Abstract
Replication of the poliovirus genome is localized to cytoplasmic replication factories that are fashioned out of a mixture of viral proteins, scavenged cellular components, and new components that are synthesized within the cell due to viral manipulation/up-regulation of protein and phospholipid synthesis. These membranous replication factories are quite complex, and include markers from multiple cytoplasmic cellular organelles. This review focuses on the role of electron microscopy in advancing our understanding of poliovirus RNA replication factories. Structural data from the literature provide the basis for interpreting a wide range of biochemical studies that have been published on virus-induced lipid biosynthesis. In combination, structural and biochemical experiments elucidate the dramatic membrane remodeling that is a hallmark of poliovirus infection. Temporal and spatial membrane modifications throughout the infection cycle are discussed. Early electron microscopy studies of morphological changes following viral infection are re-considered in light of more recent data on viral manipulation of lipid and protein biosynthesis. These data suggest the existence of distinct subcellular vesicle populations, each of which serves specialized roles in poliovirus replication processes.
1. Introduction
The focus of this review is on changes in cellular morphology during replication of poliovirus, a positive sense (+) RNA virus of approximately 7500 nucleotides. The poliovirus genome is encapsidated in a non-enveloped icosahedral virion, 28–30 nm in diameter [1]. The virion first attaches to human cells via the receptor CD155 [2], and binding initiates an irreversible conformational change in the capsid [3,4]. This structural change exposes capsid proteins that attach the particle to the membrane in a now receptor-independent manner [5,6], and cell entry occurs via endocytosis that does not require clathrin, but is actin- and tyrosine kinase- dependent [7]. A recent review by Paul and Wimmer [8] includes details on the process of poliovirus replication after cell entry.
Poliovirus RNA replication is always membrane-associated [9] and it has been shown that pre-existing cell membranes do not support genome replication [10]. Therefore, it is not surprising that lipid synthesis is upregulated [11] in infected cells, resulting in dramatic cellular changes. Newly formed membranous structures include specialized sites of RNA replication that have been described as “replication factories” [12]. To facilitate the replication process, replication factories are comprised of cellular membranes that are remodeled and expanded with newly synthesized lipids.
Excellent reviews on RNA viruses have been written recently [13,14,15], including a table in the Neuman et al., review enumerating membrane rearrangements from many (+) RNA viruses [15], as well as in this issue [16]. Our review focuses on the major role that electron microscopy has played in elucidating the extensive protein-lipid structures that are induced to support replication of the picornavirus poliovirus (PV) RNA. In addition, discussion is included on upregulation and changes in the lipid species that are incorporated into replication factories.
Microscopy of poliovirus-infected cells began almost 60 years ago to document the wide-ranging morphological changes that occur within infected cells. Reports beginning in 1956 detailed the first visible cellular changes, appearing by three hours post infection (hpi), using phase light microscopy at 100× magnification [17]. In 1958, electron microscopy was first used to visualize details of cytopathic effects and ultrastructure changes in poliovirus-infected cells [18]. Early electron microscopy studies include morphological data that has not been discussed in detail in recent literature. These early results, and more recent work, are described below, and included in a discussion of the membrane remodeling and expansion required for replication of the poliovirus genome.
2. Poliovirus-Modulated Lipid Metabolism and Trafficking, and Their Effect on Cellular Morphology
(+) RNA viruses are dependent on cellular lipid metabolism and transport machinery for efficient genome replication. Phospholipid synthesis is significantly up-regulated [19,20,21] as early as 2 hpi in poliovirus infected cells [11]. Specific upregulated lipid species (Table 1) include phosphatidylcholine [19], sphingomyelin [11], and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) [22,23]. Fatty acid chain lengths of phosphatidylcholine are altered, with a longer acyl chain (C18/C18 and C18/C16) observed in infected cells as compared to mock-infected cells (C14/C16 and C16/C16) [24]. This alteration in the structural composition in poliovirus-infected cells indicates that membranes of poliovirus replication complexes are clearly distinct from pre-existing cellular membranes [25]. Lipid metabolism itself is critical for virus replication, as blocking de novo generation of phospholipids inhibits poliovirus RNA synthesis [26], indicating that poliovirus replication and virally induced lipid biosynthesis are coupled.
The mechanism by which the altered lipid metabolism induced by poliovirus infection contributes to virus replication is unclear. Various lengths of acyl chains and sizes of head groups of lipid components favor different membrane curvatures (reviewed in [27]). The spontaneous curvature caused by phosphatidylcholine (C10-14) is zero, forming flat lamellar structures [28]. Longer acyl chain lengths (C16-18) adapt phospholipids for forming more negative curvature membrane (formation of a concave surface) [29]. The longer acyl chains in infected cells [24] suggest that these newly synthesized phosphatidylcholines [11] may help induce the tubular deformation of proliferating membrane.
PI4P and cholesterol are enriched in the newly synthesized membrane structures and are critical for building poliovirus replication machinery and for efficient progeny RNA production. During infection, the phospholipid-modifying enzyme PI4KIIIβ is recruited to the replication site by poliovirus 3A (Table 1), resulting in a local elevation of its catalyzed product PI4P [23,30,31]. Since the poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (3D) can bind directly to PI4P in vitro, a model has been proposed in which one of the functions of PI4P in poliovirus replication is to recruit and maintain association of soluble 3D within membranous replication factories [23,32]. This interaction could be mediated by the negatively charged head group of PI4P and the net positive charge of 3D. Additionally, PI4P incorporation has been demonstrated to increase membrane curvature by interacting with membrane-remodeling proteins via its head group [33,34] as has been shown in cells infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) [35]. Such interactions are expected to induce membrane remodeling that facilitates efficient RNA replication.

Table 1.
