Evaluation of the Cytotoxic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Immunomodulatory Effects of Withaferin A (WA) against Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in Immune Cells Derived from BALB/c Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, Antibodies, and Assay Kits
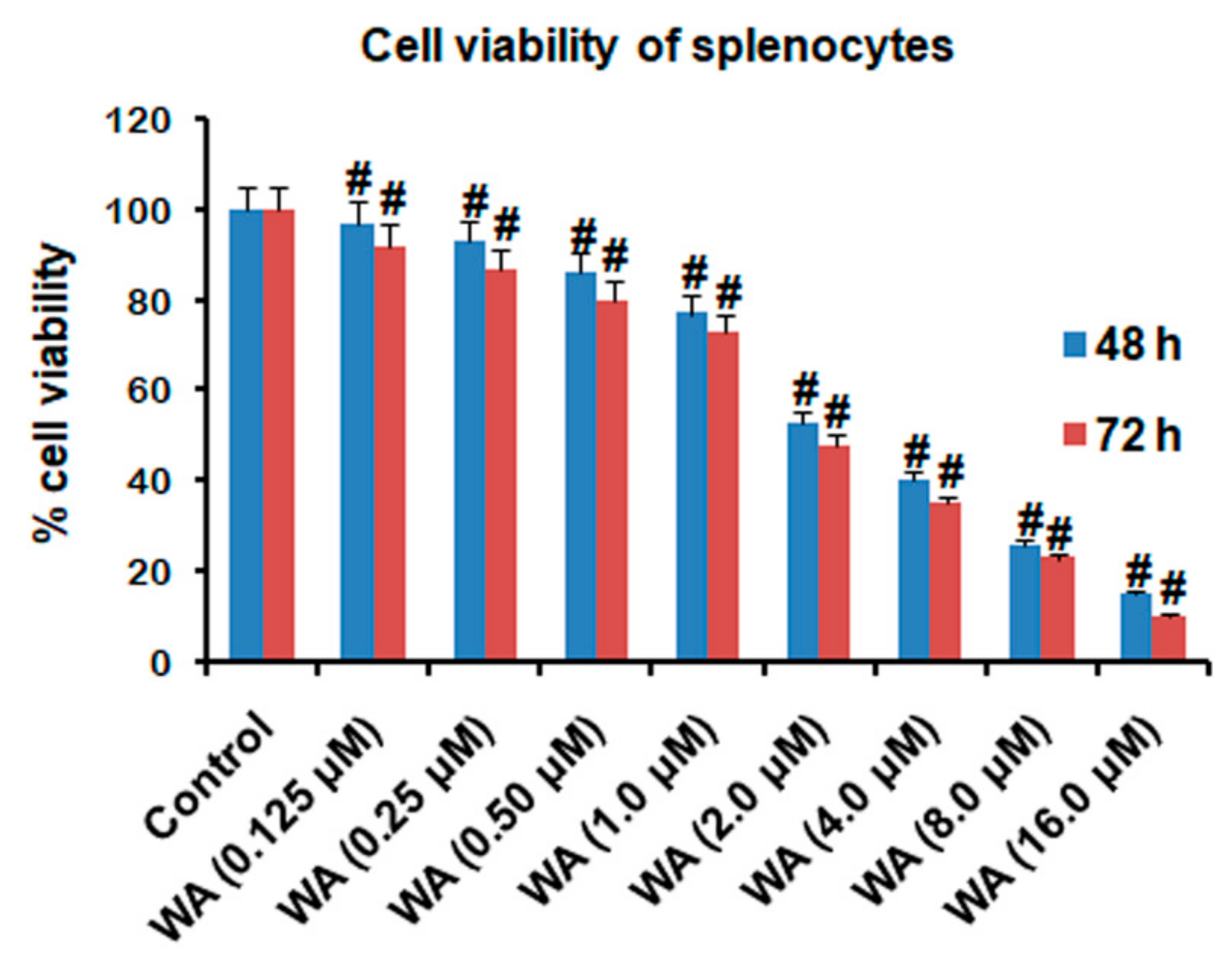
2.2. Isolation of Splenocytes (Lymphocytes) and Determination of Cell Viability
2.3. Collection of Peritoneal Macrophages and Estimation of Nitrite Content by Nitrite Assay
2.4. Evaluation of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β) in Peritoneal Macrophages
2.5. Immunophenotyping of Spleen-Derived Lymphocytes
2.6. Immunoblotting Analysis
2.7. Real-Time (RT) Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
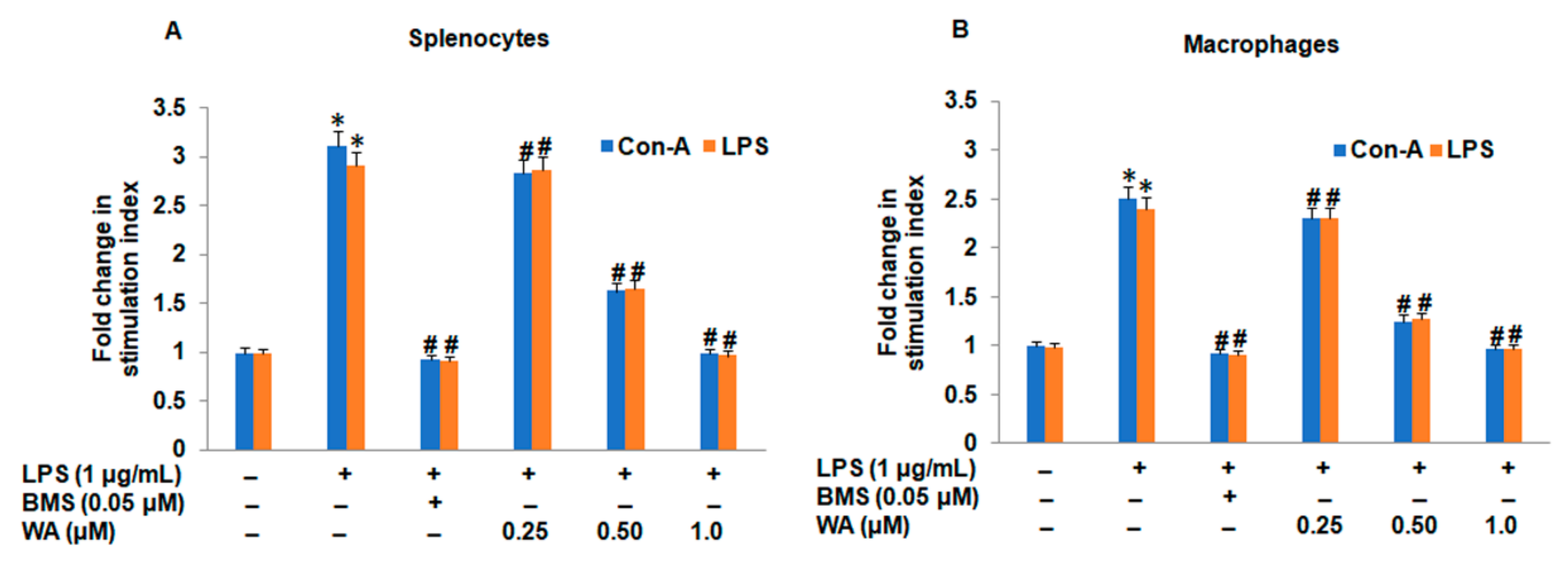
3.1. The Effect of WA on Splenic Cell Viability and Splenocyte/Macrophage Proliferation Stimulated by ConA/LPS
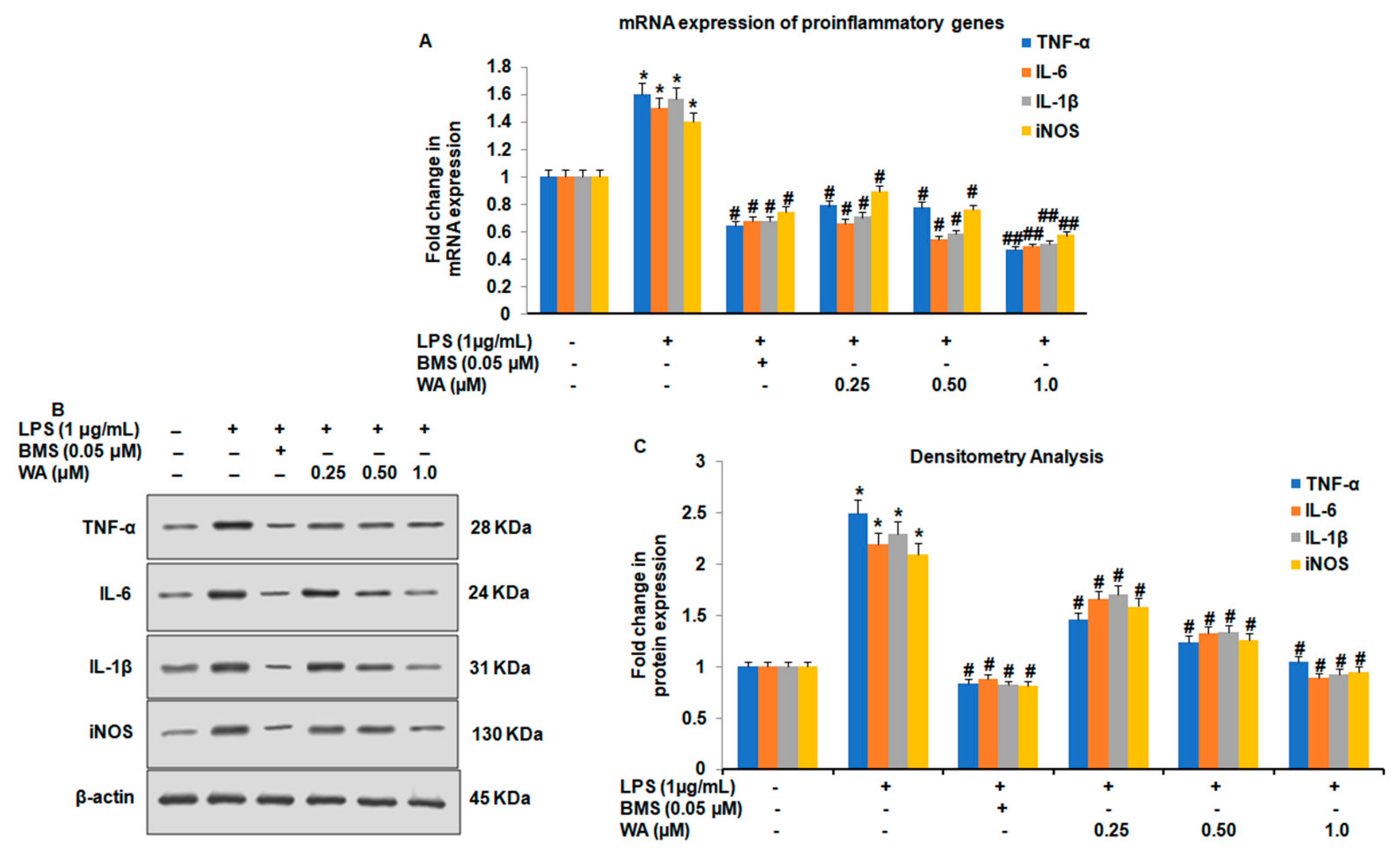
3.2. WA Modulates Both the Expression and Secretion of Proinflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages
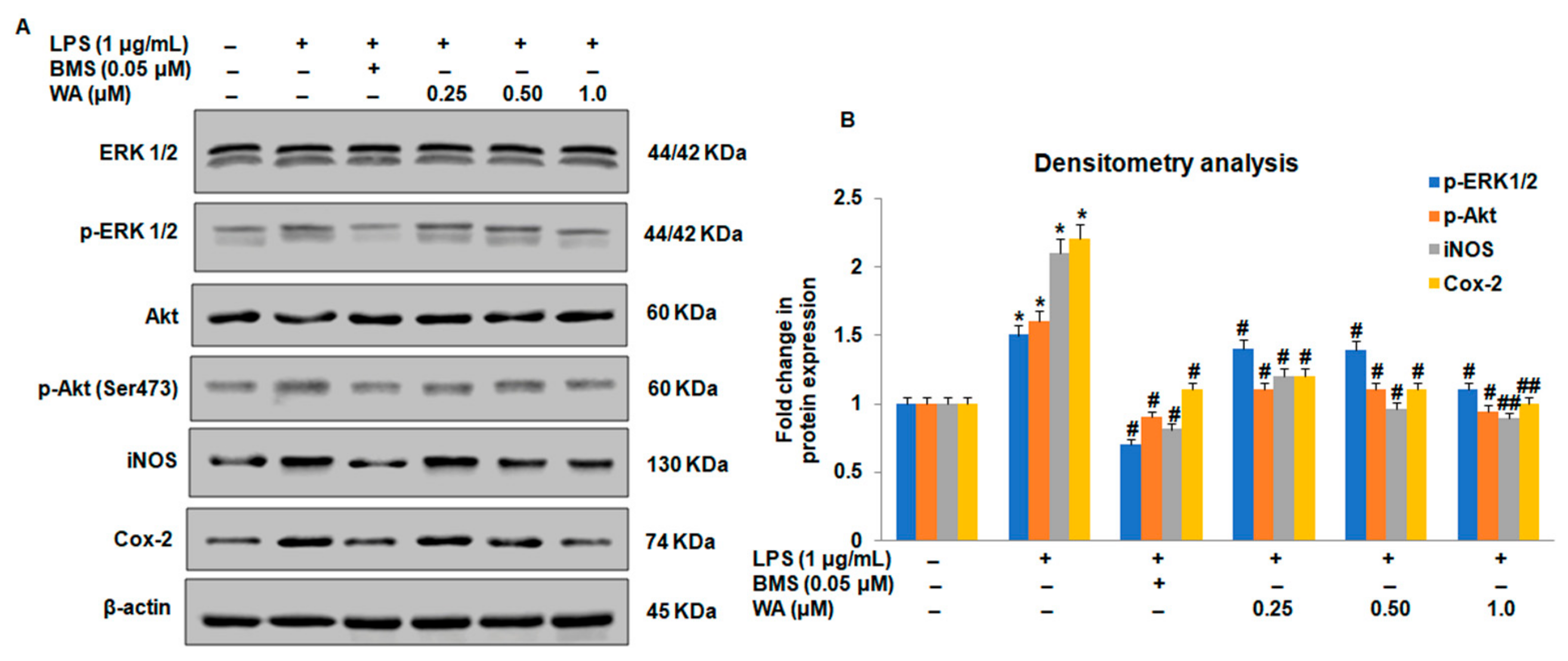
3.3. Effect of WA on the NF-ĸB-Mediated Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages
3.4. WA Modulates the Immunophenotyping of Spleen-Derived Lymphocytes from BALB/c Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Wang, G. Mechanisms of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Challenges and Opportunities for Molecular Targeted Therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and Physiological Roles of Inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabas, I. Macrophage Death and Defective Inflammation Resolution in Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Age-Associated Chronic Diseases Require Age-Old Medicine: Role of Chronic Inflammation. Prev. Med. 2012, 54, S29–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christ, A.; Bekkering, S.; Latz, E.; Riksen, N.P. Long-Term Activation of the Innate Immune System in Atherosclerosis. In Proceedings of the Seminars in Immunology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 28, pp. 384–393. [Google Scholar]
