Interplay of Extracellular Vesicles and TLR4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathophysiology and Therapeutics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epidemiology and Management
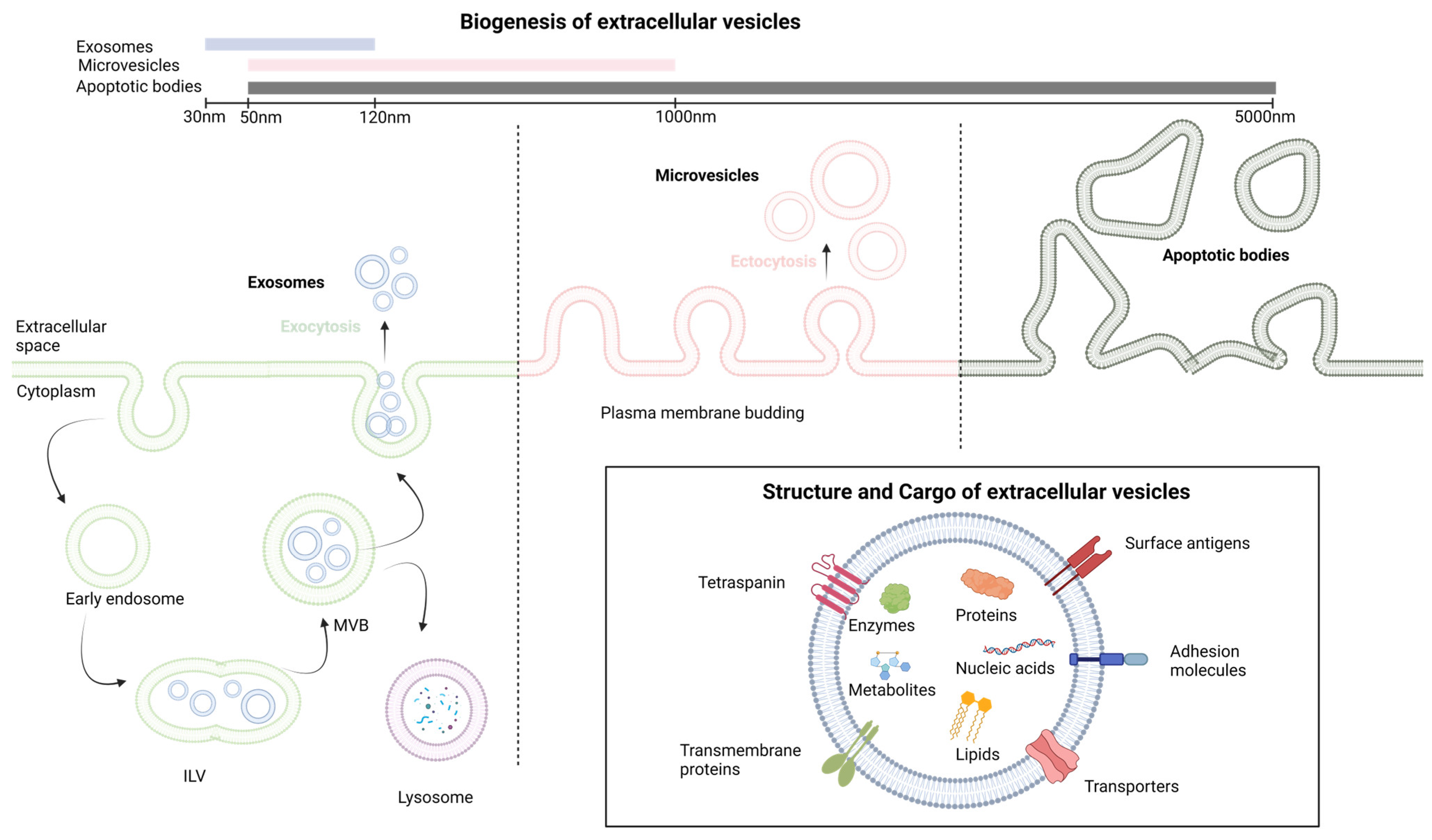
1.2. Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis and Functions
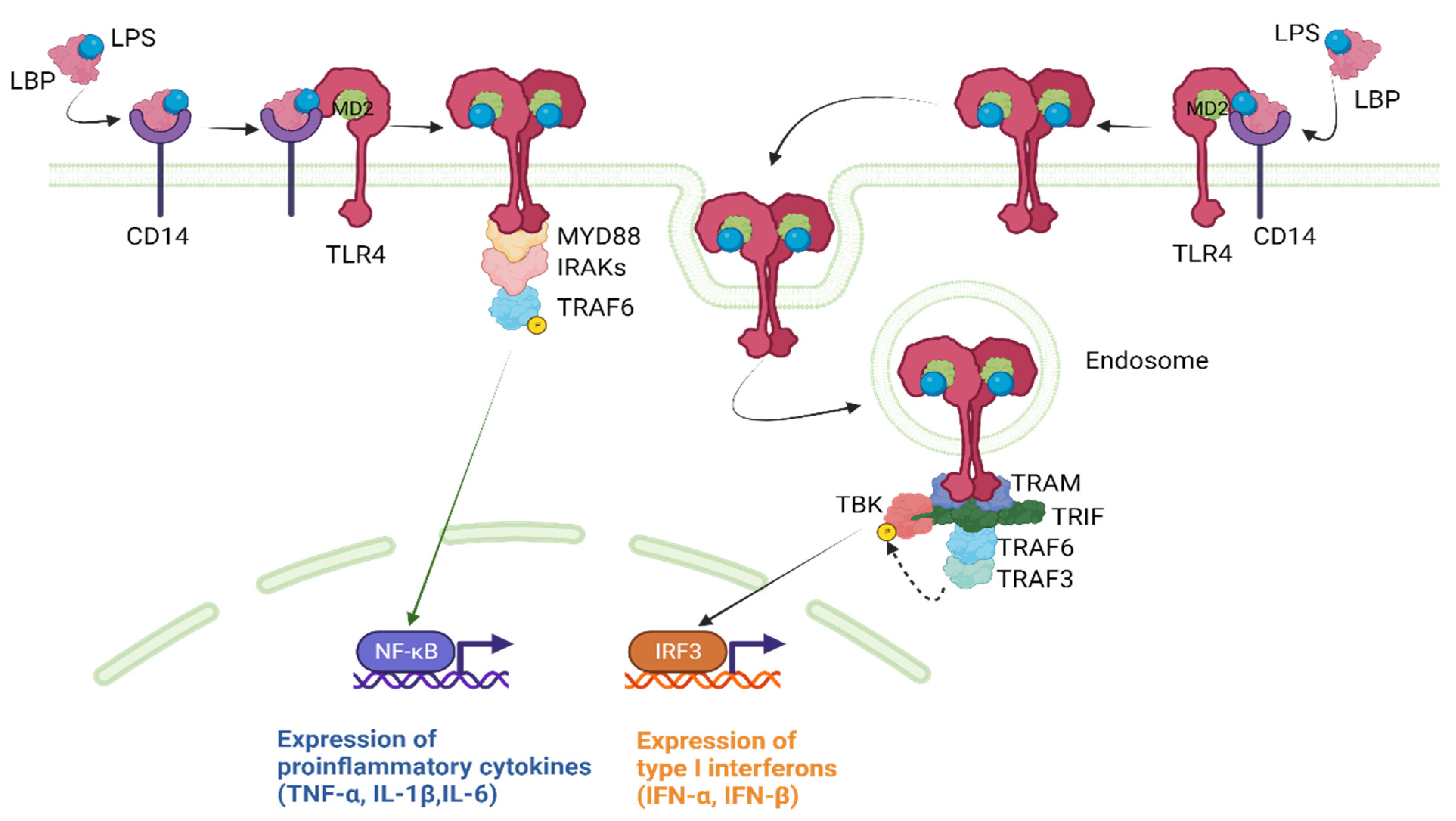
1.3. The Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathway
1.3.1. Ligand Recognition and TLR4 Activation
- The MyD88-Dependent Pathway:
- The MyD88-Independent Pathway:
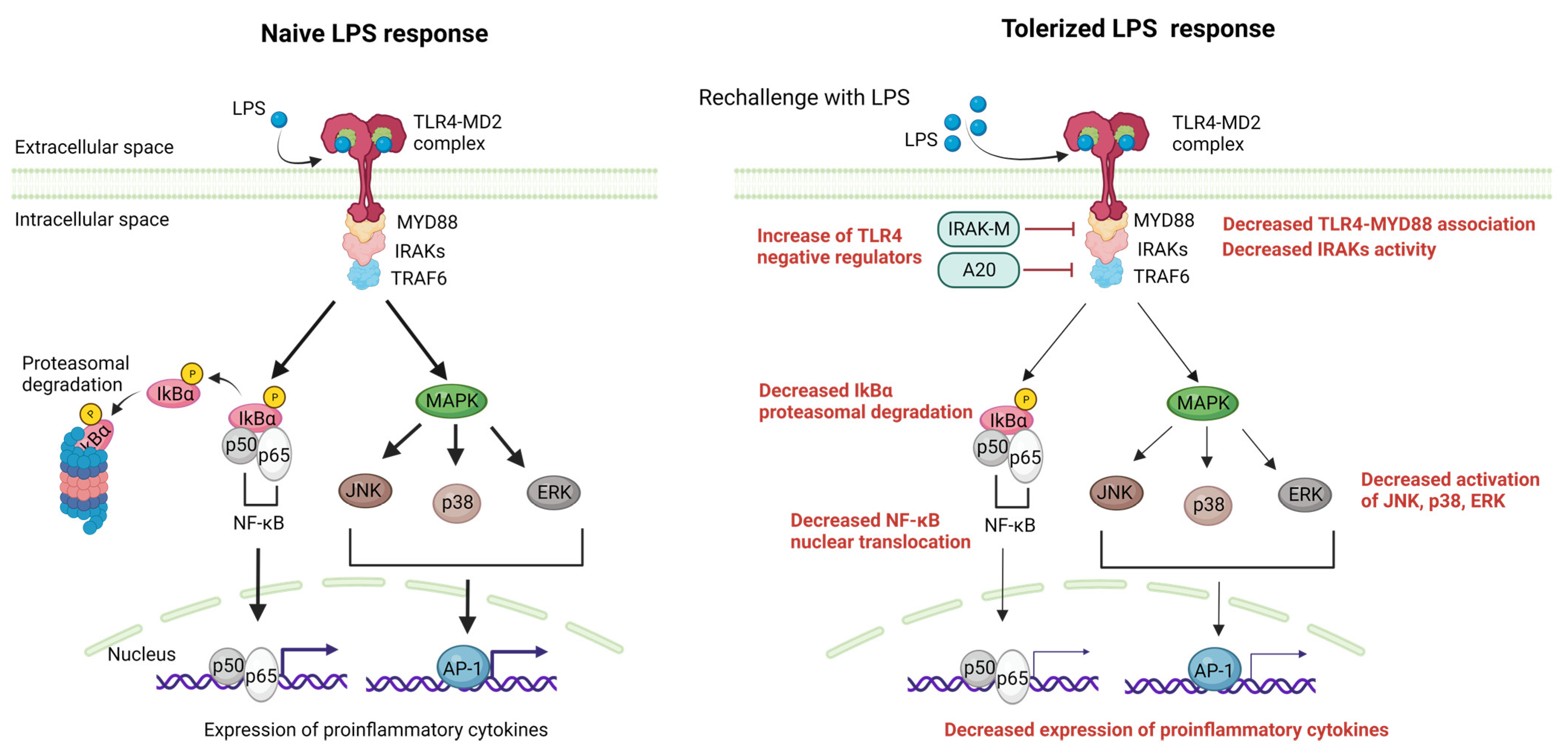
1.3.2. Negative Regulators of TLR4 Signaling
2. The Molecular Mechanisms of LPS Tolerance
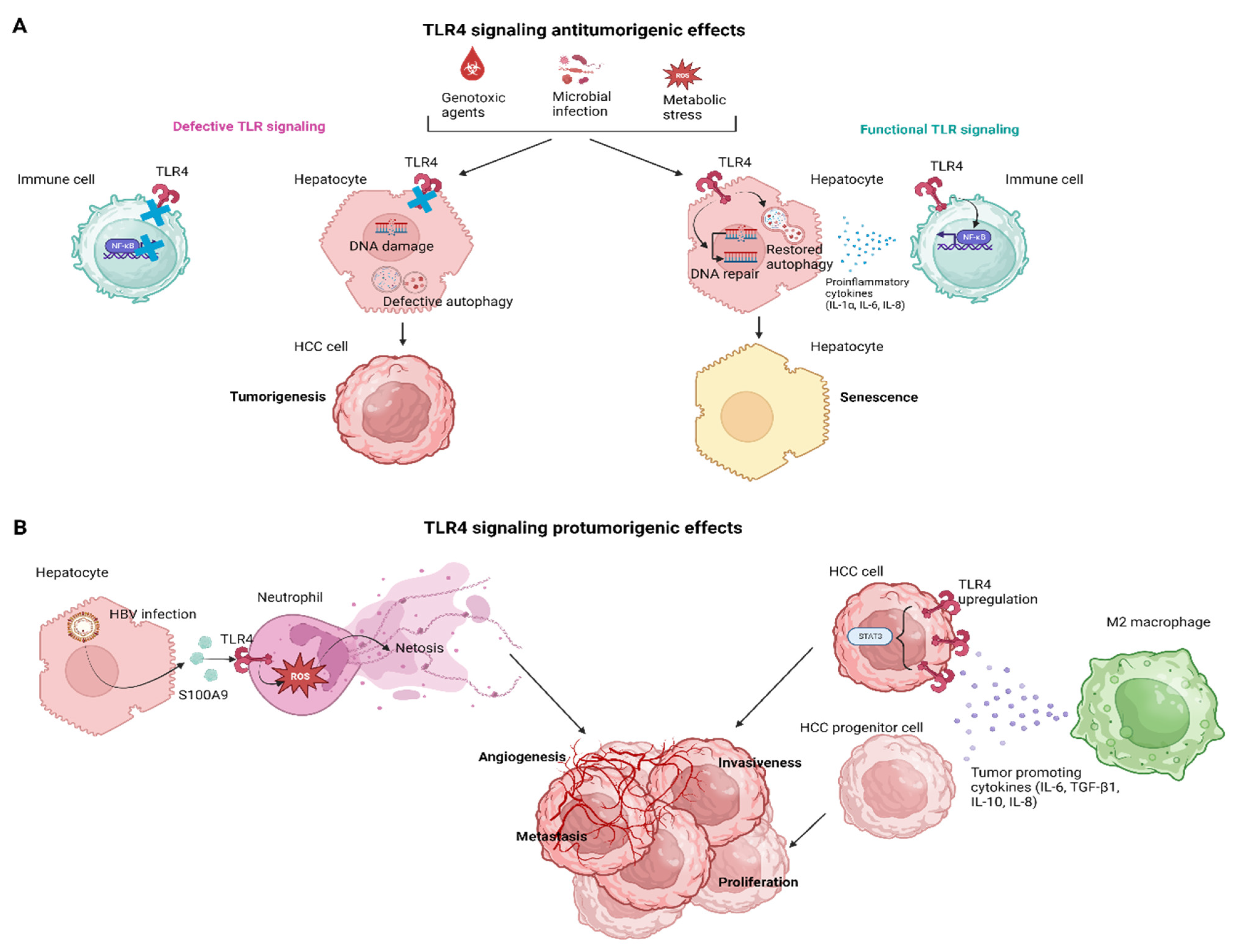
3. The Effects of TLR4 Signaling in Hepatocarcinogenesis
3.1. The TLR4 Signaling in HCC Senescence
3.2. TLR4 Signaling in Innate Cellular Populations
4. The Role of TLR4 Signaling in HCC Patients
4.1. TLR4 Polymorphisms in HCC
4.2. TLR4 as Biomarker in HCC
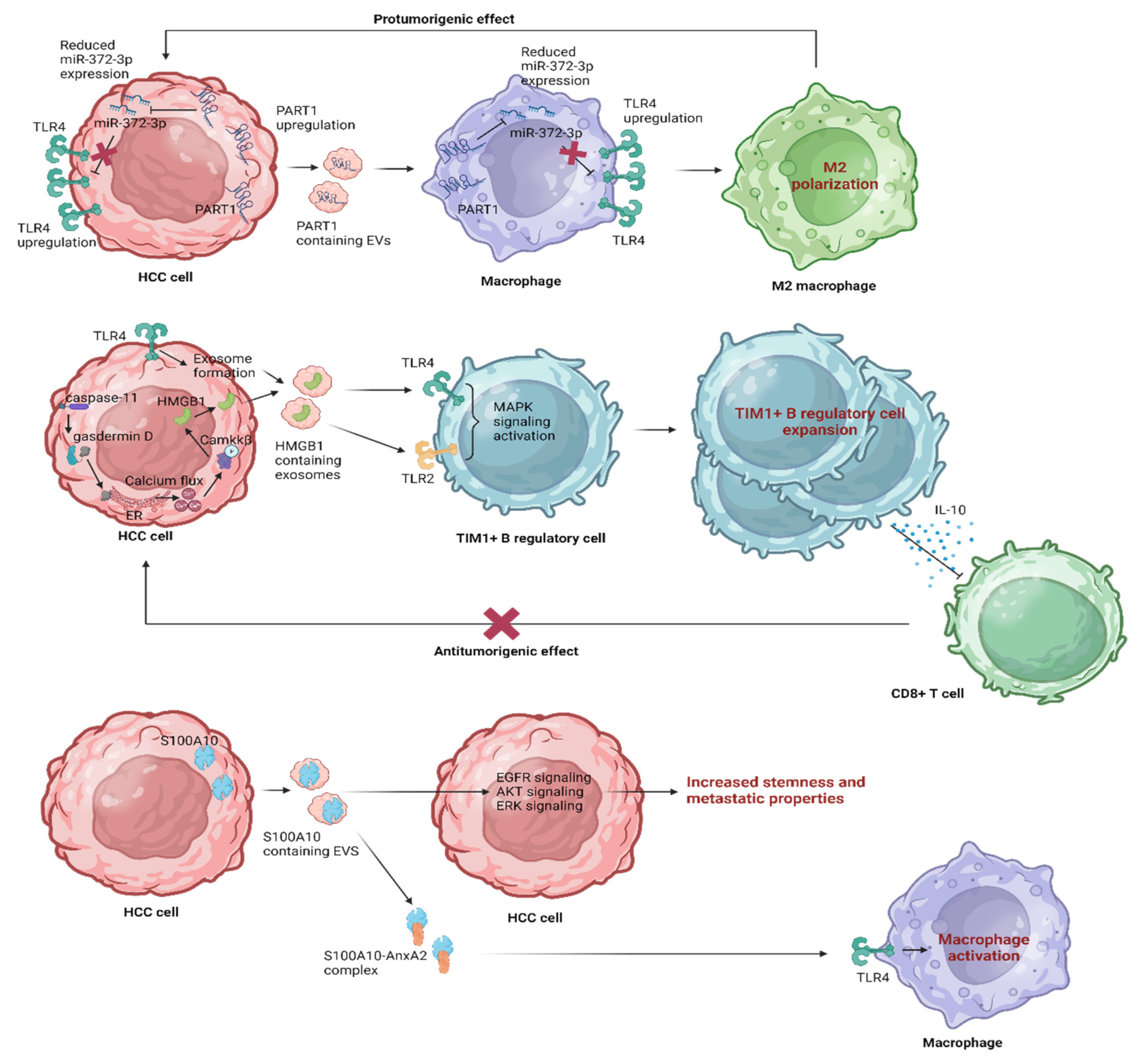
5. Leveraging EV Influence on TLR4 Pathways in HCC
5.1. The Therapeutic Immune Modulation of TLR4 Signaling by EVs
5.2. Strategic Approaches for HCC Prevention
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; Artaman, A.; et al. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level results from the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, A.B.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Abrams, T.; Abbott, D.E.; Ahmed, A.; Anaya, D.A.; Anders, R.; Are, C.; Bachini, M.; Binder, D.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Biliary Tract Cancers, Version 2.2023. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2023, 21, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkasy, O.M.; Nordin, J.Z.; Hagey, D.W.; De Jong, O.G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Vader, P. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Why and how? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Dedes, N.; Pergaris, A.; Gazouli, M.; Theocharis, S. Exosomes in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer: A Moonshot to PDAC Treatment? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seay, T.W.; Suo, Z. Roles of Extracellular Vesicles on the Progression and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2023, 12, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, W.S.; Yarani, R.; El Andaloussi, S.; Cho, B.S.; Choi, C.; Corteling, R.; De Fougerolles, A.; Gimona, M.; Herz, J.; Khoury, M.; et al. A report on the International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy 2022 Scientific Signature Series, “Therapeutic advances with native and engineered human extracellular vesicles”. Cytotherapy 2023, 25, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, E.; Cabañas, C.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.A.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity: Subpopulations, Isolation Techniques, and Diverse Functions in Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; McAndrews, K.M. The role of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Cell 2023, 186, 1610–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuana, Y.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Extracellular vesicles in physiological and pathological conditions. Blood Rev. 2013, 27, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, D.; Roy, S.; Saha, P.; Chatterjee, N.; Bishayee, A. Trends in Research on Exosomes in Cancer Progression and Anticancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Jin, D.; et al. Extracellular vesicles of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts creates a pre-metastatic niche in the lung through activating fibroblasts. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Machairas, N.; Stergiou, I.E.; Arvanitakis, K.; Germanidis, G.; Frampton, A.E.; Theocharis, S. Unveiling the Yin-Yang Balance of M1 and M2 Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Role of Exosomes in Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Modulation. Cells 2023, 12, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwantwi, L.B. Exosome-mediated crosstalk between tumor cells and innate immune cells: Implications for cancer progression and therapeutic strategies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 9487–9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Guo, S.; Ren, X.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yao, X. Current Strategies for Exosome Cargo Loading and Targeting Delivery. Cells 2023, 12, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castilla, P.E.M.; Tong, L.; Huang, C.; Sofias, A.M.; Pastorin, G.; Chen, X.; Storm, G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Wang, J.-W. Extracellular vesicles as a drug delivery system: A systematic review of preclinical studies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.M.; Tey, S.K.; Mao, X.; Ma, A.P.Y.; Yeung, C.L.S.; Wong, S.W.K.; Ng, T.H.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Fung, E.Y.M.; et al. TPI1-reduced extracellular vesicles mediated by Rab20 downregulation promotes aerobic glycolysis to drive hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liao, W.; Dong, M.; Zhu, R.; Xiao, J.; Sun, T.; Chen, Z.; Wu, B.; Jin, J. Exosomal neutral sphingomyelinase 1 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma via decreasing the ratio of sphingomyelin/ceramide. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3835–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yang, P.; Si, A.; Xiang, D.; Tang, X.; Guo, G.; Zhou, J.; Hüser, N. Exosome-transmitted p120-catenin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression via STAT3 pathways. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shen, H.; Zhangyuan, G.; Huang, R.; Zhang, W.; He, Q.; Jin, K.; Zhuo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. 14-3-3ζ delivered by hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomes impaired anti-tumor function of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, J.; Renner, B.; Pickering, M.C.; Serkova, N.J.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Clambey, E.T.; Nemenoff, R.A.; Thurman, J.M. Complement factor H–deficient mice develop spontaneous hepatic tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4039–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.D.; Trent, M.S. Fortifying the barrier: The impact of lipid A remodelling on bacterial pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.L.; Kono, H. The Inflammatory Response to Cell Death. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2008, 3, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Bowie, A.G. The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Xu, D.; Brint, E.K.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtale, G.; Mirolo, M.; Renzi, T.A.; Rossato, M.; Bazzoni, F.; Locati, M. Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by IL-10–dependent microRNA-146b. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11499–11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Arvanitakis, K.; Stergiou, I.E.; Lekakis, V.; Davakis, S.; Christodoulou, M.-I.; Germanidis, G.; Theocharis, S. The Role of TLR4 in the Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Can We Teach an Old Dog New Tricks? Cancers 2023, 15, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Hu, S.; Luo, Y.; He, K. Exosome Cargos as Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitakis, K.; Papadakos, S.P.; Lekakis, V.; Koufakis, T.; Lempesis, I.G.; Papantoniou, E.; Kalopitas, G.; Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Stergiou, I.E.; Theocharis, S.; et al. Meeting at the Crossroad between Obesity and Hepatic Carcinogenesis: Unique Pathophysiological Pathways Raise Expectations for Innovative Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martinez, I.; Alen, R.; Pereira, L.; Povo-Retana, A.; Astudillo, A.M.; Hitos, A.B.; Gomez-Hurtado, I.; Lopez-Collazo, E.; Boscá, L.; Francés, R.; et al. Saturated fatty acid-enriched small extracellular vesicles mediate a crosstalk inducing liver inflammation and hepatocyte insulin resistance. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racanelli, V.; Rehermann, B. The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology 2006, 43, S54–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, D.G. Immunity, tolerance and autoimmunity in the liver: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 66, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, J.J.; Ghosh, S. Molecular mechanisms of innate memory and tolerance to LPS. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calne, R. Immunological tolerance: The liver effect. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17, S488–S490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaskou, E.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Gershwin, M.E. Mechanisms of tissue injury in autoimmune liver diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, S.; Han, Y.; Cao, X. Apoptotic cells attenuate fulminant hepatitis by priming Kupffer cells to produce interleukin-10 through membrane-bound TGF-β. Hepatology 2011, 53, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.L.; Wherry, E.J.; Masopust, D.; Zhu, B.; Allison, J.P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 2006, 439, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.B.; Schuler, G. Immature, semi-mature and fully mature dendritic cells: Which signals induce tolerance or immunity? Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Fahey, R.; Fletcher, J.M.; Keogh, C.; Carroll, A.G.; Siddachari, R.; Geoghegan, J.; Hegarty, J.E.; Ryan, E.J.; O’farrelly, C. CD141+ myeloid dendritic cells are enriched in healthy human liver. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Gong, Z.-J.; Wang, Z.-W.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Sun, H.-C.; Liu, S.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Peng, Z.-H. IDO-competent-DCs induced by IFN-γ attenuate acute rejection in rat liver transplantation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhardt, A.; Biburger, M.; Papadopoulos, T.; Tiegs, G. IL-10, regulatory T cells, and Kupffer cells mediate tolerance in concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology 2007, 45, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.-L. Inhibition of allogeneic T-cell response by Kupffer cells expressing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.V.; Swanson, C.; Morgan, M.; Erickson, K.; Hubbard, N.E.; German, J.B. Portal venous transfusion up-regulates kupffer cell cyclooxygenase activity. Transplantation 1997, 64, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-J.; Yan, L.-N.; Li, X.-H.; Xu, F.-L.; Chen, X.-F.; You, H.-B.; Gong, J.-P. Up-Regulation of IRAK-M is Essential for Endotoxin Tolerance Induced by a Low Dose of Lipopolysaccharide in Kupffer Cells. