Synthesis, Principles, and Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles for In Vivo Imaging Applications—A Review
Abstract
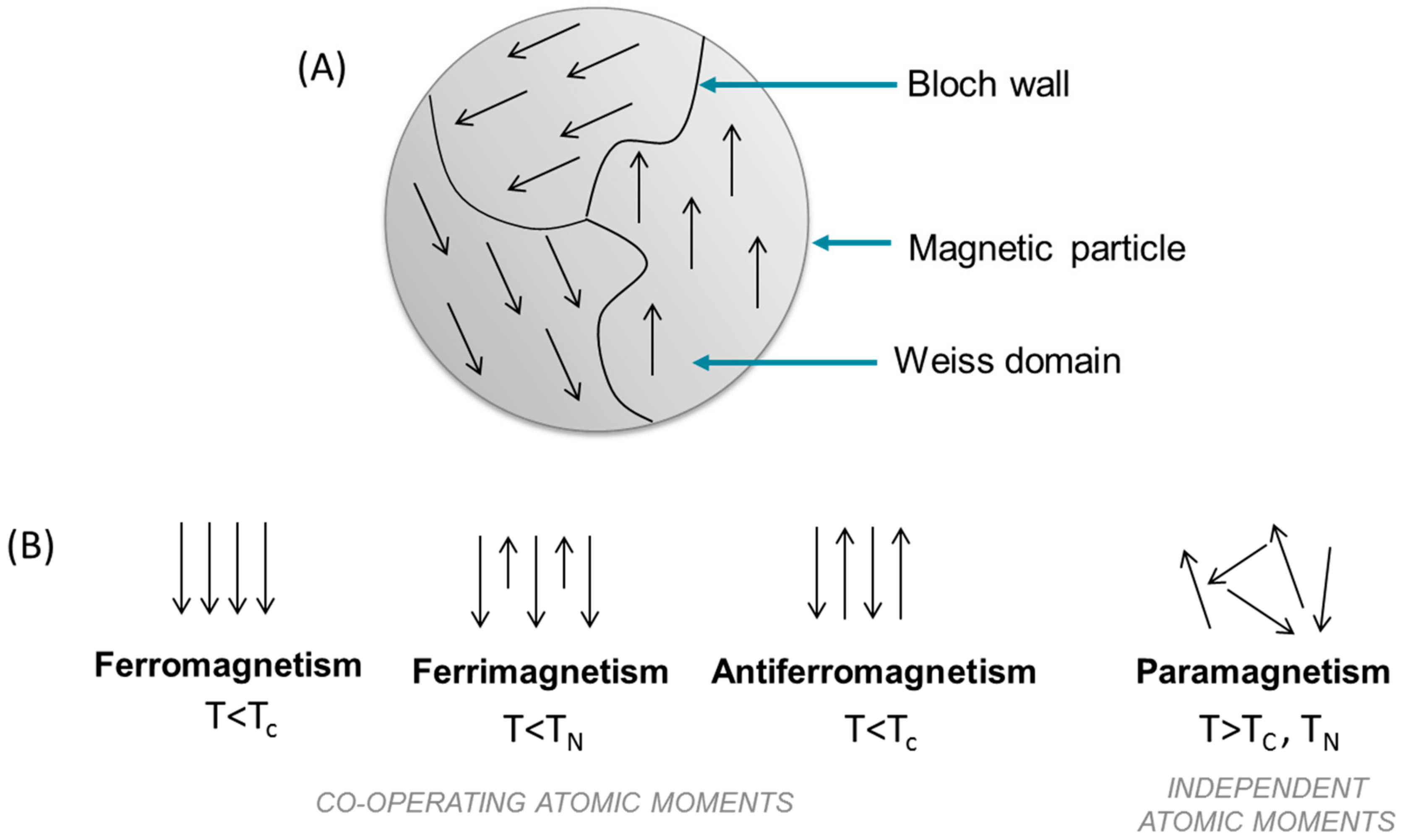
1. Introduction to Magnetism: From Particles to Nanoparticles
2. Nanoscale Magnetic Material for Biomedical Applications: Current Trends and Requirements
3. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
3.1. Three Main Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
3.2. The Need of Surface Functionalization and Stabilization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
3.3. Effect of Iron Oxide Design on Magnetism
3.4. What About the Consequence After In Vivo Injection of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles?
4. Preparation of Magnetite
4.1. Formation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
4.2. Synthesis of Magnetite SPIONs
5. Further Outlook
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaefthymiou, G.C. Nanoparticle magnetism. Nano Today 2009, 4, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, S.; Ericsson, T.; Wäppling, R. Characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Thin Solid Films 2006, 515, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, N.A.; Peng, S.; Cheng, K.; Sun, S. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, functionalization, and applications in bioimaging and magnetic energy storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teja, A.S.; Koh, P. Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2009, 55, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulwahab, K.; Malik, M.A.; O’Brien, P.; Govender, K.; Muryn, C.A.; Timco, G.A.; Tunac, F.; Winpenny, R.E.P. Synthesis of monodispersed magnetite nanoparticles from iron pivalate clusters. Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.J.; Dunnill, P.; Lilly, M.D. The properties of magnetic supports in relation to immobilized enzyme reactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1973, 15, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Multifunctional nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzyna, P.A.; Gianella, A.; Skajaa, T.; Knudsen, G.; Deddens, L.H.; Cormode, D.P.; Fayad, Z.A.; Mulder, W.J.M. Multifunctional imaging nanoprobes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 2, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, H.B.; Song, I.C.; Hyeon, T. Inorganic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goesmann, H.; Feldmann, C. Nanoparticulate functional materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1362–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Lee, J.S.H.; Zhang, M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimpha, N.; Chaleawlert-Umpon, S.; Sunintaboon, P. Core/shell polymethyl methacrylate/polyethyleneimine particles incorporating large amounts of iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization. Polymer 2012, 53, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. Recent metallic materials for biomedical applications. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadghiri, Y.Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Hoang, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Xu, H.; Tsui, W.; Li, Y.; Boutajangout, A.; Wang, A.; et al. Detection of Amyloid Plaques Targeted by Bifunctional USPIO in Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mice Using Magnetic Resonance Microimaging. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.A.M.K.; Ficiarà, E.; Ruffinatti, F.A.; Stura, I.; Argenziano, M.; Abollino, O.; Cavalli, R.; Guiot, C.; D’Agata, F. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Functionalization for Biomedical Applications in the Central Nervous System. Materials 2019, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T.; Jiang, C.; Kim, W.-S. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 23501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharisov, B.I.; Rasika Dias, H.V.; Kharissova, O.V.; Manuel Jiménez-Pérez, V.; Olvera Pérez, B.; Muñoz Flores, B. Iron-containing nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, and environmental applications. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 9325–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molday, R.S.; MacKenzie, D. Immunospecific ferromagnetic iron-dextran reagents for the labeling and magnetic separation of cells. J. Immunol. Methods 1982, 52, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasset, F.; Duguet, E.; Mornet, S.; Vasseur, S.; Grasset, F.; Duguet, E. Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical diagnosis and therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Bañobre-López, M.; Teijeiro, A.; Rivas, J. Magnetic nanoparticle-based hyperthermia for cancer treatment. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2013, 18, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Fan, K.; Yan, X. Iron Oxide Nanozyme: A Multifunctional Enzyme Mimetic for Biomedical Applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3207–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, B.; Devi, K.S.P.; Dutta, S.; Maiti, T.K.; Pramanik, P.; Dhara, D. Biocompatible mesoporous silica-coated superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and MR imaging applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 431, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.A.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, P.; Brown, S.C.; Moudgil, B.M. Nanoparticles as contrast agents for in-vivo bioimaging: Current status and future perspectives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouli, S.K.; Tyler, P.; McDevitt, J.L.; Eifler, A.C.; Guo, Y.; Nicolai, J.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Li, W.; Procissi, D.; Ryu, R.K.; et al. Image-guided local delivery strategies enhance therapeutic nanoparticle uptake in solid tumors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7724–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Sant, S.; Wang, B.; Laurent, S.; Sen, T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): Development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormode, D.P.; Skajaa, T.; Fayad, Z.A.; Mulder, W.J.M. Nanotechnology in medical imaging: Probe design and applications. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhatkar, A.G.; Jamison, A.C.; Litvinov, D.; Willson, R.C.; Lee, T.R. Tuning the magnetic properties of nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15977–16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, R.; Chen, W.; Bartels, M.; Perez-Torres, C.; Botero, M.F.; McAninch, R.W.; Contreras, A.; Schiff, R.; Pautler, R.G.; Halas, N.J.; et al. Tracking of multimodal therapeutic nanocomplexes targeting breast cancer in vivo. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4920–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Gao, F.; Gu, H. Magnetic polymer nanospheres with high and uniform magnetite content. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 288, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, I.J.; Taylor, J.; Todd, M.; Davies, M.J.; Borioni, E.; Sangregorio, C.; Sen, T. Synthesis, characterisation and application of silica-magnetite nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 284, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Asadi, R.; Doak, S.H. Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev. 2010, 1, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonov, I.; Yaresko, A.N. On the Verwey charge ordering in magnetite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Vander Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüle, A.; Nieken, U.; Shekhah, O.; Ranke, W.; Schlögl, R.; Kolios, G. Styrene synthesis over iron oxide catalysts: From single crystal model system to real catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 3619–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girginova, P.I.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.; Lopes, C.B.; Figueira, P.; Otero, M.; Amaral, V.S.; Pereira, E.; Trindade, T. Silica coated magnetite particles for magnetic removal of Hg2+from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, S.L.; Pessan, P.J.; Vieira, P.A.; Lima, M.T.; Delbem, C.A.; Monteiro, R.D. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: A Perspective on Synthesis, Drugs, Antimicrobial Activity, and Toxicity. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Yeap, S.P.; Che, H.X.; Low, S.C. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticle by dynamic light scattering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodhia, J.; Mandarano, G.; Ferris, N.J.; Eu, P.; Cowell, S.F. Development and use of iron oxide nanoparticles (Part 1): Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2010, 6, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulińska-Litewka, J.; Łazarczyk, A.; Hałubiec, P.; Szafrański, O.; Karnas, K.; Karewicz, A. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles—Current and Prospective Medical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhosh, P.B.; Ulrih, N.P. Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Promising tools in cancer theranostics. Cancer Lett. 2013, 336, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daou, T.J.; Grenèche, J.M.; Pourroy, G.; Buathong, S.; Derory, A.; Ulhaq-Bouillet, C.; Donnio, B.; Guillon, D.; Begin-Colin, S. Coupling agent effect on magnetic properties of functionalized magnetite-based nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5869–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.H.; Wang, J.P.; Luo, H.L. Crystallite size effect on saturation magnetization of fine ferrimagnetic particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1994, 136, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, N.R.; Chen, Y.; Peng, X. Size- and shape-controlled magnetic (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) oxide nanocrystals via a simple and general approach. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3931–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMer, V.K.; Dinegar, R.H. Theory, Production and Mechanism of Formation of Monodispersed Hydrosols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 4847–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.D.; Lorber, B.; Witz, J.; Théobald-Dietrich, A.; Kern, D.; Giegé, R. The crystallization of biological macromolecules from precipitates: Evidence for Ostwald ripening. J. Cryst. Growth 1996, 168, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaj, P.; del Puerto Morales, M.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; González-Carreño, T.; Serna, C.J. The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, B.; Feng, L. Preparation and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2012, 68, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharde, A.; Wani, A.; Shouche, Y.; Joy, P.A.; Prasad, B.L.V.; Sastry, M. Bacterial aerobic synthesis of nanocrystalline magnetite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9326–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharde, A.; Rautaray, D.; Bansal, V.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, I.; Yusuf, S.M.; Sanyal, M.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetite using fungi. Small 2006, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Bae, C.J.; Park, J.G.; Noh, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Hyeon, T. Large-scale synthesis of uniform and crystalline magnetite nanoparticles using reverse micelles as nanoreactors under reflux conditions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, G.; Fibvet-vincent, F.; Fibvet, F. Monodisperse iron-based particles - Precipitation in liquid polyols. J. Mater. Chem. 1996, 6, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toneguzzo, P.; Viau, G.; Acher, O.; Guillet, F.; Vievet-Vincent, F.; Fievet, F. CoNi and FeCoNi fine particles prepared by the polyol process: Physico-chemical characterization and dynamic magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fievet, F.; Lagier, J.P.; Blin, B.; Beaudoin, B.; Figlarz, M. Homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleations in the polyol process for the preparation of micron and submicron size metal particles. Solid State Ion. 1989, 32–33, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Cai, W.; Meng, X.; Liu, E. Monodisperse water-soluble magnetite nanoparticles prepared by polyol process for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Chem. Commun. 2007, 4, 5004–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wu, H.; Guo, B.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xie, A. Facile synthesis and excellent recyclable photocatalytic activity of pine cone-like Fe3O4@Cu2O/Cu porous nanocomposites. Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 4915–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daou, T.J.; Pourroy, G.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Grenèche, J.M.; Ulhaq-Bouillet, C.; Legaré, P.; Bernhardt, P.; Leuvrey, C.; Rogez, G. Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4399–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, F.; Kockar, H.; Karaagac, O. Growth of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Process: Effect of Reaction Parameters on the Nanoparticle Size. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2015, 28, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sun, J.; Fan, F.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; et al. Ferumoxytol of ultrahigh magnetization produced by hydrocooling and magnetically internal heating co-precipitation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 7369–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, R.; Koltypin, Y.; Felner, I.; Gedanken, A. Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of pure nanometer-sized Fe3O4particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 286, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, L.; Gutierrez, S.; Menendez, N.; Morales, M.P.; Herrasti, P. Magnetite nanoparticles: Electrochemical synthesis and characterization. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indira, T.K.; Lakshmi, P.K. Magnetic nanoparticles—A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotech. 2010, 3, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, M.; Schultz, E.A.; Sun, T.; Meade, T.; Dravid, V.P. Synthesis of amine-stabilized aqueous colloidal iron oxide nanoparticles. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Zhang, W. Green synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Zhang, X.; Chang, W. Novel Bifuncitonal One-Dimensional Fe3O4/Se Nanocomposites via Facile Green Synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4846–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, J.L.; Fleming, D.A.; Stone, M.B.; Schiffer, P.; Williams, M.E.; Park, U.V.; Pennsyl, V. Synthesis of Fe Oxide CoreAu Shell. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Risbud, S.; Rabolt, J.F.; Stroeve, P. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanometer-Size Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 Particles. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 2209–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruntu, D.; Cushing, B.L.; Caruntu, G.; O’Connor, C.J. Attachment of Gold Nanograins onto Colloidal Magnetite Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3398–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, S.; Hou, P.; Yang, Y.; Weng, J.; Li, X.; Li, M. Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 67, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Shi, X.; Van Antwerp, M.; Cao, Z.; Swanson, S.D.; Bi, X.; Baker, J.R. Dendrimer-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for specific targeting and imaging of cancer cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3043–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeon, T.; Lee, S.S.; Park, J.; Chung, Y.; Na, H.B. Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse maghemite nanocrystallites without a size-selection process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 12798–12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockenberger, J.; Scher, E.C.; Alivisatos, A.P. A new non-hydrolytic single-precursor approach to surfactant-capped nanocrystals of transition metal oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11595–11596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G. Monodisperse MFe2O4(M = Fe, Co, Mn) Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, II, 8204–8205. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Fan, Q.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, I.S.; Engelhard, M.H.; Lin, Y.; Kim, N.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhong, C.J. Monodispersed core-shell Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 21593–21601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, J.; García, I.; Padro, D.; Arnáiz, B.; Penadés, S. Water-soluble magnetic glyconanoparticles based on metal-doped ferrites coated with gold: Synthesis and characterization. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10010–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, I.; Gallo, J.; Genicio, N.; Padro, D.; Penadés, S. Magnetic glyconanoparticles as a versatile platform for selective immunolabeling and imaging of cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, C.M.; Sharma, A.; Sumana, G.; Tiwari, I.; Malhotra, B.D. Cationic poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) iron oxide microspheres for nucleic acid detection. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3800–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Li, Y.; Niu, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Gu, J.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, J. A simple route to prepare monodisperse Au NP-decorated, dye-doped, superparamagnetic nanocomposites for optical, MR, and CT trimodal imaging. Small 2013, 9, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carril, M.; Fernández, I.; Rodríguez, J.; García, I.; Penadés, S. Gold-coated iron oxide glyconanoparticles for MRI, CT, and US multimodal imaging. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Bao, H.; Gao, M. One-Pot Reaction to Synthesize Water-Soluble Magnetite Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Falkner, J.C.; Yavuza, C.T.; Colvin, V.L. Synthesis of monodisperse iron oxide nanocrystals by thermal decomposition of iron carboxylate salts. Chem. Comm. 2004, 20, 2306–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.E.G.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, N.M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Cho, H.R.; Oh, M.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, B.H.; Shin, K.; Ahn, T.Y.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, Y.W.; et al. Multifunctional Fe3O4/TaOxcore/shell nanoparticles for simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging and X-ray computed tomography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10309–10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra-Sanchez, J.J.; Fuentes-Ramirez, R.; Roca, A.G.; Del Puerto Morales, M.; Cabrera-Lara, L.I. Key parameters for scaling up the synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles in organic media: Stirring rate and growth kinetic. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 17841–17847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.P.; Pecharroman, C.; Gonzalez Carreno, T.; Serna, C.J. Structural Characteristics of Uniform γ-Fe2O3 Particles with Different Axial (Length/Width) Ratios. J. Solid State Chem. 1994, 108, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.P.; Montero, M.I.; Serna, C.J. Structural effects on the magnetic properties of -Fe O nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 203, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigue-Millot, N.; Champion, Y.; Hÿtch, M.J.; Bernard, F.