Development of Self-Associating SN-38-Conjugated Poly(ethylene oxide)-Poly(ester) Micelles for Colorectal Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
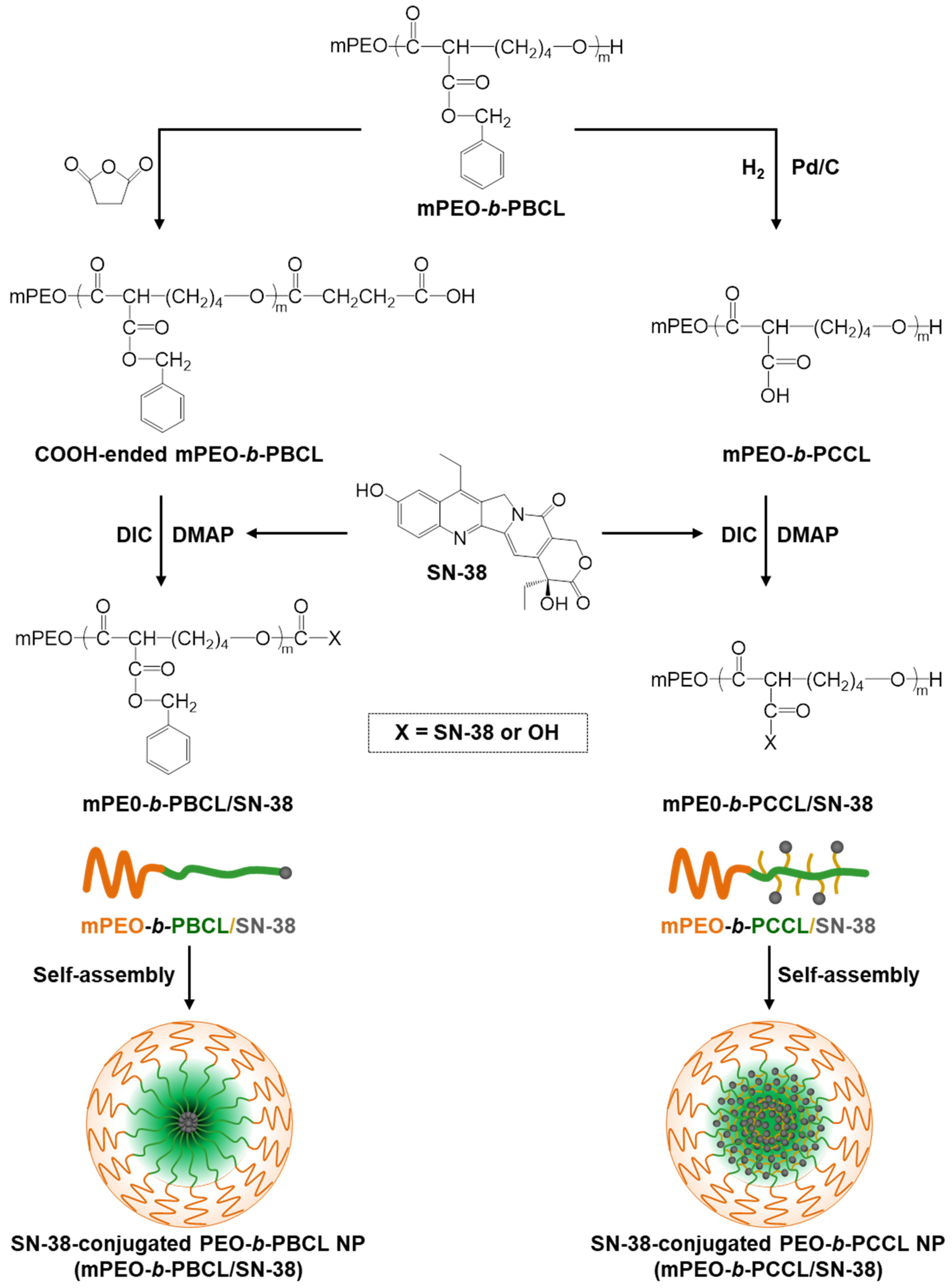
2.2. Synthesis of Block Copolymers
2.3. Synthesis of Carboxyl-Terminated mPEO-b-PBCL Block Copolymers
2.4. Conjugation of SN-38 to mPEO-b-PBCL-COOH Copolymers
2.5. Conjugation of SN-38 to mPEO-b-PCCL Copolymers
2.6. Characterization of Block Copolymers and Drug-Copolymer Conjugates
2.7. Self-Assembly of Block Copolymers and Physicochemical Characterization of Self-Assembled Structures
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.9. In Vitro Drug Release
2.10. Cell Lines
2.11. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.12. Caspase 3/7 Activity Measurements
2.13. Hemolytic Activity Assessment
2.14. Statistical Analysis
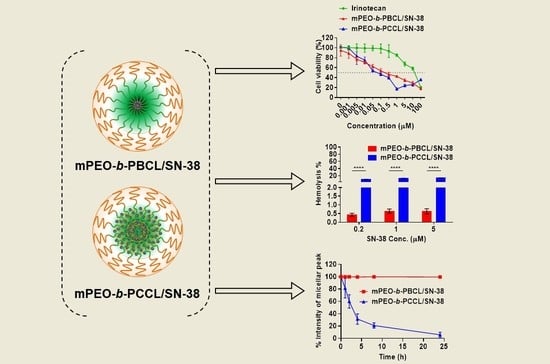
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.3. Kinetic Stability of Block Copolymeric Micelles
3.4. In Vitro Drug Release
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
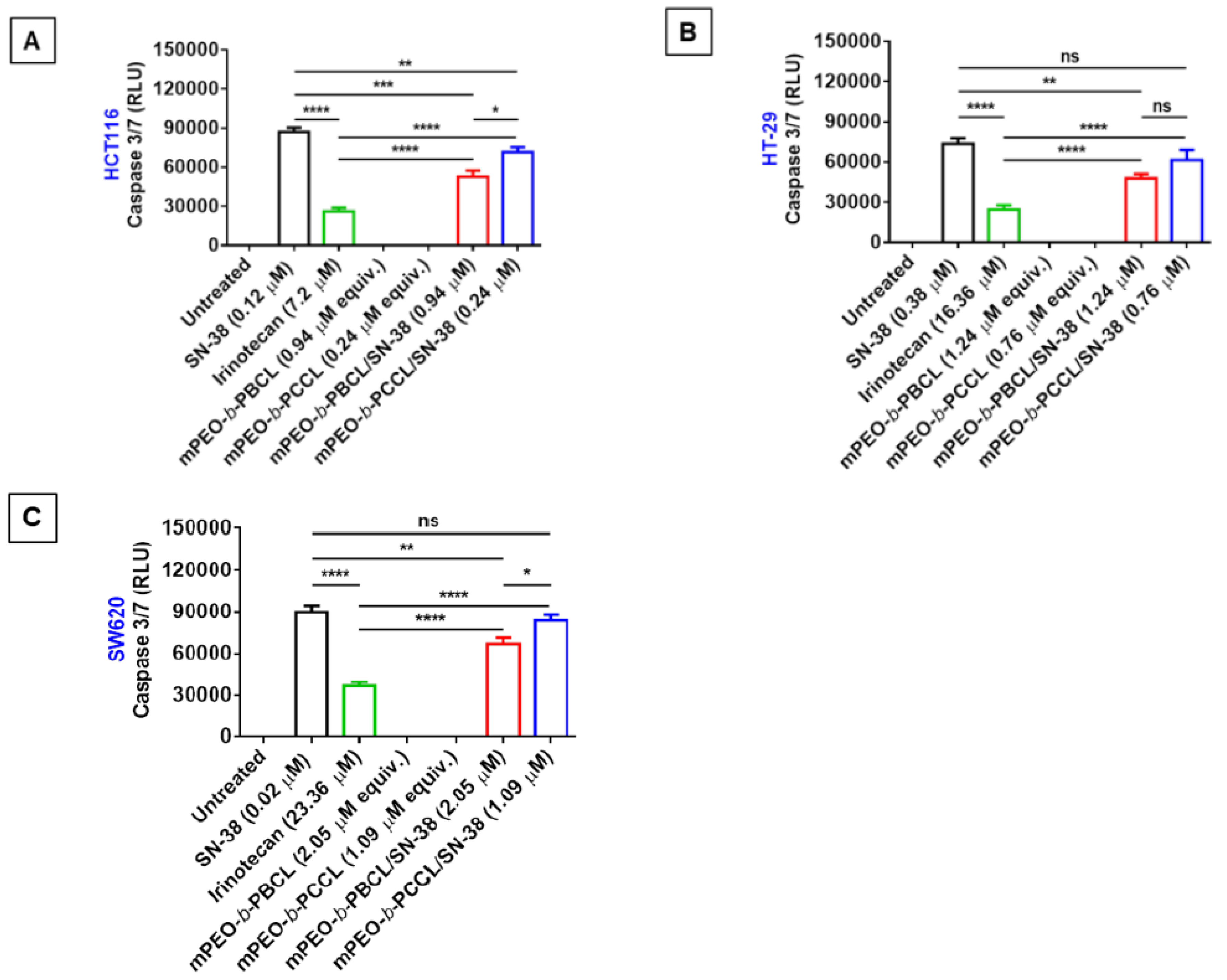
3.6. Caspase 3/7 Activity
3.7. Hemolytic Activity Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCL | α-benzyl carboxylate-ε-caprolactone |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CDCl3 | deuterated chloroform |
| CMC | critical micellar concentration |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| DIC | N,N′-diisopropylcarbodiimide |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| DMAP | 4-dimethylaminopyridine |
| DMEM/F12 | dulbecco’s modified eagle medium and F12 |
| DMF | dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNA | deoxy ribonucleic acid |
| DP | degree of polymerization |
| EPR | enhanced permeability and retention effect |
| Kcps | kilo counts per second |
| mPEO | methoxy-polyethylene oxide |
| mPEO-b-PBCL | methoxy-poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(α-benzyl carboxylate-ε-caprolactone) |
| mPEO-b-PBCL/SN-38 | SN-38-incorporated mPEO-b-PBCL micelle |
| mPEO-b-PCCL | methoxy-poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(α-carboxyl-ε-caprolactone) |
| mPEO-b-PCCL/SN-38 | SN-38-incorporated mPEO-b-PCCL micelle |
| MW | molecular weight |
| PDI | polydispersity index |
| RBC | red blood cell |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SN-38 | 7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| Topo-I | topoisomerase I |
| ZP | zeta potential |
References
