Interplay between the Hepatitis B Virus and Innate Immunity: From an Understanding to the Development of Therapeutic Concepts
Abstract
:1. Role of Liver Innate Immunity in Pathogen Clearance and Immune-Driven Pathogenesis: Generalities
2. Interplay between HBV and Innate Immunity: Basic Insights
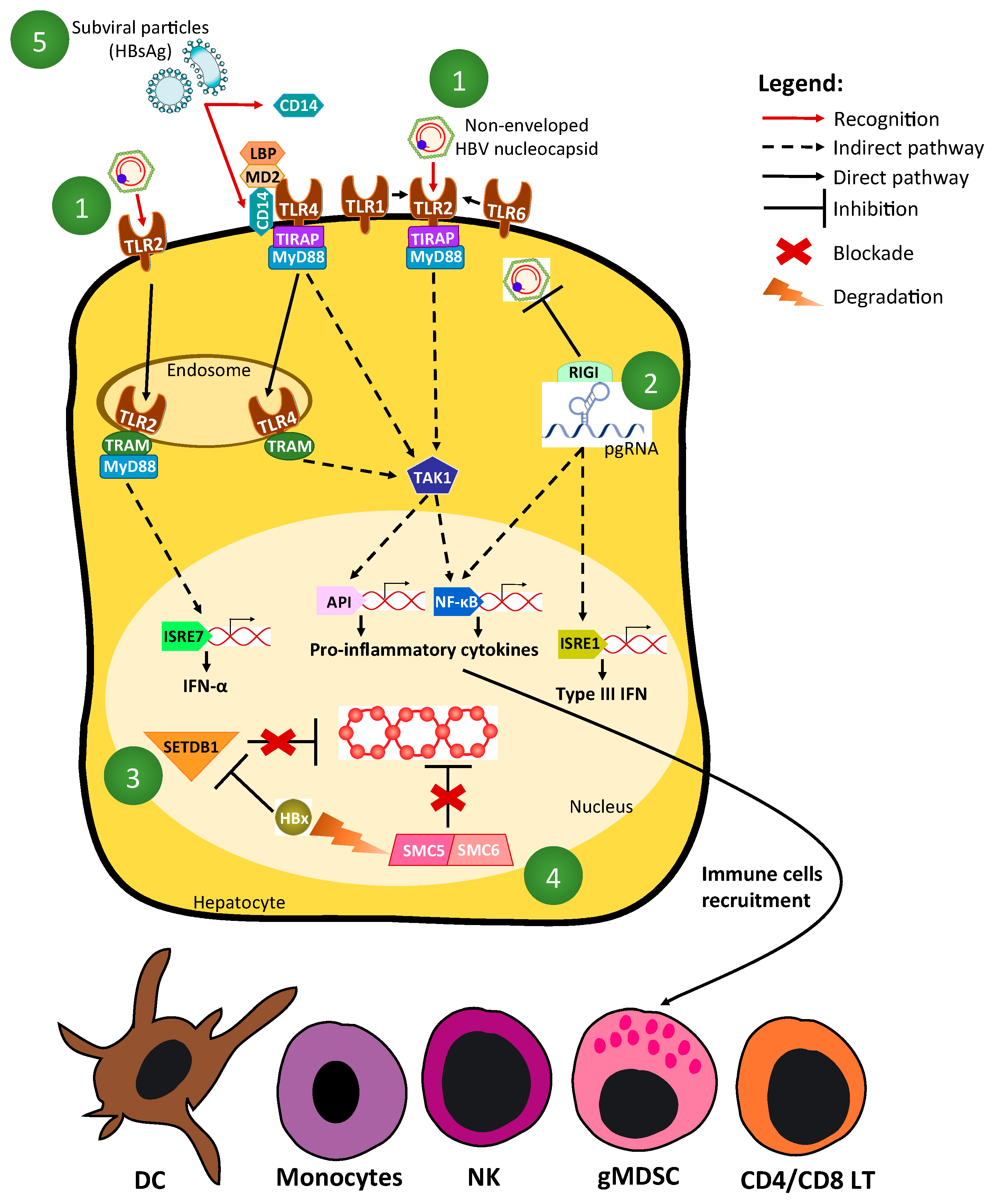
2.1. HBV Recognition by Innate Sensors
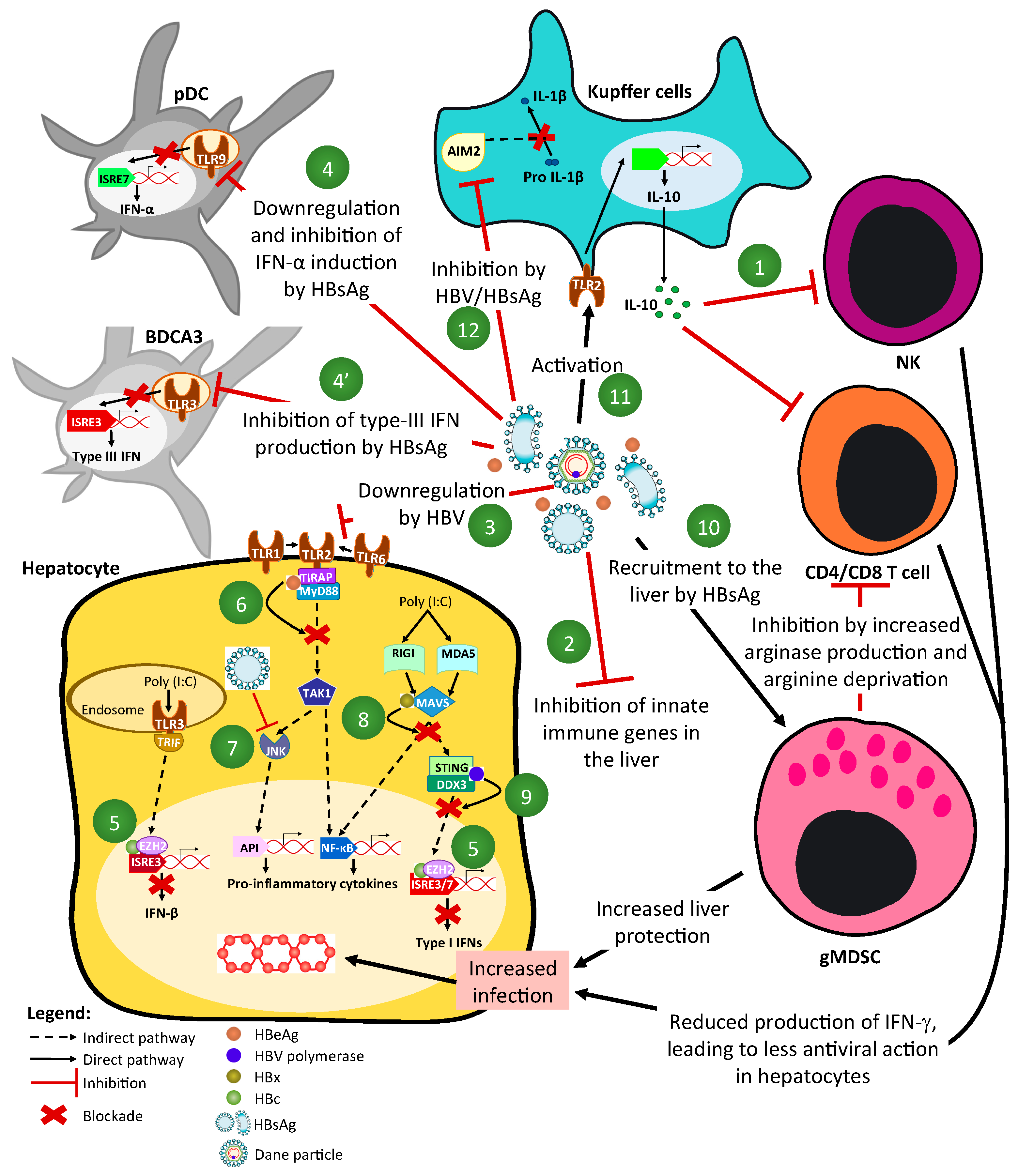
2.2. Mechanisms of HBV-Driven Inhibition of Innate-Signaling Pathways (Figure 1 and Figure 2)
2.3. Modulation of Innate Cell Number/Frequency by HBV
2.4. Modulation of Dendritic and NK/NKT Cells Functions by HBV (Figure 2)
2.5. Interplay between HBV and Monocytes/Macrophages (Figure 2)
3. Interplay between HBV and Innate Immunity: Therapeutic Insights
3.1. Can We Improve the Efficacy and Use of IFN-α-Based Therapy?
3.2. Is There a Place for Other Innate Immune Stimulators?
3.3. Development of PRR Agonists for Combinational Therapeutic Approaches
3.4. Manipulation of the Numbers or Biological Activity of Innate Immune Cells with Impaired Functions in CHB Patients to Help Restore HBV Immune Control
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crispe, I.N. The Liver as a Lymphoid Organ. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispe, I.N. Liver antigen-presenting cells. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzer, U.; Maini, M.K.; Knolle, P.A. Living in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2006, 1, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Immunology in the liver—From homeostasis to disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knolle, P.A.; Thimme, R. Hepatic immune regulation and its involvement in viral hepatitis infection. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispe, I.N. Immune tolerance in liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 60, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Adaptive immunity in HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64 (Suppl. S1), S71–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Rehermann, B. Immune responses to HCV and other hepatitis viruses. Immunity 2014, 40, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections: Towards restoration of immune control of viral infection. Gut 2012, 61, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, M.K.; Gehring, A.J. The role of innate immunity in the immunopathology and treatment of HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64 (Suppl. S1), S60–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Microbial sensing by Toll-like receptors and intracellular nucleic acid sensors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, S.M.; Vallance, B.A.; Knodler, L.A. Noncanonical inflammasomes: Antimicrobial defense that does not play by the rules. Cell. Microbiol. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispe, I.N. Hepatocytes as Immunological Agents. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangsay, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Michelet, M.; Floriot, O.; Bonnin, M.; Gruffaz, M.; Rivoire, M.; Fletcher, S.; Javanbakht, H.; Lucifora, J.; et al. Expression and functionality of Toll- and RIG-like receptors in HepaRG cells. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegna, S.; Gregoire, D.; Moreau, M.; Lassus, P.; Durantel, D.; Assenat, E.; Hibner, U.; Simonin, Y. NOD1 Participates in the Innate Immune Response Triggered by Hepatitis C Virus Polymerase. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6022–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.K.; Nandakumar, R.; Stadler, D.; Malo, A.; Valls, R.M.; Wang, F.; Reinert, L.S.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Hollensen, AK.; Mikkelsen, J.G.; et al. Lack of immunological DNA sensing in hepatocytes facilitates hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2016, 64, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannetti, C.; Roblot, G.; Charrier, E.; Ainouze, M.; Tout, I.; Briat, F.; Isorce, F.; Faure-Dupuy, S.; Michelet, M.; Marotel, M.; et al. Characterization of the Inflammasome in Human Kupffer Cells in Response to Synthetic Agonists and Pathogens. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Le Seyec, J.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, S.K.; Otto, M.J.; Barker, C.S.; Zaifert, K.; Wang, G.H.; Guo, J.T.; Seeger, C.; King, R.W. Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: A novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gripon, P.; Diot, C.; Thézé, N.; Fourel, I.; Loreal, O.; Brechot, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Hepatitis B virus infection of adult human hepatocytes cultured in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4136–4143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Urban, S. Entry of hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus into hepatocytes: Basic insights and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64 (Suppl. S1), S32–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangsay, S.; Gruffaz, M.; Isorce, N.; Testoni, B.; Michelet, M.; Faure-Dupuy, S.; Maadadi, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Parent, R.; Rivoire, M.; et al. Early inhibition of hepatocyte innate responses by hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1314–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanlandschoot, P.; Van Houtte, F.; Serruys, B.; Leroux-Roels, G. Contamination of a recombinant hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid preparation with a human B-cell activator. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2535–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.; Tal, G.; Lider, O.; Shaul, Y. Cytokine induction by the hepatitis B virus capsid in macrophages is facilitated by membrane heparan sulfate and involves TLR2. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Ge, J.; Pang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Liao, B.; Huang, X.; Zuo, D.; Sun, J.; Lu, M.; et al. Aberrant expression and dysfunction of TLR2 and its soluble form in chronic HBV infection and its regulation by antiviral therapy. Antivir. Res. 2015, 118, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Hyun, J.; Jakubski, S.; Saito, S.; Nakajima, A.; Schiff, E.R.; Thomas, E. Hepatitis B Virus and DNA Stimulation Trigger a Rapid Innate Immune Response through NF-kappaB. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, C.; Zoulim, F.; Mason, W.S. Hepadnaviruses. In Field’s Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; p. 2185. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA sensor RIG-I dually functions as an innate sensor and direct antiviral factor for hepatitis B virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, L.; Gerossier, L.; Ducroux, A.; Dion, S.; Deng, Q.; Michel, M.L.; Buendia, M.A.; Hantz, O.; Neuveut, C. HBx relieves chromatin-mediated transcriptional repression of hepatitis B viral cccDNA involving SETDB1 histone methyltransferase. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decorsiere, A.; Mueller, H.; van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlandschoot, P.; Van Houtte, F.; Roobrouck, A.; Farhoudi, A.; Stelter, F.; Peterson, D.L.; Gomez-Gutierrez, J.; Gavilanes, F.; Leroux-Roels, G. LPS-binding protein and CD14-dependent attachment of hepatitis B surface antigen to monocytes is determined by the phospholipid moiety of the particles. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.J.; Haniffa, M.; Kennedy, P.T.; Ho, Z.Z.; Boni, C.; Shin, A.; Banu, N.; Chia, A.; Lim, S.G.; Ferrari, C.; et al. Mobilizing monocytes to cross-present circulating viral antigen in chronic infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3766–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Montfoort, N.; van der Aa, E.; van den Bosch, A.; Brouwers, H.; Vanwolleghem, T.; Janssen, H.L.; Javanbakht, H.; Buschow, S.I.; Woltman, A.M. Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Activates Myeloid Dendritic Cells via a Soluble CD14-Dependent Mechanism. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6187–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacey, A.R.; Norris, P.J.; Qin, L.; Haygreen, E.A.; Taylor, E.; Heitman, J.; Lebedeva, M.; DeCamp, A.; Li, D.; Grove, D.; et al. Induction of a striking systemic cytokine cascade prior to peak viremia in acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection, in contrast to more modest and delayed responses in acute hepatitis B and C virus infections. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3719–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.; Peppa, D.; Khanna, P.; Nebbia, G.; Jones, M.; Brendish, N.; Lascar, R.M.; Brown, D.; Gilson, R.J.; Tedder, R.J.; et al. Temporal analysis of early immune responses in patients with acute hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Ellis, G.; Pallant, C.; Lopes, A.R.; Khanna, P.; Peppa, D.; Chen, A.; Blair, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Gill, U.; et al. IL-10-producing regulatory B cells in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosel, M.; Quasdorff, M.; Wiegmann, K.; Webb, D.; Zedler, U.; Broxtermann, M.; Tedjokusumo, R.; Esser, K.; Arzberger, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. Not interferon, but interleukin-6 controls early gene expression in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlomai, A.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ramanan, V.; Bhatta, A.; de Jong, Y.P.; Bhatia, S.N.; Rice, C.M. Modeling host interactions with hepatitis B virus using primary and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12193–12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebosse, F.; Testoni, B.; Fresquet, J.; Facchetti, F.; Galmozzi, E.; Fournier, M.; Hervieu, V.; Berthillon, P.; Berby, F.; Bordes, I.; et al. Intrahepatic innate immune response pathways are downregulated in untreated chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2016, 66, 897–909. [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan, K.; Skinner, N.A.; Thompson, A.J.; Riordan, S.M.; Sozzi, V.; Edwards, R.; Rodgers, S.; Kurtovic, J.; Chang, J.; Lewin, S.; et al. Regulation of Toll-like receptor-2 expression in chronic hepatitis B by the precore protein. Hepatology 2007, 45, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, I.E.; Zannetti, C.; Lucifora, J.; Norder, H.; Protzer, U.; Hainaut, P.; Zoulim, F.; Tommasino, M.; Trépo, C.; Hasan, U.; et al. Hepatitis B virus impairs TLR9 expression and function in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26315. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, S.P.; Chin, D.J.; Ji, Y.; Iniguez, A.L.; Taillon, B.; Swinney, D.C.; Ravindran, P.; Cheng, D.T.; Bitter, H.; Lopatin, U.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of the woodchuck model of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2012, 56, 820–830. [Google Scholar]
- Giersch, K.; Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Bierwolf, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Pollok, J.M.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Lütgehetmann, M. Hepatitis Delta co-infection in humanized mice leads to pronounced induction of innate immune responses in comparison to HBV mono-infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaiate, D.; Lucifora, J.; Abeywickrama-Samarakoon, N.; Michelet, M.; Testoni, B.; Cortay, J.C.; Sureau, C.; Zoulim, F.; Dény, P.; Durantel, D. HDV RNA replication is associated with HBV repression and interferon-stimulated genes induction in super-infected hepatocytes. Antivir. Res. 2016, 136, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor-mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruffaz, M.; Testoni, B.; Luangsay, S.; Fusil, F.; Malika, A.G.; Mancip, J.; Petit, M.; Javanbakht, H.; Cosset, F.L.; Zoulim, F.; et al. The nuclear function of Hepatitis B capsid (HBc) protein is to inhibit IFN response very early after infection of hepatocytes. Hepatology 2013, 58, 276A. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, C.T.; Schwinn, S.; Locarnini, S.; Fyfe, J.; Manns, M.P.; Trautwein, C.; Zentgraf, H. Structural organization of the hepatitis B virus minichromosome. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Quiroga, J.A.; Carreno, V. Hepatitis B virus downregulates the human interferon-inducible MxA promoter through direct interaction of precore/core proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 8, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.H.; Li, Y.N.; Zhao, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Z. HBc binds to the CpG islands of HBV cccDNA and promotes an epigenetic permissive state. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Chen, J.; Kozlowski, M.; Yuan, Z. Innate detection of hepatitis B and C virus and viral inhibition of the response. Cell. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Broering, R.; Trippler, M.; Poggenpohl, L.; Fiedler, M.; Gerken, G.; Lu, M.; Schlaak, J.F. Toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses are attenuated in the presence of high levels of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.; Lo, C.; Skinner, N.; Locarnini, S.; Visvanathan, K.; Mansell, A. The hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) targets and suppresses activation of the toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Qian, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, M.; Shi, B.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen selectively inhibits TLR2 ligand-induced IL-12 production in monocytes/macrophages by interfering with JNK activation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5142–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S. Innate immune evasion by hepatitis B virus-mediated downregulation of TRIF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Tang, H. Mechanism of inhibiting type I interferon induction by hepatitis B virus X protein. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Jung, S.Y.; Hodgson, A.J.; Madden, C.R.; Qin, J.; Slagle, B.L. Hepatitis B virus regulatory HBx protein binds to adaptor protein IPS-1 and inhibits the activation of beta interferon. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Ni, C.; Song, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, K.; Xu, Y.; et al. The hepatitis B virus X protein disrupts innate immunity by downregulating mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagle, B.L.; Andrisani, O.M.; Bouchard, M.J.; Lee, C.G.; Ou, J.H.; Siddiqui, A. Technical standards for hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) research. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Du, X.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus polymerase disrupts K63-linked ubiquitination of STING to block innate cytosolic DNA-sensing pathways. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ryu, W.S. Hepatitis B virus polymerase blocks pattern recognition receptor signaling via interaction with DDX3: Implications for immune evasion. PLoS Pathog 2010, 6, e1000986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltjes, A.; Groothuismink, Z.M.; van Oord, G.W.; Janssen, H.L.; Woltman, A.M.; Boonstra, A. Monocytes from chronic HBV patients react in vitro to HBsAg and TLR by producing cytokines irrespective of stage of disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groen, R.A.; Hou, J.; van Oord, G.W.; Groothuismink, Z.M.; van der Heide, M.; de Knegt, R.J.; Boonstra, A. NK cell phenotypic and functional shifts coincide with specific clinical phases in the natural history of chronic HBV infection. Antivir. Res. 2017, 140, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinet, J.; Dufeu-Duchesne, T.; Bruder Costa, J.; Larrat, S.; Marlu, A.; Leroy, V.; Plumas, J.; Aspord, C. Altered functions of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and reduced cytolytic activity of natural killer cells in patients with chronic HBV infection. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjwa, E.T.; Zoutendijk, R.; van Oord, G.W.; Boeijen, L.L.; Reijnders, J.G.; van Campenhout, M.J.; de Knegt, R.J.; Janssen, H.L.; Woltman, A.M.; Boonstra, A. Similar frequencies, phenotype and activation status of intrahepatic NK cells in chronic HBV patients after long-term treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF). Antivir. Res. 2016, 132, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, E.; Buschow, S.I.; Biesta, P.J.; Janssen, H.L.; Woltman, A.M. The effect of chronic hepatitis B virus infection on BDCA3+ dendritic cell frequency and function. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallett, L.J.; Gill, U.S.; Quaglia, A.; Sinclair, L.V.; Jover-Cobos, M.; Schurich, A.; Singh, K.P.; Thomas, N.; Das, A.; Chen, A.; et al. Metabolic regulation of hepatitis B immunopathology by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, D.; Ren, G.; Shi, B.; Wang, C.; Kosinska, A.D.; Wang, S.; Zhou, X.; et al. Polarization of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells by hepatitis B surface antigen is mediated via ERK/IL-6/STAT3 signaling feedback and restrains the activation of T-cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4873–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiecki, M.; Colonna, M. The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woltman, A.M.; Op den Brouw, M.L.; Biesta, P.J.; Shi, C.C.; Janssen, H.L. Hepatitis B virus lacks immune activating capacity, but actively inhibits plasmacytoid dendritic cell function. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Gong, Z.J. Human plasmacytoid dendritic cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection induce the generation of a higher proportion of CD4(+) and CD25(+) regulatory T-cells compared with healthy patients. Hepatol. Res. 2008, 38, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, S.; Yuan, Z. Hbsag inhibits TLR9-mediated activation and IFN-alpha production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2640–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliet, M.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.J. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: Sensing nucleic acids in viral infection and autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, E.; van Montfoort, N.; Woltman, A.M. BDCA3(+)CLEC9a(+) human dendritic cell function and development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 41, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isorce, N.; Testoni, B.; Locatelli, M.; Fresquet, J.; Rivoire, M.; Luangsay, S.; Zoulim, F.; Durantel, D. Antiviral activity of various interferons and pro-inflammatory cytokines in non-transformed cultured hepatocytes infected with hepatitis B virus. Antivir. Res. 2016, 130, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Stadler, D.; Lucifora, J.; Reisinger, F.; Webb, D.; Hosel, M.; Michler, T.; Wisskirchen, K.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, K.; et al. Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha produced by T-cells reduce the HBV persistence form, cccDNA, without cytolysis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Boni, C.; Massari, M.; Mori, C.; Zerbini, A.; Orlandini, A.; Sacchelli, L.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C. Early kinetics of innate and adaptive immune responses during hepatitis B virus infection. Gut 2009, 58, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, C.S.; Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Churchill, N.D.; Michalak, T.I. Intrahepatic expression of genes affiliated with innate and adaptive immune responses immediately after invasion and during acute infection with woodchuck hepadnavirus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8579–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, G.J.; Reignat, S.; Maini, M.K.; Whalley, S.A.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.; Brown, D.; Amlot, P.L.; Williams, R.; Vergani, D.; et al. Incubation phase of acute hepatitis B in man: Dynamic of cellular immune mechanisms. Hepatology 2000, 32, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliviero, B.; Varchetta, S.; Paudice, E.; Michelone, G.; Zaramella, M.; Mavilio, D.; De Filippi, F.; Bruno, S.; Mondelli, M.U. Natural killer cell functional dichotomy in chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C virus infections. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppa, D.; Micco, L.; Javaid, A.; Kennedy, P.T.; Schurich, A.; Dunn, C.; Pallant, C.; Ellis, G.; Khanna, P.; Dusheiko, G.; et al. Blockade of immunosuppressive cytokines restores NK cell antiviral function in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS Pathog 2010, 6, e1001227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, A.