma, Y.N.; Chen, Y.Z.; Yang, G.Z.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Gao, Y.H. Preparation and evaluation of dissolving microneedle loaded with azelaic acid for acne vulgaris therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.S.; Zhao, D.R.; Sun, J.Y.; Luo, X.L.; Li, H.H.; Sun, X.T.; Zheng, F.P. Analysis of antioxidant effect of two tripeptides isolated from fermented grains (Jiupei) and the antioxidative interaction with 4-methylguaiacol, 4-ethylguaiacol, and vanillin. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2391–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.S.; Xing, M.Z.; Kang, Q.; Sun, J.Y.; Zeng, X.A.; Gao, W.H.; Li, H.H.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, A.J. Pulse electric field assisted process for extraction of Jiuzao glutelin extract and its physicochemical properties and biological activities investigation. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunter, D.J.; Daniels, R. New film forming emulsions containing Eudragit (R) NE and/or RS 30D for sustained dermal delivery of nonivamide. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dathathri, E.; Lal, S.; Mittal, M.; Thakur, G.; De, S. Fabrication of low-cost composite polymer-based micro needle patch for transdermal drug delivery. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ma, J.G.; Liu, Z.J.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Qian, S.S.; Chen, L.J.; Gu, L.Y.; Sun, C.Q.; Hou, J.C.; et al. Preparation of shell-core fiber-encapsulated Lactobacillus rhamnosus 1.0320 using coaxial electrospinning. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junlapong, K.; Boonsuk, P.; Chaibundit, C.; Chantarak, S. Highly water resistant cassava starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.Y.; Wu, Z.Z.; Chen, L.Z.; Wu, F.; Wei, L.M.; Yuan, W.E. Hydrogel Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nanomicro Lett. 2014, 6, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfud, M.A.S.; Fitri, A.M.N.; Elim, D.; Sultan, N.A.F.; Saputra, M.D.; Afika, N.; Friandini, R.A.; Himawan, A.; Rahman, L.; Permana, A.D. Combination of synthetic and natural polymers on the characteristics and evaluation of transdermal hydrogel-forming microneedles preparations integrated with direct compressed tablets reservoir sildenafil citrate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 85, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.J.; He, Y.F.; Jin, X.X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, Y.B.; Xu, M.M.; Liu, K.Y.; Yao, Y.; Lu, F. Light-regulated nitric oxide release from hydrogel-forming microneedles integrated with graphene oxide for biofilm-infected-wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, Y.A.; Tekko, I.A.; Vora, L.K.; Peng, K.; Anjani, Q.K.; Greer, B.; Elliott, C.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Hydrogel-forming microarray patches with solid dispersion reservoirs for transdermal long-acting microdepot delivery of a hydrophobic drug. J. Control. Release 2023, 356, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, A.R.J.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Larraneta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Influence of molecular weight on transdermal delivery of model macromolecules using hydrogel-forming microneedles: Potential to enhance the administration of novel low molecular weight biotherapeutics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 4202–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.C.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.R.; Cheng, A.G.; Zhang, S.H.; Gao, Y.H. Novel dissolving microneedles preparation for synergistic melasma therapy: Combined effects of tranexamic acid and licorice extract. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Q.; Gao, Y.H.; Hu, K.J.; Li, F. Enhancement of Skin Permeation of Docetaxel: A Novel Approach Combining Microneedle and Elastic Liposomes. J. Control. Release 2008, 129, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Hu, H.M.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.H.; Wu, T.; Feng, N.P. Improved Biosafety and Transdermal Delivery of Aconitine via Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether-Mediated Microemulsion Assisted with Microneedles. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Yang, G.Z.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Gao, Y.H. Exploring Trehalose on the Release of Levonorgestrel from Implantable PLGA Microneedles. Polymer 2020, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedle patch tattoos. Iscience 2022, 25, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, M.; Ma, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, C.; Peng, X.; Ma, Y.; Liang, B.; Gao, Y.; Wu, J. Preparation and Evaluation of Auxiliary Permeable Microneedle Patch Composed of Polyvinyl Alcohol and Eudragit NM30D Aqueous Dispersion. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072007
Xing M, Ma Y, Wei X, Chen C, Peng X, Ma Y, Liang B, Gao Y, Wu J. Preparation and Evaluation of Auxiliary Permeable Microneedle Patch Composed of Polyvinyl Alcohol and Eudragit NM30D Aqueous Dispersion. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072007
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Mengzhen, Yuning Ma, Xiaocen Wei, Chen Chen, Xueli Peng, Yuxia Ma, Bingwen Liang, Yunhua Gao, and Jibiao Wu. 2023. "Preparation and Evaluation of Auxiliary Permeable Microneedle Patch Composed of Polyvinyl Alcohol and Eudragit NM30D Aqueous Dispersion" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 7: 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072007
APA StyleXing, M., Ma, Y., Wei, X., Chen, C., Peng, X., Ma, Y., Liang, B., Gao, Y., & Wu, J. (2023). Preparation and Evaluation of Auxiliary Permeable Microneedle Patch Composed of Polyvinyl Alcohol and Eudragit NM30D Aqueous Dispersion. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072007





