Doxorubicin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Molecular Weight Effect of PLGA in Doxorubicin Release for Controlling Immunogenic Cell Death
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of DOX-Loaded PLGA NPs
2.3. In Vitro Characterization of DOX-PLGA7K NPs and DOX-PLGA12K NPs
2.4. In Vitro Cellular Uptake, Cytotoxicity, and Immunogenic Cell Death Analysis
2.5. In Vivo Drug Release Analysis
2.6. Tumor Growth Inhibition and Mechanism Analysis
2.7. Tumor Re-Challenging and Interferon-Gamma (INF-γ) Detection
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
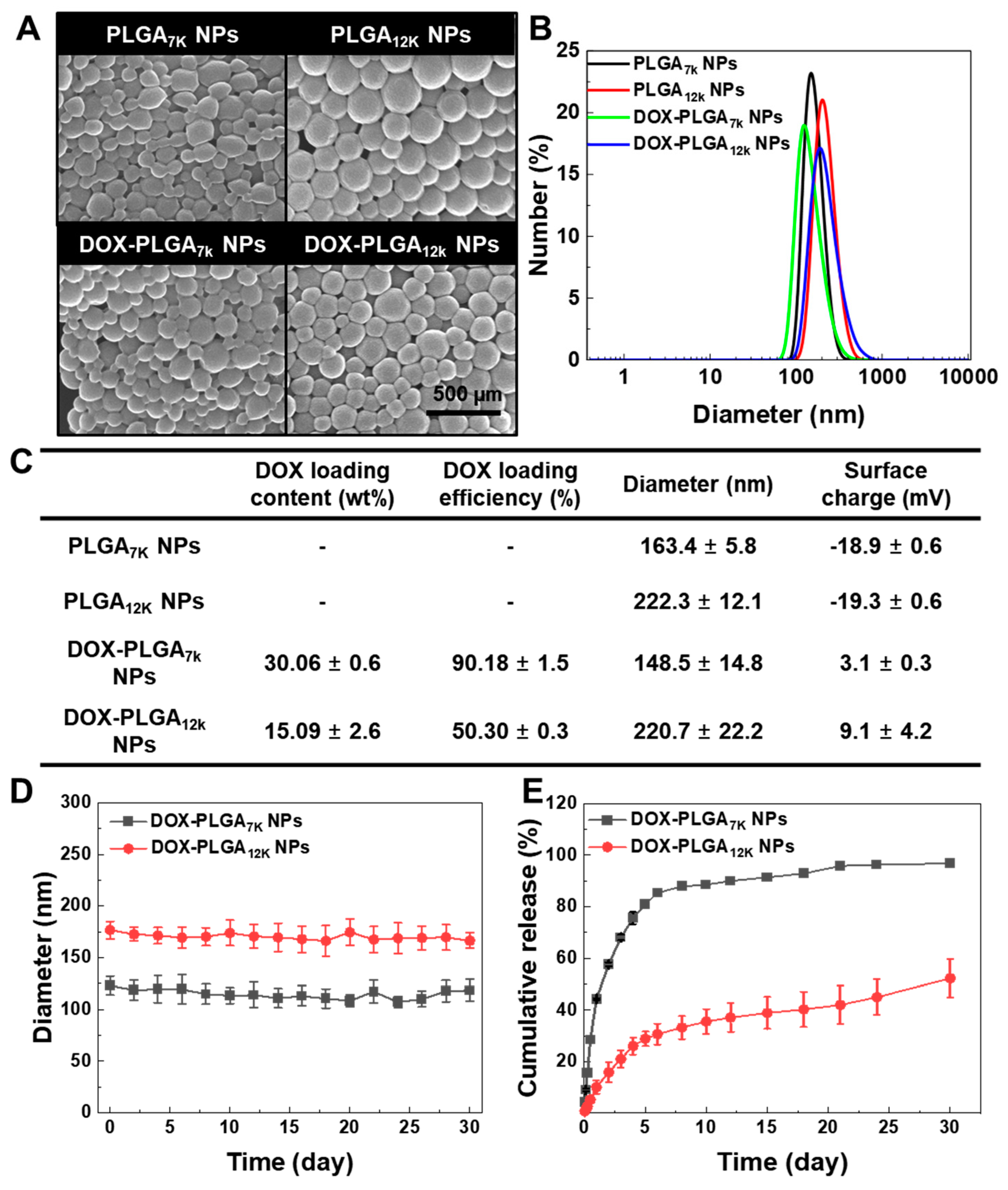
3.1. Formulation and In Vitro Characterization of the DOX-PLGA7K NPs and DOX-PLGA12K NPs
3.2. In Vitro Cellular Uptake and Immunogenic Cell Death on the CT-26 Tumor Cells
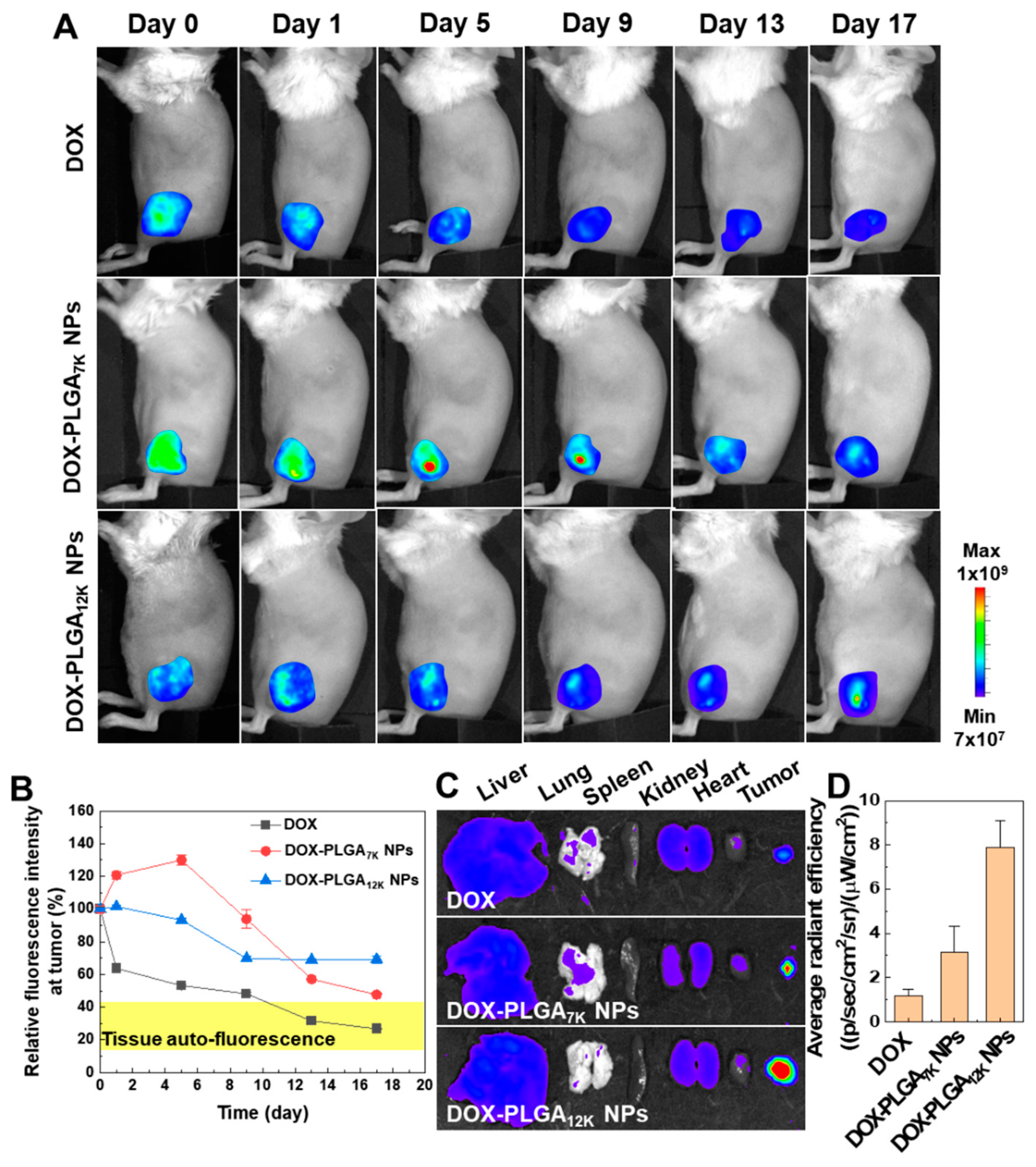
3.3. In Vivo Drug Release and Tumor Growth Inhibition
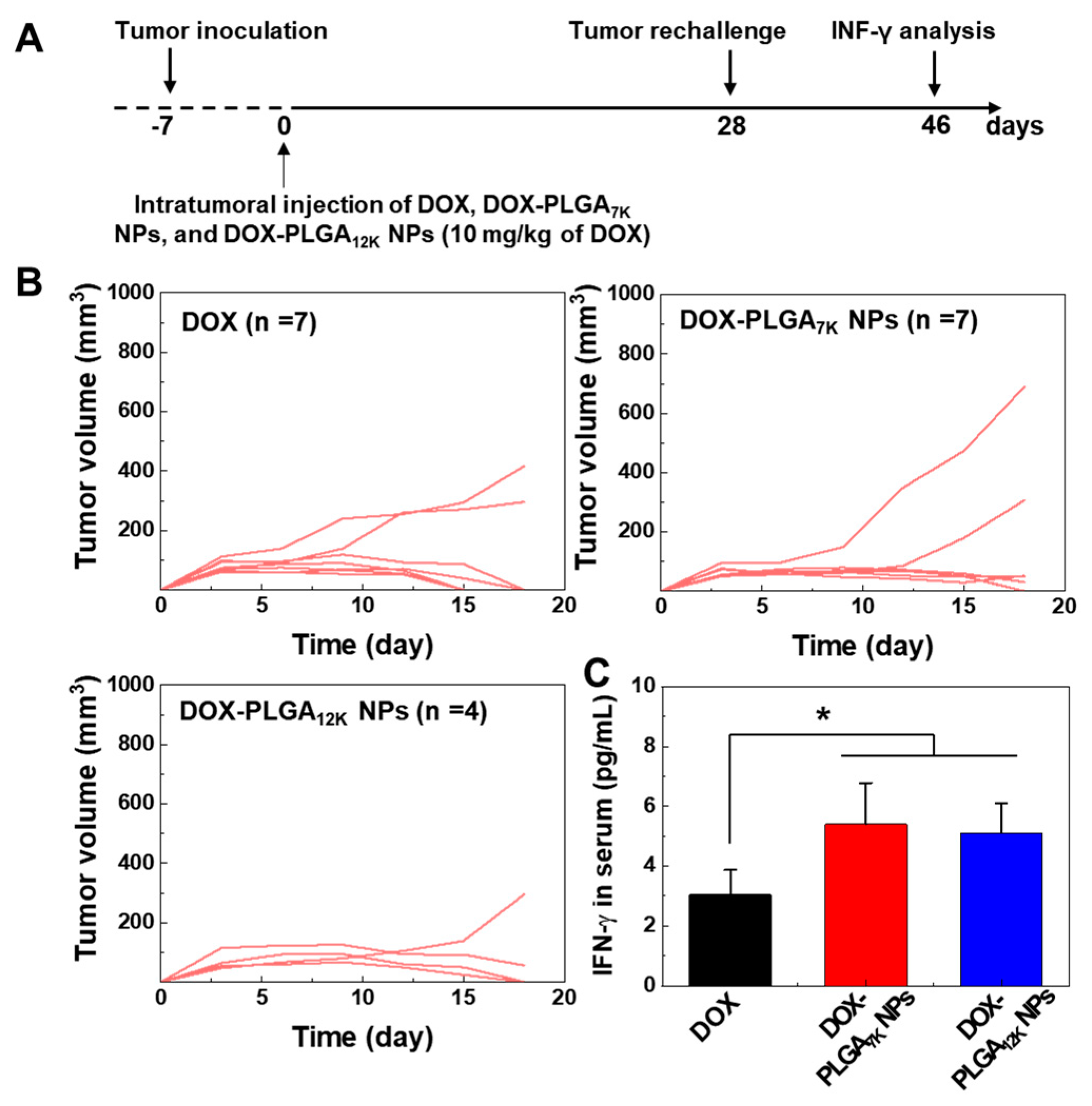
3.4. Immune-Memory Effect Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Photothermal therapy with immune-adjuvant nanoparticles together with checkpoint blockade for effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Liu, C.; Xing, J.; Akakuru, O.U.; Fang, Q.; Li, Z.; Dai, Y.; Li, A.; Guan, Y. Engineered nano-immunopotentiators efficiently promote cancer immunotherapy for inhibiting and preventing lung metastasis of melanoma. Biomaterials 2019, 223, 119464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, E.; Jäger, D.; Knuth, A. Clinical cancer vaccine trials. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyi, J.L.; Bobisse, S.; Ophir, E.; Tuyaerts, S.; Roberti, A.; Genolet, R.; Baumgartner, P.; Stevenson, B.J.; Iseli, C.; Dangaj, D. Personalized cancer vaccine effectively mobilizes antitumor T cell immunity in ovarian cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mougel, A.; Terme, M.; Tanchot, C. Therapeutic Cancer Vaccine and Combinations With Antiangiogenic Therapies and Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terenzi, A.; Pirker, C.; Keppler, B.K.; Berger, W. Anticancer metal drugs and immunogenic cell death. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 165, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepp, O.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Vacchelli, E.; Adjemian, S.; Agostinis, P.; Apetoh, L.; Aranda, F.; Barnaba, V.; Bloy, N. Consensus guidelines for the detection of immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e955691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Ju, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y.; Ren, M.; Zhang, H. Immunogenic cell death in anticancer chemotherapy and its impact on clinical studies. Cancer Lett. 2018, 438, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Chan, C.; Lin, W. Nanoparticle-Mediated Immunogenic Cell Death Enables and Potentiates Cancer Immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tongchusak, S.; Mizukami, Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Ioji, T.; Touma, M.; Reinhold, B.; Keskin, D.B.; Reinherz, E.L.; Sasada, T. Induction of anti-tumor cytotoxic T cell responses through PLGA-nanoparticle mediated antigen delivery. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3666–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Roche, K.C.; Tian, S.; Eblan, M.J.; McKinnon, K.P.; Caster, J.M.; Chai, S.; Herring, L.E.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T. Antigen-capturing nanoparticles improve the abscopal effect and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mittal, G.; Sahana, D.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kumar, M.R. Estradiol loaded PLGA nanoparticles for oral administration: Effect of polymer molecular weight and copolymer composition on release behavior in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumskova, N.; Ermolenko, Y.; Osipova, N.; Semyonkin, A.; Kildeeva, N.; Gorshkova, M.; Kovalskii, A.; Kovshova, T.; Tarasov, V.; Kreuter, J. How subtle differences in polymer molecular weight affect doxorubicin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles degradation and drug release. J. Microencapsul. 