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M.; Hayes, C.N.; Tsuge, M.; Takahashi, S.; Aikata, H.; Abe, H.; Miki, D.; Ochi, H.; et al. Severe necroinflammatory reaction caused by natural killer cell-mediated Fas/Fas ligand interaction and dendritic cells in human hepatocyte chimeric mouse. Hepatology 2012, 56, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zou, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Fan, R.; Qin, E.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; et al. Hypercytolytic activity of hepatic natural killer cells correlates with liver injury in chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatology 2011, 53, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehermann, B. Natural killer cells in Viral Hepatitis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltjes, A.; Movita, D.; Boonstra, A.; Woltman, A.M. The role of Kupffer cells in hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus infections. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brempelis, K.J.; Crispe, I.N. Infiltrating monocytes in liver injury and repair. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitia, G.; Iannacone, M.; Aiolfi, R.; Isogawa, M.; van Rooijen, N.; Scozzesi, C.; Bianchi, M.E.; von Andrian, U.H.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G. Kupffer cells hasten resolution of liver immunopathology in mouse models of viral hepatitis. PLoS Pathog 2011, 7, e1002061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yin, W.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Kupffer cell-derived IL-10 plays a key role in maintaining humoral immune tolerance in hepatitis B virus-persistent mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watashi, K.; Liang, G.; Iwamoto, M.; Marusawa, H.; Uchida, N.; Daito, T.; Kitamura, K.; Muramatsu, M.; Ohashi, H.; Kiyohara, T.; et al. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha trigger restriction of hepatitis B virus infection via a cytidine deaminase activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31715–31727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, F.; Peusquens, J.; Ludwig-Portugall, I.; Kohlhepp, M.; Ergen, C.; Niemietz, P.; Martin, C.; van Rooijen, N.; Ochando, J.C.; Randolph, G.J.; et al. Liver inflammation abrogates immunological tolerance induced by Kupffer cells. Hepatology 2015, 62, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, R.; Xu, L.; Yin, W.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lian, Z.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Kupffer cells support hepatitis B virus-mediated CD8+ T-cell exhaustion via Hepatitis B Core Antigen-TLR2 interactions in mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Zou, Z.S.; Huang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.L.; Xu, X.S.; Chen, L.M.; Li, B.S.; Wang, F.S. Hyper-activated pro-inflammatory CD16 monocytes correlate with the severity of liver injury and fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konerman, M.A.; Lok, A.S. Interferon treatment for Hepatitis B. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 645–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, V.; Duong, F.; Bernsmeier, C.; Sun, D.; Nassal, M.; Heim, M.H. Inhibition of alpha interferon signaling by hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutgehetmann, M.; Bornscheuer, T.; Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Bockmann, J.H.; Pollok, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M. Hepatitis B virus limits response of human hepatocytes to interferon-alpha in chimeric mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 2074–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. Ifn-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccdna minichromosome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Xia, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Zhang, K.