A Non-Viral Plasmid DNA Delivery System Consisting on a Lysine-Derived Cationic Lipid Mixed with a Fusogenic Lipid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
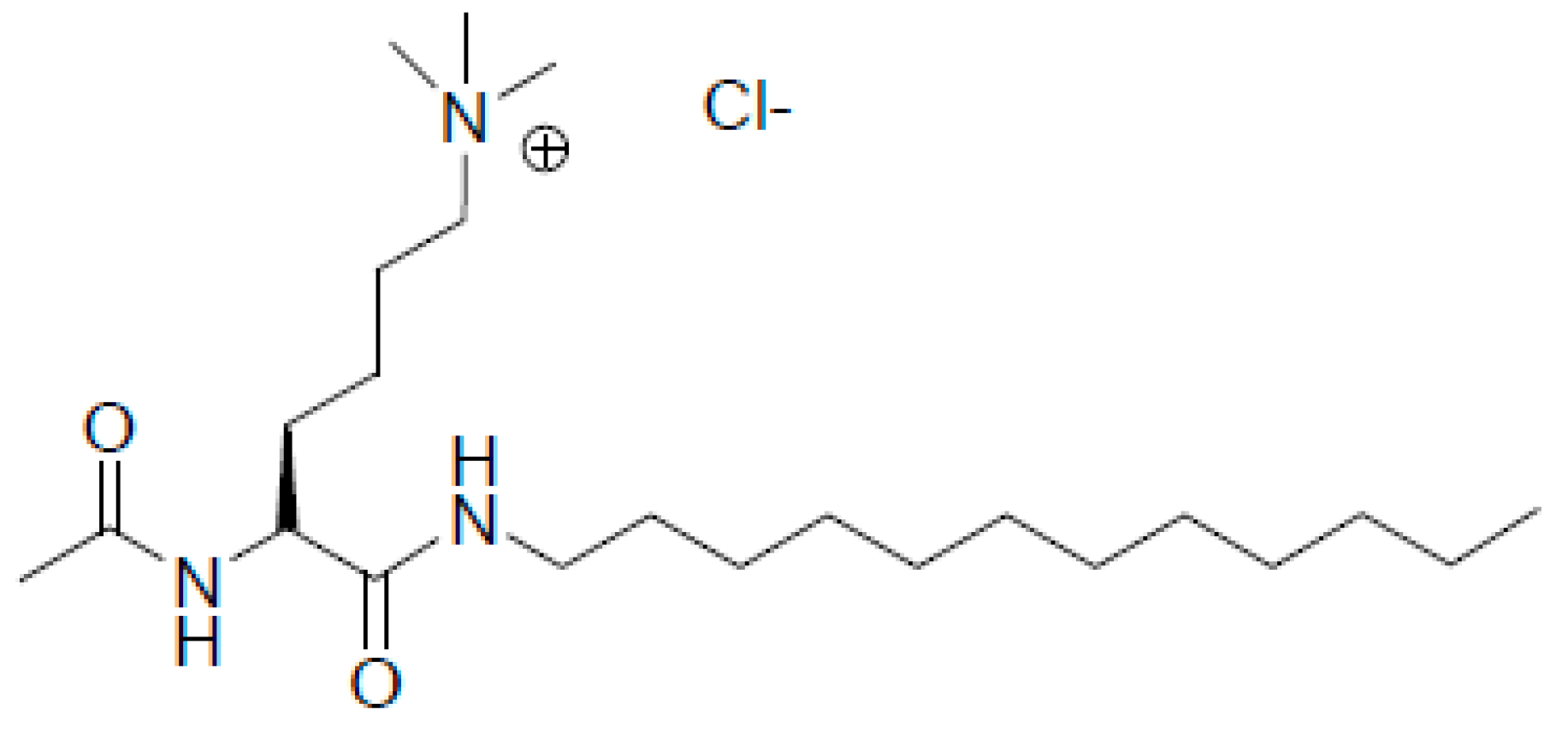
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Lipoplexes
2.3. Zeta Potential and Particle Size
2.4. Gel Electrophoresis
2.4.1. DNA Compaction Assay
2.4.2. DNA Protection Assay
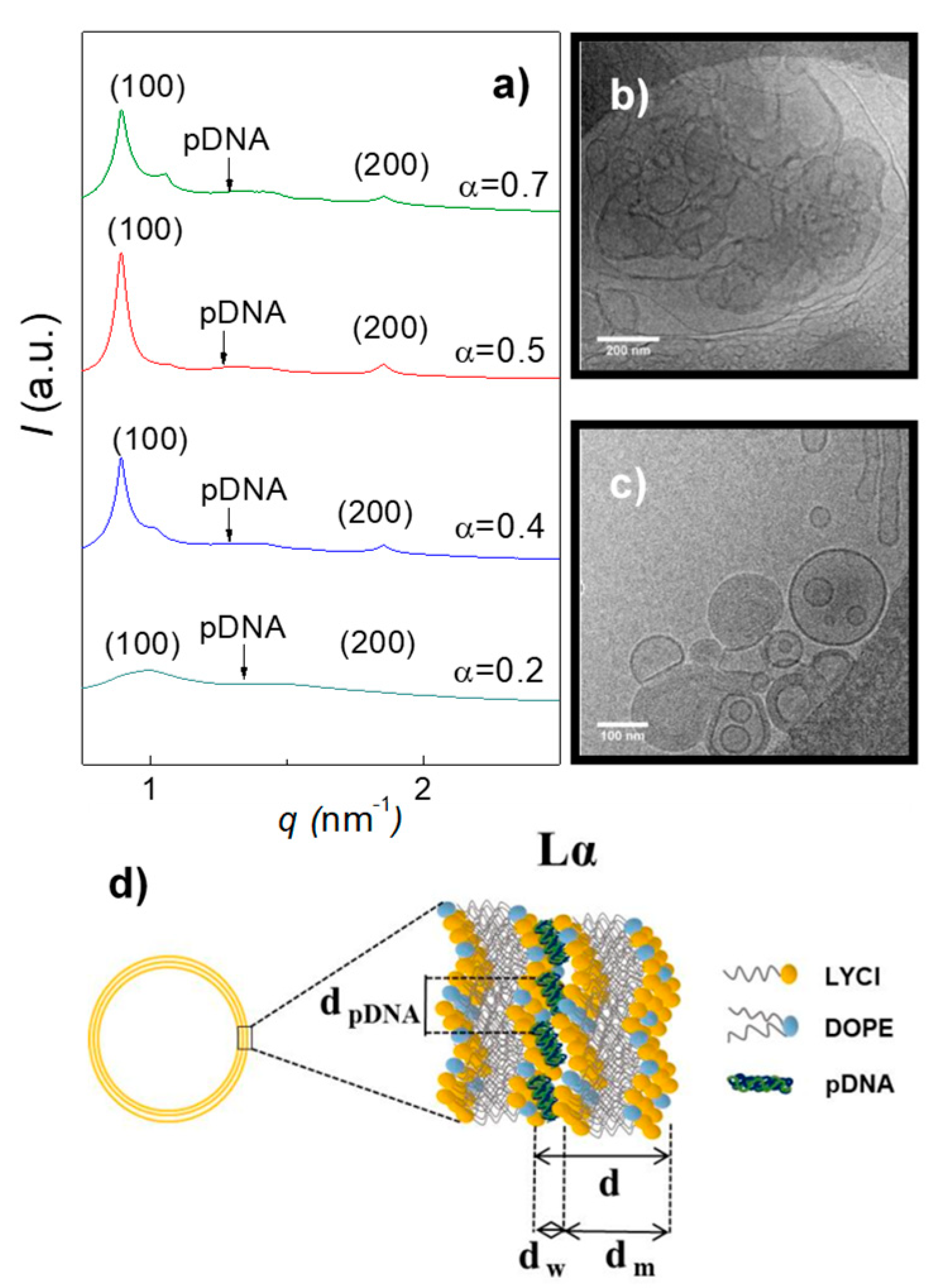
2.5. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering
2.6. Cryo-TEM
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. In Vitro Transfection Efficiency
2.8.1. Luminometry
2.8.2. FACS
2.9. Cell Viability
2.10. Computational Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical and Structural Characterization of LYCl/DOPE-pDNA Lipoplexes
3.2. In Vitro Transfection and Cell Viability of LYCl/DOPE-pDNA Lipoplexes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Si, J. Nanocarriers in gene therapy: A review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 3483–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakshoor, O.; Kool, E.T. Chemistry of nucleic acids: Impacts in multiple fields. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7018–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Devi, G.R. siRNA-based approaches in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Firdous, J.; Choi, Y.-J.; Yun, C.-H.; Cho, C.-S. Regulation of endocytosis by non-viral vectors for efficient gene activity. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintzer, M.A.; Simanek, E.E. Nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Chem. Rev. 2008, 109, 259–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dosari, M.S.; Gao, X. Nonviral gene delivery: Principle, limitations, and recent progress. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junquera, E.; Aicart, E. Cationic lipids as transfecting agents of DNA in gene therapy. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montier, T.; Benvegnu, T.; Jaffres, P.A.; Yaouanc, J.J.; Lehn, P. Progress in cationic lipid-mediated gene transfection: A series of bio-inspired lipids as an example. Curr. Gene Ther. 2008, 8, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Bajaj, A. Advances in gene delivery through molecular design of cationic lipids. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4632–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aied, A.; Greiser, U.; Pandit, A.; Wang, W.X. Polymer gene delivery: Overcoming the obstacles. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Y.; Pelet, J.M.; Putnam, D. Polymer systems for gene delivery-past, present, and future. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 799–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, D.-M.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Yu, X.-Q. Functionalized asymmetric bola-type amphiphiles for efficient gene and drug delivery. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzmitruk, V.; Apartsin, E.; Ihnatsyeu-Kachan, A.; Abashkin, V.; Shcharbin, D.; Bryszewska, M. Dendrimers Show Promise for siRNA and microRNA Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lee, J.-J.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, H.-S. Electrostatically assembled dendrimer complex with a high-affinity protein binder for targeted gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Mellet, C.; Garcia Fernandez, J.M.; Benito, J.M. Glycotransporters for gene delivery. In Carbohydrate Chemistry: Chemical and Biological Approaches; Rauter, A.P., Lindhorst, T.K., Eds.; RCS Publishing Inc.: Cambridge, UK, 2012; Volume 38, pp. 338–375. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Narain, R. Carbohydrate-based materials for targeted delivery of drugs and genes to the liver. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2263–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Negro, M.; Caracciolo, G.; Palchetti, S.; Pozzi, D.; Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; Lagana, A.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; Benito, J.M.; García Fernandez, J.M.; et al. Biophysics and protein corona analysis of Janus cyclodextrin-DNA nanocomplexes. Efficient cellular transfection on cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.F. Cyclodextrins in non-viral gene delivery. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.E.; Rice, K.G. Peptide-guided gene delivery. AAPS J. 2007, 9, E18–E29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Fukuda, T.; Takashima, Y.; Okada, H. Versatile nuclear localization signal-based oligopeptide as a gene vector. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Han, G.; De, M.; Kim, C.K.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in delivery applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Jin, S.; Ma, X.; Xue, X.; Yang, K.; Kumar, A.; Wang, P.C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Liang, X.-J. Ultrasmall gold nanoparticles as carriers for nucleus-based gene therapy due to size-dependent nuclear entry. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5852–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.E.; Ehrhardt, A.; Kay, M.A. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somia, N.; Verma, I.M. Gene therapy: Trials and tribulations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2000, 1, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junquera, E.; Aicart, E. Recent progress in gene therapy to deliver nucleic acids with multivalent cationic vectors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 233, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Negro, M.; Kumar, K.; Barrán-Berdón, A.L.; Datta, S.; Kondaiah, P.; Junquera, E.; Bhattacharya, S.; Aicart, E. Efficient cellular knockdown mediated by siRNA nanovectors of gemini cationic lipids having delocalizable headgroups and oligo-oxyethylene spacers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22113–22126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehto, T.; Simonson, O.E.; Mager, I.; Ezzat, K.; Sork, H.; Copolovici, D.