Design-of-Experiments (DoE)-Assisted Fabrication of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoemulgel and Its Evaluation against Human Skin Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodologies
2.2.1. Preparation of Stock Solution and Calibration Curve
2.2.2. Solubility Studies
2.2.3. Design-of-Experiment (DoE)
2.2.4. Preparation of QCT@NE
2.2.5. Characterization of QCT@NE
Determination of Globule Size, Zeta Potential and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
Entrapment Efficiency (EE)
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform-Infra Red (ATR-FTIR) Analysis
In Vitro Drug Release
2.2.6. Preparation of QCT-loaded Nanoemulgel (QCT@NG)
2.2.7. Characterization of QCT@NG
Measurement of pH
Viscosity
Drug Content
Texture Profile Analysis
2.2.8. Stability Study
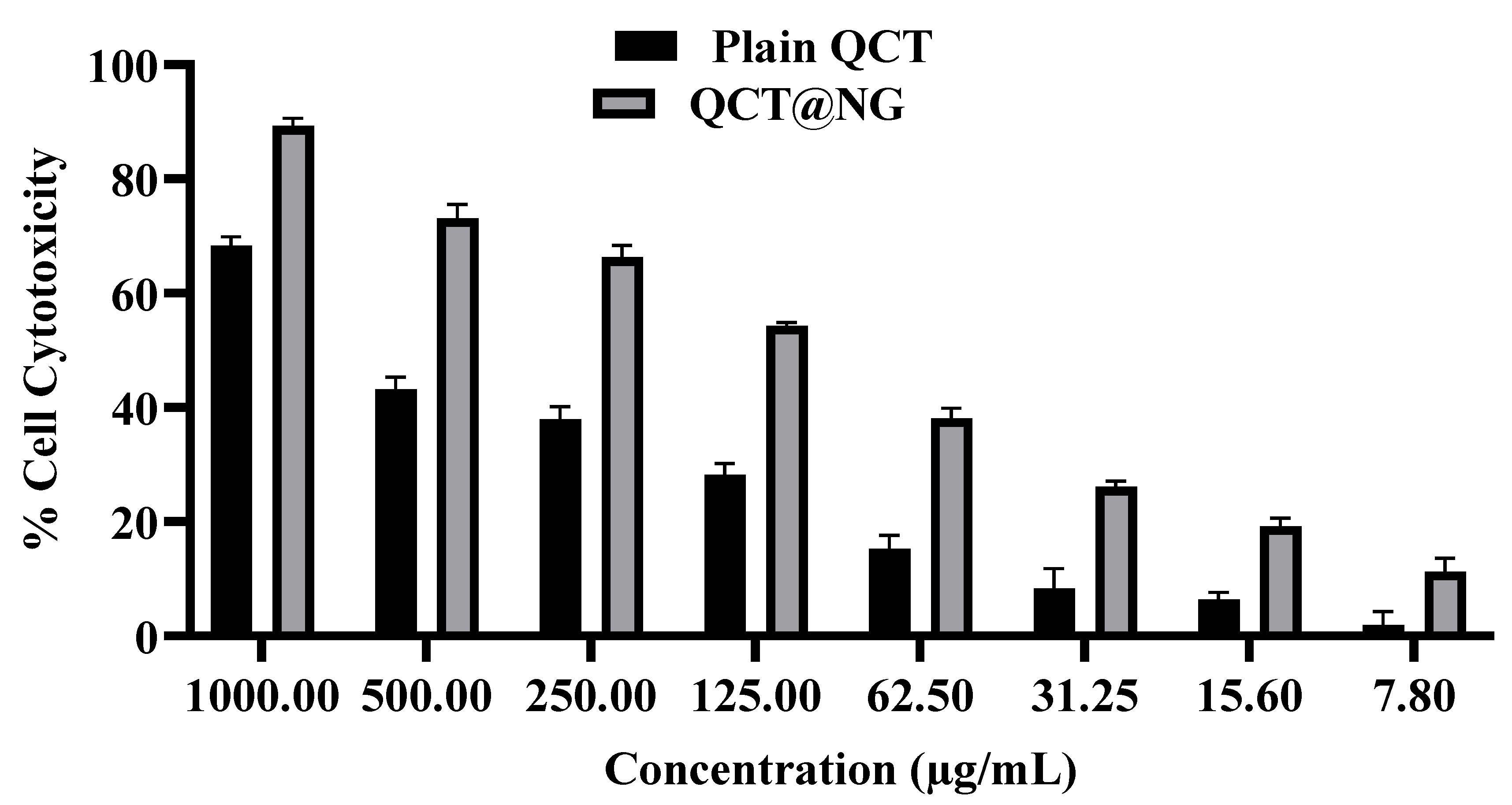
2.2.9. Percent Cell Cytotoxicity
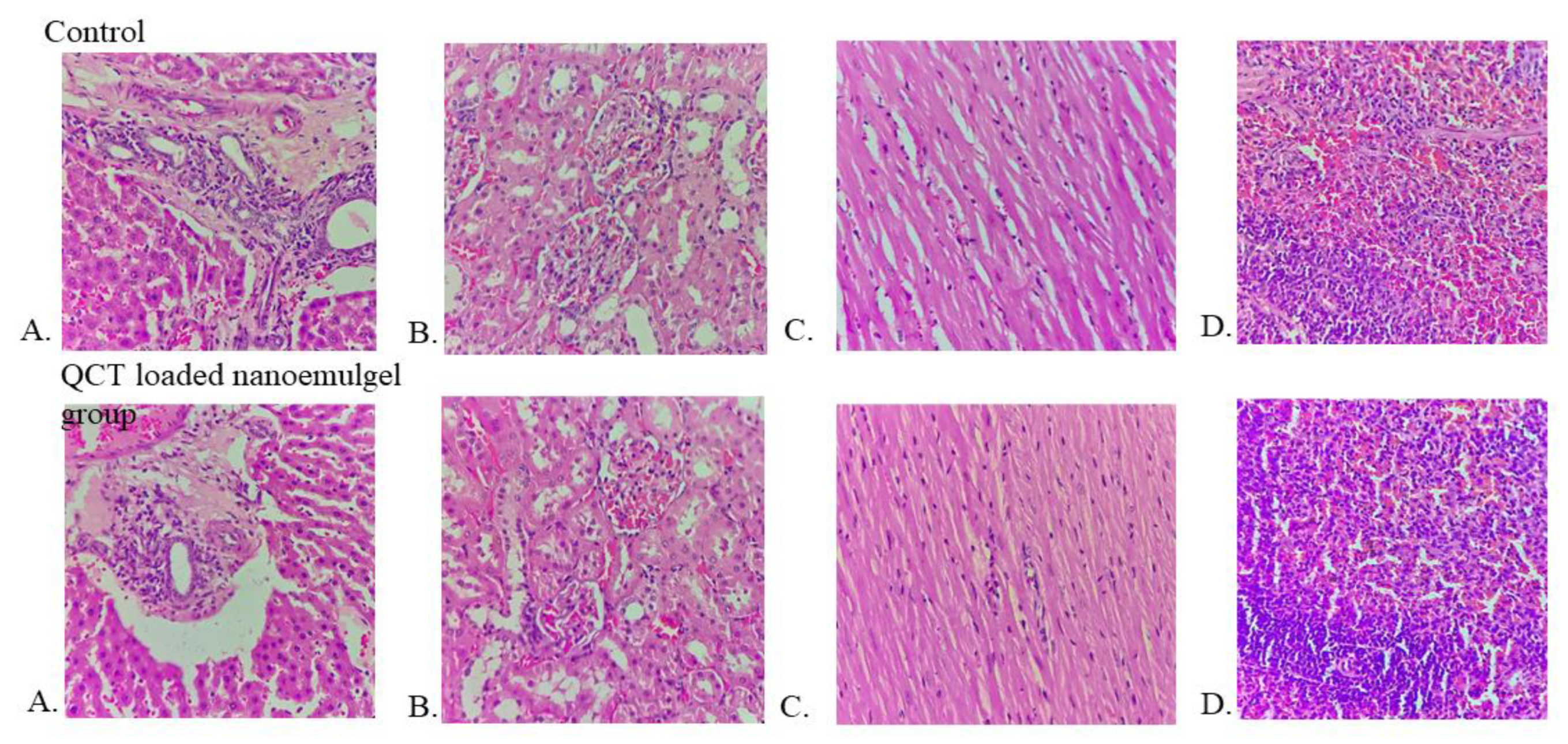
2.2.10. Animal Studies
Skin Irritation Study
Acute Toxicity Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
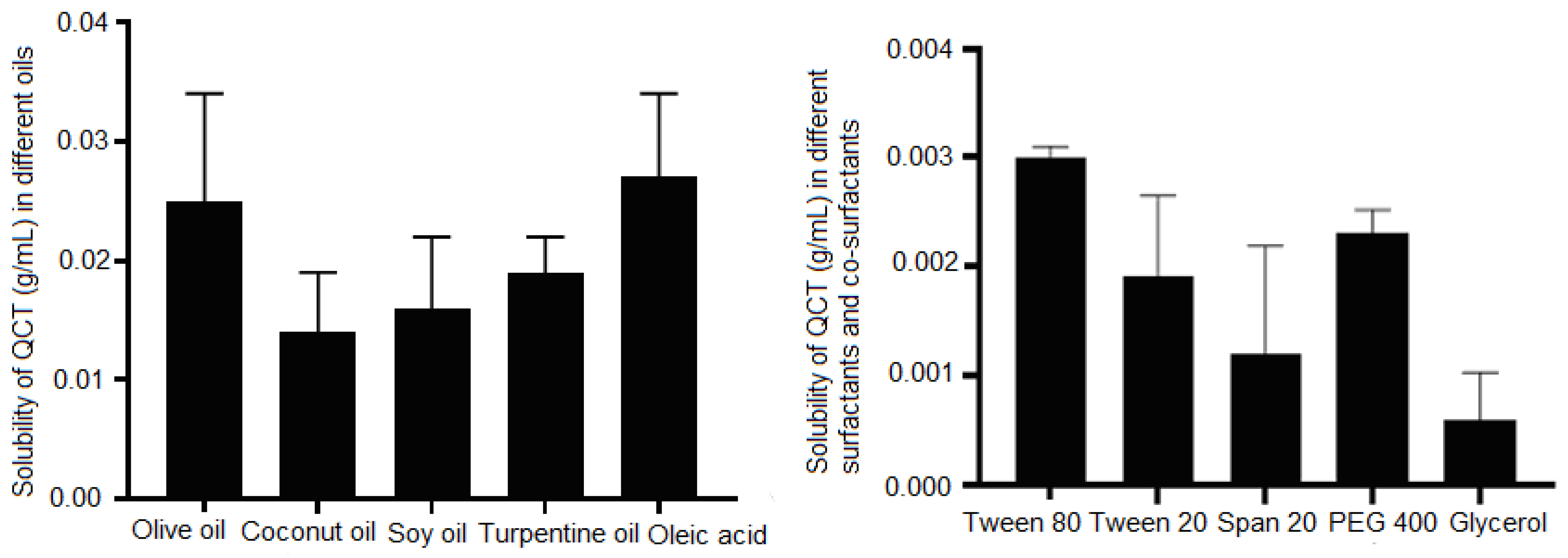
3.2. Solubility Studies
3.3. Optimization of QCT@NE Using Design-of-Experiment (DoE)
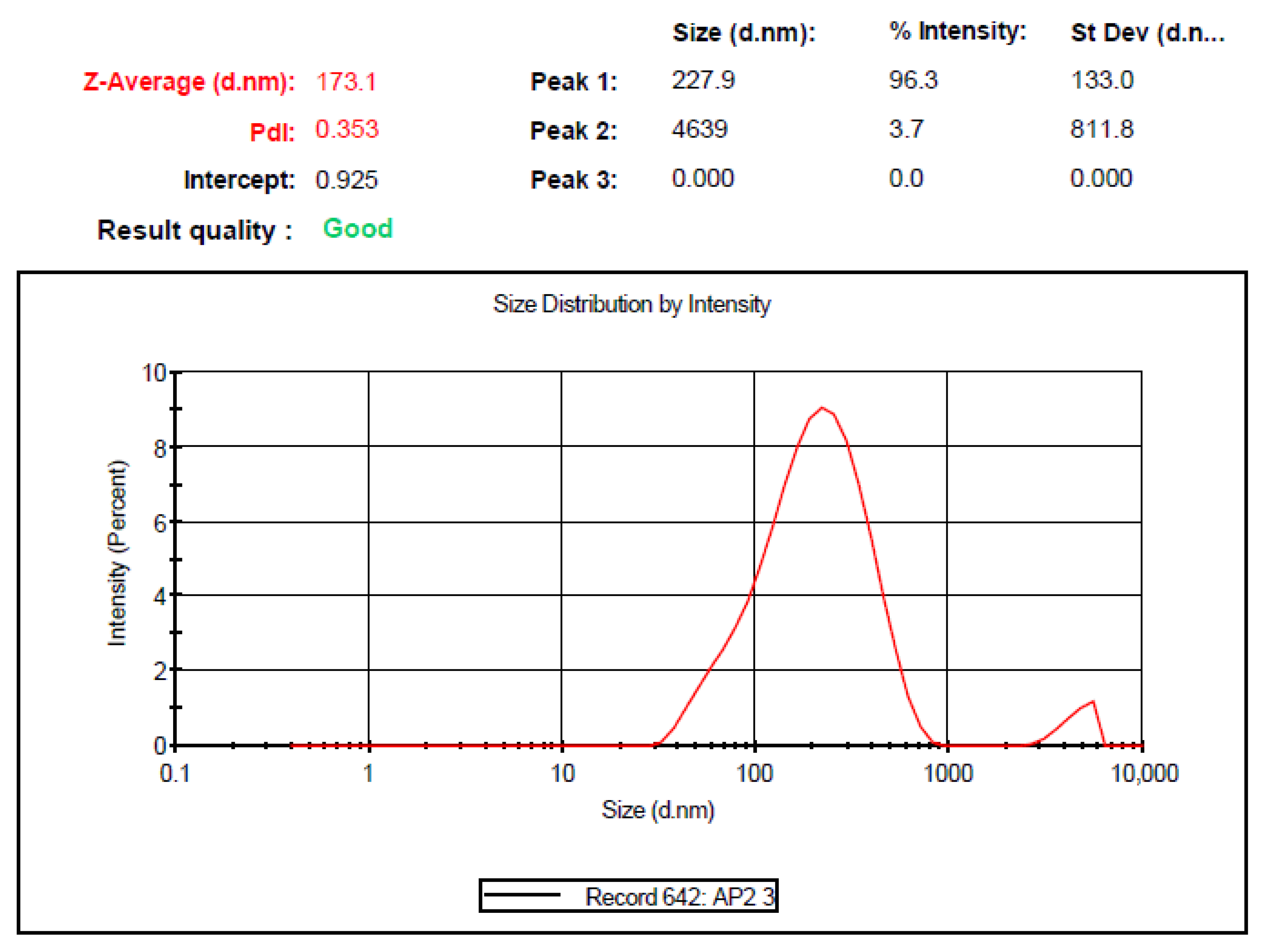
3.4. Globule Size and PDI
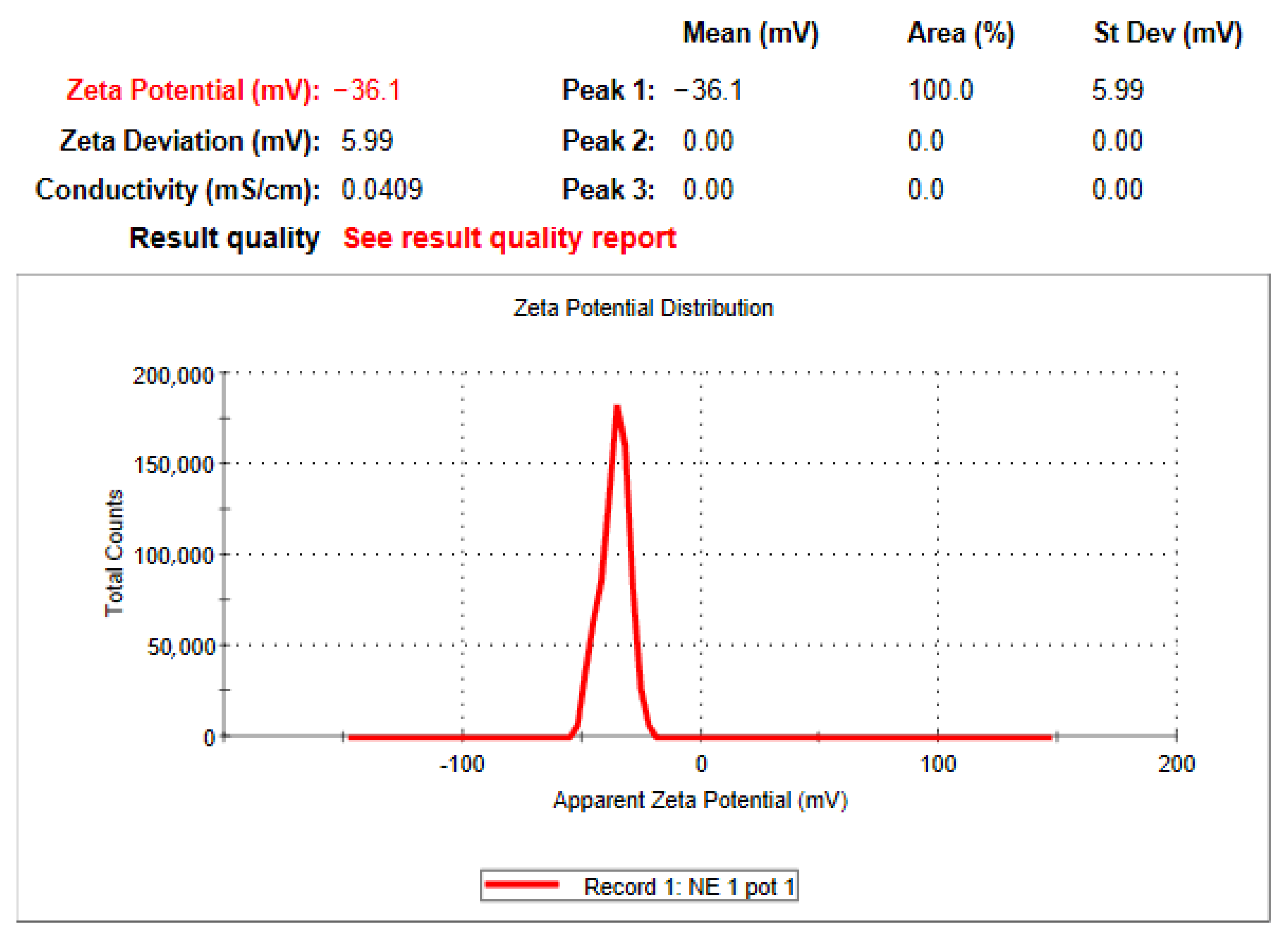
3.5. Zeta Potential
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release Study
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.8. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
3.9. Entrapment Efficiency
3.10. In Vitro Characterization of QCT@NG
