Nanoemulsions for “Nose-to-Brain” Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
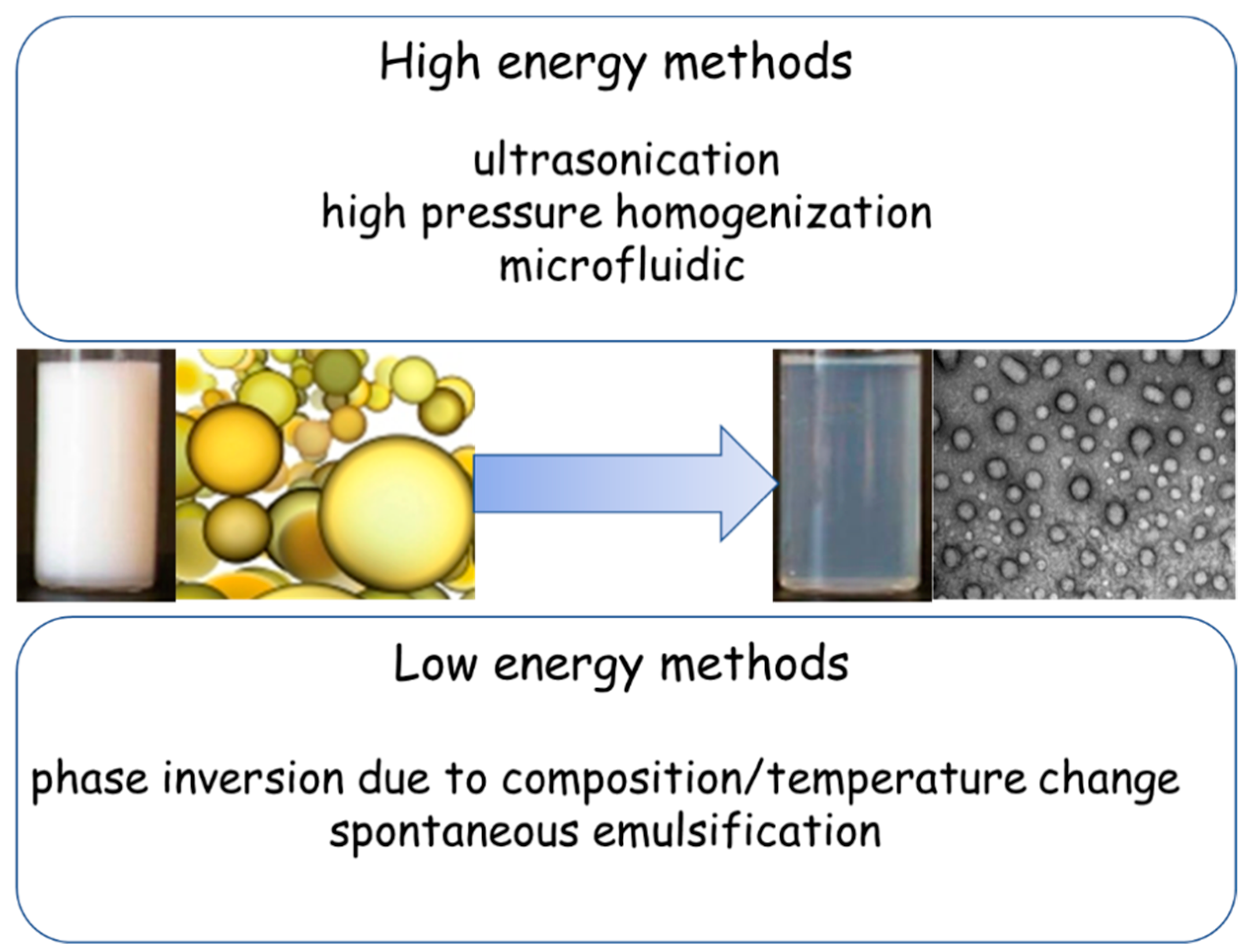
2. General Characteristics of NEs in Brief
3. General Overview of NEs for Nose-to-Brain Delivery
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloor, S.M.; Wachtel, M.; Bolliger, M.F.; Ishihara, H.; Landmann, R.; Frei, K. Molecular and cellular permeability control at the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 36, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokovic, B.V. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 2008, 57, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A. From blood-brain barrier to blood-brain interface: New opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Jayant, R.D.; Bhardwaj, V.; Nair, M. Personalized nanomedicine for CNS diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhuria, S.V.; Hanson, L.R.; Frey, W.H., 2nd. Intranasal delivery to the central nervous system: Mechanisms and experimental considerations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1654–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourganis, V.; Kammona, O.; Alexopoulos, A.; Kiparissides, C. Recent advances in carrier mediated nose-to-brain delivery of pharmaceutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, R.G.; Pronk, G.J.; Padmanabhan, V.; Frey, W.H. Delivery of insulin-like growth factor-I to the rat brain and spinal cord along olfactory and trigeminal pathways following intranasal administration. Neuroscience 2004, 127, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, A.; Stolnik, S.; Illum, L. Nanoparticles for direct nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.I.; Beg, S.; Samad, A.; Baboota, S.; Kohli, K.; Ali, J.; Ahuja, A.; Akbar, M. Strategy for effective brain drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeshi, C.V.; Belgamwar, V.S. Direct nose to brain drug delivery via integrated nerve pathways bypassing the blood-brain barrier: An excellent platform for brain targeting. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalpiaz, A.; Fogagnolo, M.; Ferraro, L.; Capuzzo, A.; Pavan, B.; Rassu, G.; Salis, A.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Nasal chitosan microparticles target a zidovudine prodrug to brain HIV sanctuaries. Antiviral Res. 2015, 123, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasuriya, A.; Mizisin, A.P. The blood-nerve barrier: Structure and functional significance. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 686, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Ferraro, L.; Beggiato, S.; Alhalaweh, A.; Velaga, S.; Marchetti, N.; Bandiera, P.; Giunchedi, P.; Dalpiaz, A. Influence of polymeric microcarriers on the in vivo intranasal uptake of an anti-migraine drug for brain targeting. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Sharma, R.K.; Sharma, N.; Gabrani, R.; Sharma, S.K.; Ali, J.; Dang, S. Nose-To-Brain Delivery of PLGA-Diazepam Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015, 16, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, A.; Soddu, E.; Turunc Bayrakdar, E.; Uyanikgil, Y.; Kanit, L.; Armagan, G.; Rassu, G.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Neuroprotective Effects of Engineered Polymeric Nasal Microspheres Containing Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on β-Amyloid (1-42)-Induced Toxicity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Porcu, E.P.; Fancello, S.; Obinu, A.; Senes, N.; Galleri, G.; Migheli, R.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2019, 111, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, M.I.; Verbeke, N.; Kinget, R. The biopharmaceutical aspects of nasal mucoadhesive drug delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, D.S.; Westlye, L.T.; Rustan, Ø.G.; Tesli, N.; Poppy, C.L.; Smevik, H.; Tesli, M.; Røine, M.; Mahmoud, R.A.; Smerud, K.T.; et al. Low-dose oxytocin delivered intranasally with Breath Powered device affects social-cognitive behavior: A randomized four-way crossover trial with nasal cavity dimension assessment. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stützle, M.; Flamm, J.; Carle, S.; Schindowski, K. Nose-to-brain delivery of insulin for Alzheimer’s disease. Admet Dmpk. 2015, 3, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Posadino, A.M.; Pintus, G.; Sarmento, B.