- Legein, B.; Temmerman, L.; Biessen, E.A.; Lutgens, E. Inflammation and Immune System Interactions in Atherosclerosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3847–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.J.; Smith, A.M. The Role of the Innate Immune System in Granulomatous Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Leuti, A.; Maccarrone, M. Bioactive Lipids and Chronic Inflammation: Managing the Fire Within. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagán, A.J.; Ramakrishnan, L. The Formation and Function of Granulomas. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 639–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.-M.; Rothwell, N.J.; Gibson, R.M. The Role of Inflammation in CNS Injury and Disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S232–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucin, K.M.; Wyss-Coray, T. Immune Activation in Brain Aging and Neurodegeneration: Too Much or Too Little? Neuron 2009, 64, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buttgereit, F.; Burmester, G.R.; Simon, L.S. Gastrointestinal Toxic Side Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Cyclooxygenase-2–Specific Inhibitors. Am. J. Med. 2001, 110, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Corticosteroids: The Drugs to Beat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 533, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.; Reker, D.; Schneider, P.; Schneider, G. Counting on Natural Products for Drug Design. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.M.; Ribnicky, D.M.; Lipsky, P.E.; Raskin, I. Revisiting the Ancient Concept of Botanical Therapeutics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The Re-Emergence of Natural Products for Drug Discovery in the Genomics Era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koparde, A.A.; Doijad, R.C.; Magdum, C.S. Natural