Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids in Oncology: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
3. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Gene Delivery
3.1. Nucleic Acid Delivery by Surface-Functionalized MSNs
3.2. Nucleic Acid Delivery by Polycation-Coated MSNs
3.3. Nucleic Acid Delivery within MSN Pores
4. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Nucleic Acids and Small-Molecule Drugs
4.1. Avoiding Non-Pump Resistance
4.2. Avoiding Pump-Mediated Resistance
4.3. Inducing Direct Cancer Cell Death
4.4. Inducing Indirect Cancer Cell Death through Expressing Prodrug-Activating Enzymes
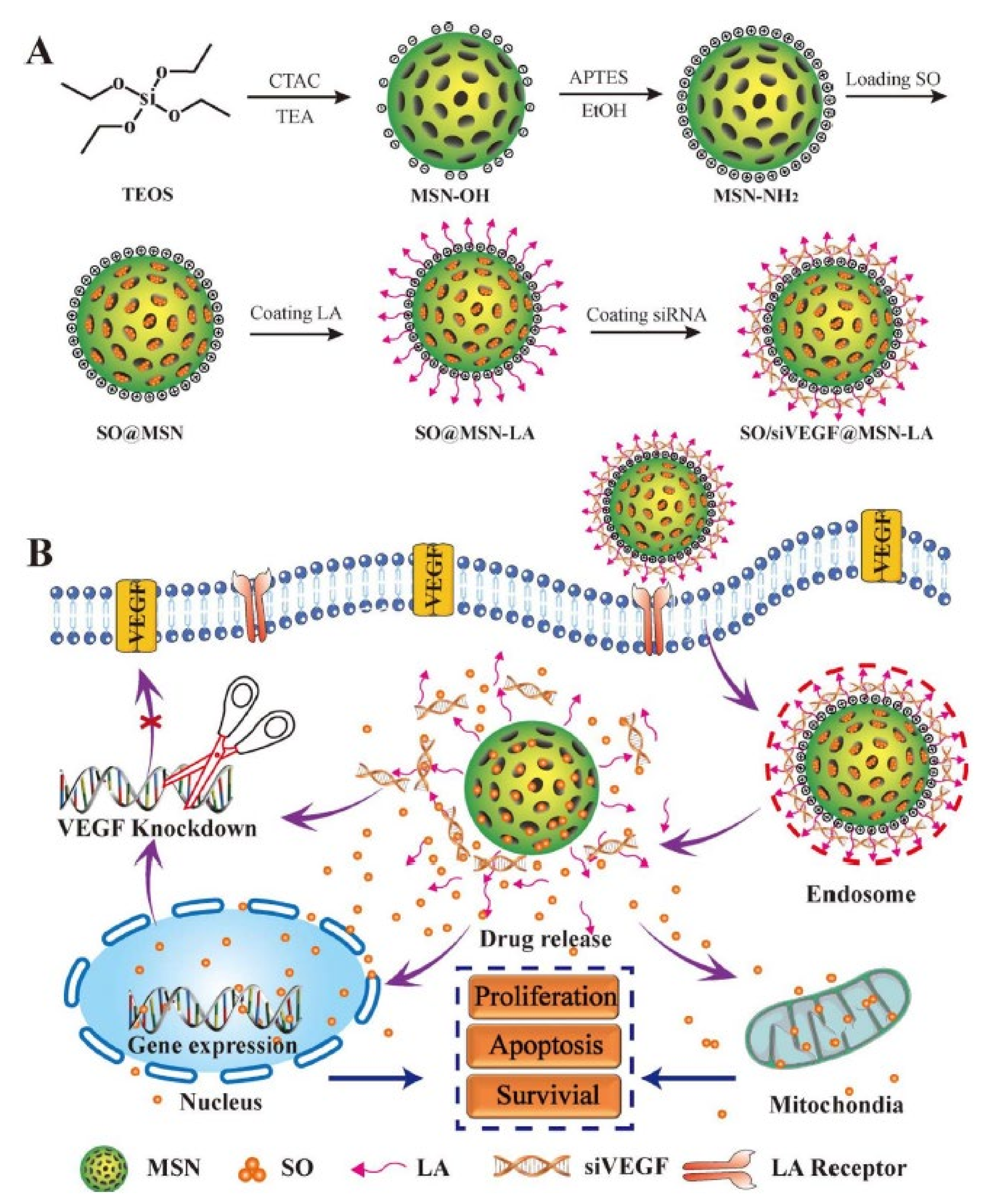
4.5. Inhibiting Angiogenesis
| Small Molecule Cargo | Nucleic Acid Cargo | Responsive Release Trigger | In Vivo Model | Function of the Nucleic Acid | Reference |
| Doxorubicin | Bcl-2 siRNA | None | None | Avoiding non-pump resistance | [109] |
| Doxorubicin | Bcl-2 siRNA | Redox | Zebrafish | Avoiding non-pump resistance | [110] |
| Doxorubicin | Bcl-2 siRNA | Redox | Mouse | Avoiding non-pump resistance | [111] |
| Epirubicin | Bcl-2 siRNA | pH | Mouse | Avoiding non-pump resistance | [112] |
| Doxorubicin | Survivin shRNA-expressing plasmid | pH | Mouse | Avoiding non-pump resistance | [113] |
| Doxorubicin | CTGF siRNA | Hyaluronidase | Mouse | Avoiding non-pump resistance | [114] |
| Doxorubicin | Pgp siRNA | pH | None | Avoiding pump-mediated resistance | [115] |
| Doxorubicin | Pgp siRNA | pH | Mouse | Avoiding pump-mediated resistance | [116] |
| Doxorubicin | MDR1 (Pgp1) siRNA | None | Mouse | Avoiding pump-mediated resistance | [117] |
| Doxorubicin | T-type Ca2+ channel siRNA | pH | Mouse | Avoiding pump-mediated resistance | [118] |
| Doxorubicin and cisplatin | Bcl-2 siRNA and MRP1 siRNA | None | Mouse | Avoiding non-pump and pump-mediated resistance | [119] |
| Doxorubicin | p53 plasmid | Redox | None | Inducing direct cancer cell death | [120] |
| Bortezomib | p53 plasmid | pH | None | Inducing direct cancer cell death | [122] |
| Daunorubicin | Anti-TWIST siRNA | Oscillating Magnetic Fields | None | Inducing direct cancer cell death | [123] |
| Sorafenib | VEGF siRNA | pH | None | Inhibiting angiogenesis | [130] |
| Doxorubicin | VEGF siRNA | pH, Redox | Mouse | Inhibiting angiogenesis | [131] |
| Ursolic acid | VEGF siRNA | None | None | Inhibiting angiogenesis | [132] |
| Doxorubicin | VEGF shRNA | None | None | Inhibiting angiogenesis | [133] |
4.6. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Rethinking cancer nanotheranostics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: Improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, N.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Kamaly, N.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanotechnology: The impact of passive and active targeting in the era of modern cancer biology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steichen, S.D.; Caldorera-Moore, M.; Peppas, N.A. A review of current nanoparticle and targeting moieties for the delivery of cancer therapeutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.W.; Bae, Y.H. EPR: Evidence and fallacy. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, S.; Syed, A.M.; Ngai, J.; Kingston, B.R.; Maiorino, L.; Rothschild, J.; MacMillan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Rajesh, N.U.; Hoang, T.; et al. The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidczyk, C.M.; Kim, C.; Park, J.H.; Russell, L.M.; Lee, K.H.; Pomper, M.G.; Searson, P.C. State-of-the-art in design rules for drug delivery platforms: Lessons learned from FDA-approved nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvioni, L.; Rizzuto, M.A.; Bertolini, J.A.; Pandolfi, L.; Colombo, M.; Prosperi, D. Thirty Years of Cancer Nanomedicine: Success, Frustration, and Hope. Cancers 2019, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meel, R.; Lammers, T.; Hennink, W.E. Cancer nanomedicines: Oversold or underappreciated? Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.L.; Mohseni, R.; Hamidieh, A.A.; MacLaren, R.E.; Habib, N.; Seifalian, A.M. Will Nanotechnology Bring New Hope for Gene Delivery? Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 434–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.X.; Wong, H.L.; Xue, H.Y.; Eoh, J.Y.; Wu, X.Y. Nanomedicine of synergistic drug combinations for cancer therapy—Strategies and perspectives. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, C. Alnylam prepares to land first RNAi drug approval. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 156–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.V.; Rosa da Costa, A.M.; Silva, G.A. Non-viral strategies for ocular gene delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1275–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, C.; Wagner, E. Therapeutic plasmid DNA versus siRNA delivery: Common and different tasks for synthetic carriers. