ERVK Polyprotein Processing and Reverse Transcriptase Expression in Human Cell Line Models of Neurological Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Cytokine Treatment
2.2. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (Q-PCR)
2.3. Reverse Transcriptase (RT) Assay
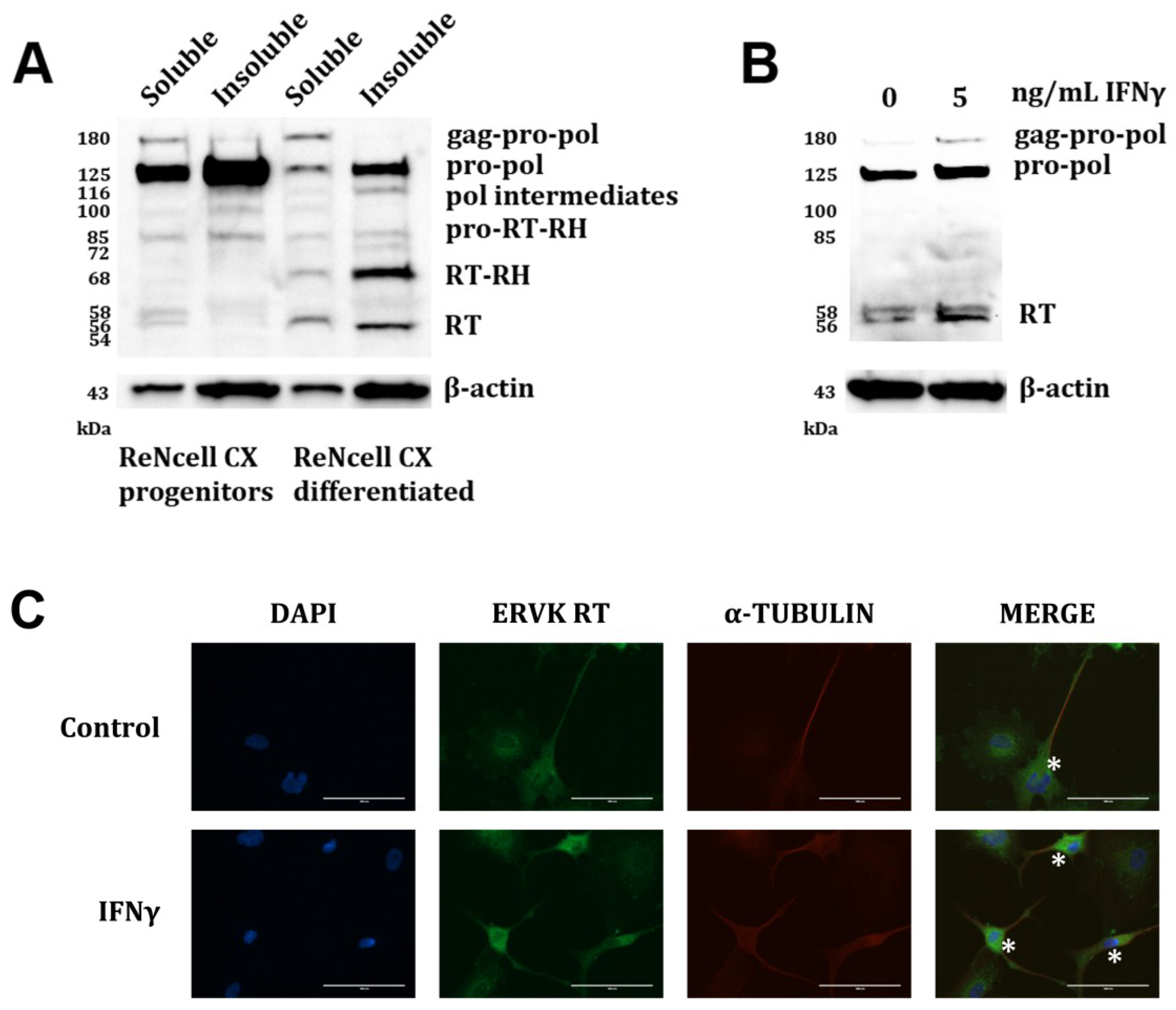
2.4. Western Blotting
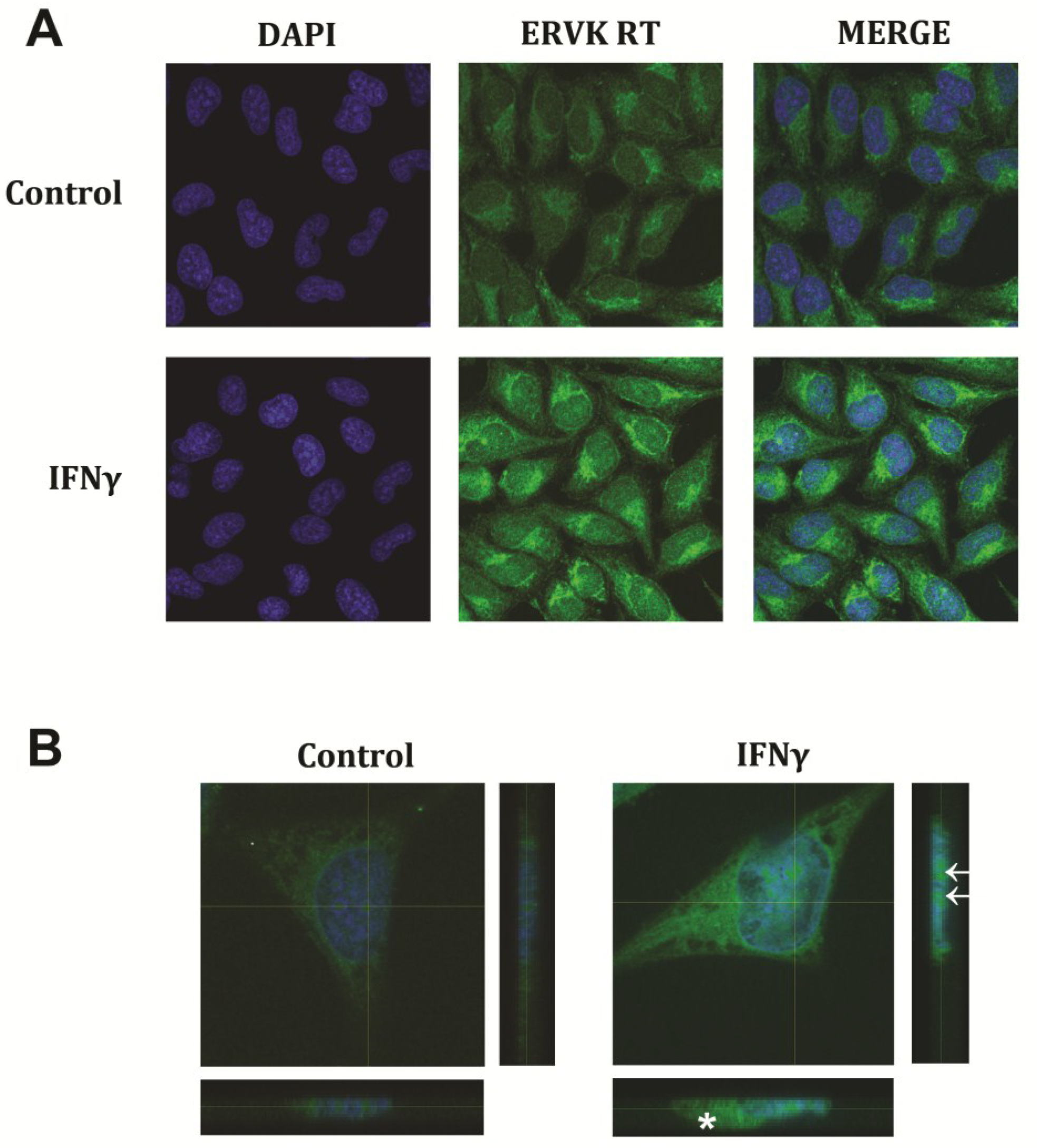
2.5. Fluorescent Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
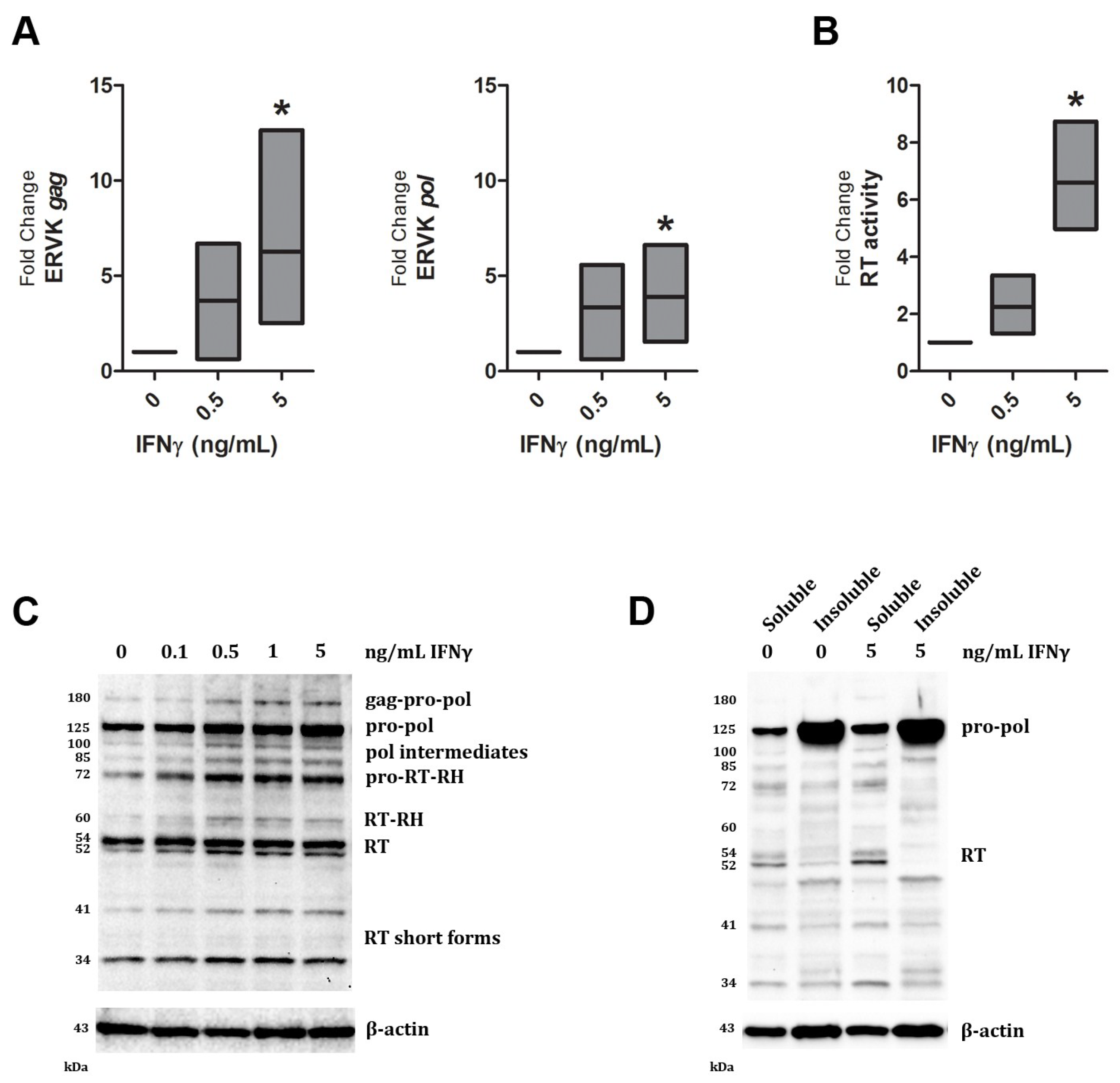
| Band size (kDa) | IFNγ dose (ng/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | 5 | |
| 180 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| 125 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 3.0 |
| 100 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 2.0 |
| 85 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 4.2 |
| 72 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.6 |
| 60 | 1.0 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 1.7 | 2.0 |
| 54 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| 52 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 2.1 |
| 41 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.8 |
| 34 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dube, D.; Contreras-Galindo, R.; He, S.; King, S.R.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.J.; Gitlin, S.D.; Kaplan, M.H.; Markovitz, D.M. Genomic flexibility of human endogenous retrovirus type K. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9673–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douville, R.N.; Nath, A. Human endogenous retroviruses and the nervous system. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 123, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manghera, M.; Ferguson, J.; Douville, R. Endogenous retrovirus-K and nervous system diseases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2014, 14, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohn, O.; Hanke, K.; Bannert, N. HERV-K(HML-2), the Best Preserved Family of HERVs: Endogenization, Expression, and Implications in Health and Disease. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Hera, B.; Varade, J.; Garcia-Montojo, M.; Lamas, J.R.; de la Encarnacion, A.; Arroyo, R.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, B.; Alvarez-Lafuente, R.; Urcelay, E. Role of the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K18 in autoimmune disease susceptibility: Study in the Spanish population and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e62090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, J.M.; Deslauriers, A.M.; Bhat, R.K.; Ellestad, K.K.; Power, C. Human endogenous retroviruses and multiple sclerosis: Innocent bystanders or disease determinants? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, C.; Mameli, G.; Arru, G.; Sotgiu, S.; Rosati, G.; Dolei, A. In vitro modulation of the multiple sclerosis (MS)-associated retrovirus by cytokines: Implications for MS pathogenesis. J. Neurovirol. 2003, 9, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Douville, R.; Liu, J.; Rothstein, J.; Nath, A. Identification of active loci of a human endogenous retrovirus in neurons of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muster, T.; Waltenberger, A.; Grassauer, A.; Hirschl, S.; Caucig, P.; Romirer, I.; Fodinger, D.; Seppele, H.; Schanab, O.; Magin-Lachmann, C.; et al. An endogenous retrovirus derived from human melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8735–8741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Galindo, R.; Kaplan, M.H.; Markovitz, D.M.; Lorenzo, E.; Yamamura, Y. Detection of HERV-K(HML-2) viral RNA in plasma of HIV type 1-infected individuals. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2006, 22, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Brusic, V.; McColl, G.; Harrison, L.C. Direct evidence for the expression of multiple endogenous retroviruses in the synovial compartment in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, A.L.