Products in Drug Discovery. In Pharmacognosy: Medicinal Plants; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Alnuqaydan, A.M.; Rah, B.; Almutary, A.G.; Chauhan, S.S. Synergistic Antitumor Effect of 5-Fluorouracil and Withaferin-A Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Autophagy and Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 799. [Google Scholar]
- Rah, B.; Amin, H.; Yousuf, K.; Khan, S.; Jamwal, G.; Mukherjee, D.; Goswami, A. A Novel MMP-2 Inhibitor 3-Azidowithaferin A (3-AzidoWA) Abrogates Cancer Cell Invasion and Angiogenesis by Modulating Extracellular Par-4. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rah, B.; Rasool, R.U.; Nayak, D.; Yousuf, S.K.; Mukherjee, D.; Kumar, L.D.; Goswami, A. PAWR-Mediated Suppression of BCL2 Promotes Switching of 3-Azido Withaferin A (3-AWA)-Induced Autophagy to Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells. Autophagy 2015, 11, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rasool, R.; Rah, B.; Amin, H.; Nayak, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Rawoof, A.; Mintoo, M.J.; Yousuf, K.; Mukherjee, D.; Kumar, L.D. Corrigendum: Dual Modulation of Ras-Mnk and PI3K-AKT-MTOR Pathways: A Novel c-FLIP Inhibitory Mechanism of 3-AWA Mediated Translational Attenuation through Dephosphorylation of EIF4E. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.H.; Lee, T.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, T.K. Withaferin A Inhibits INOS Expression and Nitric Oxide Production by Akt Inactivation and Down-Regulating LPS-Induced Activity of NF-ΚB in RAW 264.7 Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 599, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, R.R.; Marron, M.T.; Gunaherath, G.K.B.; Shirahatti, N.; Mahadevan, D.; Gunatilaka, A.L.; Whitesell, L. Actin Microfilament Aggregation Induced by Withaferin A Is Mediated by Annexin II. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghe, W.V.; Sabbe, L.; Kaileh, M.; Haegeman, G.; Heyninck, K. Molecular Insight in the Multifunctional Activities of Withaferin A. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Paul, A.M.; Sun, H.; He, J.; Yang, M.; Bai, F.; Chen, Q. A Plant-Produced Vaccine Protects Mice against Lethal West Nile Virus Infection without Enhancing Zika or Dengue Virus Infectivity. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Pan, M.-H.; Shahidi, F. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Lipophilic Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) Derivatives in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malutan, A.M.; Drugan, T.; Costin, N.; Ciortea, R.; Bucuri, C.; Rada, M.P.; Mihu, D. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines for Evaluation of Inflammatory Status in Endometriosis. Cent.-Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 40, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepański, T.; van der Velden, V.H.; van Dongen, J.J. Flow-Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Normal and Malignant Lymphocytes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2006, 44, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rah, B.; Lone, S.H.; Rasool, R.U.; Farooq, S.; Nayak, D.; Chikan, N.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Behl, A.; Mondhe, D.M.; Goswami, A. Design and Synthesis of Antitumor Heck-Coupled Sclareol Analogues: Modulation of BH3 Family Members by SS-12 in Autophagy and Apoptotic Cell Death. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3432–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.; He, L. Houttuynia Cordata, a Novel and Selective COX-2 Inhibitor with Anti-Inflammatory Activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovats, S. Estrogen Receptors Regulate Innate Immune Cells and Signaling Pathways. Cell. Immunol. 