Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) and Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CTAB or DODAB Dispersions in Water Solution
2.3. Synthesis of Waterborne PMMA/QACs Nanoparticles (NPs) by Emulsion Polymerization
2.4. Determination of Sizes, Zeta-Potentials, and Polydispersity of PMMA/QAC Dispersions by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.5. Visualization and Morphology of PMMA/QAC NPs from Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Microorganisms Cultures and Effect of CTAB, DODAB, or PMMA/QAC NPs on Cell Viability in the Presence of the Cationic Amphiphiles Solutions or Dispersions
2.7. Determination of Growth Inhibition Zones by PMMA/QAC NPs
2.8. Determination of QAC Concentration from Halide Microtitration
3. Results and Discussion
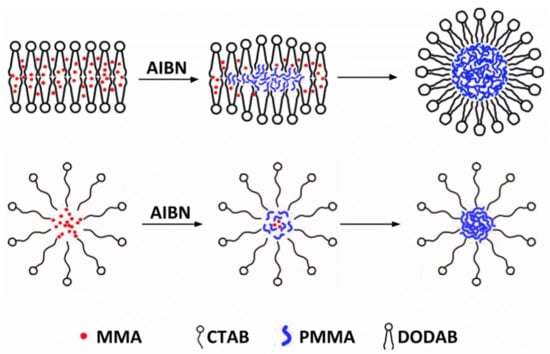
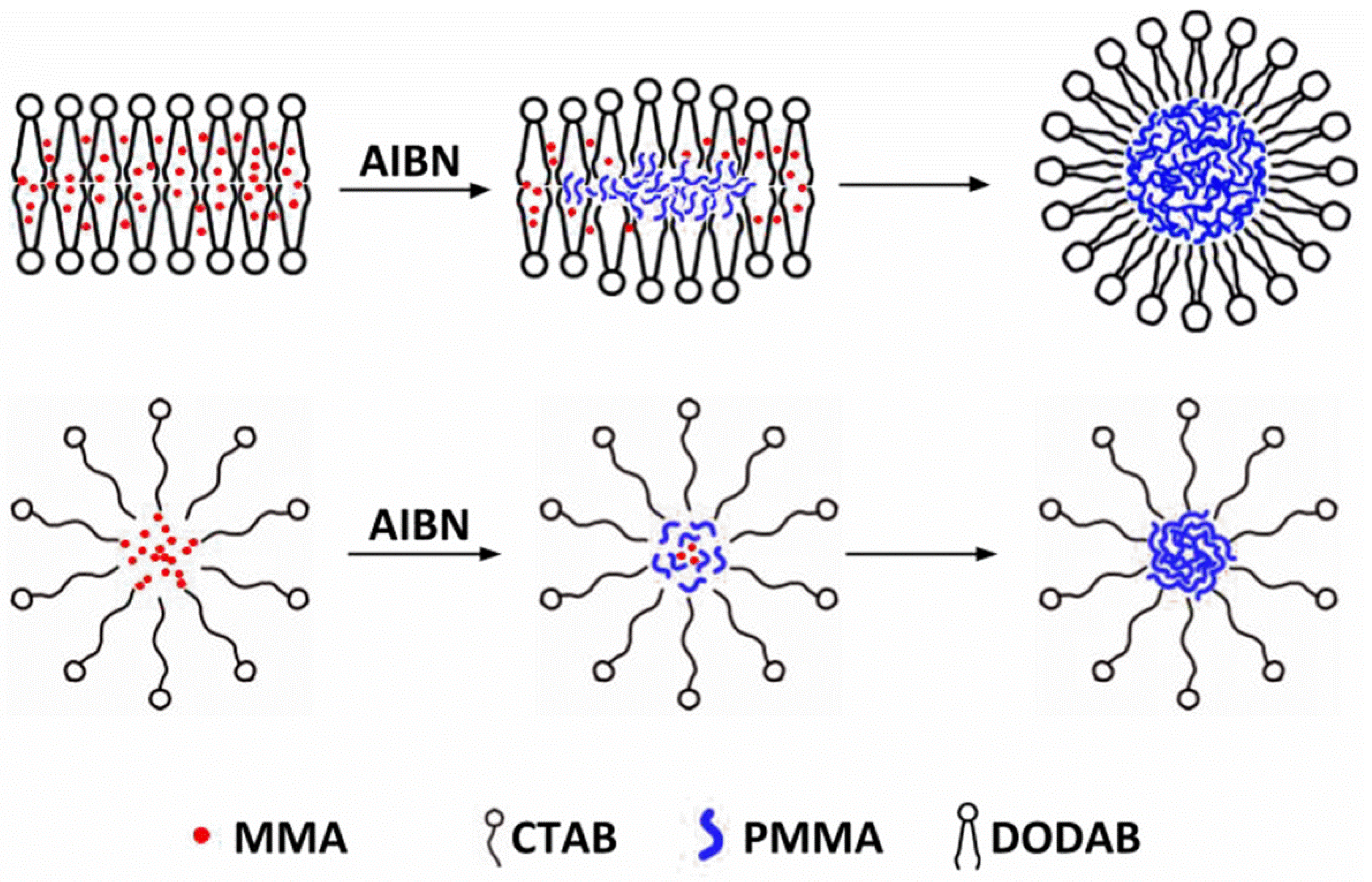
3.1. Synthesis of PMMA/QACs NPs by Emulsion Polymerization and their Physical Characterization from SEM and DLS
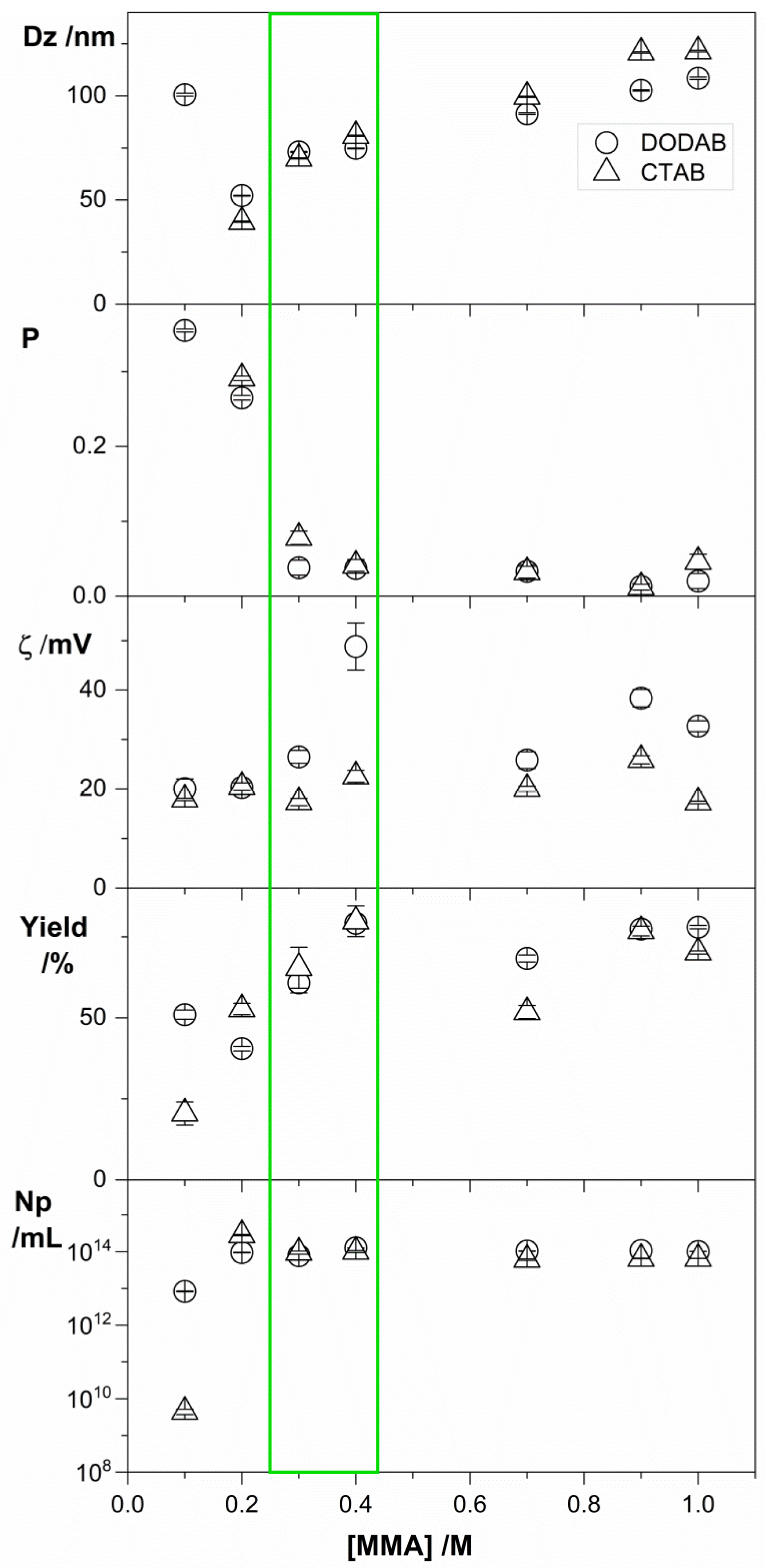
3.2. Effects of MMA Concentration, QAC Concentration, and Initiator Type on Physico-Chemical Properties of PMMA/QAC NPs Obtained by Emulsion Polymerization
3.3. Incorporation of QACs in the PMMA/QAC NPs
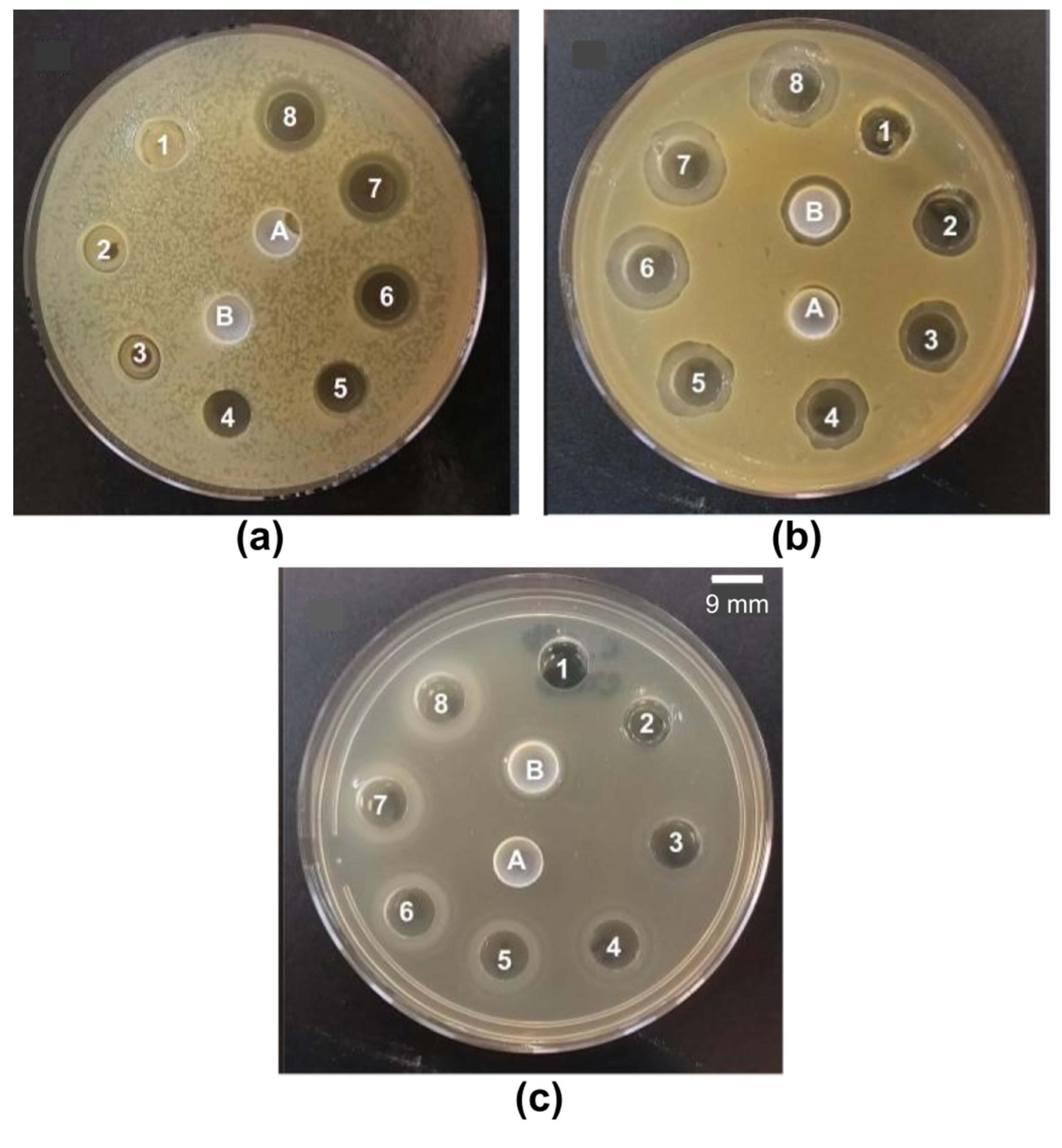
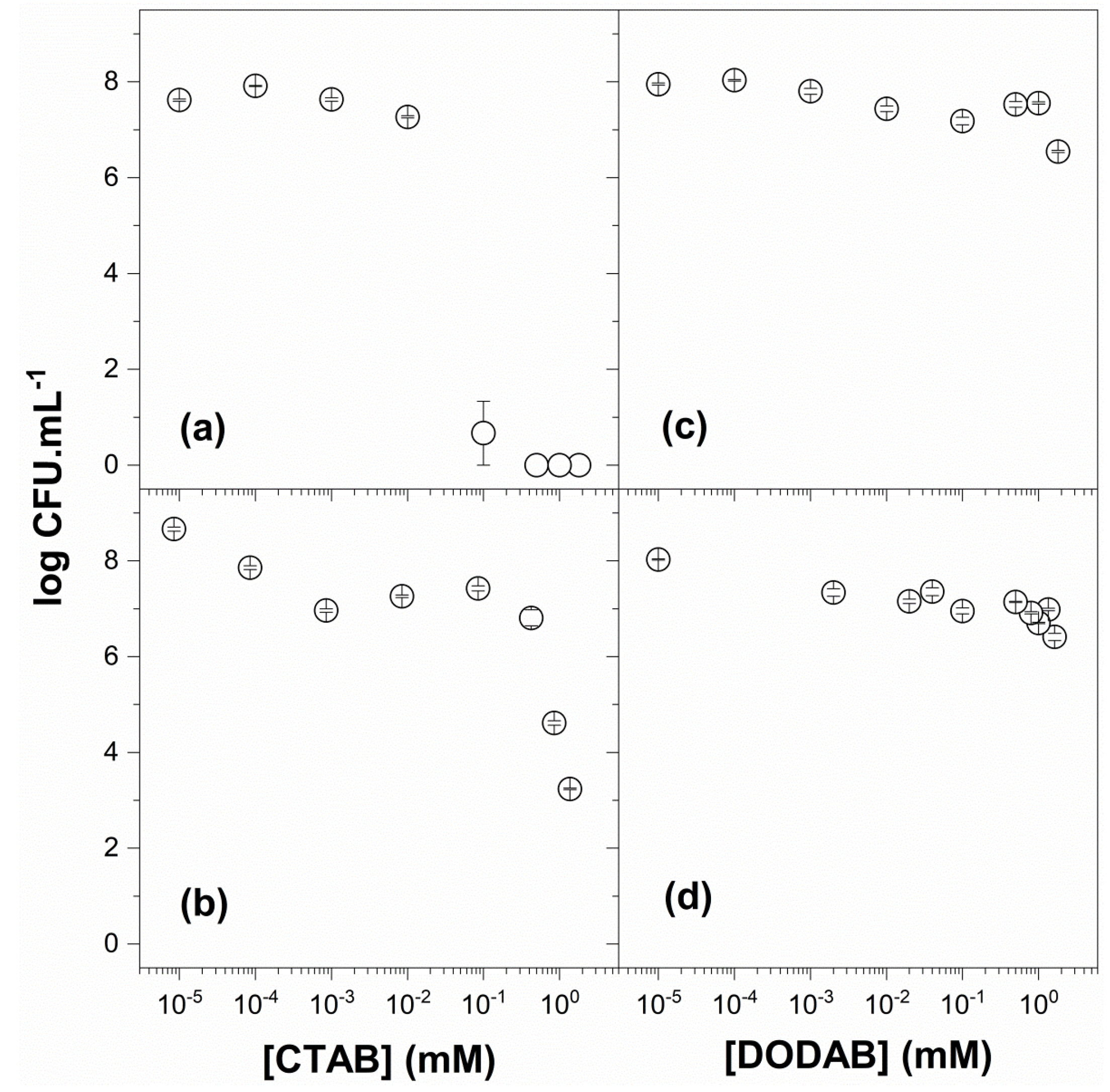
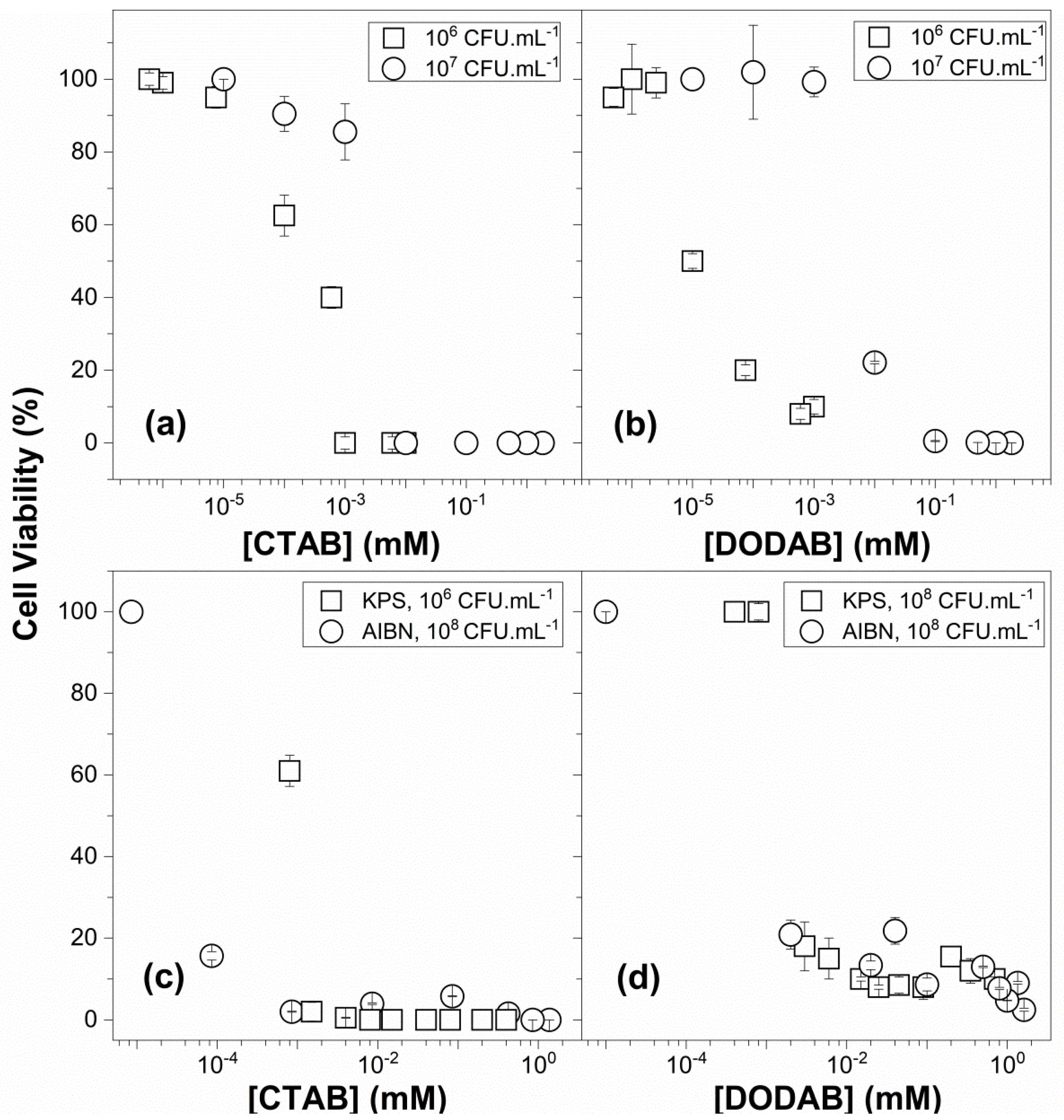
3.4. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of QACs and PMMA/QAC NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arif, U.; Haider, S.; Haider, A.; Khan, N.; Alghyamah, A.A.; Jamila, N.; Khan, M.I.; Almasry, W.A.; Kang, I.-K. Biocompatible Polymers and their Potential Biomedical Applications: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3608–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastri, V.P. Non-Degradable Biocompatible Polymers in Medicine: Past, Present and Future. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2003, 4, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzoni, E.; Cesaretti, A.; Polchi, A.; Di Michele, A.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. Biocompatible Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Disorder Therapies. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, C.N.; Priya, R.; Swain, S.; Kumar Jena, G.; Panigrahi, K.C.; Ghose, D. Pharmaceutical significance of Eudragit: A review. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 3, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, S.; Thakral, N.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Eudragit®: A technology evaluation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Karim, K.J.B.A.; Buang, N.A. A Review of the Properties and Applications of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA). Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic Nanomaterials from the Assembly of Polymers, Lipids, and Surfactants. In Surfactants and Detergents; Dutta, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Volume 1, ISBN 978-1-78984-661-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.L. Basic Transport Phenomena in Biomedical Engineering, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4398-2670-6. [Google Scholar]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malikmammadov, E.; Tanir, T.E.; Kiziltay, A.; Hasirci, V.; Hasirci, N. PCL and PCL-based materials in biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 863–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasprilla, A.J.R.; Martinez, G.A.R.; Lunelli, B.H.; Jardini, A.L.; Filho, R.M. Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices—A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Briso, A.L.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate): Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Azad, M.A.K.; Lin, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, H. Biological Effects and Applications of Chitosan and Chito-Oligosaccharides. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan Preparation from Marine Sources. Structure, Properties and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moohan, J.; Stewart, S.A.; Espinosa, E.; Rosal, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F.; Domínguez-Robles, J. Cellulose Nanofibers and Other Biopolymers for Biomedical Applications. A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, S.; Lamberti, G. Hydrogel-based commercial products for biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, E. Cytotoxic effects of acrylates and methacrylates: Relationships of monomer structures and cytotoxicity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 37, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X. Preparation, stability and film properties of cationic polyacrylate latex particles with various substituents on the nitrogen atom. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 143, 105628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.M.A.; Kosaka, P.M.; Rosa, H.; Vieira, D.B.; Kawano, Y.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Hybrid Materials from Intermolecular Associations between Cationic Lipid and Polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 9301–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.D.; Palombo, R.R.; Petri, D.F.S.; Bruns, M.; Pereira, E.M.