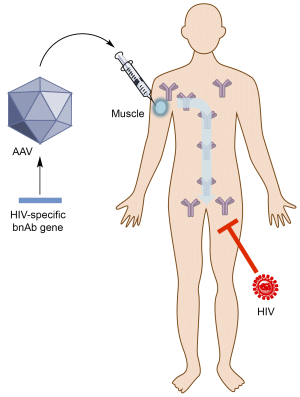
Passive Immunization against HIV/AIDS by Antibody Gene Transfer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
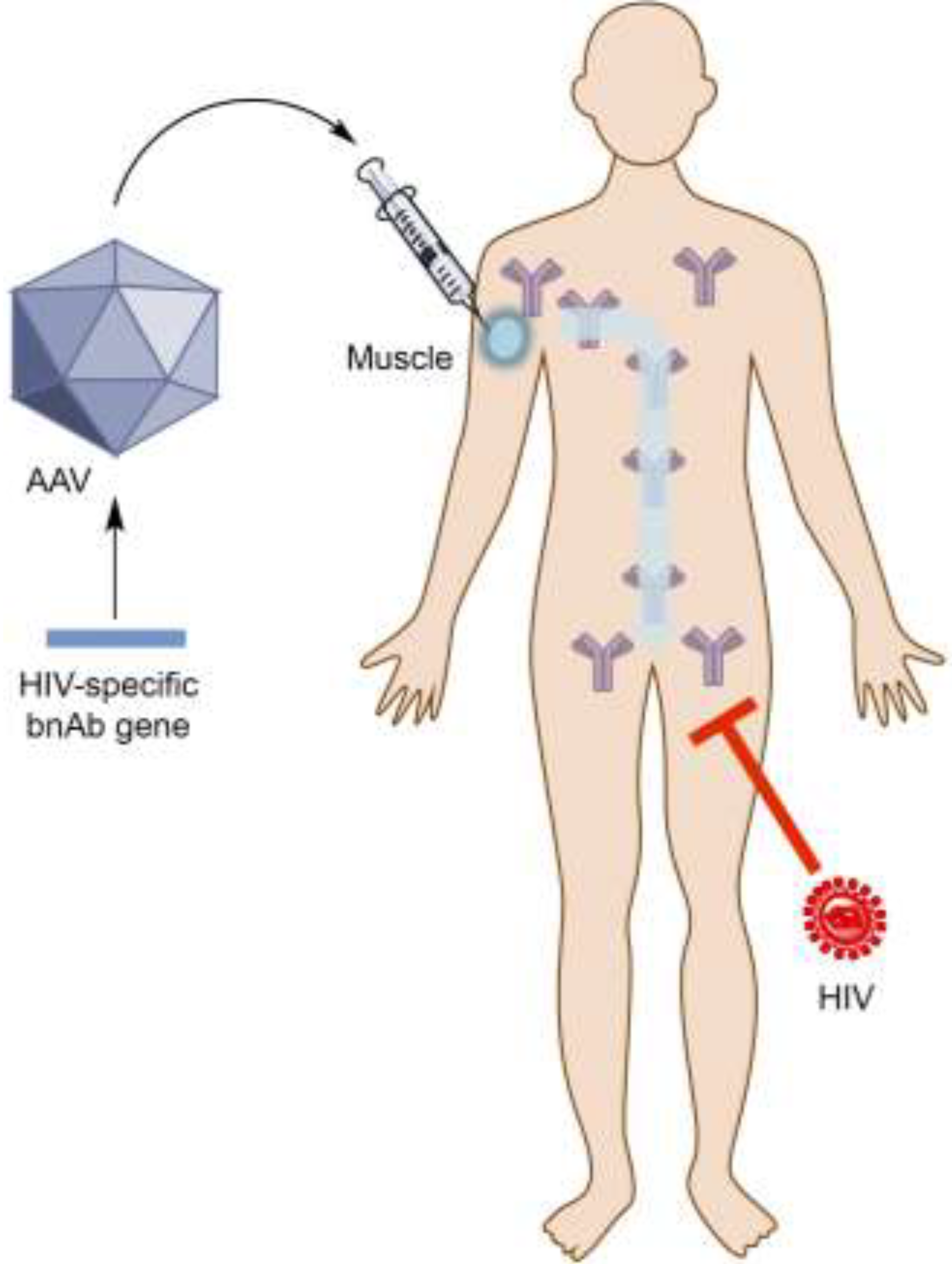
2. Antibody Gene Transfer
2.1. Delivery Methods
2.2. Diseases Targeted by Antibody Gene Transfer
3. Discovery of HIV-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies
3.1. First-Generation bnAbs against HIV
3.2. Second-Generation bnAbs against HIV
4. Vectored Immunoprophylaxis for HIV by Antibody Gene Transfer
4.1. VIP against HIV in Mice
4.2. VIP against SIV in Macaques
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- McElrath, M.J.; Haynes, B.F. Induction of immunity to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 by vaccination. Immunity 2010, 33, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piot, P.; Quinn, T.C. Response to the AIDS pandemic—A global health model. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2210–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R.; Ahmed, R.; Barouch, D.H.; Butera, S.T.; Crotty, S.; Godzik, A.; Kaufmann, D.E.; McElrath, M.J.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Pulendran, B.; et al. A blueprint for HIV vaccine discovery. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltimore, D. Steering a course to an AIDS vaccine. Science 2002, 296, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.I.; Fauci, A.S. HIV vaccine development—Improving on natural immunity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R. Antibodies, viruses and vaccines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Doms, R.W.; Koff, W.C.; Kwong, P.D.; Moore, J.P.; Nabel, G.J.; Sodroski, J.; Wilson, I.A.; Wyatt, R.T. HIV vaccine design and the neutralizing antibody problem. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A. Vaccines: Correlates of vaccine-induced immunity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G.; Schweighardt, B.; Wrin, T.; Galovich, J.; Hoh, R.; Sinclair, E.; Hunt, P.; McCune, J.M.; Martin, J.N.; Petropoulos, C.J.; et al. Neutralizing antibody responses against autologous and heterologous viruses in acute versus chronic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection: Evidence for a constraint on the ability of HIV to completely evade neutralizing antibody responses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6155–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascola, J.R.; Lewis, M.G.; Stiegler, G.; Harris, D.; VanCott, T.C.; Hayes, D.; Louder, M.K.; Brown, C.R.; Sapan, C.V.; Frankel, S.S.; et al. Protection of macaques against pathogenic simian/human immunodeficiency virus 89.6pd by passive transfer of neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4009–4018. [Google Scholar]
- Mascola, J.R.; Stiegler, G.; VanCott, T.C.; Katinger, H.; Carpenter, C.B.; Hanson, C.E.; Beary, H.; Hayes, D.; Frankel, S.S.; Birx, D.L.; et al. Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, R.; Igarashi, T.; Haigwood, N.; Buckler-White, A.; Ogert, R.; Ross, W.; Willey, R.; Cho, M.W.; Martin, M.A. Neutralizing antibody directed against the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein can completely block HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus infections of macaque monkeys. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parren, P.W.; Marx, P.A.; Hessell, A.J.; Luckay, A.; Harouse, J.; Cheng-Mayer, C.; Moore, J.P.; Burton, D.R. Antibody protects macaques against vaginal challenge with a pathogenic r5 simian/human immunodeficiency virus at serum levels giving complete neutralization in vitro. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8340–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veazey, R.S.; Shattock, R.J.; Pope, M.; Kirijan, J.C.; Jones, J.; Hu, Q.; Ketas, T.; Marx, P.A.; Klasse, P.J.; Burton, D.R.; et al. Prevention of virus transmission to macaque monkeys by a vaginally applied monoclonal antibody to HIV-1 gp120. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessell, A.J.; Rakasz, E.G.; Poignard, P.; Hangartner, L.; Landucci, G.; Forthal, D.N.; Koff, W.C.; Watkins, D.I.; Burton, D.R. Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2G12 is effective in protection against mucosal SHIV challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, J.D.; Siddappa, N.B.; Lakhashe, S.K.; Humbert, M.; Sholukh, A.; Hemashettar, G.; Wong, Y.L.; Yoon, J.K.; Wang, W.; Novembre, F.J.; et al. An anti-HIV-1 v3 loop antibody fully protects cross-clade and elicits t-cell immunity in macaques mucosally challenged with an r5 clade c sHIV. PLoS One 2011, 6, e18207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolla-Pazner, S.; Cardozo, T. Structure-function relationships of HIV-1 envelope sequence-variable regions refocus vaccine design. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simek, M.D.; Rida, W.; Priddy, F.H.; Pung, P.; Carrow, E.; Laufer, D.S.; Lehrman, J.K.; Boaz, M.; Tarragona-Fiol, T.; Miiro, G.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 elite neutralizers: Individuals with broad and potent neutralizing activity identified by using a high-throughput neutralization assay together with an analytical selection algorithm. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7337–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, A.B.; Chen, J.; Hong, C.M.; Rao, D.S.; Yang, L.; Baltimore, D. Antibody-based protection against HIV infection by vectored immunoprophylaxis. Nature 2012, 481, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.R.; Schnepp, B.C.; Zhang, J.; Connell, M.J.; Greene, S.M.; Yuste, E.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Clark, K.R. Vector-mediated gene transfer engenders long-lived neutralizing activity and protection against SIV infection in monkeys. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, B.; Sanders, R.W. Gene therapy as a vaccine for HIV-1. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.A. Gene-based passive antibody protection from HIV. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 156–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, A.B.; West, A.P., Jr. Antibody gene transfer for HIV immunoprophylaxis. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.C.; Carter, P.J. Therapeutic antibodies for autoimmunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, L.M.; Surana, R.; Wang, S. Monoclonal antibodies: Versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, J.; Fasano, C.; Dos Santos, C. From orthoclone to denosumab, the fast growing market of monoclonal antibodies. Med. Sci. (Paris) 2009, 25, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, A. Number of monoclonal antibodies on market nearly doubles by 2008. Biotechnol. Healthc. 2005, 2, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Reichert, J.; Pavolu, A. Monoclonal antibodies market. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, S.S. Economic drivers and trade-offs in antibody purification processes. Biopharm. Int. 2009, 22, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, P. Next-generation monoclonals less profitbable than trailblazers? Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, G.P.; Viswanathan, M.; Hou, Y.; Rank, D.L.; Lindberg, A.P.; Cramer, S.M.; Ladner, R.C.; Nixon, A.E.; Chen, J. Evaluation of protein engineering and process optimization approaches to enhance antibody drug manufacturability. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 2634–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Rey, M.; Lang, D.A. Aggregates in monoclonal antibody manufacturing processes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 1494–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lee, B.; Zhou, J.X.; Tressel, T.; Yang, X. Current therapeutic antibody production and process optimization. BioProcess J. 2006, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tjelle, T.E.; Corthay, A.; Lunde, E.; Sandlie, I.; Michaelsen, T.E.; Mathiesen, I.; Bogen, B. Monoclonal antibodies produced by muscle after plasmid injection and electroporation. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, N.; Bigey, P.; Scherman, D.; Danos, O.; Piechaczyk, M.; Pelegrin, M. Regulatable systemic production of monoclonal antibodies by in vivo muscle electroporation. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2004, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.M.; Bleeker, W.K.; Parren, P.W. Therapeutic antibody gene transfer: An active approach to passive immunity. Mol. Ther. 2004, 10, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Nagashima, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Arai, Y.; Teshima, Y.; Fujimoto, A.; Ainai, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Chiba, J. Passive immune-prophylaxis against influenza virus infection by the expression of neutralizing anti-hemagglutinin monoclonal antibodies from plasmids. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 64, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, I.M.; Weitzman, M.D. Gene therapy: Twenty-first century medicine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005, 74, 711–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, D.; Pelegrin, M.; Kramer, S.; Jacquet, C.; Skander, N.; Piechaczyk, M. High in vivo production of a model monoclonal antibody on adenoviral gene transfer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.H.; Shi, W.F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.H.; Guo, M.G.; Cui, Z.F.; Su, C.Q.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.M.; Sham, J.; et al. Gene therapy using adenovirus-mediated full-length anti-HER-2 antibody for HER-2 overexpression cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6179–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofer-Podesta, C.; Ang, J.; Hackett, N.R.; Senina, S.; Perlin, D.; Crystal, R.G.; Boyer, J.L. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of an anti-v antigen monoclonal antibody protects mice against a lethal yersinia pestis challenge. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Muruve, D.A. Molecular basis of the inflammatory response to adenovirus vectors. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jooss, K.; Chirmule, N. Immunity to adenovirus and adeno-associated viral vectors: Implications for gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacca, M. Gene Therapy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mingozzi, F.; High, K.A. Immune responses to aav vectors: Overcoming barriers to successful gene therapy. Blood 2013, 122, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, A.; Schaffer, D.V.; Samulski, R.J. The AAV vector toolkit: Poised at the clinical crossroads. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, A.M.; Simonelli, F.; Pierce, E.A.; Pugh, E.N., Jr.; Mingozzi, F.; Bennicelli, J.; Banfi, S.; Marshall, K.A.; Testa, F.; Surace, E.M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of gene transfer for leber’s congenital amaurosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, A.M.; High, K.A.; Auricchio, A.; Wright, J.F.; Pierce, E.A.; Testa, F.; Mingozzi, F.; Bennicelli, J.L.; Ying, G.S.; Rossi, S.; et al. Age-dependent effects of rpe65 gene therapy for leber’s congenital amaurosis: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, J.W.; Smith, A.J.; Barker, S.S.; Robbie, S.; Henderson, R.; Balaggan, K.; Viswanathan, A.; Holder, G.E.; Stockman, A.; Tyler, N.; et al. Effect of gene therapy on visual function in leber’s congenital amaurosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauswirth, W.W.; Aleman, T.S.; Kaushal, S.