Poliovirus induced alterations in lipids and proteins.
| Lipids/Proteins | Changes upon Infection (Superscripts Correspond to Methods Described in Next Column) | Experimental Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Lipid Biosynthesis and Lipid Composition | ||
| Phosphatidylcholine |
|
|
| Sphingomyelin |
|
|
| PI4P |
|
|
| Host long chain acyl-CoA synthetase |
|
|
| PI4KIIIβ |
|
|
| Poliovirus protein 2A |
|
|
| Poliovirus protein 3A |
|
|
| Lipid Transport and Lipid Redistribution | ||
| PI4P |
|
|
| Cholesterol |
|
|
| OSBP |
|
|
| Poliovirus protein 2BC |
|
|
| Poliovirus protein 3A |
|
|
PI4P: phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate, acyl-CoA: Acetyl coenzyme A; OSBP: Oxysterol-binding protein.
Cholesterol is a critical determinant of membrane fluidity and flexibility. It enters the cell from the extracellular medium through clathrin-mediated endocytosis from the plasma (reviewed in [42]), and is trafficked to replication factories with the aid of poliovirus protein 3A [41] (see Table 1). Formation of such cholesterol-enriched domains within replication membranes is proposed to counter potential over-fluidity and over-bending caused by the presence of the PI4P enrichment [41]. It has been reported that cholesterol helps build active virus replication complexes consisting of lipid rafts (detergent-resistant membrane microdomains that are enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids), in HCV, where RNA and proteins are enclosed and protected from cellular immune responses [43,44]. Observed non-uniform distribution of free cholesterol, segregated into patches, in poliovirus-infected cells [41] strongly suggests lipid rafts play a similar role in poliovirus replication.
A question arose regarding how PI4P and cholesterol are transported and enriched at the site of virus replication. Oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) has been demonstrated to be responsible for the transport of cholesterol and PI4P between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi [45], a pathway stimulated during poliovirus infection (see Table 1). Disruption of PI4KIIIβ or OSBP activity dramatically suppresses poliovirus RNA replication, possibly by obstructing the formation of viral replication complexes [40]. Together, PI4P and cholesterol enrichment, and synthesis of phospholipids with longer acyl chains, cooperate with viral proteins (discussed below) to modulate membrane remodeling for efficient RNA replication.
Membrane-associated poliovirus proteins are key participants in the membrane remodeling that is essential for viral RNA replication [46]. The role of individual proteins has been explored through gene expression or direct delivery of poliovirus proteins in cultured cells, with visualization of their cellular effects by electron microscopy. Results of these experiments are described in Table 2.

Table 2.
Membrane remodeling induced by individual poliovirus proteins in the cell. Roles of individual poliovirus proteins in membrane remodeling.
| Poliovirus Protein | Membrane Structures Induced upon Protein Expression/Delivery in Cells |
|---|---|
| 2BC |
|
| 2C |
|
| 3AB |
|
| 3A |
|
| 2BC and 3A |
|
| 2C and 3A |
|
Based on the lipid biochemical experiments discussed above and the studies shown in Table 2, ER membrane structures have been proposed to be, at least partially, the origin of poliovirus-induced vesicles [30,49]. It has also been shown that an individual viral protein is capable of invaginating liposomes [51], suggesting that viral proteins directly, in the absence of cellular proteins, are sufficient for membrane remodeling. Optimal poliovirus replication is dependent on newly synthesized lipids (Table 1) and virus proteins (Table 2) that together produce efficient replication factories.
3. Viral Replication Cycle as Observed by Electron Microscopy
3.1. Overview of Cellular Changes
Poliovirus-infected cells display distinct morphological changes throughout infection. In overview, during early infection light microscopy data show a loss of chromatin from the central region of the nucleus and chromatin appears to be condensed near the nuclear membrane [17]. At 2.5 hpi, poliovirus-induced blebbing from the ER membrane is observed by electron microscopy [52], and at 3–3.5 hpi vesicles appear within the cytoplasm [52,53,54,55]. Large numbers of cytoplasmic bodies, originally called “U bodies”, were first observed by electron microscopy at 4–7 hpi [18]. Vesicles become more numerous over the course of infection, until the cytoplasm is vesicle-filled, as seen by electron microscopy of thin-sectioned cells [18,53,54]. Virus-induced vesicles are generally smooth-walled, with sizes that range from 50-200 nm in diameter. Late in infection, 7.5–9 hpi, cells round up and the cytoplasm has small and large clear vacuoles [18]. In addition, the nucleus is further distorted and can be difficult to distinguish, mitochondria are swollen, and U bodies are no longer visible. No further changes are observed in the cellular ultrastructure after this time and before cell lysis [56], and it has been suggested that major alterations in cell morphology beyond 7 hpi are an indication of the disruption of all physiological systems in the cell rather than related to virus replication [18].
The morphology of poliovirus-induced vesicles has been investigated for nearly 60 years. Here we interpret these data, and discuss morphology information from these studies. While we are not able to include the original images, scaled, schematized versions are shown in Figure 1. It is important to note that while these drawings are our interpretation of the data, results from different groups show similar features and are consistent with what we describe here. A schematic of an uninfected HeLa cell, shown in Figure 1A, schematized from Schlegel et al., 1996 [54], provides a point of reference for cell morphology changes that are visible in poliovirus-infected cells.
