Beyond the Barrier: Targeted Radionuclide Therapy in Brain Tumors and Metastases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Problem of the Brain
3. Matching the Vehicle to the Emitter
4. Clinical Applications
4.1. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy
4.1.1. Somatostatin Receptors
4.1.2. Neurokinin Type-1 Receptor
4.1.3. Prostate Membrane Antigen
4.2. Radioimmunotherapy
4.2.1. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
4.2.2. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Variant III
4.2.3. DNA-Histone H1 Complex
4.2.4. Tenascin
4.2.5. Fibronectin
5. Preclinical Validation
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Vecchione-Koval, T.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, v1–v88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M.; et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A “state of the science” review. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, L.J.; Rutten, J.; Huveneers, H.A.M.; Twijnstra, A. Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer 2002, 94, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, G.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Farina, P.; Zagonel, V.; Tabouret, E. Systemic treatments for brain metastases from breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma and renal cell carcinoma: An overview of the literature. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu-Emerson, C.; Eichler, A.F. Brain Metastases. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2012, 18, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, M.N.; Lloyd, N.; Wong, R.K.S.; Chow, E.; Rakovitch, E.; Laperriere, N.; Xu, W.; Sahgal, A. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD003869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanderup, K.; Menard, C.; Polgar, C.; Lindegaard, J.C.; Kirisits, C.; Potter, R. Advancements in brachytherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 109, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, A.; Khan, R.; Ghosh, M.K. Blood brain barrier: A challenge for effectual therapy of brain tumors. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 320941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newlands, E.S.; Stevenst, M.F.G.; Wedge, S.R.; Wheelhouse, R.T.; Brock, C. Temozolomide: A review of its discovery, chemical properties, pre-clinical development and clinical trials. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1997, 23, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecci, P.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Whitesides, J.F.; Xie, W.; Friedman, A.H.; Archer, G.E.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Bigner, D.D.; Dranoff, G.; Sampson, J.H. Increased regulatory T-cell fraction amidst a diminished CD4 compartment explains cellular immune defects in patients with malignant glioma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3294–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Andaloussi, A.; Lesniak, M.S. An increase in CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of human glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro Oncol. 2006, 8, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woroniecka, K.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Rhodin, K.; Kemeny, H.; Dechant, C.; Farber, S.H.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Cui, X.; Koyama, S.; Jackson, C.; et al. T-Cell Exhaustion Signatures Vary with Tumor Type and Are Severe in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4175–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn-Pirio, A.M.; Vlahovic, G. Immunotherapy approaches in the treatment of malignant brain tumors. Cancer 2017, 123, 734–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabraji, S.; Ni, J.; Lin, N.U.; Xie, S.; Winer, E.P.; Zhao, J.J. Drug Resistance in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Brain Metastases: Blame the Barrier or the Brain? Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.N.; Bhatt, R.; Rotow, J.; Rohrberg, J.; Olivas, V.; Wang, V.E.; Hemmati, G.; Martins, M.M.; Maynard, A.; Kuhn, J.; et al. Aurora kinase A drives the evolution of resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.G.; Shih, J.Y. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.K.; Su, Y.; Bidlingmaier, S.; Liu, B. Manipulation of cell-type selective antibody internalization by a guide-effector bispecific design. Mol. Cancer 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudacher, A.H.; Bezak, E.; Borysenko, A.; Brown, M.P. Targeted alpha-therapy using 227Th-APOMAB and cross-fire antitumour effects: Preliminary in-vivo evaluation. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2014, 35, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNardo, G.L. Concepts in radioimmunotherapy and immunotherapy: Radioimmunotherapy from a Lym-1 perspective. In Seminars in Oncology; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; Volume 32, pp. 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekempeneer, Y.; Keyaerts, M.; Krasniqi, A.; Puttemans, J.; Muyldermans, S.; Lahoutte, T.; D’Huyvetter, M.; Devoogdt, N. Targeted alpha therapy using short-lived alpha-particles and the promise of nanobodies as targeting vehicle. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, A.M.; Li, C.; Pryma, D.A.; Brem, S.; Coukos, G.; Muzykantov, V. Targeted delivery of antibody-based therapeutic and imaging agents to CNS tumors: Crossing the blood-brain barrier divide. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 907–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalutsky, M.R.; Reardon, D.A.; Akabani, G.; Coleman, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Friedman, H.S.; McLendon, R.E.; Wong, T.Z.; Bigner, D.D. Clinical experience with alpha-particle emitting 211At: Treatment of recurrent brain tumor patients with 211At-labeled chimeric antitenascin monoclonal antibody 81C6. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.; Hofer, S.; Eichhorn, K.; Wasner, M.; Zimmerer, S.; Freitag, P.; Probst, A.; Gratzl, O.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, R.; et al. Local injection of the 90Y-labelled peptidic vector DOTATOC to control gliomas of WHO grades II and III: An extended pilot study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casaco, A.; Lopez, G.; Garcia, I.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Fernandez, R.; Figueredo, J.; Torres, L.; Perera, A.; Batista, J.; Leyva, R.; et al. Phase I single-dose study of intracavitary-administered Nimotuzumab labeled with 188 Re in adult recurrent high-grade glioma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, K.; Kawakami, M.; Kioi, M.; Husain, S.R.; Puri, R.K. Distribution kinetics of targeted cytotoxin in glioma by bolus or convection-enhanced delivery in a murine model. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Singh, R.; Souweidane, M.M. Convection-Enhanced Delivery for Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma Treatment. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, R.; Howell, R.W.; Zalutsky, M.R. A model for optimizing delivery of targeted radionuclide therapies into resection cavity margins for the treatment of primary brain cancers. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boockvar, J.A.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Fralin, S.; Kesavabhotla, K.; Seedial, S.M.; Pannullo, S.C.; Schwartz, T.H.; Stieg, P.; et al. Safety and maximum tolerated dose of superselective intraarterial cerebral infusion of bevacizumab after osmotic blood-brain barrier disruption for recurrent malignant glioma. Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, R.A.; Neuwelt, E.A. Outwitting the blood-brain barrier for therapeutic purposes: Osmotic opening and other means. Neurosurgery 1998, 42, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Han, R. The effect of mannitol on intraoperative brain relaxation in patients undergoing supratentorial tumor surgery: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2014, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Krailo, M.; Mehta, M.; Warren, K.; Allen, J.; Jakacki, R.; Villablanca, J.G.; Chiba, A.; Reaman, G. A Phase I study of concurrent RMP-7 and carboplatin with radiation therapy for children with newly diagnosed brainstem gliomas. Cancer 2005, 104, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.D.; Lind, M.J.; Ford, J.; Bleehen, N.; Calvert, A.H.; Boddy, A.V. Pharmacokinetics of carboplatin administered in combination with the bradykinin agonist Cereport (RMP-7) for the treatment of brain tumours. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2000, 45, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prados, M.D.; Schold, S.C., Jr.; Fine, H.A.; Jaeckle, K.; Hochberg, F.; Mechtler, L.; Fetell, M.R.; Phuphanich, S.; Feun, L.; Janus, T.J.