Application of Pharmacometrics in Pharmacotherapy: Open-Source Software for Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Population PK Modeling
2.4. Covariate Evaluation
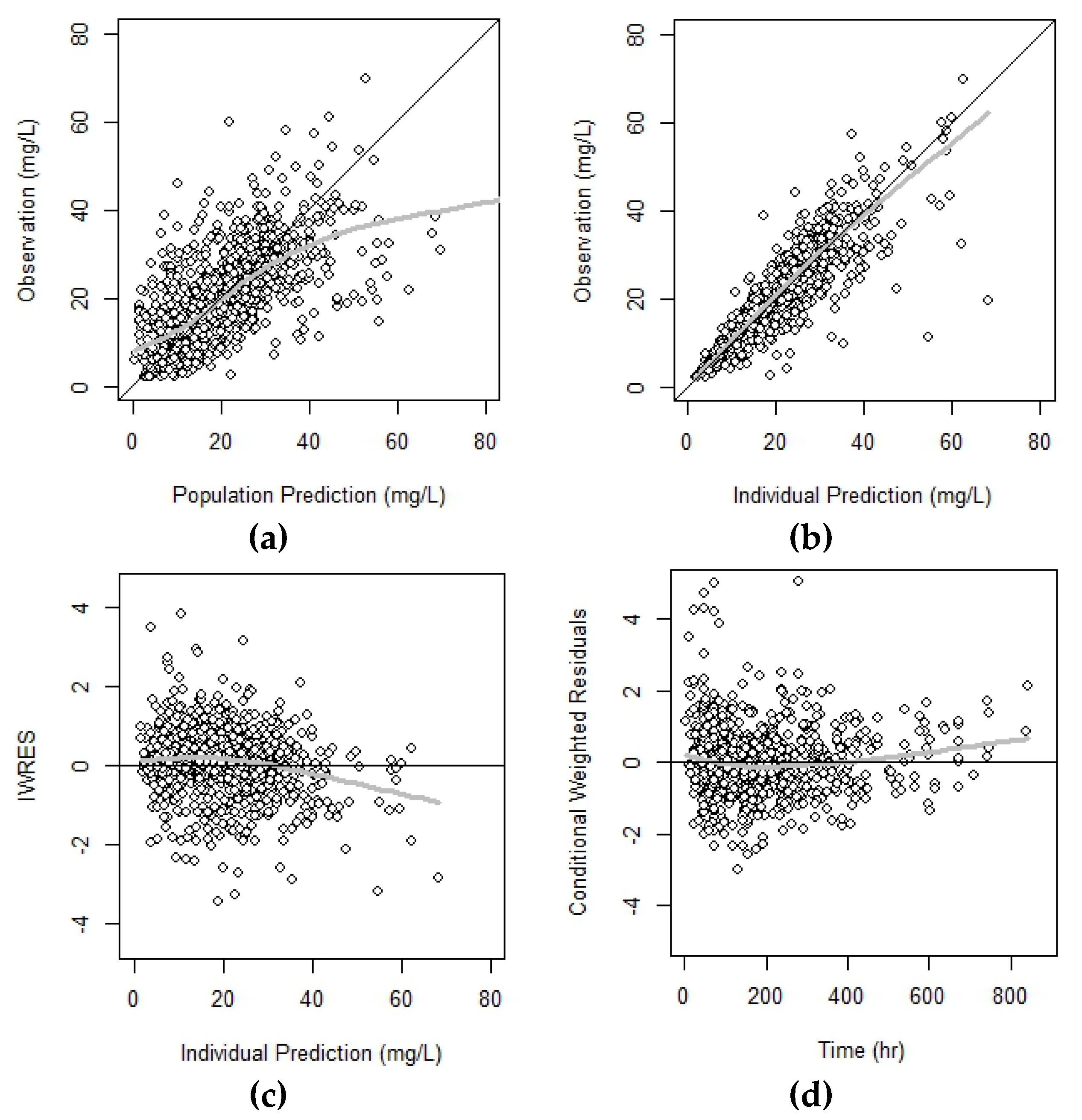
2.5. Model Evaluation and Simulation
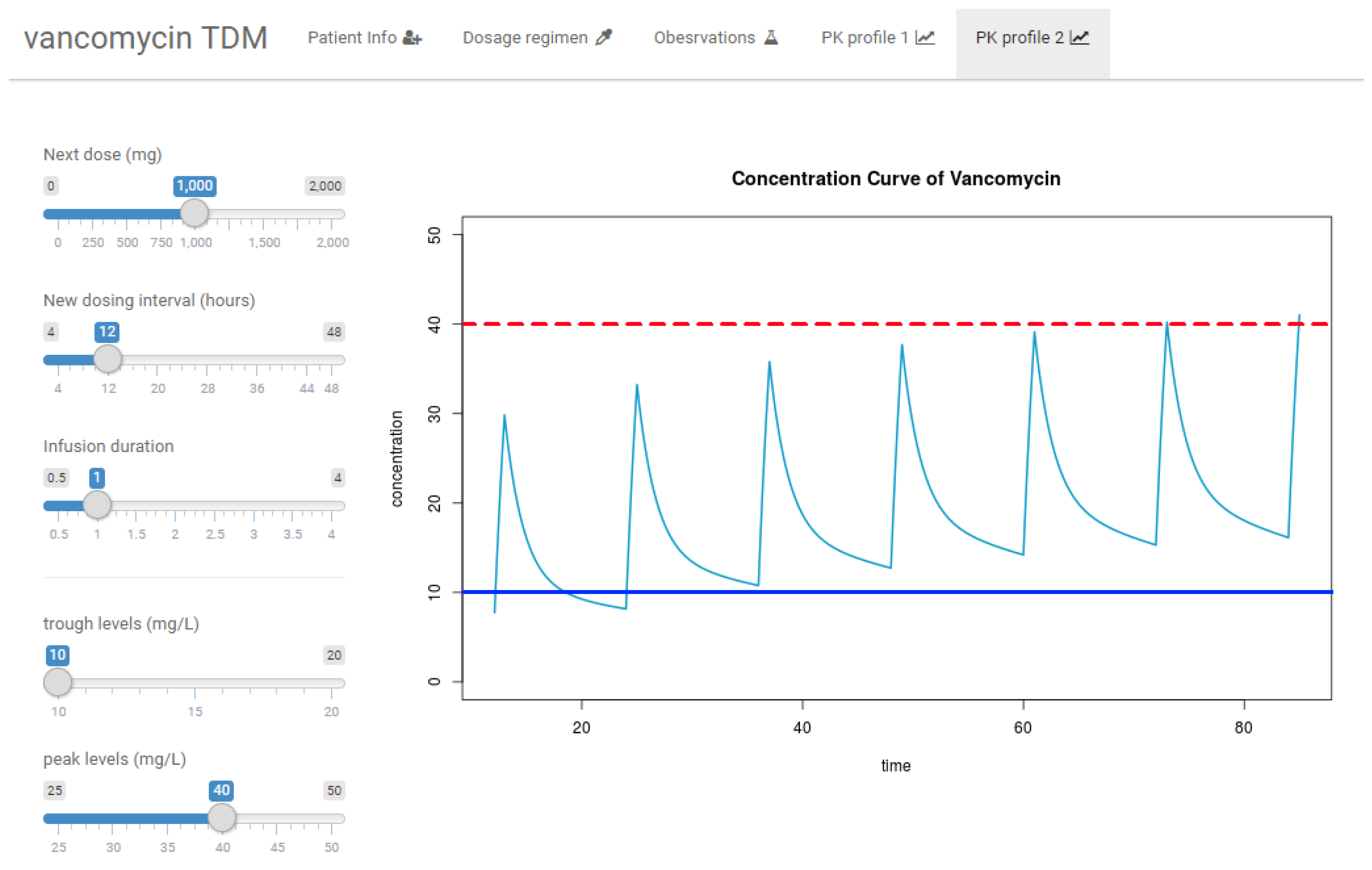
2.6. R Shiny Application for VCM TDM
3. Results
3.1. Population PK Modeling
3.2. Model Assessment and Simulation
3.3. R Shiny Application for VCM TDM
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Bayer, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Daum, R.S.; Fridkin, S.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levine, D.P.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children: Executive summary. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rybak, M.J.; Lomaestro, B.M.; Rotschafer, J.C.; Moellering, R.C.; Craig, W.A.; Billeter, M.; Dalovisio, J.R.; Levine, D.P. Vancomycin therapeutic guidelines: A summary of consensus recommendations from the infectious diseases Society of America; the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannsson, B.; Beekmann, S.E.; Srinivasan, A.; Hersh, A.L.; Laxminarayan, R.; Polgreen, P.M. Improving antimicrobial stewardship: The evolution of programmatic strategies and barriers. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzke, G.R.; Zhanel, G.G.; Guay, D.R. Clinical pharmacokinetics of vancomycin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1986, 11, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsot, A.; Boulamery, A.; Bruguerolle, B.; Simon, N. Vancomycin: A review of population pharmacokinetic analyses. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong-Beringer, A.; Joo, J.; Tse, E.; Beringer, P. Vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity: A critical appraisal of risk with high-dose therapy. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2011, 37, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.K.; Li, C.; Zhai, S.D. Guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elyasi, S.; Khalili, H.; Dashti-Khavidaki, S.; Mohammadpour, A. Vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: Mechanism; incidence; risk factors and special populations. A literature review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 68, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.K.; An, H.; Shin, K.H.; Shin, D.