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.L.; Newell, L.F.; Stuart, R.K.; Michaelis, L.C.; Rubenstein, S.E.; Pentikis, H.S.; Callahan, T.; Alvarez, D.; Mayer, L.D.; Louie, A.C. CPX-351 ((Cytarabine:Daunorubicin) Liposome Injection, (Vyxeos)) Does Not Prolong Qtcf Intervals, Requires No Dose Adjustment for Impaired Renal Function and Induces High Rates of Complete Remission in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Current insights. Molecules 2018, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, J.; Avnir, D.; Fairbridge, C.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haynes, J.M.; Pernicone, N.; Ramsay, J.D.F.; Sing, K.S.W.; Unger, K.K. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kuroda, K.; Kato, C. The Preparation of Alkyltriinethylaininonium–Kaneinite Complexes and Their Conversion to Microporous Materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 63, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Drug delivery from ordered mesoporous matrices. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 1383–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. New developments in ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5593–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, A.; Balas, F.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Functionalization degree of SBA-15 as key factor to modulate sodium alendronate dosage. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 116, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M. Bone-regenerative bioceramic implants with drug and protein controlled delivery capability. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2008, 36, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.L.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Doadrio, J.C.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. A molecular model to explain the controlled release from SBA-15 functionalized with APTES. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 195, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.L.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Doadrio, J.C.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a new carrier methodology in the controlled release of the active components in a polypill. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.; Salinas, A.; Sánchez-Montero, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Drug release from ordered mesoporous silicas. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 6213–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.L.; Doadrio, J.C.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. A rational explanation of the vancomycin release from SBA-15 and its derivative by molecular modelling. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 132, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Biocompatibility and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Overcoming the stability, toxicity, and biodegradation challenges of tumor stimuli-responsive inorganic nanoparticles for delivery of cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 1095–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauda, V.; Argyo, C.; Bein, T. Impact of different PEGylation patterns on the long-term bio-stability of colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8693–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Tuning mesoporous silica dissolution in physiological environments: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8761–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, R.; Cheney, D.L.; Grunberger, J.W.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Jedrzkiewicz, J.; Isaacson, K.J.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Ghandehari, H. One-year chronic toxicity evaluation of single dose intravenously administered silica nanoparticles in mice and their Ex vivo human hemocompatibility. J. Control. Release 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Smart Mesoporous Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1906–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Ultrasound-Responsive Drug Carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Agarwal, A.; Mueller, L.J.; Feng, P. pH-responsive nanogated ensemble based on gold-capped mesoporous silica through an acid-labile acetal linker. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1500–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyo, C.; Weiss, V.; Bräuchle, C.; Bein, T. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Universal Platform for Drug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Yin, Q.; Lu, L. Multifunctional envelope-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Hu, J.-J.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Jia, H.-Z.; Sun, Y.-X.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. A redox-responsive drug delivery system based on RGD containing peptide-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Huang, P.