2015, 294, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rittirsch, D.; Flierl, M.A.; Ward, P.A. Harmful Molecular Mechanisms in Sepsis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCulloch, C.A.; Downey, G.P.; El-Gabalawy, H. Signalling Platforms That Modulate the Inflammatory Response: New Targets for Drug Development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descotes, J. Methods of Evaluating Immunotoxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginwala, R.; Bhavsar, R.; Chigbu, D.G.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Potential Role of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobhani, M.; Farzaei, M.H.; Kiani, S.; Khodarahmi, R. Immunomodulatory; Anti-Inflammatory/Antioxidant Effects of Polyphenols: A Comparative Review on the Parental Compounds and Their Metabolites. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 37, 759–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyninck, K.; Sabbe, L.; Chirumamilla, C.S.; vel Szic, K.S.; Vander Veken, P.; Lemmens, K.J.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Naulaerts, S.; de Beeck, K.O.; Laukens, K. Withaferin A Induces Heme Oxygenase (HO-1) Expression in Endothelial Cells via Activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 109, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Huang, Y.-W.; Oshima, K.; Yearsley, M.; Zhang, J.; Arnold, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.-S. The Immunomodulatory Potential of Natural Compounds in Tumor-Bearing Mice and Humans. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 992–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mosser, D.M. Macrophage Activation by Endogenous Danger Signals. J. Pathol. A J. Pathol. Soc. G. B. Irel. 2008, 214, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kumar, R.K.; Hansbro, P.M.; Foster, P.S. Emerging Roles of Pulmonary Macrophages in Driving the Development of Severe Asthma. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, M. Many Cytokines Are Very Useful Therapeutic Targets in Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3533–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, K.; Torres, R. Role of Interleukin-1β during Pain and Inflammation. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neurath, M.F.; Finotto, S. IL-6 Signaling in Autoimmunity, Chronic Inflammation and Inflammation-Associated Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, N.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Vallyathan, V. Inflammation and Lung Cancer: Roles of Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2008, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Catravas, J.D. Endothelial Nitric Oxide (NO) and Its Pathophysiologic Regulation. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 49, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, E.D.; Riches, D.W. IFN-Γ+ LPS Induction of INOS Is Modulated by ERK, JNK/SAPK, and P38 Mapk in a Mouse Macrophage Cell Line. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C441–C450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, D.K.; Eden, K.; Ringel, V.M.; Allen, I.C. Emerging Roles for Noncanonical NF-ΚB Signaling in the Modulation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathobiology. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Su, D.; Li, L.; Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, J.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Hu, K. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Aureusidin in Lps-Stimulated Raw264. 7 Macrophages via Suppressing NF-ΚB and Activating Ros-and Mapks-Dependent Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 387, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: Pivotal Roles in Inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attiq, A.; Jalil, J.; Husain, K.; Ahmad, W. Raging the War against Inflammation with Natural Products. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaer, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Resveratrol: An Overview of Its Anti-Cancer Mechanisms. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, N.; Dhawan, D.K.; Bhatia, A.; Mahmood, A.; Mahmood, S. Doxycycline Promotes Carcinogenesis & Metastasis via Chronic Inflammatory Pathway: An in Vivo Approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151539. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Lewis, E.D.; Pae, M.; Meydani, S.N. Nutritional Modulation of Immune Function: Analysis of Evidence, Mechanisms, and Clinical Relevance. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. The Secret Ally: Immunostimulation by Anticancer Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.; Latz, E.; Mills, K.H.; Natoli, G.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; O’Neill, L.A.; Xavier, R.J. Trained Immunity: A Program of Innate Immune Memory in Health and Disease. Science 2016, 352, aaf1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Y.X.; Janakiraman, N.; Chapman, R.A.; Gautam, S.C. Immunomodulatory Activity of Resveratrol: Suppression of Lymphocyte Proliferation, Development of Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity, and Cytokine Production. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 62, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. The Role of CD4 T Cell Help for CD8 CTL Activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 384, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rie, M.A.; Schumacher, T.N.; van Schijndel, G.M.; van Lier, R.W.; Miedema, F. Regulatory Role of CD19 Molecules in B-Cell Activation and Differentiation. Cell. Immunol. 1989, 118, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


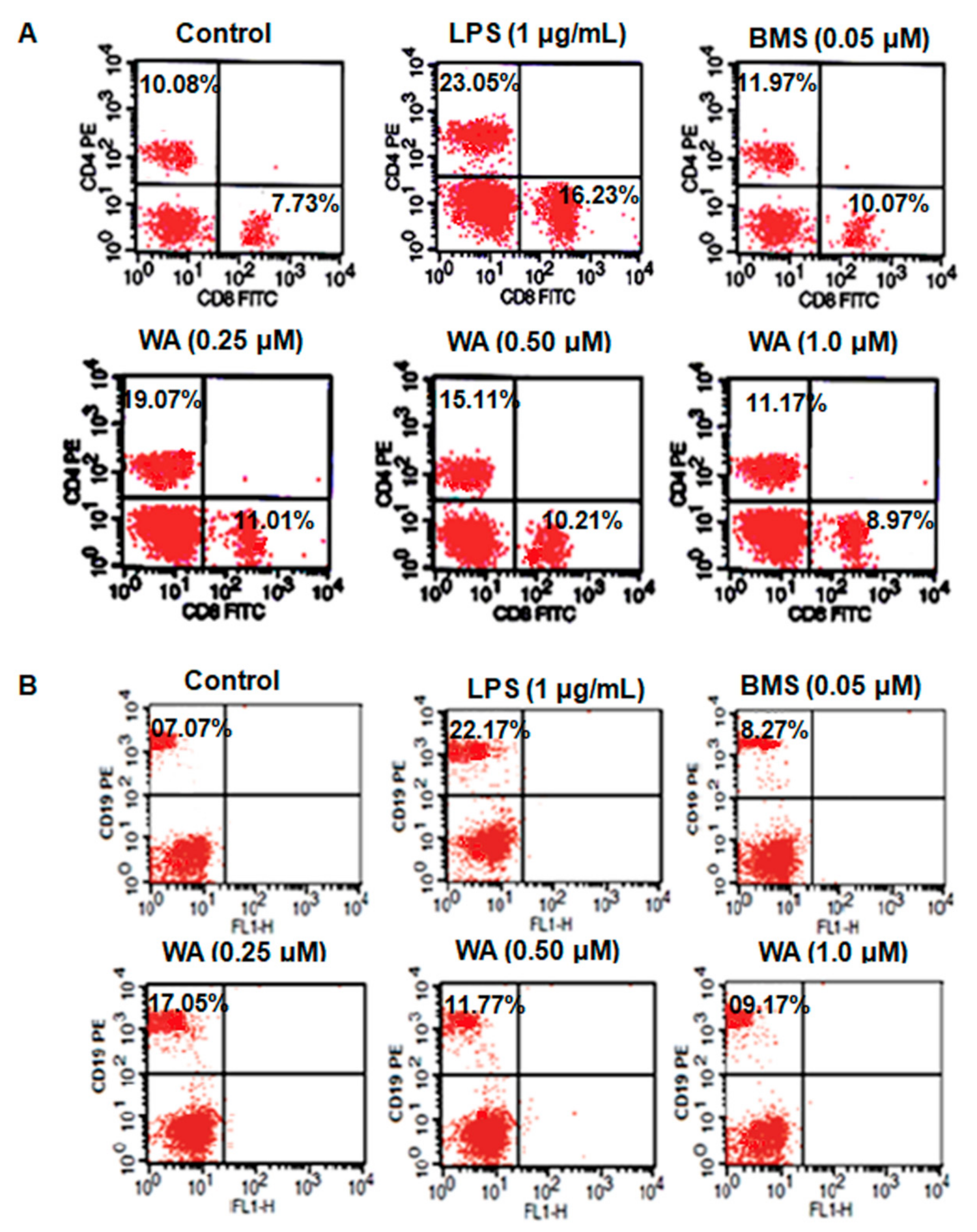

| Treatment | Dose (µM) | % CD4+ | % CD8+ | % CD19+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 10.08 ± 1.04 | 7.73 ± 0.98 | 7.07± 0.88 |
| LPS | (1 μg/mL) | 23.05 ± 1.24 * | 16.23 ± 1.4 * | 22.17 ± 1.23 * |
| BMS | 0.05 | 11.97 ± 0.13 # | 10.07 ± 0.17 # | 8.27 ± 0.4 # |
| WA | 0.25 | 19.07 ± 0.18 ## | 11.01 ± 0.11 ## | 17.05 ± 0.14 ## |
| WA | 0.50 | 15.11 ± 0.12 ## | 10.21 ± 0.16 ## | 11.77 ± 0.09 ## |
