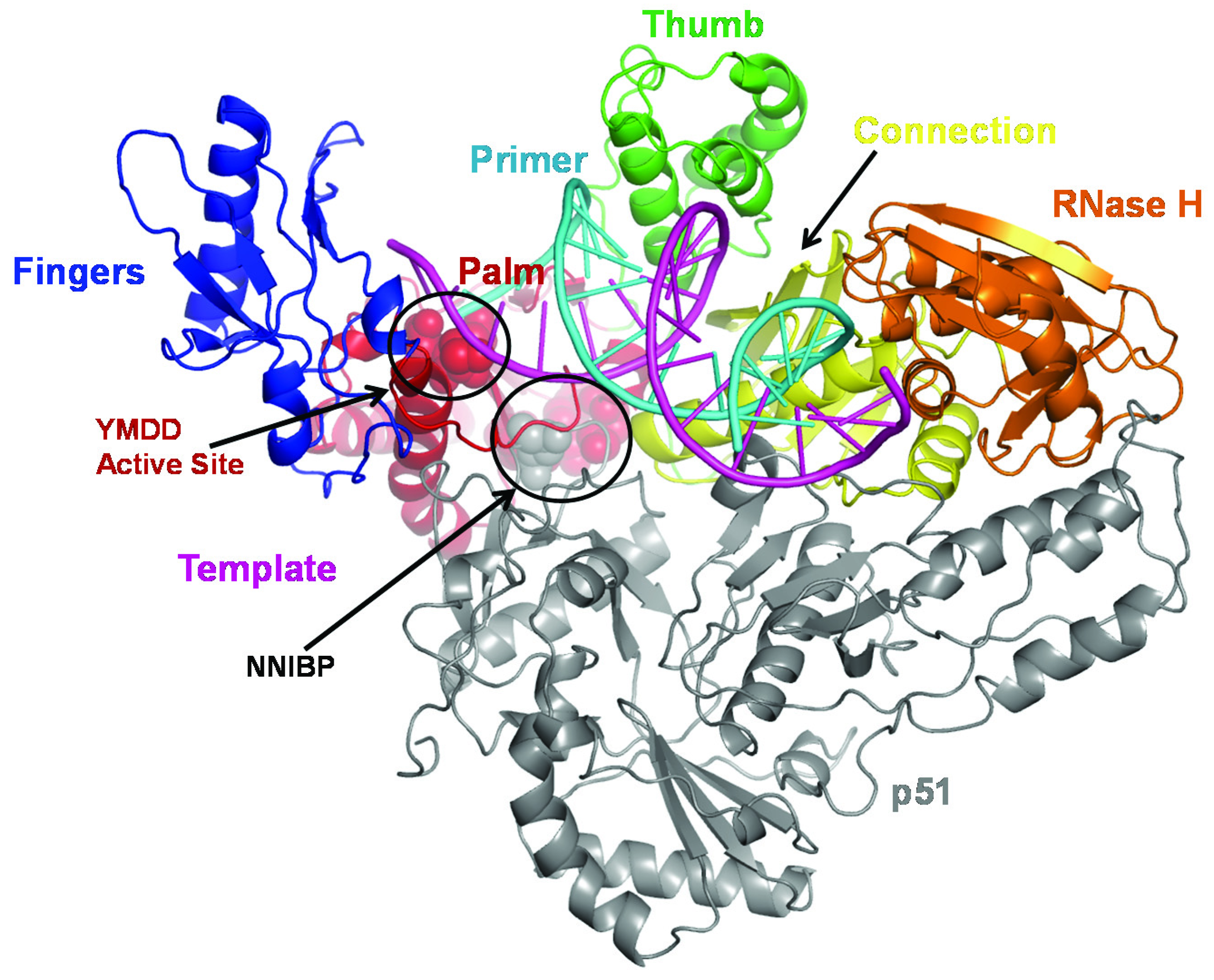
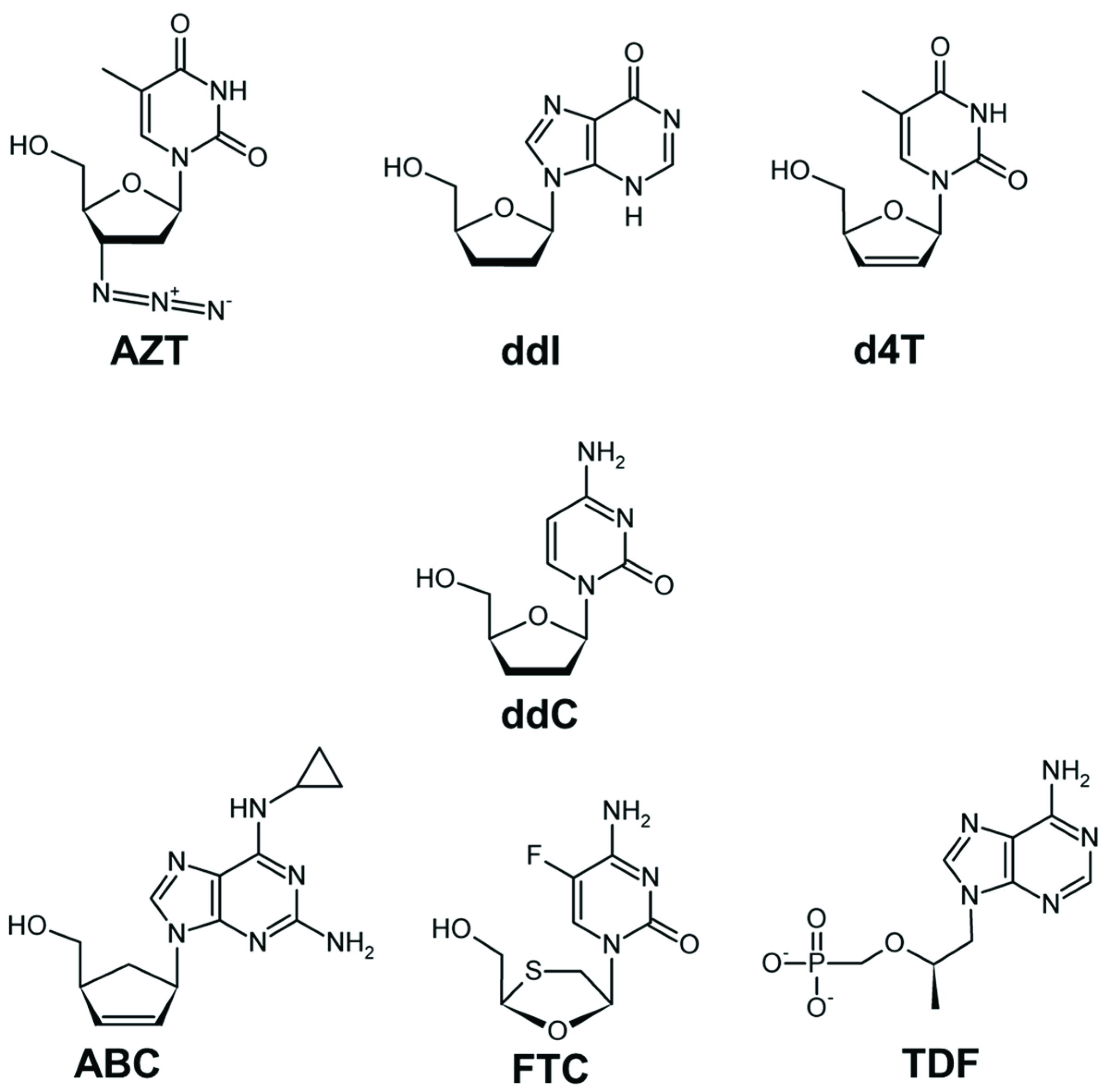
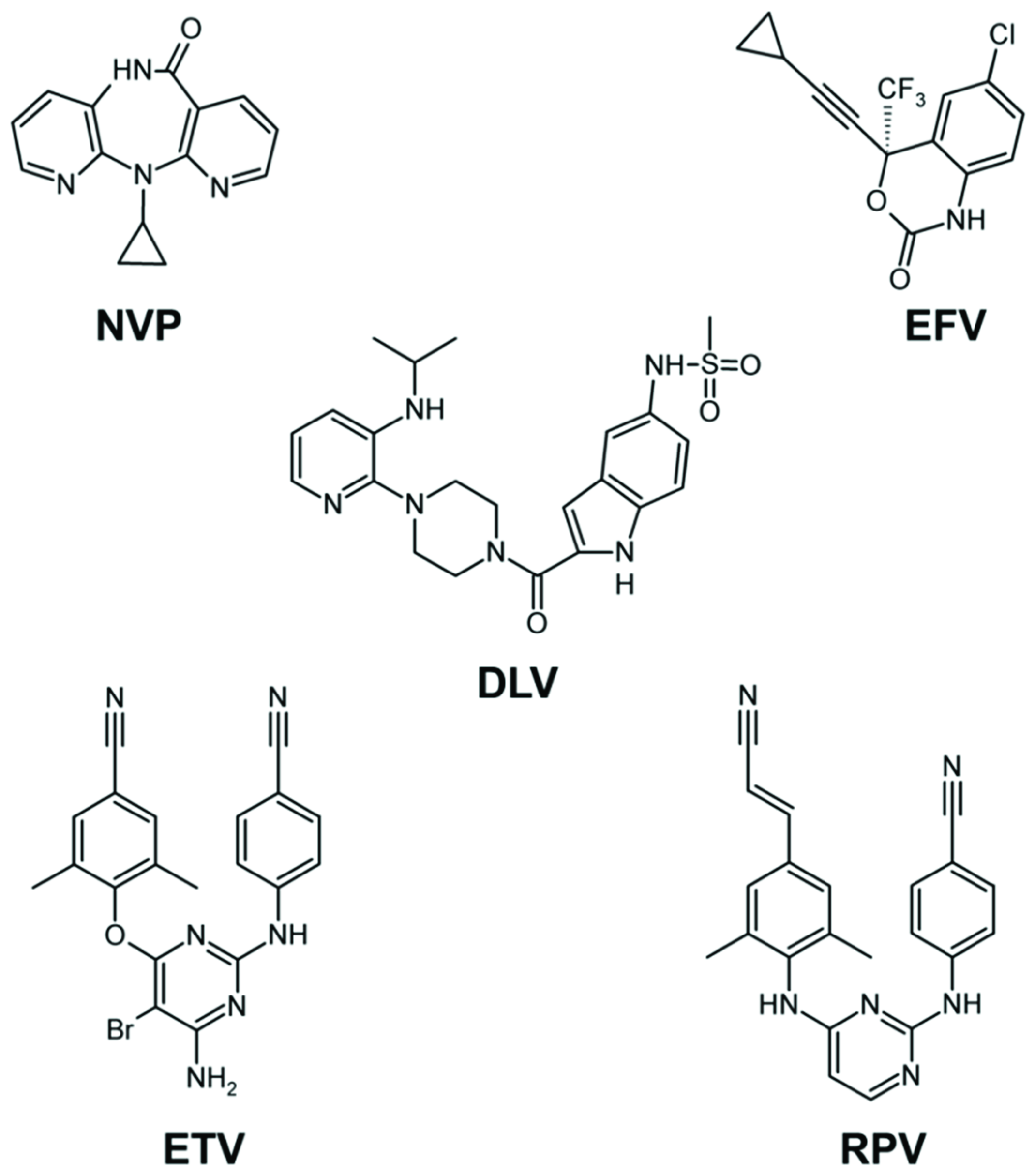
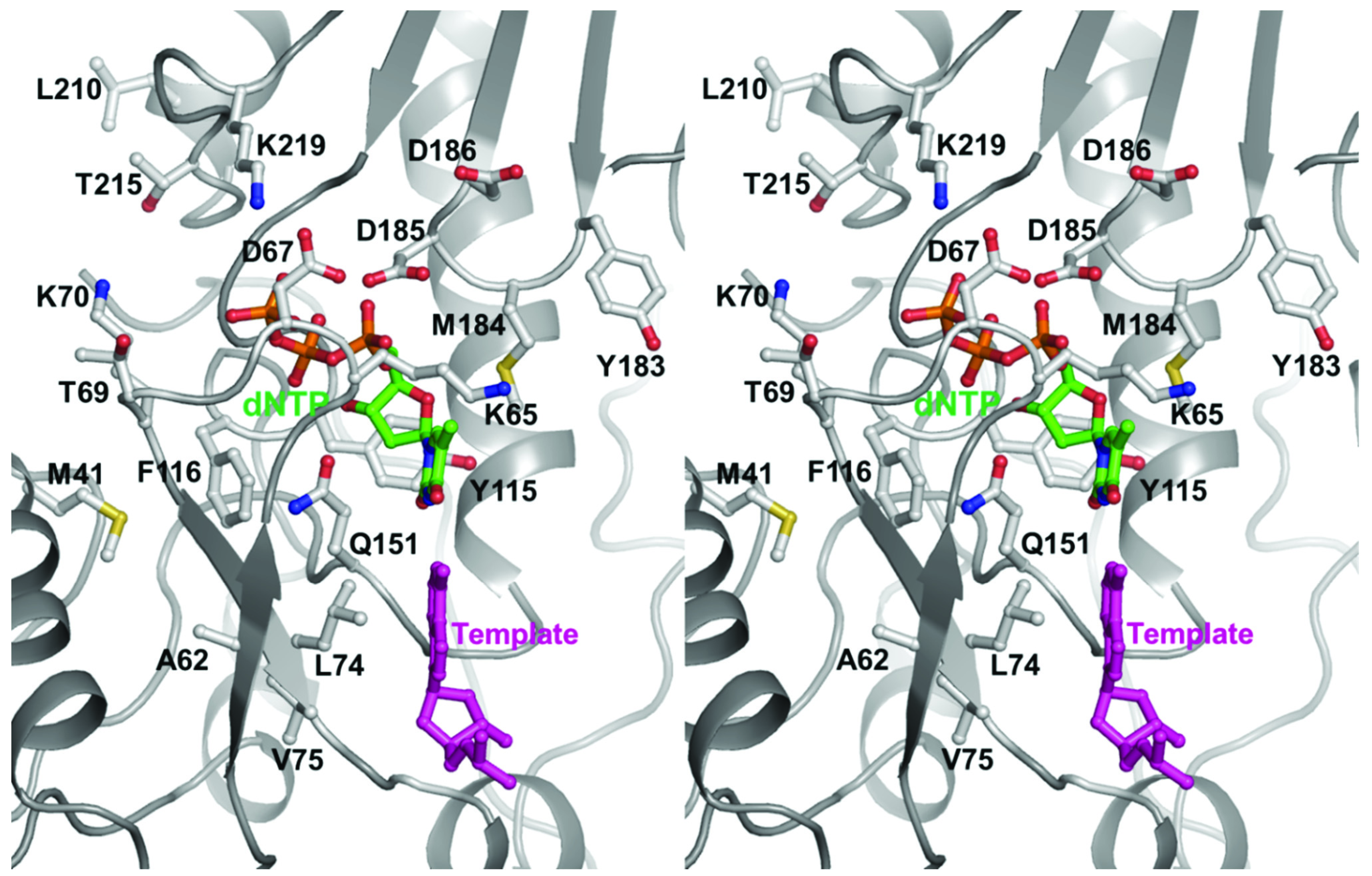
Drug Resistance in Non-B Subtype HIV-1: Impact of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
3. Transmitted Drug Resistance (TDR) in HIV-Non-B
4. Polymorphisms in HIV-Non-B
| Subtype | Subtype Reference Sequences | RT Sequence PM Position, NRTI RAMs | RT Sequence PM Position, NNRTI RAMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | U455 | A62V, V118I | E138A, V179I/T, K238R |
| B | HXB2 | V118I | A98S, V179I/D/E |
| C | C2220 | V118I | A98S, E138A, V179I |
| D | NDK | V118I (comparable to B) | V179I |
| F | 93BR020 | V41I, M184V | E138A/G, V179I/D |
| G | SE6165 | A98S, V179E | |