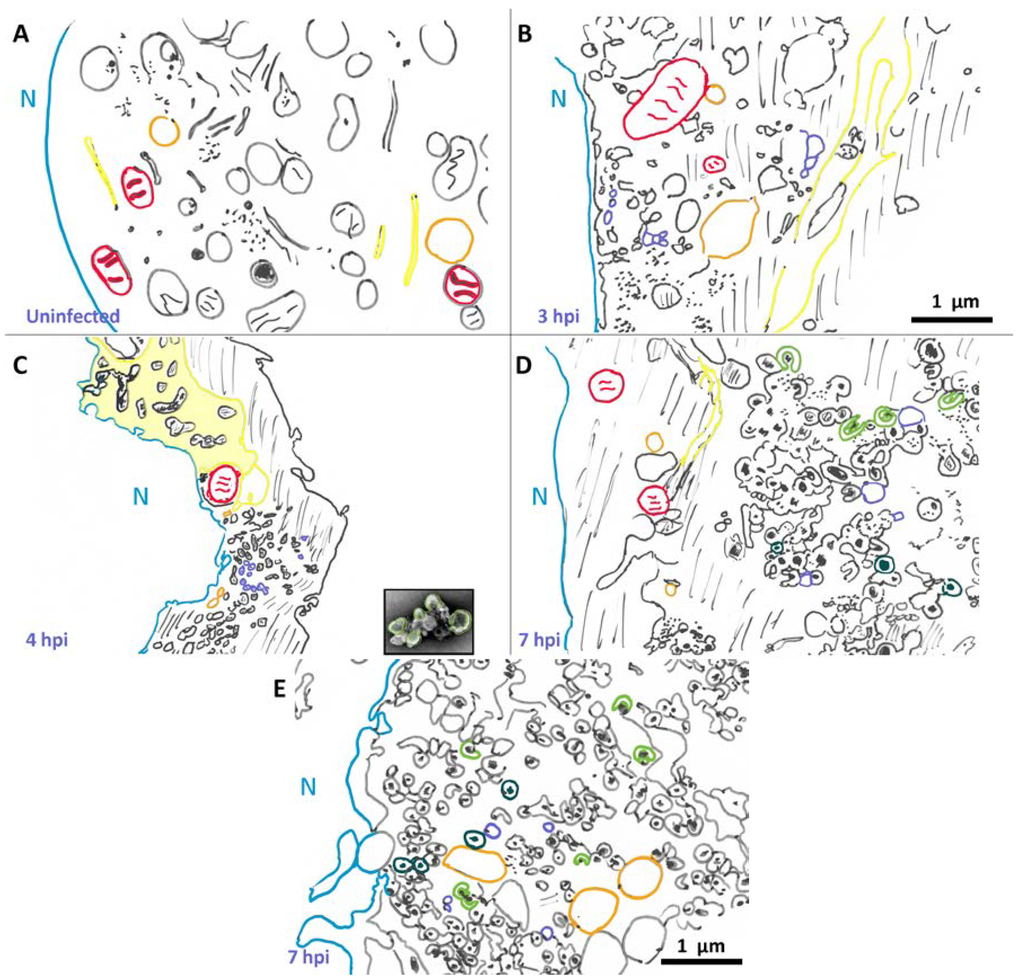
Figure 1.
Changes in cellular morphology after poliovirus infection. Schematized cells from electron micrographs in Schlegel et al., (A,D) [54], Dales et al., (B,E) [53], and Mattern and Daniels (C) [57]. Representative structures are marked: nuclear membrane (blue), mitochondria (red), vacuoles (orange). Lines denote cytoplasm, and dots represent “viroplasm”. Endoplasmic reticulum (yellow) becomes enlarged and sometimes called “nuclear extrusions” (as in panel C). Early in infection single membrane vesicles (purple) are visible, and later the appearance of U bodies/horseshoe-shaped vesicles (green) and double membrane vesicles (teal). In panel C, an image of a fractionated rosette (from Figure 3) is shown to scale, highlighting its similarity to structures seen within infected cells. Scale bar 1 μm.
3.2. Morphological Details of Virus-Induced Membranes throughout Infection
The first morphological changes within the infected cell are apparent in the ER at 2.5 hpi [52]. Dramatic cellular changes are observed at 3 hpi. In 1965, Dales et al. [53] showed the appearance of single membrane vesicular bodies in the perinuclear region of the cytoplasm in infected cells at 3 hpi, as seen in Figure 1B. More recently, Belov et al. [55] collected three-dimensional data and have shown that what appeared to be vesicles in two dimensions are, in fact, inter-connected branching tubular structures. In addition to the appearance of single membrane tubular structures, the endoplasmic reticulum itself has undergone a transformation by 3 hpi. The lumenal space in the endoplasmic reticulum is enlarged, forming structures described as “nuclear extrusions” by Mattern and Daniel [57], as depicted in Figure 1C. These extended, altered endoplasmic reticulum-derived structures appear adjacent to newly formed perinuclear membranous structures. It is tempting to envision that poliovirus-induced vesicles derive from such nuclear extrusions.
By 1996, Schlegel et al. [54] were able to achieve enhanced sample preservation using high pressure freezing and freeze substitution. Their data show similar structures to those seen in earlier studies, with additional details visible. Particularly notable are double membrane structures preserved by tannic acid. Vesicles observed by these researchers 5 hpi (Figure 1D) are substantially different than those seen at 3 hpi. While single membrane vesicles are still visible at 5 hpi, there are now multiple clusters of poliovirus-induced vesicles evident within the cytoplasm, varying in location from perinuclear to peripheral. Vesicles within these clusters appear to be predominantly round or oval, and frequently display double membrane morphology. We note that some of these vesicles show lumenal content with increased densities compared to cytoplasm.
Even more striking is that some of these double membrane morphologies are not completely closed, but instead maintain a horseshoe-like appearance with a gated lumen that is connected to the cytoplasm through a neck approximately 15 nm in diameter. These structures appear similar in shape and size to U bodies described earlier [18] and resemble those discussed above in work by Dales et al. [53]. The U bodies may represent a transition state from single to double membrane vesicles or vice versa, but this is not yet clear. As seen in Figure 1D, at 5 hpi vesicles range in size from 100–200 nm in diameter, and clusters of vesicles are on the order of 1–2 μm across.
By 7 hpi (Figure 1E, schematized from [53]), there are more double membrane vesicles, as well as fewer single membrane vesicles. The changes are not as dramatic from 5 to 7 hpi as they are from 3–5 hpi, but poliovirus capsids are visible dispersed through the vesicle clusters, occasionally appearing as crystals, and frequently within the lumen of double-membrane vesicles.
