The Expanding Family of Virophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Virophage Discovery and History
3. Morphological Features of Virophages
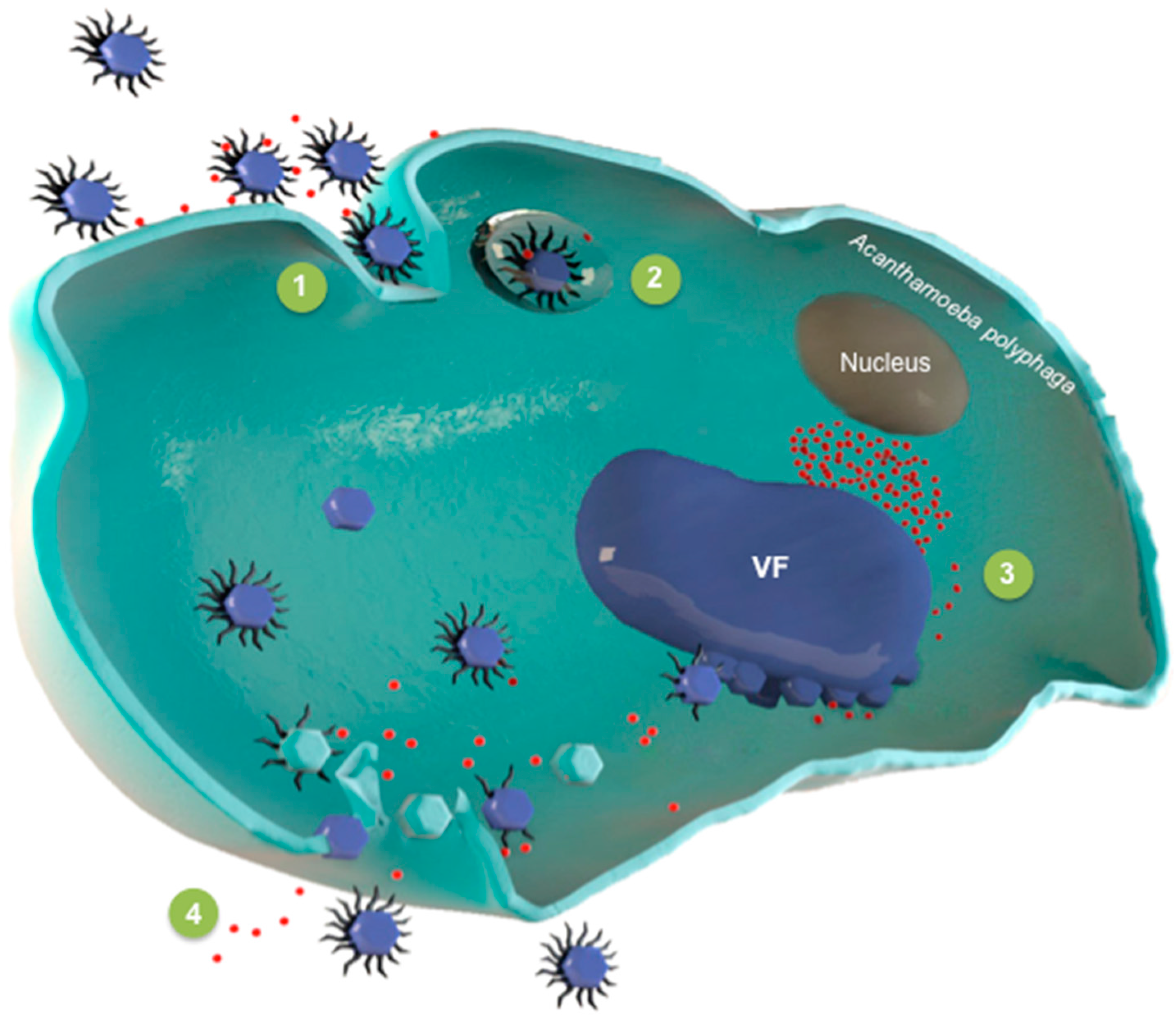
4. Replicative Cycle of Virophages
4.1. Entry of Sputnik in the Amoeba
4.2. Virophages Invade the Giant Virus Factory
4.3. The Spread of Progeny Virophages
4.4. Replicative Cycle of Other Virophages
4.4.1. Zamilon
4.4.2. Mavirus
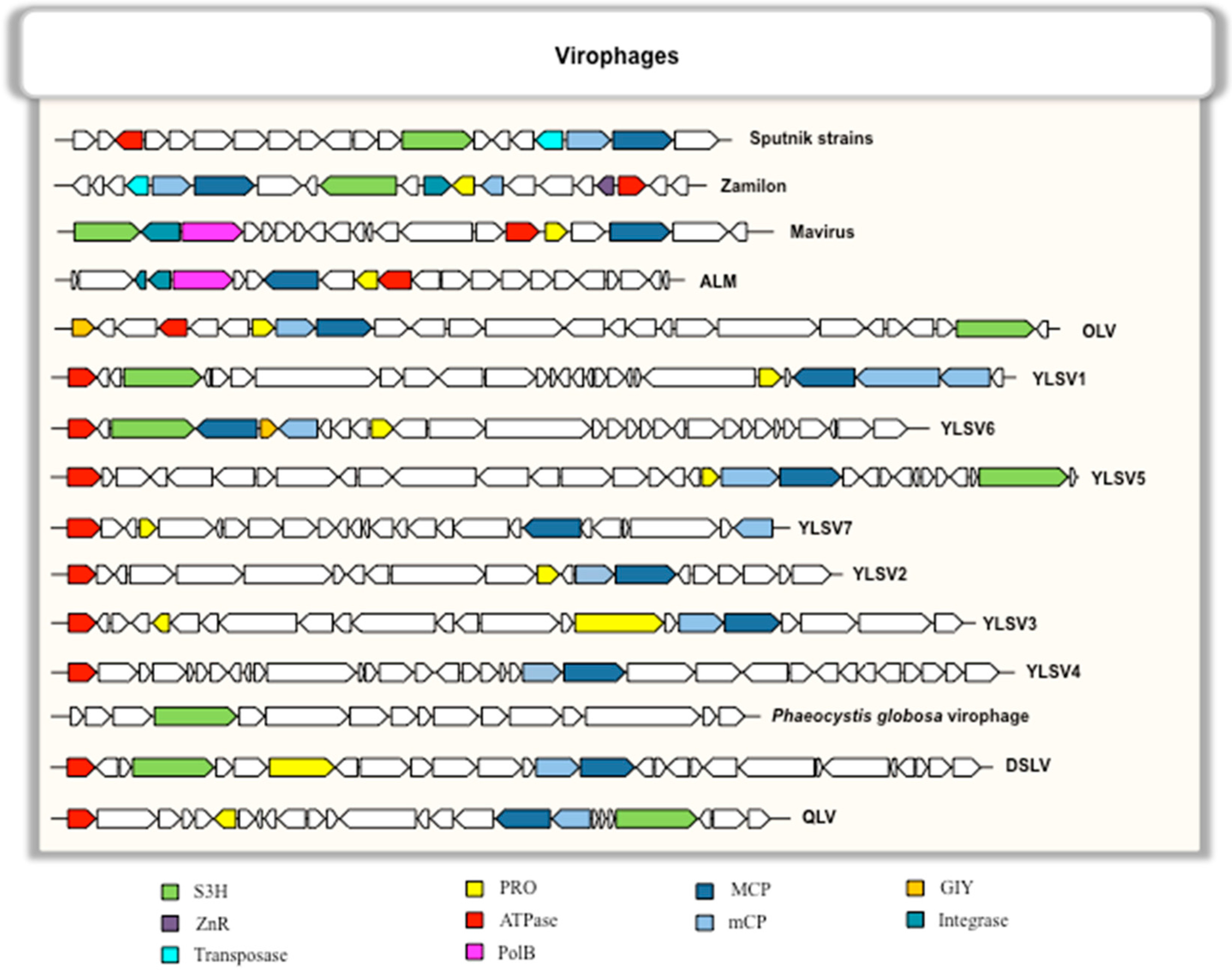
5. Genomic Structure and Features of Virophages
5.1. Genomic Organization
5.1.1. Isolated Virophages
● Sputnik isolates
● Mavirus
● Zamilon
5.1.2. Metagenomics and Genomics Detection
● Organic Lake Virophage (OLV)
● Phaeocystis globosa virophage
● Ace Lake Mavirus (ALM)
● Yellowstone Lake virophages (YSLVs)
● Hybrid virophages
● Zamilon 2
● Virophage sequences integrated in Bigelowiella natans genomes
● Dishui Lake Virophage (DSLV1)
● Qinghai Lake Virophage (QLV)
● Virophage capsid encoding sequences found in metagenomes
5.2. Conserved and Core Genes
5.3. Phylogeny of Virophages
6. Classification of Virophages, New Agents in the Field of Virology
7. Virophages as Part of the Mobilome Associated to Giant Viruses
8. MIMIVIRE, a Defence Mechanism against Virophages
9. Abundance and Distribution of Virophages, and their Potential Impact on Virus-Host Ecology
10. Virophages in Humans
11. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
Box: Glossary
| MIMIVIRE: | A mimivirus nucleic acid-based defense system against virophage infection. |
| Mobilome: | Mobile genetic elements in mimiviruses (including provirophages, transpovirons, and introns/inteins). |
| Polintons/Mavericks: | Large DNA transposons characterized by a unique set of proteins necessary for their transposition, including DNA polymerase B, a retroviral integrase, a cysteine protease, and an ATPase. Polintons are typically 15–25 kbp in length, and encode up to ten proteins. |
| Plasmid: | A DNA molecule that is physically separated from the genomic DNA and can replicate independently. |
| Provirophage: | A virophage genome integrated into the giant virus DNA. |
| Satellite virus: | A small subviral agent that depends on the presence of a helper virus for its propagation. |
| Transposon: | Linear DNA sequence of approximately 7 kbp that encodes six to eight proteins and is capable of moving independently within a genome. They are considered to be powerful motors of evolution and biodiversity. |
| Transpoviron: | Derived from “transposon”. It is a small linear transposable element detected in mimiviruses. |
| Virophage: | A viral parasite of giant viruses. It requires a giant virus factory co-infection for its replication. |
References
- Lwoff, A. The concept of virus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1957, 17, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; Forterre, P. Redefining viruses: Lessons from Mimivirus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scola, B.