Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3. Dynamic Vapor Sorption (DVS)
2.4. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) and Raman Spectroscopy
2.6. In Vitro Non-Sink Dissolution Test
2.7. Preparation of Bisacodyl Containing Solid Dispersion Using the Hot-Melt Extrusion Process
2.8. Preparation of Enteric-Coated Tablet Containing Bisacodyl Amorphous Solid Dispersion
2.9. In Vitro Dissolution Test of Enteric-Coated Tablet
2.10. In Vivo Efficacy in Constipation-Induced Rabbits
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pre-Formulation Strategies for Evaluation of Drug–Polymer Miscibility and Interaction
3.1.1. Calculation of Hansen Solubility Parameter
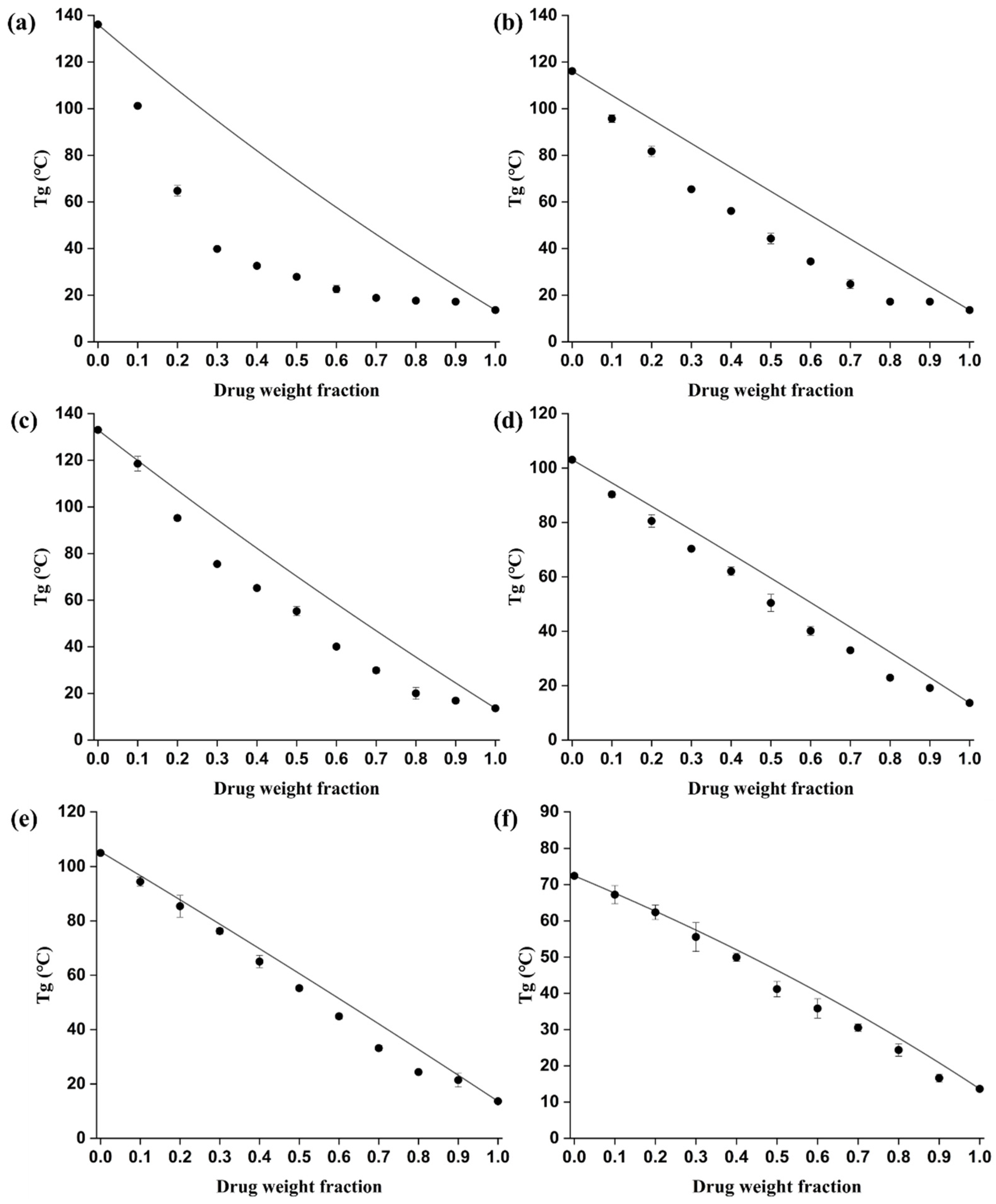
3.1.2. Comparison of Theoretical and Experimental Glass Transition Temperatures
3.2. Characterization of the Solid Dispersion Prepared by Hot-Melt Extrusion
3.2.1. PXRD Analysis
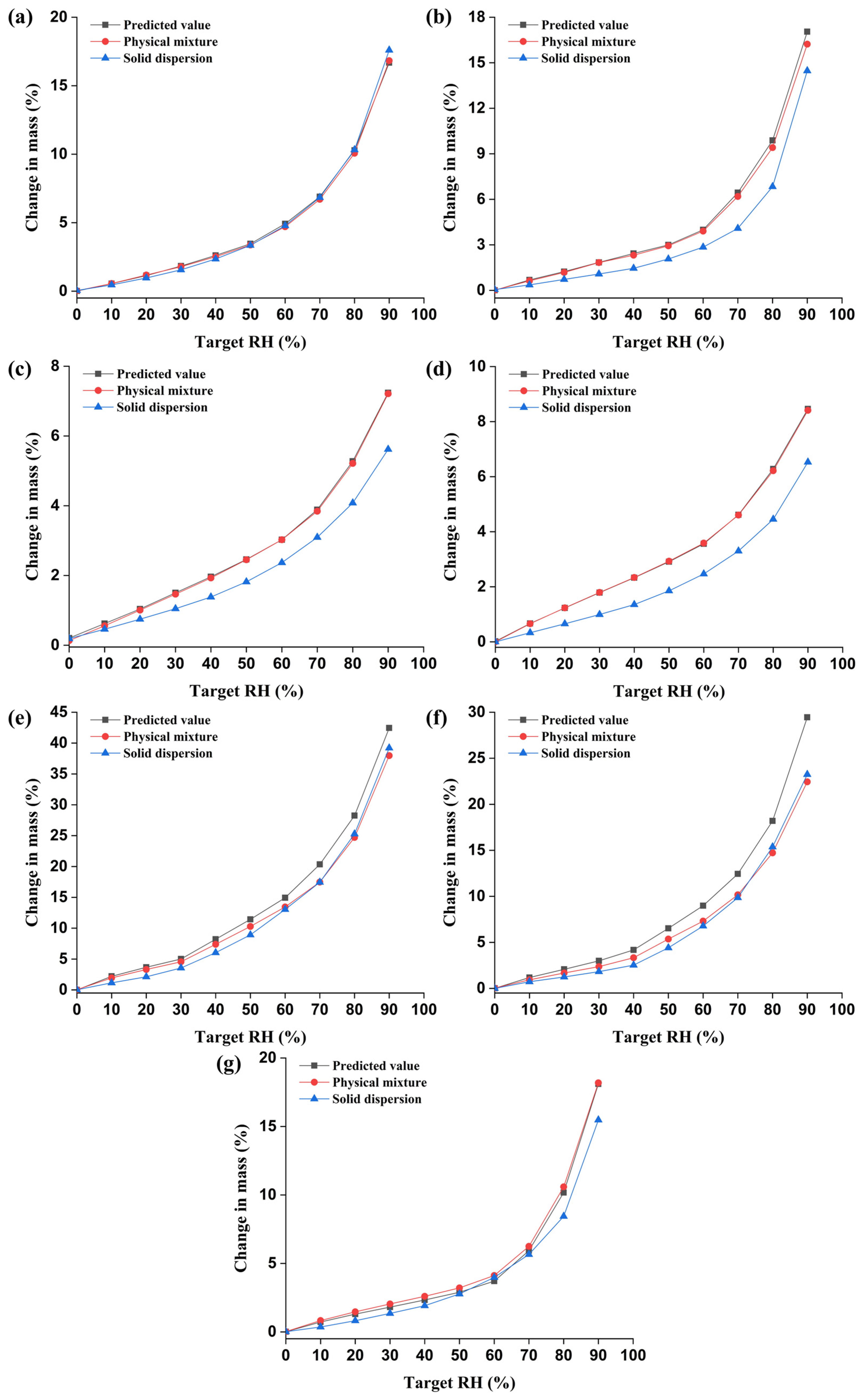
3.2.2. DVS Analysis
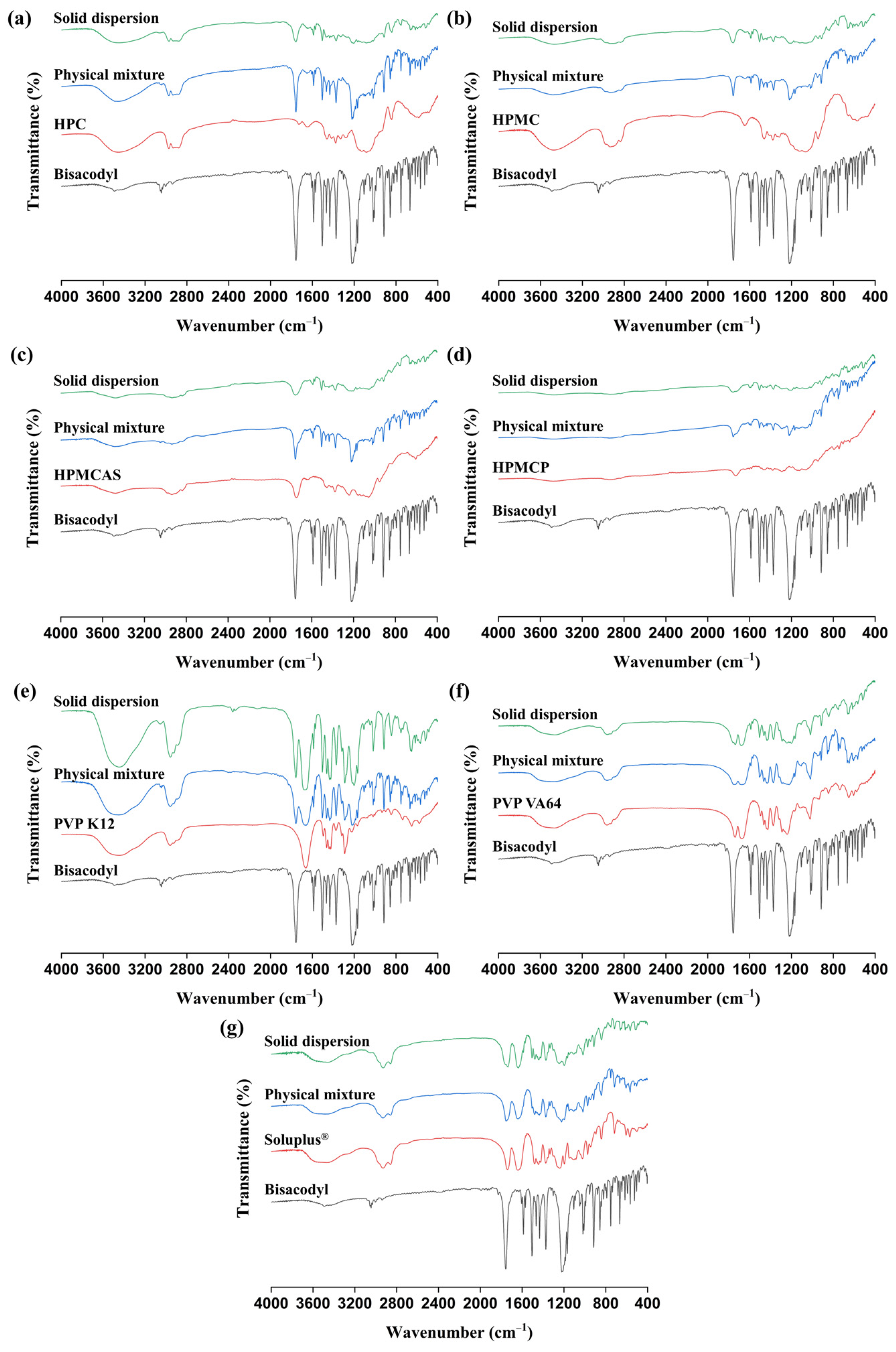
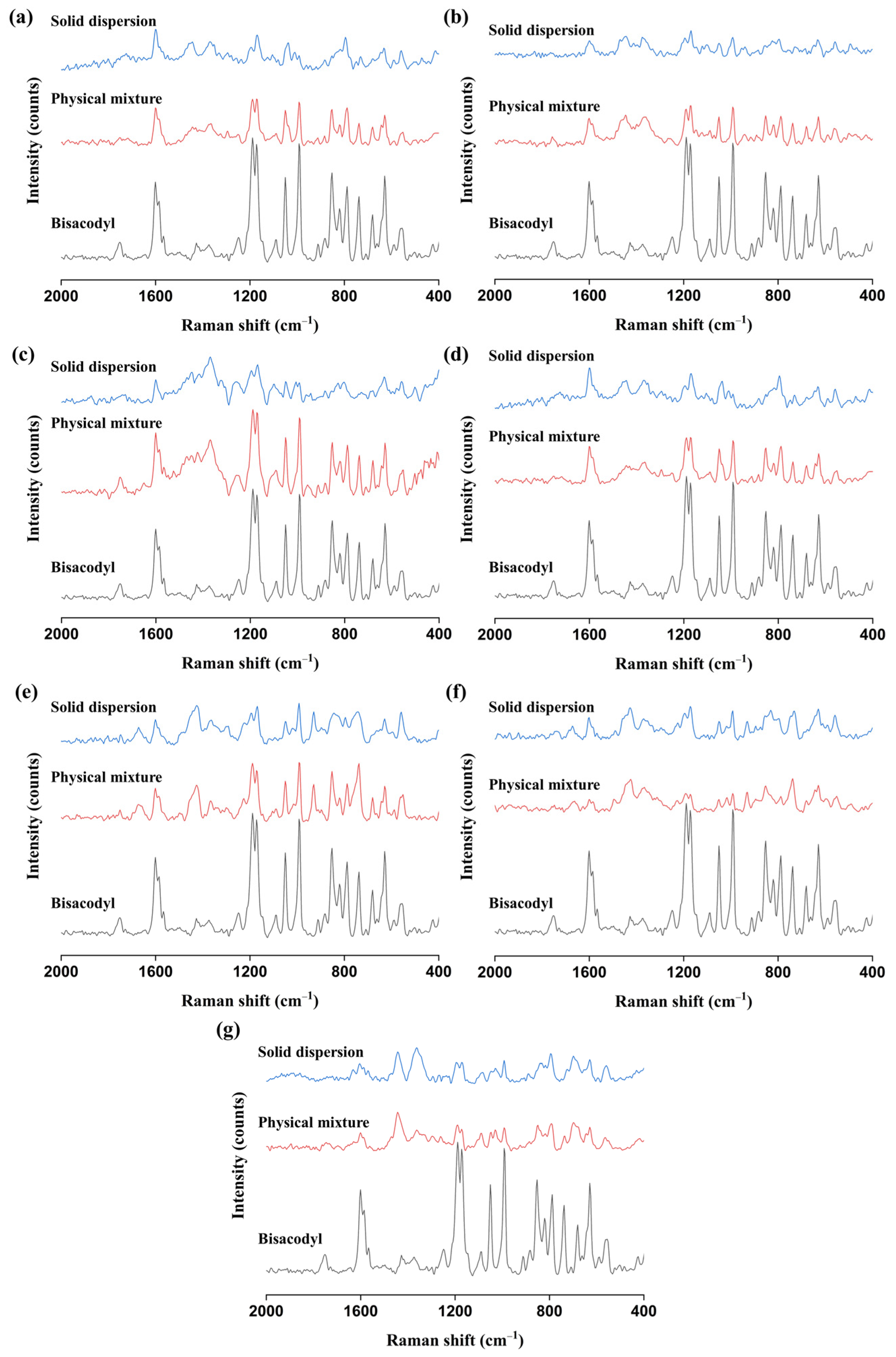
3.2.3. FT-IR and Raman Analyses
3.3. A Summary of the Assessment of Miscibility and Molecular Interaction
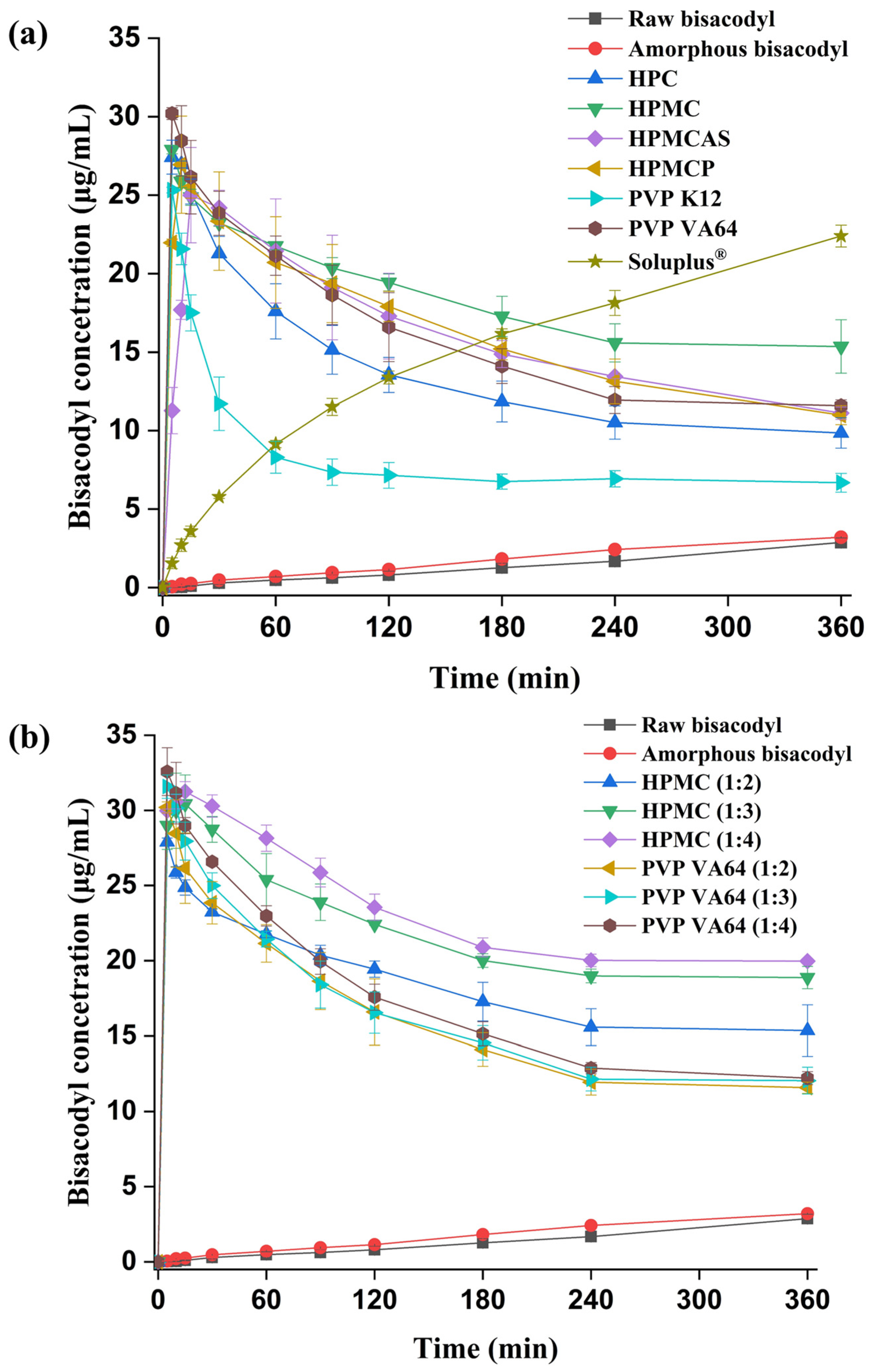
3.4. Non-Sink Dissolution Test
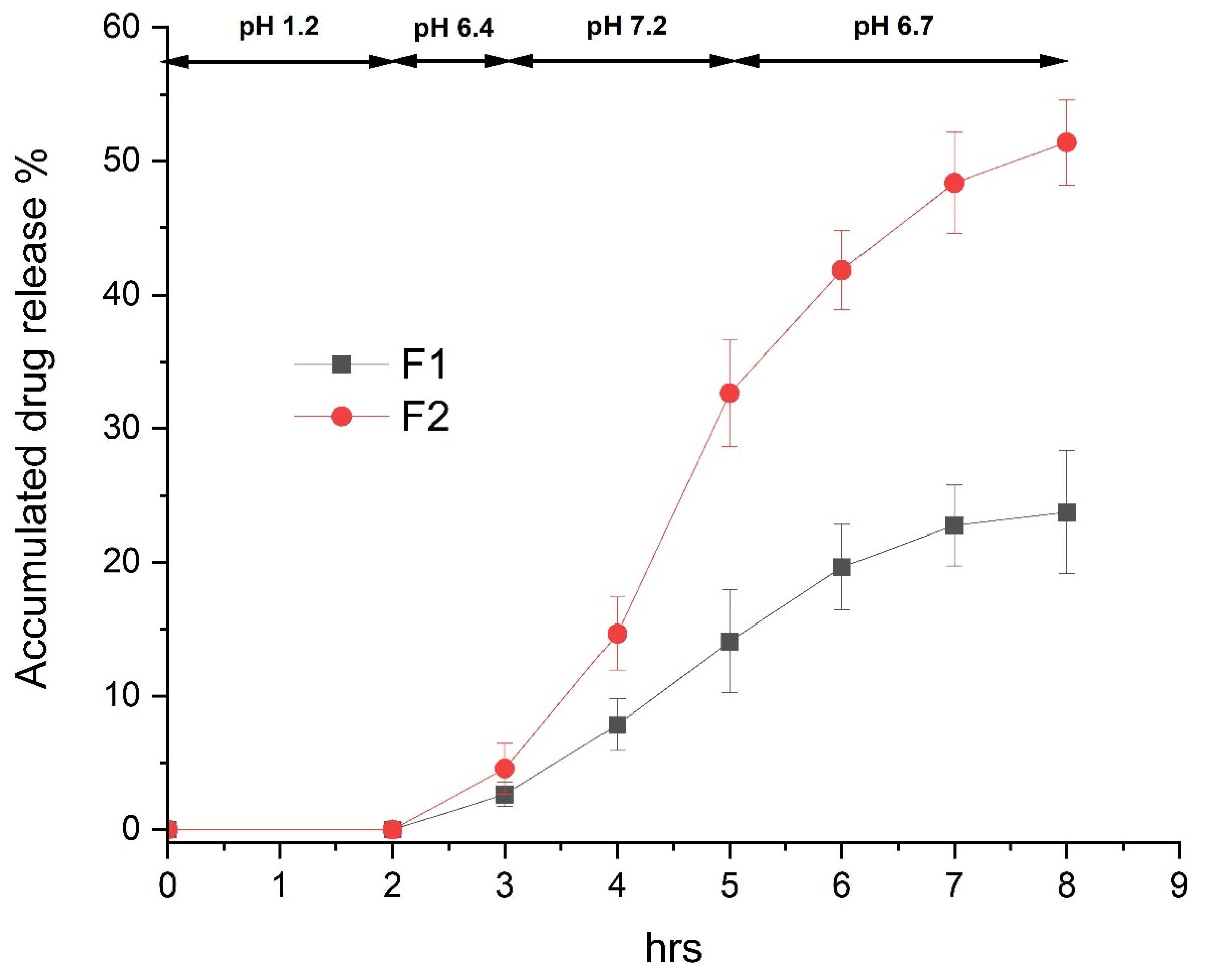
3.5. In Vitro Dissolution Test of Enteric-Coated Tablet Containing Bisacodyl Solid Dispersions
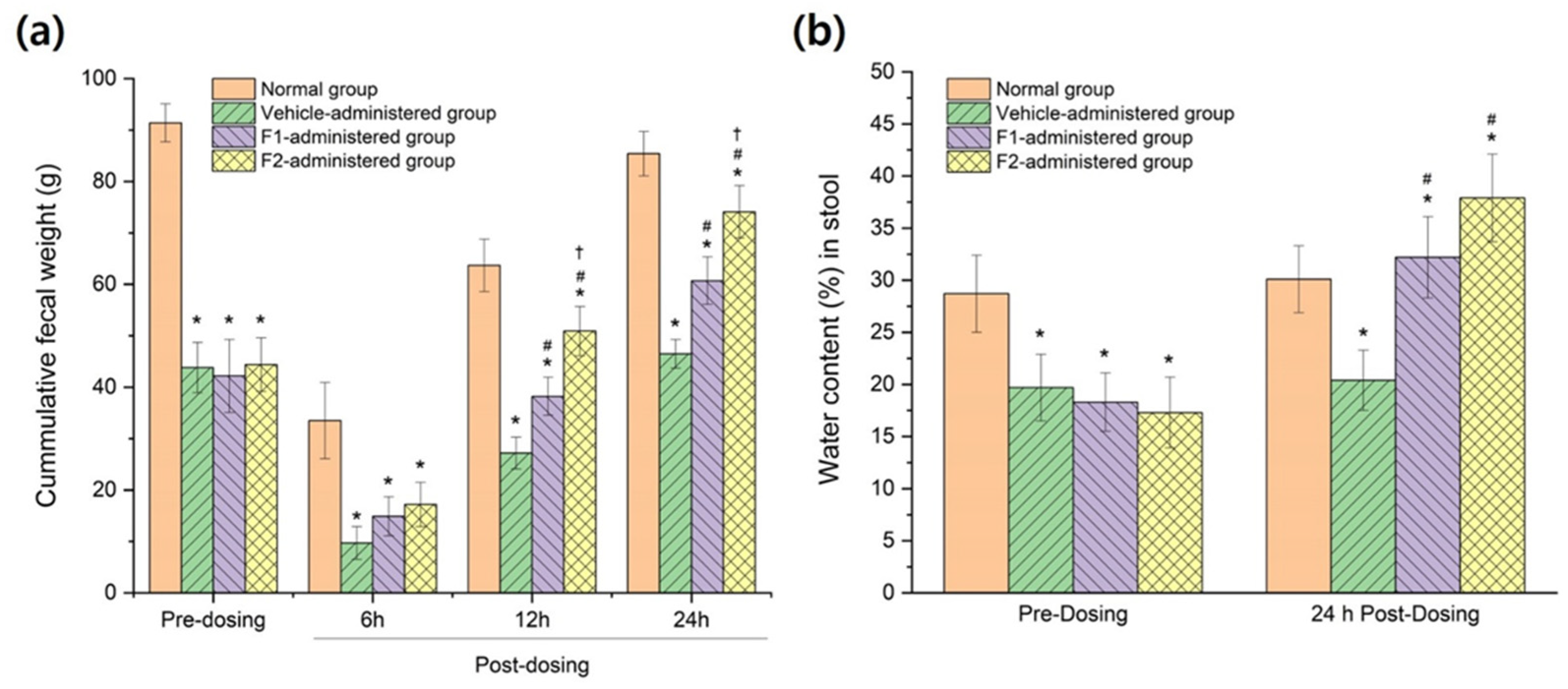
3.6. In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy in Constipation-Induced Rabbits
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, E.S.; Kim, J.S.; Baek, I.H.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, M.S. Enhancement of dissolution and bioavailability of ezetimibe by amorphous solid dispersion nanoparticles fabricated using supercritical antisolvent process. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 45, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.A.; Oh, H.K.; Lee, J.C.; Choi, Y.H.; Jeong, S.H. Comparison of solubility enhancement by solid dispersion and micronized butein and its correlation with in vivo study. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, H.; Kang, K.T.; Ha, E.S.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, S.J. Micronization of a poorly water-soluble drug, fenofibrate, via supercritical-fluid-assisted spray-drying. J. Pharm. Investig. 2022, 52, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhai, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Li, H. Effect of preparation processes and structural insight into the supermolecular system: Bisacodyl and β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Seo, H.J.; Hong, S.H.; Ha, E.