Enteric Hard Capsules for Targeting the Small Intestine: Positive Correlation between In Vitro Disintegration and Dissolution Times
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Capsule Filling
2.3. Capsule Coating
2.4. Disintegration Test
2.5. Acid Uptake Test
2.6. Dissolution Test
2.7. Correlation between Disintegration and Dissolution Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Disintegration and Acid Uptake
3.2. Dissolution
3.3. Correlation between Disintegration and Dissolution Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Gousous, J.; Langguth, P. Oral Solid Dosage Form Disintegration Testing-The Forgotten Test. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2664–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Conference on Harmonization. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q6A_Guideline.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2019).
- Gupta, A.; Hunt, R.L.; Shah, R.B.; Sayeed, V.A.; Khan, M.A. Disintegration of highly soluble immediate release tablets: A surrogate for dissolution. Aaps Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2009, 10, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, A.; Amidon, G.L.; Langguth, P. Mechanistic investigation of food effect on disintegration and dissolution of BCS class III compound solid formulations: The importance of viscosity. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2012, 33, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, B.; Kong, A.; Gerst, P.; Kao, S. Correlation of dissolution and disintegration results for an immediate-release tablet. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gousous, J.; Amidon, G.L.; Langguth, P. Toward Biopredictive Dissolution for Enteric Coated Dosage Forms. Mol. Pharmaceutics. 2016, 13, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tabakha, M.M.; Arida, A.I.; Fahelelbom, K.M.S.; Sadek, B.; Jarad, R.A.A. Performances of New Generation of Delayed Release Capsules. J. Young Pharm. 2015, 7, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VassarStats. Available online: http://vassarstats.net/ (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Kamba, M.; Seta, Y.; Takeda, N.; Hamaura, T.; Kusai, A.; Nakane, H.; Nishimura, K. Measurement of agitation force in dissolution test and mechanical destructive force in disintegration test. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, D.M.; Corrigan, O.I.; Healy, A.M. Evaluation of hydrodynamics in the basket dissolution apparatus using computational fluid dynamics–Dissolution rate implications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 27, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagavan, H.N.; Wolkoff, B.I. Correlation between the disintegration time and the bioavailability of vitamin C tablets. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, J.; Tack, J.; Augustijns, P. Parallel monitoring of plasma and intraluminal drug concentrations in man after oral administration of fosamprenavir in the fasted and fed state. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, J.; Anneveld, B.; Goudappel, G.J.; Duchateau, G.; Annaert, P.; Augustijns, P.; Zeijdner, E. Food-dependent disintegration of immediate release fosamprenavir tablets: In vitro evaluation using magnetic resonance imaging and a dynamic gastrointestinal system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
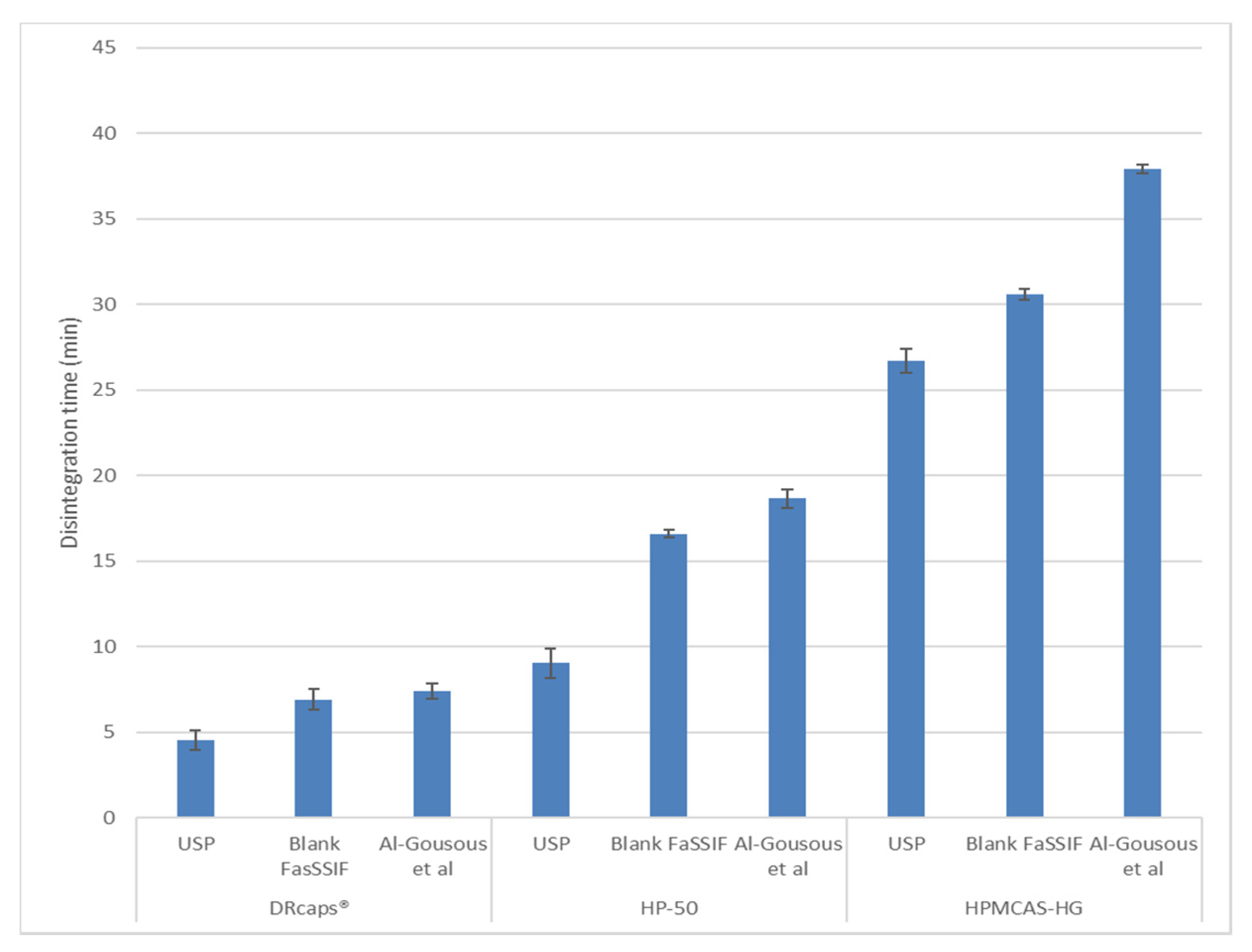



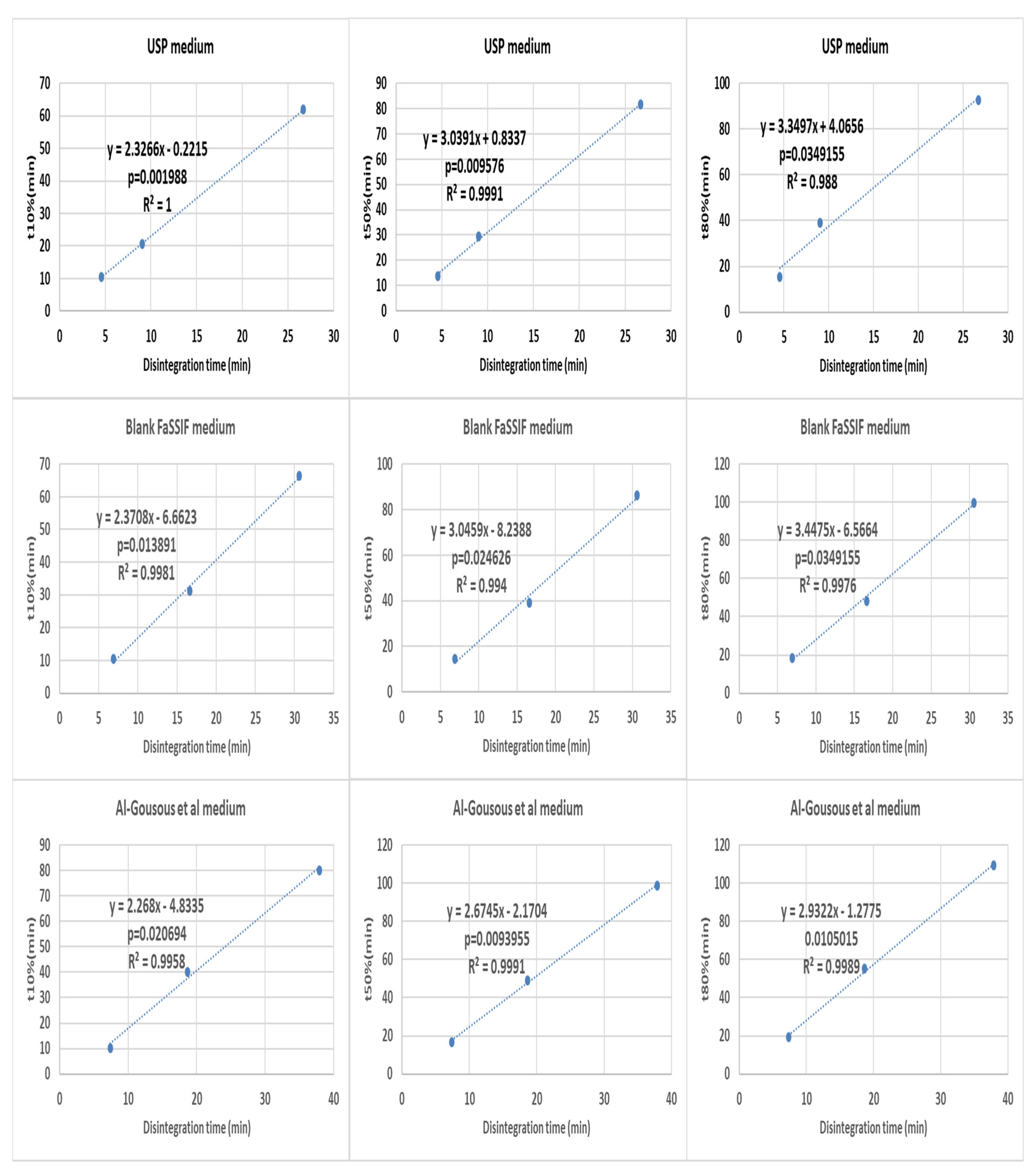


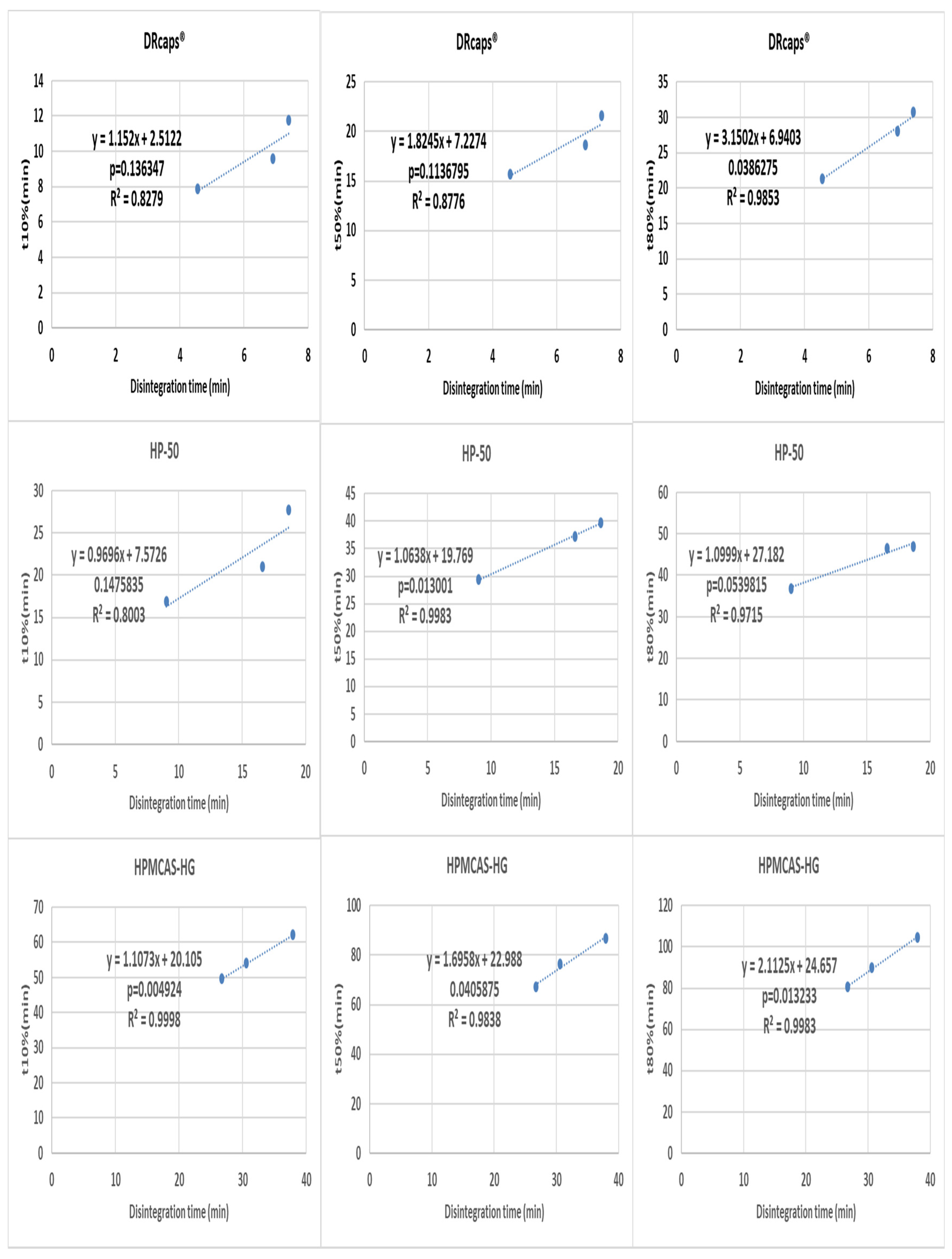

| Substance | % (m/m) | Weights of the Components per Capsule (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | 20 | 75 |
| L-HPC | 15 | 56.25 |
| Lactose | 63.75 | 239.06 |
| Silica | 0.25 | 0.94 |
| Magnesium stearate | 1 | 3.75 |
| Total | 100 | 375 |
| Substance | HP-50 Formulation | HPMCAS-HG Formulation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % (m/m) | Weights of the Components (g) | % (m/m) | Weights of the Components (g) | |
| Polymer | 6 | 60 | 5 | 40 |
| Talc | 7.5 | 75 | 7.5 | 60 |
| TEC | - | - | 2 | 16 |
| Ethanol | 69.2 | 747.7 | 68.4 | 591.25 |
| Water | 17.3 | 117.3 | 17.1 | 92.75 |
| Formulation | % Weight gain in 0.1 M HCl | % Weight gain in 0.01 M HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After 1 h | After 2 h | After 1 h | After 2 h | |