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Perriat, P. Chemical heterogeneities in nanometric titanomagnetites prepared by soft chemistry and studied ex situ: Evidence for fe-segregation and oxidation kinetics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 7125–7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perriat, P.; Domenichini, B.; Gillot, B. A model for oxidation in finely divided ferrites taking into account the stresses generated during reaction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1996, 57, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparazzo, E. On the quantitative XPS analysis of Fe2O3 and Fe1-xO oxides. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenomena 2006, 154, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, U.; Jing, J.; Birringer, R.; Gonser, U.; Gleiter, H. Investigation of nanocrystalline iron materials by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 50, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zboril, R.; Mashlan, M.; Petridis, D. Iron(III) Oxides from Thermal Processes Synthesis, structural and magnetic properties, Mössbauer spectroscopy characterization, and applications. Chem. Mater. 2002, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutry, S.; Forge, D.; Burtea, C.; Mahieu, I.; Murariu, O.; Laurent, S.; Van der Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. How to quantify iron in an aqueous or biological matrix: A technical note. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2009, 4, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, J.R. Thermogravimetric Analysis. Nature 1954, 173, 1011–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, J.; Mitra, A.; Bahadur, D.; Aslam, M. Surface controlled synthesis of MFe2O4(M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni and Zn) nanoparticles and their magnetic characteristics. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashzadeh, E.R.; Hobson, M.; Henry Bryant, L., Jr.; Dean, D.D.; Frank, J.A. Rapid Spectrophotometric Technique for Quantifying Iron in Cells Labeled with Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Potential Translation to the Clinic. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2014, 8, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henoumont, C.; Laurent, S.; Muller, R.N.; Vander Elst, L. HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy: An innovative tool for the characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles tracers for molecular imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangopadhyay, S.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Dale, B.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J.; Papaefthymiou, V.; Kostikas, A. Magnetic properties of ultrafine iron particles. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 45, 9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolphi, N.L.; Huber, D.L.; Jaetaoc, J.E.; Bryant, H.C.; Lovato, D.M.; Fegan, D.L.; Venturini, E.L.; Monson, T.C.; Tessier, T.E.; Hathaway, H.J.; et al. Characterization of magnetite nanoparticles for SQUID-relaxometry and magnetic needle biopsy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 321, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Henoumont, C.; Laurent, S.; Vander Elst, L. How to perform accurate and reliable measurements of longitudinal and transverse relaxation times of MRI contrast media in aqueous solutions. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2009, 4, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huai, Y.; Hossen, M.N.; Wilhelm, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Nanoparticle Interactions with the Tumor Microenvironment. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 2247–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerathunge, P.; Pooja, D.; Singh, M.; Kulhari, H.; Mayes, E.L.H.; Bansal, V.; Ramanathan, R. Transferrin-conjugated quasi-cubic SPIONs for cellular receptor profiling and detection of brain cancer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, M.A.; Parkhurst, A.; Matuczinski, E.; Balenger, S.; Giancarlo, L.C. Synthesis of a superparamagnetic iron oxide based nano-complex for targeted cell death of glioblastoma cells. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 465101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruniaux, J.; Allard-Vannier, E.; Aubrey, N.; Lakhrif, Z.; Ben Djemaa, S.; Eljack, S.; Marchais, H.; Hervé-Aubert, K.; Chourpa, I.; David, S. Magnetic nanocarriers for the specific delivery of siRNA: Contribution of breast cancer cells active targeting for down-regulation efficiency. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; George Thomas, R.; Ju Moon, M.; Ju Park, H.; Park, I.-K.; Lee, B.