Celecoxib Inhibits the Lytic Activation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus through Down-Regulation of RTA Expression by Inhibiting the Activation of p38 MAPK
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Chemical Agents
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. Infectivity Assay
2.4. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) and Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Fluorescence Detection and Analysis
2.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
3. Results
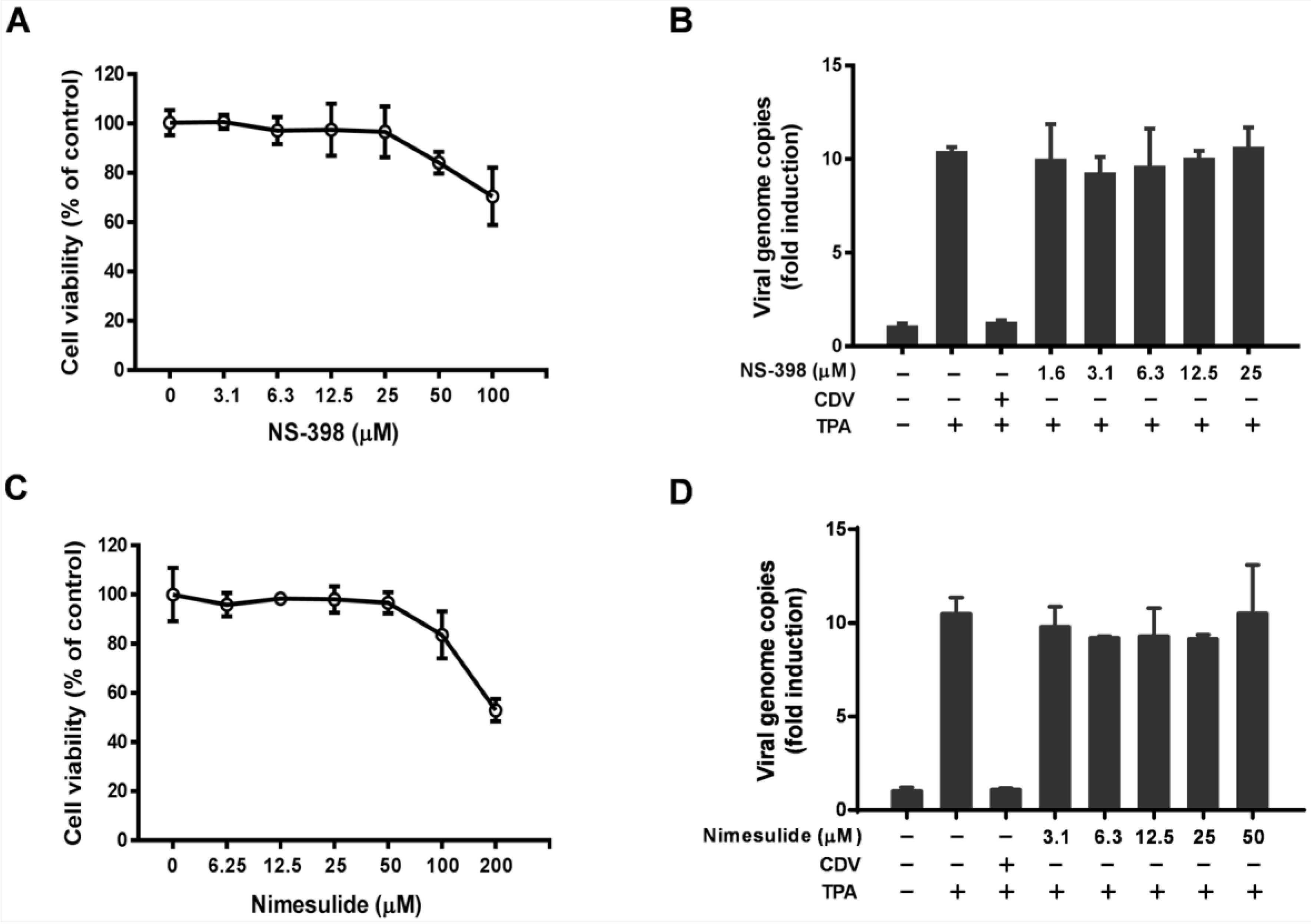
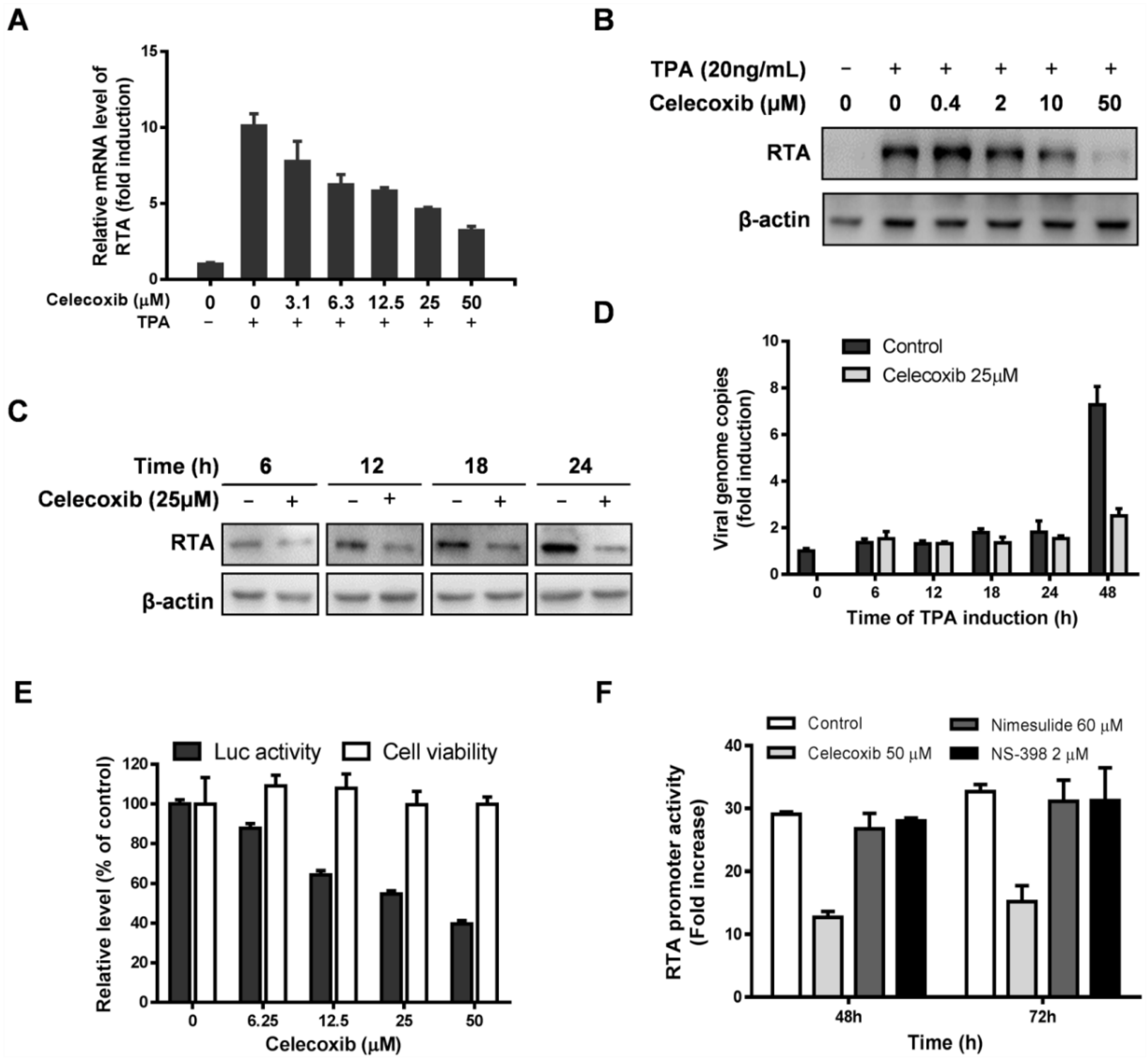
3.1. Effect of Celecoxib on the Lytic and Latent Replication of KSHV in BCBL-1 Cells
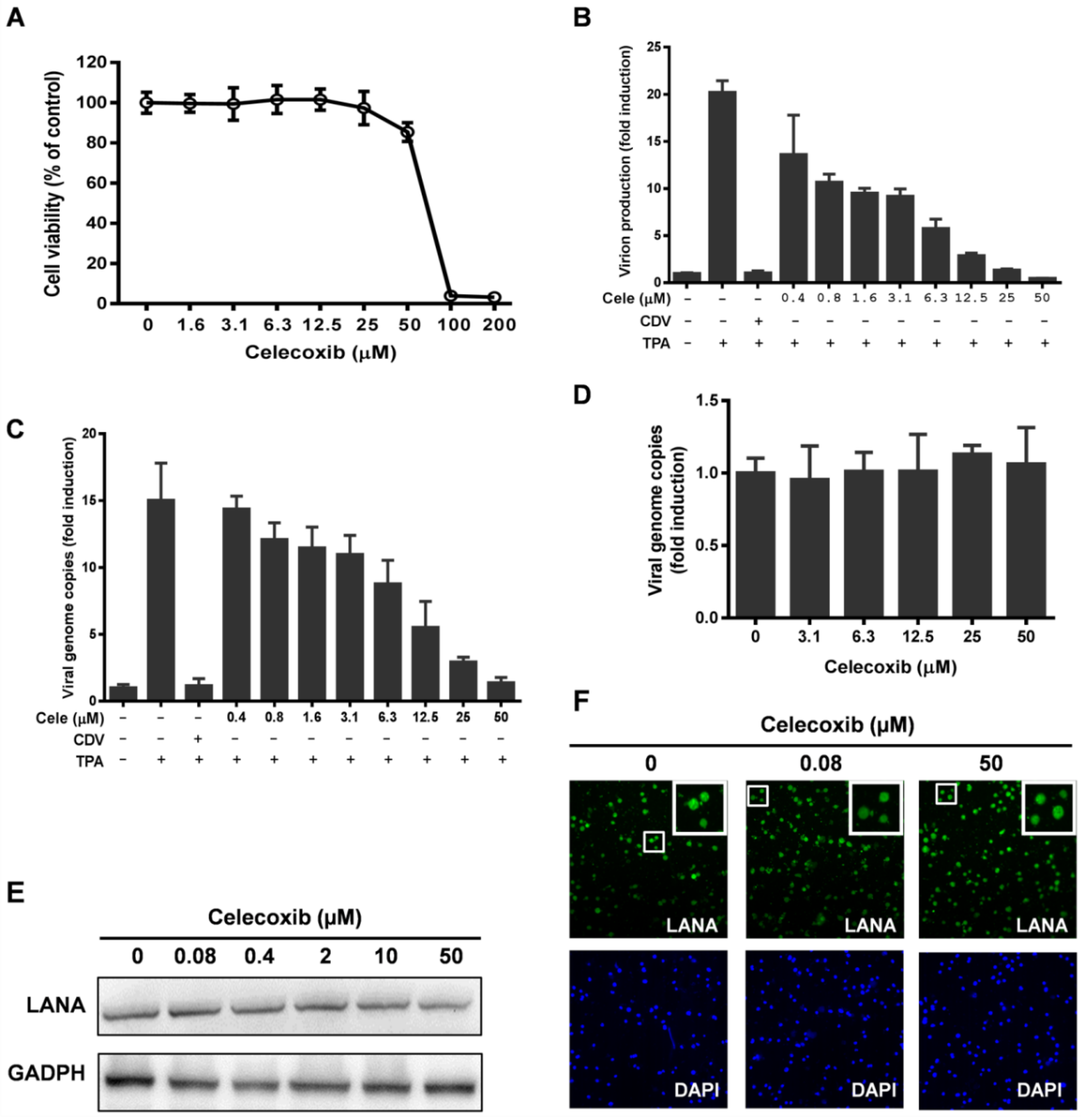
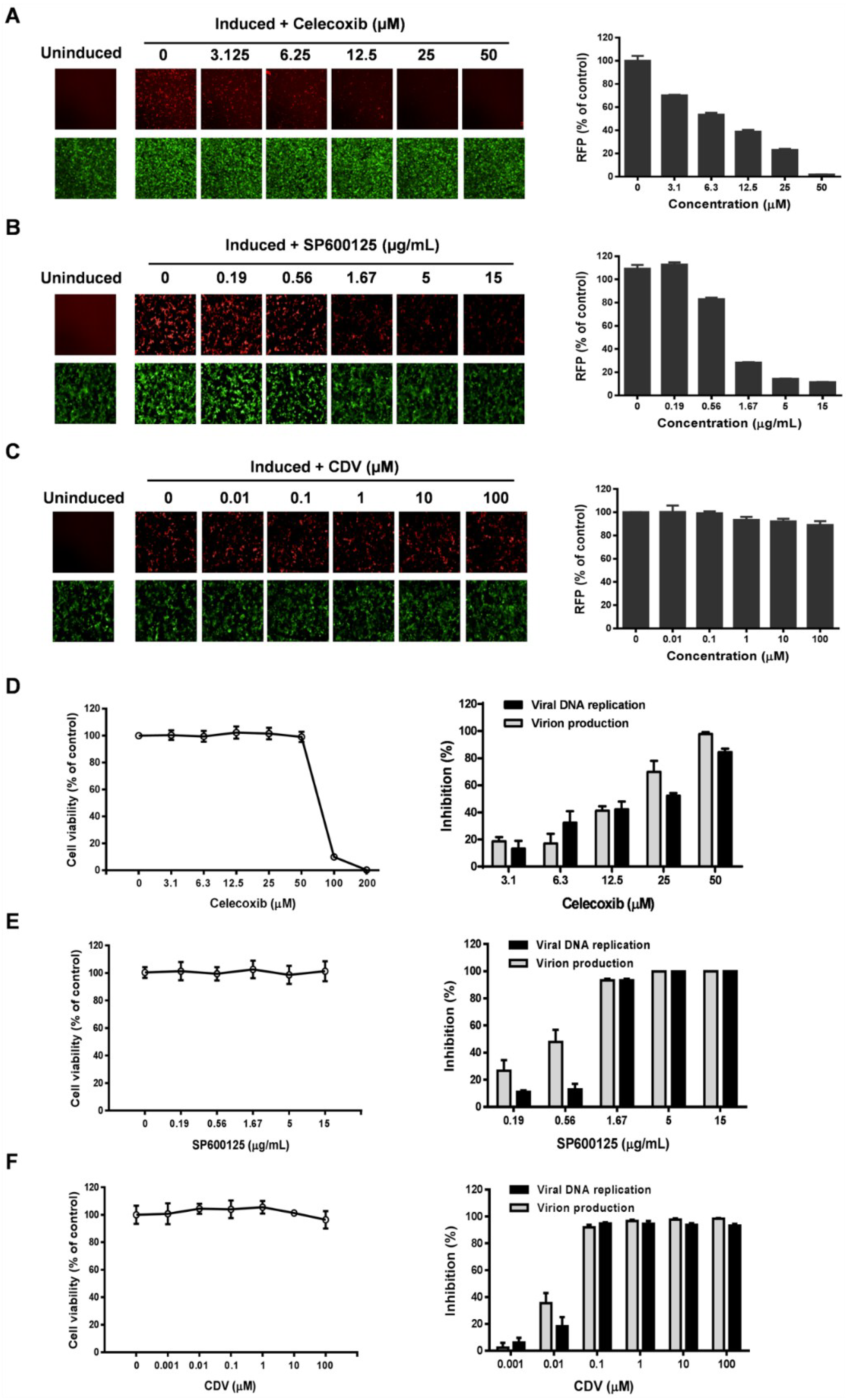
3.3. Celecoxib Affects the Early Stages of KSHV Reactivation from Latency in iSLK.219 Cells
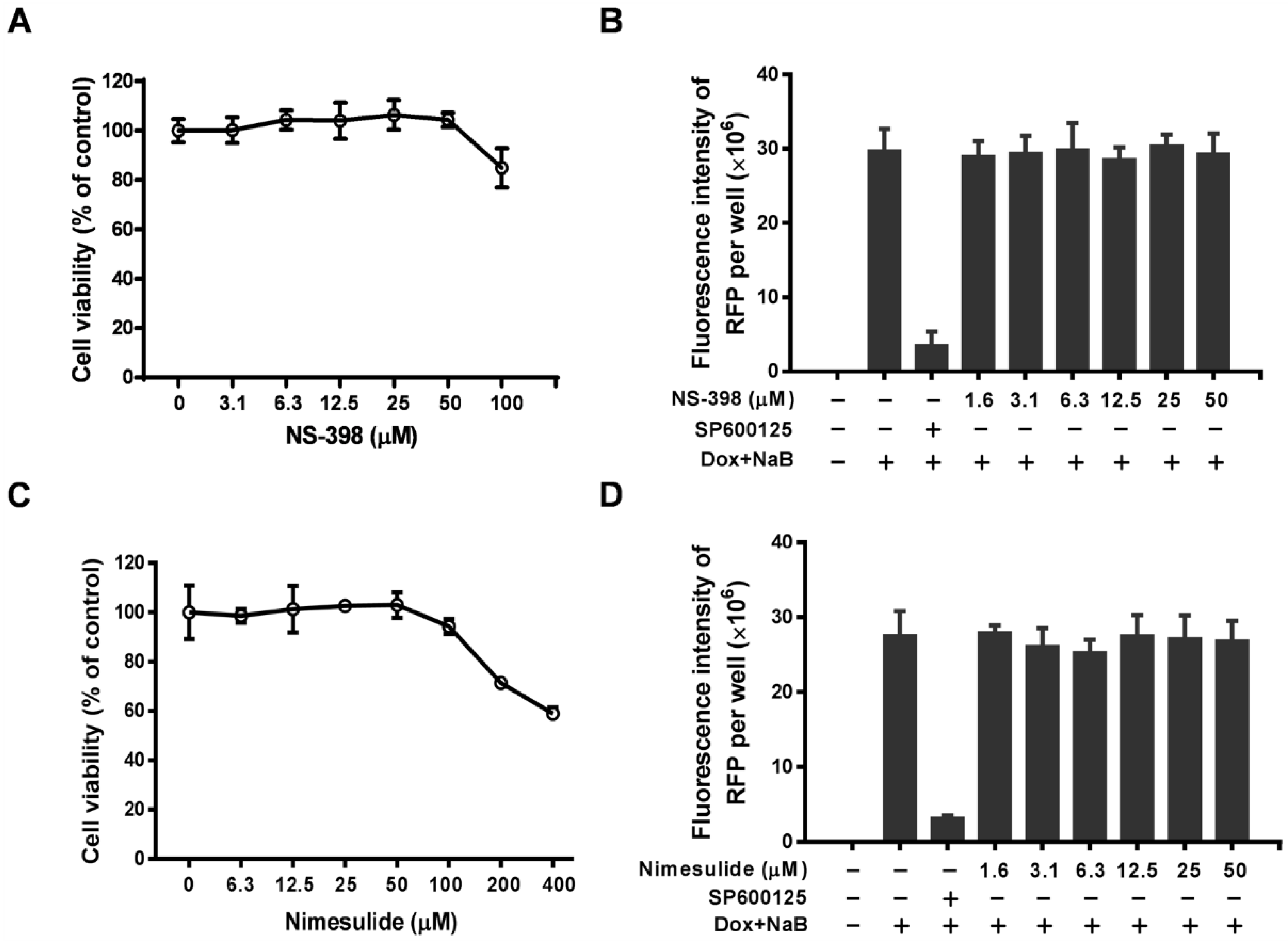
3.4. Celecoxib Suppresses RTA Expression
3.5. Celecoxib Affects Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK during KSHV Lytic Phase
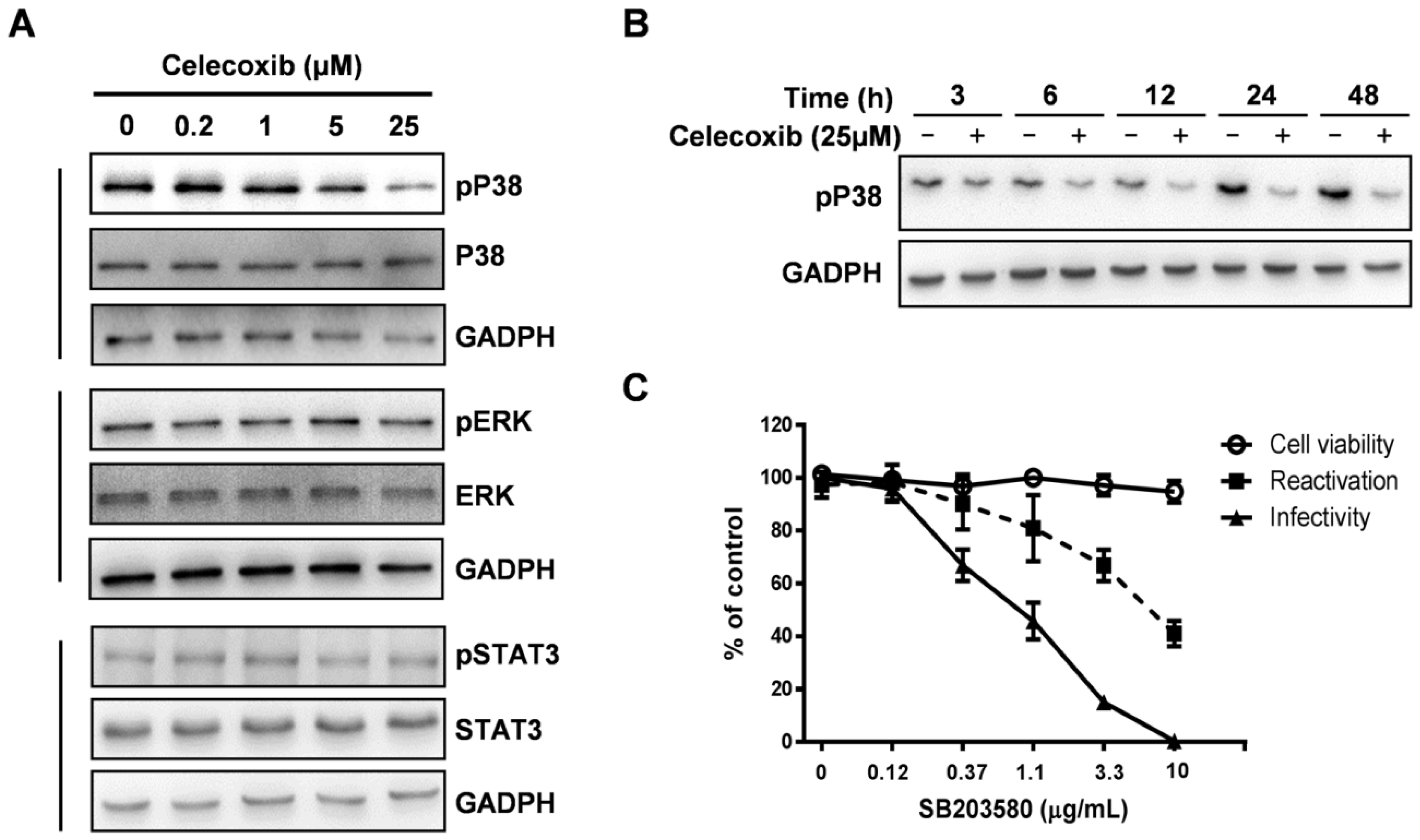
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Y.; Cesarman, E.; Pessin, M.S.; Lee, F.; Culpepper, J.; Knowles, D.M.; Moore, P.S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science 1994, 266, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, E.D.; Kaye, K.M. Rapid and quantitative assessment of KSHV LANA-mediated DNA replication. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antman, K.; Chang, Y. Kaposi’s Sarcoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, D.P.; Krown, S.E. Targeted therapy for Kaposi’s sarcoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2007, 19, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.; Heston, L.; Grogan, E.; Gradoville, L.; Rigsby, M.; Sun, R.; Shedd, D.; Kushnaryov, V.M.; Grossberg, S.; Chang, Y. Selective switch between latency and lytic replication of Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus and Epstein-Barr virus in dually infected body cavity lymphoma cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 314–324. [Google Scholar]