| CRF01_AE | CM240 | V41I, A62V | V75L, V106I, V179I/D |
| CRF02_AG | IbNG | V41I, V118I | V106I, V179I |
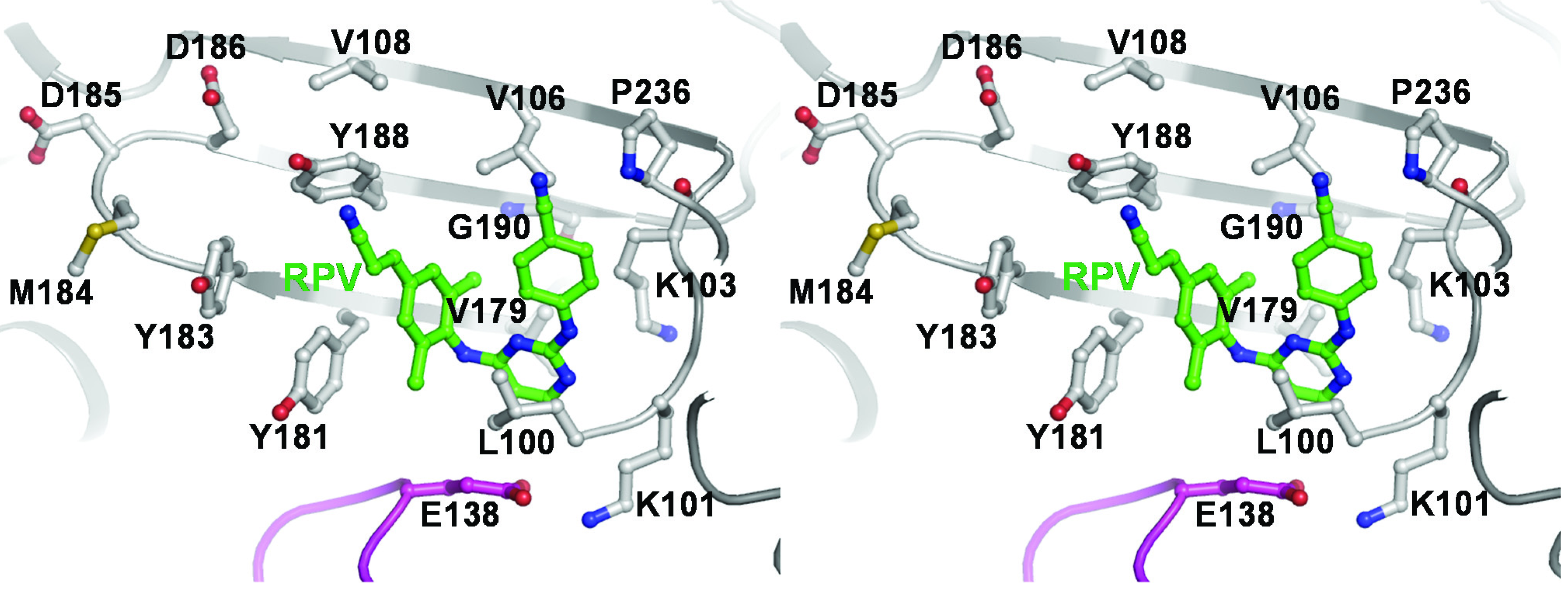
5. Therapeutic Response in HIV-Non-B subtypes in the Presence of Drug Resistance Mutations
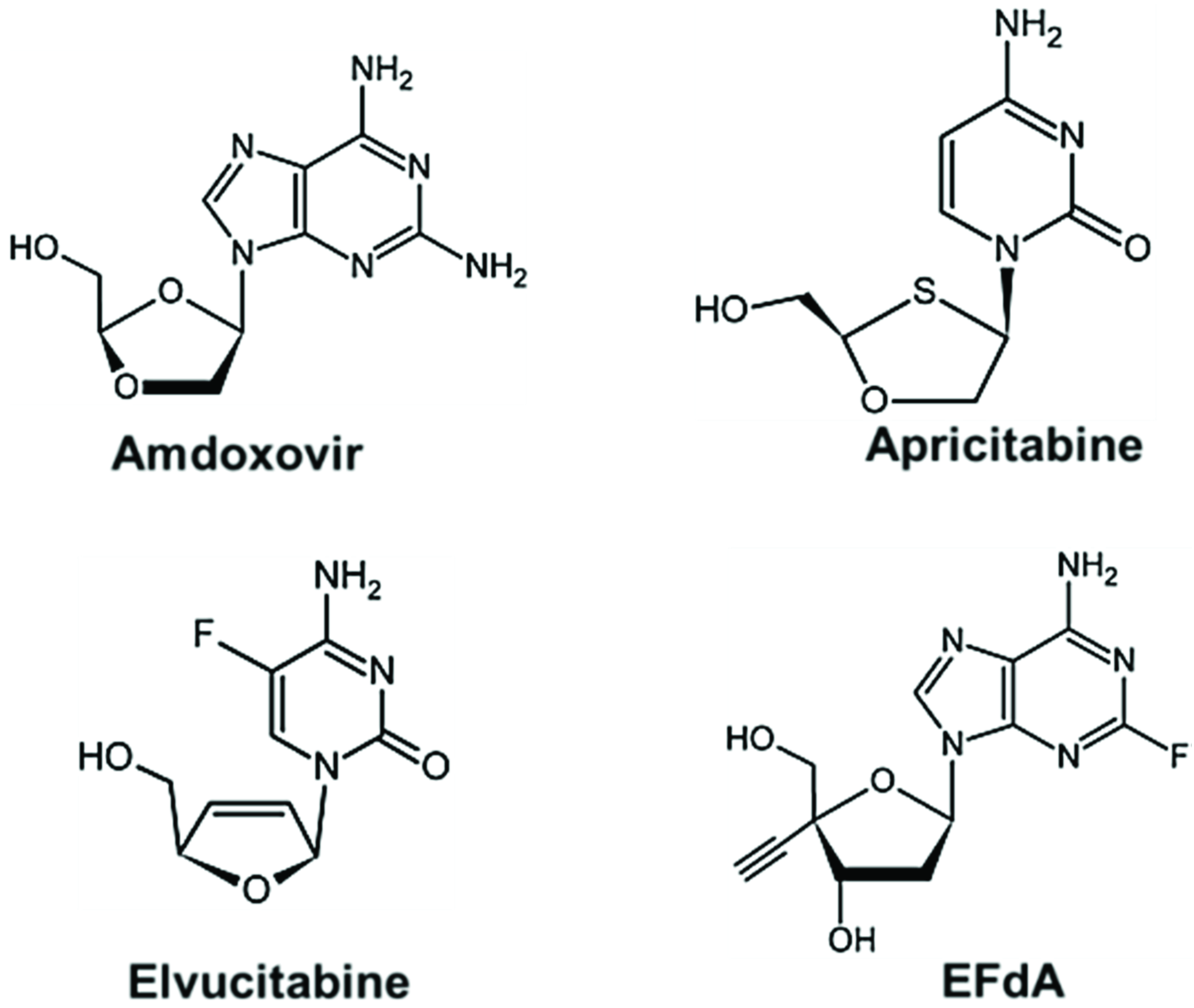
6. Future Perspectives: New Class of NRTIs
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Plantier, J.C.; Leoz, M.; Dickerson, J.E.; de Oliveira, F.; Cordonnier, F.; Lemee, V.; Damond, F.; Robertson, D.L.; Simon, F. A new human immunodeficiency virus derived from gorillas. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 871–872. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, D.L.; Anderson, J.P.; Bradac, J.A.; Carr, J.K.; Foley, B.; Funkhouser, R.K.; Gao, F.; Hahn, B.H.; Kalish, M.L.; Kuiken, C.; et al. HIV-1 nomenclature proposal. Science 2000, 288, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.J.; Lycett, S.J.; Kalish, M.L.; Rambaut, A.; Leigh Brown, A.J. Estimating the rate of intersubtype recombination in early HIV-1 group M strains. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemelaar, J.; Gouws, E.; Ghys, P.D.; Osmanov, S.; WHO-UNAIDS Network for HIV Isolation and Characterisation. Global trends in molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 during 2000–2007. AIDS 2011, 25, 679–689. [Google Scholar]
- Los Alamos National Laboratory. HIV Circulating Recombinant Forms (CRFs). Available online: http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/sequence/HIV/CRFs/CRFs.html (accessed on 15 September 2014).