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Jungang, L.; De Lamballerie, X.; Drancourt, M.; Birtles, R.; Claverie, J.M.; Raoult, D. A giant virus in amoebae. Science 2003, 299, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Abergel, C.; Renesto, P.; Ogata, H.; La Scola, B.; Suzan, M.; Claverie, J.M. The 1.2-megabase genome sequence of Mimivirus. Science 2004, 306, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippe, N.; Legendre, M.; Doutre, G.; Coute, Y.; Poirot, O.; Lescot, M.; Arslan, D.; Seltzer, V.; Bertaux, L.; Bruley, C.; et al. Pandoraviruses: Amoeba viruses with genomes up to 2.5 Mb reaching that of parasitic eukaryotes. Science 2013, 341, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheid, P.; Balczun, C.; Schaub, G.A. Some secrets are revealed: Parasitic keratitis amoebae as vectors of the scarcely described pandoraviruses to humans. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3759–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, M.; Bartoli, J.; Shmakova, L.; Jeudy, S.; Labadie, K.; Adrait, A.; Lescot, M.; Poirot, O.; Bertaux, L.; Bruley, C.; et al. Thirty-thousand-year-old distant relative of giant icosahedral DNA viruses with a pandoravirus morphology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4274–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reteno, D.G.; Benamar, S.; Khalil, J.B.; Andreani, J.; Armstrong, N.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Faustovirus, an asfarvirus-related new lineage of giant viruses infecting amoebae. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, M.; Lartigue, A.; Bertaux, L.; Jeudy, S.; Bartoli, J.; Lescot, M.; Alempic, J.M.; Ramus, C.; Bruley, C.; Labadie, K.; et al. In-depth study of Mollivirus sibericum, a new 30,000-y-old giant virus infecting Acanthamoeba. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5327–E5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Koonin, E.V. Hidden evolutionary complexity of Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Large DNA viruses of eukaryotes. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; Raoult, D. Gene repertoire of amoeba-associated giant viruses. Intervirology 2010, 53, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Etten, J.L.; Lane, L.C.; Dunigan, D.D. DNA viruses: The really big ones (giruses). Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V. Eukaryotic large nucleo-cytoplasmic DNA viruses: Clusters of orthologous genes and reconstruction of viral genome evolution. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; De Lamballerie, X.; Yutin, N.; Asgari, S.; Bigot, Y.; Bideshi, D.K.; Cheng, X.W.; Federici, B.A.; Van Etten, J.L.; Koonin, E.V.; et al. “Megavirales”, a proposed new order for eukaryotic nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Colson, P.; Chabrol, O.; Pontarotti, P.; Raoult, D. Pithovirus sibericum, a new bona fide member of the “Fourth TRUC” club. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Colson, P.; Pontarotti, P.; Raoult, D. Mimivirus inaugurated in the 21st century the beginning of a reclassification of viruses. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 31, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scola, B.; Desnues, C.; Pagnier, I.; Robert, C.; Barrassi, L.; Fournous, G.; Merchat, M.; Suzan-Monti, M.; Forterre, P.; Koonin, E.; et al. The virophage as a unique parasite of the giant mimivirus. Nature 2008, 455, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desnues, C.; La Scola, B.; Yutin, N.; Fournous, G.; Robert, C.; Azza, S.; Jardot, P.; Monteil, S.; Campocasso, A.; Koonin, E.V.; et al. Provirophages and transpovirons as the diverse mobilome of giant viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18078–18083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.G.; Suttle, C.A. A virophage at the origin of large DNA transposons. Science 2011, 332, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, M.; Gimenez, G.; Suzan-Monti, M.; Raoult, D. Classification and determination of possible origins of ORFans through analysis of nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Intervirology 2010, 53, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forterre, P.; Prangishvili, D. The origin of viruses. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D. A need to discover the world of giant viruses. Intervirology 2013, 56, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claverie, J.M.; Abergel, C. Mimivirus and its virophage. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desnues, C.; Boyer, M.; Raoult, D. Sputnik, a virophage infecting the viral domain of life. Adv. Virus Res. 2012, 82, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.G.; Allen, M.J.; Wilson, W.H.; Suttle, C.A. Giant virus with a remarkable complement of genes infects marine zooplankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19508–19513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaia, M.; Pagnier, I.; Campocasso, A.; Fournous, G.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Broad spectrum of mimiviridae virophage allows its isolation using a mimivirus reporter. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaia, M.; Benamar, S.; Boughalmi, M.; Pagnier, I.; Croce, O.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Zamilon, a novel virophage with Mimiviridae host specificity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.; Lauro, F.M.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Brown, M.V.; Thomas, T.; Raftery, M.J.; Andrews-Pfannkoch, C.; Lewis, M.; Hoffman, J.M.; Gibson, J.A.; et al. Virophage control of antarctic algal host-virus dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6163–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, S.; Jeudy, S.; Bartoli, J.; Poirot, O.; Lescot, M.; Abergel, C.; Barbe, V.; Wommack, K.E.; Noordeloos, A.A.; Brussaard, C.P.; et al. Genome of Phaeocystis globosa virus PgV-16T highlights the common ancestry of the largest known DNA viruses infecting eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10800–10805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Yan, S.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y. Diversity of virophages in metagenomic data sets. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4225–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Childers, A.; McDermott, T.R.; Wang, Y.; Liles, M.R. Three novel virophage genomes discovered from Yellowstone Lake metagenomes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekliz, M.; Verneau, J.; Benamar, S.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B.; Colson, P. A New Zamilon-like virophage partial genome assembled from a bioreactor metagenome. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, G.; Xiao, J.