3.10.1. Measurement of pH
3.10.2. Viscosity
3.10.3. Drug Content
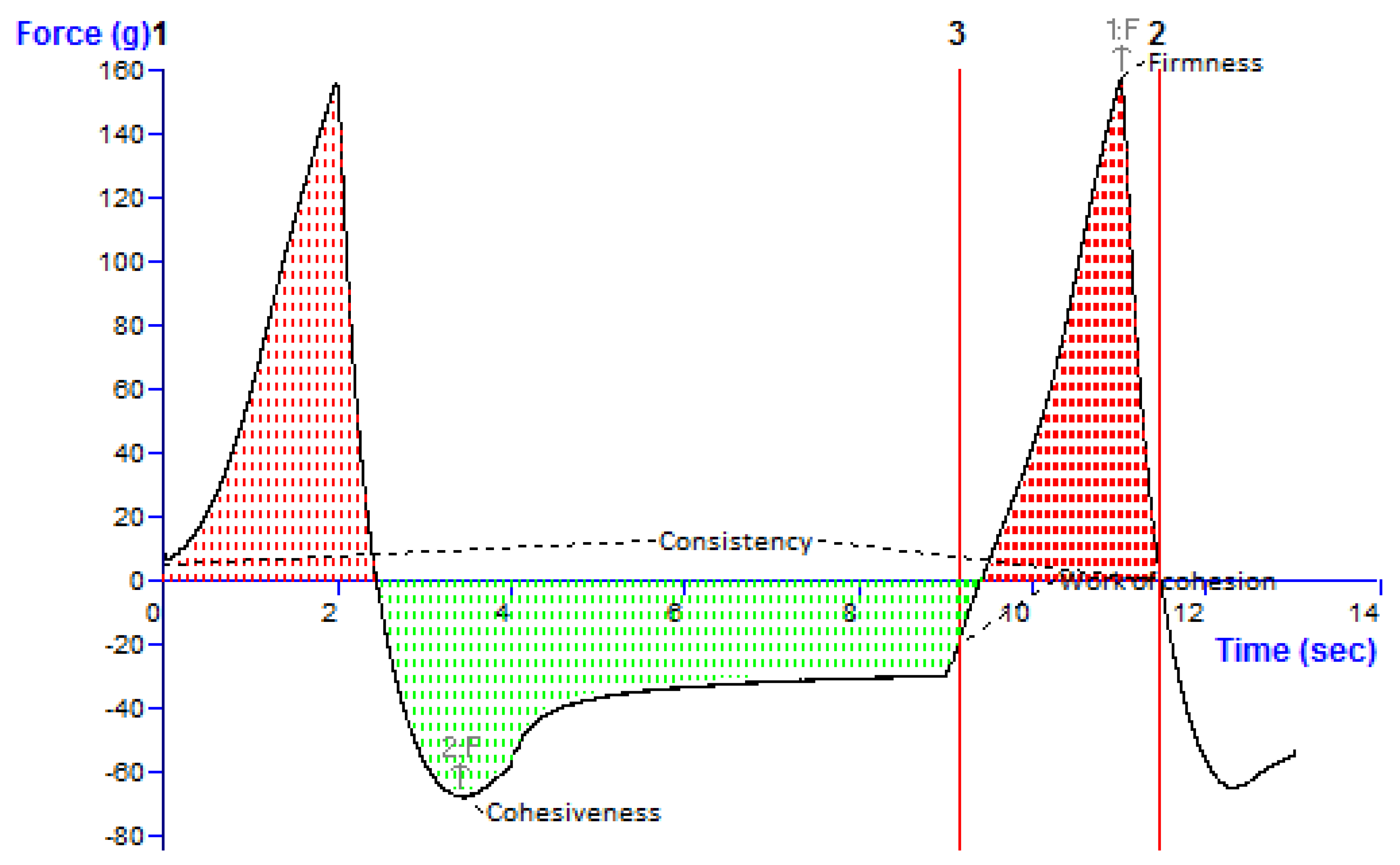
3.10.4. Texture Profile Analysis
3.11. Stability Study
3.12. Percent Cell Cytotoxicity Study
3.13. Skin Irritation Study
3.14. Acute Toxicity Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davey, M.G.; Miller, N.; McInerney, N.M. A review of epidemiology and cancer biology of malignant melanoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e15087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labani, S.; Asthana, S.; Rathore, K.; Sardana, K. Incidence of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers in Indian and the global regions. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladi, R.N.; Persaud, A.N. The causes of skin cancer: A comprehensive review. Drugs Today 2005, 41, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cives, M.; Mannavola, F.; Lospalluti, L.; Sergi, M.C.; Cazzato, G.; Filoni, E.; Cavallo, F.; Giudice, G.; Stucci, L.S.; Porta, C.; et al. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: Biological and Clinical Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedberg, M.L.; Berry, C.T.; Moshiri, A.S.; Xiang, Y.; Yeh, C.J.; Attilasoy, C.; Capell, B.C.; Seykora, J.T. Molecular Mechanisms of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.; Gupta, J.; Gupta, R. Miracles of herbal phytomedicines in treatment of skin disorders: Natural healthcare perspective. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Ikram, M.; Mulla, Z.S.