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Structure–Activity Relationship for Quaternary Ammonium Compounds Hybridized with Poly(methyl methacrylate). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches, L.M.; Petri, D.F.S.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. The antimicrobial activity of free and immobilized poly (diallyldimethylammonium) chloride in nanoparticles of poly (methylmethacrylate). J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, C.N.; Sanches, L.M.; Mathiazzi, B.I.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial Coatings from Hybrid Nanoparticles of Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Polymers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.T.; Galvão, C.N.; Betancourt, Y.P.; Mathiazzi, B.I.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Microbicidal Dispersions and Coatings from Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate), Poly (Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium) Chloride, Lipids, and Surfactants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincopan, N.; Espíndola, N.M.; Vaz, A.J.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic supported lipid bilayers for antigen presentation. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 340, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Betancourt, Y.; Távora, B.D.C.L.F.; Colombini, M.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Simple Nanoparticles from the Assembly of Cationic Polymer and Antigen as Immunoadjuvants. Vaccines 2020, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efron, N. Contact Lens Practice E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2016; ISBN 978-0-7020-6661-0. [Google Scholar]
- Naves, A.F.; Palombo, R.R.; Carrasco, L.D.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial Particles from Emulsion Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate in the Presence of Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9677–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlström, B.; Chelminska-Bertilsson, M.; Thompson, R.A.; Edebo, L. Submicellar complexes may initiate the fungicidal effects of cationic amphiphilic compounds on Candida albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.M.S.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Vesicles as Bactericides. Langmuir 1997, 13, 5583–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Vieira, D.B.; Lincopan, N. Cationic Surfactants and Lipids as Anti-Infective Agents. Anti-Infect. Agents Med. Chem. 2006, 5, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic lipids and surfactants as antifungal agents: Mode of action. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Mitchell, D.J.; Ninham, B.W. Theory of self-assembly of hydrocarbon amphiphiles into micelles and bilayers. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 2 Mol. Chem. Phys. 1976, 72, 1525–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-08-092363-5. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Synthetic amphiphile vesicles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1992, 21, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Lipid Bilayer Fragments and Disks in Drug Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. The Versatile Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Bromide. In Application and Characterization of Surfactants; Najjar, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 157–181. ISBN 978-953-51-3325-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tapias, G.N.; Sicchierolli, S.M.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Cationic Vesicles and Escherichia coli. Langmuir 1994, 10, 3461–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicchierolli, S.M.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Bacteria Flocculation and Death by Cationic Vesicles. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2991–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanhã, M.T.N.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between cationic liposomes and bacteria: The physical-chemistry of the bactericidal action. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campanhã, M.T.N.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Cationic Vesicles and Candida albicans. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 8230–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Liposomes as Antimicrobial Agents. In Communicating Current Research and Educational Topics and Trends in Applied Microbiology; A. Méndez Vila: Badajoz, Spain, 2007; Volume 2, pp. 636–647, ISBN 13: 978-84-611-9423-0. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic nanoparticles for delivery of amphotericin B: Preparation, characterization and activity in vitro. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2008, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Cationic Vesicles and Serum Proteins. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6077–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, G.R.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragioto, D.A.; Carrasco, L.D.