How Charge, Size and Protein Corona Modulate the Specific Activity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) against Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)
2.1.1. NLC Production and Optimization
2.1.2. NLC Characterization
2.2. NLC Activity against H. pylori
2.2.1. Bacterial Growth Conditions
2.2.2. NLC Antibacterial Performance
2.2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. NLC Activity against Gut Bacteria
2.3.1. Bacterial Growth Conditions
2.3.2. NLC Antibacterial Performance
2.4. NLC Protein Corona
2.4.1. NLC Protein Corona Characterization
2.4.2. Effect of Protein Corona on NLC Bactericidal Activity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. NLC Optimization
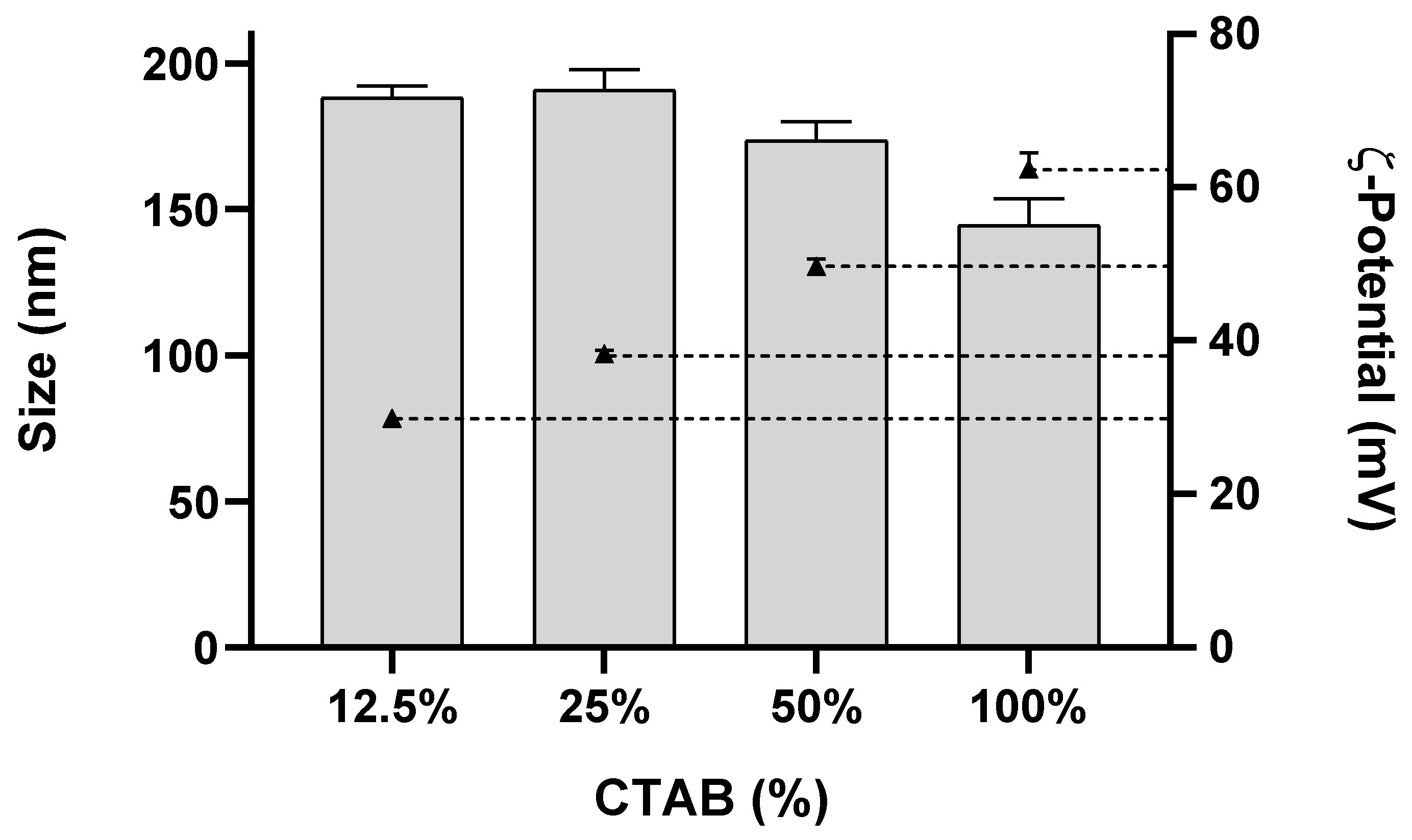
3.1.1. NLC with Different Surface Charge
3.1.2. NLC with Different Sizes and Surfactants
3.1.3. NLC for In Vitro Assays
3.2. NLC Antibacterial Performance
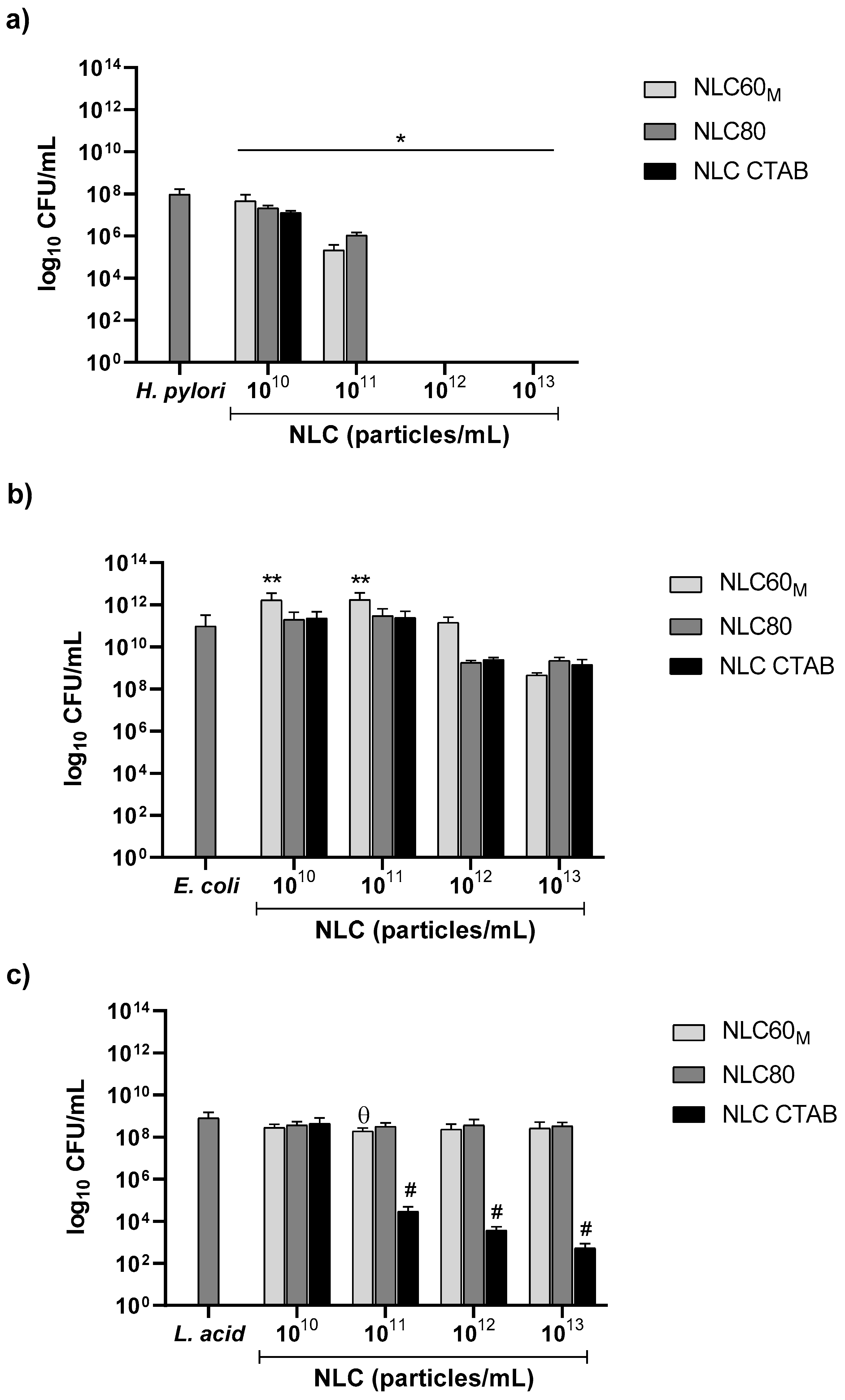
3.2.1. Effect of NLC Charge (Surfactant Composition)
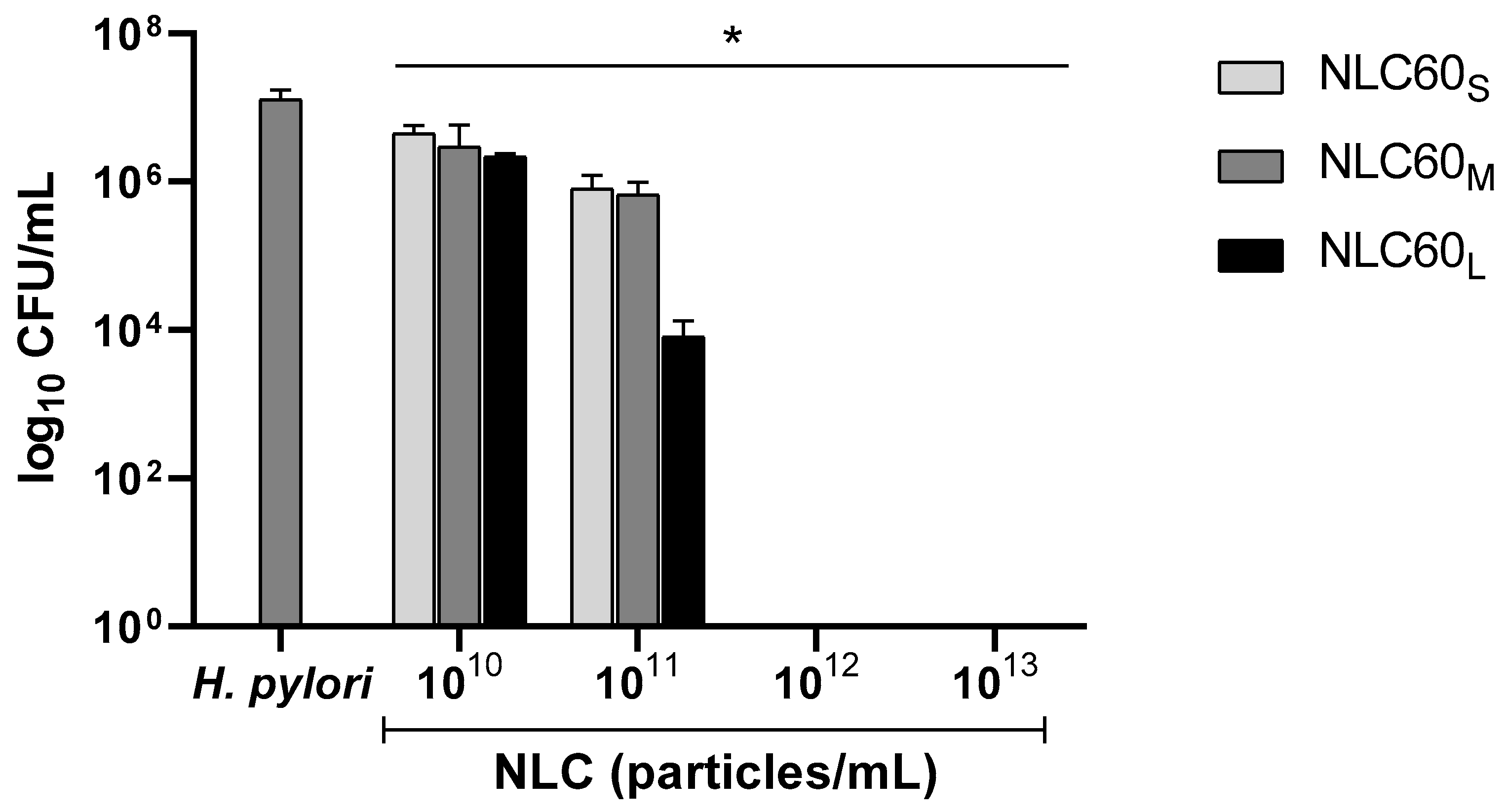
3.2.2. Effect of Size
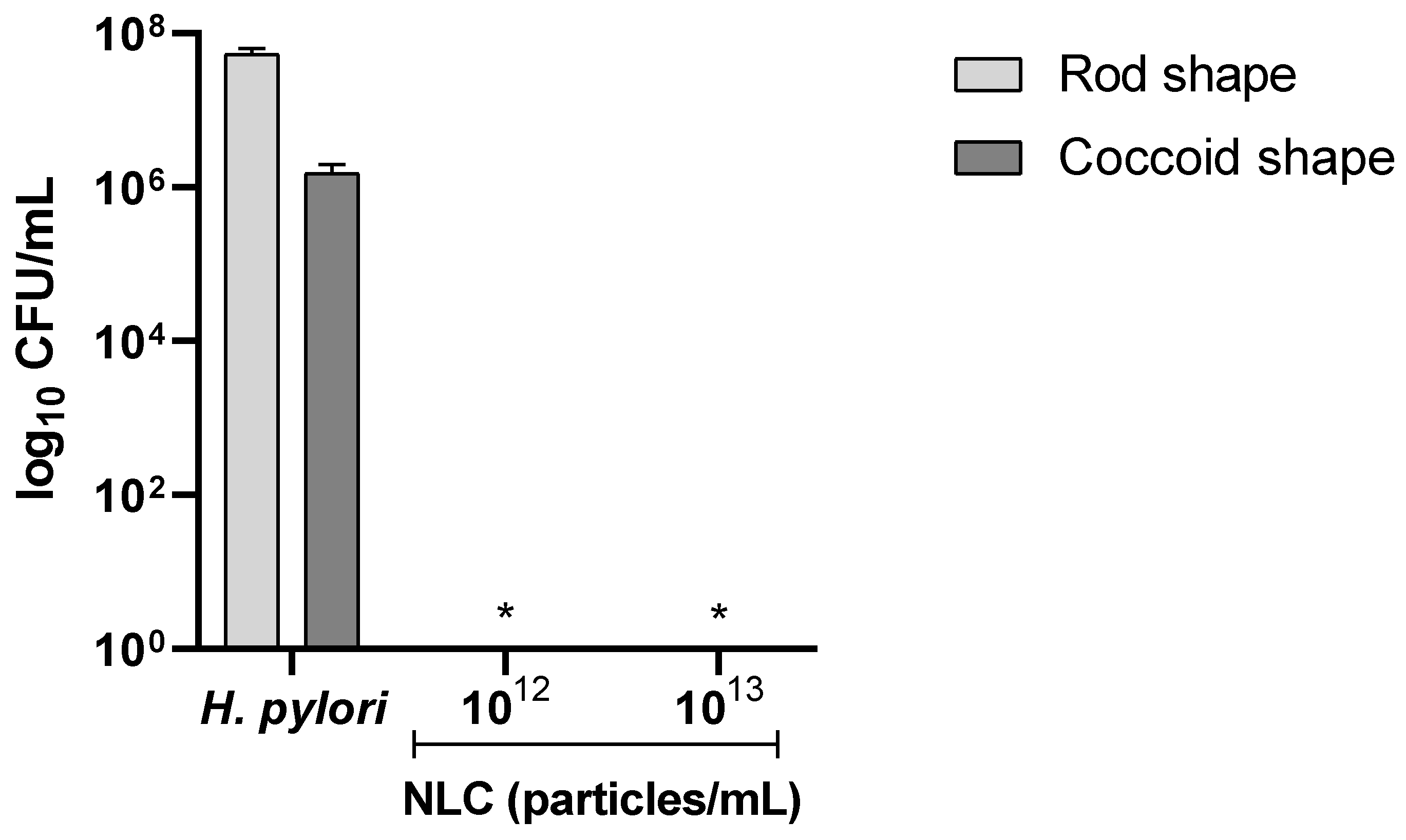
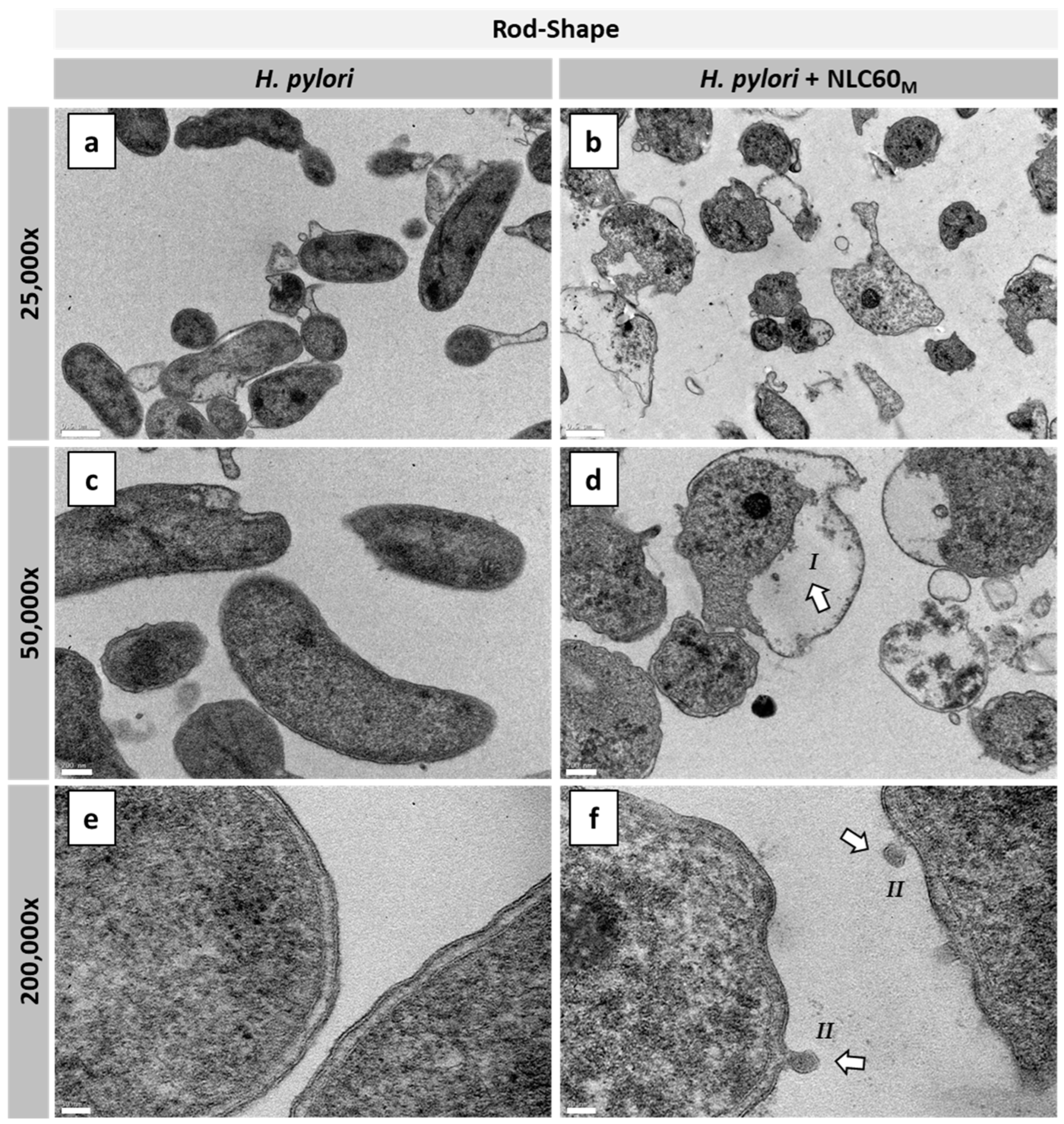
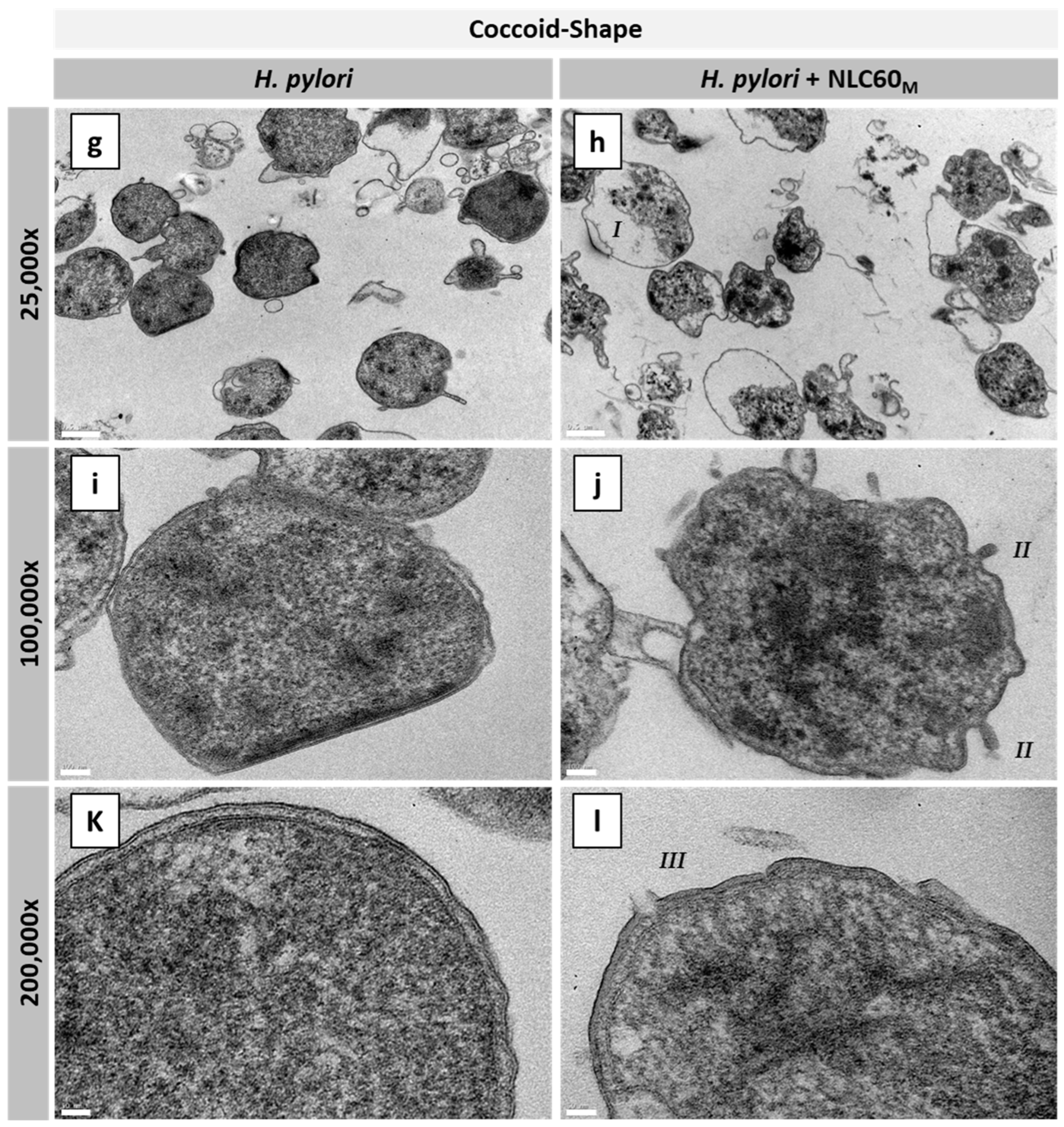
3.2.3. Effect on Different H. pylori Morphologies
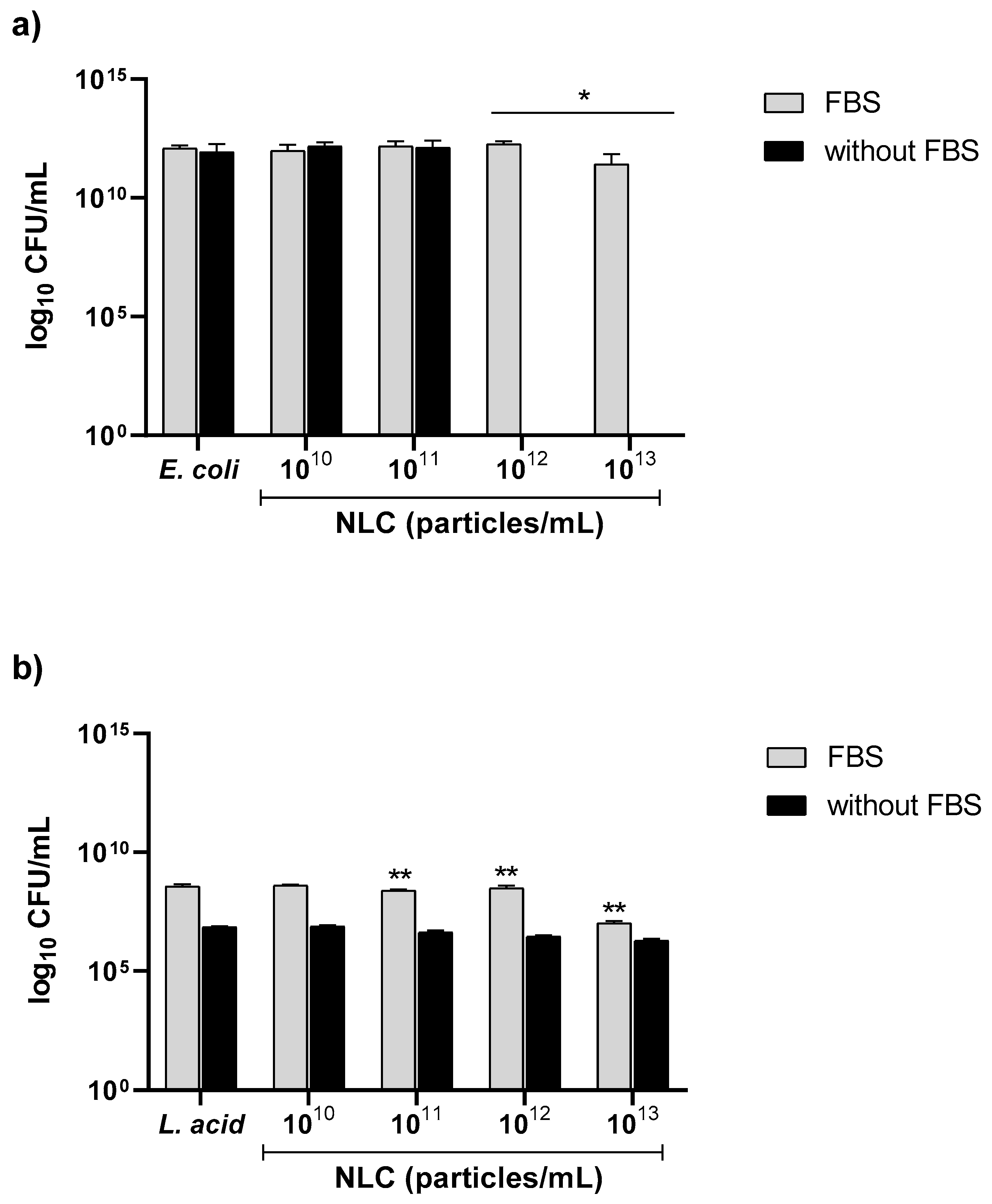
3.2.4. Effect of FBS on NLC Antibacterial Performance against E. coli and L. acidophilus
3.3. NLC Protein Corona
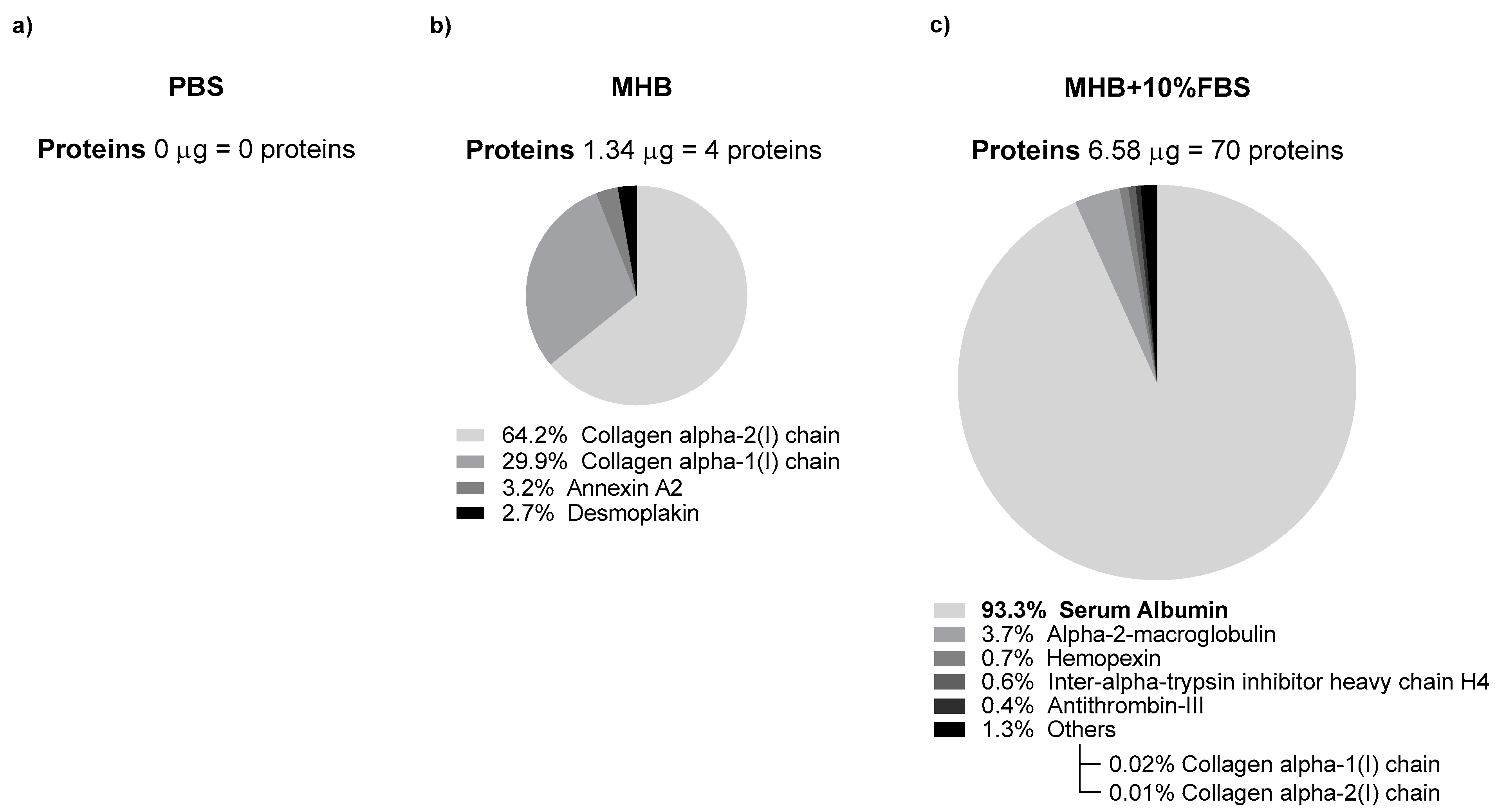
3.3.1. Characterization of NLC Protein Corona
3.3.2. Effect of NLC Protein Corona on Antibacterial Performance against H. pylori
3.4. Discussion
3.5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Espinoza, J.L.; Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, H.; Matsumura, I. Gastric microbiota: An emerging player in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric malignancies. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.Y.; Xu, J.L.; Sun, S.P.; Wang, K.J.; Lv, B. Helicobacter pylori eradication: Exploring its impacts on the gastric mucosa. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5152–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardos, I.A.; Zaha, D.C.; Sindhu, R.K.; Cavalu, S. Revisiting Therapeutic Strategies for H. pylori Treatment in the Context of Antibiotic Resistance: Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies. Molecules 2021, 26, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of gastric cancer: Global trends, risk factors and prevention. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.M.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.H.; Leja, M.; O’Morain, C.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut 2022, 71, 1724–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, O.A.; Wu, F.; Chen, Y. The role of gastric microbiota in gastric cancer. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Howden, C.W.; Moss, S.F. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 212–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; McNicholl, A.G. Optimization strategies aimed to increase the efficacy of H. pylori eradication therapies. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francino, M.P. Antibiotics and the Human Gut Microbiome: Dysbioses and Accumulation of Resistances. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Kamiya, S. Biofilm Formation by Helicobacter pylori and Its Involvement for Antibiotic Resistance. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 914791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathroubi, S.; Servetas, S.L.; Windham, I.; Merrell, D.S.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Formation and Its Potential Role in Pathogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2018, 82, e00001-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadkhodaei, S.; Siavoshi, F.; Akbari Noghabi, K. Mucoid and coccoid Helicobacter pylori with fast growth and antibiotic resistance. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ierardi, E.; Losurdo, G.; Mileti, A.; Paolillo, R.; Giorgio, F.; Principi, M.; Di Leo, A. The Puzzle of Coccoid Forms of Helicobacter pylori: Beyond Basic Science. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshetnyak, V.I.; Reshetnyak, T.M. Significance of dormant forms of Helicobacter pylori in ulcerogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4867–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzek, P.; Migdal, P.; Grande, R.; Gosciniak, G. Biofilm Formation of Helicobacter pylori in Both Static and Microfluidic Conditions Is Associated With Resistance to Clarithromycin. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 868905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Yin, F.; Wang, S.; Zhao, A.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Helicobacter pylori Biofilm-Related Drug Resistance and New Developments in Its Anti-Biofilm Agents. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshibangu-Kabamba, E.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and antibiotic resistance—From biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, C.L.; Nunes, C.; Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Correia, M.; Machado, J.C.; Goncalves, I.C.; Reis, C.A.; Reis, S.; Martins, M.C.L. Docosahexaenoic acid loaded lipid nanoparticles with bactericidal activity against Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, C.L.; Nunes, C.; Bras, M.; Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Reis, C.A.; Goncalves, I.C.; Reis, S.; Martins, M.C.L. Lipid nanoparticles to counteract gastric infection without affecting gut microbiota. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Michalowski, C.B.; Beloqui, A. Advances in lipid carriers for drug delivery to the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 52, 101414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Solinis, M.A.; Rodriguez-Gascon, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Preat, V. Nanostructured lipid carriers: Promising drug delivery systems for future clinics. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordillo-Galeano, A.; Mora-Huertas, C.E. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: A review emphasizing on particle structure and drug release. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 133, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, A.S.; Seabra, C.L.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S.; MC, L.M.; Parreira, P. Helicobacter pylori biofilms are disrupted by nanostructured lipid carriers: A path to eradication? J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, J.; Pinto, V.; Fernandes, T.; Malheiro, A.R.; Osorio, H.; Figueiredo, C.; Leite, M. Isolation Method and Characterization of Outer Membranes Vesicles of Helicobacter pylori Grown in a Chemically Defined Medium. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 654193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, P.; Magalhaes, A.; Goncalves, I.C.; Gomes, J.; Vidal, R.; Reis, C.A.; Leckband, D.E.; Martins, M.C. Effect of surface chemistry on bacterial adhesion, viability, and morphology. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2011, 99, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; CLSI Supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.S.; Moggridge, S.; Muller, T.; Sorensen, P.H.; Morin, G.B.; Krijgsveld, J. Single-pot, solid-phase-enhanced sample preparation for proteomics experiments. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, H.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Yang, T.C.; Ong, L.L.; Chang, C.C.; Muthusamy, S.; Abera, A.B.; Wu, M.S.; Gervay-Hague, J.; Mong, K.T.; et al. Cholesteryl alpha-D-glucoside 6-acyltransferase enhances the adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to gastric epithelium. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn-Orachai, K.; Smith, S.M.; Phunpee, S.; Treethong, A.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Pratontep, S.; Ruktanonchai, U.R. The effect of surfactant composition on the chemical and structural properties of nanostructured lipid carriers. J. Microencapsul. 