-M.; Viola, J.R.; Zaghloul, E.M.; Lundin, P.; Moreno, P.M.D.; et al. A peptide-based vector for efficient gene transfer in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arukuusk, P.; Paernaste, L.; Oskolkov, N.; Copolovici, D.-M.; Margus, H.; Padari, K.; Moell, K.; Maslovskaja, J.; Tegova, R.; Kivi, G.; et al. New generation of efficient peptide-based vectors, NickFects, for the delivery of nucleic acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccardo, P.; Villaverde, A.; Gonzalez-Montalban, N. Peptide-mediated DNA condensation for non-viral gene therapy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Y.; Wu, C.H. Receptor-mediated in vitro gene transformation by a soluble DNA carrier system. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 4429–4432. [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh, D.Y.; Coffin, C.C.; Lollo, C.P.; Jovenal, J.; Banaszczyk, M.G.; Mullen, P.; Phillips, A.; Amini, A.; Fabrycki, J.; Bartholomew, R.M.; et al. Stabilization of poly-l-lysine/DNA polyplexes for in vivo gene delivery to the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Struct. Expr. 1999, 1444, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziady, A.G.; Gedeon, C.R.; Miller, T.; Quan, W.; Payne, J.M.; Hyatt, S.L.; Fink, T.L.; Muhammad, O.; Oette, S.; Kowalczyk, T.; et al. Transfection of airway epithelium by stable PEGylated poly-l-lysine DNA nanoparticles in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2003, 8, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midoux, P.; Pichon, C.; Yaouanc, J.J.; Jaffres, P.A. Chemical vectors for gene delivery: A current review on polymers, peptides and lipids containing histidine or imidazole as nucleic acids carriers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, Y.; Suzuki, D.; Takeoka, S. Evaluation of cationic assemblies constructed with amino acid based lipids for plasmid DNA delivery. Bioconj. Chem. 2008, 19, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damen, M.; Cristobal-Lecina, E.; Sanmarti, G.C.; van Dongen, S.F.M.; Garcia Rodriguez, C.L.; Dolbnya, I.P.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Feiters, M.C. Structure-delivery relationships of lysine-based gemini surfactants and their lipoplexes. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 5702–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.-C.; Liu, Q.; Yi, W.-J.; Zheng, L.-T.; Zhao, Z.-G. Lipoic acid functionalized amino acids cationic lipids as gene vectors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4692–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.T.; Yi, W.J.; Su, R.C.