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X. A Facile Strategy to Prepare an Enzyme-Responsive Mussel Mimetic Coating for Drug Delivery Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5511–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Lozano, D.; Baeza, A.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. A novel visible light responsive nanosystem for cancer treatment. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15967–15973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Talelli, M.; Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Design of thermoresponsive polymeric gates with opposite controlled release behaviors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42510–42516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Asín, L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Heating at the Nanoscale through Drug-Delivery Devices: Fabrication and Synergic Effects in Cancer Treatment with Nanoparticles. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1800007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; de la Torre, P.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Grau, M.; Flores, A.I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Vectorization of ultrasound-responsive nanoparticles in placental mesenchymal stem cells for cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 5528–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Villaverde, G.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. From proof-of-concept material to PEGylated and modularly targeted ultrasound-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Santamaria, C.M.; Wei, T.; Zhao, C.; Ji, T.; Yang, T.; Shomorony, A.; Wang, B.Y.; Kohane, D.S. Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Penetrate the Peripheral Nerve and Enhance the Nerve Blockade from Tetrodotoxin. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Lafuente-Gómez, N.; Cabañas, M.V.; Román, J.; Peña, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Fabrication of a nanoparticle-containing 3D porous bone scaffold with proangiogenic and antibacterial properties. Acta Biomater. 2019, 86, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, D.L.; Lee, B.-Y.; Xue, M.; Thomas, C.R.; Meng, H.; Ferris, D.; Nel, A.E.; Zink, J.I.; Horwitz, M.A. Targeted Intracellular Delivery of Antituberculosis Drugs to Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Infected Macrophages via Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Nanoparticles to Knockdown Osteoporosis-Related Gene and Promote Osteogenic Marker Expression for Osteoporosis Treatment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Liang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Liao, H.; Li, L. Development of a hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles vaccine to protect against house dust mite induced allergic inflammation. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Nanoparticles in targeted cancer therapy: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles entering preclinical development stage. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, P.Z.; Nguyen, K.T.; Wang, X.J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, N.S.; Zhao, Y. Biocompatible, uniform, and redispersible mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer-targeted drug delivery in vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2450–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, H.; Kim, W.J. Nano “chocolate Waffle” for near-IR Responsive Drug Releasing System. Small 2015, 11, 5315–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liang, C.; Wang, X.; Tsai, H.; Liu, G.; Peng, Y.; Nie, J.; Huang, L.; Mei, L.; Zeng, X. A drug-self-gated and tumor microenvironment-responsive mesoporous silica vehicle: “four-in-one” versatile nanomedicine for targeted multidrug-resistant cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17063–17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, M.; Tiwari, N.; Tiwari, M.; Lahiri, M.; Gupta, S. Sen Poly-L-arginine grafted silica mesoporous nanoparticles for enhanced cellular uptake and their application in DNA delivery and controlled drug release. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2013, 30, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Tehrani, Z.M.; Mahmoudi, N. The effect of protein corona on doxorubicin release from the magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles with polyethylene glycol coating. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 2007, 3, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Selective topotecan delivery to cancer cells by targeted pH-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50923–50932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Meng, H.; Kabehie, S.; George, S.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Polyethyleneimine Coating Enhances the Cellular Uptake of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Allows Safe Delivery of siRNA and DNA Constructs. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3273–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Situ, A.; Wu, B.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Nel, A.E. Use of a lipid-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticle platform for synergistic gemcitabine and Paclitaxel delivery to human pancreatic cancer in mice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3540–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; She, X.; Wang, T.; He, L.; Shigdar, S.; Duan, W.; Kong, L. Overcoming acquired drug resistance in colorectal cancer cells by targeted delivery of 5-FU with EGF grafted hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14080–14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneuer, C.; Sameti, M.; Bakowsky, U.; Schiestel, T.; Schirra, H.; Schmidt, H.; Lehr, C.M. A nonviral DNA delivery system based on surface modified silica-nanoparticles can efficiently transfect cells in vitro. Bioconjug. Chem. 2000, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Saltzman, W.M. Nonviral gene delivery: Thinking of silica. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, K.; Gouda, N.; Takemoto, H.; Oba, M.; Lee, Y.; Koyama, H.; Yamasaki, Y.; Itaka, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Enhanced transfection with silica-coated polyplexes loading plasmid DNA. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4764–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hom, C.; Lu, J.; Tamanoi, F. Silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for nucleic acid-based reagents. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6308–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, R.R.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent applications of the combination of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nucleic acids: Development of bioresponsive devices, carriers and sensors. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Meng, W.; Gao, H.; Hanagata, N. Hollow mesoporous silica/poly(l-lysine) particles for codelivery of drug and gene with enzyme-triggered release property. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 13630–13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwalski, A.; Dabboue, H.; Delalande, A.; Bensamoun, S.F.; Canon, F.; Midoux, P.; Saillant, G.; Klatzmann, D.; Salvetat, J.P.; Pichon, C. Accelerated Achilles tendon healing by PDGF gene delivery with mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5237–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Tsai, P.H.; Hung, Y.; Chiou, S.H.; Mou, C.Y. Nonviral cell labeling and differentiation agent for induced pluripotent stem cells based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8423–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, M.; Eltohamy, M.; Yun, Y.R.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, H.W. Efficacy of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in delivering BMP-2 plasmid DNA for in vitro osteogenic stimulation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2013, 101 A, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Tsai, P.H.; Chen, W.; Chiou, S.H.; Mou, C.Y. Dual delivery of siRNA and plasmid DNA using mesoporous silica nanoparticles to differentiate induced pluripotent stem cells into dopaminergic neurons. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3012–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevet, D.; Hocine, O.; Delalande, A.; Raehm, L.; Charnay, C.; Midoux, P.; Durand, J.O.; Pichon, C. Improved gene transfer with histidine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Behzad-Behbahani, A.; Sharifzadeh, S.; Abolmaali, S.S.; Tamaddon, A.M. Co-condensation synthesis of well-defined mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Effect of surface chemical modification on plasmid DNA condensation and transfection. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Morita, H.; Hanagata, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhancing the delivery efficiency of immunostimulatory DNA drugs. Dalt. Trans. 2014, 43, 5142–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, D.R.; Lai, C.Y.; Jeftinija, K.; Rowe, E.W.; Jeftinija, S.; Lin, V.S.Y. A polyamidoamine dendrimer-capped mesoporous silica nanosphere-based gene transfection reagent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13216–13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, Á.; Fuentes-Paniagua, E.; Baeza, A.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; Cicuéndez, M.; Gómez, R.; de la Mata, F.J.; González, B.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Decorated with Carbosilane Dendrons as New Non-viral Oligonucleotide Delivery Carriers. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15651–15666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, H.H.P.; McBain, S.C.; El Haj, A.J.; Dobson, J. A triple-layer design for polyethyleneimine-coated, nanostructured magnetic particles and their use in DNA binding and transfection. Nanotechnology 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.Y.; Kim, I.Y.; Yoo, M.