- Renne, R.; Zhong, W.; Herndier, B.; McGrath, M.; Abbey, N.; Kedes, D.; Ganem, D. Lytic growth of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) in culture. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staskus, K.A.; Zhong, W.; Gebhard, K.; Herndier, B.; Wang, H.; Renne, R.; Beneke, J.; Pudney, J.; Anderson, D.J.; Ganem, D.; et al. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus gene expression in endothelial (spindle) tumor cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parravicini, C.; Chandran, B.; Corbellino, M.; Berti, E.; Paulli, M.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Differential viral protein expression in Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-infected diseases-Kaposi’s sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma, and multicentric Castleman’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Liao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded LANA Down-Regulates IL-22R1 Expression through a cis-Acting Element within the Promoter Region. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e19106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ballestas, M.E.; Chatis, P.A.; Kaye, K.M. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science 1999, 284, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte-Real, S.; Collins, C.; Aires da Silva, F.; Simas, J.P.; Barbas, C.F., 3rd; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.; Goncalves, J. Intrabodies targeting the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency antigen inhibit viral persistence in lymphoma cells. Blood 2005, 106, 3797–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradoville, L.; Gerlach, J.; Grogan, E.; Shedd, D.; Nikiforow, S.; Metroka, C.; Miller, G. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus open reading frame 50/Rta protein activates the entire viral lytic cycle in the HH-B2 primary effusion lymphoma cell line. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6207–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, J.; Huang, M.L.; Koelle, D.M.; Corey, L. Transmissible Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) in saliva of men with a history of Kaposi’s sarcoma. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7083–7087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Lin, S.-F.; Gradoville, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, F.; Miller, G. A viral gene that activates lytic cycle expression of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1998, 95, 10866–10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Lei, X.; Gao, S.-J. Mechanisms of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency and Reactivation. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Liang, Y.; Sun, R. Regulation of KSHV lytic gene expression. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 312, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Sun, Y.; Sun, R.; Rettig, M.B. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoded vFLIP induces cellular IL-6 expression: The role of the NF-[kappa]B and JNK//AP1 pathways. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3371–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.; Cohen, A.; Kazimirsky, G.; Dovrat, S.; Rubinfeld, H.; Brodie, C.; Sarid, R. Role of protein kinase C delta in reactivation of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10187–10192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasparri, I.; Keller, S.A.; Cesarman, E. KSHV vFLIP is essential for the survival of infected lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Xie, J.; Ye, F.; Gao, S.-J. Modulation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection and Replication by MEK/ERK, JNK, and p38 Multiple Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways during Primary Infection. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5371–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Pan, H.; Yoo, S.; Gao, S.J. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induction of AP-1 and interleukin 6 during primary infection mediated by multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15027–15037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Ajibade, A.O.; Ye, F.; Kuhne, K.; Gao, S.-J. Reactivation of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus from latency requires MEK/ERK, JNK and p38 multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Virology 2008, 371, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.; Brodie, C.; Sarid, R. An essential role of ERK signalling in TPA-induced reactivation of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, P.W.; Bryan, B.A.; Dyson, O.F.; Weidner, D.A.; Chintalgattu, V.; Akula, S.M. Raf/MEK/ERK signalling triggers reactivation of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantt, S.; Casper, C. Human herpesvirus 8-associated neoplasms: The roles of viral replication and antiviral treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myoung, J.; Ganem, D. Generation of a doxycycline-inducible KSHV producer cell line of endothelial origin: Maintenance of tight latency with efficient reactivation upon induction. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 174, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, J.; O’Hearn, P.M. Use of the red fluorescent protein as a marker of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic gene expression. Virology 2004, 325, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.M.; Ahn, A.K.; Seo, T.; Hong, H.B.; Chung, M.A.; Jung, S.D.; Cho, H.; Lee, M.S. Centrifugal enhancement of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated virus infection of human endothelial cells in vitro. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 154, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Stedman, W.; Yousef, M.; Renne, R.; Lieberman, P.M. Epigenetic Regulation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency by Virus-Encoded MicroRNAs That Target Rta and the Cellular Rbl2-DNMT Pathway. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Suen, J.; Frias, C.; Pfeiffer, R.; Tsai, M.H.; Chuang, E.; Zeichner, S.L. Dissection of the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus gene expression program by using the viral DNA replication inhibitor cidofovir. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13637–13652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marechal, V.; Lallemand, F.; Desire, N.; Rozenbaum, W.; Nicolas, J.C. Quantitative analysis of human herpesvirus 8 viral load using a real-time PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1404–1408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asahi-Ozaki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kanno, T.; Sata, T.; Katano, H. Quantitative Analysis of Kaposi Sarcoma–Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) in KSHV-Associated Diseases. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.M.; Zhou, F.-C.; Ye, F.-C.; Pan, H.-Y.; Gao, S.-J. Early and sustained expression of latent and host modulating genes in coordinated transcriptional program of KSHV productive primary infection of human primary endothelial cells. Virology 2005, 343, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, F.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Green tea extract and its major component epigallocatechin gallate inhibits hepatitis B virus in vitro. Antiviral. Res. 2008, 78, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, K.; Kuppers, D.A.; Verma, S.C.; Robertson, E.S. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Latency-Associated Nuclear Antigen Inhibits Lytic Replication by Targeting Rta: A Potential Mechanism for Virus-Mediated Control of Latency. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pica, F.; Serafino, A.; Garaci, E.; Volpi, A. Cidofovir on HHV-8 in BCBL-1 cells. Antivir. Ther. 2004, 9, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friborg, J., Jr.; Kong, W.; Hottiger, M.O.; Nabel, G.J. p53 inhibition by the LANA protein of KSHV protects against cell death. Nature 1999, 402, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leung, H.J.; Duran, E.M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Andreansky, S.; Lampidis, T.J.; Mesri, E.A. Activation of the Unfolded Protein Response by 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Inhibits Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Replication and Gene Expression. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5794–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guito, J.; Lukac, D.M. KSHV Rta Promoter Specification and Viral Reactivation. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Paul, A.; Sharma-Walia, N.; Chandran, B. Targeting KSHV/HHV-8 Latency with COX-2 Selective Inhibitor Nimesulide: A Potential Chemotherapeutic Modality for Primary Effusion Lymphoma. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e24379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma-Walia, N.; Raghu, H.; Sadagopan, S.; Sivakumar, R.; Veettil, M.V.; Naranatt, P.P.; Smith, M.M.; Chandran, B. Cyclooxygenase 2 Induced by Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Early during In Vitro Infection of Target Cells Plays a Role in the Maintenance of Latent Viral Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6534–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, K.S.; Kim, S.H.; Song, Y.S.; Surh, Y.J. Celecoxib inhibits phorbol ester-induced expression of COX-2 and activation of AP-1 and p38 MAP kinase in mouse skin. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, J.; Darnell, J.E. The role of STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular function. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Feldman, G.M.; Tosato, G. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and decreases survivin expression in primary effusion lymphoma. Blood 2003, 101, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grösch, S.; Maier, T.J.; Schiffmann, S.; Geisslinger, G. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)–Independent Anticarcinogenic Effects of Selective COX-2 Inhibitors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederberger, E.; Tegeder, I.; Vetter, G.; Schmidtko, A.; Schmidt, H.; Euchenhofer, C.; Bräutigam, L.; Grösch, S.; Geisslinger, G. Celecoxib loses its anti-inflammatory efficacy at high doses through activation of NF-κB. FASEB 2001, 15, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Shimizu, T.; Tago, K.; Nakamura, M.; Itoh, H.; Sonoda, Y.; Kasahara, T. Celecoxib potently inhibits TNFα-induced nuclear translocation and activation of NF-κB. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Song, S.