2014, 31, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, G.E.; Alfei, S.; Caviglia, D.; Domenicotti, C.; Marengo, B. Antimicrobial Peptides and Cationic Nanoparticles: A Broad-Spectrum Weapon to Fight Multi-Drug Resistance Not Only in Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, E.R.; Billings, G.; Odermatt, P.D.; Auer, G.K.; Zhu, L.; Miguel, A.; Chang, F.; Weibel, D.B.; Theriot, J.A.; Huang, K.C. The outer membrane is an essential load-bearing element in Gram-negative bacteria. Nature 2018, 559, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, W.; Wang, X. Insights into the structure of Escherichia coli outer membrane as the target for engineering microbial cell factories. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figura, N.; Marcolongo, R.; Cavallo, G.; Santucci, A.; Collodel, G.; Spreafico, A.; Moretti, E. Polysorbate 80 and Helicobacter pylori: A microbiological and ultrastructural study. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, M.; Pagani, E.; Pesatori, E.V.; Bergonzi, M.; Figura, N.; Corazza, G.R.; Di Sabatino, A. Polysorbate 80 add-on therapy in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Polysorbate 80 and HP antibiotic resistance. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 34, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymczyk, K.; Zdziennicka, A.; Janczuk, B. Adsorption and Aggregation Properties of Some Polysorbates at Different Temperatures. J. Solut. Chem. 2018, 47, 1824–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qushawi, A.; Rassouli, A.; Atyabi, F.; Peighambari, S.M.; Esfandyari-Manesh, M.; Shams, G.R.; Yazdani, A. Preparation and Characterization of Three Tilmicosin-loaded Lipid Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Properties and in-vitro Antibacterial Activities. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 663–676. [Google Scholar]