| WA | 1.0 | 11.97 ± 0.11 ## | 8.97 ± 0.22 ## | 9.17 ± 0.13 ## |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alnuqaydan, A.M.; Almutary, A.; Bhat, G.R.; Mir, T.A.; Wani, S.I.; Rather, M.Y.; Mir, S.A.; Alshehri, B.; Alnasser, S.; Ali Zainy, F.M.; et al. Evaluation of the Cytotoxic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Immunomodulatory Effects of Withaferin A (WA) against Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in Immune Cells Derived from BALB/c Mice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061256
Alnuqaydan AM, Almutary A, Bhat GR, Mir TA, Wani SI, Rather MY, Mir SA, Alshehri B, Alnasser S, Ali Zainy FM, et al. Evaluation of the Cytotoxic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Immunomodulatory Effects of Withaferin A (WA) against Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in Immune Cells Derived from BALB/c Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(6):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061256
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlnuqaydan, Abdullah M., Abdulmajeed Almutary, Gh Rasool Bhat, Tanveer Ahmad Mir, Shadil Ibrahim Wani, Mohd Younis Rather, Shabir Ahmad Mir, Bader Alshehri, Sulaiman Alnasser, Faten M. Ali Zainy, and et al. 2022. "Evaluation of the Cytotoxic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Immunomodulatory Effects of Withaferin A (WA) against Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in Immune Cells Derived from BALB/c Mice" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 6: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061256
APA StyleAlnuqaydan, A. M., Almutary, A., Bhat, G. R., Mir, T. A., Wani, S. I., Rather, M. Y., Mir, S. A., Alshehri, B., Alnasser, S., Ali Zainy, F. M., & Rah, B. (2022). Evaluation of the Cytotoxic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Immunomodulatory Effects of Withaferin A (WA) against Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in Immune Cells Derived from BALB/c Mice. Pharmaceutics, 14(6), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061256