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Cudkowicz, M.E.; al-Chalabi, A.; Garson, J.A. Quantification of reverse transcriptase in ALS and elimination of a novel retroviral candidate. Neurology 2008, 70, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, M.; Hizi, A.; Resau, J.H.; Yaal-Hahoshen, N.; Reichman, H.; Keydar, I.; Tsarfaty, I. Human endogenous retrovirus (HERV-K) reverse transcriptase as a breast cancer prognostic marker. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Galindo, R.; Kaplan, M.H.; Contreras-Galindo, A.C.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.J.; Ferlenghi, I.; Giusti, F.; Lorenzo, E.; Gitlin, S.D.; Dosik, M.H.; Yamamura, Y.; et al. Characterization of human endogenous retroviral elements in the blood of HIV-1-infected individuals. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.K.; Rudnick, W.; Antony, J.M.; Maingat, F.; Ellestad, K.K.; Wheatley, B.M.; Tonjes, R.R.; Power, C. Human endogenous retrovirus-K(II) envelope induction protects neurons during HIV/AIDS. PLoS One 2014, 9, e97984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, O.; Giehl, M.; Zheng, C.; Hehlmann, R.; Leib-Mosch, C.; Seifarth, W. Human endogenous retrovirus expression profiles in samples from brains of patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10890–10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freimanis, G.; Hooley, P.; Ejtehadi, H.D.; Ali, H.A.; Veitch, A.; Rylance, P.B.; Alawi, A.; Axford, J.; Nevill, A.; Murray, P.G.; et al. A role for human endogenous retrovirus-K (HML-2) in rheumatoid arthritis: Investigating mechanisms of pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 160, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S. The prevalence of human endogenous retroviruses in cerebrospinal fluids from patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balada, E.; Ordi-Ros, J.; Vilardell-Tarres, M. Molecular mechanisms mediated by human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) in autoimmunity. Rev. Med. Virol. 