- Kuipers, E.J.; Rösch, T.; Bretthauer, M. Colorectal cancer screening—Optimizing current strategies and new directions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Peng, J.-J.; Huang, L.-Y.; Shi, D.-B.; Liang, L.; Cai, S.-J. RNA-seq reveals determinants for irinotecan sensitivity/resistance in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.-C.; Chiou, Y.-C.; Wong, J.-M.; Peng, C.-L.; Shieh, M.-J. Targeting colorectal cancer cells with single-walled carbon nanotubes conjugated to anticancer agent SN-38 and EGFR antibody. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8756–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Hamasaki, Y.; Ueki, H. Protooncogene (C-Myc) Expression in the Infiltrating Cells of Lesional Skin from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, E.; Lagarce, F.; Benoit, J.-P. Development and characterization of a novel lipid nanocapsule formulation of Sn38 for oral administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, E.; Lestingi, T.M.; Mick, R.; Ramirez, J.; Vokes, E.E.; Ratain, M.J. Metabolic fate of irinotecan in humans: Correlation of glucuronidation with diarrhea. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 3723–3725. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Supko, J.G. Current perspectives on the clinical experience, pharmacology, and continued development of the camptothecins. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 641–661. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Ghandi, A.; Liebes, L.; Louie, S.G.; Hofman, F.M.; Schönthal, A.H.; Chen, T.C. Effective conversion of irinotecan to SN-38 after intratumoral drug delivery to an intracranial murine glioma model in vivo. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, F.; Kitagawa, M.; Negishi, T.; Onda, T.; Matsumoto, S.-I.; Hamaguchi, T.; Matsumura, Y. Novel SN-38–Incorporating Polymeric Micelles, NK012, Eradicate Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor–Secreting Bulky Tumors. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10048–10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Kataoka, K. Preclinical and clinical studies of anticancer agent-incorporating polymer micelles. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidczyk, C.M.; Kim, C.; Park, J.H.; Russell, L.M.; Lee, K.H.; Pomper, M.G.; Searson, P.C. State-of-the-art in design rules for drug delivery platforms: Lessons learned from FDA-approved nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estanqueiro, M.; Amaral, M.H.; Conceição, J.; Lobo, J.M.S. Nanotechnological carriers for cancer chemotherapy: The state of the art. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Herrero, E.; Fernández-Medarde, A. Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, K.; Harada, A.; Nagasaki, Y. Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: Design, characterization and biological significance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, R.B.; Pendri, A.; Conover, C.; Gilbert, C.; Yang, A.R.; Xia, J. Drug Delivery Systems. 2. Camptothecin 20-O-Poly(ethylene glycol) Ester Transport Forms. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 1938–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.C.; Nicholas, A.W.; Manikumar, G.; Wall, M.E. Plant antitumor agents. 25. Total synthesis and antileukemic activity of ring A substituted camptothecin analogues. Structure-activity correlations. J. Med. Chem. 1987, 30, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.-D.; Liu, H.-Y.; Sun, P.-Y.; Zhu, C.-G.; Yang, J.; Yuan, K.-H.; Han, R. Synthesis and antitumor activity of 20-O-linked camptothecin ester derivatives. Yao Xue Xue Bao Acta Pharm. Sin. 2004, 39, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Pan, X.D.; Liu, H.Y.; Wei, X.Y.; Yang, L.X. Synthesis and antitumor activity of 20-O-linked nitrogen-based camptothecin ester derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y. Preclinical and clinical studies of NK012, an SN-38-incorporating polymeric micelles, which is designed based on EPR effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Yasunaga, M.; Goto, K.; Nagano, T.; Kuroda, J.-I.; Koga, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Matsumura, Y. The antitumor activity of NK012, an SN-38-incorporating micelle, in combination with bevacizumab against lung cancer xenografts. Cancer 2010, 116, 4597–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, A.; Xiong, X.-B.; Lavasanifar, A. Development of novel polymeric micellar drug conjugates and nano-containers with hydrolyzable core structure for doxorubicin delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.M.; Vakili, M.R.; Lavasanifar, A. Polymeric micelles based on poly(ethylene oxide) and alpha-carbon substituted poly(varepsilon-caprolactone): An in vitro study on the effect of core forming block on polymeric micellar stability, biocompatibility, and immunogenicity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 132, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakala, R.A.; Korhonen, H.; Holappa, S.; Seppälä, J.V. Hydrophobicities of poly(ε-caprolactone) oligomers functionalized with different succinic anhydrides. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shire, Z.; Vakili, M.R.; Morgan, T.D.R.; Hall, D.G.; Lavasanifar, A.; Weinfeld, M. Nanoencapsulation of Novel Inhibitors of PNKP for Selective Sensitization to Ionizing Radiation and Irinotecan and Induction of Synthetic Lethality. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2316–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqr, A.; Vakili, M.R.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lai, R.; Lavasanifar, A. Development of Traceable Rituximab-Modified PEO-Polyester Micelles by Postinsertion of PEG-phospholipids for Targeting of B-cell Lymphoma. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18867–18879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Lu, W. Total Synthesis of Camptothecin and SN-38. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 77, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Liu, Y.; Piao, H.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Tang, B.; Zou, M. Comparison of two self-assembled macromolecular prodrug micelles with different conjugate positions of SN38 for enhancing antitumor activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, H.M.; Lavasanifar, A. Polymeric micelles for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Harpe, K.M.; Kondiah, P.P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Marimuthu, T.; Du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. The Hemocompatibility of Nanoparticles: A Review of Cell–Nanoparticle Interactions and Hemostasis. Cells 2019, 8, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.S.; Vijayalakshmi, N.; Swaan, P.W.; Ghandehari, H. G3.5 PAMAM dendrimers enhance transepithelial transport of SN38 while minimizing gastrointestinal toxicity. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimnejad, P.; Dinarvand, R.; Jafari, M.R.; Tabasi, S.A.S.; Atyabi, F. Characterization, blood profile and biodistribution properties of surface modified PLGA nanoparticles of SN-38. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 406, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimnejad, P.; Dinarvand, R.; Sajadi, S.A.; Atyabi, F.; Ramezani, F.; Jaafari, M.R. Preparation and characterization of poly lactide-co-glycolide nanoparticles of SN-38. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2010, 63, 512–520. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimnejad, P.; Dinarvand, R.; Sajadi, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Nomani, A.R.; Azizi, E.; Rad-Malekshahi, M.; Atyabi, F. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of actively targetable nanoparticles for SN-38 delivery against HT-29 cell lines. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Tsuji, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takeda, K.; Uetake, H.; Esaki, T.; Amagai, K.; Sakai, D.; Baba, H.; Kimura, M.; et al. A phase II study of NK012, a polymeric micelle formulation of SN-38, in unresectable, metastatic or recurrent colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.C.; Chan, D.P.; Shoichet, M.S. Polymeric micelle stability. Nano Today 2012, 7, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, G.; Dufresne, M.-H.; Sant, V.P.; Kang, N.; Maysinger, D.; Leroux, J.-C. Block copolymer micelles: Preparation, characterization and application in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 109, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Guo, S.; Lu, C. Degradation behaviors of monomethoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(ɛ-caprolactone) nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Ge, H.; Jiang, X.; Yang, C. Degradation behavior of poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) micelles in aqueous solution. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boice, A.; Bouchier-Hayes, L. Targeting apoptotic caspases in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Serafini, S.; Pierigè, F.; Antonelli, A.; Cerasi, A.; Fraternale, A.; Chiarantini, L.; Magnani, M. Erythrocyte-based drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lai, W.; Cui, M.; Liang, L.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. An Evaluation of Blood Compatibility of Silver Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.N.Q.; Fukushima, E.O.; Muranaka, T. Structure and hemolytic activity relationships of triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 71, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falamarzian, A.; Lavasanifar, A. Chemical Modification of Hydrophobic Block in Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Poly(Caprolactone) Based Nanocarriers: Effect on the Solubilization and Hemolytic Activity of Amphotericin B. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

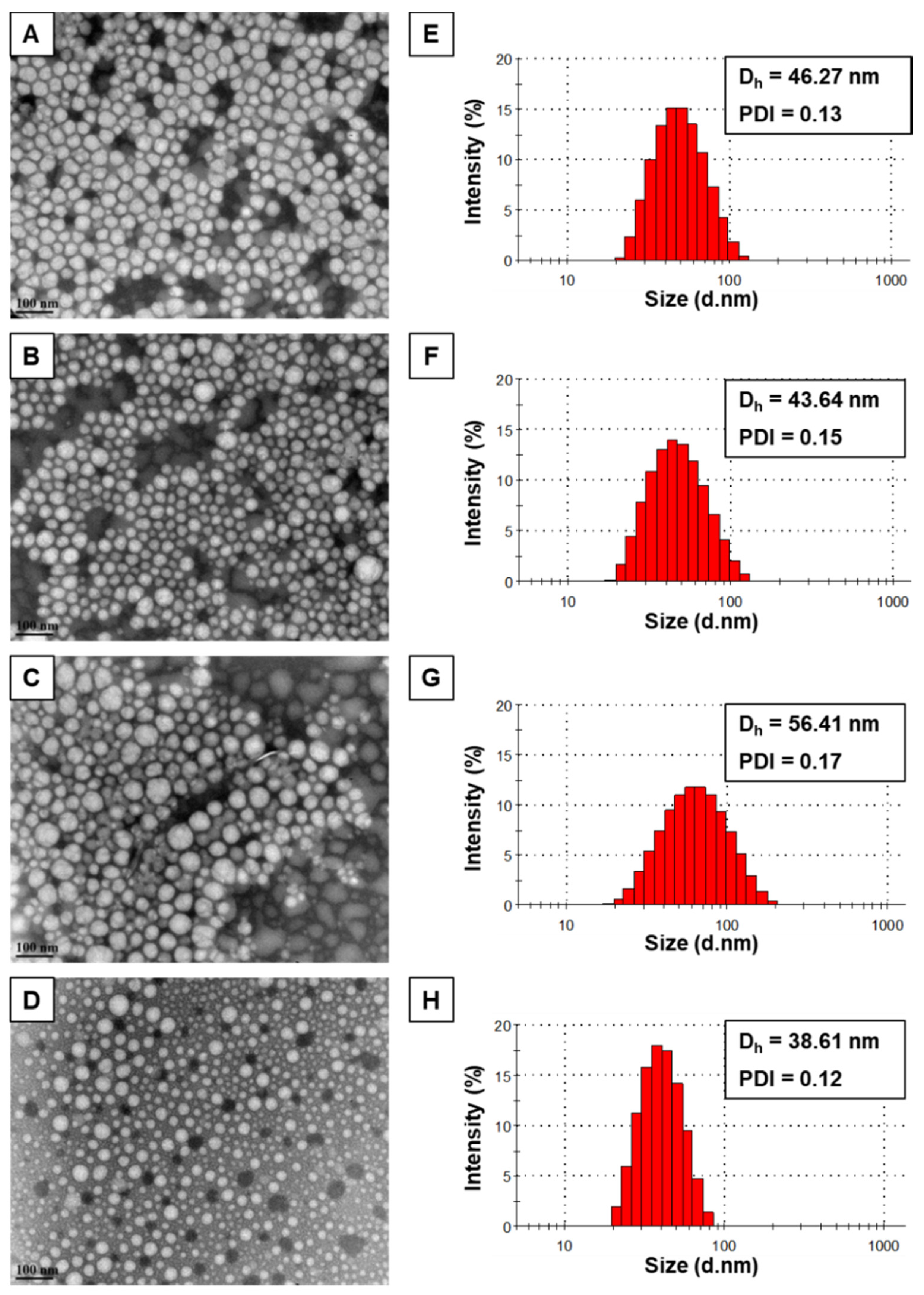



| Micellar Formulations a | Size b ± SD (nm) | PDI c ± SD | Zeta Potential d ± SD (mV) | CMC e ± SD (µg·mL−1) | SN-38 Loading f (% w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mPEO114-b-PBCL12 | 46.25 ± 0.11 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 4.43 ± 0.21 | - |