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 150, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrig, A.; Banafsche, R.; Kremer, M.; Hegenbarth, S.; Hamann, A.; Neurath, M.; Gerken, G.; Limmer, A.; Knolle, P.A.; Knolle, P.A. Development and functional consequences of LPS tolerance in sinusoidal endothelial cells of the liver. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, F.; Akashi, S.; Sakao, Y.; Sato, S.; Kawai, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakanishi, K.; Kimoto, M.; Miyake, K.; Takeda, K.; et al. Cutting edge: Endotoxin tolerance in mouse peritoneal macrophages correlates with down-regulation of surface toll-like receptor 4 expression. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 3476–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Lentschat, A.; Wahl, L.M.; Golenbock, D.T.; Vogel, S.N. Dysregulation of LPS-induced Toll-like receptor 4-MyD88 complex formation and IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 activation in endotoxin-tolerant cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5209–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Kopydlowski, K.M.; Vogel, S.N. Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Signal Transduction in Endotoxin-Tolerized Mouse Macrophages: Dysregulation of Cytokine, Chemokine, and Toll-Like Receptor 2 and 4 Gene Expression. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5564–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Henneke, P.; Schromm, A.; Lien, E.; Ingalls, R.; Fenton, M.J.; Golenbock, D.T.; Vogel, S.N. Induction of tolerance to lipopolysaccharide and mycobacterial components in Chinese hamster ovary/CD14 cells is not affected by overexpression of Toll-like receptors 2 or 4. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Qiu, F.; Piao, W.; Song, C.; Wahl, L.M.; Medvedev, A.E. Endotoxin tolerance impairs IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) 4 and TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 activation, K63-linked polyubiquitination and assembly of IRAK1, TNF receptor-associated factor 6, and IkappaB kinase gamma and increases A20 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7905–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Medvedev, A.E. Induction of endotoxin tolerance in vivo inhibits activation of IRAK4 and increases negative regulators IRAK-M, SHIP-1, and A20. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hernandez, L.D.; Galán, J.E.; Janeway, C.A.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. IRAK-M is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gazzar, M.; Yoza, B.K.; Hu, J.Y.-Q.; Cousart, S.L.; McCall, C.E. Epigenetic silencing of tumor necrosis factor alpha during endotoxin tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26857–26864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.F.; Yoza, B.K.; El Gazzar, M.; Vachharajani, V.T.; McCall, C.E. NAD+-dependent SIRT1 deacetylase participates in epigenetic reprogramming during endotoxin tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9856–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoza, B.K.; Hu, J.Y.-Q.; Cousart, S.L.; Forrest, L.M.; McCall, C.E. Induction of RelB Participates in Endotoxin Tolerance. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4080–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; El Gazzar, M.; Yoza, B.K.; McCall, C.E. The NF-κB factor RelB and histone H3 lysine methyltransferase G9a directly interact to generate epigenetic silencing in endotoxin tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27857–27865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Maekawa, T.; Zhu, Y.; Renard-Guillet, C.; Chatton, B.; Inoue, K.; Uchiyama, T.; Ishibashi, K.-I.; Yamada, T.; Ohno, N.; et al. The transcription factor ATF7 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced epigenetic changes in macrophages involved in innate immunological memory. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostuni, R.; Piccolo, V.; Barozzi, I.; Polletti, S.; Termanini, A.; Bonifacio, S.; Curina, A.; Prosperini, E.; Ghisletti, S.; Natoli, G. Latent enhancers activated by stimulation in differentiated cells. Cell 2013, 152, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.-X.; Yan, H.-X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wu, H.-P.; Dong, W.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; He, Y.-Q.; Zou, S.-S.; et al. Endotoxin accumulation prevents carcinogen-induced apoptosis and promotes liver tumorigenesis in rodents. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, M.; Lowe, S.W. Senescence comes of age. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Elledge, S.J. How autophagy both activates and inhibits cellular senescence. Autophagy 2016, 12, 898–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuollo, L.; Antonangeli, F.; Santoni, A.; Soriani, A. The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) in the Challenging Future of Cancer Therapy and Age-Related Diseases. Biology 2020, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, J.; Lin, H.; Hua, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Lv, X.; Yu, J.; Mi, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 activity protects against hepatocellular tumorigenesis and progression by regulating expression of DNA repair protein Ku70 in mice. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, H.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.-W. Repairing DNA damage by XRCC6/KU70 reverses TLR4-deficiency-worsened HCC development via restoring senescence and autophagic flux. Autophagy 2013, 9, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, K.; Mitroulis, I.