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Z.G. Reducible Amino Acid Based Cationic Lipids as Highly Efficient and Serum-Tolerant Gene Vectors. ChemPlusChem 2016, 81, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmali, P.P.; Majeti, B.K.; Sreedhar, B.; Chaudhuri, A. In vitro gene transfer efficacies and serum compatibility profiles of novel mono-, di-, and tri-histidinylated cationic transfection lipids: A structure-activity investigation. Bioconj. Chem. 2006, 17, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.V.; Pichon, C.; Refregiers, M.; Guerin, B.; Midoux, P.; Chaudhuri, A. Single histidine residue in head-group region is sufficient to impart remarkable gene transfection properties to cationic lipids: Evidence for histidine-mediated membrane fusion at acidic pH. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Su, R.C.; Yi, W.J.; Zheng, L.T.; Lu, S.S.; Zhao, Z.G. pH and reduction dual-responsive dipeptide cationic lipids with α-tocopherol hydrophobic tail for efficient gene delivery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloskova, O.O.; Nikonova, A.A.; Budanova, U.A.; Shilovskiy, I.P.; Kofiadi, I.A.; Ivanov, A.V.; Smirnova, O.A.; Zverev, V.V.; Sebaykin, Y.L.; Andreev, S.M.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of novel lipopeptide as a vehicle for efficient gene delivery and gene silencing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 102, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.J.; Chandra, P.; Mann, A.; Ganguli, M. Exogenous and cell surface glycosaminoglycans alter DNA delivery efficiency of arginine and lysine homopeptides in distinctly different ways. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 18982–18993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.R.; Aoshima, Y.; Hokama, R.; Inoue, T.; Sou, K.; Takeoka, S. Arginine-based cationic liposomes for efficient in vitro plasmid DNA delivery with low cytotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1361–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.R.; Hokama, R.; Takeoka, S. Intracellular delivery of universal proteins using a lysine headgroup containing cationic liposomes: Deciphering the uptake mechanism. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monpara, J.; Velga, D.; Verma, T.; Gupta, S.; Vavia, P. Cationic cholesterol derivative efficiently delivers the genes: In silico and in vitro studies. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Negro, M.; Blanco-Fernandez, L.; Tentori, P.M.; Perez, L.; Pinazo, A.; de Ilarduya, C.T.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E. A gemini cationic lipid with histidine residues as a novel lipid-based gene nanocarrier: A biophysical and biochemical study. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrán-Berdón, A.L.; Muñoz-Úbeda, M.; Aicart-Ramos, C.; Pérez, L.; Infante, M.R.; Castro-Hartmann, P.; Martín-Molina, A.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E. Ribbon-type and cluster-type lipoplexes constituted by a chiral lysine based cationic gemini lipid and plasmid DNA. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7368–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.I.; Sarrion, B.; Lopez-Lopez, M.; Lopez-Cornejo, P.; Robina, I.; Moya, M.L. Reversibility of the interactions between a novel surfactant derived from lysine and biomolecules. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 135, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.K.; Muñoz-Úbeda, M.; Datta, S.; Barrán-Berdón, A.L.; Aicart-Ramos, C.; Castro-Hartmann, P.; Kondaiah, P.; Junquera, E.; Bhattacharya, S.; Aicart, E. Effects of a delocalizable cation on the headgroup of gemini lipids on the lipoplex-type nano-aggregates directly formed from plasmid DNA. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3951–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Úbeda, M.; Misra, S.K.; Barrán-Berdón, A.L.; Datta, S.; Aicart-Ramos, C.; Castro-Hartmann, P.; Kondaiah, P.; Junquera, E.; Bhattacharya, S.; Aicart, E. How does the spacer length of cationic gemini lipids influence the lipoplex formation with plasmid DNA? Physicochemical and biochemical characterizations and their relevance in gene therapy. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3926–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Negro, M.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; García-Río, L.; Domènech, O.; Aicart, E.; Tros de Ilarduya, C.; Junquera, E. Multidisciplinary approach to the transfection of plasmid DNA by a nonviral nanocarrier based on a gemini–bolaamphiphilic hybrid lipid. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Negro, M.; Barran-Berdon, A.L.; Aicart-Ramos, C.; Moya, M.L.; de Ilarduya, C.T.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E. Transfection of plasmid DNA by nanocarriers containing a gemini cationic lipid with an aromatic spacer or its monomeric counterpart. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2018, 161, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednar, J.; Woodcock, C.L. Chromatin; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999; Volume 304, pp. 191–213. [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet, J.; Adrian, M.; Chang, J.J.; Homo, J.C.; Lepault, J.; McDowall, A.W.; Schultz, P. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1988, 21, 129–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubochet, J.; Zuber, B.; Eltsov, M.; Bouchet-Marquis, C.; Al-Amoudi, A.; Livolant, F. How to “read” a vitreous section. Methods Cell. Biol. 2007, 79, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.; Cramer, R.D.; Vanopdenbosch, N. Validation of the general-purpose tripos 5.2 force-field. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. New model for calculating atomic charges in molecules. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 3181–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—A rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M. Molecular silverware. I. General-solutions to excluded volume constrained problems. J. Comput. Chem. 1991, 12, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, Y.; Faucher, H.; Gagnaire, D.; Rassat, A. Minimization program of empirical energy of a molecule by simple method. Tetrahedron 1975, 31, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Úbeda, M.; Misra, S.K.; Barrán-Berdón, A.L.; Aicart-Ramos, C.; Sierra, M.B.; Biswas, J.; Kondaiah, P.; Junquera, E.; Bhattacharya, S.; Aicart, E. Why is less cationic lipid required to prepare lipoplexes from plasmid DNA than linear DNA in gene therapy? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18014–18017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrán-Berdón, A.L.; Misra, S.K.; Datta, S.; Muñoz-Úbeda, M.; Kondaiah, P.; Junquera, E.; Bhattacharya, S.; Aicart, E. Cationic gemini lipids containing polyoxyethylene spacers as improved transfecting agents of plasmid DNA in cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4640–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barran-Berdon, A.L.; Martinez-Negro, M.; Garcia-Rio, L.; Domenech, O.; de Ilarduya, C.T.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E. A biophysical study of gene nanocarriers formed by anionic/zwitterionic mixed lipids and pillar-5-arene polycationic macrocycles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3122–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes; Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Micelle shape and size. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 3020–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Theory of micelle formation in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1974, 78, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Nowroozi, A.; Shahlaei, M. Correction: Shedding light on the structural properties of lipid bilayers using molecular dynamics simulation: A review study. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antipina, A.Y.; Gurtovenko, A.A. Molecular-level insight into the interactions of DNA with phospholipid bilayers: Barriers and triggers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36425–36432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Tarek, M.; Klein, M.L. Molecular dynamics study of a lipid-DNA complex. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 10075–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M. Membrane electroporation: A molecular dynamics simulation. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 4045–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtovenko, A.A.; Patra, M.; Karttunen, M.; Vattulainen, I. Cationic DMPC/DMTAP lipid bilayers: Molecular dynamics study. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 3461–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, C.S.; Jas, G.S.; Choosakoonkriang, S.; Koe, G.S.; Smith, J.G.; Middaugh, C.R. The structure of DNA within cationic lipid/DNA complexes. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, P.; Sucunza, D.; Mendicuti, F.; Domingo, A.; Vaquero, J.J. Dibenzopyridoimidazocinnolinium cations: A new family of light-up fluorescent DNA probes. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, P.; Garcia, V.; Bilen, B.S.; Sucunza, D.; Domingo, A.; Mendicuti, F.; Vaquero, J.J. Imidazopyridinium cations: A new family of azonia aromatic heterocycles with applications as DNA intercalators. Dyes Pigments 2017, 138, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Blanco, J.L.; Ortega-Caballero, F.; Blanco-Fernández, L.; Carmona, T.; Marcelo, G.; Martínez-Negro, M.