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, M.H.; Cho, C.S. Mannosylated polyethylenimine coupled mesoporous silica nanoparticles for receptor-mediated gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hom, C.; Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Luo, H.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles facilitate delivery of siRNA to shutdown signaling pathways in mammalian cells. Small 2010, 6, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Morry, J.; Gu, S.; Castro, D.J.; Goodyear, S.M.; Sangvanich, T.; Reda, M.M.; Lee, R.; Mihelic, S.A.; Beckman, B.L.; et al. Cationic Polymer Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted siRNA Delivery to HER2 + Breast Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2646–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.T.; Xue, Y.N.; Peng, N.; Liu, W.M.; Zhuo, R.X.; Huang, S.W. One-pot preparation of polyethylenimine-silica nanoparticles as serum-resistant gene delivery vectors: Intracellular trafficking and transfection. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10496–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Quan, G.; Yang, P.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. The Serum-Resistant Transfection Evaluation and Long-Term Stability of Gene Delivery Dry Powder Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Polyethyleneimine by Freezing-Drying. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, S.R.; Muthuswamy, E.; Wani, A.; Brichacek, M.; Castañeda, A.L.; Brock, S.L.; Oupicky, D. Enhanced Gene and siRNA Delivery by Polycation-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Chloroquine. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2556–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, H.; Kazemi Oskuee, R.; Hanafi-Bojd, M.Y.; Gholami, L.; Ansari, L.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Enhanced gene delivery by polyethyleneimine coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Cheng, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Han, S.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, S.; Liang, Z.; Dong, A. Intracellular cleavable poly(2-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient siRNA delivery in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4291–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, N.; Yan, P.; Hu, H.; Xu, F.J. The shape and size effects of polycation functionalized silica nanoparticles on gene transfection. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Botella, P.; Corma, A.; Blesa, J.; Dong, L. Monodispersed mesoporous silica nanoparticles with very large pores for enhanced adsorption and release of DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wu, M.; Lai, H.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, J. Nanoparticle-enhanced generation of gene-transfected mesenchymal stem cells for in vivo cardiac repair. Biomaterials 2016, 74, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, Q.R.; Zhang, J.; Xia, W.; Gu, H. The packaging of siRNA within the mesoporous structure of silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9546–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Na, H.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Ryoo, S.R.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, K.E.; Jeon, H.; Ryoo, R.; Min, D.H. Facile synthesis of monodispersed mesoporous silica nanoparticles with ultralarge pores and their application in gene delivery. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3568–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Müller, K.; Engelke, H.; Bräuchle, C.; Wagner, E.; Bein, T. Highly efficient siRNA delivery from core-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles with multifunctional polymer caps. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y.; Xia, W.; Gu, H. A mesoporous silica nanoparticle–PEI–Fusogenic peptide system for siRNA delivery in cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hei, M.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhu, W. Ammonium salt modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual intracellular-responsive gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, N.; Zhang, J.; Desai, D.; Casals, E.; Gulin-Sarfraz, T.; Näreoja, T.; Westermarck, J.; Rosenholm, J.M. Stimuli-responsive hybrid nanocarriers developed by controllable integration of hyperbranched PEI with mesoporous silica nanoparticles for sustained intracellular siRNA delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6591–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, M.R.; Baeza, A.; Noureddine, A.; Durfee, P.N.; Butler, K.S.; Agola, J.O.; Brinker, C.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Multifunctional Protocells for Enhanced Penetration in 3D Extracellular Tumoral Matrices. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, C.E.; Carnes, E.C.; Epler, K.E.; Padilla, D.P.; Phillips, G.K.; Castillo, R.E.; Wilkinson, D.C.; Wilkinson, B.S.; Burgard, C.A.; Kalinich, R.M.; et al. Delivery of Small Interfering RNA by Peptide-Targeted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Supported Lipid Bilayers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2174–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.D.; Vorhies, J.S.; Senzer, N.; Nemunaitis, J. siRNA vs. shRNA: Similarities and differences. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.B. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Zhang, W.; Niu, D.; Gong, J. Large-pore mesoporous silica nanospheres as vehicles for delivering TRAF3-shRNA plasmids to Kupffer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duo, Y.; Bi, J.; Zeng, X.; Mei, L.; Bao, S.; He, L.; Shan, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X. Targeted delivery of anti-miR-155 by functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for colorectal cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1241–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Duo, Y.; Zhai, P.; He, L.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X. Dual targeting delivery of miR-328 by functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for colorectal cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahir, M.; Upadhyay, P.; Ghosh, A.; Sarker, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Gupta, P.; Ghosh, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Adhikary, A. Delivery of dual miRNA through CD44-targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhanced and effective triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafi-Bojd, M.Y.; Ansari, L.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Codelivery of anticancer drugs and siRNA by mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, B.; Farahmand, L.; Majidzadeh-A, K. Stimuli-Responsive Mesoporous Silica NPs as Non-viral Dual siRNA/Chemotherapy Carriers for Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.T.; Liao, P.Y.; Sheu, H.S.; Tseng, Y.J.; Cheng, F.Y.; Yeh, C.S. Near-Infrared light-responsive intracellular drug and sirna release using au nanoensembles with oligonucleotide-capped silica shell. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3309–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-S.; Liu, T.-P.; Chien, F.-C.; Mou, C.-Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-P. Codelivery of Plasmid and Curcumin with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Promoting Neurite Outgrowth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15322–15331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.M.; Zhang, M.; Wei, D.; Stueber, D.; Taratula, O.; Minko, T.; He, H. Co-delivery of Doxorubicin and Bcl-2 siRNA by mesoporous silica nanoparticles enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy in multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Small 2009, 5, 2673–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Teh, C.; Zhang, Q.; Borah, P.; Choong, C.; Korzh, V.; Zhao, Y. Redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A physiologically sensitive codelivery vehicle for siRNA and doxorubicin. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xu, M.; Cao, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J. A redox-responsive strategy using mesoporous silica nanoparticles for co-delivery of siRNA and doxorubicin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6908–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya Hanafi-Bojd, M.; Reza Jaafari, M.; Ramezanian, N.; Abnous, K.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Co-Delivery of Epirubicin and siRNA Using Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Enhances In vitro and In vivo Drug Efficacy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and Survivin shRNA-Expressing Plasmid Via Microenvironment-Responsive Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2829–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liang, T.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; Min, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, J. Hyaluronidase-triggered anticancer drug and siRNA delivery from cascaded targeting nanoparticles for drug-resistant breast cancer therapy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Liong, M.; Xia, T.; Li, Z.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Engineered design of mesoporous silica nanoparticles to deliver doxorubicin and p-glycoprotein siRNA to overcome drug resistance in a cancer cell line. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4539–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Mai, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, M.; Xia, T.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; et al. Codelivery of an optimal drug/siRNA combination using mesoporous silica nanoparticles to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Meng, L.