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Novel gramicidin formulations in cationic lipid as broad-spectrum microbicidal agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, I.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between DNA and Synthetic Cationic Liposomes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, H.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Bacteriophage DNA and Cationic Biomimetic Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16422–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenfeld, J.H.K.; Silva, S.R.; Ranéia, P.A.; Faquim-Mauro, E.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Stable assemblies of cationic bilayer fragments and CpG oligonucleotide with enhanced immunoadjuvant activity in vivo. J. Controll. Release 2012, 160, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Bilayer-Forming Synthetic Lipids: Drugs or Carriers? Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 2425–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Synthetic Bilayer Fragments for Solubilization of Amphotericin B. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 244, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.A.; Olivares-Ortega, C.; Soto-Arriaza, M.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interaction of gramicidin with DPPC/DODAB bilayer fragments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 3064–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.D.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial Particles from Cationic Lipid and Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12300–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D. Novel Formulations for Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18040–18083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D. Cationic Antimicrobial Polymers and Their Assemblies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9906–9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schales, O.; Schales, S. A simple and accurate method for the determination of chloride in biological fluids. J. Biol. Chem. 1941, 140, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Preparation and Characterization of Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. In Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 283–294. ISBN 978-1-61779-952-5. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski, E.; Morrison, I. Particle size distribution from analysis of quasi-elastic light scattering data. In Measurement of Suspended Particles by Quasi-elastic Light Scattering; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 21, pp. 199–236. [Google Scholar]