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E.; Mendicuti, F.; Tros de Ilarduya, C.; et al. Trehalose-based Janus cyclooligosaccharides: The “click” synthesis and DNA-directed assembly into pH-sensitive transfectious nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10117–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego-Yerga, L.; Blanco-Fernandez, L.; Urbiola, K.; Carmona, T.; Marcelo, G.; Benito, J.M.; Mendicuti, F.; Tros de Ilarduya, C.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; Garcia Fernandez, J.M. Host-guest-mediated DNA templation of polycationic supramolecules for hierarchical nanocondensation and the delivery of gene material. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 12093–12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


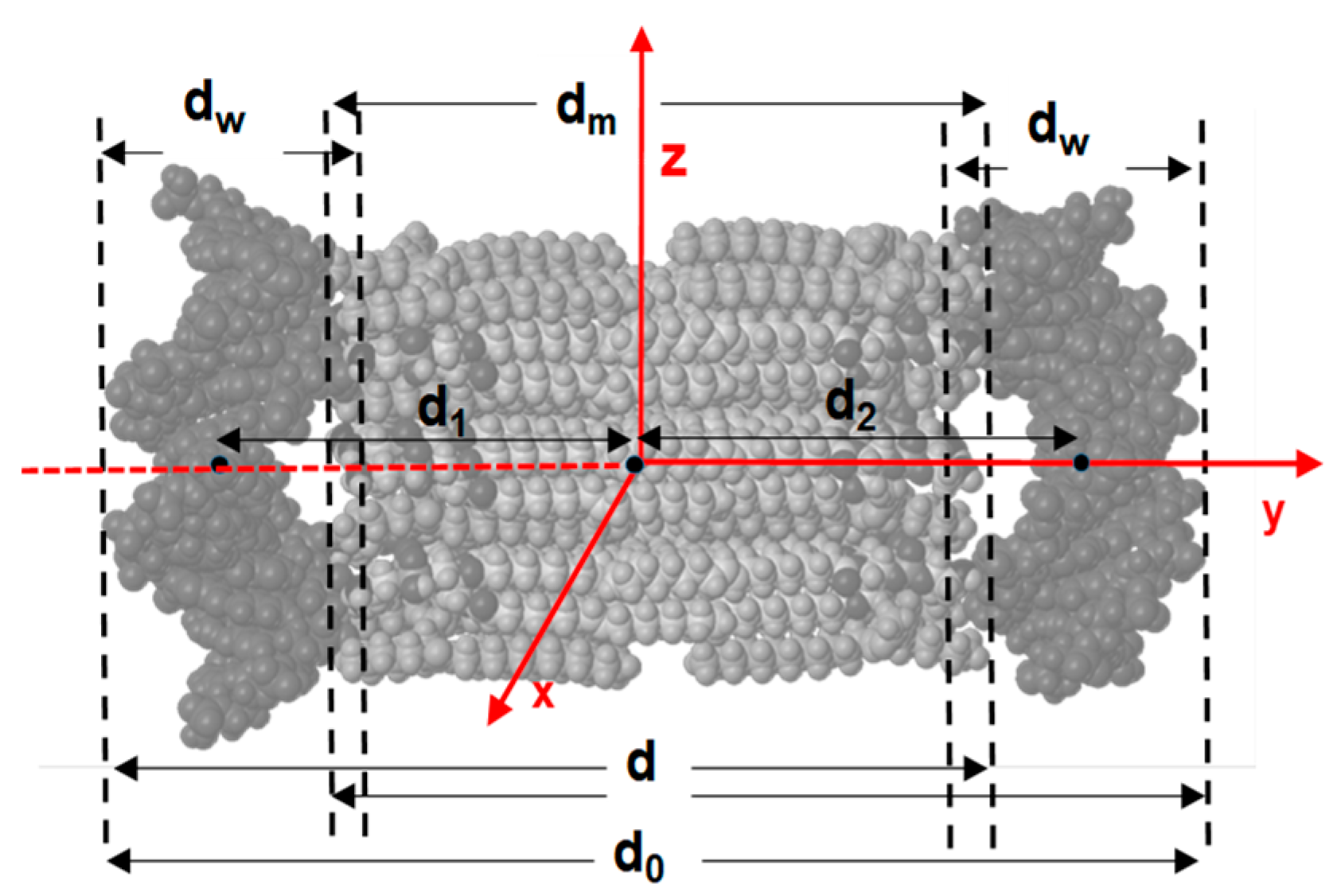


| Distance, nm | MD1 | MD2 | MD3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| d0 | 8.8 ± 0.2 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 8.4 ± 0.1 |
| dm | 4.6 ± 0.3 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 4.6 ± 0.2 |
| dw | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 |
| d | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.1 |
| d1 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.1 |
| d2 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.3 ± 0.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Negro, M.; Sánchez-Arribas, N.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Moyá, M.L.; Tros de Ilarduya, C.; Mendicuti, F.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E. A Non-Viral Plasmid DNA Delivery System Consisting on a Lysine-Derived Cationic Lipid Mixed with a Fusogenic Lipid. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120632
Martínez-Negro M, Sánchez-Arribas N, Guerrero-Martínez A, Moyá ML, Tros de Ilarduya C, Mendicuti F, Aicart E, Junquera E. A Non-Viral Plasmid DNA Delivery System Consisting on a Lysine-Derived Cationic Lipid Mixed with a Fusogenic Lipid. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(12):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120632
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Negro, María, Natalia Sánchez-Arribas, Andrés Guerrero-Martínez, María Luisa Moyá, Conchita Tros de Ilarduya, Francisco Mendicuti, Emilio Aicart, and Elena Junquera. 2019. "A Non-Viral Plasmid DNA Delivery System Consisting on a Lysine-Derived Cationic Lipid Mixed with a Fusogenic Lipid" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 12: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120632
APA StyleMartínez-Negro, M., Sánchez-Arribas, N., Guerrero-Martínez, A., Moyá, M. L., Tros de Ilarduya, C., Mendicuti, F., Aicart, E., & Junquera, E. (2019). A Non-Viral Plasmid DNA Delivery System Consisting on a Lysine-Derived Cationic Lipid Mixed with a Fusogenic Lipid. Pharmaceutics, 11(12), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120632