-H.; Kim, S.-G.; Chun, K.-S.; Lim, S.-Y.; Na, H.-K.; Kim, J.; Surh, Y.-J.; Bang, Y.-J.; Song, Y.-S. Celecoxib induces apoptosis in cervical cancer cells independent of cyclooxygenase using NF-κB as a possible target. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 130, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonthal, A.H. Direct non-cyclooxygenase-2 targets of celecoxib and their potential relevance for cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelby, B.D.; Nelson, A.; Morris, C. γ-Herpesvirus neoplasia: A growing role for COX-2. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2005, 68, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steer, S.A.; Corbett, J.A. The role and regulation of COX-2 during viral infection. Viral. Immunol. 2003, 16, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma-Walia, N.; Paul, A.G.; Bottero, V.; Sadagopan, S.; Veettil, M.V.; Kerur, N.; Chandran, B. Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated Herpes Virus (KSHV) Induced COX-2: A Key Factor in Latency, Inflammation, Angiogenesis, Cell Survival and Invasion. PLOS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma-Walia, N.; Patel, K.; Chandran, K.; Marginean, A.; Bottero, V.; Kerur, N.; Paul, A.G. COX-2/PGE2: Molecular ambassadors of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpes virus oncoprotein-v-FLIP. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.G.; Chandran, B.; Sharma-Walia, N. Concurrent targeting of EP1/EP4 receptors and COX-2 induces synergistic apoptosis in KSHV and EBV associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines. Trans. Res. 2013, 161, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, P.E.; Isakson, P.C. Outcome of specific COX-2 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1997, 49, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, R.C.; Koepp, R.J.; Yu, S.; Talwalker, S.; Geis, G.S.; Wiesenhutter, C.W.; Makarowski, W.S.; Paulus, H.A. SC-58635 (celecoxib), a novel COX-2 selective inhibitor, is effective as a treatment for osteoarthritis (OA) in a short-term pilot study. Arthritis. Rheum. 