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.H.; Kang, H.R.; Jang, I.J.; Yu, K.S.; Lim, K.S. Trough concentration over 12.1 mg/L is a major risk factor of vancomycin-related nephrotoxicity in patients with therapeutic drug monitoring. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2014, 36, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Pai, M.P.; Rodvold, K.A.; Lomaestro, B.; Drusano, G.L.; Lodise, T.P. Vancomycin: We can’t get there from here. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, M.P.; Neely, M.; Rodvold, K.A.; Lodise, T.P. Innovative approaches to optimizing the delivery of vancomycin in individual patients. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2014, 77, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.G.; Kim, H.K.; Roe, E.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Ahn, B.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, M.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, J.M. Therateutic Drug Monitoring of Vancomycin in Korean Patients. Infect. Chemother. 2004, 36, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrand, M.; Hooker, A.C.; Wallin, J.E.; Karlsson, M.O. Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. The AAPS J. 2011, 13, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Bae, K.S.; Houk, B.E.; Savic, R.M.; Karlsson, M.O. Standard Error of Empirical Bayes Estimate in NONMEM(R) VI. Korean. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Step-By-Step Guide to Prediction Corrected Visual Predictive Checks (VPC) of NONMEM Models. Available online: https://www.pmxsolutions.com/2018/09/21/a-step-by-step-guide-to-prediction-corrected-visual-predictive-checks-vpc-of-nonmem-models/ (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Kim, M.G.; Yim, D.S.; Bae, K.S. R-based reproduction of the estimation process hidden behind NONMEM® Part 1: first-order approximation method. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


| Variables (Unit) | Mean (Range) |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 63 (21–98) |
| Sex (male/female) | 139/81 |
| Weight (kg) | 61.6 (30.0–126.7) |
| Serum creatinine, Scr (mg/dL) | 1.7 (0.20–13.3) |
| Creatinine clearance, CLCR (mL/min) 1 | 77.0 (4.57–279) |
| Application of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) | 9 |
| Patients who received hemodialysis (HD) | 20 |