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Elefsiniotis, I.; Germanidis, G. The Liver Cancer Immune Microenvironment: Emerging Concepts for Myeloid Cell Profiling with Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2023, 15, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, K.; Mitroulis, I.; Germanidis, G. Tumor-associated neutrophils in hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis, prognosis, and therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Wu, R.; Kong, X.; You, Y.; He, K.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Duan, L. Elevated neutrophil extracellular traps by HBV-mediated S100A9-TLR4/RAGE-ROS cascade facilitate the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2022, 43, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitakis, K.; Koletsa, T.; Mitroulis, I.; Germanidis, G. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathogenesis, Prognosis and Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Cheng, T.; Zhan, J.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, X.; Ying, M. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Ishioka, M.; Minami, S.; Horie, Y.; Ohshima, S.; Goto, T.; Ohnishi, H. Toll-like receptor 4 on macrophage promotes the development of steatohepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11504–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, G.-Y.; He, G.; Ali, S.R.; Holzer, R.G.; Österreicher, C.H.; Takahashi, H.; Karin, M. Dietary and Genetic Obesity Promote Liver Inflammation and Tumorigenesis by Enhancing IL-6 and TNF Expression. Cell 2010, 140, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.-R.; Li, J.-H.; Zhang, R.; Chen, R.-X.; Wang, Y.-H. M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages facilitated migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HCC cells via the TLR4/STAT3 signaling pathway. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-C.; Chen, P.-H.; Cheng, C.-I.; Tsai, M.-S.; Chang, C.-Y.; Lu, S.-C.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, P.-H.; Kao, Y.-H. Toll-like receptor-4 is a target for suppression of proliferation and chemoresistance in HepG2 hepatoblastoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 368, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaba, T.; Nakayama, T.; Yamazumi, K.; Yakata, Y.; Yoshizaki, A.; Nagayasu, T.; Sekine, I. Expression of p-STAT3 in human colorectal adenocarcinoma and adenoma; correlation with clinicopathological factors. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphorst, A.O.; Pillai, R.N.; Yang, S.; Nasti, T.H.; Akondy, R.S.; Wieland, A.; Sica, G.L.; Yu, K.; Koenig, L.; Patel, N.T.; et al. Proliferation of PD-1+ CD8 T cells in peripheral blood after PD-1–targeted therapy in lung cancer patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4993–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Mei, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Qian, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Su, R.; et al. Combination with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) agonist reverses GITR agonism mediated M2 polarization of macrophage in Hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoImmunology 2022, 11, 2073010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.-C.; Tang, X.-M.; Zhao, Y.-R.; Zheng, L. A functional variant at miR-34a binding site in toll-like receptor 4 gene alters susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese Han population. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 12345–12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, A.M.; Zahran, Z.A.M.; El-Badawy, O.; Abdel-Rahim, M.H.; Ali, W.A.M.; Rayan, A.; El-Masry, M.A.; Abozaid, M.A.A.; Hetta, H.F. Prognostic impact of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 expression on monocytes in Egyptian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunol. Res. 2019, 67, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsakos, T.; Bakasis, A.-D.; Pouliakis, A.; Gazouli, M.; Vallilas, C.; Hatzis, G. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Toll-like Receptor 4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Single-Center Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, P.; Ji, L.; Xu, S.; Tan, X.; Li, H. Donor Polymorphisms of Toll-like Receptor 4 rs1927914 Associated with the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence Following Liver Transplantation. Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamatallah, M.; El-Bendary, M.; Elalfy, H.; Besheer, T.; El-Maksoud, M.A.; Elhammady, D.; Abed, S.; Elegezy, M.; Kandeel, L.; Eldeib, D.; et al. Impact of Toll-like Receptors 2(TLR2) and TLR 4 Gene Variations on HCV Susceptibility, Response to Treatment and Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic HCV Patients. Immunol. Investig. 2020, 49, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Du, R.; Wang, Z.; Shen, W.; Gao, R.; Jiang, S.; Fang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chang, A.; Liu, L.; et al. TLR4 increases the stemness and is highly expressed in relapsed human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2325–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkammah, M.; Gowily, A.; Okda, T.; Houssen, M. Serum soluble Toll-like receptor 4 and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C virus patients. Wspolczesna Onkol. 