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. Novel virophages discovered in a freshwater lake in China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Yoo, D.; Liu, W.T. Metagenomics reveals a novel virophage population in a Tibetan mountain lake. Microbes Environ. 2016, 31, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zauberman, N.; Mutsafi, Y.; Halevy, D.B.; Shimoni, E.; Klein, E.; Xiao, C.; Sun, S.; Minsky, A. Distinct DNA exit and packaging portals in the virus Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desnues, C.; Raoult, D. Inside the lifestyle of the virophage. Intervirology 2010, 53, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, M.; Azza, S.; Barrassi, L.; Klose, T.; Campocasso, A.; Pagnier, I.; Fournous, G.; Borg, A.; Robert, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Mimivirus shows dramatic genome reduction after intraamoebal culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10296–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhy, H.; La Scola, B.; Pagnier, I.; Raoult, D.; Colson, P. Identification of giant Mimivirus protein functions using RNA interference. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Hoffart, L.; La Scola, B.; Raoult, D.; Drancourt, M. Ameba-associated keratitis, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; Gimenez, G.; Boyer, M.; Fournous, G.; Raoult, D. The giant Cafeteria roenbergensis virus that infects a widespread marine phagocytic protist is a new member of the fourth domain of Life. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza, D.R.; Suttle, C.A. The effect of cyanophages on the mortality of Synechococcus spp. and selection for UV resistant viral communities. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 36, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Koonin, E.V. Polintons: A hotbed of eukaryotic virus, transposon and plasmid evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.B.; Larsen, A.; Bratbak, G.; Sandaa, R.A. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the Phycodnaviridae virus family, using amplified fragments of the major capsid protein gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3048–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Bamford, D.H.; Koonin, E.V. Conservation of major and minor jelly-roll capsid proteins in Polinton (Maverick) transposons suggests that they are bona fide viruses. Biol. Direct 2014, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Kapitonov, V.V.; Koonin, E.V. A new family of hybrid virophages from an animal gut metagenome. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, G.; Gallot-Lavallee, L.; Maumus, F. Provirophages in the Bigelowiella genome bear testimony to past encounters with giant viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5318–E5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zablocki, O.; van, Z.L.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Rubagotti, E.; Tuffin, M.; Cary, S.C.; Cowan, D. High-level diversity of tailed phages, eukaryote-associated viruses, and virophage-like elements in the metaviromes of antarctic soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6888–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Fischer, M.G. A classification system for virophages and satellite viruses. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Cvirkaite-Krupovic, V. Virophages or satellite viruses? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 762–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desnues, C.; Raoult, D. Virophages question the existence of satellites. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.G. Sputnik and Mavirus: More than just satellite viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V. Virophages, polintons, and transpovirons: A complex evolutionary network of diverse selfish genetic elements with different reproduction strategies. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughalmi, M.; Saadi, H.; Pagnier, I.; Colson, P.; Fournous, G.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. High-throughput isolation of giant viruses of the Mimiviridae and Marseilleviridae families in the Tunisian environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scola, B.; Campocasso, A.; N’Dong, R.; Fournous, G.; Barrassi, L.; Flaudrops, C.; Raoult, D. Tentative characterization of new environmental giant viruses by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Intervirology 2010, 53, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnier, I.; Reteno, D.G.; Saadi, H.; Boughalmi, M.; Gaia, M.; Slimani, M.; Ngounga, T.; Bekliz, M.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; et al. A decade of improvements in Mimiviridae and Marseilleviridae isolation from amoeba. Intervirology 2013, 56, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, H.; Reteno, D.G.; Colson, P.; Aherfi, S.; Minodier, P.; Pagnier, I.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Shan virus: A new mimivirus isolated from the stool of a Tunisian patient with pneumonia. Intervirology 2013, 56, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, H.; Pagnier, I.; Colson, P.; Cherif, J.K.; Beji, M.; Boughalmi, M.; Azza, S.; Armstrong, N.; Robert, C.; Fournous, G.; et al. First isolation of Mimivirus in a patient with pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngounga, T.; Pagnier, I.; Reteno, D.G.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B.; Colson, P. Real-time PCR systems targeting giant viruses of amoebae and their virophages. Intervirology 2013, 56, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; De Lamballerie, X.; Fournous, G.; Raoult, D. Reclassification of giant viruses composing a fourth domain of life in the new order Megavirales. Intervirology 2012, 55, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levasseur, A.; Bekliz, M.; Chabriere, E.; Pontarotti, P.; La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. MIMIVIRE is a defence system in mimivirus that confers resistance to virophage. Nature 2016, 531, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claverie, J.M.; Abergel, C. CRISPR-Cas-like system in giant viruses: Why MIMIVIRE is not likely to be an adaptive immune system. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Expanding Family of Virophages. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/d/edit?mid=1xSUvKIFTCzHLaHfOUIcKPuMoI4A&ll=-6.832760593400437%2C0&z=2 (accessed on 5 June 2016).