Electron tomography data from Belov et al., 2012 [55] revealed that the three-dimensional morphology of poliovirus vesicles is even more complicated than what had been visualized in two dimensions. At 3 hpi, vesicles in the cytoplasm consist of irregularly shaped, branching clusters of single membrane vesicles. The diameters of individual vesicles range from approximately 25–300 nm. These tubular vesicles appear tightly clustered, with their morphologies influenced by neighboring vesicles. At 4 hpi, individual vesicles appear larger in volume and some have associated viruses on their cytoplasmic side. At 7 hpi, most of the vesicular structures are composed of double membrane vesicles, with tightly apposed membranes. These more oval structures appear to be better separated, and less convoluted, with larger interior regions than the membranous structures visible at 3 and 4 hpi. As mentioned above, some of these double membrane structures appear to have gated lumenal areas, with a roughly round central lumen of diameter ~250 nm and a gate opening of ~20 nm. These three-dimensional data may correspond to similar horseshoe shaped structures observed earlier [18,54].
4. Cell Fractionation for Investigation of Poliovirus Replication Factories
Fractionated samples may represent isolation of clusters of poliovirus vesicles. Membrane-associated cellular and viral processes such as virus replication and protein translation are well separated by subcellular fractionation, as shown in Figure 2. The work of Caliguiri and Tamm [58] showed that sucrose density fractions arising from infected cells display significant increases in lipids and that the fraction containing twice the phospholipid content, as compared to the corresponding mock-infected sample, comprises vesicles with a smooth membrane (Fraction 2 in Figure 2) and contains newly synthesized phospholipids. The relative amount of smooth membrane increases during the course of virus infection, as compared to rough membrane [59]. Both Caliguiri and Mosser [60] and Butterworth et al. [61] provided evidence that the most abundant protein in this smooth membrane fraction is a 37 kDa polypeptide “X”, which has since been renamed poliovirus protein 2C (see [62] for a table of poliovirus protein nomenclature). Poliovirus protein 2C is associated with membrane remodeling (see Table 2), and is known to play a critical role in virus replication, which occurs on smooth membrane. A fraction containing rough membrane (membrane decorated with ribosomes; Fraction 5 in Figure 2), contains the majority of infectious virus. These data indicate that fractionation successfully separates RNA replication factories from virions as evidenced by a discrete distribution of replicative intermediates. This ability to resolve, by buoyancy, vesicles associated with infectious virus from those associated with RNA production, indicates that vesicles associated with replication are distinct from those associated with protein translation or virion packaging.
Within Fraction 2 (Figure 2), replication complexes active in replication have been named “rosettes” and characterized by the work of Bienz et al., 1990 [63]. As seen in Figure 3, rosettes appear as multivesicular aggregates, the overall configuration appearing as an oval shape approximately 1 μm by 500 nm, with an unknown height. These structures were called rosettes because they are composed of large (200–400 nm diameter) vesicles (“petals”) surrounding a more compact central structure [54,63,64,65]. While rosette structure is not necessary for RNA replication [21], the overall organization and morphology between isolated samples and clusters seen in sections prepared from virus-infected cells appears to be conserved, as seen in a to-scale schematic of Figure 3 included in panel D of Figure 1.
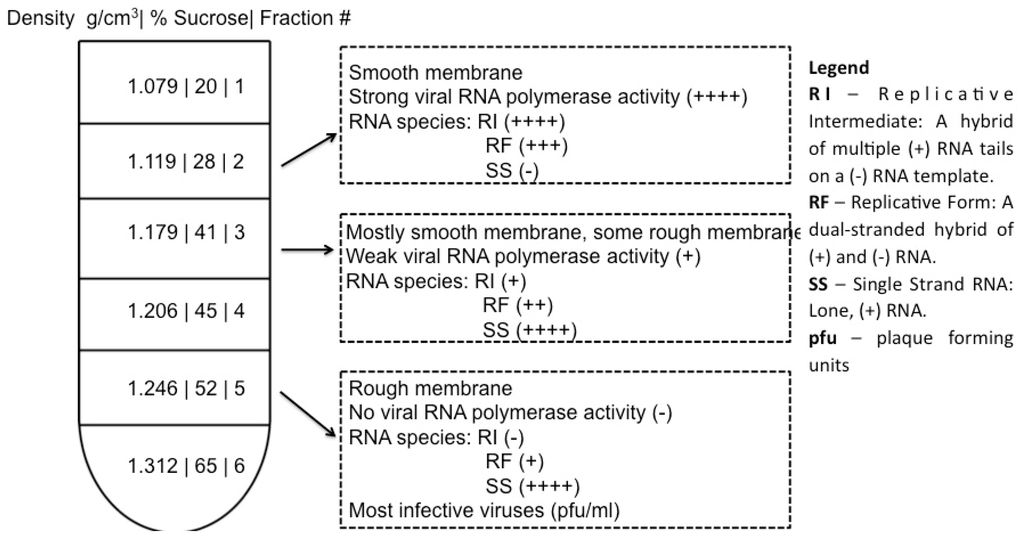
Figure 2.
Subcellular fractionation of functionally distinct vesicles associated with replication processes. In work by Caliguiri and Tamm, Dounce homogenates of HeLa cells were layered in a discontinuous sucrose gradient, centrifuged at 86,000 x g. Upon fractionation of the gradient, membrane bands with the indicated densities were collected. Properties of fractions 2, 3, and 5 are shown. Vesicle content was examined by electron microscopy [58]; RNA polymerase activity of the isolated fraction was measured by tritiated ATP incorporation; the abundance of RNA species (RI, RF, SS) was determined by gel electrophoresis; and viral titer was measured by plaque assay [58,66]. Note: data from Caliguiri and Tamm [58,66,67].