2021, 24, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agúndez, J.A.; García-Martín, E.; Devesa, M.J.; Carballo, M.; Martínez, C.; Lee-Brunner, A.; Fernández, C.; Díaz-Rubio, M.; Ladero, J.M. Polymorphism of the TLR4 gene reduces the risk of hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2012, 82, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Anazi, M.R.; Al-Zoghaibi, F.; Abdo, A.A.; Sanai, F.M.; Khan, M.Q.; Albenmousa, A.; Al-Ashgar, H.I.; Al-Ahdal, M.N. The association of toll-like receptor 4 polymorphism with hepatitis C virus infection in Saudi Arabian patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 357062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, I.; Zidi, S.; Mouelhi, L.; Ghazoueni, E.; Brochot, E.; Almawi, W.; Loueslati, B. TLR3 and TLR4 SNP variants in the liver disease resulting from hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 76, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Peng, L.-J.; Cao, Y.-R.; Zeng, Z.-P.; Wu, Y.-J.; Shi, H.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Friedman, S.L.; Sninsky, J.J.; et al. Risk Factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2016, 20, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salum, G.M.; Dawood, R.M.; El-Meguid, M.A.; Ibrahim, N.E.; Aziz, A.O.A.; El Awady, M.K. Correlation between IL28B/TLR4 genetic variants and HCC development with/without DAAs treatment in chronic HCV patients. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiró, N.; Altadill, A.; Juárez, L.M.; Rodríguez, M.; González, L.O.; Atienza, S.; Bermúdez, S.; Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Fresno-Forcelledo, M.F.; Rodrigo, L.; et al. Toll-like receptors 3, 4 and 9 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Su, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Activation of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway contributes to the development of human hepatocellular carcinoma via upregulation of IL-23 and IL-17A. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9647–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, R.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, H. Lipopolysaccharide-induced toll-like receptor 4 signaling in cancer cells promotes cell survival and proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 2223–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Hou, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Z. Toll-like receptor 4 and its associated proteins as prognostic factors for HCC treated by post-radiotherapy surgery. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9599–9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ling, C.C.; Yeung, W.H.O.; Pang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Ng, T.P.K.; Yang, X.X.; et al. Monocytic MDSC mobilization promotes tumor recurrence after liver transplantation via CXCL10/TLR4/MMP14 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, P.; Yu, C.; Shi, Q.; Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Cao, Q.; Guo, C.; Wu, X.; et al. Hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomal miR -182-5p promotes liver regeneration via FOXO1 -mediated macrophage polarization. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Che, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, C. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles containing long noncoding RNA PART1 exert oncogenic effect in hepatocellular carcinoma by polarizing macrophages into M2. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Chang, Y.; Liang, X.; Cardinal, J.S.; Huang, H.; Thorne, S.H.; Monga, S.P.; Geller, D.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Tsung, A. High-mobility group box 1 activates caspase-1 and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness and metastases. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Deng, M.; Loughran, P.A.; Yang, M.; Lin, M.; Yang, C.; Gao, W.; Jin, S.; Li, S.; Cai, J.; et al. LPS Induces Active HMGB1 Release from Hepatocytes Into Exosomes through the Coordinated Activities of TLR4 and Caspase-11/GSDMD Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Cao, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal HMGB1 fosters hepatocellular carcinoma immune evasion by promoting TIM-1+ regulatory B cell expansion. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretz, N.P.; Ridinger, J.; Rupp, A.-K.; Rimbach, K.; Keller, S.; Rupp, C.; Marmé, F.; Umansky, L.; Umansky, V.; Eigenbrod, T.; et al. Body Fluid Exosomes Promote Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines in Monocytic Cells via Toll-like Receptor Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36691–36702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, M.; Zhang, B.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; et al. S100A family is a group of immune markers associated with poor prognosis and immune cell infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, M.; Cao, J.; Yuan, T.; Yu, G.; Chen, Y.; Fang, W.; Li, H. S100 Calcium Binding Protein A10, A Novel Oncogene, Promotes the Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 695036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yu, M.; Guo, Q.; Li, R.; Li, G.; Tan, S.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Wu, M. Annexin A2 binds to endosomes and negatively regulates TLR4-triggered inflammatory responses via the TRAM-TRIF pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swisher, J.F.A.; Burton, N.; Bacot, S.M.; Vogel, S.N.; Feldman, G.M. Annexin A2 tetramer activates human and murine macrophages through TLR4. Blood 2010, 115, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Sze, K.M.