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of RMP-7 in combination with carboplatin administered intravenously for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2003, 5, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treat, L.H.; McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Zhang, Y.; Tam, K.; Hynynen, K. Targeted delivery of doxorubicin to the rat brain at therapeutic levels using MRI-guided focused ultrasound. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitran, B.; Guler, R.; Roche, F.P.; Lindstrom, E.; Selvaraju, R.K.; Fleetwood, F.; Rinne, S.S.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Tolmachev, V.; Stahl, S.; et al. Radionuclide imaging of VEGFR2 in glioma vasculature using biparatopic affibody conjugate: Proof-of-principle in a murine model. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4462–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Ishikawa, E.; Yamamoto, T.; Hatano, K.; Joraku, A.; Iizumi, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Nishiyama, H.; Matsumura, A. Potential use of prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) for detecting the tumor neovasculature of brain tumors by PET imaging with (89)Zr-Df-IAB2M anti-PSMA minibody. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 138, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razpotnik, R.; Novak, N.; Curin Serbec, V.; Rajcevic, U. Targeting Malignant Brain Tumors with Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.; Valkema, R.; Jamar, F.; Kvols, L.K.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; Breeman, W.A.P.; Krenning, E.P. Somatostatin receptor-targeted radionuclide therapy of tumors: Preclinical and clinical findings. In Seminars in Nuclear Medicine; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; Volume 32, pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkema, R.; Pauwels, S.; Kvols, L.K.; Barone, R.; Jamar, F.; Bakker, W.H.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; Bouterfa, H.; Krenning, E.P. Survival and response after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with [90Y-DOTA0, Tyr3] octreotide in patients with advanced gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. In Seminars in Nuclear Medicine; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; Volume 36, pp. 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cives, M.; Strosberg, J. Radionuclide Therapy for Neuroendocrine Tumors. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heute, D.; Kostron, H.; von Guggenberg, E.; Ingorokva, S.; Gabriel, M.; Dobrozemsky, G.; Stockhammer, G.; Virgolini, I.J. Response of recurrent high-grade glioma to treatment with (90)Y-DOTATOC. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, A.; Hausmann, O.; Wasner, M.; Steiner, P.; Otte, A.; Jermann, E.; Freitag, P.; Reubi, J.C.; Müller-Brand, J.; Gratzl, O.; et al. Locoregional Regulatory Peptide Receptor Targeting with the Diffusible Somatostatin Analogue 90Y-Labeled DOTA0-D-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide (DOTATOC): A Pilot Study in Human Gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Kneifel, S.; Cordier, D.; Good, S.; Ionescu, M.C.; Ghaffari, A.; Hofer, S.; Kretzschmar, M.; Tolnay, M.; Apostolidis, C.; Waser, B.; et al. Local targeting of malignant gliomas by the diffusible peptidic vector 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1-glutaric acid-4,7,10-triacetic acid-substance p. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3843–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, D.; Forrer, F.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Morgenstern, A.; Apostolidis, C.; Good, S.; Muller-Brand, J.; Macke, H.; Reubi, J.C.; Merlo, A. Targeted alpha-radionuclide therapy of functionally critically located gliomas with 213Bi-DOTA-[Thi8,Met(O2)11]-substance P: A pilot trial. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krolicki, L.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Kunikowska, J.; Koziara, H.; Krolicki, B.; Jakucinski, M.; Pawlak, D.; Apostolidis, C.; Mirzadeh, S.; Rola, R.; et al. Safety and efficacy of targeted alpha therapy with (213)Bi-DOTA-substance P in recurrent glioblastoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, D.; Merlo, A. Long-Term Results of Targeted Low-Grade Glioma Treatment with 213Bi-DOTA-[Thi8,Met(O2)11]-Substance P. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, D.; Krolicki, L.; Morgenstern, A.; Merlo, A. Targeted Radiolabeled Compounds in Glioma Therapy. In Seminars in Nuclear Medicine; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; Volume 46, pp. 