Incorporation of Zinc into Binary SiO2-CaO Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Enhances Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Ion Release Behavior of Zn-MBGs
2.2. Preparation of Extracts
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
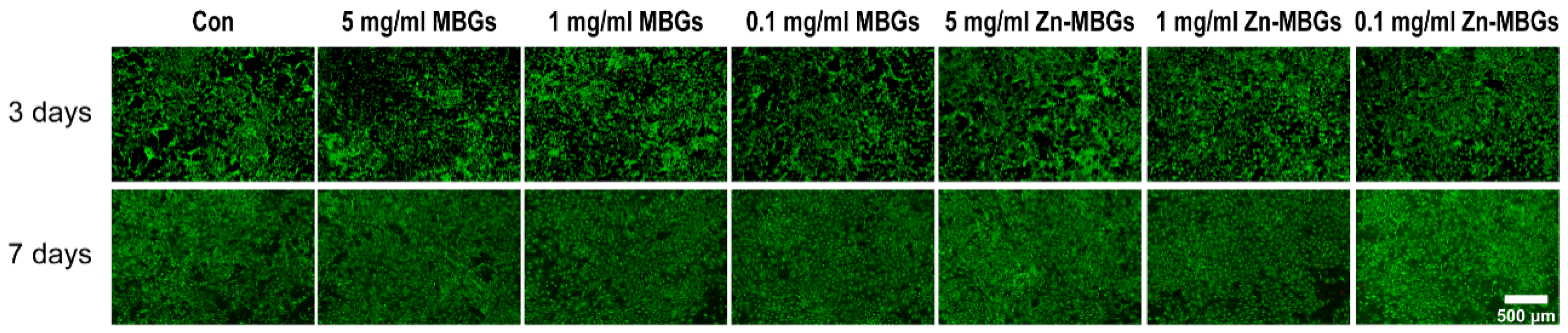
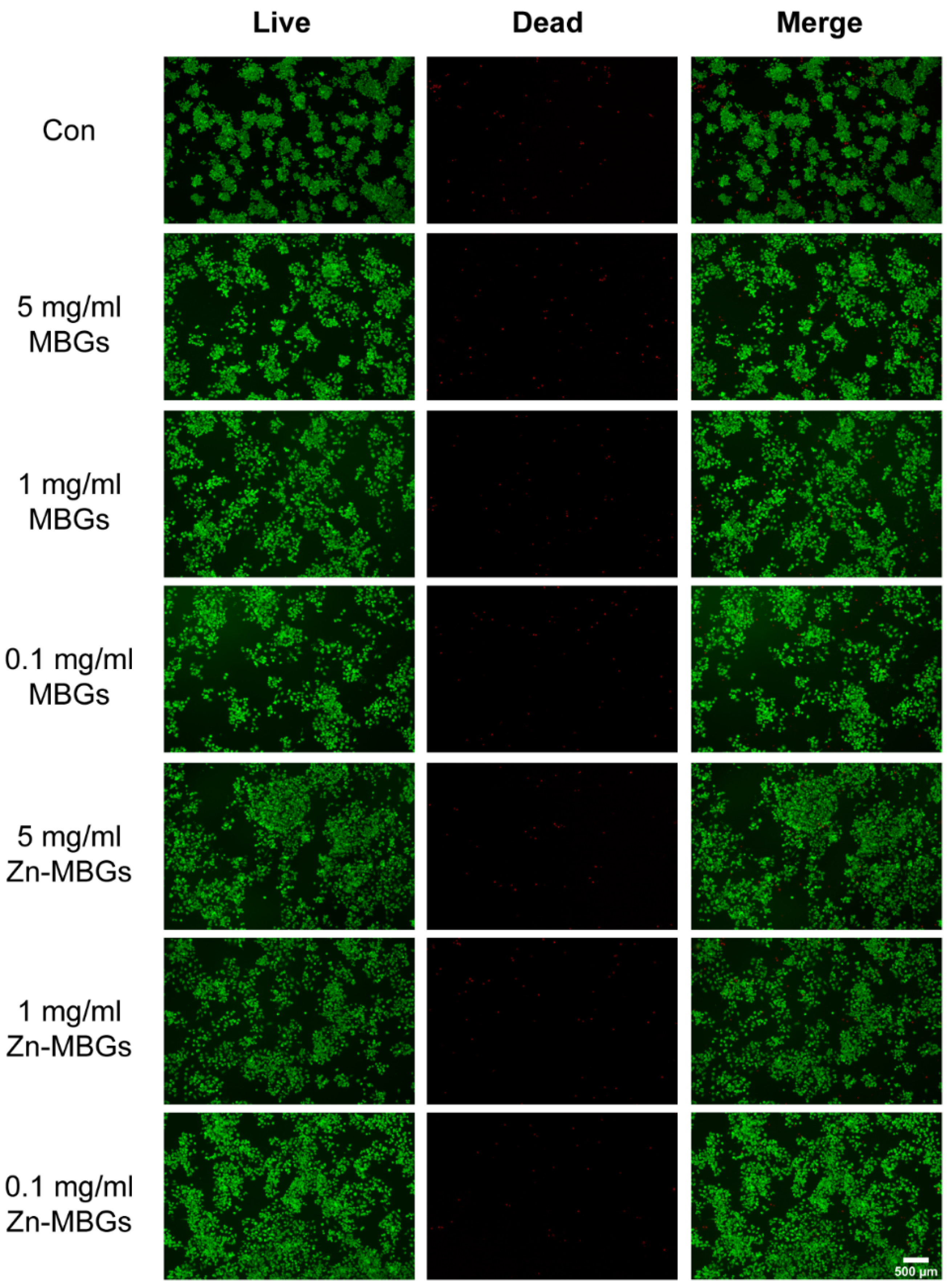
2.5. Live/Dead Fluorescence Staining
2.6. Alizarin Red S Staining
2.7. Expression of Osteogenesis-Related Genes
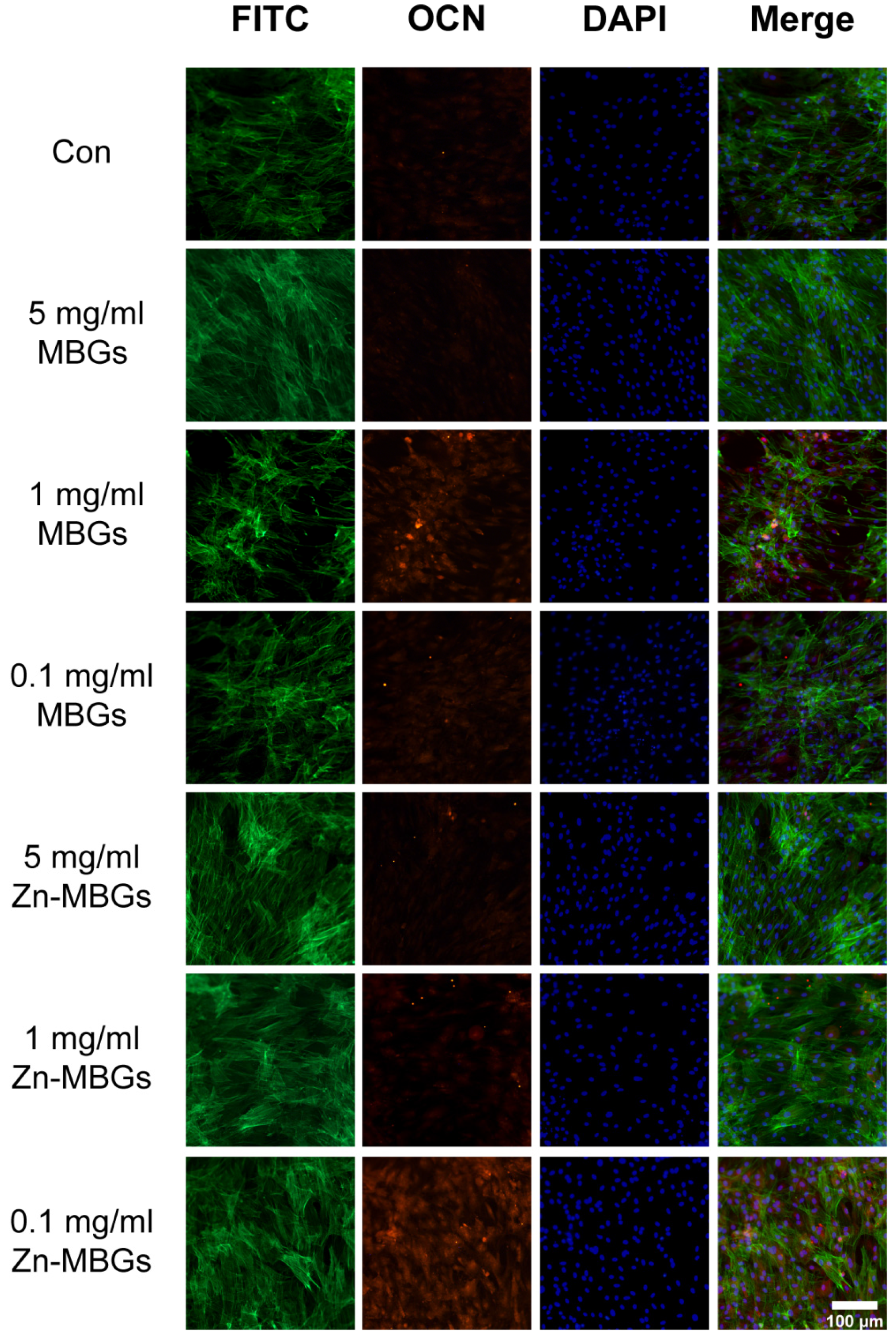
2.8. Immunostaining of Osteocalcin (OCN)
2.9. Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Related Genes
2.10. iNOS Fluorescence Staining
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ion Release of Zn-MBGs in Cell Culture Medium
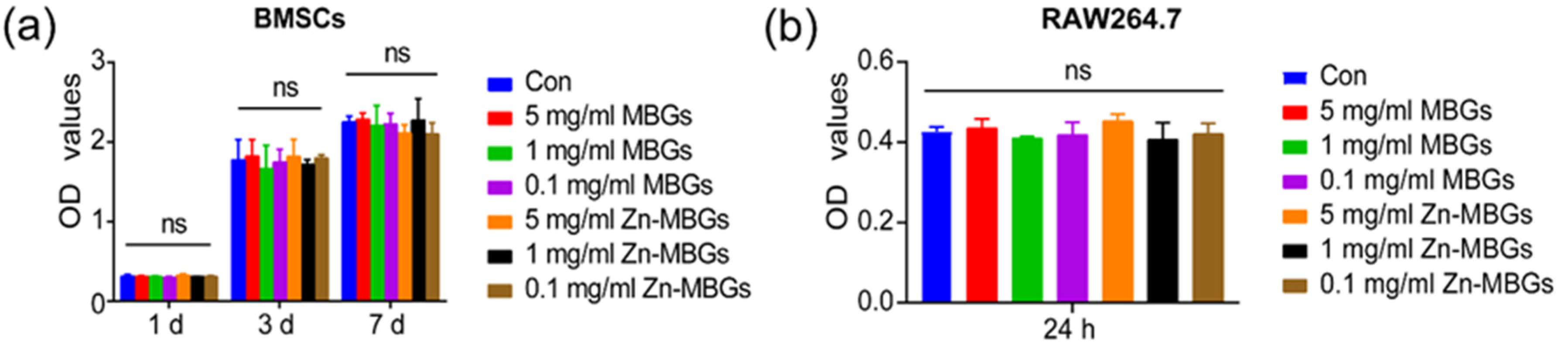
3.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
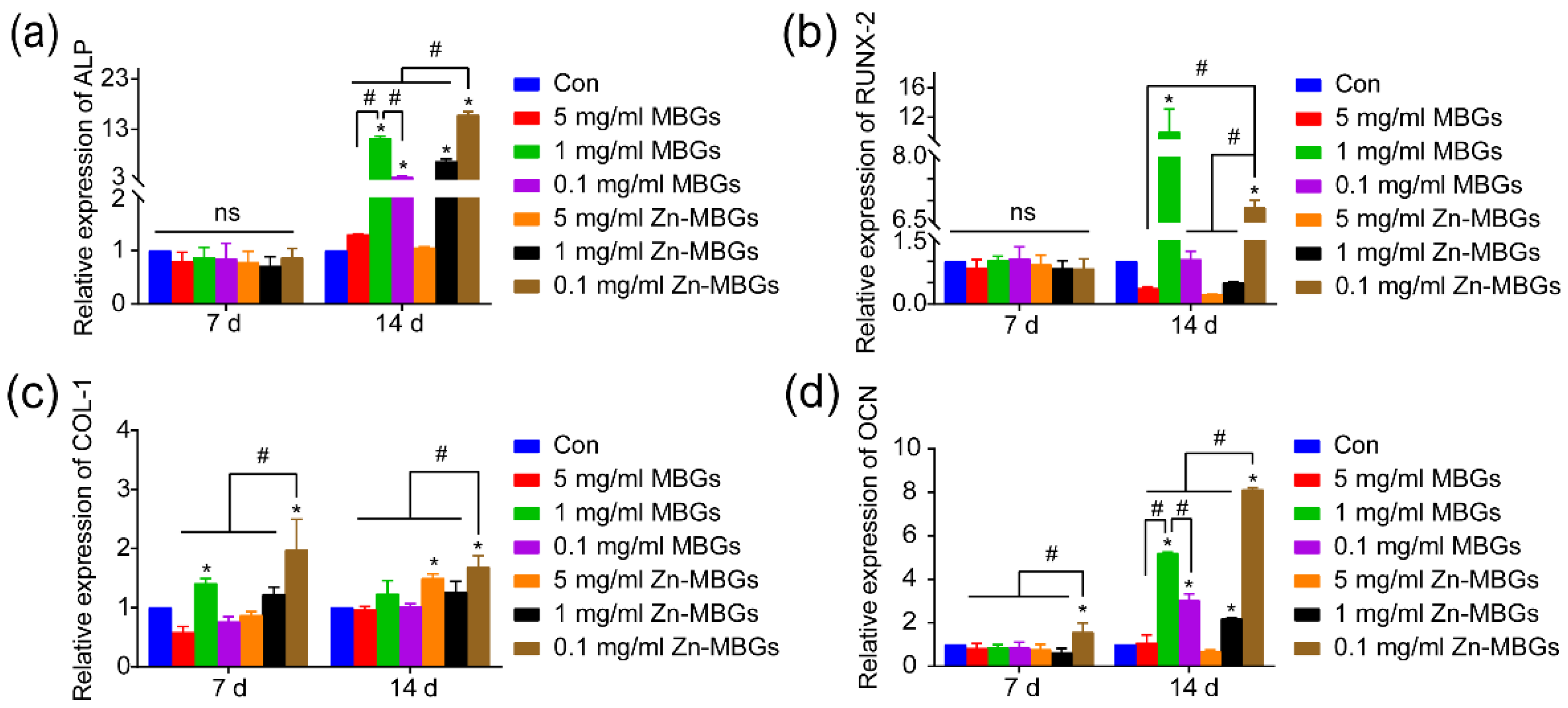
3.3. In Vitro Cell Mineralization and Osteogenic Activities
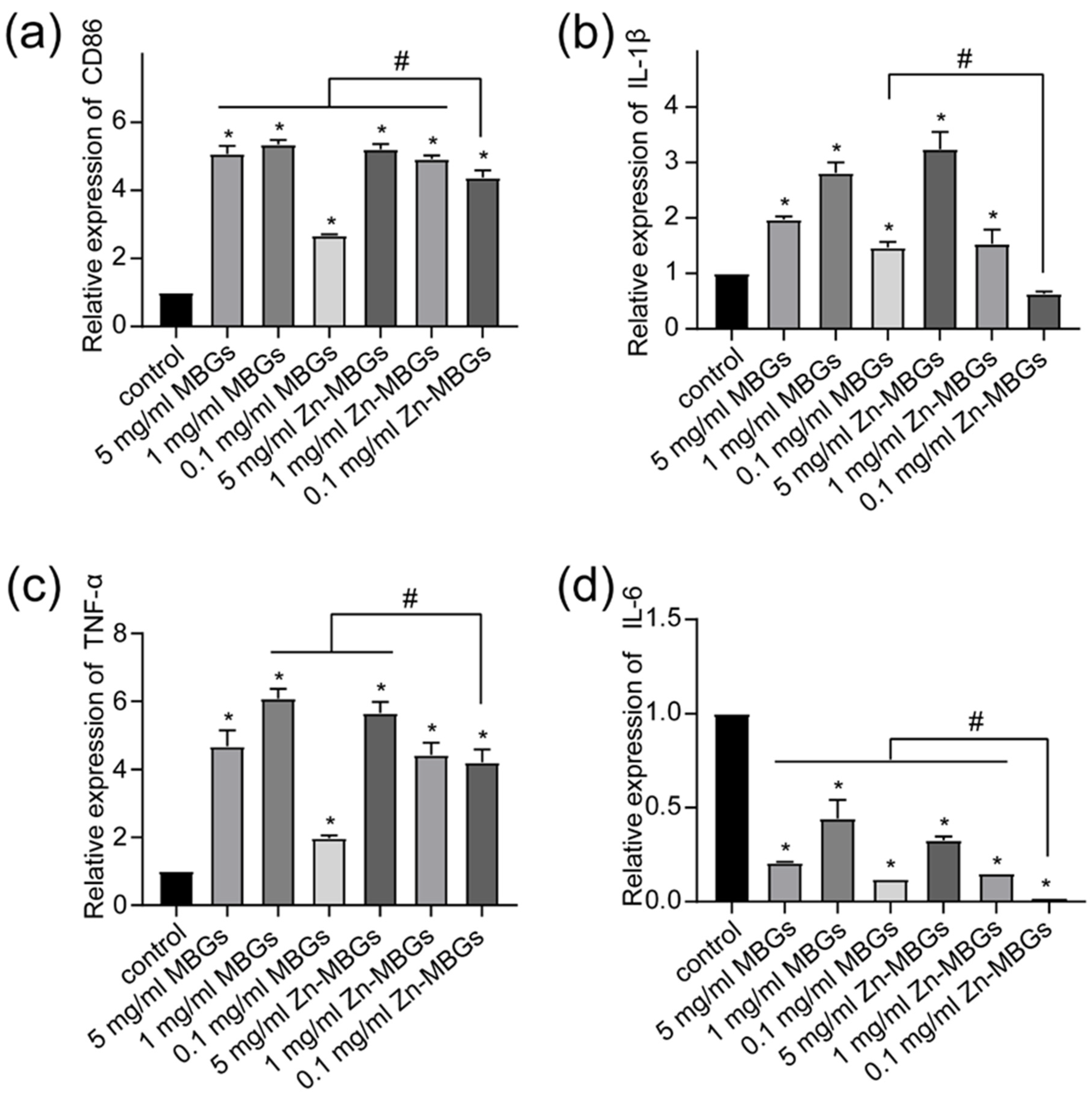
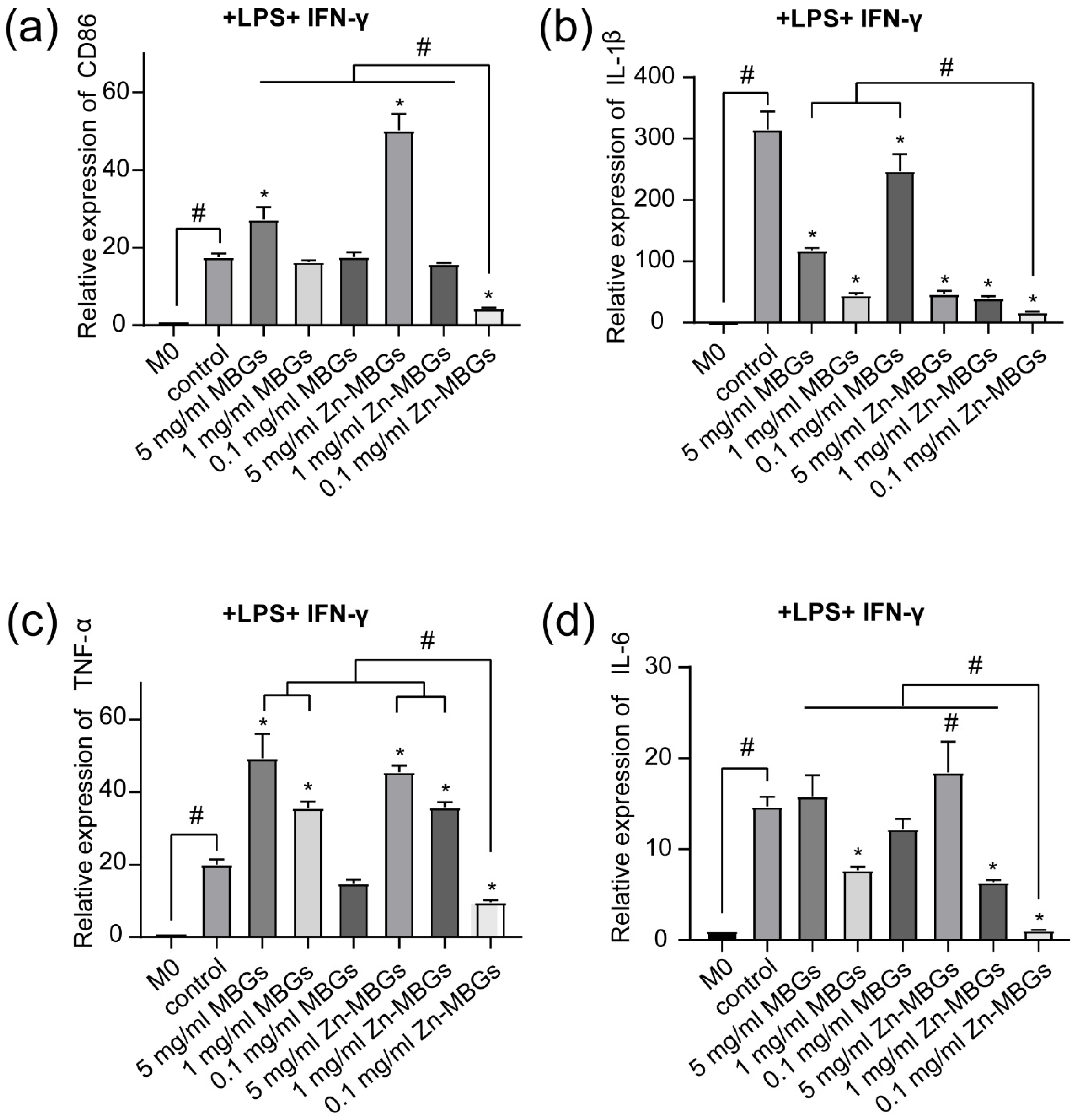
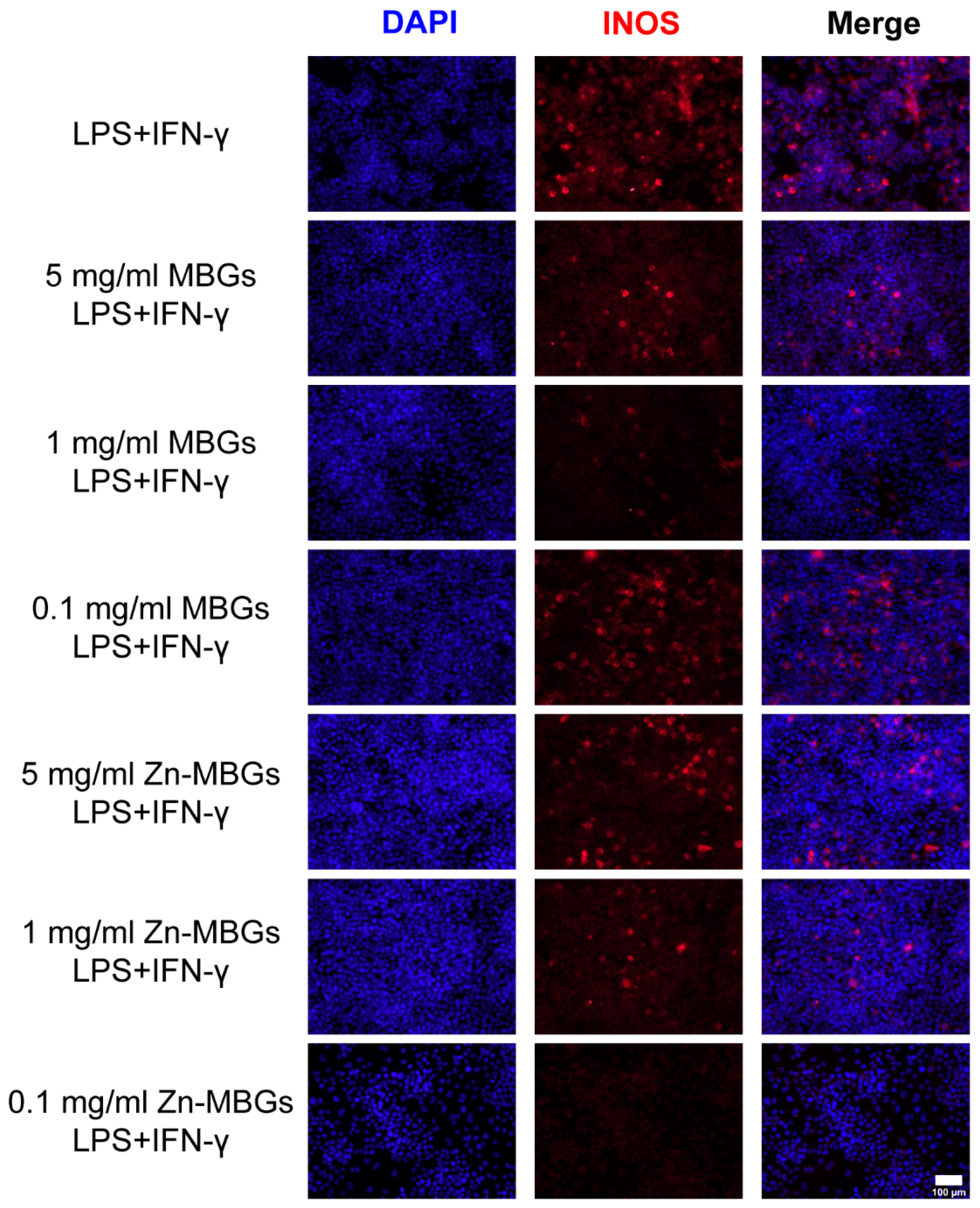
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zn-MBGs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koons, G.L.; Diba, M.; Mikos, A.G. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 584–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, G.; Petralia, S.; Franco, D.; Nocito, G.; Fabbi, C.; Forte, L.; Guglielmino, S.; Squarzoni, S.; Traina, F.; Conoci, S. A new Ag-nanostructured hydroxyapatite porous scaffold: Antibacterial effect and cytotoxicity study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; TerBush, J.; Li, W.; Setty, M.; Guan, S.; Nguyen, T.D.; Qin, L.; Zheng, Y. Biodegradable metal-derived magnesium and sodium enhances bone regeneration by angiogenesis aided osteogenesis and regulated biological