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 2014, 343, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micco, L.; Peppa, D.; Loggi, E.; Schurich, A.; Jefferson, L.; Cursaro, C.; Panno, A.M.; Bernardi, M.; Brander, C.; Bihl, F.; et al. Differential boosting of innate and adaptive antiviral responses during pegylated-interferon-alpha therapy of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, A.; Laccabue, D.; Libri, I.; Giuberti, T.; Schivazappa, S.; Alfieri, A.; Mori, C.; Canetti, D.; Lampertico, P.; Vigano, M.; et al. Peginterferon-alpha does not improve early peripheral blood HBV-specific T-cell responses in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, C.; Laccabue, D.; Lampertico, P.; Giuberti, T.; Vigano, M.; Schivazappa, S.; Alfieri, A.; Pesci, M.; Gaeta, G.B.; Brancaccio, G.; et al. Restored function of HBV-specific T-cells after long-term effective therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Dandri, M. Dissecting the divergent effects of interferon-alpha on immune cells: Time to rethink combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B? J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcellin, P.; Ahn, S.H.; Ma, X.; Caruntu, F.A.; Tak, W.Y.; Elkashab, M.; Chuang, W.L.; Lim, S.G.; Tabak, F.; Mehta, R.; et al. Combination of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and peginterferon alpha-2a increases loss of hepatitis B surface antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.; Ahn, S.H.; Chang, T.T.; Peng, C.Y.; Wong, D.; Coffin, C.S.; Lim, S.G.; Chen, P.J.; Janssen, H.L.; Marcellin, P.; et al. Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: A randomized phase 2b study (LIRA-B). J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isorce, N.; Lucifora, J.; Zoulim, F.; Durantel, D. Immune-modulators to combat hepatitis B virus infection: From INF-alpha to novel investigational immunotherapeutic strategies. Antiviral Res. 2015, 122, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogawa, M.; Robek, M.D.; Furuichi, Y.; Chisari, F.V. Toll-like receptor signaling inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7269–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Maadadi, S.; Floriot, O.; Daffis, S.; Fletcher, S.; Zoulim, F.; Durantel, D. Direct antiviral effects of various pattern recognition receptor (PRR) agonists in HBV-replicating hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S515–S516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Meng, Z.; Broering, R.; Yang, D.; Schlaak, J.F.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M. Role of toll-like receptor 2 in the immune response against hepadnaviral infection. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F. Interplay between hepatitis B virus and TLR2-mediated innate immune responses: Can restoration of TLR2 functions be a new therapeutic option? J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Wohlleber, D.; Reisinger, F.; Jenne, C.N.; Cheng, R.L.; Abdullah, Z.; Schildberg, F.A.; Odenthal, M.; Dienes, H.P.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Intrahepatic myeloid-cell aggregates enable local proliferation of CD8(+) T-cells and successful immunotherapy against chronic viral liver infection. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Wang, J.; Dou, S.; Yang, X.; Ni, X.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. Nanoparticles encapsulating hepatitis B virus cytosine-phosphate-guanosine induce therapeutic immunity against HBV infection. Hepatology 2014, 59, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Pei, R.; Zhang, E.; Kemper, T.; Vollmer, J.; Davis, H.L.; Glebe, D.; Gerlich, W.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. Combination therapy including CpG oligodeoxynucleotides and entecavir induces early viral response and enhanced inhibition of viral replication in a woodchuck model of chronic hepadnaviral infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 125, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dansako, H.; Ueda, Y.; Okumura, N.; Satoh, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Mizokami, M.; Ikeda, M.; Kato, N. The cyclic GMP-AMP synthetase-STING signaling pathway is required for both the innate immune response against HBV and the suppression of HBV assembly. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Han, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, C.; Wei, L.; Jiang, J.D.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T.; et al. STING agonists induce an innate antiviral immune response against hepatitis B virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Hao, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Tien, P.; Guo, D. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 3368–3378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korolowicz, K.E.; Iyer, R.P.; Czerwinski, S.; Suresh, M.; Yang, J.; Padmanabhan, S.; Sheri, A.; Pandey, R.K.; Skell, J.; Marquis, J.K.; et al. Antiviral efficacy and host innate immunity associated with SB 9200 treatment in the woodchuck model of chronic hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanford, R.E.; Guerra, B.; Chavez, D.; Giavedoni, L.; Hodara, V.L.; Brasky, K.M.; Fosdick, A.; Frey, C.R.; Zheng, J.; Wolfgang, G.; et al. GS-9620, an oral agonist of Toll-Like receptor-7, induces prolonged suppression of hepatitis B virus in chronically infected chimpanzees. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, S.; Tumas, D.B.; Liu, K.H.; Thampi, L.; AlDeghaither, D.; Baldwin, B.H.; Bellezza, C.A.; Cote, P.J.; Zheng, J.; Halcomb, R.; et al. Sustained efficacy and seroconversion with the Toll-Like receptor 7 agonist GS-9620 in the woodchuck model of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.J.; Lim, Y.-S.; Gordon, S.C.; Visvanathan, K.; Sicard, E.; Fedorak, R.N.; Roberts, S.; Massetto, B.; Ye, Z.; Pflanz, S.; et al. The oral Toll-Like receptor-7 agonist GS-9620 in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawitz, E.; Gruener, D.; Marbury, T.; Hill, J.; Webster, L.; Hassman, D.; Nguyen, A.H.; Pflanz, S.; Mogalian, E.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral Toll-Like receptor 7 agonist GS-9620 in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C. Antivir. Ther. 2015, 20, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ries, C.H.; Cannarile, M.A.; Hoves, S.; Benz, J.; Wartha, K.; Runza, V.; Rey-Giraud, F.; Pradel, L.P.; Feuerhake, F.; Klaman, I.; et al. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages with anti-CSF-1R antibody reveals a strategy for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, R.P.; Davis, D.; Jordan, K.R.; McCarter, M.D. The clinical evidence for targeting human myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer patients. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinet, J.; Leroy, V.; Dufeu-Duchesne, T.; Larrat, S.; Richard, M.J.; Zoulim, F.; Plumas, J.; Aspord, C. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce efficient stimulation of antiviral immunity in the context of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.C.; Dhillon, A.P.; Reid, S.P.; Thi, E.P.; Phelps, J.R.; McClintock, K.; Li, A.H.; Pasetka, C.; Cobarrubias, K.D.; Majeski, S.; et al. Exploring combination therapy for curing HBV: Preclinical studies with capsid inhibitor AB-423 and a sirna agent, ABR-1740. Hepatology 2016, 64, 122A–123A. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, N.; Cole, A.G.; Ardzinski, A.; Cai, D.W.; Cuconati, A.; Dorsey, B.D.; Guo, F.; Guo, H.T.; Guo, J.T.; Kultgen, S.; et al. The HBV capsid inhibitor AB-423 exhibits a dual mode of action and displays additive/synergistic effects in in vitro combination studies. Hepatology 2016, 64, 123A–124A. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faure-Dupuy, S.; Lucifora, J.; Durantel, D. Interplay between the Hepatitis B Virus and Innate Immunity: From an Understanding to the Development of Therapeutic Concepts. Viruses 2017, 9, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050095
Faure-Dupuy S, Lucifora J, Durantel D. Interplay between the Hepatitis B Virus and Innate Immunity: From an Understanding to the Development of Therapeutic Concepts. Viruses. 2017; 9(5):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050095
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaure-Dupuy, Suzanne, Julie Lucifora, and David Durantel. 2017. "Interplay between the Hepatitis B Virus and Innate Immunity: From an Understanding to the Development of Therapeutic Concepts" Viruses 9, no. 5: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050095
APA StyleFaure-Dupuy, S., Lucifora, J., & Durantel, D. (2017). Interplay between the Hepatitis B Virus and Innate Immunity: From an Understanding to the Development of Therapeutic Concepts. Viruses, 9(5), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050095