-F.; Wang, J.; Tian, L.; Lu, J.; Tsui, Y.-M.; Ma, H.T.; Lee, E.; Chen, A.; et al. S100A10 promotes HCC development and progression via transfer in extracellular vesicles and regulating their protein cargos. Gut 2023, 72, 1370–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Kasinski, A.L.; Shen, H.; Slack, F.J.; Tang, D.G. MicroRNA-34a: Potent Tumor Suppressor, Cancer Stem Cell Inhibitor, and Potential Anticancer Therapeutic. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 640587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Meyer, T.; Sapisochin, G.; Salem, R.; Saborowski, A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2022, 400, 1345–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, F.; Gairing, S.J.; Müller, L.; Galle, P.R. NAFLD-driven HCC: Safety and efficacy of current and emerging treatment options. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Vianna, C.R.; Fukuda, M.; Berglund, E.D.; Liu, C.; Tao, C.; Sun, K.; Liu, T.; Harper, M.J.; Lee, C.E.; et al. Hepatocyte Toll-like receptor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, J.; Serna-Salas, S.A.; Villanueva, A.H.; Buist-Homan, M.; Arrese, M.; Olinga, P.; Blokzijl, H.; Moshage, H. Hepatic stellate cells induce an inflammatory phenotype in Kupffer cells via the release of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Hosono, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yuyama, K.; Nakamura, H.; Fu, Q.; Maehara, O.; Suda, G.; Sakamoto, N. Extracellular Vesicles from Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3212643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villard, A.; Boursier, J.; Andriantsitohaina, R. Bacterial and eukaryotic extracellular vesicles and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New players in the gut-liver axis? Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G485–G495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Tan, J.; Qian, W.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X. Gut inflammation exacerbates hepatic injury in the high-fat diet induced NAFLD mouse: Attention to the gut-vascular barrier dysfunction. Life Sci. 2018, 209, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Wan, F.; Lan, J.; Jiang, X.; Wu, S.; Pan, J.; Tang, Z.; Hu, L. Arsenic exposure induces intestinal barrier damage and consequent activation of gut-liver axis leading to inflammation and pyroptosis of liver in ducks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas-Paz, A.; Morán, L.; Peng, J.; Salinas, B.; López-Alcántara, N.; Sydor, S.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Asensio, I.; Hao, F.; Zheng, K.; et al. Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Hepatic Injury via the Gut-Liver Axis During Acute Alcohol Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 603771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizanne, L.; Villard, A.; Benabbou, N.; Recoquillon, S.; Soleti, R.; Delage, E.; Wertheimer, M.; Vidal-Gómez, X.; Oullier, T.; Chaffron, S.; et al. Faeces-derived extracellular vesicles participate in the onset of barrier dysfunction leading to liver diseases. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouries, J.; Brescia, P.; Silvestri, A.; Spadoni, I.; Sorribas, M.; Wiest, R.; Mileti, E.; Galbiati, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Adorini, L.; et al. Microbiota-driven gut vascular barrier disruption is a prerequisite for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engevik, M.A.; Danhof, H.A.; Ruan, W.; Engevik, A.C.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Engevik, K.A.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Brand, C.K.; Krystofiak, E.S.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Secretes Outer Membrane Vesicles and Promotes Intestinal Inflammation. Mbio 2021, 12, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zheng, W.; Tian, P.; Liu, H.; He, Y.; Peng, M.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Administration of glycyrrhetinic acid reinforces therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome against acute liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11211–11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Yau, T.; Kang, Y.-K.; Kim, T.-Y.; Santoro, A.; Sangro, B.; Melero, I.; Kudo, M.; Hou, M.-M.; Matilla, A.; et al. Nivolumab (NIVO) plus ipilimumab (IPI) combination therapy in patients (Pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC): Long-term results from CheckMate 040. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Dedes, N.; Kouroumalis, E.; Theocharis, S. The Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in HCC Carcinogenesis and Treatment: Harnessing Innate Immunity. Cancers 2022, 14, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Ferraro, D.; Carbone, G.; Frampton, A.E.; Vennarecci, G.; Kykalos, S.; Schizas, D.; Theocharis, S.; Machairas, N. The Emerging Role of Metformin in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Is There Any Value in Repurposing Metformin for HCC Immunotherapy? Cancers 2023, 15, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, B.; Heinrich, B.; Greten, T.F. Immunobiology and immunotherapy of HCC: Spotlight on innate and innate-like immune cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 18, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xun, Z.; Ma, K.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Identification of a tumour immune barrier in the HCC microenvironment that determines the efficacy of immunotherapy. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zheng, L.; Yoo, J.-K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Kang, B.; Hu, R.; Huang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Landscape of Infiltrating T Cells in Liver Cancer Revealed by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2017, 169, 1342–1356.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, K.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, D.; et al. Single-cell landscape of the ecosystem in early-relapse hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell 2021, 184, 404–421.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizarani, N.; Saviano, A.; Sagar; Mailly, L.; Durand, S.; Herman, J.S.; Pessaux, P.; Baumert, T.F.; Grün, D. A human liver cell atlas reveals heterogeneity and epithelial progenitors. Nature 2019, 572, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.J.; Perez, M.C.; Ayoubi, N.; Zhao, S.; Ye, F.; Wang, D.Y.; Sosman, J.A.; Al-Rohil, R.N.; Eroglu, Z.; Johnson, D.B. Clinical Correlates of Response to Anti-PD-1–based Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. J. Immunother. 2019, 42, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, R.C.; Abugabal, Y.I.; Xiao, L.; Hassan, M.; Hassan, R.A.W.; Girard, L.; Raghav, K.P.S.; Morris, J.; Rashid, A.; Qayyum, A.; et al. Molecular profiling by circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and benefit from anti-PD-1 in HCC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e15679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Stergiou, I.E.; Gkolemi, N.; Arvanitakis, K.; Theocharis, S. Unraveling the Significance of EPH/Ephrin Signaling in Liver Cancer: Insights into Tumor Progression and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2023, 15, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Goswami, S.; Raychaudhuri, D.; Siddiqui, B.A.; Singh, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Liu, J.; Subudhi, S.K.; Poon, C.; Gant, K.L.; et al. Immune checkpoint therapy—Current perspectives and future directions. Cell 2023, 186, 1652–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supabphol, S.; Li, L.; Goedegebuure, S.P.; Gillanders, W.E. Neoantigen vaccine platforms in clinical development: Understanding the future of personalized immunotherapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davakis, S.; Kapelouzou, A.; Sakellariou, S.; Kyriakoulis, K.G.; Mylonakis, A.; Papadakos, S.P.; Mpoura, M.; Vailas, M.; Ziogas, D.; Liakakos, T.; et al. Clinical and Oncological Impact of the Toll-like Receptor-3 and -4 in Esophageal and Gastro-esophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2023, 43, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, R.; Kirschning, C.J.; Sing, A.; Schrottner, P.; Fukase, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Wagner, H.; Heesemann, J.; Ruckdeschel, K. A Dominant Role of Toll-Like Receptor 4 in the Signaling of Apoptosis in Bacteria-Faced Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 4294–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.K.; Lizzio, V.; Merkel, O.M. Folate receptor targeted delivery of siRNA and paclitaxel to ovarian cancer cells via folate conjugated triblock copolymer to overcome TLR4 driven chemotherapy resistance. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, S.; Tsagkaris, C.; Moysidis, D.V.; Papadakos, S.; Galkin, O.Y.; Orel, V.E.; Syvak, L.A. Nanotherapy based on magneto-mechanochemical modulation of tumor redox state. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 15, e1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyuri, A.; Baghermanesh, S.S.; Davatgaran-Taghipour, Y.; Eslami, S.S.; Shaygan, N.; Parsaie, H.; Barati, M.; Jafari, D. Diagnostic accuracy of serum derived exosomes for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Bu, J.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lin, J. Spotlights on extracellular vesicles in hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and treatment: An update review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1215518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ye, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J. Mechanism of M2 type macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles regulating PD-L1 expression via the MISP/IQGAP1 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy resistance. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 110848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luan, G.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T. Exosomal miR-200b-3p induce macrophage polarization by regulating transcriptional repressor ZEB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 17, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.W.K.; Tey, S.K.; Mao, X.; Fung, H.L.; Xiao, Z.; Wong, D.K.H.; Mak, L.; Yuen, M.; Ng, I.O.; Yun, J.P.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicle-Derived vWF Induces a Positive Feedback Loop between Tumor and Endothelial Cells to Promote Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Jiao, J.; Ke, H.