- Vidal, N.; Peeters, M.; Mulanga-Kabeya, C.; Nzilambi, N.; Robertson, D.; Ilunga, W.; Sema, H.; Tshimanga, K.; Bongo, B.; Delaporte, E. Unprecedented degree of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) group M genetic diversity in the Democratic Republic of Congo suggests that the HIV-1 pandemic originated in Central Africa. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10498–10507. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, B.G. Resistance and viral subtypes: How important are the differences and why do they occur? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2007, 2, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.N.; Dunn, D.; Sabin, C.; Pozniak, A.; Matthias, R.; Geretti, A.M.; Clarke, J.; Churchill, D.; Williams, I.; Hill, T.; et al. Long term probability of detection of HIV-1 drug resistance after starting antiretroviral therapy in routine clinical practice. AIDS 2005, 19, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg, M.A.; Brenner, B.G. Role of HIV Subtype Diversity in the Development of Resistance to Antiviral Drugs. Viruses 2010, 2, 2493–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, A.; Marchand, B.; Kirby, K.A.; Michailidis, E.; Tu, X.; Palczewski, K.; Ong, Y.T.; Li, Z.; Griffin, D.T.; Schuckmann, M.M.; et al. HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase (RT) Polymorphism 172K Suppresses the Effect of Clinically Relevant Drug Resistance Mutations to Both Nucleoside and Non-nucleoside RT Inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29988–29999. [Google Scholar]
- Hachiya, A.; Kodama, E.N.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Schuckmann, M.M.; Sakagami, Y.; Matsuoka, M.; Takiguchi, M.; Gatanaga, H.; Oka, S. Amino acid mutation N348I in the connection subdomain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase confers multiclass resistance to nucleoside and nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, S.H.; Sheen, C.W.; Fahey, J.; Zanin, M.; Tyssen, D.; Lima, V.D.; Wynhoven, B.; Kuiper, M.; Sluis-Cremer, N.; Harrigan, P.R.; et al. N348I in the connection domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confers zidovudine and nevirapine resistance. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancor, G.; Puertas, M.C.; Nevot, M.; Garriga, C.; Martinez, M.A.; Martinez-Picado, J.; Menendez-Arias, L. Mechanisms involved in the selection of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase thumb subdomain polymorphisms associated with nucleoside analogue therapy failure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4799–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.W.; Deuzing, I.P.; Flandre, P.; van den Eede, P.; Govaert, M.; Setiawan, L.; Coveney, P.V.; Marcelin, A.G.; Calvez, V.; Boucher, C.A.; et al. A polymorphism at position 400 in the connection subdomain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase affects sensitivity to NNRTIs and RNaseH activity. PLoS One 2013, 8, e74078. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, M.; Palmer, S.; Maldarelli, F.; Shao, W.; Polis, M.A.; Mican, J.; Rock-Kress, D.; Margolick, J.B.; Coffin, J.M.; Mellors, J.W. Frequent polymorphism at drug resistance sites in HIV-1 protease and reverse transcriptase. AIDS 2008, 22, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.D.; Shi, C.; Bloor, S.; Harrigan, P.R.; Mellors, J.W.; Larder, B.A. A novel polymorphism at codon 333 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase can facilitate dual resistance to zidovudine and L-2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5093–5098. [Google Scholar]
- Delviks-Frankenberry, K.A.; Nikolenko, G.N.; Pathak, V.K. The “Connection” between HIV drug resistance and RNase H. Viruses 2010, 2, 1476–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainberg, M.A.; Brenner, B.G. The impact of HIV genetic polymorphisms and subtype differences on the occurrence of resistance to antiretroviral drugs. Mol. Biol. Int. 2012, 2012, 256982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Quinones-Mateu, M.E.; Mansky, L.M. Drug resistance, virus fitness and HIV-1 mutagenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 4065–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Das, K.; Hsiou, Y.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Jacobo-Molina, A.; Tantillo, C.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Structure and functional implications of the polymerase active site region in a complex of HIV-1 RT with a double-stranded DNA template-primer and an antibody Fab fragment at 2.8 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 284, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chopra, R.; Verdine, G.L.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: Implications for drug resistance. Science 1998, 282, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Das, K.; Tantillo, C.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Ding, J.; Whitcomb, J.M.; Boyer, P.L.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Crystal structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in complex with a polypurine tract RNA:DNA. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuske, S.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Ding, J.; Naeger, L.K.; White, K.L.; Miller, M.D.; Gibbs, C.S.; Boyer, P.L.; Clark, P.; et al. Structures of HIV-1 RT-DNA complexes before and after incorporation of the anti-AIDS drug tenofovir. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Bandwar, R.P.; White, K.L.; Feng, J.Y.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Tuske, S.; Tu, X.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Boyer, P.L.; Hou, X.; et al. Structural basis for the role of the K65R mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase polymerization, excision antagonism, and tenofovir resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35092–35100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Martinez, S.E.; Bauman, J.D.; Arnold, E. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complex with DNA and nevirapine reveals non-nucleoside inhibition mechanism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobo-Molina, A.; Ding, J.; Nanni, R.G.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Lu, X.; Tantillo, C.; Williams, R.L.; Kamer, G.; Ferris, A.L.; Clark, P.; et al. Crystal structure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase complexed with double-stranded DNA at 3.0 A resolution shows bent DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6320–6324. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Esnouf, R.; Garman, E.; Somers, D.; Ross, C.; Kirby, I.; Keeling, J.; Darby, G.; Jones, Y.; Stuart, D.; et al. High resolution structures of HIV-1 RT from four RT-inhibitor complexes. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1995, 2, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Unge, T.; Knight, S.; Bhikhabhai, R.; Lovgren, S.; Dauter, Z.; Wilson, K.; Strandberg, B. 2.2 A resolution structure of the amino-terminal half of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (fingers and palm subdomains). Structure 1994, 2, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Milton, J.; Weaver, K.L.; Short, S.A.; Stuart, D.I.; Stammers, D.K. Structural basis for the resilience of efavirenz (DMP-266) to drug resistance mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Structure 2000, 8, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Bauman, J.D.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Frenkel, Y.V.; Lewi, P.J.; Shatkin, A.J.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. High-resolution structures of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase/TMC278 complexes: Strategic flexibility explains potency against resistance mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, J.D.; Stirtan, W.G.; Goldstein, S.W.; Steitz, T.A. Structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase bound to an inhibitor active against mutant reverse transcriptases resistant to other nonnucleoside inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10548–10553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiou, Y.; Ding, J.; Das, K.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Structure of unliganded HIV-1 reverse transcriptase at 2.7 A resolution: Implications of conformational changes for polymerization and inhibition mechanisms. Structure 1996, 4, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt, L.A.; Wang, J.; Friedman, J.M.; Rice, P.A.; Steitz, T.A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science 1992, 256, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Lapkouski, M.; Tian, L.; Miller, J.T.; Le Grice, S.F.; Yang, W. Complexes of HIV-1 RT, NNRTI and RNA/DNA hybrid reveal a structure compatible with RNA degradation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Arnold, E. Structural requirements for RNA degradation by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1341–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 1.5.0.4; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2014.
- Ren, J.; Bird, L.E.; Chamberlain, P.P.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.; Stuart, D.I.; Stammers, D.K. Structure of HIV-2 reverse transcriptase at 2.35-A resolution and the mechanism of resistance to non-nucleoside inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14410–14415. [Google Scholar]
- Schuckmann, M.M.; Marchand, B.; Hachiya, A.; Kodama, E.N.; Kirby, K.A.; Singh, K.; Sarafianos, S.G. The N348I mutation at the connection subdomain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase decreases binding to nevirapine. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38700–38709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Miller, J.T.; Lapkouski, M.; Tian, L.; Yang, W.; Le Grice, S.F. Examining the role of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase p51 subunit in positioning and hydrolysis of RNA/DNA hybrids. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 16177–16184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Marchand, B.; Kirby, K.A.; Michailidis, E.; Sarafianos, S.G. Structural aspects of drug resistance and inhibition of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase. Viruses 2010, 2, 606–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. Antiviral drugs in current clinical use. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 30, 115–133. [Google Scholar]
- Parniak, M.A.; Sluis-Cremer, N. Inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Adv. Pharmacol. 2000, 49, 67–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Marchand, B.; Das, K.; Himmel, D.M.; Parniak, M.A.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Structure and function of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: Molecular mechanisms of polymerization and inhibition. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 693–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Das, K.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Ding, J.; Boyer, P.L.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Lamivudine (3TC) resistance in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase involves steric hindrance with beta-branched amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10027–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerdon, S.J.; Jager, J.; Wang, J.; Kohlstaedt, L.A.; Chirino, A.J.; Friedman, J.M.; Rice, P.A.; Steitz, T.A. Structure of the binding site for nonnucleoside inhibitors of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3911–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantillo, C.; Ding, J.; Jacobo-Molina, A.; Nanni, R.G.; Boyer, P.L.; Hughes, S.H.; Pauwels, R.; Andries, K.; Janssen, P.A.; Arnold, E. Locations of anti-AIDS drug binding sites and resistance mutations in the three-dimensional structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Implications for mechanisms of drug inhibition and resistance. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 243, 369–387. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, V.A.; Calvez, V.; Gunthard, H.F.; Paredes, R.; Pillay, D.; Shafer, R.W.; Wensing, A.M.; Richman, D.D. Update of the drug resistance mutations in HIV-1: March 2013. Top. Antivir. Med. 2013, 21, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.D.; Margot, N.; Lu, B.; Zhong, L.; Chen, S.S.; Cheng, A.; Wulfsohn, M. Genotypic and phenotypic predictors of the magnitude of response to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment in antiretroviral-experienced patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcomb, J.M.; Parkin, N.T.; Chappey, C.; Hellmann, N.S.; Petropoulos, C.J. Broad nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor cross-resistance in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clinical isolates. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuritzkes, D.R.; Bassett, R.L.; Hazelwood, J.D.; Barrett, H.; Rhodes, R.A.; Young, R.K.; Johnson, V.A.; Adult, A.P.T. Rate of thymidine analogue resistance mutation accumulation with zidovudine- or stavudine-based regimens. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2004, 36, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACD/ChemSketch Advanced Chemistry Development, I.: Toronto, ON, Canada. Available online: http://www.acdlabs.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2014).