| Parameter | Description | Estimate | %RSE | Bootstrap Median (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural model | ||||
| (L/h) | Clearance in patients not receiving CRRT nor HD treatment | |||
| θ1 | 2.82 | 4.18 | 2.80 (2.56–3.04) | |
| θ2 | 0.836 | 6.89 | 0.837 (0.717–0.971) | |
| CLCRRT (L/h) | CL in patients with CRRT | 0.716 | 11.0 | 0.733 (0.437–1.72) |
| CLHD (L/h) | CL in patients with HD | 0.334 | 11.9 | 0.335 (0.142–0.452) |
| V1 (L) | Volume of central compartment | 31.8 | 7.01 | 32.8 (25.6–42.8) |
| Q (L/h) | Intercompartmental clearance | 11.7 | 7.42 | 11.3 (6.93–13.8) |
| ) (L) | Volume of peripheral compartment | |||
| θ3 | 75.4 | 7.91 | 75.7 (58.6–94.9) | |
| Inter-individual variability | ||||
| ωCL (%) | Interindividual variability of CL | 99.2 | 6.55 | 101 (83.4–116) |
| ωV2 (%) | Interindividual variability of V2 | 49.2 | 3.08 | 48.8 (40.5–57.4) |
| Residual error | ||||
| σprop | Proportional error | 0.253 | 2.91 | 0.250 (0.222–0.281) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, S.H.; Yim, D.-S.; Lee, H.; Park, A.-R.; Kwon, J.-E.; Sumiko, H.; Han, S. Application of Pharmacometrics in Pharmacotherapy: Open-Source Software for Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Management. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050224
Bae SH, Yim D-S, Lee H, Park A-R, Kwon J-E, Sumiko H, Han S. Application of Pharmacometrics in Pharmacotherapy: Open-Source Software for Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Management. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(5):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050224
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Soo Hyeon, Dong-Seok Yim, Hyemi Lee, Ae-Ryoung Park, Ji-Eun Kwon, Hirata Sumiko, and Seunghoon Han. 2019. "Application of Pharmacometrics in Pharmacotherapy: Open-Source Software for Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Management" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 5: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050224
APA StyleBae, S. H., Yim, D.-S., Lee, H., Park, A.-R., Kwon, J.-E., Sumiko, H., & Han, S. (2019). Application of Pharmacometrics in Pharmacotherapy: Open-Source Software for Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Management. Pharmaceutics, 11(5), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050224