- Belteky, P.; Ronavari, A.; Zakupszky, D.; Boka, E.; Igaz, N.; Szerencses, B.; Pfeiffer, I.; Vagvolgyi, C.; Kiricsi, M.; Konya, Z. Are Smaller Nanoparticles Always Better? Understanding the Biological Effect of Size-Dependent Silver Nanoparticle Aggregation Under Biorelevant Conditions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3021–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles of different particle size against Vibrio Natriegens. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obonyo, M.; Zhang, L.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Pornpattananangkul, D.; Fu, V.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial activities of liposomal linolenic acids against antibiotic-resistant Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, P.; Monteiro, C.; Graca, V.; Gomes, J.; Maia, S.; Gomes, P.; Goncalves, I.C.; Martins, M.C.L. Surface Grafted MSI-78A Antimicrobial Peptide has High Potential for Gastric Infection Management. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Bryers, J.D.; Jiang, S. Inhibition of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation on zwitterionic surfaces. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4192–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, T.; Bernfur, K.; Vilanova, M.; Cedervall, T. Understanding the Lipid and Protein Corona Formation on Different Sized Polymeric Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yin, D.; Tang, C.; He, E.; Zou, L.; Peng, Q. The protein corona and its effects on nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Acta Biomater. 2021, 129, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.K.; Ahmad, A.; Vyawahare, A.; Alam, P.; Khan, T.H.; Khan, R. Biological effects of formation of protein corona onto nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Ganesh, S.; Wang, W.; Amiji, M. The role of surface chemistry in serum protein corona-mediated cellular delivery and gene silencing with lipid nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8760–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wu, E.; Tang, W.; Qian, J.; Zhan, C. Interplay between nanomedicine and protein corona. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6713–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Baker, H.; Hancock, W.S.; Fawaz, F.; McCaman, M.; Pungor Jr, E. Proteomic analysis for the assessment of different lots of fetal bovine serum as a raw material for cell culture. Part IV. Application of proteomics to the manufacture of biological drugs. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.L. Albumin and mammalian cell culture: Implications for biotechnology applications. Cytotechnology 2010, 62, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishchenko, N.; Tretiakova, D.; Vodovozova, E. Spotlight on the protein corona of liposomes. Acta Biomater. 2021, 134, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amici, A.; Caracciolo, G.; Digiacomo, L.; Gambini, V.; Marchini, C.; Tilio, M.; Capriotti, A.; Colapicchioni, V.; Matassa, R.; Familiari, G. In vivo protein corona patterns of lipid nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francia, V.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Cullis, P.R.; Witzigmann, D. The biomolecular corona of lipid nanoparticles for gene therapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 2046–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| NLC Formulation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipids | Surfactants | |||||
| Code | Milli-Q® Water (mL) | Precirol®ATO5 (mg) | Miglyol®812 (mg) | Tween®60 (mg) | Tween®80 (mg) | CTAB (mg) |
| NCL60_1 | 4.2 | 60.0 | - | - | ||
| NLC60_2 | 5.0 | 60.0 | - | - | ||
| NLC80_1 | 4.2 | - | 60.5 | - | ||
| NLC CTAB_1 | 4.2 | 200 | 90 | - | - | 17 |
| NLC CTAB_2 | 4.2 | 30.0 | - | 8.5 | ||
| NLC CTAB_3 | 4.2 | 45.0 | - | 4.3 | ||
| NLC CTAB_4 | 4.2 | 52.5 | - | 2.2 | ||
| Sonication Parameters | Characterization | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEM | DLS | ELS | |||||