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, L.; Pan, J.; Li, X. Role of exosomes in the development of the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1200201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Cao, J.; Feng, Z.; Tang, Y.; Han, X.; Mao, T.; Li, S.; Guo, Q.; Ke, X.; Zhang, X. Oroxylin a promoted apoptotic extracellular vesicles transfer of glycolytic kinases to remodel immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 975, 176037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yu, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Mao, X.; Mao, X.; et al. Clathrin light chain A-enriched small extracellular vesicles remodel microvascular niche to induce hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xie, L.; Tang, X.; Tian, J.; Xiao, S. Blood exosome marker miRNA-30d-5p: Role and regulation mechanism in cell stemness and gemcitabine resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Probes 2023, 71, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author/Year | Reference | Study Design | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agúndez et al. (2012) | [89] | rs2149356, rs4986791 and rs5030719 SNPs in 155 Patients with HCV-induced HCC, including 153 patients with HCV and 390 healthy controls | In comparison to the healthy controls, patients with HCC had a significantly lower frequency of the rs2149356 T allele carrier state (OR 0.421, 95% CI 0.285–0.625). This trend was also observed in patients with HCV (OR 0.426, 95% CI 0.236–0.767) |
| The proportion of rs2149356 T allele carriers progressively decreased as the clinical stage of HCC increased | |||
| Al-Qahtani et al. (2014) | [90] | rs4986790 (A/G) and rs4986791 (C/T), in 450 HCV-infected and 600 uninfected controls | rs4986790 (A/G) and rs4986791 (C/T) had significantly different distributions between HCV-infected patients and uninfected controls (p < 0.0001; OR = 0.404, AC was found more frequently in chronic HCV-infected patients compared to cirrhosis/HCC patients (frequency = 94.7% and p = 0.04) |
| Neamatallah et al. (2019) | [86] | 3295 individuals were divided into groups based on their HCV infection status and control subjects. Patients with liver cirrhosis and HCC | Haplotype CAGT of TLR4 was significantly associated with the CH and HCC groups |
| Sghaier et al. (2018) | [91] | 174 HCV patients, 100 HBV patients and 360 healthy controls TLR4(rs4986790) | The minor (GG) genotype of TLR4 rs4985790 exhibited a notable positive correlation with HBV-associated HCC (p < 0.001) |
| Zhang et al. (2016) | [92] | 949 HBsAg-positive patients: Group1-234 HBV carriers and CHB patients without cirrhosis or HCC; Group 2-281 cirrhotic patients without HCC and Group 3-434 cirrhotic patients with HCC | TLR4 SNP rs11536889 was found to be associated with an increased risk of HCC in patients with cirrhosis and CHB. TLR4 rs2149356 polymorphisms were linked to an increased risk of HCC in cirrhotic patients after conducting stratified analyses based on gender, age, and drinking history. |
| Salum et al. (2019) | [93] | 493 blood samples for TLR4 rs4986791 SNP: 70 controls-252 SOF/DCV-treated HCV patients (65 HCC-187 patients did not develop HCC)-171 naıve HCV patients (48 early liver fibrosis, 21 late liver fibrosis and 102 HCC) | TLR4 rs4986791: the CC genotype was present in 100%, 81%, and 97% of EF, LF, and HCC patients, respectively. The minor protective TT genotype was completely absent in all subjects, while the CT genotype was absent in the EF group and was present in only 19% and 3% of LF and HCC patients, respectively (p = 0.001). The frequency of the protective T allele was higher in LF than in HCC (OR 0.047, 95% CI 0.005–0.43, p = 0.001) |
| Elkammah et al. (2020) | [88] | Soluble Toll-like receptor 4 (sTLR4) in 150 participants (50 HCV-related HCC, 50 HCV without HCC and 50 healthy controls) | sTLR4 levels in patients with HCV-related HCC (4436.1 ± 7089.8 pg/mL) compared to those with hepatitis C but without HCC (1561.4 ± 532.0 pg/mL) (p = 0.002) and the control group (1170.38 ± 159.42 pg/mL) (p < 0.001). Serum sTLR4 was positively correlated with serum alpha-fetoprotein levels and the tumor stages of HCC according to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging system (BCLC). The combination of serum alpha-fetoprotein and serum sTLR4 increased the sensitivity of HCC detection to 76% and specificity to 94%. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadakos, S.P.; Arvanitakis, K.; Stergiou, I.E.; Vallilas, C.; Sougioultzis, S.; Germanidis, G.; Theocharis, S. Interplay of Extracellular Vesicles and TLR4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathophysiology and Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102460
Papadakos SP, Arvanitakis K, Stergiou IE, Vallilas C, Sougioultzis S, Germanidis G, Theocharis S. Interplay of Extracellular Vesicles and TLR4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathophysiology and Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(10):2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102460
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadakos, Stavros P., Konstantinos Arvanitakis, Ioanna E. Stergiou, Christos Vallilas, Stavros Sougioultzis, Georgios Germanidis, and Stamatios Theocharis. 2023. "Interplay of Extracellular Vesicles and TLR4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathophysiology and Therapeutics" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 10: 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102460
APA StylePapadakos, S. P., Arvanitakis, K., Stergiou, I. E., Vallilas, C., Sougioultzis, S., Germanidis, G., & Theocharis, S. (2023). Interplay of Extracellular Vesicles and TLR4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathophysiology and Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics, 15(10), 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102460










