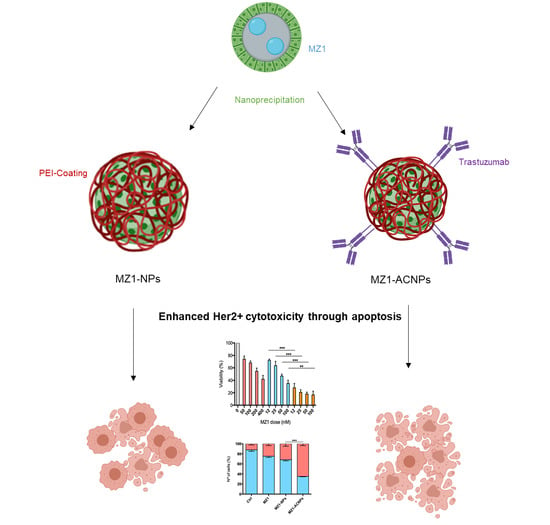
Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Preparation of Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.4. In Vitro Assays
3. Results
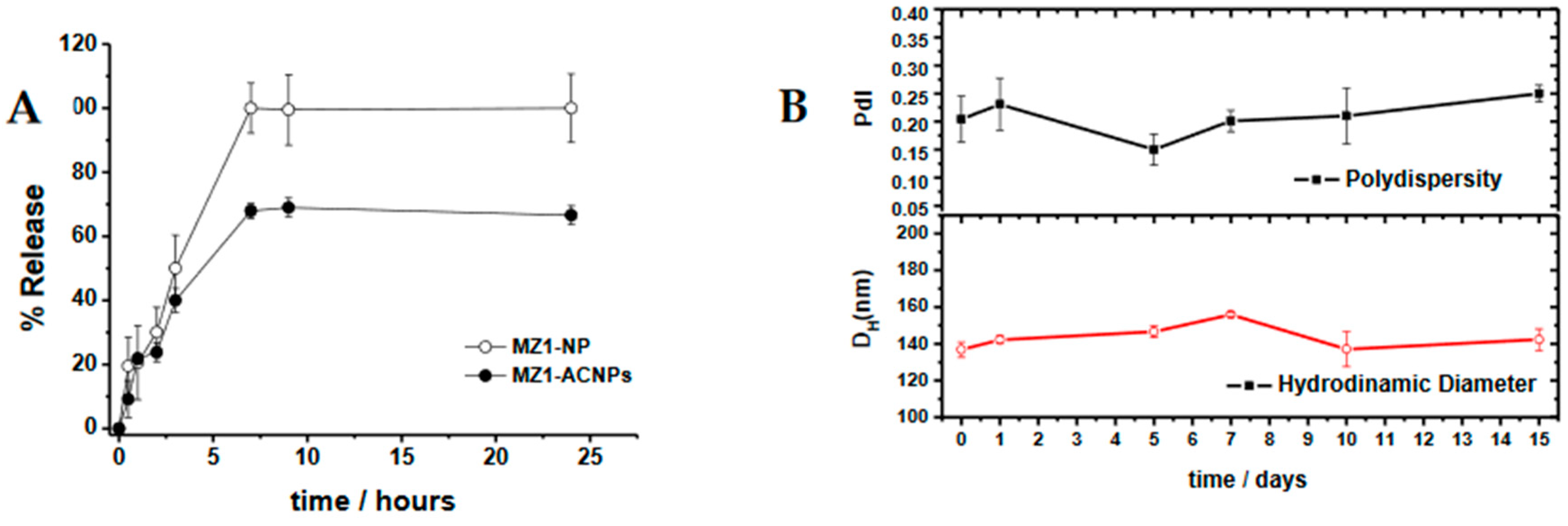
3.1. MZ1-Loaded Trastuzumbab Conjugated NPs (MZ1-ACNPs)
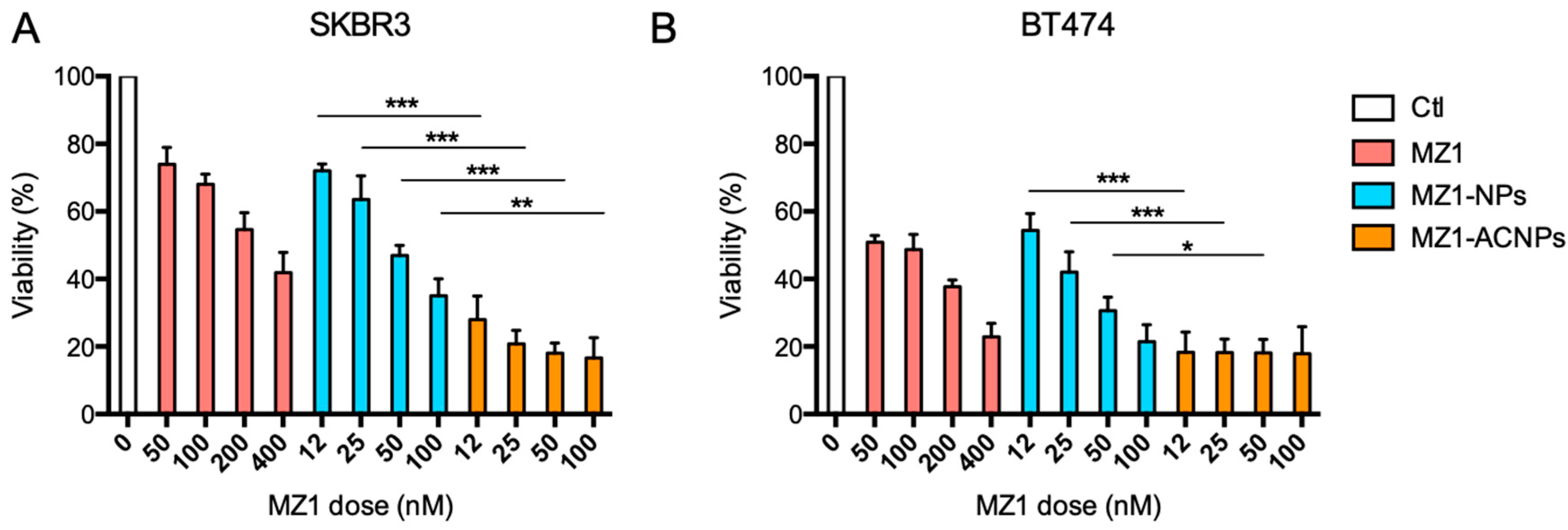
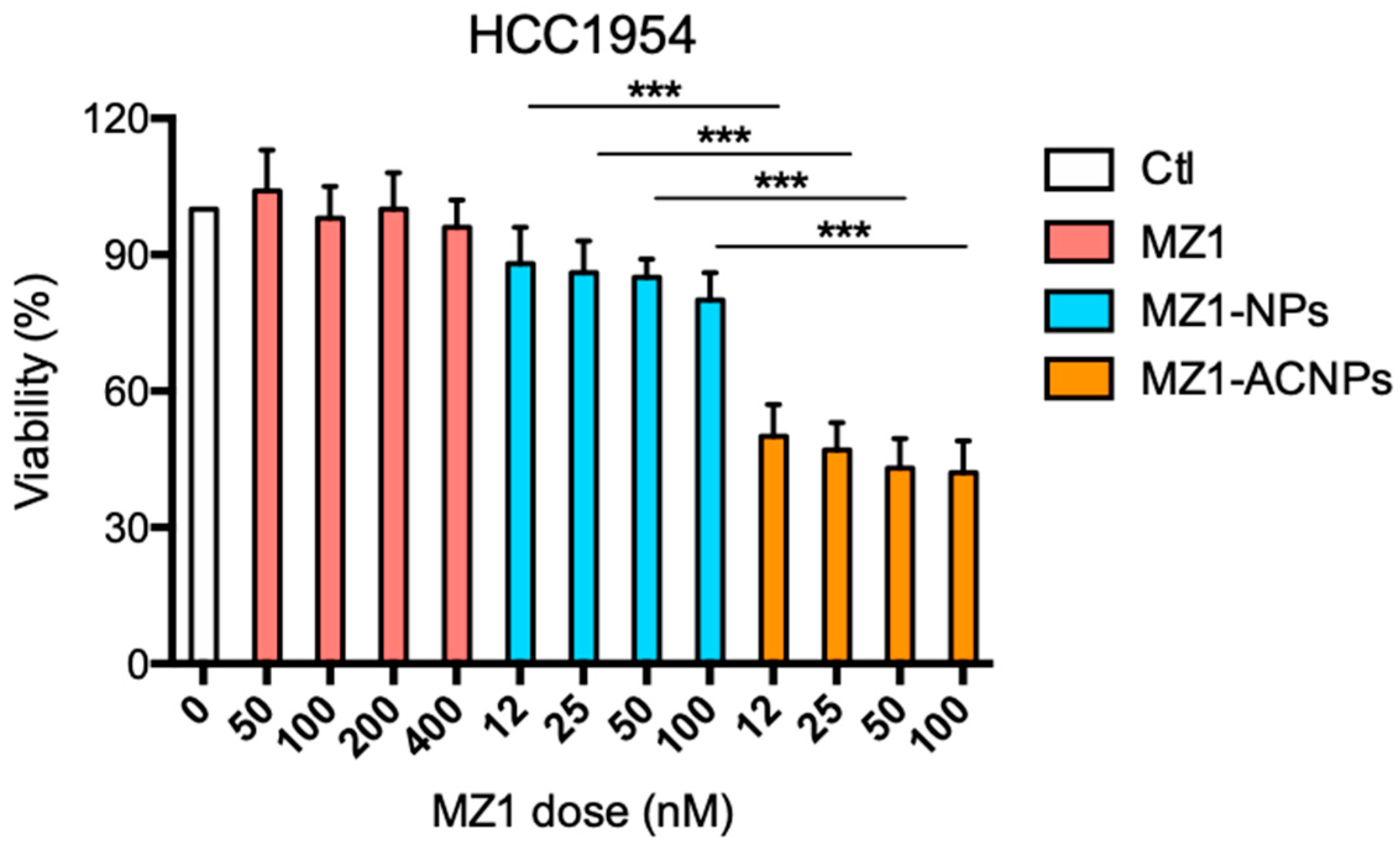
3.2. Cytotoxic Effect
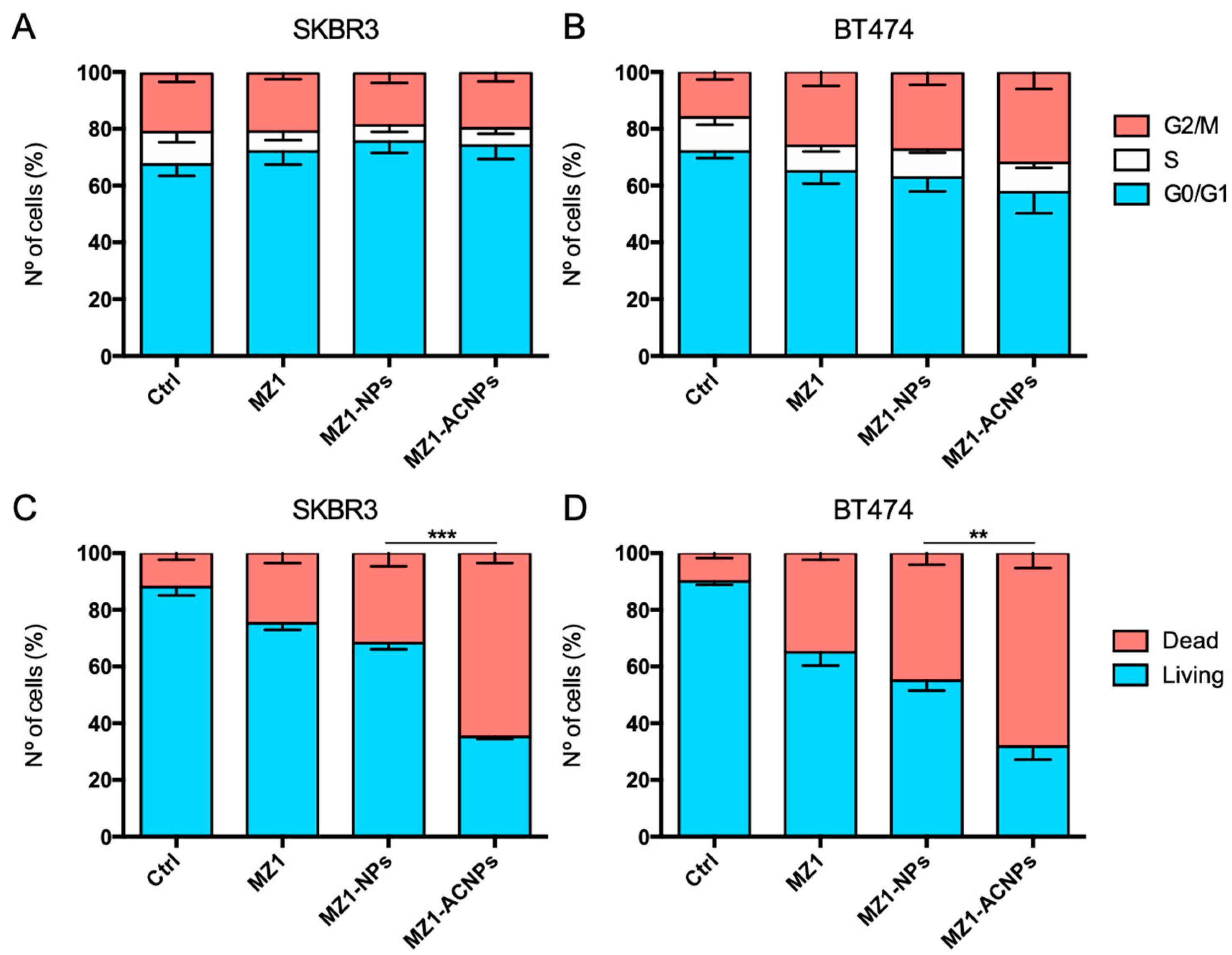
3.3. Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
3.4. Cytotoxic Effect in HER2+, MZ1-Resistant Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chau, C.H.; Steeg, P.S.; Figg, W.D. Antibody–drug conjugates for cancer. Lancet 2019, 394, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, S.; Williams, M.; Kebble, B.; Dixit, R.; Tseng, L.; Yao, N.-S.; Tice, D.A.; Soria, J.-C. Antibody-drug conjugates: Future Directions in clinical and translational strategies to improve the therapeutic index. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5441–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska-Washer, A.; Robak, T. Safety and Tolerability of Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Cancer. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Maruvka, Y.E.; Michor, F.; Pao, W. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor–resistant disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protacs: Chimeric Molecules That Target Proteins to the Skp1–Cullin–F Box Complex for Ubiquitination and Degradation PNAS. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/content/98/15/8554 (accessed on 3 June 2020).
- Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Wei, W. PROTACs: A novel strategy for cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, M.; Crews, C.M. PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs)—Past, present and future. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2019, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, J.J.; Neklesa, T.K. Targeting nuclear receptors with PROTAC degraders. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 493, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanover, A. The unravelling of the ubiquitin system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neklesa, T.; Snyder, L.B.; Willard, R.R.; Vitale, N.; Raina, K.; Pizzano, J.; Gordon, D.; Bookbinder, M.; Macaluso, J.; Dong, H.; et al. Abstract 5236: ARV-110: An androgen receptor PROTAC degrader for prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5236. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, J.J.; Qian, Y.; Gough, S.M.; Andreoli, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Cadelina, G.; Bradley, J.; Rousseau, E.; Willard, R.; Pizzano, J.; et al. Abstract P5-04-18: ARV-471, an Oral Estrogen Receptor PROTAC Degrader for Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Rao, Y. PROTACs as potential therapeutic agents for cancer drug resistance. Biochemistry 2019, 59, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Miao, B.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Hayes, D.F.; Chinnaswamy, K.; et al. Discovery of ERD-308 as a highly potent proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) degrader of estrogen receptor (ER). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1420–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, K.; Lu, J.; Qian, Y.; Altieri, M.; Gordon, D.; Rossi, A.M.K.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Dong, H.; Siu, K.; et al. PROTAC-induced BET protein degradation as a therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7124–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, G.E.; Buckley, D.L.; Paulk, J.; Roberts, J.M.; Souza, A.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Bradner, J.E. Phthalimide conjugation as a strategy for in vivo target protein degradation. Science 2015, 348, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, A.; Gollavilli, P.N.; Wang, S.; Asangani, I.A. Resistance to BET Inhibitor leads to alternative therapeutic vulnerabilities in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, P.