| DRcaps® | 6.5 ± 0.7 | 7.4 ± 0.3 | 11.2 ± 0.2 | 13.5 ± 0.6 |
| HP-50 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 6.1 ± 0.7 |
| HPMCAS-HG | 2.5 ± 0.4 | Ruptured | 2.8 ± 0.6 | Ruptured |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, M.; Al-Gousous, J.; Blechar, J.A.; Langguth, P. Enteric Hard Capsules for Targeting the Small Intestine: Positive Correlation between In Vitro Disintegration and Dissolution Times. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020123
Fu M, Al-Gousous J, Blechar JA, Langguth P. Enteric Hard Capsules for Targeting the Small Intestine: Positive Correlation between In Vitro Disintegration and Dissolution Times. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(2):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020123
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Maoqi, Jozef Al-Gousous, Johannes Andreas Blechar, and Peter Langguth. 2020. "Enteric Hard Capsules for Targeting the Small Intestine: Positive Correlation between In Vitro Disintegration and Dissolution Times" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 2: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020123
APA StyleFu, M., Al-Gousous, J., Blechar, J. A., & Langguth, P. (2020). Enteric Hard Capsules for Targeting the Small Intestine: Positive Correlation between In Vitro Disintegration and Dissolution Times. Pharmaceutics, 12(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020123