apatite formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 127616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Su, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, D. Toward a Better Regeneration through Implant-Mediated Immunomodulation: Harnessing the Immune Responses. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanley, L.C.; Mahon, O.R.; Kelly, D.J.; Dunne, A. Harnessing the innate and adaptive immune system for tissue repair and regeneration: Considering more than macrophages. Acta Biomater. 2021, 133, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, R.; Hernaez-Estrada, B.; Hernandez, R.M.; Santos-Vizcaino, E.; Spiller, K.L. Immunomodulatory Biomaterials for Tissue Repair. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11305–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Niu, W.; Lei, B.; Boccaccini, A.R. Immunomodulatory bioactive glasses for tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2021, 133, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, S.; Rammelt, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Simon, J.C. Immune responses to implants—A review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6692–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R. Reprint of Review of bioactive glass: From Hench to hybrids. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23, S53–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Sui, B.; Ilyas, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Porous bioactive glass micro- and nanospheres with controlled morphology: Developments, properties and emerging biomedical applications. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 300–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Multi-Functional Silica-Based Mesoporous Materials for Simultaneous Delivery of Biologically Active Ions and Therapeutic Biomolecules. Acta Biomater. 2021, 129, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, E.; Awale, G.; Daneshmandi, L.; Umerah, O.; Lo, K.W.H. The roles of ions on bone regeneration. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, A.; Güldal, N.S.; Boccaccini, A.R. A review of the biological response to ionic dissolution products from bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yi, D.; Friis, T.; Zheng, X.; Chang, J.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, Y. Clinoenstatite coatings have high bonding strength, bioactive ion release, and osteoimmunomodulatory effects that enhance in vivo osseointegration. Biomaterials 2015, 71, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Chen, Z.; Farnaghi, S.; Friis, T.; Mao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, C. Copper-doped mesoporous silica nanospheres, a promising immunomodulatory agent for inducing osteogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2015, 30, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffany, A.S.; Gray, D.L.; Woods, T.J.; Subedi, K.; Harley, B.A.C. The inclusion of zinc into mineralized collagen scaffolds for craniofacial bone repair applications. Acta Biomater. 2019, 93, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean-Laquerriere, A.; Laquerriere, P.; Jallot, E.; Nedelec, J.M.; Guenounou, M.; Laurent-Maquin, D.; Phillips, T.M. Influence of the zinc concentration of sol-gel derived zinc substituted hydroxyapatite on cytokine production by human monocytes in vitro. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3195–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fielding, G.A.; Smoot, W.; Bose, S. Effects of SiO2, SrO, MgO, and ZnO dopants in tricalcium phosphates on osteoblastic Runx2 expression. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Q.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Chu, P.K.; Zhang, X. Zinc-Modified Sulfonated Polyetheretherketone Surface with Immunomodulatory Function for Guiding Cell Fate and Bone Regeneration. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neščáková, Z.; Zheng, K.; Liverani, L.; Nawaz, Q.; Galusková, D.; Kaňková, H.; Michálek, M.; Galusek, D.; Boccaccini, A.R. Multifunctional zinc ion doped sol-gel derived mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Sun, N.; Jiang, F.; Lu, Y.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. The Translation from in Vitro Bioactive Ion Concentration Screening to in Vivo Application for Preventing Peri-implantitis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5782–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Mei, J.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Chu, L.; Qiao, H.; Tang, T. Kinsenoside attenuates osteoarthritis by repolarizing macrophages through inactivating NF-κB/MAPK signaling and protecting chondrocytes. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Qin, H.; An, Z. Magnesium enhances the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting activated macrophage-induced inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Kang, J.; Rutkowski, B.; Gawȩda, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Founier, N.; Sitarz, M.; Taccardi, N.; Boccaccini, A.R. Toward Highly Dispersed Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles with High Cu Concentration Using Cu/Ascorbic Acid Complex as Precursor. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aina, V.; Malavasi, G.; Pla, A.F.; Munaron, L.; Morterra, C. Zinc-containing bioactive glasses: Surface reactivity and behaviour towards endothelial cells. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Kapp, M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Protein interactions with bioactive glass surfaces: A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 15, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Fan, L.; Zhang, F.M.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, M.; Dai, C.; Luo, Y.A.; Tu, L.J.; Zhou, Z.N.; Li, X.J.; et al. Hybrid gelatin/oxidized chondroitin sulfate hydrogels incorporating bioactive glass nanoparticles with enhanced mechanical properties, mineralization, and osteogenic differentiation. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Wan, Y.; Guo, X.; Shao, Z. Thermally triggered injectable chitosan/silk fibroin/bioactive glass nanoparticle hydrogels for in-situ bone formation in rat calvarial bone defects. Acta Biomater. 2019, 91, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhauser, F.; Rehder, F.; Decker, S.; Kunisch, E.; Moghaddam, A.; Zheng, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Ionic dissolution products of Cerium-doped bioactive glass nanoparticles promote cellular osteogenic differentiation and extracellular matrix formation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 035028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Torre, E.; Bari, A.; Taccardi, N.; Cassinelli, C.; Morra, M.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Iviglia, G.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antioxidant mesoporous Ce-doped bioactive glass nanoparticles with anti-inflammatory and pro-osteogenic activities. Mater. Today Bio 2020, 5, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Chang, J.; Sun, J. Odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp cells induced by silicate-based bioceramics via activation of P38/MEPE pathway. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72536–72543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoch, M.L.; Clemens, T.L.; Riddle, R.C. New insights into the biology of osteocalcin. Bone 2016, 82, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, D.S.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.W. Zinc Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Via Activation of the cAMP-PKA-CREB Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2018, 27, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimi, S.; Gorianc, G.; Moimas, L.; Lindroos, B.; Huhtala, H.; Räty, S.; Kuokkanen, H.; Sándor, G.K.; Schmid, C.; Miettinen, S.; et al. Characterization of zinc-releasing three-dimensional bioactive glass scaffolds and their effect on human adipose stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3122–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras, C.; Sanchez-Salcedo, S.; Lozano, D.; Peña, J.; Esbrit, P.; Vallet-Regi, M.; Salinas, A.J. Osteostatin potentiates the bioactivity of mesoporous glass scaffolds containing Zn2+ ions in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019, 89, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Dai, K.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Improved osteogenesis and angiogenesis of magnesium-doped calcium phosphate cement: Via macrophage immunomodulation. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierichs, L.; Kloubert, V.; Rink, L. Cellular zinc homeostasis modulates polarization of THP-1-derived macrophages. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montes-Casado, M.; Sanvicente, A.; Casarrubios, L.; Feito, M.J.; Rojo, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Arcos, D.; Portolés, P.; Portolés, M.T. An immunological approach to the biocompatibility of mesoporous SiO2-CaO nanospheres. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Liu, X.; Pan, Z. Zinc deficiency and cellular oxidative stress: Prognostic implications in cardiovascular diseases review-article. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarosz, M.; Olbert, M.; Wyszogrodzka, G.; Młyniec, K.; Librowski, T. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olechnowicz, J.; Tinkov, A.; Skalny, A.; Suliburska, J. Zinc status is associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid, and glucose metabolism. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, K.; Zhu, R.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.C. Low level laser (LLL) attenuate LPS-induced inflammatory responses in mesenchymal stem cells via the suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Ntoupa, P.S.A.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Recent aspects of the effects of zinc on human health. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chen, S.; Huang, P.; Liu, G.; Luo, P.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Immunomodulation-Based Strategy for Improving Soft Tissue and Metal Implant Integration and Its Implications in the Development of Metal Soft Tissue Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, R.; Cameron, A.R.; Kelly, D.J.; Kearney, C.J.; O’Brien, F.J. Biomaterial based modulation of macrophage polarization: A review and suggested design principles. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
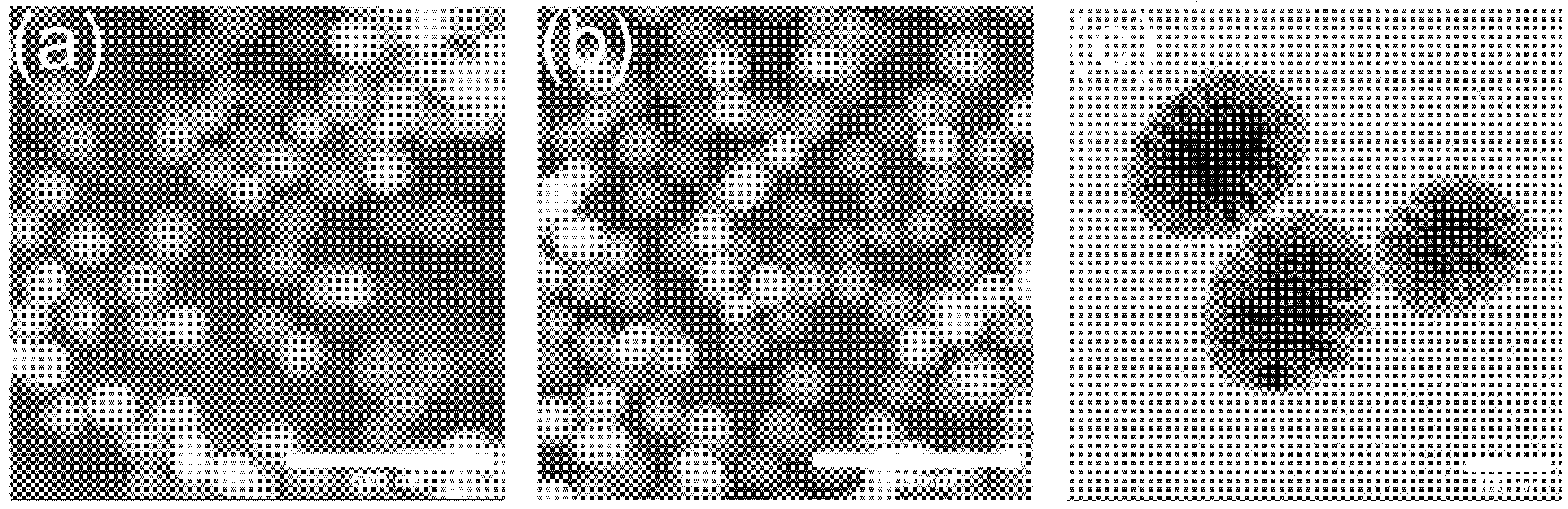


| Genes | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ALP | ATGCTCAGGACAGGATCAAA | CGGGACATAAGCGAGTTTCT |
| RUNX2 | GGGACTGGTACTCGGACAAT | GGCCTTCTCATCCAGTTCAT |
| COL-I | AGCTCGATACACAATGGCCT | CCTATGACTTCTGCGTCTGG |