| NLC | Formulation (Table 1) | Amplitude (%) | Time (min) | Dry Diameter (nm) | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) | PdI | ζ-Potential (mV) |
| NLC60S | NLC60_2 | 40 | 5 | 102 ± 21 | 147 ± 10 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | −28 ± 0.9 |
| NLC60M | NLC60_1 | 60 | 5 | 202 ± 59 | 263 ± 8 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | −27 ± 0.4 |
| NLC60L | NLC60_1 | 90 | 20 | 342 ± 82 | 443 ± 11 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | −26 ± 0.8 |
| NLC80 | NLC80_1 | 90 | 5 | 195 ± 41 | 237 ± 8 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | −30 ± 0.7 |
| NLC CTAB | NLC CTAB_4 | 90 | 10 | 189 ± 45 | 211 ± 6 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | +38 ± 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chitas, R.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S.; Parreira, P.; Martins, M.C.L. How Charge, Size and Protein Corona Modulate the Specific Activity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) against Helicobacter pylori. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122745
Chitas R, Nunes C, Reis S, Parreira P, Martins MCL. How Charge, Size and Protein Corona Modulate the Specific Activity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) against Helicobacter pylori. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122745
Chicago/Turabian StyleChitas, Rute, Cláudia Nunes, Salette Reis, Paula Parreira, and Maria Cristina L. Martins. 2022. "How Charge, Size and Protein Corona Modulate the Specific Activity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) against Helicobacter pylori" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122745
APA StyleChitas, R., Nunes, C., Reis, S., Parreira, P., & Martins, M. C. L. (2022). How Charge, Size and Protein Corona Modulate the Specific Activity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) against Helicobacter pylori. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122745