- Lincopan, N.; Santana, M.R.; Faquim-Mauro, E.; da Costa, M.H.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Silica-based cationic bilayers as immunoadjuvants. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.D.; de, M.; Bertolucci, R.J.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Sampaio, J.L.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Nanostructures against Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, P.S.; Dasannacharya, B.A.; Kelkar, V.K.; Manohar, C.; Srinivasa Rao, K.; Valaulikar, B.S. Shapes and sizes of micelles in CTAB solutions. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1991, 174, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Chaimovich, H. Preparation and characterization of large dioctadecyldimethylammonium chloride liposomes and comparison with small sonicated vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 1983, 733, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Yoshida, L.S.; Chaimovich, H. Salt effects on the stability of dioctadecyldimethylammonium chloride and sodium dihexadecyl phosphate vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 2928–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.T.; Van Tassel, P.R.; Saltzman, W.M. Simultaneous release of multiple molecules from poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles assembled onto medical devices. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4889–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, P.; Ottoor, D. pH Dependent Controlled Release of CTAB Incorporated Dipyridamole Drug from Agar-Based Hydrogel. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet-Bataillon, S.; Tattevin, P.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A. Emergence of resistance to antibacterial agents: The role of quaternary ammonium compounds—A critical review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ding, Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, G.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Zhen, M. Antifungal effects of BiOBr nanosheets carrying surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. J. Biomed. Res. 2018, 32, 380–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Mayer, J.; Wintermantel, E.; Leong, K.W. Biomedical applications of polymer-composite materials: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1189–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.J.; Tietjen, G.T.; Saucier-Sawyer, J.K.; Saltzman, W.M. A holistic approach to targeting disease with polymeric nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The “accidental” pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, K.; Tan, J.P.K.; Korevaar, P.A.; Yang, Y.Y.; Pitera, J.; Nelson, A.; Maune, H.; Coady, D.J.; Frommer, J.E.; Engler, A.C.; et al. Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Supramolecular Assemblies with Distinctive Size and Shape. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9191–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona Ribeiro, A.M.; Carrasco, L.D.M. Fungicidal assemblies and their mode of action. OA Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| NPs | D (nm) | Dz (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| PMMA/DODAB | 56 ± 7 | 75 ± 1 |
| PMMA/CTAB | 85 ± 11 | 81 ± 1 |
| QAC | [MMA] /M | Dz /nm | ζ /mV | P | Solid Contents /mg·mL−1 | Conversion /% | Np /mL−1 | Aggregates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DODAB | 0.1 | 101 ± 1 | +20 ± 2 | 0.355 ± 0.002 | 0.0051 ± 0.0001 | 51 | 8.35 × 1012 | No |
| 0.2 | 52 ± 1 | +20 ± 1 | 0.265 ± 0.003 | 0.0081 ± 0.0001 | 40 | 9.52 × 1013 | No | |
| 0.3 | 73 ± 1 | +27 ± 1 | 0.038 ± 0.010 | 0.0183 ± 0.0009 | 61 | 7.76 × 1013 | No | |
| 0.4 | 75 ± 1 | +49 ± 5 | 0.037 ± 0.005 | 0.0317 ± 0.0001 | 79 | 1.26 × 1014 | No | |
| 0.7 | 94 ± 1 | +26 ± 2 | 0.033 ± 0.009 | 0.0479 ± 0.0008 | 68 | 1.04 × 1014 | Yes | |
| 0.9 | 103 ± 1 | +38 ± 2 | 0.013 ± 0.004 | 0.0697 ± 0.0001 | 77 | 1.07 × 1014 | Yes | |
| 1.0 | 109 ± 1 | +33 ± 1 | 0.020 ± 0.010 | 0.0781 ± 0.0005 | 78 | 1.02 × 1014 | Yes | |
| CTAB | 0.1 | 916 ± 56 | +18 ± 1 | 0.477 ± 0.042 | 0.0021 ± 0.0004 | 20 | 4.43 × 109 | No |
| 0.2 | 40 ± 1 | +20 ± 1 | 0.291 ± 0.003 | 0.0105 ± 0.0004 | 53 | 2.82 × 1014 | No | |
| 0.3 | 70 ± 1 | +17 ± 1 | 0.078 ± 0.009 | 0.0197 ± 0.0019 | 65 | 9.52 × 1013 | No | |
| 0.4 | 81 ± 1 | +23 ± 1 | 0.041 ± 0.008 | 0.0320 ± 0.0019 | 80 | 1.01 × 1014 | No | |
| 0.7 | 100 ± 1 | +20 ± 1 | 0.032 ± 0.008 | 0.0363 ± 0.0014 | 52 | 6.10 × 1013 | Yes | |
| 0.9 | 121 ± 1 | +26 ± 1 | 0.012± 0.004 | 0.0692 ± 0.0013 | 77 | 6.52 × 1013 | Yes | |
| 1.0 | 121 ± 1 | +17 ± 1 | 0.046 ± 0.010 | 0.0702 ± 0.0005 | 70 | 6.52 × 1013 | Yes |
| QAC | [QAC] /mM | Dz /nm | ζ /mV | P | Solid Contents /mg·mL−1 | Conversion /% | Np /mL−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DODAB | 0.3 | 99 ± 1 | +50 ± 2 | 0.035 ± 0.009 | 0.0303 ± 0.0003 | 76 | 5.24 × 1013 |
| 0.5 | 93 ± 1 | +44 ± 2 | 0.045 ± 0.014 | 0.0300 ± 0.0004 | 75 | 6.21 × 1013 | |
| 1.0 | 85 ± 1 | +33 ± 2 | 0.028 ± 0.008 | 0.0303 ± 0.0006 | 76 | 8.08 × 1013 | |
| 2.0 | 75 ± 1 | +49 ± 5 | 0.037 ± 0.005 | 0.0317 ± 0.0001 | 79 | 1.26 × 1014 | |
| 4.0 | 69 ± 1 | +31 ± 1 | 0.072 ± 0.008 | 0.0349 ± 0.0006 | 87 | 1.79 × 1014 | |
