Preparation and Evaluation of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanoemulgel on Wound-Healing Efficacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Topical ATR Formulations
2.2.1. Preparation of Gel
2.2.2. Preparation of Emulgel
2.2.3. Preparation of Nanoemulgel
2.3. Physical Examination
2.3.1. Spreadability Test
2.3.2. Rheological Studies
2.3.3. Particle Characterization
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release Study
- a.
- Zero order model Q = Q0 + kt;
- b.
- First order model Q = Q0 × ekt;
- c.
- Higuchi model Q = k × t0.5;
- d.
- Korsmeyer-Peppas model Q = k × tn;
2.5. Preliminary Stability Testing
2.6. Ex Vivo Evaluation of ATR Release (Permeation Study)
2.6.1. Preparation of Rat Skin
2.6.2. Permeation of ATR from Different Formulations
- SSTF = amount of permeated drug/(area × time);
- ER = SSTF from test/SSTF from control.
2.7. In Vivo Evaluation of Wound Healing Efficiency
2.7.1. Experimental Design
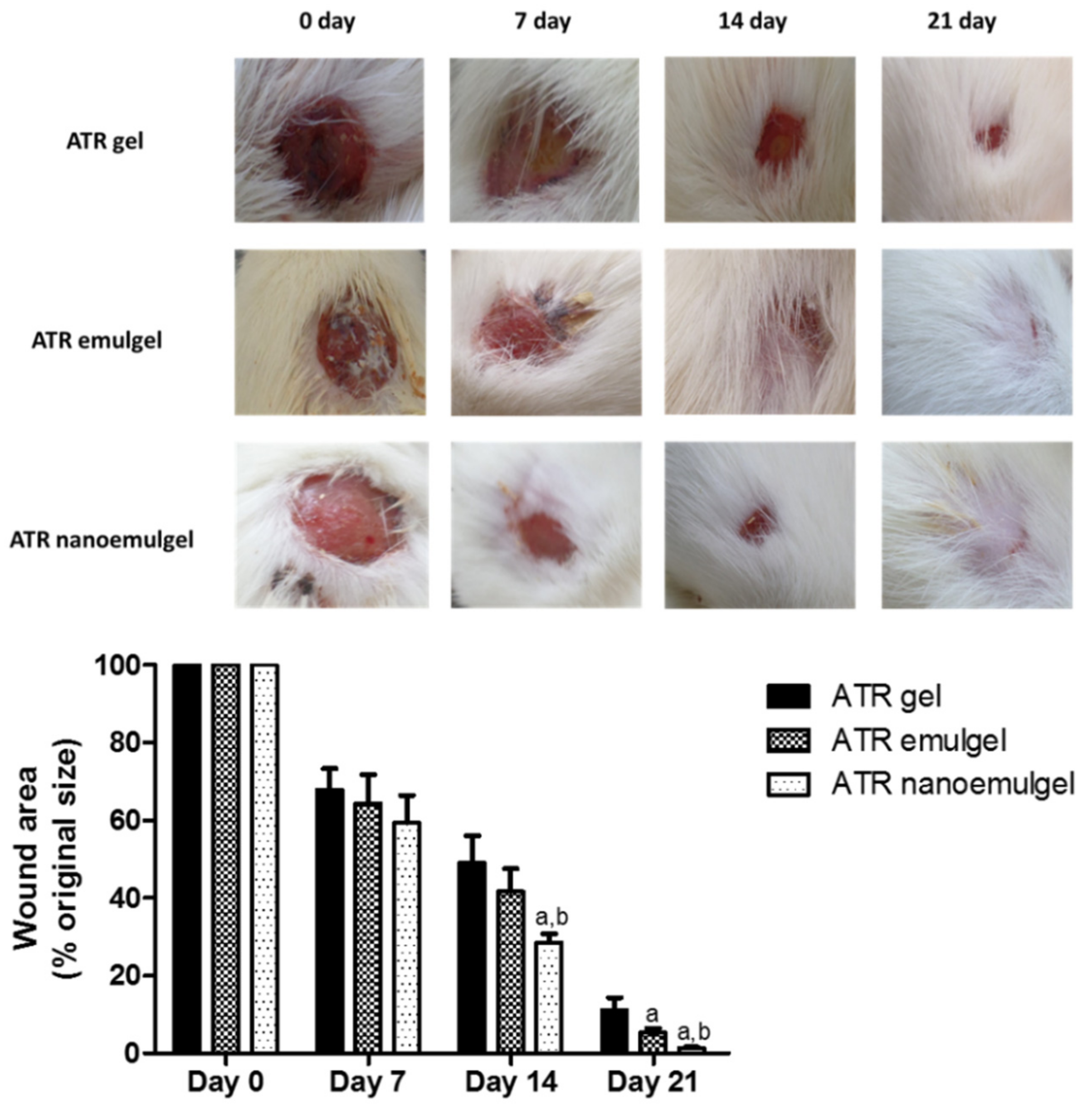
2.7.2. Quantification of Wound Area
2.8. Skin Irritation Studies
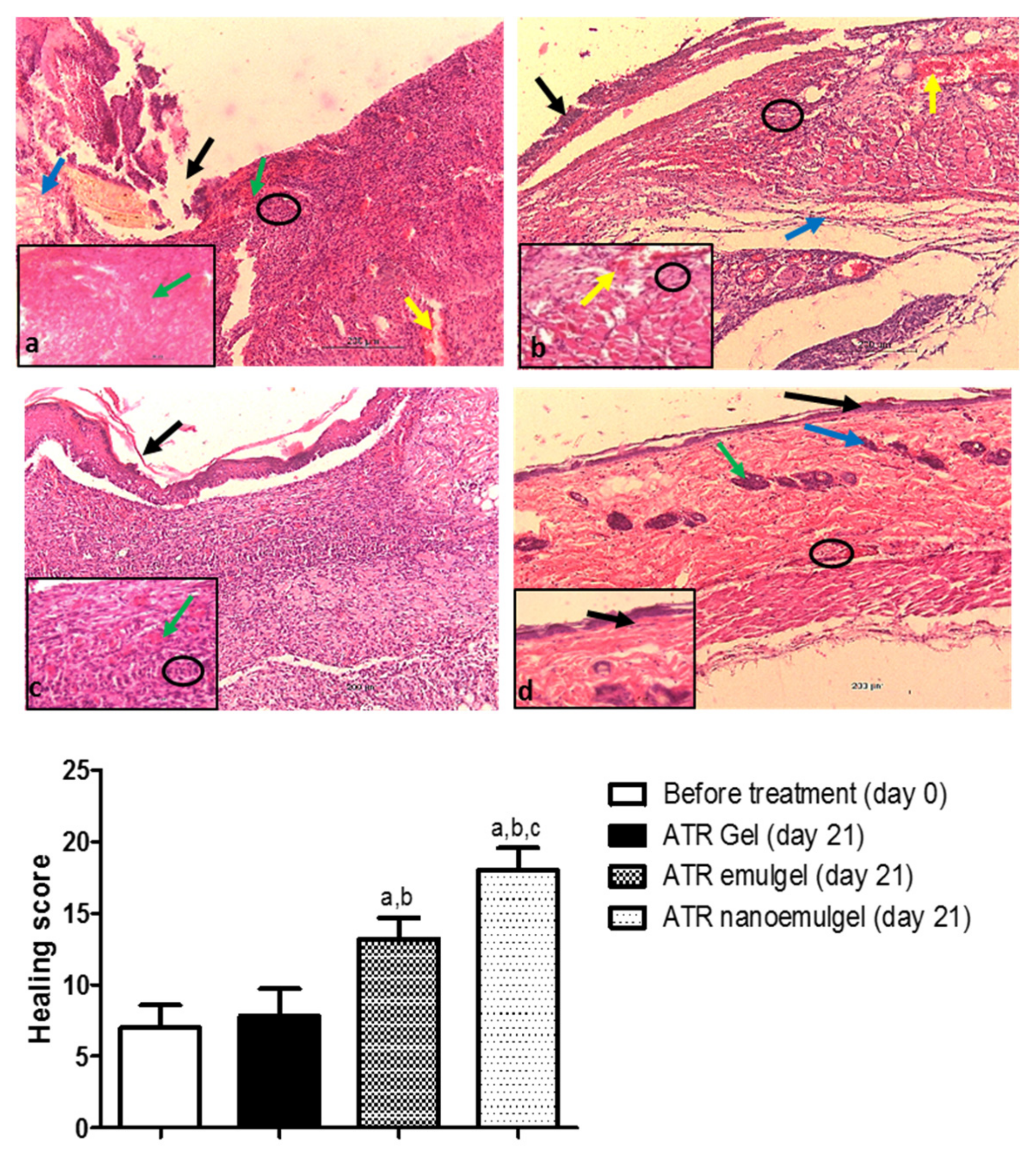
2.9. Histologic Evaluations
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Examination
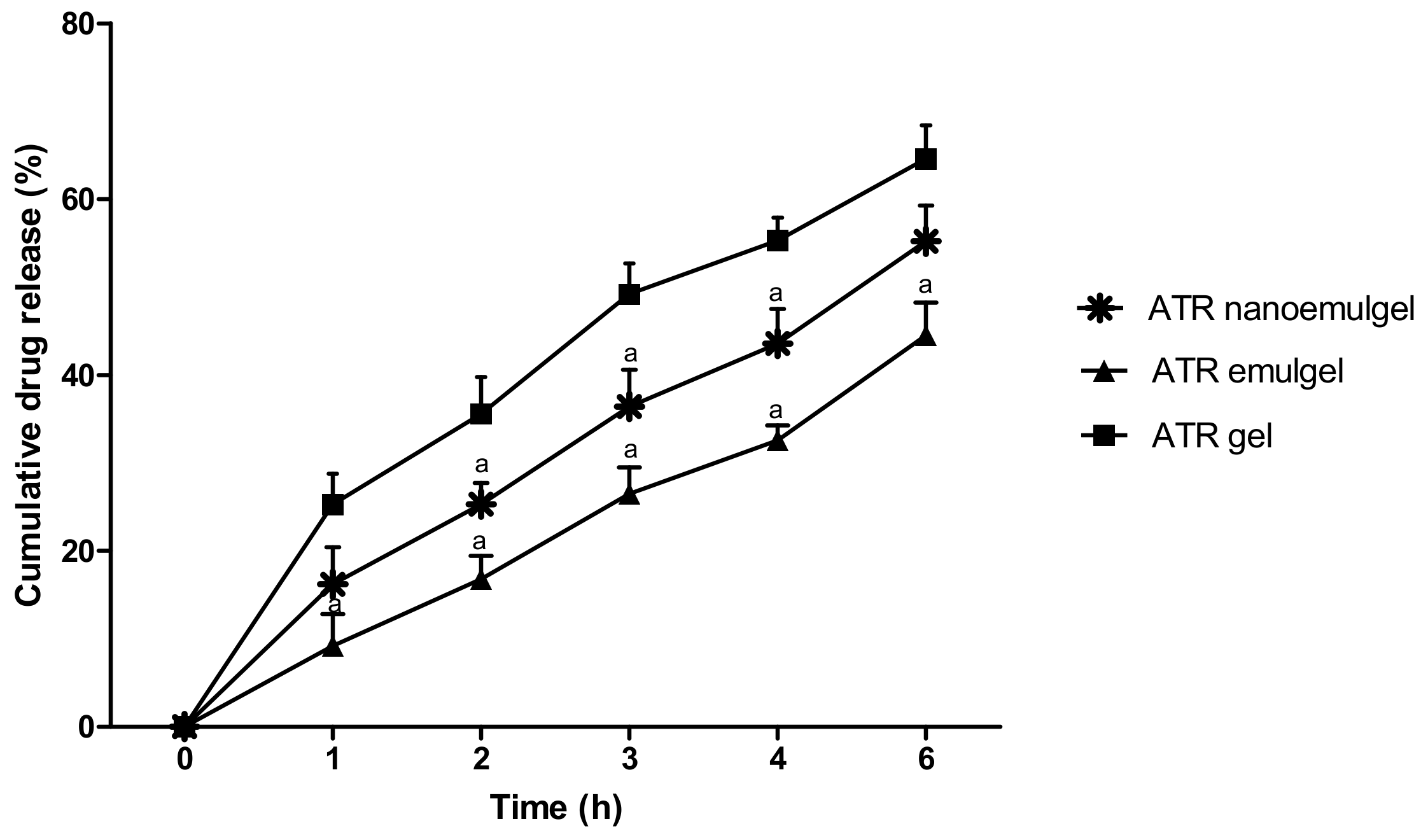
3.2. In Vitro Release of the Drug
3.3. Stability Study of ATR-Loaded Formulations
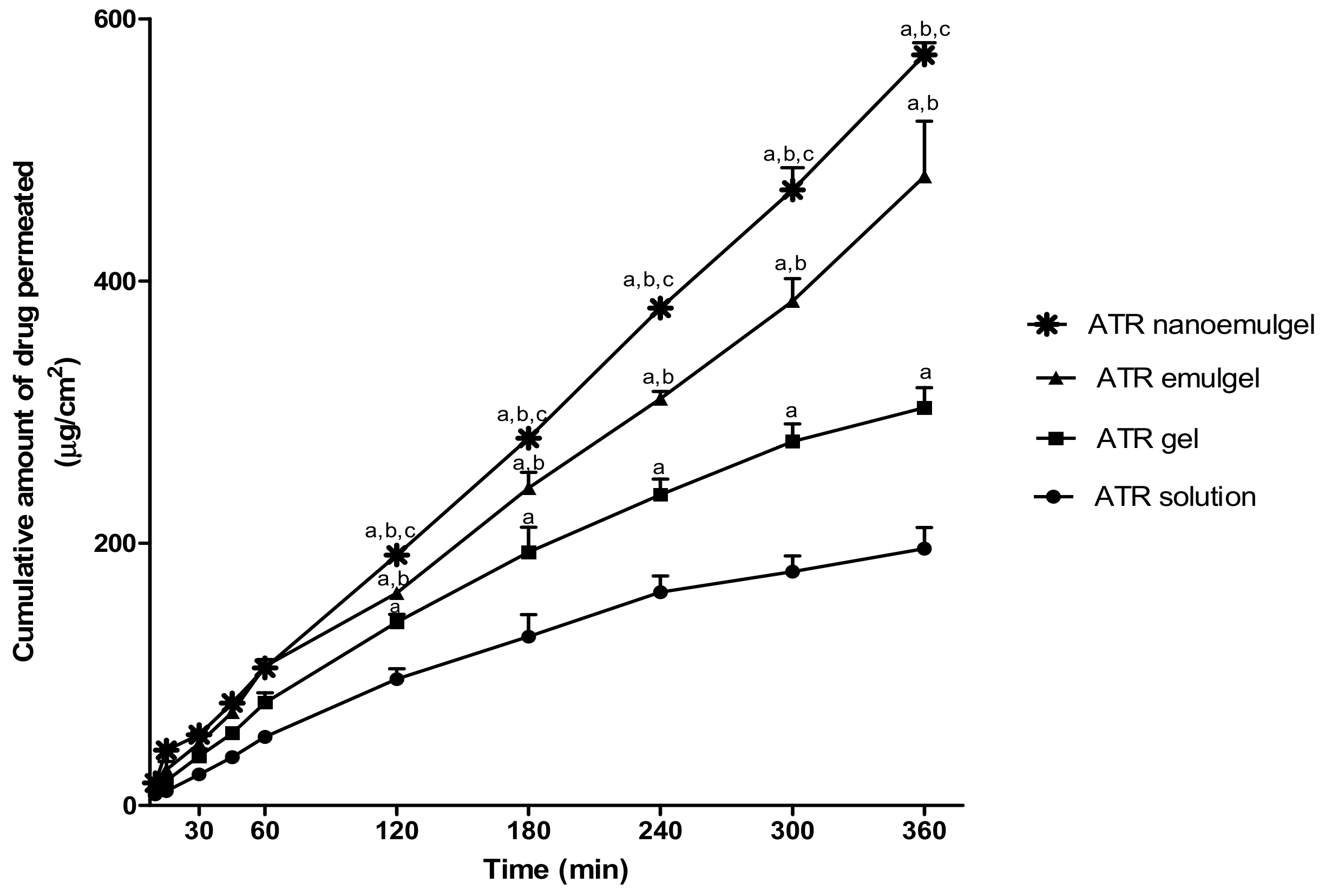
3.4. Ex Vivo Study (Permeation Study)
3.5. In Vivo Wound Healing Efficiency
3.6. Skin Irritation Testing
3.7. Histopathological Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, J.; Sorg, H. Wound repair and regeneration. Eur. Surg. Res. 2012, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooradian, A.D. Evidence-Based Cardiovascular Risk Management in Diabetes. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drug 2019, 19, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Korashi, L.; Soliman, M.; Attwa, E.; Mohamed, N. Role of Atorvastatin in Treatment of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Patients: A Controlled Clinical Trial. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2018, 25, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramessur, R.; Gill, D. The effect of statins on severity of psoriasis: A systematic review. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2017, 83, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadvand, A.; Yazdanfar, A.; Yasrebifar, F.; Mohammadi, Y.; Mahjub, R.; Mehrpooya, M. Evaluating the effects of oral and topical simvastatin in the treatment of acne vulgaris: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Banhesse, V.F.; Azevedo, F.F.; Araujo, E.P.; do Amaral, M.E.; Caricilli, A.M.; Saad, M.J.; Lima, M.H. Effect of atorvastatin on wound healing in rats. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2015, 17, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liao, J.K. Pleiotropic effects of statins. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, H.; Gorain, B.; Pandey, M.; Chatterjee, L.A.; Sengupta, P.; Das, A.; Molugulu, N.; Kesharwani, P. Recent update on nanoemulgel as topical drug delivery system. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, J.; Takenaka, H.; Hirakawa, S.; Sakabe, J.-i.; Hagura, A.; Kishimoto, S.; Maruyama, K.; Kajiya, K.; Kinoshita, S.; Tokura, Y. Topical simvastatin accelerates wound healing in diabetes by enhancing angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracht, L.; Caparroz-Assef, S.M.; Magon, T.F.d.S.; Ritter, A.M.V.; Cuman, R.K.N.; Bersani-Amado, C.A. Topical anti-inflammatory effect of hypocholesterolaemic drugs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuvonen, P.J.; Niemi, M.; Backman, J.T. Drug interactions with lipid-lowering drugs: Mechanisms and clinical relevance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 80, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennernäs, H. Clinical pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 1141–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellosta, S.; Corsini, A. Statin drug interactions and related adverse reactions: An update. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2018, 17, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsaei, S.; Khalili, H.; Farboud, E.S. Potential role of statins on wound healing: Review of the literature. Int. Wound J. 2012, 9, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Verma, R. In vitro evaluation of topical gel prepared using natural polymer. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2010, 2, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvey, S.; Rao, J.V.; Arumugam, K.M. Transdermal drug delivery system: A mini review. Pharma Innov. 2019, 8, 181–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, R.; Ahmed, N.; Ullah, N.; Khan, M.I.; Elaissari, A. Biodegradable ingredient-based emulgel loaded with ketoprofen nanoparticles. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2018, 19, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.; Dudhe, R.; Sharma, P. Nanoemulsion: An advanced mode of drug delivery system. 3 Biotech. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtab, A.; Anwar, M.; Mallick, N.; Naz, Z.; Jain, G.K.; Ahmad, F.J. Transungual delivery of ketoconazole nanoemulgel for the effective management of onychomycosis. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2016, 17, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Bonde, S.R.; Gaikwad, S.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.K.; Rai, M. Lawsonia inermis-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Activity against human pathogenic fungi and bacteria with special reference to formulation of an antimicrobial nanogel. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 8, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.S.; Ali, M.S.; Alam, N.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Shamim, M.; Safhi, M. In vivo study of clobetasol propionate loaded nanoemulsion for topical application in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Drug Invent. Today 2013, 5, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Shehata, T. The enhancement of transdermal permeability of water soluble drug by niosome-emulgel combination. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, M.G.; Reis, S.A.; Damasceno, C.M.; Rolim, L.A.; Rolim-Neto, P.J.; Carvalho, F.O.; Quintans-Junior, L.J.; Almeida, J.R. Development and evaluation of stability of a gel formulation containing the monoterpene borneol. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 7394685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S.; Patel, R.K.; Shah, H.; Shehata, T.M.; Morsy, M.A. Nanoemulsion based vehicle for effective ocular delivery of moxifloxacin using experimental design and pharmacokinetic study in rabbits. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, H. Transdermal permeation of drugs in various animal species. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ravenzwaay, B.; Leibold, E. A comparison between in vitro rat and human and in vivo rat skin absorption studies. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2004, 23, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmataeeshy, M.E.; Sokar, M.S.; Bahey-El-Din, M.; Shaker, D.S. Enhanced transdermal permeability of Terbinafine through novel nanoemulgel formulation; Development, in vitro and in vivo characterization. FJPS 2018, 4, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, P.; Mounika, K.; Saroja, C. Transdermal permeation enhancement of lamotrigine using terpenes. J. Pharma Care Health Sys. 2014, 1, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Si, S.; Swain, S.; Kanungo, S.; Gupta, R. Preparation and evaluation of gels from gum of Moringa oleifera. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 68, 777–780. [Google Scholar]
- Hazrati, M.; Mehrabani, D.; Japoni, A.; Montasery, H.; Azarpira, N.; Hamidian-Shirazi, A.; Tanideh, N. Effect of honey on healing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infected burn wounds in rat. Appl. Anim. Res. 2010, 37, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ala, S.; Alvandipour, M.; Saeedi, M.; Hamidian, M.; Shiva, A.; Rahmani, N.; Faramarzi, F. Effects of topical atorvastatin (2%) on posthemorrhoidectomy pain and wound healing: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, G.; Puri, V.; Kumar, L.; Bansal, A.K. Solid state characterization of commercial crystalline and amorphous atorvastatin calcium samples. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2010, 11, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palanisamy, M.; James, A.; Khanam, J. Atorvastatin–cyclodextrin systems: Physiochemical and biopharmaceutical evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.S.; Swapna, G.; Lakshmi, G.S.S.; Swathi, S.; Jyothi, G.N.; Devi, A.S. Formulation and evaluation of herbal emulgel of Lantana camara leaves extract for wound healing activity in diabetic rats. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 6, 6404–6417. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, N.K.; Wang, D. Salt effects on the diffusion and release rate of propranolol from poloxamer 407 gels. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 167, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, U.F. Preparation and evaluation of novel topical gel preparations for wound healing in diabetics. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 532–536. [Google Scholar]
- Majithiya, R.J.; Ghosh, P.K.; Umrethia, M.L.; Murthy, R.S. Thermoreversible-mucoadhesive gel for nasal delivery of sumatriptan. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2006, 7, E80–E86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Setouhy, D.A.; Ahmed El-Ashmony, S.M. Ketorolac trometamol topical formulations: Release behaviour, physical characterization, skin permeation, efficacy and gastric safety. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.M.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Aziz, R.; Elmarzugi, N.A. Preparation, characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of Swietenia macrophylla nanoemulgel. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, B.; Aggarwal, G.; Harikumar, S. Enhanced transdermal permeability of piroxicam through novel nanoemulgel formulation. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 4, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rai, V.K.; Mishra, N.; Yadav, K.S.; Yadav, N.P. Nanoemulsion as pharmaceutical carrier for dermal and transdermal drug delivery: Formulation development, stability issues, basic considerations and applications. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamala, U. Development & optimization of allyl amine antifungal nanoemulgel using 23 factorial design: For the treatment of tinea pedis. Eur. Sci. J. 2013, 4, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, J.; Gautam, A.; Komath, S.; Bano, M.; Garg, A.; Jain, K. Topical nano-emulgel for skin disorders: Formulation approach and characterization. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-C.; Chiang, B.-H.; Huang, D.-W.; Li, P.-H. Skin permeation of D-limonene-based nanoemulsions as a transdermal carrier prepared by ultrasonic emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefelbein, D.; Goren, I.; Fisslthaler, B.; Schmidt, H.; Geisslinger, G.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Frank, S. Biphasic regulation of HMG-CoA reductase expression and activity during wound healing and its functional role in the control of keratinocyte angiogenic and proliferative responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15479–15490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandya, V.M.; Patel, J.K.; Patel, D.J. Formulation, optimization and characterization of simvastatin nanosuspension prepared by nanoprecipitation technique. Pharm. Lett. 2011, 3, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan, S.; Pastar, I.; Drakulich, S.; Dikici, E.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S. Nanotechnology-driven therapeutic interventions in wound healing: Potential uses and applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formulation | Atorvastatin (% w/w) | Carboxymethyl Cellulose (% w/w) | Liquid Paraffin (mL) | Tween 80 (mL) | Propylene Glycol (mL) | Water Up To (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gel | 2.5 | 1 | - | - | - | 50 |
| Emulgel | 2.5 | 1 | 12.5 | 1 | 1 | 50 |
| Nanoemulgel | 2.5 | 1 | 12.5 | 1 | 1 | 50 |
| Properties | ATR Gel | ATR Emulgel | ATR Nanoemulgel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Fresh | White, Opaque | White, Opaque | White, Opaque |
| Stored | White, Opaque | White, Opaque | White, Opaque | |
| Homogeneity | Fresh | Homogenous | Homogenous | Homogenous |
| Stored | Homogenous | Homogenous | Homogenous | |
| Spreadability (mm) | Fresh | 66 ± 0.88 | 54 ± 0.95 a | 51 ± 0.66 a |
| Stored | 61 ± 0.60 | 52 ± 0.55 a | 49 ± 0.25 a | |
| Viscosity (cp) | Fresh | 58,500 ± 450 | 97,250 ± 1150 a | 85,900 ± 2050 a,b |