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.S.; Baek, I.H.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, S.J. Characterization and therapeutic efficacy evaluation of glimepiride and L-arginine co-amorphous formulation prepared by supercritical antisolvent process: Influence of molar ratio and preparation methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Seo, H.J.; Ha, E.S.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, S.J. Preparation and characterization of glimepiride eutectic mixture with L-arginine for improvement of dissolution rate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dai, W.G. Fundamental aspects of solid dispersion technology for poorly soluble drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, R.; Gigliobianco, M.R.; Casadidio, C.; Martino, P.D. Hot melt extrusion: Highlighting physicochemical factors to be investigated while designing and optimizing a hot melt extrusion process. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, R.; Thakkar, R.; Pillai, A.; Ashour, E.A.; Repka, M.A. Systematic screening of pharmaceutical polymers for hot melt extrusion processing: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.F.; Pereira, A.; Cardoso, S.; Cadonau, S.; Werner, K.; Pinto, R.M.A.; Simões, S. Five-stage approach for a systematic screening and development of etravirine amorphous solid dispersions by hot-melt extrusion. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseson, D.E.; Taylor, L.S. The application of temperature-composition phase diagrams for hot melt extrusion processing of amorphous solid dispersions to prevent residual crystallinity. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.; Nyavanandi, D.; Mandati, P.; Youssef, A.A.A.; Narala, S.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M. A systematic and robust assessment of hot-melt extrusion-based amorphous solid dispersions: Theoretical prediction to practical implementation. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 121951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.F.; Pinto, R.M.A.; Simões, S. Hot-melt extrusion in the pharmaceutical industry: Toward filing a new drug application. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1749–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Jung, H.J.; Ho, M.J.; Lee, D.R.; Cho, H.R.; Choi, Y.S.; Jun, J.; Son, M.; Kang, M.J. Colon-targeted delivery of solubilized bisacodyl by doubly enteric-coated multiple-unit tablet. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 102, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Sim, W.Y.; Ha, E.S.; Park, H.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, M.S. Solubility of bisacodyl in fourteen mono solvents and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone + water mixed solvents at different temperatures, and its application for nanosuspension formation using liquid antisolvent precipitation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.M.; Dudhedia, M.S.; Zimny, E. Hot melt extrusion: Development of an amorphous solid dispersion for an insoluble drug from mini-scale to clinical scale. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitak, T.; Dumičić, A.; Planinšek, O.; Šibanc, R.; Srčič, S. Determination of solubility parameters of ibuprofen and ibuprofen lysinate. Molecules 2015, 20, 21549–21568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; He, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Sha, J.; Li, T.; Ren, B. Solubility, thermodynamic modeling and Hansen solubility parameter of 5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboximide in three binary solvents (methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate + DMF) from 278.15 K to 323.15 K. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 300, 112097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penumetcha, S.S.; Gutta, L.N.; Dhanala, H.; Yamili, S.; Challa, S.; Rudraraju, S.; Rudraraju, S.; Rudraraju, V. Hot melt extruded Aprepitant–Soluplus solid dispersion: Preformulation considerations, stability and in vitro study. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, J.; Lebrun, P.; Vinassa, C.; Adam, M.; Netchacovitch, L.; Ziemons, E.; Hubert, P.; Krier, F.; Evrard, B. Continuous production of itraconazole-based solid dispersions by hot melt extrusion: Preformulation, optimization and design space determination. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, S.; Thakral, N.K. Prediction of drug–polymer miscibility through the use of solubility parameter based Flory–Huggins interaction parameter and the experimental validation: PEG as model polymer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Mooter, G.; Wuyts, M.; Blaton, N.; Busson, N.; Grobet, P.; Augustijns, P.; Kinget, R. Physical stabilisation of amorphous ketoconazole in solid dispersions with polyvinylpyrrolidone K25. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshahrani, S.M.; Lu, W.; Park, J.B.; Morott, J.T.; Alsulays, B.B.; Majumdar, S.; Langley, N.; Kolter, K.; Gryczke, A.; Repka, M.A. Stability-enhanced hot-melt extruded amorphous solid dispersions via combinations of Soluplus® and HPMCAS-HF. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallakunta, V.R.; Sarabu, S.; Bandari, S.; Batra, A.; Bi, V.; Durig, T.; Repka, M.A. Stable amorphous solid dispersions of fenofibrate using hot melt extrusion technology: Effect of formulation and process parameters for a low glass transition temperature drug. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khougaz, K.; Clas, S.D. Crystallization inhibition in solid dispersions of MK-0591 and poly(vinylpyrrolidone) polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarode, A.L.; Sandhu, H.; Shah, N.; Malick, W.; Zia, H. Hot melt extrusion (HME) for amorphous solid dispersions: Predictive tools for processing and impact of drug–polymer interactions on supersaturation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbert, C.; Stoyanov, E.; Sadowski, G. Phase behavior of ASDs based on hydroxypropyl cellulose. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöstges, F.; Kayser, K.; Stoyanov, E.; Wagner, K.H. Boost of solubility and supersaturation of celecoxib via synergistic interactions of methacrylic acid-ethyl acrylate copolymer (1:1) and hydroxypropyl cellulose in ternary amorphous solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. X 2022, 4, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamweya, N.; Hoag, S.W. Assessment of polymer-polymer interactions in blends of HPMC and film forming polymers by modulated temperature differential scanning calorimetry. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeras, I.M. A novel approach for analyzing glass-transition temperature vs. composition patterns: Application to pharmaceutical compound + polymer systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 42, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, K.; Berghmans, H.; Leuner, C.; Dressman, J.; Werde, K.V.; Mullens, J.; Benoist, L.; Thimon, M.; Meublat, L.; Verreck, G.; et al. Characterization of solid dispersions of itraconazole and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose prepared by melt extrusion, Part II. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, P.D.; Joiris, E.; Gobetto, R.; Masic, A.; Palmieri, G.F.; Martelli, S. Ketoprofen-poly(vinylpyrrolidone) physical interaction. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 265, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, M.F.; Zhao, M.; Pinto, J.F.; Sousa, J.J.; Craig, D.Q.M. The influence of drug physical state on the dissolution enhancement of solid dispersions prepared via hot-melt extrusion: A case study using olanzapine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNunzio, J.C.; Brough, C.; Hughey, J.R.; Miller, D.A.; Williams, R.O.; McGinity, J.W. Fusion production of solid dispersions containing a heat-sensitive active ingredient by hot melt extrusion and Kinetisol® dispersing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, F.; Kang, A.; Shan, J.; Zhao, X.; Bi, X.; Li, J.; Di, L. Preparation of osthole-polymer solid dispersions by hot-melt extrusion for dissolution and bioavailability enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Buckton, G. Using DVS-NIR to assess the water sorption behaviour and stability of a griseofulvin/PVP K30 solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Theoretical and experimental investigation of drug-polymer interaction and miscibility and its impact on drug supersaturation in aqueous medium. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 107, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punčochová, K.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Beránek, J.; Štepánek, F. Investigation of drug–polymer interaction in solid dispersions by vapour sorption methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.G.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Moisture sorption by polymeric excipients commonly used in amorphous solid dispersion and its effect on glass transition temperature: I. Polyvinylpyrrolidone and related copolymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 616, 121532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsmann, S.; Backensfeld, T.; Bodmeier, R. Stability of extruded 17β-estradiol solid dispersions. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2001, 6, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Lamare, I.; Tiwari, N.K.; Ravi, P.R.; Pillai, R. In situ salification in polar solvents: A paradigm for enabling drug delivery of weakly ionic drugs as amorphous solid dispersion. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Démuth, B.; Farkas, A.; Szabó, B.; Balogh, A.; Nagy, B.; Vágó, E.; Vigh, T.; Tinke, A.P.; Kazsu, Z.; Demeter, Á.; et al. Development and tableting of directly compressible powder from electrospun nanofibrous amorphous solid dispersion. Adv. Powder. Technol. 2017, 28, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesallati, H.; Umerska, A.; Paluch, K.J.; Tajber, L. Amorphous polymeric drug salts as ionic solid dispersion forms of ciprofloxacin. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2209–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Ha, E.S.; Kim, M.S. Physicochemical analysis techniques specialized in surface characterization of inhalable dry powders. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J.; Tang, P.; Wang, Q.; Wu, D.; Li, H. Investigations of bisacodyl with modified β-cyclodextrins: Characterization, molecular modeling, and effect of PEG. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Trivino, A.; Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H. Investigation and correlation of drug polymer miscibility and molecular interactions by various approaches for the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 71, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lu, F. Analysis of low active-pharmaceutical-ingredient signal drugs based on thin layer chromatography and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 131, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Qian, F. Improving oral bioavailability of sorafenib by optimizing the “Spring” and “Parachute” based on molecular interaction mechanisms. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punčochová, K.; Vukosavljevic, B.; Hanuš, J.; Beránek, J.; Windbergs, M.; Štepánek, F. Non-invasive insight into the release mechanisms of a poorly soluble drug from amorphous solid dispersions by confocal Raman microscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 101, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.Q.; Lai, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, Z.Q.; Qi, X.R. On the inherent properties of Soluplus and its application in ibuprofen solid dispersions generated by microwave-quench cooling technology. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, H.R.; Tawa, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ratanabanangkoon, P.; Shaw, P.; Gardner, C.R.; Chen, H.; Moreau, J.P.; Almarsson, Ö.; Remenar, J.F. Combined use of crystalline salt forms and precipitation inhibitors to improve oral absorption of celecoxib from solid oral formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2686–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, M.M.; Nguyen, J.H.; Becker, C.; Francke, N.M.; Jørgensen, E.B.; Holm, P.; Holm, R.; Mu, H.; Rades, T.; Langguth, P. Influence of polymer molecular weight on in vitro dissolution behavior and in vivo performance of celecoxib:PVP amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 101, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Han, J.; Jiang, A.; Huang, R.; Fu, T.