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolicki, L.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Morgenstern, A.; Kunikowska, J.; Koziara, H.; Królicki, B.; Jakuciński, M.; Pawlak, D.; Apostolidis, C.; Rola, R.; et al. Safety and Therapeutic Efficacy of 225Ac-DOTA-Substance P for Therapy of Brain Tumors. JMIRS 2019, 50, S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dureja, S.; Thakral, P.; Pant, V.; Sen, I. Rare Sites of Metastases in Prostate Cancer Detected on Ga-68 PSMA PET/CT Scan-A Case Series. Indian J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 32, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.S.; Kumar, R.; Tripathi, M.; Das, C.J.; Bal, C. Detection of brain metastasis with 68Ga-labeled PSMA ligand PET/CT: A novel radiotracer for imaging of prostate carcinoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 40, 328–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Ho, B.; Chan, L.; Emmett, L. Asymptomatic Prostate Cancer Brain Metastases on 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, e382–e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Schlenkhoff, C.; Schwarz, B.; Essler, M.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. Combination of 177Lu-PSMA-617 and External Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Cerebral Metastases in Patients With Castration-Resistant Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Rathke, H.; Bronzel, M.; Apostolidis, C.; Weichert, W.; Haberkorn, U.; Giesel, F.L.; Morgenstern, A. Targeted alpha-Therapy of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer with (225)Ac-PSMA-617: Dosimetry Estimate and Empiric Dose Finding. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Rathke, H.; Hohenfellner, M.; Giesel, F.L.; Haberkorn, U.; Morgenstern, A. Targeted alpha-Therapy of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer with (225)Ac-PSMA-617: Swimmer-Plot Analysis Suggests Efficacy Regarding Duration of Tumor Control. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffar, H.; Noohi, M.; Tavangar, S.M.; Saffar, H.; Azimi, S. Expression of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) in Brain Glioma and its Correlation with Tumor Grade. Iran. J. Pathol. 2018, 13, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wernicke, A.G.; Varma, S.; Greenwood, E.A.; Christos, P.J.; Chao, K.S.C.; Liu, H.; Bander, N.H.; Shin, S.J. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in tumor-associated vasculature of breast cancers. APMIS 2014, 122, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macklis, R.M. How and why does radioimmunotherapy work? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, J.; Merdes, A.; Stumm, G.; Albert, F.K.; Forsting, M.; Hynes, N.; Kiessling, M. Amplification of the epidermal-growth-factor-receptor gene correlates with different growth behaviour in human glioblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 56, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, J.; Ren, Z.P.; Wester, K.; Sundberg, A.L.; Heldin, N.E.; Hesselager, G.; Persson, M.; Gedda, L.; Tolmachev, V.; Lundqvist, H.; et al. Planning for intracavitary anti-EGFR radionuclide therapy of gliomas. Literature review and data on EGFR expression. J. Neurooncol. 2006, 77, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emrich, J.G.; Brady, L.W.; Quang, T.S.; Class, R.; Miyamoto, C.; Black, P.; Rodeck, U. Radioiodinated (I-125) monoclonal antibody 425 in the treatment of high grade glioma patients: Ten-year synopsis of a novel treatment. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 25, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Quang, T.S.; Gracely, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Emrich, J.G.; Yaeger, T.E.; Jenrette, J.M.; Cohen, S.C.; Black, P.; Brady, L.W. A Phase II study of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor radioimmunotherapy in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, T.S.; Brady, L.W. Radioimmunotherapy as a novel treatment regimen: 125I-labeled monoclonal antibody 425 in the treatment of high-grade brain gliomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 58, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Aksoy, O.; Zheng, T.; Fan, Q.W.; Weiss, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma: Signaling pathways and targeted therapies. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.K.; Cvrljevic, A.N.; Johns, T.G. The epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII): Where wild things are altered. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5350–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reist, C.J.; Foulon, C.F.; Alston, K.; Bigner, D.D.; Zalutsky, M.R. Astatine-211 labeling of internalizing anti-EGFRvIII monoclonal antibody using N-succinimidyl 5-[211At]astato-3-pyridinecarboxylate. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1999, 26, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohman, L.; Gedda, L.; Hesselager, G.; Larsson, R.; Nister, M.; Stigbrand, T.; Wester, K.; Carlsson, J. A new antibody recognizing the vIII mutation of human epidermal growth factor receptor. Tumour Biol. 2002, 23, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Barth, R.F.; Wu, G.; Kawabata, S.; Sferra, T.J.; Bandyopadhyaya, A.K.; Tjarks, W.; Ferketich, A.K.; Moeschberger, M.L.; Binns, P.J.; et al. Molecular targeting and treatment of EGFRvIII-positive gliomas using boronated monoclonal antibody L8A4. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3792–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.J.; Shapiro, W.R.; Laske, D.W.; Jensen, R.L.; Asher, A.L.; Wessels, B.W.; Carpenter, S.P.; Shan, J.S. Safety and feasibility of convection-enhanced delivery of Cotara for the treatment of malignant glioma: Initial experience in 51 patients. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hdeib, A.; Sloan, A. Targeted radioimmunotherapy: The role of ¹³¹I-chTNT-1/B mAb (Cotara) for treatment of high-grade gliomas. Future Oncol. 2012, 8, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, W.; Carpenter, S.; Roberts, K.; Shan, J. 131I-chTNT-1/B mAb: Tumour necrosis therapy for malignant astrocytic glioma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventimiglia, J.; Wikstrand, C.; Ostrowski, L.; Bourdon, M.; Lightner, V.; Bigner, D. Tenascin expression in human glioma cell lines and normal tissues. J. Neuroimmunol. 1992, 36, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, P.; Arista, A.; Franceschi, G.; Frattarelli, M.; Sturiale, C.; Riva, N.; Casi, M.; Rossitti, R. Local treatment of malignant gliomas by direct infusion of specific monoclonal antibodies labeled with 131I: Comparison of the results obtained in recurrent and newly diagnosed tumors. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 5952–5956. [Google Scholar]
- Reardon, D.A.; Zalutsky, M.R.; Akabani, G.; Coleman, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Herndon, J.E., II; McLendon, R.E.; Pegram, C.N.; Quinn, J.A.; Rich, J.N.; et al. A pilot study: 131I-antitenascin monoclonal antibody 81c6 to deliver a 44-Gy resection cavity boost. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 10, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Akabani, G.; Coleman, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Friedman, H.S.; Herndon, J.E., II; McLendon, R.E.; Pegram, C.N.; Provenzale, J.M.; Quinn, J.A.; et al. Salvage radioimmunotherapy with murine iodine-131-labeled antitenascin monoclonal antibody 81C6 for patients with recurrent primary and metastatic malignant brain tumors: Phase II study results. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.; Akabani, G.; Coleman, R.; Friedman, A.; Friedman, H.; Herndon, J.; Cokgor, I.; McLendon, R.; Pegram, C.; Provenzale, J.; et al. Phase II trial of murine (131)I-labeled antitenascin monoclonal antibody 81C6 administered into surgically created resection cavities of patients with newly diagnosed malignant gliomas. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cokgor, I.; Akabani, G.; Kuan, C.; Friedman, H.; Friedman, A.; Coleman, R.; McLendon, R.; Bigner, S.; Zhao, X.; Garcia-Turner, A.; et al. Phase I trial results of iodine-131-labeled antitenascin monoclonal antibody 81C6 treatment of patients with newly diagnosed malignant gliomas. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3862–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomei, M.; Mazzetta, C.; Handkiewicz-Junak, D.; Bodei, L.; Rocca, P.; Grana, C.; Maira, G.; Sturiale, C.; Villa, G.; Paganelli, G. Combined treatment of glioblastoma patients with locoregional pre-targeted 90Y-biotin radioimmunotherapy and temozolomide. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2004, 48, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebbinghaus, C.; Scheuermann, J.; Neri, D.; Elia, G. Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of recombinant antibodies: Targeting the extra-domain B of fibronectin, a marker of tumor angiogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsi, L.; Balza, E.; Bestagno, M.; Castellani, P.; Carnemolla, B.; Biro, A.; Leprini, A.; Sepulveda, J.; Burrone, O.; Neri, D.; et al. Selective targeting of tumoral vasculature: Comparison of different formats of an antibody (L19) to the ED-B domain of fibronectin. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 102, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, S.; Erba, P.A.; Petrini, M.; Menrad, A.; Giovannoni, L.; Grana, C.; Hirsch, B.; Zardi, L.; Paganelli, G.; Mariani, G.; et al. Expression of the oncofetal ED-B-containing fibronectin isoform in hematologic tumors enables ED-B-targeted 131I-L19SIP radioimmunotherapy in Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Blood 2009, 113, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, P.; Sollini, M.; Boni, R.; Claudio Traino, A.; Giovannoni, L.; Neri, D.; Menssen, H.; Mariani, G. Results of a phase I/II dose-finding and efficacy study of the tumor-targeting 131I-L19SIP human recombinant mini-antibody in patients (pts) with cancer. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1153. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, G.L.; Bianchi, C.; Virotta, G.; Bettini, A.; Moretti, R.; Trachsel, E.; Elia, G.; Giovannoni, L.; Neri, D.; Bruno, A. Radretumab radioimmunotherapy in patients with brain metastasis: A 124I-L19SIP dosimetric PET study. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virotta, G.; Poli, G.L.; Bettini, A.; Bianchi, C.; Giovannoni, L.; Gerali, A.; Quadri, A.; Tondini, C.; Bruno, A. Radioimmunotherapy with 131I-L19SIP (Radretumab) in metastatic solid tumors: Preliminary results. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 498. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesparan, R.; Read, T.A.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Skaftnesmo, K.O.; Bjerkvig, R.; Engebraaten, O. Expression of extracellular matrix components in a highly infiltrative in vivo glioma model. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 105, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, T.; Williams, P.J.; Hiraga, T.; Niewolna, M.; Nishimura, R. A bone-seeking clone exhibits different biological properties from the MDA-MB-231 parental human breast cancer cells and a brain-seeking clone in vivo and in vitro. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2001, 16, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alphandéry, E. Glioblastoma Treatments: An Account of Recent Industrial Developments. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ridgway, L.D.; Wetzel, M.D.; Ngo, J.; Yin, W.; Kumar, D.; Goodman, J.C.; Groves, M.D.; Marchetti, D. The identification and characterization of breast cancer CTCs competent for brain metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 180ra48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boskovitz, A.; McLendon, R.E.; Okamura, T.; Sampson, J.H.; Bigner, D.D.; Zalutsky, M.R. Treatment of HER2-positive breast carcinomatous meningitis with intrathecal administration of alpha-particle-emitting (211)At-labeled trastuzumab. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2009, 36, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Huyvetter, M.; De Vos, J.; Xavier, C.; Pruszynski, M.; Sterckx, Y.G.J.; Massa, S.; Raes, G.; Caveliers, V.; Zalutsky, M.R.; Lahoutte, T.; et al. 131I-labeled Anti-HER2 Camelid sdAb as a Theranostic Tool in Cancer Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6616–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttemans, J.; D’Huyvetter, M.; Windhorst, B.; Lahoutte, T.; Devoogdt, N. CAM-H2 effectively targets and treats HER2 positive brain lesions: A comparative preclinical study with trastuzumab. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyaerts, M.; Xavier, C.; Everaert, H.; Vaneycken, I.; Fontaine, C.; Decoster, L.; Vanhoeij, M.; Caveliers, V.; Lahoutte, T. Phase II trial of HER2-PET/CT using 68Ga-anti-HER2 VHH1 for characterization of HER2 presence in brain metastases of breast cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyaerts, M.; Xavier, C.; Heemskerk, J.; Devoogdt, N.; Everaert, H.; Ackaert, C.; Vanhoeij, M.; Duhoux, F.P.; Gevaert, T.; Simon, P.; et al. Phase I Study of 68Ga-HER2-Nanobody for PET/CT Assessment of HER2 Expression in Breast Carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyaerts, M.; Vos, J.D.; Duhoux, F.P.; Caveliers, V.; Fontaine, C.; Vanhoeij, M.; D’Huyvetter, M.; Everaert, H.; Ghykiere, P.; Devoogdt, N.; et al. Phase I results of CAM-H2: Safety profile and tumor targeting in patients. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofou, S. Radionuclide carriers for targeting of cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: A critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampling, R.; Cruickshank, G.; Lewis, A.D.; Fitzsimmons, S.A.; Workman, P. Direct measurement of pO2 distribution and bioreductive enzymes in human malignant brain tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 29, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behling, K.; Maguire, W.F.; López Puebla, J.C.; Sprinkle, S.R.; Ruggiero, A.; O’Donoghue, J.; Gutin, P.H.; Scheinberg, D.A.; McDevitt, M.R. Vascular Targeted Radioimmunotherapy for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behling, K.; Maguire, W.F.; Di Gialleonardo, V.; Heeb, L.E.; Hassan, I.F.; Veach, D.R.; Keshari, K.R.; Gutin, P.H.; Scheinberg, D.A.; McDevitt, M.R. Remodeling the Vascular Microenvironment of Glioblastoma with α-Particles. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Sharma, R.; Khaket, T.P.; Dutta, C.; Chakraborty, B.; Mukherjee, T.K. Breast cancer metastasis: Putative therapeutic role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Cell. Oncol. 2017, 40, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, N.; Ackerman, N.L.; Rosales, L.F.; Bernal, M.A.; Liu, X.; Peeters, S.G.; Soto, M.S.; Corroyer-Dulmont, A.; Bernaudin, M.; Grimoin, E.; et al. Dosimetric evaluation of radionuclides for VCAM-1-targeted radionuclide therapy of early brain metastases. Theranostics 2018, 8, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corada, M.; Zanetta, L.; Orsenigo, F.; Breviario, F.; Lampugnani, M.G.; Bernasconi, S.; Liao, F.; Hicklin, D.J.; Bohlen, P.; Dejana, E. A monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial–cadherin inhibits tumor angiogenesis without side effects on endothelial permeability. Blood 2002, 100, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, Y.; O’Connor, M.J.; de Bono, J. Laying a trap to kill cancer cells: PARP inhibitors and their mechanisms of action. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 362ps17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannetti, S.A.; Carlucci, G.; Carney, B.; Kossatz, S.; Shenker, L.; Carter, L.M.; Salinas, B.; Brand, C.; Sadique, A.; Donabedian, P.L.; et al. PARP-1-Targeted Radiotherapy in Mouse Models of Glioblastoma. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perik, P.J.; Lub-De Hooge, M.N.; Gietema, J.A.; van der Graaf, W.T.; de Korte, M.A.; Jonkman, S.; Kosterink, J.G.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Sleijfer, D.T.; Jager, P.L.; et al. Indium-111-labeled trastuzumab scintigraphy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Suryadevara, C.M.; Batich, K.A.; Farber, S.H.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Sampson, J.H. Emerging immunotherapies for glioblastoma. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2016, 21, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Radionuclide | Abbreviation | Emission | Half-Life | Energymax (keV) | Travel Distance | Characteristics of Radiation Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinium-225 | 225Ac | Alpha/beta−/gamma | 9.92 days | 7.069 | 50–100 μm | + Short range, high energy |
| Astatine-211 | 211At | Alpha | 7.20 h | 5.867 | 50–100 μm | + Double stranded DNA breakage |
| Bismuth-213 | 213Bi | Alpha/gamma | 46 min | 6.051 | 50–100 μm | + Oxygen independent |
| Lead-212 | 212Pb | Alpha/beta−/gamma | 10.64 h | 8.785 | 50–100 μm | − No crossfire |
| Iodine-131 | 131I | Beta−/gamma | 8.02 days | 606 | 200 µm–1 mm | + Crossfire effect |
| Lutetium-177 | 177Lu | Beta−/gamma | 6.68 days | 498 | 230 µm | − Oxygen dependent |
| Rhenium-188 | 188Re | Beta−/gamma | 16.98 h | 2.110 | 11 mm | − Long range, low energy |
| Yttrium-90 | 90Y | Beta− | 2.67 days | 2.280 | 12 mm | − Single stranded DNA breakage |
| Indium-111 | 111In | Auger/gamma | 2.8 days | 245 | 4 nm | + Very short range |
| Iodine-125 | 125I | Auger/gamma | 59.49 days | 35 | 2 nm | − Necessary to be internalized |
| Disease | Target | Compound | Administration Route | Testing Phase | Results | Reference/Clinical Trial Identifier: |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
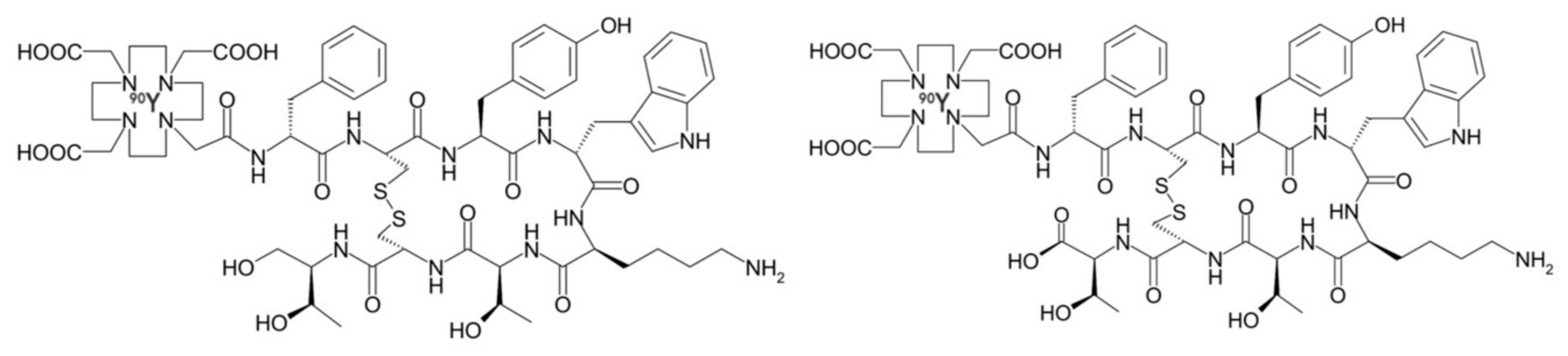