| Stored | 61,350 ± 850 | 101,550 ± 2250 a | 97,500 ± 3150 a,b | |
| Mathematical Models | ATR Gel | ATR Emulgel | ATR Nanoemulgel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero order | 0.943 | 0.989 | 0.979 |
| First order | 0.879 | 0.901 | 0.906 |
| Higuchi | 0.983 | 0.994 | 0.995 |
| Korsmeyer-Peppas | 0.975 | 0.988 | 0.989 |
| Time | ATR Sol | ATR Gel | ATR Emulgel | ATR Nanoemulgel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSTF (µg/cm2·h) | 34.39 ± 1.18 | 51.89 ± 1.71 a | 76.11 ± 3.47 a,b | 95.39 ± 1.55 a,b,c |
| Lag time (min) | 24.59 ± 5.48 | 21.08 ± 4.53 | 6.94 ± 1.77 a,b | 3.31 ± 1.33 a,b |
| ER (folds) | 1.00 | 1.55 a | 2.45 a,b | 2.92 a,b,c |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morsy, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, R.G.; Nair, A.B.; Venugopala, K.N.; Ahmed, A.F.; Elsewedy, H.S.; Shehata, T.M. Preparation and Evaluation of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanoemulgel on Wound-Healing Efficacy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110609
Morsy MA, Abdel-Latif RG, Nair AB, Venugopala KN, Ahmed AF, Elsewedy HS, Shehata TM. Preparation and Evaluation of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanoemulgel on Wound-Healing Efficacy. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(11):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110609
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorsy, Mohamed A., Rania G. Abdel-Latif, Anroop B. Nair, Katharigatta N. Venugopala, Amira F. Ahmed, Heba S. Elsewedy, and Tamer M. Shehata. 2019. "Preparation and Evaluation of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanoemulgel on Wound-Healing Efficacy" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 11: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110609
APA StyleMorsy, M. A., Abdel-Latif, R. G., Nair, A. B., Venugopala, K. N., Ahmed, A. F., Elsewedy, H. S., & Shehata, T. M. (2019). Preparation and Evaluation of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanoemulgel on Wound-Healing Efficacy. Pharmaceutics, 11(11), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110609