2020, 37, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvantalab, S.; Drude, N.I.; Moraveji, M.K.; Güvener, N.; Koons, E.K.; Shi, Y.; Lammers, T.; Kiessling, F. PLGA-Based Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engineer, C.; Parikh, J.; Raval, A. Review on hydrolytic degradation behavior of biodegradable polymers from controlled drug delivery system. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2011, 25, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Kim, C.S.; Saylor, D.M.; Koo, D. Polymer degradation and drug delivery in PLGA-based drug–polymer applications: A review of experiments and theories. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 1692–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, K.; Zhao, R.; Ji, T.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Liu, S.; Hao, J.; et al. Inducing enhanced immunogenic cell death with nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for pancreatic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkouk, A.; Joshi, V.B.; Wongrakpanich, A.; Lemke, C.D.; Gross, B.P.; Salem, A.K.; Weiner, G.J. Biodegradable microparticles loaded with doxorubicin and CpG ODN for in situ immunization against cancer. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.-M.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, M.H.; Cha, G.S.; Jung, I.D.; Kang, T.H.; Han, H.D. Nanoparticle-Based Vaccine Delivery for Cancer Immunotherapy. Immune Netw. 2013, 13, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tewes, F.; Munnier, E.; Antoon, B.; Ngaboni Okassa, L.; Cohen-Jonathan, S.; Marchais, H.; Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Soucé, M.; Dubois, P.; Chourpa, I. Comparative study of doxorubicin-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles prepared by single and double emulsion methods. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.-J.; Jeong, Y.-I.; Jang, M.-K.; Park, Y.-H.; Nah, J.