| Neuroblastoma, meningioma, glioma, GBM | Somatostatin receptors | [90Y]-DOTATOC | Directly injected or via subcutaneous reservoir system into resection cavity | Phase I/II | + Partial or complete remission. − Well tolerated, with minimal neurological toxicity. | [23,38,39,40,41,42] NCT03273712, NCT00006368, NCT02441088, NCT00006368 |
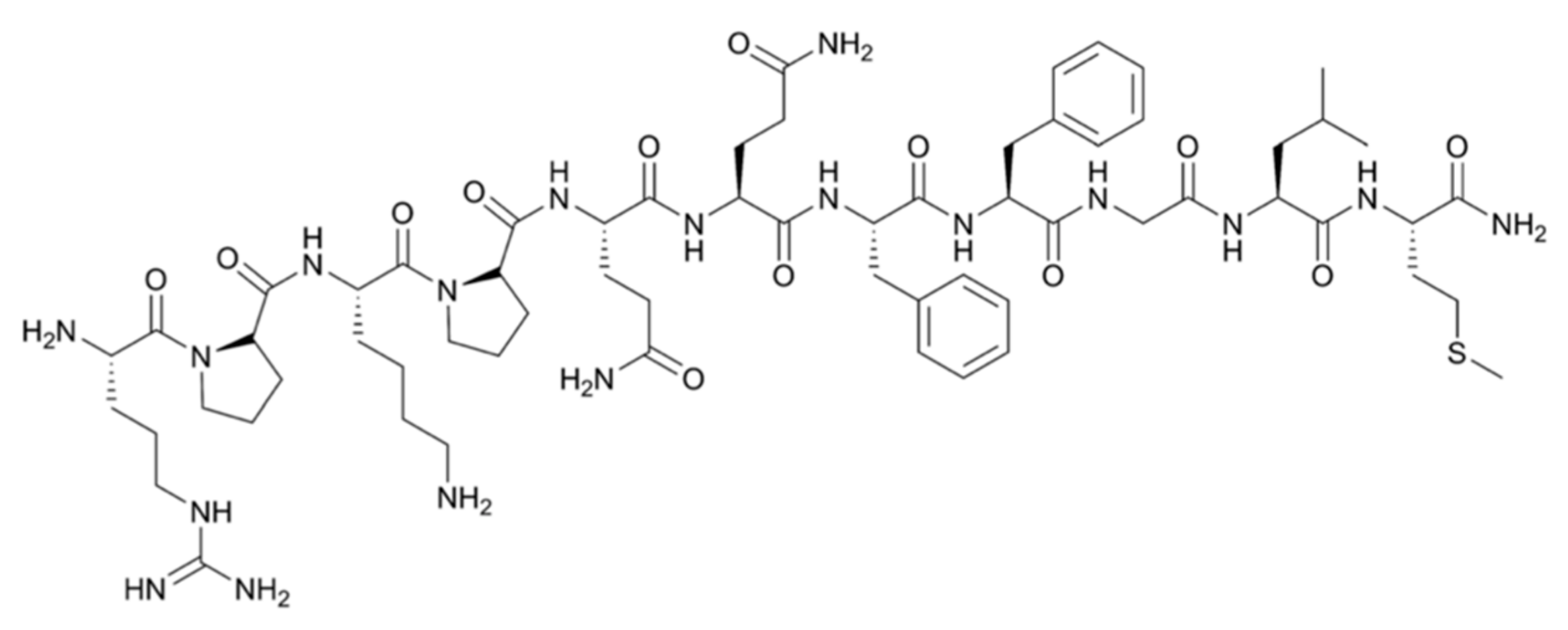
| Grade II–IV gliomas | Neurokinin type-1 receptor | [90Y]-DOTAGA-Substance P | Intratumorally via trans-cerebellar catheter | Phase I | + Disease stabilization and/or improved neurologic status. − No significant local or systemic toxicity | [43] |
| [225Ac]-DOTA-Substance P | Intratumorally or into the post-surgical cavity | Phase I/II | + OS prolongation up to 32 months − Well tolerated, with mild, transient edema, aphasia or epileptic seizures. | [48] | ||
| [213Bi]-DOTA-Substance P | Trans-cerebellar catheter | Phase I/II | + Partial or complete remission. Disease stabilization and/or improved neurologic status. − No significant local or systemic toxicity | [43,44,45,46,47] | ||
| Grade II–IV gliomas, anaplastic astrocytoma | Epidermal growth factor receptor (mutant variant III) | [125I]-mAb 425 | Intravenous | Phase II | + Median survival benefit of 20.4 months − Mild skin irritation at injection site | [60,61,62] |
| [188Re]-labeled Nimotuzumab | Directly injected into resection cavity | Phase I | + 1/11 partial response, 2/11 complete response after 3 years. − Dose-dependent neurotoxicity was observed in some patients | [24] | ||
| Grade II–IV gliomas, anaplastic astrocytoma | DNA-histone H1 complex | [131I]-chTNT-1/B MAb | Intratumorally via convection-enhanced delivery | Phase I/II | + Clinical efficacy not definitively established due to low patient number. Median survival time was noted as 37.9. weeks for subset of patients. − Edema, hemiparesis and headache | [68,69,70] NCT00677716, NCT00509301, NCT00128635, NCT00004017 |
| Grade I–IV gliomas | Tenascin | [131I]-BC-2 mAb or [131I]-BC-4 mAb | Intratumorally | Phase I/II | + Partial or complete remission. Response rate of 40% − No systemic or cerebral adverse effects, HAMA response did not affect tumor-targeting | [72] |
| 3-step pretargeting strategy with biotin-coupled BC-4 + Avidin + [90Y]-Biotin | Trans-cerebellar catheter | Phase I/II | + Disease stabilization in 75% of patients. OS prolonged to 17.5 and 25 months with TRNT alone or TRNT+TMZ resp. − Transient hematological toxicity, mild allergic reaction | [77] | ||
| [131I]- or [211At]-labeled 81C6 mAb | Directly injected into resection cavity | Phase I/II | + Median survivals of up to 22 months − Reversible hematologic and neurologic events. No adverse effects related to HAMA response | [22,73,74,75,76] NCT00003461, NCT00003484, NCT00002752, NCT00003478, NCT00002753 | ||
| Brain metastasis from breast carcinoma and NSCLC | Fibronectin | [131I]-L19SIP | Intravenous | Phase I/II | + Intra- and extracranial lesions showed reduced [18F]-FDG-uptake during 6-month follow-up − No adverse events reported | [81,82,83] NCT01125085 |
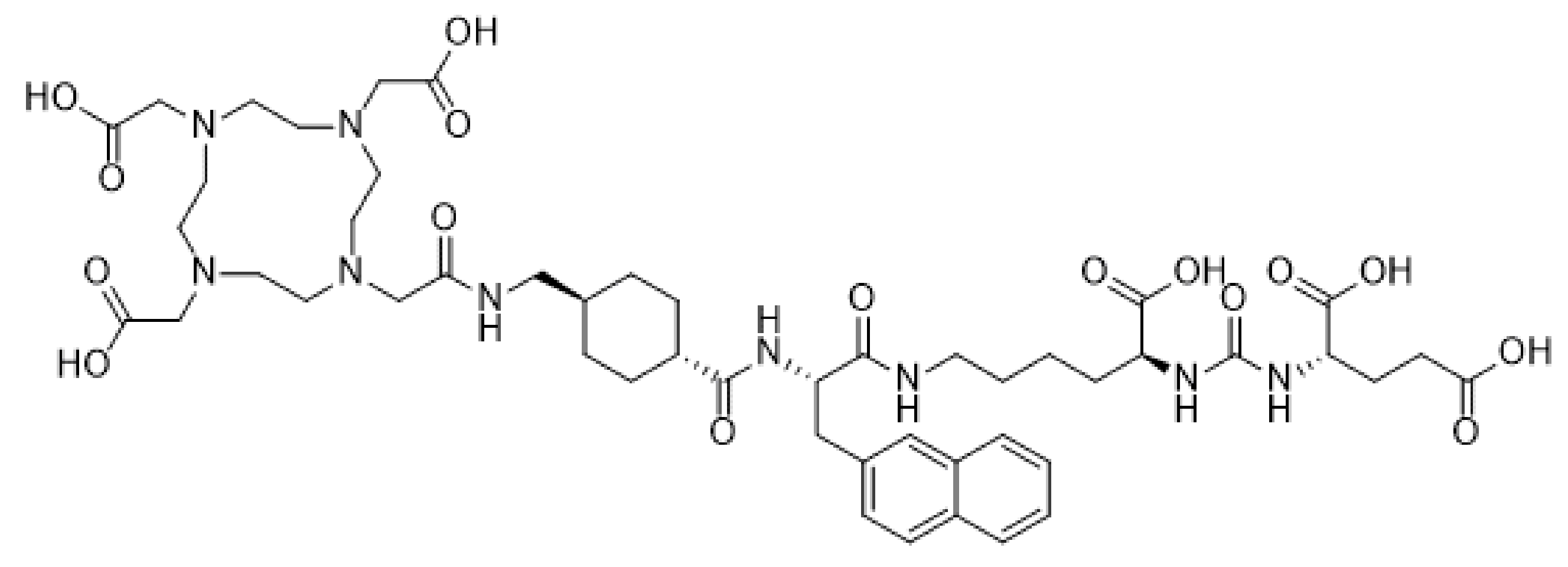
| Brain metastasis from prostate cancer | Prostate membrane antigen | [177Lu]-PSMA-617 | Intravenous | Phase I | + Significant decrease in size and PSMA expression − Minimal toxicity to salivary glands | [52] NCT03511664 |
| [225Ac]-PSMA-617 | Intravenous | Phase I/II | + More potent effect than [177Lu]-PSMA-617 − Severe xerostomia | [53,54] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puttemans, J.; Lahoutte, T.; D’Huyvetter, M.; Devoogdt, N. Beyond the Barrier: Targeted Radionuclide Therapy in Brain Tumors and Metastases. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080376
Puttemans J, Lahoutte T, D’Huyvetter M, Devoogdt N. Beyond the Barrier: Targeted Radionuclide Therapy in Brain Tumors and Metastases. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(8):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080376
Chicago/Turabian StylePuttemans, Janik, Tony Lahoutte, Matthias D’Huyvetter, and Nick Devoogdt. 2019. "Beyond the Barrier: Targeted Radionuclide Therapy in Brain Tumors and Metastases" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 8: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080376
APA StylePuttemans, J., Lahoutte, T., D’Huyvetter, M., & Devoogdt, N. (2019). Beyond the Barrier: Targeted Radionuclide Therapy in Brain Tumors and Metastases. Pharmaceutics, 11(8), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080376