- Parola, P.; Renvoise, A.; Botelho-Nevers, E.; La Scola, B.; Desnues, C.; Raoult, D. Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus virophage seroconversion in travelers returning from Laos. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1500–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagier, J.C.; Armougom, F.; Million, M.; Hugon, P.; Pagnier, I.; Robert, C.; Bittar, F.; Fournous, G.; Gimenez, G.; Maraninchi, M.; et al. Microbial culturomics: Paradigm shift in the human gut microbiome study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; Boyer, M. Amoebae as genitors and reservoirs of giant viruses. Intervirology 2010, 53, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slimani, M.; Pagnier, I.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Amoebae as battlefields for bacteria, giant viruses, and virophages. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4783–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Virophage | GenBank Accession No. | Description Year | Source | Geographical Location | Associated Giant Virus (Taxonomy) | Protistan Host | Discovery Tool | Genome | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (bp) | Number of ORFs | G + C (%) | |||||||||
| Sputnik | EU606015 | 2008 | Cooling tower water | Paris, France | Mamavirus | Acanthamoeba polyphaga | Culture | 18,343 | 21 | 27 | [17] |
| Mavirus virophage | NC_015230 | 2010 | Coastal waters | Texas, USA | Cafeteria roenbergensis virus | Marine phagotrophic flagellate | Culture | 19,063 | 20 | 30.3 | [19] |
| OLV | HQ704801 | 2011 | Organic Lake | Antarctica | Organic Lake phycodnavirus (distantly-related mimivirus) | Prasinophytes? | Metagenomics | 26,421 | 24 | 36.5 | [28] |
| Sputnik 2 | NC_023846 | 2012 | Lens liquid | Marseille, France | Lentillevirus | Acanthamoeba polyphaga | Culture | 18,338 | 20 | 27 | [18] |
| Sputnik 3 | NC_023847 | 2013 | Soil | Marseille, France | Mamavirus | Acanthamoeba polyphaga | Culture | 18,338 | 20 | 27 | [26] |
| Phaeocystis globosa virophage | NC_021333 | 2013 | Dutch coastal waters | Southern North Sea | Phaeocystis globosa virus PgV-16T (Distantly-related mimivirus) | Algae | Genomics | 19,527 | 16 | 35.8 | [29] |
| YSLV1 | KC556924 | 2013 | Yellowstone Lake | USA | Phycodna- or mimiviruses | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 27,849 | 26 | 33.4 | [30] |
| YSLV2 | KC556925 | 2013 | Yellowstone Lake | USA | Phycodna- or mimiviruses | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 23,184 | 21 | 33.6 | [30] |
| YSLV3 | KC556926 | 2013 | Yellowstone Lake | USA | Phycodna- or mimiviruses | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 27,05 | 23 | 34.9 | [30] |
| YSLV4 | KC556922 | 2013 | Yellowstone Lake | USA | Phycodna- or mimiviruses | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 28,306 | 34 | 37.2 | [30] |
| ALM | KC556923 | 2013 | Ace Lake | Antarctica | Possibly mimiviruses | Phagotrophic protozoa? | Metagenomics | 17,767 | 22 | 26.7 | [30] |
| Zamilon | NC_022990 | 2014 | Soil | Tunisia | Mont1 virus (mimivirus) | Acanthamoeba polyphaga | Culture | 17,276 | 20 | 29.,7 | [27] |
| YSLV5 | KM502589 | 2014 | Yellowstone Lake | USA | Phycodna- or mimiviruses | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 29,767 | 32 | 51.1 | [31] |
| YSLV6 | KM502590 | 2014 | Yellowstone Lake | USA | Phycodna- or mimiviruses | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 24,837 | 29 | 26.8 | [31] |
| YSLV7 | KM502591 | 2014 | Yellowstone Lake | USA | Phycodna- or mimiviruses | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 23,193 | 26 | 27.3 | [31] |
| Zamilon 2 | N/A | 2015 | A non-aerated Bioreactor | USA | mimiviruses? | Acanthamoeba sp. | Metagenomics | 6716 | 15 partial | 32 | [32] |
| DSLV1 | KT894027 | 2016 | Dishui Lake | China | N/A | Microalgae? | Metagenomics | 28,788 | 28 | 43.2 | [33] |
| QLV | KJ854379 | 2016 | Qinghai Lake | China | N/A | N/A | Metagenomics | 23,379 | 25 | 33.2 | [34] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bekliz, M.; Colson, P.; La Scola, B. The Expanding Family of Virophages. Viruses 2016, 8, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110317
Bekliz M, Colson P, La Scola B. The Expanding Family of Virophages. Viruses. 2016; 8(11):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110317
Chicago/Turabian StyleBekliz, Meriem, Philippe Colson, and Bernard La Scola. 2016. "The Expanding Family of Virophages" Viruses 8, no. 11: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110317
APA StyleBekliz, M., Colson, P., & La Scola, B. (2016). The Expanding Family of Virophages. Viruses, 8(11), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110317