-W. Effect of solvent on the preparation of surfactant-free poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles and norfloxacin release characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 207, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Shu, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, B.; Liao, X. Polyurethane/doxorubicin nanoparticles based on electrostatic interactions as pH-sensitive drug delivery carriers. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, A.C.; Voskerician, G.; Lynn, A.; Anderson, J.M.; Cima, M.J.; Langer, R. Differential degradation rates in vivo and in vitro of biocompatible poly (lactic acid) and poly (glycolic acid) homo-and co-polymers for a polymeric drug-delivery microchip. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2004, 15, 1281–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffidi, P.; Misteli, T.; Bianchi, M.E. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature 2002, 418, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetoh, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Tesniere, A.; Criollo, A.; Ortiz, C.; Lidereau, R.; Mariette, C.; Chaput, N.; Mira, J.P.; Delaloge, S. The interaction between HMGB1 and TLR4 dictates the outcome of anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 220, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hreggvidsdottir, H.S.; Palmblad, K.; Wang, H.; Ochani, M.; Li, J.; Lu, B.; Chavan, S.; Rosas-Ballina, M.; Al-Abed, Y. A critical cysteine is required for HMGB1 binding to Toll-like receptor 4 and activation of macrophage cytokine release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11942–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Babensee, J.E. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) enhances maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2004, 71A, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, D.V.; Garg, A.D.; Kaczmarek, A.; Krysko, O.; Agostinis, P.; Vandenabeele, P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-E.; Hajdu, C.H.; Liot, C.; Miller, G.; Dustin, M.L.; Bar-Sagi, D. Crosstalk between Regulatory T Cells and Tumor-Associated Dendritic Cells Negates Anti-tumor Immunity in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Disis, M.L. Immune