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.; et al. Discovery of novel small molecule induced selective degradation of the bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) Bromodomain protein BRD4 and BRD2 with cellular potencies. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, M.S.; Testa, A.; Lucas, X.; Chan, K.H.; Chen, W.; Lamont, D.J.; Zengerle, M.; Ciulli, A. Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, R.P.; Deangelo, S.L.; Buckley, D.; He, Z.; Donovan, K.A.; An, J.; Safaee, N.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Ponthier, C.M.; Ishoey, M.; et al. Plasticity in binding confers selectivity in ligand-induced protein degradation article. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Fiskus, W.; Qian, Y.; Rajapakshe, K.; Raina, K.; Coleman, K.G.; Crew, A.P.; Shen, A.; Saenz, D.T.; Mill, C.P.; et al. BET protein proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) exerts potent lethal activity against mantle cell lymphoma cells. Leukemia 2018, 32, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblejas-López, M.D.M.; Nieto-Jimenez, C.; Burgos, M.; Gómez-Juárez, M.; Montero, J.C.; Esparís-Ogando, A.; Pandiella, A.; Galán-Moya, E.M.; Ocaña, A. Activity of BET-Proteolysis targeting chimeric (PROTAC) Compounds in triple negative breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, M.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Tong, Y.; Rao, Y. PROTACs: Great opportunities for academia and industry. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Sun, X.; Rao, Y. PROTAC technology: Opportunities and challenges. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.A.; Fawell, S.; Floc’h, N.; Flemington, V.; McKerrecher, D.; Smith, P.D. Challenges and opportunities in cancer drug resistance. Chem. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, F.; Yang, F.; Jiang, X.; Sun, H.; Feng, F.; Xue, J.; Liu, W. Targeted degradation of anaplastic lymphoma kinase by gold nanoparticle-based multi-headed proteolysis targeting chimeras. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, F.; Scott, C.J. Antibody-targeted nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Immunotherapy 2011, 3, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, M.C.; Scott, C.J. Antibody Conjugated nanoparticles as a novel form of antibody drug conjugate chemotherapy. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2018, 30, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, A.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Fajardo, M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Otero, A.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; López-Solera, I.; Rodríguez, A.M. Hybrid scorpionate/cyclopentadienyl magnesium and zinc complexes: Synthesis, coordination chemistry, and ring-opening polymerization studies on cyclic esters. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 2859–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Moreno, C.; Garcés, A.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Fajardo, M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Otero, A.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Antiñolo, A.; Broomfield, L.; López-Solera, M.I.; et al. Discrete heteroscorpionate lithium and zinc alkyl complexes. synthesis, structural studies, and ROP of cyclic esters. Organometallics 2008, 27, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niza, E.; Noblejas-López, M.D.M.; Bravo, I.; Nieto-Jiménez, C.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Canales-Vázquez, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Galán Moya, E.M.; Burgos, M.; Ocaña, A.; et al. Trastuzumab-Targeted biodegradable nanoparticles for enhanced delivery of dasatinib in HER2+ metastasic breast cancer. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: Mechanisms of controlling drug release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambertini, M.; Vaz-Luis, I. Is HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer still an incurable disease? Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, C.; Hughes, S.J.; Testa, A.; Chen, W.; Lamont, D.J.; Rocha, S.; Alessi, D.R.; Romeo, R.; Ciulli, A. Homo-PROTACs: Bivalent small-molecule dimerizers of the VHL E3 ubiquitin ligase to induce self-degradation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Fu, L. Small-molecule PROTACs: An emerging and promising approach for the development of targeted therapy drugs. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, D.; Shi, C.; Ma, X.; Rong, G.; Kang, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, B. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as the delivery carrier for drug. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| NPs-Formulation | Average Size (nm) | PdI | Z-Potencial (mV) | EE 1 (%) | LE 2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZ1-NPs | 124.9 ± 3.3 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | +46.3 ± 0.9 | 55.7 | 6.3 |
| MZ1-ACNPs | 114 ± 2.3 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | +31.8 ± 0.5 | 13.9 | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cimas, F.J.; Niza, E.; Juan, A.; Noblejas-López, M.d.M.; Bravo, I.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Ocaña, A. Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986
Cimas FJ, Niza E, Juan A, Noblejas-López MdM, Bravo I, Lara-Sanchez A, Alonso-Moreno C, Ocaña A. Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(10):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986
Chicago/Turabian StyleCimas, Francisco J., Enrique Niza, Alberto Juan, María del Mar Noblejas-López, Iván Bravo, Agustín Lara-Sanchez, Carlos Alonso-Moreno, and Alberto Ocaña. 2020. "Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 10: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986
APA StyleCimas, F. J., Niza, E., Juan, A., Noblejas-López, M. d. M., Bravo, I., Lara-Sanchez, A., Alonso-Moreno, C., & Ocaña, A. (2020). Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 12(10), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986