1996, 39, 1188–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.J.; Klotz, U. Clinical use and pharmacological properties of selective COX-2 inhibitors. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, G.; Lynch, P.M.; Phillips, R.K.S.; Wallace, M.H.; Hawk, E.; Gordon, G.B.; Wakabayashi, N.; Saunders, B.; Shen, Y.; Fujimura, T.; et al. The Effect of Celecoxib, a Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor, in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusnak, K.; Roloff, G.; Singh, S. Celecoxib and Cardiac Abnormalities: A Biostatistical Analysis of Adverse Side Effects. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1021.10. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Park, Y.M.; La, H.O. Symmetrical drug-related intertriginous and flexural exanthema caused by celecoxib. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Lan, K.; Chen, X. Celecoxib Inhibits the Lytic Activation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus through Down-Regulation of RTA Expression by Inhibiting the Activation of p38 MAPK. Viruses 2015, 7, 2268-2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052268
Chen J, Jiang L, Lan K, Chen X. Celecoxib Inhibits the Lytic Activation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus through Down-Regulation of RTA Expression by Inhibiting the Activation of p38 MAPK. Viruses. 2015; 7(5):2268-2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052268
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jungang, Liangyu Jiang, Ke Lan, and Xulin Chen. 2015. "Celecoxib Inhibits the Lytic Activation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus through Down-Regulation of RTA Expression by Inhibiting the Activation of p38 MAPK" Viruses 7, no. 5: 2268-2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052268
APA StyleChen, J., Jiang, L., Lan, K., & Chen, X. (2015). Celecoxib Inhibits the Lytic Activation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus through Down-Regulation of RTA Expression by Inhibiting the Activation of p38 MAPK. Viruses, 7(5), 2268-2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052268