| OCN | CAGACAAGTCCCACACAGCA | CCAGCAGAGTGAGCAGAGAG |
| β-actin | CCTCTATGACAACACAGT | AGCCACCAATCCACACAG |
| Genes | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | GCCTATGTCTCAGCCTCTT | GGTTGACTTTCTCCTGGTAT |
| IL-6 | CGATAGTCAATTCCAGAAACCGC | TTGGGAGTGGTATCCTCTGTGAAG |
| IL-1β | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| CD86 | TGTTTCCGTGGAGACGCAAG | TTGAGCCTTTGTAAATGGGCA |
| GAPDH | GGACACTGAGCAAGAGAGGC | TTATGGGGGTCTGGGATGGA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Zheng, K.; Zhou, T.; Boccaccini, A.R. Incorporation of Zinc into Binary SiO2-CaO Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Enhances Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Activities. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122124
Sun H, Zheng K, Zhou T, Boccaccini AR. Incorporation of Zinc into Binary SiO2-CaO Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Enhances Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Activities. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(12):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122124
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haishui, Kai Zheng, Tian Zhou, and Aldo R. Boccaccini. 2021. "Incorporation of Zinc into Binary SiO2-CaO Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Enhances Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Activities" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 12: 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122124
APA StyleSun, H., Zheng, K., Zhou, T., & Boccaccini, A. R. (2021). Incorporation of Zinc into Binary SiO2-CaO Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Enhances Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Activities. Pharmaceutics, 13(12), 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122124