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Li, W.; Li, J. Involvement of metabolism-permeability in enhancing the oral bioavailability of curcumin in excipient-free solid dispersions co-formed with piperine. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonzo, D.E.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Zhou, D.; Gao, Y.; Taylor, L.S. Understanding the behavior of amorphous pharmaceutical systems during dissolution. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Handa, T.; Alonzo, D.E.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of polymer type on the dissolution profile of amorphous solid dispersions containing felodipine. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.R.; Lakshman, Y.D.; Anand, V.S.K.; Sree, K.S.N.; Bhat, K.; Dengale, S.J. Overview of extensively employed polymeric carriers in solid dispersion technology. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters. A User’s Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 0849372488. [Google Scholar]

| Content | F1 (mg/Tablet) | F2 (mg/Tablet) |
|---|---|---|
| Tablet | ||
| Raw bisacodyl | 2.5 | |
| Hot-melt-extruded solid dispersions (Bisacodyl:HPMC = 1:4 w/w) | 12.5 | |
| Aerosil 200 | 10 | 10 |
| Avicel PH102 | 40 | 30 |
| HPC-EXF | 5 | 5 |
| Kollidon CL | 5 | 5 |
| Magnesium stearate | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| Enteric-coating layer | ||
| Eudragit L100 | 13.75 | 13.75 |
| Eudragit S100 | 13.75 | 13.75 |
| TEC | 2.25 | 2.25 |
| Talc | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| Total weight of enteric-coated tablet | 100 | 100 |
| Compound/Polymer | Solubility Parameter (MPa1/2) | ∆δ (MPa1/2) | Interaction Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bisacodyl | 26.2 | ||
| HPC | 22.4 | 3.8 | 1.29 |
| HPMC | 23.7 | 2.5 | 0.56 |
| HPMCAS | 29.1 | 2.9 | 0.75 |
| HPMCP | 22.4 | 3.8 | 1.29 |
| PVP K12 | 19.4 | 6.8 | 4.13 |
| PVP VA64 | 21.1 | 5.1 | 2.32 |
| Soluplus® | 23.4 | 2.8 | 0.70 |
| Bisacodyl (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPC (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPMC (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPMCAS (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPMCP (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–PVP K12 (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–PVP VA64 (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–Soluplus® (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1757 | 1760 | 1759 | 1754 | 1759 | 1757 | 1758 | 1759 | C=O group |
| 1506 | 1506 | 1507 | 1506 | 1507 | 1506 | 1506 | 1506 | Aromatic group |