regulation of cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, S.; Molavi, O.; Ma, Z.; Haddadi, A.; Alshamsan, A.; Gobti, Z.; Elhasi, S.; Samuel, J.; Lavasanifar, A. Co-delivery of cancer-associated antigen and Toll-like receptor 4 ligand in PLGA nanoparticles induces potent CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5046–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolete, R.; dos Santos, D.F.; Faccioli, L.H. The uptake of PLGA micro or nanoparticles by macrophages provokes distinct in vitro inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.W.; Moon, Y.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.; Shim, M.K.; et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Molecular Weight Effect of PLGA in Doxorubicin Release for Controlling Immunogenic Cell Death. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121165
Choi Y, Yoon HY, Kim J, Yang S, Lee J, Choi JW, Moon Y, Kim J, Lim S, Shim MK, et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Molecular Weight Effect of PLGA in Doxorubicin Release for Controlling Immunogenic Cell Death. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(12):1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121165
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yongwhan, Hong Yeol Yoon, Jeongrae Kim, Suah Yang, Jaewan Lee, Ji Woong Choi, Yujeong Moon, Jinseong Kim, Seungho Lim, Man Kyu Shim, and et al. 2020. "Doxorubicin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Molecular Weight Effect of PLGA in Doxorubicin Release for Controlling Immunogenic Cell Death" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 12: 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121165
APA StyleChoi, Y., Yoon, H. Y., Kim, J., Yang, S., Lee, J., Choi, J. W., Moon, Y., Kim, J., Lim, S., Shim, M. K., Jeon, S., Kwon, I. C., & Kim, K. (2020). Doxorubicin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Molecular Weight Effect of PLGA in Doxorubicin Release for Controlling Immunogenic Cell Death. Pharmaceutics, 12(12), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121165