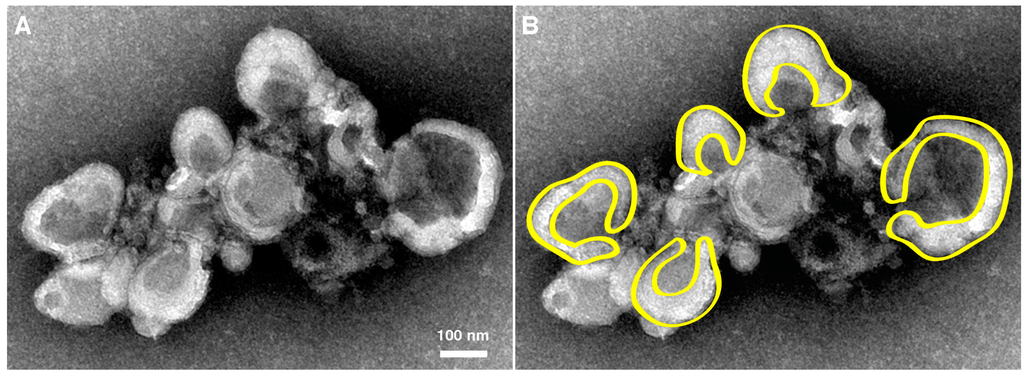
Figure 3.
Morphology of rosette isolated from poliovirus-infected cells. (A) U body-like densities surround a dense central region of smaller vesicles. Cell fractionated material was prepared and imaged by Evan Rossignol using methods from Schlegel et al., 1996 [54]. Sample from 4 hpi is negatively stained and imaged by electron microscopy; (B) Cartoon highlights the horseshoe-shaped (U body-like) configurations of individual vesicles of the cluster. Magnification bar, 100 nm.
5. Conclusions
During poliovirus infection there is a continuum of membranous structures that are formed in concert with assembly of replication factories and in support of RNA replication, as shown schematized in Figure 4. Virus-induced membranous structures begin to appear at 2.5 hpi [52] (Figure 4A), and dominate the cytoplasmic space by 7 hpi [18,53]. These structures serve multiple roles in virus-infected cells, including as a site for RNA replication [68] (Figure 4B,C), for RNA packaging (Figure 4B) [69,70], and for virus maturation [71,72,73,74,75] (Figure 4D,E). It is not clear whether membranous structures transition between roles or are independently formed. Indeed, if there are independent membrane formation paths for different viral roles, this could explain the observed presence in replication factories of markers from different cellular origins (ER, Golgi, etc.).
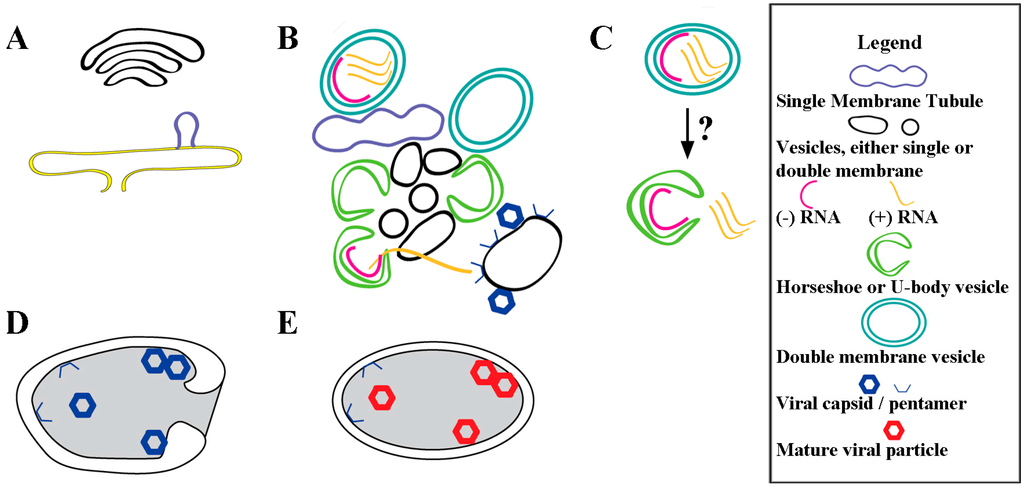
Figure 4.
Virus-induced membrane remodeling and expansion for poliovirus replication. (A) As early as 2.5 hpi, lipid buds off the ER [52], producing structures comprised of mostly virally induced lipids [11]; (B) New and pre-existing cellular vesicles are dynamically remodeled [55] and invaginated from tubules into vesicles, and U-bodies, using a unique lipid composition and specific virus proteins (listed in Table 1 and Table 2). Only a fraction of the membranous structures are involved in active RNA replication within lumenal spaces. Throughout infection (+) RNA exits the replication factory, destined for translation or packaging. For virus assembly, (+) RNA interacts with membrane-associated capsid protein pentamers on membranes that are distinct from replication factory membranes [70]; (C) Possible mechanism by which closed DMVs transitions to U-body with gated lumen. These structures are visible at timepoints beginning 4 hpi and are believed to continue active replication; (D) Autophagosome-like vesicle formation engulfs immature virus particles. These vesicles have twice the diameter of replication vesicles [71], and we posit that these membranes are distinct from those in RNA replication factories, which are still present in the cell; (E) Acidification of the autophagosome-like vesicles produces mature virus particles [72].
On a cellular scale, RNA synthesis is compartmentalized in infected cells. Negative-sense RNA is synthesized in a perinuclear region of ER, and (+) RNA in a more peripheral location [76]. Despite the fact that packaging of RNA is coupled to its replication [77], differing buoyant densities of fractionated vesicles indicate that packaging of RNA into virions occurs in a population of vesicles separate from those active in replication [64]. This suggests spatial compartmentalization of the viral processes, where (+) RNA migrates from the membranous site of RNA synthesis to membranous packaging sites, as shown in Figure 4B. Thus active replication involves only a fraction of the available membranous structures.