-I.; Yeon Jeong, Y. Near-Infrared Heptamethine Cyanine Based Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Tumor Targeted Multimodal Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Singh, A.; Debnath, A.; Kaul, A.; Garg, N.; Mathur, R.; Singh, A.; Randhawa, J.K. Multifunctional Magneto-Fluorescent Nanocarriers for Dual Mode Imaging and Targeted Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3060–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shen, S.; Guo, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, K.; Kuang, M.; Shuai, X. Nanomedicines reveal how PBOV1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma for effective gene therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferjaoui, Z.; Jamal Al Dine, E.; Kulmukhamedova, A.; Bezdetnaya, L.; Soon Chang, C.; Schneider, R.; Mutelet, F.; Mertz, D.; Begin-Colin, S.; Quilès, F.; et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded Thermoresponsive Superparamagnetic Nanocarriers for Controlled Drug Delivery and Magnetic Hyperthermia Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 30610–30620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirshaghaghi, A.; Yan, L.; Miller, J.; Daniel, Y.; Stein, J.M.; Busch, T.M.; Cheng, Z.; Tsourkas, A. Chlorin e6-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (SPION) Nanoclusters as a Theranostic Agent for Dual-Mode Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Luo, L.; Amirshaghaghi, A.; Miller, J.; Meng, C.; You, T.; Busch, T.; Tsourkas, A.; Cheng, Z. Dextran-Benzoporphyrin Derivative (BPD) Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (SPION) Micelles for T2-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.; Boudon, J.; Maurizi, L.; Moreau, M.; Walker, P.; Severin, I.; Oudot, A.; Goze, C.; Poty, S.; Vrigneaud, J.-M.; et al. Innovative Magnetic Nanoparticles for PET/MRI Bimodal Imaging. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 2637–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, P.; Markert, J.; Rückert, M.A.; Herz, S.; Keßler, B.; Dremel, K.; Althoff, D.; Weber, M.; Buzug, T.M.; Bley, T.A.; et al. Magnetic Particle Imaging meets Computed Tomography: First simultaneous imaging. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallyn, J.; Anton, N.; Mertz, D.; Begin-Colin, S.; Perton, F.; Serra, C.A.; Franconi, F.; Lemaire, L.; Chiper, M.; Libouban, H.; et al. Magnetite- and Iodine-Containing Nanoemulsion as a Dual Modal Contrast Agent for X-ray/Magnetic Resonance Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janikowska, A.; Matuszak, J.; Lyer, S.; Schreiber, E.; Unterweger, H.; Zaloga, J.; Groll, J.; Alexiou, C.; Cicha, I. A novel human artery model to assess the magnetic accumulation of SPIONs under flow conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Xia, Y.; Qian, K.; Akakuru, O.U.; Luo, L.; Zheng, J.; Cui, P.; Shen, Z.; Wu, A. A pH-sensitive polymer based precise tumor targeting strategy with reduced uptake of nanoparticles by non-cancerous cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5983–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Iron Oxide | Chemical Formula (Current Name) | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous oxide (iron(II) oxides) | FeO (Wüstite) | Black |
| Mixed-oxide (iron(II, III) oxides) | Fe3O4 or FeO.Fe2O3 (Magnetite) | Black |
| Ferric oxides (iron(III) oxides) | α-Fe2O3 (Hematite) β-Fe2O3 γ-Fe2O3 (Maghemite) ε-Fe2O3 | Grey, brown, red |
| Iron Oxide | Hematite | Maghemite | Magnetite | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic saturation | 0.3 A.m2/kg | 60–80 A.m2/kg | 92–100 A.m2/kg | ||
| Curie Transition | ~1000 K | ~820–980 K | ~850 K | ||
| Grain size | - | ≥10 nm | ≤10 nm | ≥6 nm | ≤6 nm |
| Magnetism ordering at room temperature | Ferromagnetic | Ferrimagnetic | SPM | Ferromagnetic | SPM |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wallyn, J.; Anton, N.; Vandamme, T.F. Synthesis, Principles, and Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles for In Vivo Imaging Applications—A Review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110601
Wallyn J, Anton N, Vandamme TF. Synthesis, Principles, and Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles for In Vivo Imaging Applications—A Review. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(11):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110601
Chicago/Turabian StyleWallyn, Justine, Nicolas Anton, and Thierry F. Vandamme. 2019. "Synthesis, Principles, and Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles for In Vivo Imaging Applications—A Review" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 11: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110601
APA StyleWallyn, J., Anton, N., & Vandamme, T. F. (2019). Synthesis, Principles, and Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles for In Vivo Imaging Applications—A Review. Pharmaceutics, 11(11), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110601