- Deval, J.; Selmi, B.; Boretto, J.; Egloff, M.P.; Guerreiro, C.; Sarfati, S.; Canard, B. The molecular mechanism of multidrug resistance by the Q151M human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase and its suppression using alpha-boranophosphate nucleotide analogues. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 42097–42104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deval, J.; Navarro, J.M.; Selmi, B.; Courcambeck, J.; Boretto, J.; Halfon, P.; Garrido-Urbani, S.; Sire, J.; Canard, B. A loss of viral replicative capacity correlates with altered DNA polymerization kinetics by the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase bearing the K65R and L74V dideoxynucleoside resistance substitutions. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25489–25496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deval, J.; White, K.L.; Miller, M.D.; Parkin, N.T.; Courcambeck, J.; Halfon, P.; Selmi, B.; Boretto, J.; Canard, B. Mechanistic basis for reduced viral and enzymatic fitness of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase containing both K65R and M184V mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluis-Cremer, N.; Sheen, C.W.; Zelina, S.; Torres, P.S.; Parikh, U.M.; Mellors, J.W. Molecular mechanism by which the K70E mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase confers resistance to nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Arnold, E. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and antiviral drug resistance. Part 2. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, R.; Immendorfer, U.; Thrall, S.H.; Wohrl, B.M.; Goody, R.S. Single-step kinetics of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase mutants responsible for virus resistance to nucleoside inhibitors zidovudine and 3-TC. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 10292–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Clair, M.H.; Martin, J.L.; Tudor-Williams, G.; Bach, M.C.; Vavro, C.L.; King, D.M.; Kellam, P.; Kemp, S.D.; Larder, B.A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science 1991, 253, 1557–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.L.; Wilson, J.E.; Haynes, R.L.; Furman, P.A. Mechanism of resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6135–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, T.; Kim, B.; Menendez-Arias, L. Mechanistic insights into the role of Val75 of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in misinsertion and mispair extension fidelity of DNA synthesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Mitsuya, H. Comparative enzymatic study of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase resistant to 2',3'-dideoxynucleotide analogs using the single-nucleotide incorporation assay. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdale, M.; Kemp, S.D.; Parry, N.R.; Larder, B.A. Rapid in vitro selection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistant to 3'-thiacytidine inhibitors due to a mutation in the YMDD region of reverse transcriptase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5653–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, B.; Boretto, J.; Sarfati, S.R.; Guerreiro, C.; Canard, B. Mechanism-based suppression of dideoxynucleotide resistance by K65R human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase using an alpha-boranophosphate nucleoside analogue. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48466–48472. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.Y.; Myrick, F.T.; Margot, N.A.; Mulamba, G.B.; Rimsky, L.; Borroto-Esoda, K.; Selmi, B.; Canard, B. Virologic and enzymatic studies revealing the mechanism of K65R- and Q151M-associated HIV-1 drug resistance towards emtricitabine and lamivudine. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2006, 25, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasaka, T.; Kavlick, M.F.; Ueno, T.; Gao, W.Y.; Kojima, E.; Alcaide, M.L.; Chokekijchai, S.; Roy, B.M.; Arnold, E.; Yarchoan, R.; et al. Emergence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants with resistance to multiple dideoxynucleosides in patients receiving therapy with dideoxynucleosides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2398–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchesnokov, E.P.; Obikhod, A.; Massud, I.; Lisco, A.; Vanpouille, C.; Brichacek, B.; Balzarini, J.; McGuigan, C.; Derudas, M.; Margolis, L.; et al. Mechanisms associated with HIV-1 resistance to acyclovir by the V75I mutation in reverse transcriptase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21496–21504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangeul, A.; Bussetta, C.; Deval, J.; Barral, K.; Alvarez, K.; Canard, B. Gln151 of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase acts as a steric gate towards clinically relevant acyclic phosphonate nucleotide analogues. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, P.R.; Matsuura, S.E.; So, A.G.; Scott, W.A. Unblocking of chain-terminated primer by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase through a nucleotide-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13471–13476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arion, D.; Kaushik, N.; McCormick, S.; Borkow, G.; Parniak, M.A. Phenotypic mechanism of HIV-1 resistance to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT): Increased polymerization processivity and enhanced sensitivity to pyrophosphate of the mutant viral reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 15908–15917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Das, K.; Tuske, S.; Birktoft, J.J.; Ilankumaran, P.; Ramesha, A.R.; Sayer, J.M.; Jerina, D.M.; Boyer, P.L.; et al. Structures of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with pre- and post-translocation AZTMP-terminated DNA. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Clark, A.D., Jr.; Tuske, S.; Squire, C.J.; Das, K.; Sheng, D.; Ilankumaran, P.; Ramesha, A.R.; Kroth, H.; Sayer, J.M.; et al. Trapping HIV-1 reverse transcriptase before and after translocation on DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16280–16288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Arnold, E. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and antiviral drug resistance. Part 1. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, S.F.; Reardon, J.E.; Furfine, E.S.; Kunkel, T.A.; Bebenek, K.; Eckert, K.A.; Kemp, S.D.; Larder, B.A. Biochemical studies on the reverse transcriptase and RNase H activities from human immunodeficiency virus strains resistant to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 15789–15794. [Google Scholar]
- Betancor, G.; Nevot, M.; Mendieta, J.; Gomez-Puertas, P.; Martinez, M.A.; Menendez-Arias, L. Molecular basis of the association of H208Y and thymidine analogue resistance mutations M41L, L210W and T215Y in the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase of treated patients. Antivir. Res. 2014, 106, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arion, D.; Parniak, M.A. HIV resistance to zidovudine: The role of pyrophosphorolysis. Drug Resist. Updat 1999, 2, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, A.; Parera, M.; Briones, C.; Soriano, V.; Martinez, M.A.; Domingo, E.; Menendez-Arias, L. Role of a dipeptide insertion between codons 69 and 70 of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in the mechanism of AZT resistance. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5752–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, P.L.; Imamichi, T.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Arnold, E.; Hughes, S.H. Effects of the Delta67 complex of mutations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase on nucleoside analog excision. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9987–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, P.R.; Matsuura, S.E.; Mian, A.M.; So, A.G.; Scott, W.A. A mechanism of AZT resistance: An increase in nucleotide-dependent primer unblocking by mutant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, P.R.; Matsuura, S.E.; Schinazi, R.F.; So, A.G.; Scott, W.A. Differential removal of thymidine nucleotide analogues from blocked DNA chains by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in the presence of physiological concentrations of 2'-deoxynucleoside triphosphates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.T.; Lu, M.; Felock, P.J.; Hrin, R.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Yan, Y.; Munshi, S.; McGaughey, G.B.; Tynebor, R.M.; Tucker, T.J.; et al. Distinct mutation pathways of non-subtype B HIV-1 during in vitro resistance selection with nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4812–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, P.L.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Arnold, E.; Hughes, S.H. Selective excision of AZTMP by drug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4832–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arion, D.; Sluis-Cremer, N.; Parniak, M.A. Mechanism by which phosphonoformic acid resistance mutations restore 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) sensitivity to AZT-resistant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9251–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafianos, S.G.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Designing anti-AIDS drugs targeting the major mechanism of HIV-1 RT resistance to nucleoside analog drugs. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novitsky, V.; Wester, C.W.; DeGruttola, V.; Bussmann, H.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Thomas, A.; Moyo, S.; Musonda, R.; van Widenfelt, E.; Marlink, R.G.; et al. The reverse transcriptase 67N 70R 215Y genotype is the predominant TAM pathway associated with virologic failure among HIV type 1C-infected adults treated with ZDV/ddI-containing HAART in southern Africa. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2007, 23, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Jauvin, V.; Magnin, N.; Pinson, P.; Faure, M.; Masquelier, B.; Aurillac-Lavignolle, V.; Fleury, H.J. Resistance mutations in subtype C HIV type 1 isolates from Indian patients of Mumbai receiving NRTIs plus NNRTIs and experiencing a treatment failure: Resistance to AR. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2007, 23, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinipour, M.C.; van Oosterhout, J.J.; Weigel, R.; Phiri, S.; Kamwendo, D.; Parkin, N.; Fiscus, S.A.; Nelson, J.A.; Eron, J.J.; Kumwenda, J. The public health approach to identify antiretroviral therapy failure: High-level nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistance among Malawians failing first-line antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2009, 23, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, R.E.; Wensing, A.M.; Tempelman, H.A.; Moraba, R.; Schuurman, R.; Hoepelman, A.I. Rapid accumulation of nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-associated resistance: Evidence of transmitted resistance in rural South Africa. AIDS 2008, 22, 2210–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doualla-Bell, F.; Avalos, A.; Brenner, B.; Gaolathe, T.; Mine, M.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Oliveira, M.; Moisi, D.; Ndwapi, N.; Moffat, H.; et al. High prevalence of the K65R mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C isolates from infected patients in Botswana treated with didanosine-based regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 4182–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunpath, H.; Wu, B.; Gordon, M.; Hampton, J.; Johnson, B.; Moosa, M.Y.; Ordonez, C.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Marconi, V.C. High rate of K65R for antiretroviral therapy-naive patients with subtype C HIV infection failing a tenofovir-containing first-line regimen. AIDS 2012, 26, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.G.; Coutsinos, D. The K65R mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: Genetic barriers, resistance profile and clinical implications. HIV Ther. 2009, 3, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrell, C.; Walensky, R.P.; Losina, E.; Pitt, J.; Freedberg, K.A.; Wood, R. HIV type-1 clade C resistance genotypes in treatment-naive patients and after first virological failure in a large community antiretroviral therapy programme. Antivir. Ther. 2009, 14, 523–531. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.; Shahar, E.; Katchman, E.; Kedem, E.; Matus, N.; Katzir, M.; Hassoun, G.; Pollack, S.; Kessner, R.; Wainberg, M.A.; et al. Prevalence of the K65R resistance reverse transcriptase mutation in different HIV-1 subtypes in Israel. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Jeannot, A.C.; Schrive, M.H.; Wittkop, L.; Pinson, P.; Fleury, H.J. Analysis of RT sequences of subtype C HIV-type 1 isolates from indian patients at failure of a first-line treatment according to clinical and/or immunological WHO guidelines. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2010, 26, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Chrystie, I.L.; O’Shea, S.; Mullen, J.E.; Kulasegaram, R.; Tong, C.Y. K65R and Y181C are less prevalent in HAART-experienced HIV-1 subtype A patients. AIDS 2005, 19, 1916–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontella, R.; Soares, M.A.; Schrago, C.G. On the origin of HIV-1 subtype C in South America. AIDS 2008, 22, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutsinos, D.; Invernizzi, C.F.; Moisi, D.; Oliveira, M.; Martinez-Cajas, J.L.; Brenner, B.G.; Wainberg, M.A. A template-dependent dislocation mechanism potentiates K65R reverse transcriptase mutation development in subtype C variants of HIV-1. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutsinos, D.; Invernizzi, C.F.; Xu, H.; Moisi, D.; Oliveira, M.; Brenner, B.G.; Wainberg, M.A. Template usage is responsible for the preferential acquisition of the K65R reverse transcriptase mutation in subtype C variants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinori, A.; Zaccarelli, M.; Cingolani, A.; Forbici, F.; Rizzo, M.G.; Trotta, M.P.; di Giambenedetto, S.; Narciso, P.; Ammassari, A.; Girardi, E.; et al. Cross-resistance among nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors limits recycling efavirenz after nevirapine failure. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2002, 18, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.; Turner, D.; Oliveira, M.; Moisi, D.; Detorio, M.; Carobene, M.; Marlink, R.G.; Schapiro, J.; Roger, M.; Wainberg, M.A. A V106M mutation in HIV-1 clade C viruses exposed to efavirenz confers cross-resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. AIDS 2003, 17, F1–F5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, A.; Campbell, T.; Clotet, B.; Johnson, M.; Katlama, C.; Moll, A.; Towner, W.; Trottier, B.; Peeters, M.; Vingerhoets, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of TMC125 (etravirine) in treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected patients in DUET-2: 24-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madruga, J.V.; Cahn, P.; Grinsztejn, B.; Haubrich, R.; Lalezari, J.; Mills, A.; Pialoux, G.; Wilkin, T.; Peeters, M.; Vingerhoets, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of TMC125 (etravirine) in treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected patients in DUET-1: 24-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.A.; Lewi, P.J.; Arnold, E.; Daeyaert, F.; de Jonge, M.; Heeres, J.; Koymans, L.; Vinkers, M.; Guillemont, J.; Pasquier, E.; et al. In search of a novel anti-HIV drug: Multidisciplinary coordination in the discovery of 4-[[4-[[4-[(1E)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2- pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile (R278474, rilpivirine). J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, E.; Singh, K.; Ryan, E.M.; Hachiya, A.; Ong, Y.T.; Kirby, K.A.; Marchand, B.; Kodama, E.N.; Mitsuya, H.; Parniak, M.A.; et al. Effect of translocation defective reverse transcriptase inhibitors on the activity of N348I, a connection subdomain drug resistant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase mutant. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 2012, 58, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, R.; Babaoglu, K.; Lansdon, E.B.; Rimsky, L.; Van Eygen, V.; Picchio, G.; Svarovskaia, E.; Miller, M.D.; White, K.L. The HIV-1 reverse transcriptase M184I mutation enhances the E138K-associated resistance to rilpivirine and decreases viral fitness. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2012, 59, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.A.; Kati, W.M.; Anderson, K.S.; Johnson, K.A. Mechanism of inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by nonnucleoside inhibitors. Science 1995, 267, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.A.; Anderson, K.S.; Johnson, K.A. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase resistance to nonnucleoside inhibitors. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maga, G.; Amacker, M.; Ruel, N.; Hubscher, U.; Spadari, S. Resistance to nevirapine of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase mutants: Loss of stabilizing interactions and thermodynamic or steric barriers are induced by different single amino acid substitutions. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 274, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Nichols, C.; Bird, L.; Chamberlain, P.; Weaver, K.; Short, S.; Stuart, D.I.; Stammers, D.K. Structural mechanisms of drug resistance for mutations at codons 181 and 188 in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and the improved resilience of second generation non-nucleoside inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 312, 795–805. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Stammers, D.K. Structural basis for drug resistance mechanisms for non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase. Virus Res. 2008, 134, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.G.; Oliveira, M.; Doualla-Bell, F.; Moisi, D.D.; Ntemgwa, M.; Frankel, F.; Essex, M.; Wainberg, M.A. HIV-1 subtype C viruses rapidly develop K65R resistance to tenofovir in cell culture. AIDS 2006, 20, F9–F13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrive, E.; Newell, M.L.; Ekouevi, D.K.; Chaix, M.L.; Thiebaut, R.; Masquelier, B.; Leroy, V.; Perre, P.V.; Rouzioux, C.; Dabis, F.; et al. Prevalence of resistance to nevirapine in mothers and children after single-dose exposure to prevent vertical transmission of HIV-1: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshleman, S.H.; Guay, L.A.; Wang, J.; Mwatha, A.; Brown, E.R.; Musoke, P.; Mmiro, F.; Jackson, J.B. Distinct patterns of emergence and fading of K103N and Y181C in women with subtype A vs. D after single-dose nevirapine: HIVNET 012. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2005; 40, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Eshleman, S.H.; Mracna, M.; Guay, L.A.; Deseyve, M.; Cunningham, S.; Mirochnick, M.; Musoke, P.; Fleming, T.; Glenn Fowler, M.; Mofenson, L.M.; et al. Selection and fading of resistance mutations in women and infants receiving nevirapine to prevent HIV-1 vertical transmission (HIVNET 012). AIDS 2001, 15, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loemba, H.; Brenner, B.; Parniak, M.A.; Ma'ayan, S.; Spira, B.; Moisi, D.; Oliveira, M.; Detorio, M.; Wainberg, M.A. Genetic divergence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Ethiopian clade C reverse transcriptase (RT) and rapid development of resistance against nonnucleoside inhibitors of RT. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, V.C.; Sunpath, H.; Lu, Z.; Gordon, M.; Koranteng-Apeagyei, K.; Hampton, J.; Carpenter, S.; Giddy, J.; Ross, D.; Holst, H.; et al. Prevalence of HIV-1 drug resistance after failure of a first highly active antiretroviral therapy regimen in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, N.; Recordon-Pinson, P.; Phoung, V.; Srey, C.; Kruy, L.S.; Koum, K.; Chhum, V.; Glaziou, P.; Fleury, H.J.; Reynes, J.M. Characterization of mutations in HIV type 1 isolates from 144 Cambodian recently infected patients and pregnant women naive to antiretroviral drugs. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2005, 21, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, L.; Karunaianantham, R.; Narayanan, P.R.; Swaminathan, S. Antiretroviral drug-resistant mutations at baseline and at time of failure of antiretroviral therapy in HIV type 1-coinfected TB patients. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2009, 25, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, Z.; Istomin, V.; Averbuch, D.; Lorber, M.; Risenberg, K.; Levi, I.; Chowers, M.; Burke, M.; Bar Yaacov, N.; Schapiro, J.M. Genetic variation at NNRTI resistance-associated positions in patients infected with HIV-1 subtype C. AIDS 2004, 18, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.J.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.; Clotet, B.; Fourie, J.; Johnson, M.A.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Wu, H.; Zorrilla, C.; Crauwels, H.; Rimsky, L.T.; et al. Rilpivirine versus efavirenz with two background nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors in treatment-naive adults infected with HIV-1 (THRIVE): A phase 3, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Kuritzkes, D.R. Interaction of reverse transcriptase (RT) mutations conferring resistance to lamivudine and etravirine: Effects on fitness and RT activity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11309–11314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.T.; Asahchop, E.L.; Oliveira, M.; Quashie, P.K.; Quan, Y.; Brenner, B.G.; Wainberg, M.A. Compensation by the E138K mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase for deficits in viral replication capacity and enzyme processivity associated with the M184I/V mutations. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11300–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiga, A.I.; Descamps, D.; Morand-Joubert, L.; Malet, I.; Derache, A.; Cisse, M.; Koita, V.; Akonde, A.; Diarra, B.; Wirden, M.; et al. Resistance-associated mutations to etravirine (TMC-125) in antiretroviral-naive patients infected with non-B HIV-1 subtypes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahchop, E.L.; Oliveira, M.; Wainberg, M.A.; Brenner, B.G.; Moisi, D.; Toni, T.; Tremblay, C.L. Characterization of the E138K resistance mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase conferring susceptibility to etravirine in B and non-B HIV-1 subtypes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, U.; Shet, A.; Shamsundar, R.; Ekstrand, M.L. Selection of nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-associated mutations in HIV-1 subtype C: Evidence of etravirine cross-resistance. AIDS 2011, 25, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert-Niclot, S.; Charpentier, C.; Storto, A.; Fofana, D.; Soulie, C.; Fourati, S.; Wirden, M.; Morand-Joubert, L.; Masquelier, B.; Flandre, P.; et al. Rilpivirine, emtricitabine and tenofovir resistance in HIV-1-infected rilpivirine-naive patients failing antiretroviral therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, M.T.; Menon, L.; Myshakina, N.S.; Ahn, J.; Parniak, M.A.; Ishima, R. Structural basis of the allosteric inhibitor interaction on the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase RNase H domain. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 80, 706–716, PMCID: PMC3465473. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Edurant® 25 mg Film-coated Tablets: Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/002264/WC500118874.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2014).
- Wensing, A.M.; van de Vijver, D.A.; Angarano, G.; Asjo, B.; Balotta, C.; Boeri, E.; Camacho, R.; Chaix, M.L.; Costagliola, D.; De Luca, A.; et al. Prevalence of drug-resistant HIV-1 variants in untreated individuals in Europe: Implications for clinical management. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluis-Cremer, N.; Jordan, M.R.; Huber, K.; Wallis, C.L.; Bertagnolio, S.; Mellors, J.W.; Parkin, N.T.; Harrigan, P.R. E138A in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is more common in subtype C than B: Implications for rilpivirine use in resource-limited settings. Antivir. Res. 2014, 107, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunupuradah, T.; Ananworanich, J.; Chetchotisakd, P.; Kantipong, P.; Jirajariyavej, S.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Munsakul, W.; Prasithsirikul, W.; Sungkanuparph, S.; Bowonwattanuwong, C.; et al. Etravirine and rilpivirine resistance in HIV-1 subtype CRF01_AE-infected adults failing non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-based regimens. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, R.; Katzenstein, D.A.; Efron, B.; Carvalho, A.P.; Wynhoven, B.; Cane, P.; Clarke, J.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Soares, M.A.; Snoeck, J.; et al. Impact of HIV-1 subtype and antiretroviral therapy on protease and reverse transcriptase genotype: Results of a global collaboration. PLoS Med 2005, 2, e112. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.M.; Perno, C.F. HIV-1 Genetic Variability and Clinical Implications. ISRN Microbiol 2013, 2013, 481314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.M.; Alteri, C.; Ronga, L.; Flandre, P.; Fabeni, L.; Mercurio, F.; D'Arrigo, R.; Gori, C.; Palamara, G.; Bertoli, A.; et al. Comparative analysis of drug resistance among B and the most prevalent non-B HIV type 1 subtypes (C, F, and CRF02_AG) in Italy. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flys, T.S.; Chen, S.; Jones, D.C.; Hoover, D.R.; Church, J.D.; Fiscus, S.A.; Mwatha, A.; Guay, L.A.; Mmiro, F.; Musoke, P.; et al. Quantitative analysis of HIV-1 variants with the K103N resistance mutation after single-dose nevirapine in women with HIV-1 subtypes A, C, and D. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 42, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Li, J.F.; Morris, L.; Martinson, N.; Gray, G.; McIntyre, J.; Heneine, W. Emergence of drug-resistant HIV-1 after intrapartum administration of single-dose nevirapine is substantially underestimated. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, R.W. Rationale and uses of a public HIV drug-resistance database. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, S51–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.L.; Parry, C.M.; Crombe, A.; Goodall, R.L.; Gupta, R.K.; Kaleebu, P.; Kityo, C.; Chirara, M.; Towers, G.J.; Pillay, D. Impact of the N348I mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase on nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistance in non-subtype B HIV-1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, J.H.; Koontz, D.L.; Wallis, C.L.; Shutt, K.A.; Sanne, I.; Wood, R.; McIntyre, J.A.; Stevens, W.S.; Sluis-Cremer, N.; Mellors, J.W.; et al. Frequent emergence of N348I in HIV-1 subtype C reverse transcriptase with failure of initial therapy reduces susceptibility to reverse-transcriptase inhibitors. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolenko, G.N.; Delviks-Frankenberry, K.A.; Palmer, S.; Maldarelli, F.; Fivash, M.J., Jr.; Coffin, J.M.; Pathak, V.K. Mutations in the connection domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase increase 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, R.S.; Arnold, E.; Das, K. Molecular dynamics study of HIV-1 RT-DNA-nevirapine complexes explains NNRTI inhibition and resistance by connection mutations. Proteins 2014, 82, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delviks-Frankenberry, K.A.; Lengruber, R.B.; Santos, A.F.; Silveira, J.M.; Soares, M.A.; Kearney, M.F.; Maldarelli, F.; Pathak, V.K. Connection subdomain mutations in HIV-1 subtype-C treatment-experienced patients enhance NRTI and NNRTI drug resistance. Virology 2013, 435, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, P.; Chrystie, I.; Dunn, D.; Evans, B.; Geretti, A.M.; Green, H.; Phillips, A.; Pillay, D.; Porter, K.; Pozniak, A.; et al. Time trends in primary resistance to HIV drugs in the United Kingdom: Multicentre observational study. BMJ 2005, 331, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shet, A.; Berry, L.; Mohri, H.; Mehandru, S.; Chung, C.; Kim, A.; Jean-Pierre, P.; Hogan, C.; Simon, V.; Boden, D.; et al. Tracking the prevalence of transmitted antiretroviral drug-resistant HIV-1: A decade of experience. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 41, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Moini, N.; Pesano, R.; Cachay, E.; Aiem, H.; Lie, Y.; Richman, D.; Little, S. Clinical utility of HIV standard genotyping among antiretroviral-naive individuals with unknown duration of infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.E.; Camacho, R.J.; Otelea, D.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Fleury, H.; Kiuchi, M.; Heneine, W.; Kantor, R.; Jordan, M.R.; Schapiro, J.M.; et al. Drug resistance mutations for surveillance of transmitted HIV-1 drug-resistance: 2009 update. PLoS One 2009, 4, e4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, R.W.; Rhee, S.Y.; Bennett, D.E. Consensus drug resistance mutations for epidemiological surveillance: Basic principles and potential controversies. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kantor, R.; Katzenstein, D. Polymorphism in HIV-1 non-subtype B protease and reverse transcriptase and its potential impact on drug susceptibility and drug resistance evolution. AIDS Rev. 2003, 5, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Cajas, J.L.; Pant-Pai, N.; Klein, M.B.; Wainberg, M.A. Role of genetic diversity amongst HIV-1 non-B subtypes in drug resistance: A systematic review of virologic and biochemical evidence. AIDS Rev. 2008, 10, 212–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, M.S.; Brun-Vezinet, F.; Clotet, B.; Conway, B.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; D’Aquila, R.T.; Demeter, L.M.; Hammer, S.M.; Johnson, V.A.; Loveday, C.; et al. Antiretroviral drug resistance testing in adults infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1: 2003 recommendations of an International AIDS Society-USA Panel. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, D.; Collin, G.; Letourneur, F.; Apetrei, C.; Damond, F.; Loussert-Ajaka, I.; Simon, F.; Saragosti, S.; Brun-Vezinet, F. Susceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group O isolates to antiretroviral agents: In vitro phenotypic and genotypic analyses. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8893–8898. [Google Scholar]
- Tuaillon, E.; Gueudin, M.; Lemee, V.; Gueit, I.; Roques, P.; Corrigan, G.E.; Plantier, J.C.; Simon, F.; Braun, J. Phenotypic susceptibility to nonnucleoside inhibitors of virion-associated reverse transcriptase from different HIV types and groups. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2004, 37, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez-Arias, L.; Betancor, G.; Matamoros, T. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase connection subdomain mutations involved in resistance to approved non-nucleoside inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Silveira, J.; Muniz, C.P.; Tornatore, M.; Goes, L.R.; Mendoza-Sassi, R.A.; Martinez, A.M.; Tupinambas, U.; Greco, D.B.; Soares, M.A. Primary HIV-1 drug resistance in the C-terminal domains of viral reverse transcriptase among drug-naive patients from Southern Brazil. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuma, J.; Hachiya, A.; Ishigaki, K.; Gatanaga, H.; Lien, T.T.; Hien, N.D.; Kinh, N.V.; Kaku, M.; Oka, S. Impact of CRF01_AE-specific polymorphic mutations G335D and A371V in the connection subdomain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT) on susceptibility to nucleoside RT inhibitors. Microbes. Infect. 2010, 12, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.P.; Soares, M.A.; Santos, A.F. Early selection of resistance-associated mutations in HIV-1 RT C-terminal domains across different subtypes: Role of the genetic barrier to resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2741–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.J.; Charalambous, S.; Sim, J.; Ledwaba, J.; Schwikkard, G.; Chaisson, R.E.; Fielding, K.L.; Churchyard, G.J.; Morris, L.; Grant, A.D. Viremia, resuppression, and time to resistance in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) subtype C during first-line antiretroviral therapy in South Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khatib, Z.; Ekstrom, A.M.; Ledwaba, J.; Mohapi, L.; Laher, F.; Karstaedt, A.; Charalambous, S.; Petzold, M.; Katzenstein, D.; Morris, L. Viremia and drug resistance among HIV-1 patients on antiretroviral treatment: A cross-sectional study in Soweto, South Africa. AIDS 2010, 24, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, U.; Heylen, E.; Shet, A.; Chandy, S.; Shamsunder, R.; Sonnerborg, A.; Ekstrand, M.L. Long-term efficacy of first line antiretroviral therapy in Indian HIV-1 infected patients: A longitudinal cohort study. PLoS One 2013, 8, e55421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihlar, T.; Ray, A.S. Nucleoside and nucleotide HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors: 25 years after zidovudine. Antivir. Res. 2010, 85, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, L.J.; Moyle, G.; Bonora, S.; D'Avolio, A.; Else, L.; Mandalia, S.; Pozniak, A.; Nelson, M.; Gazzard, B.; Back, D.; et al. Abacavir plasma pharmacokinetics in the absence and presence of atazanavir/ritonavir or lopinavir/ritonavir and vice versa in HIV-infected patients. Antivir. Ther. 2007, 12, 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- Cahn, P.; Wainberg, M.A. Resistance profile of the new nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor apricitabine. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphey-Corb, M.; Rajakumar, P.; Michael, H.; Nyaundi, J.; Didier, P.J.; Reeve, A.B.; Mitsuya, H.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Parniak, M.A. Response of simian immunodeficiency virus to the novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor 4'-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4707–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, E.; Marchand, B.; Kodama, E.N.; Singh, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Kirby, K.A.; Ryan, E.M.; Sawani, A.M.; Nagy, E.; Ashida, N.; et al. Mechanism of inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by 4'-Ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine triphosphate, a translocation-defective reverse transcriptase inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35681–35691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muftuoglu, Y.; Sohl, C.D.; Mislak, A.C.; Mitsuya, H.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Anderson, K.S. Probing the molecular mechanism of action of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor 4'-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine (EFdA) using pre-steady-state kinetics. Antivir. Res. 2014, 106, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, E.; Huber, A.D.; Ryan, E.M.; Ong, Y.T.; Leslie, M.D.; Matzek, K.B.; Singh, K.; Marchand, B.; Hagedorn, A.N.; Kirby, K.A.; et al. 4'-Ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine (EFdA) Inhibits HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase with Multiple Mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24533–24548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, A.; Kodama, E.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Sakagami, Y.; Kohgo, S.; Kitano, K.; Ashida, N.; Iwai, Y.; Hayakawa, H.; Nakata, H.; et al. 2'-deoxy-4'-C-ethynyl-2-halo-adenosines active against drug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohl, C.D.; Singh, K.; Kasiviswanathan, R.; Copeland, W.C.; Mitsuya, H.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Anderson, K.S. Mechanism of interaction of human mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma with the novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor 4'-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine indicates a low potential for host toxicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, E.; Ryan, E.M.; Hachiya, A.; Kirby, K.A.; Marchand, B.; Leslie, M.D.; Huber, A.D.; Ong, Y.T.; Jackson, J.C.; Singh, K.; et al. Hypersusceptibility mechanism of Tenofovir-resistant HIV to EFdA. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, K.; Flores, J.A.; Kirby, K.A.; Neogi, U.; Sonnerborg, A.; Hachiya, A.; Das, K.; Arnold, E.; McArthur, C.; Parniak, M.; et al. Drug Resistance in Non-B Subtype HIV-1: Impact of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. Viruses 2014, 6, 3535-3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6093535
Singh K, Flores JA, Kirby KA, Neogi U, Sonnerborg A, Hachiya A, Das K, Arnold E, McArthur C, Parniak M, et al. Drug Resistance in Non-B Subtype HIV-1: Impact of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. Viruses. 2014; 6(9):3535-3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6093535
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Kamalendra, Jacqueline A. Flores, Karen A. Kirby, Ujjwal Neogi, Anders Sonnerborg, Atsuko Hachiya, Kalyan Das, Eddy Arnold, Carole McArthur, Michael Parniak, and et al. 2014. "Drug Resistance in Non-B Subtype HIV-1: Impact of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors" Viruses 6, no. 9: 3535-3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6093535
APA StyleSingh, K., Flores, J. A., Kirby, K. A., Neogi, U., Sonnerborg, A., Hachiya, A., Das, K., Arnold, E., McArthur, C., Parniak, M., & Sarafianos, S. G. (2014). Drug Resistance in Non-B Subtype HIV-1: Impact of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. Viruses, 6(9), 3535-3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6093535