Early in infection poliovirus morphology and other (+) RNA viruses all appear to produce single membrane tubular structures [55,78]. The progression of the structures to double membrane vesicles is also shared. Evidence shows that RNA replication occurs within vesicle lumenal regions for multiple (+) RNA viruses (e.g., [79,80,81,82]). These structures may serve to sequester from host cell defenses the double-stranded RNA intermediate during RNA synthesis. In the case of a prototypical arterivirus, equine arteritis virus, the double membrane vesicles formed during infection label strongly for double-stranded RNA. These labeled vesicles display the same dark phenotype seen in a population of poliovirus vesicles. Analysis of the phosphorous content using electron spectroscopy reveals these vesicles in arterivirus infection contain the phosphorous content equivalent to roughly a dozen copies of the viral genome [81]. Although the method by which RNA products can exit the lumen of a double membrane vesicle is unclear for some viruses, poliovirus-infected cells display a possible intermediate. The U-bodies or horseshoe vesicles commonly observed late in poliovirus infection [18,53,54] display a gated lumenal morphology that is consistent with membrane fusion between the outer and inner vesicles, a feat possibly mediated in part by 3AB [51] (see Figure 4C).
Autophagosome-like vesicles are large double membrane structures, about twice the size of U bodies. They play a critical role in maturation of viruses, through acidification of the vesicle, which promotes the final step in virus maturation and viral transmission [46,71,72,83,84]. Better understanding of the pathways of vesicle transitions can help elucidate the infection cycle and the compartmentalization of function.
The complex cellular changes that occur throughout infection require specialized phospholipid biosynthesis that evolves over the time of infection [11,24,59]. In our model each vesicle population serves specialized roles (and perhaps some shared roles) that support the poliovirus replication processes. Different membranous species can co-exist temporally, providing a complex environment for efficient coordination of all aspects of poliovirus replication.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grant no. GM102474 to E.B.
Author Contributions
All authors participated in writing and editing this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Filman, D.J.; Syed, R.; Chow, M.; Macadam, A.J.; Minor, P.D.; Hogle, J.M. Structural factors that control conformational transitions and serotype specificity in type 3 poliovirus. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, C.L.; Wimmer, E.; Racaniello, V.R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell 1989, 56, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joklik, W.K.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The adsorption and early fate of purified poliovirus in HeLa cells. Virology 1961, 13, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sena, J.; Mandel, B. Studies on the in vitro uncoating of poliovirus. II. Characteristics of the membrane-modified particle. Virology 1977, 78, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricks, C.E.; Hogle, J.M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: Externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1934–1945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuthill, T.J.; Bubeck, D.; Rowlands, D.J.; Hogle, J.M. Characterization of early steps in the poliovirus infection process: Receptor-decorated liposomes induce conversion of the virus to membrane-anchored entry-intermediate particles. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, B.; Lee, L.Y.; Lakadamyali, M.; Rust, M.J.; Zhuang, X.; Hogle, J.M. Imaging Poliovirus Entry in Live Cells. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E. Initiation of protein-primed picornavirus RNA synthesis. Virus Res. 2015, 206, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, F.; Koch, G. The Molecular Biology of Poliovirus; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1985; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Egger, D.; Teterina, N.; Ehrenfeld, E.; Bienz, K. Formation of the poliovirus replication complex requires coupled viral translation, vesicle production, and viral RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6570–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornatzer, W.E.; Fischer, R.G. Effect of poliomyelitis virus on phospholipid metabolism of HeLa cell. JAMA 1961, 178, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, P.R. The organization of replication and transcription. Science 1999, 284, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Boon, J.A.; Diaz, A.; Ahlquist, P. Cytoplasmic viral replication complexes. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Brey, I.; Bartenschlager, R. Membranous replication factories induced by plus-strand RNA viruses. Viruses 2014, 6, 2826–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, B.W.; Angelini, M.M.; Buchmeier, M.J. Does form meet function in the coronavirus replicative organelle? Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, L.; Wolthers, K.C.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. Replication and Inhibitors of Enteroviruses and Parechoviruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 4529–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, D.W.; Melnick, J.L.; Reissig, M. Sequence of morphological changes in epithelial cell cultures infected with poliovirus. J. Exp. Med. 1956, 104, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kallman, F.; Williams, R.C.; Dulbecco, R.; Vogt, M. Fine Structure of Changes Produced in Cultured Cells Sampled at Specified Intervals During a Single Growth Cycle of Polio Virus. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1958, 4, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.E.; Trip, E.M.; Paddon, H.B. Poliovirus increases phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in HeLa cells by stimulation of the rate-limiting reaction catalyzed by CTP: Phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guinea, R.; Carrasco, L. Effects of fatty acids on lipid synthesis and viral RNA replication in poliovirus-infected cells. Virology 1991, 185, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, M.H.; Teterina, N.L.; Ehrenfeld, E. Membrane requirements for uridylylation of the poliovirus VPg protein and viral RNA synthesis in vitro. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11408–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Penman, S.; Summers, D. Effects on host cell metabolism following synchronous infection with poliovirus. Virology 1965, 27, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.Y.; Ilnytska, O.; Belov, G.; Santiana, M.; Chen, Y.H.; Takvorian, P.M.; Pau, C.; van der Schaar, H.; Kaushik-Basu, N.; Balla, T.; et al. Viral reorganization of the secretory pathway generates distinct organelles for RNA replication. Cell 2010, 141, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nchoutmboube, J.A.; Viktorova, E.G.; Scott, A.J.; Ford, L.A.; Pei, Z.; Watkins, P.A.; Ernst, R.K.; Belov, G.A. Increased Long Chain acyl-Coa Synthetase Activity and Fatt383y Acid Import Is Linked to Membrane Synthesis for Development of Picornavirus Replication Organelles. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, A.G.; Caliguiri, L.A.; Tamm, I. Incorporation of lipid precursors into cytoplasmic membranes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology 1972, 47, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, R.; Carrasco, L. Phospholipid biosynthesis and poliovirus genome replication, two coupled phenomena. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McMahon, H.T.; Gallop, J.L. Membrane curvature and mechanisms of dynamic cell membrane remodelling. Nature 2005, 438, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.N.A.H.; Mannock, D.A.; McElhaney, R.N.; Turner, D.C.; Gruner, S.M. Effect of fatty acyl chain length and structure on the lamellar gel to liquid-crystalline and lamellar to reversed hexagonal phase transitions of aqueous phosphatidylethanolamine dispersions. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szule, J.A.; Fuller, N.L.; Peter Rand, R. The Effects of Acyl Chain Length and Saturation of Diacylglycerols and Phosphatidylcholines on Membrane Monolayer Curvature. Biophys. J. 2015, 83, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, G.A.; Altan-Bonnet, N.; Kovtunovych, G.; Jackson, C.L.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Ehrenfeld, E. Hijacking components of the cellular secretory pathway for replication of poliovirus RNA. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Kojima, H.; Nagano, T.; Okabe, T.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Oxysterol-binding protein family I is the target of minor enviroxime-like compounds. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4252–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.L.; Soares-Martins, J.A.P.; Riddell, G.T.; Jackson, W.T. Generation of unique poliovirus RNA replication organelles. MBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, N.; Hill, C.M.; Bates, I.R.; Harauz, G. The formation of helical tubular vesicles by binary monolayers containing a nickel-chelating lipid and phosphoinositides in the presence of basic polypeptides. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2002, 114, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, M.; Grzybek, M.; Majkowski, M.; Rajesh, S.; Kaur, J.; Whittaker, S.B.-M.; Coskun, Ü.; Overduin, M. Structural Basis of Dynamic Membrane Recognition by trans-Golgi Network Specific FAPP Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Katikaneni, D.S.; Han, Q.; Sanchez-Felipe, L.; Hanada, K.; Ambrose, R.L.; Mackenzie, J.M.; Konan, K.V. Modulation of Hepatitis C Virus Genome Replication by Glycosphingolipids and Four-Phosphate Adaptor Protein 2. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12276–12295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowler, S.; Kular, G.; Alessi, D.R. Protein Lipid Overlay Assay. Sci. Signal. 2002, 2002, pl6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strating, J.R.P.M.; van der Linden, L.; Albulescu, L.; Bigay, J.; Arita, M.; Delang, L.; Leyssen, P.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Lanke, K.H.W.; Thibaut, H.J.; et al. Itraconazole Inhibits Enterovirus Replication by Targeting the Oxysterol-Binding Protein. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, E.M.; Samuvel, D.J.; Fog, J.U.; Eriksen, J.; Jayanthi, L.D.; Vaegter, C.B.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Gether, U. Membrane Mobility and Microdomain Association of the Dopamine Transporter Studied with Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy and Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 10484–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.M.; Williamson, D.; Rentero, C.; Gaus, K. Quantitative Microscopy: Protein Dynamics and Membrane Organisation. Traffic 2009, 10, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M. Phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase III beta and oxysterol-binding protein accumulate unesterified cholesterol on poliovirus-induced membrane structure. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilnytska, O.; Santiana, M.; Hsu, N.Y.; Du, W.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Viktorova, E.G.; Belov, G.; Brinker, A.; Storch, J.; Moore, C.; Dixon, J.L.; Altan-Bonnet, N. Enteroviruses harness the cellular endocytic machinery to remodel the host cell cholesterol landscape for effective viral replication. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-Y.; Chang, C.C.Y.; Ohgami, N.; Yamauchi, Y. Cholesterol Sensing, Trafficking, and Esterification. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizaki, H.; Lee, K.-J.; Sung, V.M.-H.; Ishiko, H.; Lai, M.M.C. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus RNA replication complex associated with lipid rafts. Virology 2004, 324, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Hoppe, S.; Saher, G.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Bartenschlager, R. Morphological and Biochemical Characterization of the Membranous Hepatitis C Virus Replication Compartment. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10612–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesmin, B.; Bigay, J.; Moser von Filseck, J.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Drin, G.; Antonny, B. A four-step cycle driven by PI(4)P hydrolysis directs sterol/PI(4)P exchange by the ER-Golgi tether OSBP. Cell 2013, 155, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, W.T. Poliovirus-induced changes in cellular membranes throughout infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 9, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.W.; Teterina, N.; Egger, D.; Bienz, K.; Ehrenfeld, E. Membrane rearrangement and vesicle induction by recombinant poliovirus 2C and 2BC in human cells. Virology 1994, 202, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doedens, J.R.; Giddings, T.H.; Kirkegaard, K. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi traffic by poliovirus protein 3A: Genetic and ultrastructural analysis. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 9054–9064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suhy, D.A.; Giddings, T.H.; Kirkegaard, K. Remodeling the endoplasmic reticulum by poliovirus infection and by individual viral proteins: An autophagy-like origin for virus-induced vesicles. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8953–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teterina, N.L.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Egger, D.; Bienz, K.; Ehrenfeld, E. Poliovirus 2C protein determinants of membrane binding and rearrangements in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8962–8972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ptacek, J.B.; Kirkegaard, K.; Bullitt, E. Double-membraned liposomes sculpted by poliovirus 3AB protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 27287–27298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienz, K.; Egger, D.; Pasamontes, L. Association of polioviral proteins of the P2 genomic region with the viral replication complex and virus-induced membrane synthesis as visualized by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry and autoradiography. Virology 1987, 160, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, S.; Eggers, H.J.; Tamm, I. Electron Microscopic Study of the Formation of Poliovirus. Virology 1965, 26, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, A.; Giddings, T.H.