| mPEO114-b-PBCL12/SN-38 | 43.60 ± 0.14 g | 0.13 ± 0.01 | −1.14 ± 0.23 g | 3.88 ± 0.11 g | 11.47 ± 0.10 |
| mPEO114-b-PCCL20 | 56.76 ± 0.41 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 69.92 ± 0.82 | - |
| mPEO114-b-PCCL20/SN-38 | 38.47 ± 0.34 g | 0.11 ± 0.02 | −1.69 ± 0.18 g | 54.57 ± 0.12 g | 12.03 ± 0.17 |
| Formulations | Difference Factor (f1) | Similarity Factor (f2) |
|---|---|---|
| Free SN-38 and mPEO114-b-PBCL12 | 75.01 | 8.73 |
| Free SN-38 and mPEO114-b-PCCL20/SN-38 | 68.27 | 10.65 |
| mPEO114-b-PBCL12/SN-38 and mPEO114-b-PCCL20/SN-38 | 26.95 | 56.97 |
| Cells | Time (h) | SN-38 (µM) | Irinotecan (µM) | mPEO-b-PBCL/SN-38 (µM) | mPEO-b-PCCL/SN-38 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT116 | 24 | 0.092–0.145 | 4.135–12.550 | 0.696–1.262 | 0.189–0.425 |
| 48 | 0.039–0.065 | 3.367–6.409 | 0.711–1.308 | 0.032–0.067 | |
| 72 | 0.007–0.009 | 5.387–8.941 | 0.084–0.148 | 0.027–0.059 | |
| HT-29 | 24 | 0.296–0.496 | 8.622–31.060 | 0.742–2.069 | 0.601–0.963 |
| 48 | 0.038–0.056 | 14.120–27.760 | 0.337–0.662 | 0.0986–0.195 | |
| 72 | 0.001–0.003 | 8.847–14.560 | 0.294–0.526 | 0.062–0.115 | |
| SW620 | 24 | 0.016–0.028 | 10.470–52.080 | 1.039–4.041 | 0.920–1.300 |
| 48 | 0.012–0.018 | 8.532–18.220 | 0.171–0.303 | 0.038–0.059 | |
| 72 | 0.002–0.003 | 4.537–9.680 | 0.0792–0.136 | 0.018–0.028 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadat, S.M.A.; Vakili, M.R.; Paiva, I.M.; Weinfeld, M.; Lavasanifar, A. Development of Self-Associating SN-38-Conjugated Poly(ethylene oxide)-Poly(ester) Micelles for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111033
Sadat SMA, Vakili MR, Paiva IM, Weinfeld M, Lavasanifar A. Development of Self-Associating SN-38-Conjugated Poly(ethylene oxide)-Poly(ester) Micelles for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(11):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111033
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadat, Sams M. A., Mohammad Reza Vakili, Igor M. Paiva, Michael Weinfeld, and Afsaneh Lavasanifar. 2020. "Development of Self-Associating SN-38-Conjugated Poly(ethylene oxide)-Poly(ester) Micelles for Colorectal Cancer Therapy" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 11: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111033
APA StyleSadat, S. M. A., Vakili, M. R., Paiva, I. M., Weinfeld, M., & Lavasanifar, A. (2020). Development of Self-Associating SN-38-Conjugated Poly(ethylene oxide)-Poly(ester) Micelles for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 12(11), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111033