2009, 19, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mameli, G.; Astone, V.; Arru, G.; Marconi, S.; Lovato, L.; Serra, C.; Sotgiu, S.; Bonetti, B.; Dolei, A. Brains and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients hyperexpress MS-associated retrovirus/HERV-W endogenous retrovirus, but not Human herpesvirus 6. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denne, M.; Sauter, M.; Armbruester, V.; Licht, J.D.; Roemer, K.; Mueller-Lantzsch, N. Physical and functional interactions of human endogenous retrovirus proteins Np9 and rec with the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5607–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhout, B.; Jebbink, M.; Zsiros, J. Identification of an active reverse transcriptase enzyme encoded by a human endogenous HERV-K retrovirus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seckler, J.M.; Howard, K.J.; Barkley, M.D.; Wintrode, P.L. Solution structural dynamics of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase heterodimer. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7646–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, M.; Schwecke, T.; Beimforde, N.; Hohn, O.; Chudak, C.; Zimmermann, A.; Kurth, R.; Naumann, D.; Bannert, N. Identification of the protease cleavage sites in a reconstituted Gag polyprotein of an HERV-K(HML-2) element. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, B.; Boller, K.; Reuter, A.; Schnierle, B.S. Characterization of the human endogenous retrovirus K Gag protein: Identification of protease cleavage sites. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Maldarelli, F.; Mellors, J.; Coffin, J.M. HIV-1 infection leads to increased transcription of HERV-K (HML-2) proviruses in vivo but not to increased virion production. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11108–11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SenGupta, D.; Tandon, R.; Vieira, R.G.; Ndhlovu, L.C.; Lown-Hecht, R.; Ormsby, C.E.; Loh, L.; Jones, R.B.; Garrison, K.E.; Martin, J.N.; et al. Strong human endogenous retrovirus-specific T cell responses are associated with control