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Taha, A.E.; Algammal, A.M.; Elewa, Y.H.A. The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Machin, L.; Monzote, L.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salem, M.A.; Merghany, R.M.; El Mahdy, N.M.; Kılıç, C.S.; Sytar, O.; et al. Therapeutic potential of Quercetin: New insights and perspectives for human health. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11849–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ma, X.; Qi, X.; Xiao, J.; Xue, W.; Luo, Y.; Yue, T. Advance on the absorption, metabolism, and efficacy exertion of quercetin and its important derivatives. Food Front. 2020, 1, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algahtani, M.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Nourein, I.H.; Albarqi, H.A.; Alyami, H.S.; Alyami, M.H.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Alasiri, A.; Algahtani, T.S.; Mohammed, A.A.; et al. Preparation and characterization of Curcumin nanoemulgel utilizing ultrasonication technique for wound healing: In vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo evaluation. Gels 2021, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Guerra, M.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Lopez-Machado, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Camins, A.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, E.B. Current applications of nanoemulsions in cancer therapeutics. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.; Ahmad, J.; Asif, M.; Khan, S.U.; Irfan, M.; YIbrahim, A.; Asghar, S.; Khan, I.U.; Iqbal, M.S.; Haseeb, A.; et al. Nanoemulgel, an innovative carrier for Diflunisal topical delivery with profound anti-inflammatory effect: In Vitro and In Vivo evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1457–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Khan, B.; Ullah, S.; Khan, M.K.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Braga, V.A. Formulation and evaluation of Ocimum basilicum-based emulgel for wound healing using animal model. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesharwani, P.; Jain, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Keshari, M.K. Systematic development and characterization of curcumin-loaded nanogel for topical application. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, K.; Mujtaba, A.; Akhter, M.H.; Zafar, A.; Kohli, K. Optimisation of ethosomal nanogel for topical nano-CUR and sulphoraphane delivery in effective skin cancer therapy. J. Microencapsul. 2020, 37, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmala, M.J.; Durai, L.; Gopakumar, V.; Nagarajan, R. Preparation of celery essential oil-based nanoemulsion by ultrasonication and evaluation of its potential anticancer and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7651–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Hao, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, G. Preparation and Evaluation of Stearylamine-Bearing Pemetrexed Disodium-Loaded Cationic Liposomes In Vitro and In Vivo. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2020, 21, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.B.; Cetin, M.; Orgul, D.; Taghizadehghalehjoughi, A.; Hacımuftuoglu, A.; Hekimoglu, S. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of topical nanoemulsion and nanoemulsion-based gels containing daidzein. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshaiah, A.; Padil, V.V.T.; Nagalakshmaiah, M.; Waclawek, S.; Černík, M.; Varma, R.S. Microscopic Techniques for the Analysis of Micro and Nanostructures of Biopolymers and Their Derivatives. Polymers 2020, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Cao, W.; Chu, X. Liposome and microemulsion loaded with ibuprofen: From preparation to mechanism of drug transport. J. Microencapsul. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Amin, A.; Alamoudi, R.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Alamoudi, R.A.; Nawaz, A.; Raza, M.; Nawaz, T.; Ishtiaq, S.; Abbas, S.S. Fabrication and optimization of essential-oil-loaded nanoemulsion using Box-Behnken design against Staphylococos aureus and Staphylococos epidermidis isolated from oral cavity. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, A.M.; Issa, L.; Al-Kharouf, O.; Jaber, R.; Hreash, F. Development of Coriandrum sativum oil nanoemulgel and evaluation of its antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5247816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Gaur, P.K.; Tiwari, A. Development of Topical Nanoemulgel Using Combined Therapy for Treating Psoriasis. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2022, 20, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, G.C.; Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y. Nanoemulgel: A Promising Phase in Drug Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Ali, J.; Gupta, D.K.; Warsi, M.H.; Bilgrami, A.L.; Asfour, H.Z.; Noor, A.O.; Md, S. Brucine-loaded transliposomes nanogel for topical delivery in skin cancer: Statistical optimization, in vitro and dermatokinetic evaluation. 3 Biotech. 2021, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algahtani, M.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Ahmad, J. Nanoemulgel for improved topical delivery of retinyl palmitate: Formulation design and stability evaluation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, S.; Basavarajappa, G.M.; Attimarad, M.; Pund, S. Topical nanoemulgel for the treatment of skin cancer: Proof-of-technology. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, B.; Shen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Chaurasiya, B.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Xing, X.; Chen, D. Eprinomectin nanoemulgel for transdermal delivery against endoparasites and ectoparasites: Preparation, In Vitro and In Vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setya, S.; Madaan, T.; Razdan, B.K.; Farswan, M.; Talegaonkar, S. Design and development of novel transdermal nanoemulgel for Alzheimer’s disease: Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and biochemical investigations. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, D.S.; Ishak, R.A.H.; Ghoneim, A.; Elhuoni, M.A. Nanoemulsion: A review on mechanisms for the transdermal delivery of hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharat, M.; Aberg, J.; Dai, T.; McClements, D.J. Comparison of Emulsion and Nanoemulsion Delivery Systems: The Chemical Stability of Curcumin Decreases as Oil Droplet Size Decreases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9205–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodolazkaya, N.; Nikolskaya, M.; Laguta, A.; Farafonov, V.; Balklava, Z.; Stich, M.; Mchedlov-Petrossyan, N.; Nerukh, D. Estimation of nanoparticle’s surface electrostatic potential in solution using acid-base molecular probes. III. Experimental hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity and charge distribution of MS2 virus surface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 8166–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuar, N.; Sabri, A.H.; Bustami Effendi, T.J.; Abdul Hamid, K. Development and characterisation of ibuprofen-loaded nanoemulsion with enhanced oral bioavailability. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulawik-Pióro, A.; Miastkowska, M. Polymeric gels and their application in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torić, J.; Marković, A.K.; Brala, C.J.; Barbarić, M. Anticancer effects of olive oil polyphenols and their combinations with anticancer drugs. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Time (Months) | pH | Drug Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5.8 ± 0.32 | 92.3 ± 1.67 |
| 1 | 5.7 ± 0.45 | 92.1 ± 1.21 |
| 2 | 5.9 ± 0.11 | 91.5 ± 2.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chitkara, A.; Mangla, B.; Kumar, P.; Javed, S.; Ahsan, W.; Popli, H. Design-of-Experiments (DoE)-Assisted Fabrication of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoemulgel and Its Evaluation against Human Skin Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112517
Chitkara A, Mangla B, Kumar P, Javed S, Ahsan W, Popli H. Design-of-Experiments (DoE)-Assisted Fabrication of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoemulgel and Its Evaluation against Human Skin Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(11):2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112517
Chicago/Turabian StyleChitkara, Aman, Bharti Mangla, Pankaj Kumar, Shamama Javed, Waquar Ahsan, and Harvinder Popli. 2022. "Design-of-Experiments (DoE)-Assisted Fabrication of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoemulgel and Its Evaluation against Human Skin Cancer Cell Lines" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 11: 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112517
APA StyleChitkara, A., Mangla, B., Kumar, P., Javed, S., Ahsan, W., & Popli, H. (2022). Design-of-Experiments (DoE)-Assisted Fabrication of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoemulgel and Its Evaluation against Human Skin Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics, 14(11), 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112517