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Nose-to-brain delivery of BACE1 siRNA loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles for Alzheimer’s therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonvico, F.; Clementino, A.; Buttini, F.; Colombo, G.; Pescina, S.; Stanisçuaski Guterres, S.; Raffin Pohlmann, A.; Nicoli, S. Surface-Modified Nanocarriers for Nose-to-Brain Delivery: From Bioadhesion to Targeting. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Gavini, E.; Carta, A.; Obinu, A.; Porcu, E.P.; Giunchedi, P. Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Formulated in Nasal Chitosan Microspheres as Candidate Therapeutic Agent in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comfort, C.; Garrastazu, G.; Pozzoli, M.; Sonvico, F. Opportunities and challenges for the nasal administration of nanoemulsions. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.F.; Costa, I.C.; Almeida, F.B.; Cruz, A.S.; Ferreira, A.M.; Vilhena, J.C.E.; Florentino, A.C.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Fernandes, C.P. Development and characterization of evening primrose (Oenothera biennis) oil nanoemulsions. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2015, 25, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Benoit, J.P.; Saulnier, P. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates-A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, D.K. Engineering of nanoemulsions for drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, H.S.; Mahajan, M.S.; Nerkar, P.P.; Agrawal, A. Nanoemulsion-based intranasal drug delivery system of saquinavir mesylate for brain targeting. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F.A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N.K.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Sandri, G.; Rossi, S.; Usai, D.; Liakos, I.; Garzoni, A.; Fiamma, M.; Zanetti, S.; Athanassiou, A.; Caramella, C.; Ferrari, F. A novel ionic amphiphilic chitosan derivative as a stabilizer of nanoemulsions: Improvement of antimicrobial activity of Cymbopogon citratus essential oil. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Riva, F.; Invernizzi, A.; Dellera, E.; Sandri, G.; Rossi, S.; Marrubini, G.; Bruni, G.; Vigani, B.; Caramella, C.; et al. Alpha tocopherol loaded chitosan oleate nanoemulsions for wound healing. Evaluation on cell lines and ex vivo human biopsies, and stabilization in spray dried Trojan microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 123, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Eral, H.B.; Hatton, T.A.; Doyle, P.S. Nanoemulsions: Formation, properties and applications. Soft Matter. 2016, 12, 2826–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, R.T.; Thiagarajan, P. Nanoemulsions for drug delivery through different routes. Res. Biotechnol. 2011, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, H.; Al-Suwayeh, S.; Elkadi, S. Design and optimization of self nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of simvastatin aiming dissolution enhancement. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 1482–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Potential biological fate of ingested nanoemulsions: Influence of particle characteristics. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, V.; Valenta, C. Lecithin-based nanoemulsions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, T.K.; Shahiwala, A.; Amiji, M.M. Improved oral bioavailability and brain transport of saquinavir upon administration in novel nanoemulsion formulations, Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 347, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Azeem, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ahmad, F.J.; Iqbal, Z.; Khar, R.K.; Aqil, M.; Talegaonkar, S. Nanoemulsion components screening and selection: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, C.; Kate, V.; Payghan, S.A. Investigation of effect of non-ionic surfactant on preparation of griseofulvin non-aqueous nanoemulsion. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2015, 5, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüsewitz, C.; Schendler, A.; Funke, A.; Wagner, T.; Lipp, R. Novel poloxamer-based nanoemulsions to enhance the intestinal absorption of active compounds. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erramreddy, V.V.; Ghosh, S. Influence of emulsifier concentration on nanoemulsion gelation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 11062–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, P.G.; Fenelon, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Kamrul Haque, M.; Roos, Y.H. Optimization of β-casein stabilized nanoemulsions using experimental mixture design. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C1108–C1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combrinck, J.; Otto, A.; du Plessis, J. Whey protein/polysaccharide-stabilized emulsions: Effect of polymer type and pH on release and topical delivery of salicylic acid. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, N.; Christensen, D.A.; Kennedy, A.M.; Nam, K.H. Cavitation properties of block copolymer stabilized phase-shift nanoemulsions used as drug carriers. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shang, Z.; Gao, C.; Du, M.; Xu, S.; Song, H.; Liu, T. Nanoemulsion for solubilization, stabilization, and in vitro release of pterostilbene for oral delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langasco, R.; Tanrıverdi, S.T.; Özer, Ö.; Roldo, M.; Cossu, M.; Rassu, G.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Prolonged skin retention of clobetasol propionate by bio-based microemulsions: A potential tool for scalp psoriasis treatment. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, E.M.; Kandil, S.M.; Miniawy, H.M.F.E. Brain targeting efficiency of antimigrain drug loaded mucoadhesive intranasal nanoemulsion. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Misra, A.; Babbar, A.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Mishra, P.; Pathak, K. Intranasal nanoemulsion based brain targeting drug delivery system of risperidone. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 358, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Misra, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Mishra, P.; Pathak, K. Mucoadhesive nanoemulsion-based intranasal drug delivery system of olanzapine for brain targeting. J. Drug Target. 2008, 16, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Cossu, M.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P.; Dalpiaz, A. Particulate formulations based on chitosan for nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. A review. J. Drug Del. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Meng, J.; Chen, J.; Tang, X. Preparation of ergoloid mesylate submicron emulsions for enhancing nasal absorption and reducing nasal ciliotoxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 375, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Akhter, S.; Jain, G.K.; Khan, Z.I.; Khar, R.K.; Ahmad, F.J. Antiepileptic intranasal Amiloride loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsion: Development and safety assessment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadur, S.; Pathak, K. Buffered nanoemulsion for nose to brain delivery of ziprasidone hydrochloride: Preformulation and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.; Dash, R.P.; Misra, M.; Nivsarkar, M. Role of mucoadhesive polymers in enhancing delivery of nimodipine microemulsion to brain via intranasal route. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, S.; Jain, K.; Gowthamarajan, K. Optimization of curcumin nanoemulsion for intranasal delivery using design of experiment and its toxicity assessment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Naiki, H.; Yamada, M. Curcumin has potent anti-amyloidogenic effects for Alzheimers beta-amyloid fibrils in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 75, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Mishra, B.; Tyagi, E.; Nath, C.; Shukla, R. Effect of curcumin on brain insulin receptors and memory functions in STZ (ICV) induced dementia model of rat. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangeni, R.; Sharma, S.; Mustafa, G.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Vitamin E loaded resveratrol nanoemulsion for brain targeting for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease by reducing oxidative stress. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 485102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, J.K.; Doggui, S.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S.; Dao, L.; Ramassamy, C. Neurotherapeutic applications of nanoparticles in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 208–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M. Development of an optimized hyaluronic acid-based lipidic nanoemulsion co-encapsulating two polyphenols for nose to brain delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Gattacceca, F.; Panicucci, R.; Amiji, M.M. Comparative Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Cyclosporine-A in the Brain upon Intranasal or Intravenous Administration in an Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion Formulation. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Gandham, S.K.; Panicucci, R.; Amiji, M.M. Intranasal brain delivery of cationic nanoemulsion-encapsulated TNFα siRNA in prevention of experimental neuroinflammation. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, R.H.; Patel, R.J. Nanoemulsions for Intranasal Delivery of Riluzole to Improve Brain Bioavailability: Formulation Development and Pharmacokinetic Studies. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.Y.; Hung, C.F.; Chi, C.H.; Chen, C.C. Transdermal permeation of selegiline from hydrogel-membrane drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 380, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Design Expert(®) supported optimization and predictive analysis of selegiline nanoemulsion via the olfactory region with enhanced behavioural performance in Parkinson’s disease. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 435101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashafaq, M.; Khan, M.M.; Shadab Raza, S.; Ahmad, A.; Khuwaja, G.; Javed, H.; Khan, A.; Islam, F.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Safhi, M.M.; et al. S-allyl cysteine mitigates oxidative damage and improves neurologic deficit in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Majed, A.A.; Al-Omar, F.A.; Nagi, M.N. Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against transient forebrain ischemia in the rat hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 543, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, R.; Alam, M.A.; Samim, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Ahmad, F.J. Quantification and evaluation of thymoquinone loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsion for treatment of cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, Y.R.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, B.K.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Intranasal delivery of paroxetine nanoemulsion via the olfactory region for the management of depression: Formulation, behavioural and biochemical estimation. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 025102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boche, M.; Pokharkar, V. Quetiapine Nanoemulsion for Intranasal Drug Delivery: Evaluation of Brain-Targeting Efficiency. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, P.; Reddy, A.V.; Reddy, G.V.S.; Panda, K.C. Formulation, design and in vitro evaluation of zolmitriptan immediate release tablets using Primojel and Ac-Di-Sol. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 545–553. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, E.; Feng, Y.; Qi, J.; Fan, W.; Ma, Y.; He, H.; Xia, F.; Dong, X.; Zhao, W.; Lu, Y.; et al. Evidence of nose-to-brain delivery of nanoemulsions: Cargoes but not vehicles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Melchiades, G.L.; Figueiró, F.; Battastini, A.M.O.; Teixeira, H.F.; Koester, L.S. Validation of an HPLC-UV method for analysis of Kaempferol-loaded nanoemulsion and its application to in vitro and in vivo tests. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Figueiró, F.; de Fraga Dias, A.; Teixeira, H.F.; Battastini, A.M.O.; Koester, L.S. Kaempferol-loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsion for intranasal administration reduces glioma growth in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 543, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, F.; Khan, S.; Gaba, B.; Alam, T.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J.; Ali, A. Optimization of rivastigmine nanoemulsion for enhanced brain delivery: In-vivo and toxicity evaluation. J. Mol. Liquids 2018, 255, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, S.H.; Basri, M.; Masoumi, H.R.; Karjiban, R.A.; Malek, E.A.; Basri, H.; Shamsuddin, A.F. Formulation optimization of palm kernel oil esters nanoemulsion-loaded with chloramphenicol suitable for meningitis treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pécoul, B.; Varaine, F.; Keita, M.; Soga, G.; Djibo, A.; Soula, G.; Abdou, A.; Etienne, J.; Rey, M. Long-acting chloramphenicol versus intravenous ampicillin for treatment of bacterial meningitis. Lancet 1991, 338, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, R.; Alam, M.A.; Ahmad, F.J.; Amir, M. Impact of ultrasonication techniques on the preparation of novel Amiloride-nanoemulsion used for intranasal delivery in the treatment of epilepsy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zaafarany, G.M.; Soliman, M.E.; Mansour, S.; Awad, G.A. Identifying lipidic emulsomes for improved oxcarbazepine brain targeting: In vitro and rat in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 503, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calias, P. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrins and the Blood-Brain Barrier: Considerations for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 6231–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shityakov, S.; Puskás, I.; Pápai, K.; Salvador, E.; Roewer, N.; Förster, C.; Jens-Albert Broscheit, J.-A. Sevoflurane-Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin Complex: Preparation, Characterization, Cellular Toxicity, Molecular Modeling and Blood-Brain Barrier Transport Studies. Molecules 2015, 20, 10264–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafourian, T.; Zandasrar, P.; Hamishekar, H.; Nokhodchi, A. The effect of penetration enhancers on drug delivery through skin: A QSAR study. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shityakov, S.; Puskás, I.; Roewer, N.; Förster, C.; Broscheit, J. Three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship and docking studies in a series of anthocyanin derivatives as cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors. Adv. Appl. Bioinform. Chem. 2014, 7, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shityakov, S.; Förster, C.Y. Computational simulation and modeling of the blood-brain barrier pathology. Histochem. Cell. Biol. 2018, 149, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Low capacity to cross the Blood-Brain-Barrier |
| Low solubility in water (and consequently poor bioavailability) |
| Low/irregular absorption (and consequently poor bioavailability) |
| Active substrate of intestinal P-glycoprotein |
| Problems of stability (pH, hydrolysis, oxidation, under gastro-intestinal conditions) |
| Intestinal metabolism (enzymatic degradation) |
| First-pass metabolism (enzymatic degradation) |
| Need to reduce dosage (i.e., in case of chronic therapy and/or to avoid side effects connected to the high oral dosage used for overcoming the Blood-Brain-Barrier) |
| Slow onset of action |
| Bitter/unpleasant taste of the drug |
| Drug/Probe | Therapy of | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Risperidone | Schizophrenia | [48] |
| Olanzapine | Schizophrenia | [49] |
| Ergoloid mesylate | Antiaging | [51] |
| Amiloride | Antiepileptic | [52] |
| Ziprasidone hydrochloride | Antipshychotic | [53] |
| Saquinavir mesylate | HIV infections | [28] |
| Nimodipine | Cerebrovascular spasm and senile dementia | [54] |
| Curcumin | Neurodegenerative diseases | [55] |
| Resveratrol | Parkinson’s disease | [58] |
| Curcumin/Resveratrol | Age-related neurodegenerative diseases | [60] |
| Cyclosporine-A | Neuro-protective | [61] |
| anti-TNFα siRNA | Neuro-inflammations | [62] |
| Riluzole | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | [63] |
| Selegiline | Parkinson’s disease | [65] |
| Thymoquinone | Cerebral ischemia | [68] |
| Paroxetine | Depression and anxiety | [69] |
| Quetiapine | Schizophrenia | [70] |
| Zolmitriptan | Migraines | [47] |
| Aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) probes | Labeling action | [72] |
| Kaempferol | Gliomas | [73,74] |
| Rivastigmine | Alzheimer’s disease | [75] |
| Chloramphenicol | Bacterial meningitis | [76] |
| Amiloride | Epilepsy | [78] |
| Oxcarbazepine | Epilepsy | [79] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Sandri, G.; Ferrari, F.; Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Giunchedi, P. Nanoemulsions for “Nose-to-Brain” Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020084
Bonferoni MC, Rossi S, Sandri G, Ferrari F, Gavini E, Rassu G, Giunchedi P. Nanoemulsions for “Nose-to-Brain” Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(2):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020084
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonferoni, Maria Cristina, Silvia Rossi, Giuseppina Sandri, Franca Ferrari, Elisabetta Gavini, Giovanna Rassu, and Paolo Giunchedi. 2019. "Nanoemulsions for “Nose-to-Brain” Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 2: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020084
APA StyleBonferoni, M. C., Rossi, S., Sandri, G., Ferrari, F., Gavini, E., Rassu, G., & Giunchedi, P. (2019). Nanoemulsions for “Nose-to-Brain” Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 11(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020084