of HIV-1 in chronic infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6977–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang-Johanning, F.; Radvanyi, L.; Rycaj, K.; Plummer, J.B.; Yan, P.; Sastry, K.J.; Piyathilake, C.J.; Hunt, K.K.; Johanning, G.L. Human endogenous retrovirus K triggers an antigen-specific immune response in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5869–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapshak, P.; Duncan, R.; Minagar, A.; Rodriguez de la Vega, P.; Stewart, R.V.; Goodkin, K. Elevated expression of IFN-gamma in the HIV-1 infected brain. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehla, R.; Guha, D.; Ayyavoo, V. Chemokine Deregulation in HIV Infection: Role of Interferon Gamma Induced Th1-Chemokine Signaling. J. Clin. Cell Immunol. 2012, S7, 004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Henderson, L.J.; Major, E.O.; al-Harthi, L. IFN-gamma mediates enhancement of HIV replication in astrocytes by inducing an antagonist of the beta-catenin pathway (DKK1) in a STAT 3-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6771–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll-Anzinger, D.; al-Harthi, L. Gamma interferon primes productive human immunodeficiency virus infection in astrocytes. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, E.O.; Miller, A.E.; Mourrain, P.; Traub, R.G.; de Widt, E.; Sever, J. Establishment of a line of human fetal glial cells that supports JC virus multiplication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, R.; Miljan, E.A.; Hines, S.J.; Aouabdi, S.; Pollock, K.; Patel, S.; Edwards, F.A.; Sinden, J.D. Differential development of neuronal physiological responsiveness in two human neural stem cell lines. BMC Neurosci. 2007, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GraphPad Prism, version 6.03; GraphPad Software: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2013.
- Image Lab Software, version 4.0; Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc: Hercules, CA, USA, 2011.