| 5.0 | 62 ± 1 | +29 ± 2 | 0.068 ± 0.010 | 0.0333 ± 0.0006 | 83 | 2.31 × 1014 | |
| 8.0 | 58 ± 1 | +32 ± 2 | 0.098 ± 0.010 | 0.0365 ± 0.0008 | 91 | 3.04 × 1014 | |
| 10.0 | 59 ± 1 | +35 ± 3 | 0.123 ± 0.007 | 0.0364 ± 0.0021 | 91 | 2.92 × 1014 | |
| CTAB | 0.3 | 126 ± 1 | +15 ± 1 | 0.055 ± 0.013 | 0.0261 ± 0.0001 | 65 | 2.16 × 1013 |
| 0.5 | 115 ± 1 | +15 ± 1 | 0.069 ± 0.016 | 0.0274 ± 0.0001 | 68 | 3.02 × 1013 | |
| 1.0 | 103 ± 1 | +27 ± 2 | 0.069 ± 0.013 | 0.0319 ± 0.0005 | 80 | 4.86 × 1013 | |
| 2.0 | 81 ± 1 | +23 ± 1 | 0.041 ± 0.008 | 0.0320 ± 0.0019 | 80 | 1.01 × 1014 | |
| 4.0 | 67 ± 1 | +24 ± 1 | 0.070 ± 0.011 | 0.0282 ± 0.0003 | 70 | 1.55 × 1014 | |
| 5.0 | 67 ± 1 | +31 ± 2 | 0.052 ± 0.012 | 0.0234 ± 0.0006 | 58 | 1.32 × 1014 | |
| 8.0 | 60 ± 1 | +34 ± 1 | 0.095 ± 0.011 | 0.0320 ± 0.0002 | 80 | 2.50 × 1014 | |
| 10.0 | 57 ± 1 | +41 ± 2 | 0.092 ± 0.008 | 0.0308 ± 0.0001 | 77 | 2.72 × 1014 |
| NPs | Initiator | Dz/nm | ζ/mV | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA/DODAB | KPS 1 | 1260 ± 43 | −10 ± 1 | 0.370 |
| AIBN | 89 ± 1 | +45 ± 2 | 0.027 ± 0.010 | |
| PMMA/CTAB | KPS 1 | 395 ± 5 | −38 ± 1 | 0.262 |
| AIBN | 96 ± 1 | +23 ± 1 | 0.033 ± 0.012 |
| Dispersion or Solution | [QAC]/mM | |
|---|---|---|
| Before Dialysis | After Dialysis | |
| CTAB dispersion in water | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| DODAB bilayer fragments in water | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| NaCl water solution | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Supernatant of PMMA/DODAB dispersion | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 1 |
| Supernatant of PMMA/CTAB dispersion | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathiazzi, B.I.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) and Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040340
Mathiazzi BI, Carmona-Ribeiro AM. Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) and Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(4):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040340
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathiazzi, Beatriz Ideriha, and Ana Maria Carmona-Ribeiro. 2020. "Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) and Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 4: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040340
APA StyleMathiazzi, B. I., & Carmona-Ribeiro, A. M. (2020). Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) and Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants. Pharmaceutics, 12(4), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040340