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Kirkegaard, K. Cellular origin and ultrastructure of membranes induced during poliovirus infection. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6576–6588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belov, G.A.; Nair, V.; Hansen, B.T.; Hoyt, F.H.; Fischer, E.R.; Ehrenfeld, E. Complex Dynamic Development of Poliovirus Membranous Replication Complexes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienz, K.; Egger, D.; Wolff, D.A. Virus replication, cytopathology, and lysosomal enzyme response of mitotic and interphase Hep-2 cells infected with poliovirus. J. Virol. 1973, 11, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattern, C.F.T.; Daniel, W.A. Replication of poliovirus in HeLa cells: Electron microscopic observations. Virology 1965, 26, 646–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliguiri, L.A.; Tamm, I. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in poliovirus biosynthesis. Virology 1970, 42, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, A.G.; Caliguiri, L.A.; Scheid, A.S.; Tamm, I. Chemical and enzymatic characteristics of cytoplasmic membranes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology 1972, 47, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliguiri, L.A.; Mosser, A.G. Proteins associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complex. Virology 1971, 46, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, B.E.; Shimshick, E.J.; Yin, F.H. Association of the polioviral RNA polymerase complex with phospholipid membranes. J. Virol. 1976, 19, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pallansch, M.A.; Kew, O.M.; Semler, B.L.; Omilianowski, D.R.; Anderson, C.W.; Wimmer, E.; Rueckert, R.R. Protein processing map of poliovirus. J. Virol. 1984, 49, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bienz, K.; Egger, D.; Troxler, M.; Pasamontes, L. Structural organization of poliovirus RNA replication is mediated by viral proteins of the P2 genomic region. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bienz, K.; Egger, D.; Pfister, T.; Troxler, M. Structural and functional characterization of the poliovirus replication complex. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egger, D.; Pasamontes, L.; Bolten, R.; Boyko, V.; Bienz, K. Reversible dissociation of the poliovirus replication complex: Functions and interactions of its components in viral RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8675–8683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caliguiri, L.A.; Tamm, I. Characterization of poliovirus-specific structures associated with cytoplasmic membranes. Virology 1970, 42, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliguiri, L.A.; Tamm, I. Membranous structures associated with translation and transcription of poliovirus RNA. Science 1969, 166, 885–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienz, K.; Egger, D.; Rasser, Y.; Bossart, W. Kinetics and location of poliovirus macromolecular synthesis in correlation to virus-induced cytopathology. Virology 1980, 100, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, R.W.; Nagington, J. Electron microscope studies of the development and structure of poliomyelitis virus. J. Mol. Biol. 1959, 1, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, T.; Pasamontes, L.; Troxler, M.; Egger, D.; Bienz, K. Immunocytochemical localization of capsid-related particles in subcellular fractions of poliovirus-infected cells. Virology 1992, 188, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Du, W.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Takvorian, P.M.; Pau, C.; Cali, A.; Brantner, C.A.; Stempinski, E.S.; Connelly, P.S.; Ma, H.-C.; et al. Phosphatidylserine Vesicles Enable Efficient En Bloc Transmission of Enteroviruses. Cell 2015, 160, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.L.; Jackson, W.T. Intracellular Vesicle Acidification Promotes Maturation of Infectious Poliovirus Particles. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.P.; Burgon, T.B.; Kirkegaard, K.; Jackson, W.T. Role of microtubules in extracellular release of poliovirus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6599–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, W.T.; Giddings, T.H.; Taylor, M.P.; Mulinyawe, S.; Rabinovitch, M.; Kopito, R.R.; Kirkegaard, K. Subversion of cellular autophagosomal machinery by RNA viruses. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, S.W.; Maynard, N.D.; Covert, M.W.; Kirkegaard, K. Nonlytic viral spread enhanced by autophagy components. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13081–13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, D.; Bienz, K. Intracellular location and translocation of silent and active poliovirus replication complexes. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, C.I.; Johnson, K.L.; Sarnow, P.; Kirkegaard, K. Functional coupling between replication and packaging of poliovirus replicon RNA. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Limpens, R.W.A.L.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Kumar, D.; Koster, A.J.; Snijder, E.J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Bárcena, M. The transformation of enterovirus replication structures: A three-dimensional study of single- and double-membrane compartments. MBio 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosert, R.; Kanjanahaluethai, A.; Egger, D.; Bienz, K.; Baker, S.C. RNA replication of mouse hepatitis virus takes place at double-membrane vesicles. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoops, K.; Kikkert, M.; van den Worm, S.H.E.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C.; van der Meer, Y.; Koster, A.J.; Mommaas, A.M.; Snijder, E.J. SARS-coronavirus replication is supported by a reticulovesicular network of modified endoplasmic reticulum. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 1957–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoops, K.; Barcena, M.; Limpens, R.W.A.L.; Koster, A.J.; Mommaas, A.M.; Snijder, E.J. Ultrastructural Characterization of Arterivirus Replication Structures: Reshaping the Endoplasmic Reticulum to Accommodate Viral RNA Synthesis. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Brey, I.; Merz, A.; Chiramel, A.; Lee, J.-Y.; Chlanda, P.; Haselman, U.; Santarella-Mellwig, R.; Habermann, A.; Hoppe, S.; Kallis, S.; et al. Three-dimensional architecture and biogenesis of membrane structures associated with hepatitis C virus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.P.; Kirkegaard, K. Modification of Cellular Autophagy Protein LC3 by Poliovirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12543–12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.M.; Tsueng, G.; Sin, J.; Mangale, V.; Rahawi, S.; McIntyre, L.L.; Williams, W.; Kha, N.; Cruz, C.; Hancock, B.M.; et al. Coxsackievirus B Exits the Host Cell in Shed Microvesicles Displaying Autophagosomal Markers. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).