| 1465 | - | - | - | - | 1465 | 1464 | 1461 | Aromatic group |
| 1431 | - | - | - | - | 1432 | 1435 | 1434 | Aromatic group |
| 1218 | - | - | - | - | 1218 | - | - | C−O group |
| 1208 | - | - | - | - | 1207 | - | - | C−O group |
| Bisacodyl (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPC (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPMC (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPMCAS (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–HPMCP (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–PVP K12 (cm−1) | Bisacodyl–PVP VA64 (cm−1) | Bisacodyl– Soluplus® (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1601 | 1601 | 1601 | 1601 | 1601 | 1601 | 1601 | 1603 | C=O group |
| 1189 | 1196 | 1196 | 1196 | 1196 | 1196 | 1196 | 1196 | C−O group |
| 1172 | 1169 | 1169 | 1169 | 1169 | 1169 | 1172 | 1172 | C−O group |
| Systems | Miscibility | Molecular Interaction | Stability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility Parameter | Deviation | DVS | FT-IR | Raman | DVS and PXRD | ||
| Bisacodyl–HPC | Miscible | - | - | No | Yes | Yes | Not stable |
| Bisacodyl–HPMC | Miscible | Miscible | Negative | Yes | Yes | Yes | Stable |
| Bisacodyl–HPMCAS | Miscible | Miscible | Negative | Yes | Yes | Yes | Stable |
| Bisacodyl–HPMCP | Miscible | Miscible | Negative | Yes | Yes | Yes | Stable |
| Bisacodyl–PVP K12 | Miscible | Miscible | Negative | Yes | No | Yes | Not stable |
| Bisacodyl–PVP VA64 | Miscible | Miscible | Negative | Yes | Yes | Yes | Not stable |
| Bisacodyl–Soluplus® | Miscible | Miscible | Negative | Yes | Yes | Yes | Stable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-K.; Ha, E.-S.; Park, H.; Kang, K.-T.; Jeong, J.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Baek, I.-h.; Kim, M.-S. Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122704
Lee S-K, Ha E-S, Park H, Kang K-T, Jeong J-S, Kim J-S, Baek I-h, Kim M-S. Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(12):2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122704
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seon-Kwang, Eun-Sol Ha, Heejun Park, Kyu-Tae Kang, Ji-Su Jeong, Jeong-Soo Kim, In-hwan Baek, and Min-Soo Kim. 2023. "Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 12: 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122704
APA StyleLee, S.-K., Ha, E.-S., Park, H., Kang, K.-T., Jeong, J.-S., Kim, J.-S., Baek, I.-h., & Kim, M.-S. (2023). Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy. Pharmaceutics, 15(12), 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122704