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Yang, B.; Sun, H. Codelivery of doxorubicin and MDR1-siRNA by mesoporous silica nanoparticles-polymerpolyethylenimine to improve oral squamous carcinoma treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X.-J.; Li, L. Regulation of Ca 2+ Signaling for Drug-Resistant Breast Cancer Therapy with Mesoporous Silica Nanocapsule Encapsulated Doxorubicin/siRNA Cocktail. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taratula, O.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Chen, A.M.; Minko, T. Innovative strategy for treatment of lung cancer: Targeted nanotechnology-based inhalation co-delivery of anticancer drugs and siRNA. J. Drug Target. 2011, 19, 900–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.T.; Liu, Z.K.; Zhu, Q.L.; Rong, X.H.; Liang, C.L.; Wang, J.; Ma, D.; Sun, J.; Wang, G.H. Redox-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene co-delivery based on chitosan derivatives modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 155, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibnat, N.; Kamaruzman, N.I.; Ashaie, M.; Chowdhury, E.H. Transfection with p21 and p53 tumor suppressor plasmids suppressed breast tumor growth in syngeneic mouse model. Gene 2019, 701, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Hu, J.; Li, W.; Song, G.; Shen, J. Combined bortezomib-based chemotherapy and p53 gene therapy using hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres for p53 mutant non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Salcedo, S.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Shahin, S.A.; Glackin, C.A.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous core-shell silica nanoparticles with anti-fouling properties for ovarian cancer therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, C.J.; Niculescu-Duvaz, I. Prodrug-activating systems in suicide gene therapy. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 105, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucerova, L.; Matuskova, M.; Pastorakova, A.; Tyciakova, S.; Jakubikova, J.; Bohovic, R.; Altanerova, V.; Altaner, C. Cytosine deaminase expressing human mesenchymal stem cells mediated tumour regression in melanoma bearing mice. J. Gene Med. 2008, 10, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; de la Torre, P.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Flores, A.I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Suicide-gene transfection of tumor-tropic placental stem cells employing ultrasound-responsive nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, P.; Hameed, S.; Dai, Z. Recent advances in anti-angiogenic nanomedicines for cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5393–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Seidi, K.; Banimohamad-Shotorbani, B.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Yousefi, B. Combination of nanotechnology with vascular targeting agents for effective cancer therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2982–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Villaverde, G.; Gómez-Graña, S.; Vallet-Regí, M. Nanoparticles for multimodal antivascular therapeutics: Dual drug release, photothermal and photodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Zhao, R.; Xu, A.; Shen, Z.; Chen, X.; Shao, J. Co-delivery of sorafenib and siVEGF based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for ASGPR mediated targeted HCC therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Dual-targeting and pH/redox-responsive multi-layered nanocomplexes for smart co-delivery of doxorubicin and siRNA. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, A.; Shao, J. Dual-Targeting Multifuntional Mesoporous Silica Nanocarrier for Codelivery of siRNA and Ursolic Acid to Folate Receptor Overexpressing Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Shen, X.; Geng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y. Folate-Functionalized Magnetic-Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug/Gene Codelivery to Potentiate the Antitumor Efficacy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13748–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paris, J.L.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids in Oncology: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060526
Paris JL, Vallet-Regí M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids in Oncology: A Review. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060526
Chicago/Turabian StyleParis, Juan L., and María Vallet-Regí. 2020. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids in Oncology: A Review" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060526
APA StyleParis, J. L., & Vallet-Regí, M. (2020). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids in Oncology: A Review. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060526