- Seifarth, W.; Baust, C.; Murr, A.; Skladny, H.; Krieg-Schneider, F.; Blusch, J.; Werner, T.; Hehlmann, R.; Leib-Mosch, C. Proviral structure, chromosomal location, and expression of HERV-K-T47D, a novel human endogenous retrovirus derived from T47D particles. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8384–8391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pettit, S.C.; Clemente, J.C.; Jeung, J.A.; Dunn, B.M.; Kaplan, A.H. Ordered processing of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 GagPol precursor is influenced by the context of the embedded viral protease. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10601–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, S.C.; Lindquist, J.N.; Kaplan, A.H.; Swanstrom, R. Processing sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Gag-Pro-Pol precursor are cleaved by the viral protease at different rates. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.J.; Carr, J.M.; Bagley, C.J.; Powell, J.; Warrilow, D.; Harrich, D.; Burrell, C.J.; Li, P. Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 reverse transcriptase exists as post-translationally modified forms in virions and cells. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebischer, J.; Moumen, A.; Sazdovitch, V.; Seilhean, D.; Meininger, V.; Raoul, C. Elevated levels of IFNgamma and LIGHT in the spinal cord of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 752–759, e45–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mameli, G.; Astone, V.; Khalili, K.; Serra, C.; Sawaya, B.E.; Dolei, A. Regulation of the syncytin-1 promoter in human astrocytes by multiple sclerosis-related cytokines. Virology 2007, 362, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgarbanti, M.; Remoli, A.L.; Marsili, G.; Ridolfi, B.; Borsetti, A.; Perrotti, E.; Orsatti, R.; Ilari, R.; Sernicola, L.; Stellacci, E.; et al. IRF-1 is required for full NF-kappaB transcriptional activity at the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat enhancer. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3632–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manghera, M.; Douville, R.N. Endogenous retrovirus-K promoter: A landing strip for inflammatory transcription factors? Retrovirology 2013, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.S.; Tozser, J.; Princler, G.; Lloyd, P.A.; Auth, A.; Derse, D. Synthesis, processing, and composition of the virion-associated HTLV-1 reverse transcriptase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 3964–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluis-Cremer, N.; Arion, D.; Abram, M.E.; Parniak, M.A. Proteolytic processing of an HIV-1 pol polyprotein precursor: Insights into the mechanism of reverse transcriptase p66/p51 heterodimer formation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, L.L.; Boyer, P.L.; Clark, P.K.; Hughes, S.H. Mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase cause misfolding and miscleavage by the viral protease. Virology 2013, 444, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hottiger, M.; Gramatikoff, K.; Georgiev, O.; Chaponnier, C.; Schaffner, W.; Hubscher, U. The large subunit of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase interacts with beta-actin. Nucl. Acids Res. 1995, 23, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, M.; Guo, J.; Wu, Y. The trinity of the cortical actin in the initiation of HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassati, A.; Gorlich, D.; Harrison, I.; Zaytseva, L.; Mingot, J.M. Nuclear import of HIV-1 intracellular reverse transcription complexes is mediated by importin 7. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3675–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idriss, H.; Kawa, S.; Damuni, Z.; Thompson, E.B.; Wilson, S.H. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is phosphorylated in vitro and in a cellular system. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, N.D.; McFate, T.; Mohyeldin, A.; Okagaki, P.; Korotchkina, L.G.; Patel, M.S.; Jeoung, N.H.; Harris, R.A.; Schell, M.J.; Verma, A. Phosphorylation status of pyruvate dehydrogenase distinguishes metabolic phenotypes of cultured rat brain astrocytes and neurons. Glia 2010, 58, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manghera, M.; Ferguson, J.; Douville, R. ERVK Polyprotein Processing and Reverse Transcriptase Expression in Human Cell Line Models of Neurological Disease. Viruses 2015, 7, 320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7010320
Manghera M, Ferguson J, Douville R. ERVK Polyprotein Processing and Reverse Transcriptase Expression in Human Cell Line Models of Neurological Disease. Viruses. 2015; 7(1):320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7010320
Chicago/Turabian StyleManghera, Mamneet, Jennifer Ferguson, and Renée Douville. 2015. "ERVK Polyprotein Processing and Reverse Transcriptase Expression in Human Cell Line Models of Neurological Disease" Viruses 7, no. 1: 320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7010320
APA StyleManghera, M., Ferguson, J., & Douville, R. (2015). ERVK Polyprotein Processing and Reverse Transcriptase Expression in Human Cell Line Models of Neurological Disease. Viruses, 7(1), 320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7010320