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Schwartz, S.B.; Wang, L.L.; Conlon, T.J.; Boye, S.L.; Flotte, T.R.; Byrne, B.J.; et al. Treatment of leber congenital amaurosis due to rpe65 mutations by ocular subretinal injection of adeno-associated virus gene vector: Short-term results of a phase i trial. Hum. Gene Ther. 2008, 19, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cideciyan, A.V.; Aleman, T.S.; Boye, S.L.; Schwartz, S.B.; Kaushal, S.; Roman, A.J.; Pang, J.J.; Sumaroka, A.; Windsor, E.A.M.; Wilson, J.M.; et al. Human gene therapy for rpe65 isomerase deficiency activates the retinoid cycle of vision but with slow rod kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15112–15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cideciyan, A.V.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Aleman, T.S.; Kaushal, S.; Schwartz, S.B.; Boye, S.L.; Windsor, E.A.; Conlon, T.J.; Sumaroka, A.; Roman, A.J.; et al. Vision 1 year after gene therapy for leber’s congenital amaurosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.R.; Campbell, K.; Rodino-Klapac, L.; Sahenk, Z.; Shilling, C.; Lewis, S.; Bowles, D.; Gray, S.; Li, C.; Galloway, G.; et al. Dystrophin immunity in duchenne's muscular dystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Rangarajan, S.; Rosales, C.; McIntosh, J.; Linch, D.C.; Chowdary, P.; Riddell, A.; Pie, A.J.; Harrington, C.; et al. Adenovirus-associated virus vector-mediated gene transfer in hemophilia b. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, A. European Agency Backs Approval of a Gene Therapy. New York Times, 20 July 2012; B1. [Google Scholar]
- Brantly, M.L.; Chulay, J.D.; Wang, L.L.; Mueller, C.; Humphries, M.; Spencer, L.T.; Rouhani, F.; Conlon, T.J.; Calcedo, R.; Betts, M.R.; et al. Sustained transgene expression despite t lymphocyte responses in a clinical trial of rAAV1-aat gene therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17606–17606. [Google Scholar]
- Flotte, T.R.; Trapnell, B.C.; Humphries, M.; Carey, B.; Calcedo, R.; Rouhani, F.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Yachnis, A.T.; Sandhaus, R.A.; McElvaney, N.G.; et al. Phase 2 clinical trial of a recombinant adeno-associated viral vector expressing alpha(1)-antitrypsin: Interim results. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 22, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroes, E.S.; Nierman, M.C.; Meulenberg, J.J.; Franssen, R.; Twisk, J.; Henny, C.P.; Maas, M.M.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Ross, C.; Aronica, E.; et al. Intramuscular administration of aav1-lipoprotein lipase(s447x) lowers triglycerides in lipoprotein lipase-deficient patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. 2008, 28, 2303–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.D.; Chen, R.; Montefiori, D.C.; Johnson, P.R.; Clark, K.R. Generation of neutralizing activity against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in serum by antibody gene transfer. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8769–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.M.; Qian, J.J.; Yi, S.L.; Harding, T.C.; Tu, G.H.; VanRoey, M.; Jooss, K. Stable antibody expression at therapeutic levels using the 2A peptide. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, M.J.; Rosenberg, J.B.; De, B.P.; Pagovich, O.E.; Young, C.N.; Qiu, J.P.; Kaminsky, S.M.; Hackett, N.R.; Worgall, S.; Janda, K.D.; et al. AAV-directed persistent expression of a gene encoding anti-nicotine antibody for smoking cessation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 140ra187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberis, M.P.; Adam, V.S.; Wong, G.; Gren, J.; Kobasa, D.; Ross, T.M.; Kobinger, G.P.; Tretiakova, A.; Wilson, J.M. Intranasal antibody gene transfer in mice and ferrets elicits broad protection against pandemic influenza. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 187ra172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Kiss, S.; Boyer, J.L.; Hackett, N.R.; Qiu, J.; Carbone, A.; Mezey, J.G.; Kaminsky, S.M.; D’Amico, D.J.; Crystal, R.G. Persistent suppression of ocular neovascularization with intravitreal administration of AAVrh. 10 coding for bevacizumab. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 22, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaricic, D.; Traube, C.; De, B.; Joh, J.; Boyer, J.; Crystal, R.G.; Worgall, S. Genetic delivery of an anti-rsv antibody to protect against pulmonary infection with rsv. Virology 2008, 378, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B.P.; Hackett, N.R.; Crystal, R.G.; Boyer, J.L. Rapid/sustained anti-anthrax passive immunity mediated by co-administration of Ad/AAV. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.X. Antibody gene therapy: An attractive approach for the treatment of cancers and other chronic diseases. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Qian, Q.J. Monoclonal antibodies as therapeutic agents in oncology and antibody gene therapy. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Su, C.Q.; Lu, Q.J.; Shi, W.F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.H.; Long, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, L.F.; Jia, X.Y.; et al. Generation of adenovirus-mediated anti-cd20 antibody and its effect on B-cell deletion in mice and nonhuman primate cynomolgus monkey. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.T.; Wykoff-Clary, S.; Gross, C.S.; Schneider, D.; Jin, F.; Kretschmer, P.J.; Hermiston, T.W. Growth inhibition of an established a431 xenograft tumor by a full-length anti-egfr antibody following gene delivery by AAV. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.M.; Qiu, Y.H.; Yao, Z.Y.; Liu, S.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Shi, J.; Zheng, D.X. 2a peptide-based, lentivirus-mediated anti-death receptor 5 chimeric antibody expression prevents tumor growth in nude mice. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothuis, J.R.; Simoes, E.A.; Levin, M.J.; Hall, C.B.; Long, C.E.; Rodriguez, W.J.; Arrobio, J.; Meissner, H.C.; Fulton, D.R.; Welliver, R.C.; et al. Prophylactic administration of respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin to high-risk infants and young children. The respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin study group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothuis, J.R.; Nishida, H. Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infections in high-risk infants by monoclonal antibody (palivizumab). Pediatr. Int. 2002, 44, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pfarr, D.S.; Losonsky, G.A.; Kiener, P.A. Immunoprophylaxis of rsv infection: Advancing from RSV-IGIV to palivizumab and motavizumab. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 317, 103–123. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.G.; Nagata, L.P. Antibody gene-based prophylaxis and therapy for biodefence. Hum. Vaccines 2008, 4, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, A.B.; Bloom, J.D.; Hong, C.M.; Rao, D.S.; Baltimore, D. Broad protection against influenza infection by vectored immunoprophylaxis in mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.B.; Hicks, M.J.; De, B.P.; Pagovich, O.; Frenk, E.; Janda, K.D.; Wee, S.; Koob, G.F.; Hackett, N.R.; Kaminsky, S.M.; et al. AAVrh.10-mediated expression of an anti-cocaine antibody mediates persistent passive immunization that suppresses cocaine-induced behavior. Hum. Gene Ther. 2012, 23, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K. The Distribution and Functions of Immunoglobulin Isotypes. In Janeway’s Immunobiology, 8th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 408–417. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, L.E.; Weiss, R.A. Neutralizing antibodies to HIV-1 induced by immunization. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forthal, D.N.; Moog, C. Fc receptor-mediated antiviral antibodies. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, N.; Sattentau, Q. The prospects for vaccines against HIV-1: More than a field of long-term nonprogression? Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2005, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, I.S.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Zhou, T.; Kwon, Y.D.; Staupe, R.P.; Moquin, S.; Chuang, G.Y.; Louder, M.K.; Schmidt, S.D.; Altae-Tran, H.R.; et al. Delineating antibody recognition in polyclonal sera from patterns of HIV-1 isolate neutralization. Science 2013, 340, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R.; Pyati, J.; Koduri, R.; Sharp, S.J.; Thornton, G.B.; Parren, P.W.; Sawyer, L.S.; Hendry, R.M.; Dunlop, N.; Nara, P.L.; et al. Efficient neutralization of primary isolates of HIV-1 by a recombinant human monoclonal antibody. Science 1994, 266, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Xu, L.; Dey, B.; Hessell, A.J.; van Ryk, D.; Xiang, S.H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zwick, M.B.; Arthos, J.; et al. Structural definition of a conserved neutralization epitope on HIV-1 gp120. Nature 2007, 445, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, J.M.; Wrin, T.; Korber, B.; Zwick, M.B.; Wang, M.; Chappey, C.; Stiegler, G.; Kunert, R.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Katinger, H.; et al. Comprehensive cross-clade neutralization analysis of a panel of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13232–13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Lapedes, A.; Tang, H.; Gnanakaran, S.; Daniels, M.G.; Zhang, M.; Bhattacharya, T.; Li, M.; Polonis, V.R.; McCutchan, F.E.; et al. Highly complex neutralization determinants on a monophyletic lineage of newly transmitted subtype c HIV-1 env clones from india. Virology 2009, 385, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trkola, A.; Purtscher, M.; Muster, T.; Ballaun, C.; Buchacher, A.; Sullivan, N.; Srinivasan, K.; Sodroski, J.; Moore, J.P.; Katinger, H. Human monoclonal antibody 2g12 defines a distinctive neutralization epitope on the gp120 glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Calarese, D.A.; Scanlan, C.N.; Zwick, M.B.; Deechongkit, S.; Mimura, Y.; Kunert, R.; Zhu, P.; Wormald, M.R.; Stanfield, R.L.; Roux, K.H.; et al. Antibody domain exchange is an immunological solution to carbohydrate cluster recognition. Science 2003, 300, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulard, M.; Phogat, S.K.; Shu, Y.; Labrijn, A.F.; Xiao, X.D.; Binley, J.M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Sidorov, I.A.; Broder, C.C.; Robinson, J.; et al. Broadly cross-reactive HIV-1-neutralizing human monoclonal fab selected for binding to gp120-CD4-CCR5 complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6913–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Poignard, P.; Raja, A.; Zwick, M.B.; Delgado, K.; Franti, M.; Binley, J.; Vivona, V.; Grundner, C.; Huang, C.C.; et al. Access of antibody molecules to the conserved coreceptor binding site on glycoprotein gp120 is sterically restricted on primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10557–10565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, G.; Bianchi, E.; Ingallinella, P.; Hurni, W.H.; Miller, M.D.; Ciliberto, G.; Cortese, R.; Bazzo, R.; SHIVer, J.W.; Pessi, A. Structural analysis of the epitope of the anti-HIV antibody 2f5 sheds light into its mechanism of neutralization and HIV fusion. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 330, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiegler, G.; Kunert, R.; Purtscher, M.; Wolbank, S.; Voglauer, R.; Steindl, F.; Katinger, H. A potent cross-clade neutralizing human monoclonal antibody against a novel epitope on gp41 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2001, 17, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehandru, S.; Wrin, T.; Galovich, J.; Stiegler, G.; Vcelar, B.; Hurley, A.; Hogan, C.; Vasan, S.; Katinger, H.; Petropoulos, C.J.; et al. Neutralization profiles of newly transmitted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by monoclonal antibodies 2G12, 2F5, and 4E10. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 14039–14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolla-Pazner, S. Identifying epitopes of HIV-1 that induce protective antibodies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, J.F.; Mouquet, H.; Feldhahn, N.; Seaman, M.S.; Velinzon, K.; Pietzsch, J.; Ott, R.G.; Anthony, R.M.; Zebroski, H.; Hurley, A.; et al. Broad diversity of neutralizing antibodies isolated from memory B cells in HIV-infected individuals. Nature 2009, 458, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.M.; Phogat, S.K.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Wagner, D.; Phung, P.; Goss, J.L.; Wrin, T.; Simek, M.D.; Fling, S.; Mitcham, J.L.; et al. Broad and potent neutralizing antibodies from an african donor reveal a new HIV-1 vaccine target. Science 2009, 326, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.S.; Pancera, M.; Carrico, C.; Gorman, J.; Julien, J.P.; Khayat, R.; Louder, R.; Pejchal, R.; Sastry, M.; Dai, K.; et al. Structure of HIV-1 gp120 v1/v2 domain with broadly neutralizing antibody PG9. Nature 2011, 480, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, D.; Langedijk, J.P.; Hinz, A.; Seaman, M.S.; Vanzetta, F.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, B.M.; Silacci, C.; Pinna, D.; Jarrossay, D.; Balla-Jhagjhoorsingh, S.; et al. Analysis of memory b cell responses and isolation of novel monoclonal antibodies with neutralizing breadth from HIV-1-infected individuals. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Hogerkorp, C.M.; Schief, W.R.; Seaman, M.S.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, S.D.; Wu, L.; Xu, L.; et al. Rational design of envelope identifies broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to HIV-1. Science 2010, 329, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Georgiev, I.; Wu, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Dai, K.; Finzi, A.; Kwon, Y.D.; Scheid, J.F.; Shi, W.; Xu, L.; et al. Structural basis for broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by antibody VRC01. Science 2010, 329, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; O’Dell, S.; Walker, L.M.; Wu, X.; Guenaga, J.; Feng, Y.; Schmidt, S.D.; McKee, K.; Louder, M.K.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; et al. Mechanism of neutralization by the broadly neutralizing HIV-1 monoclonal antibody VRC01. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8954–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.M.; Huber, M.; Doores, K.J.; Falkowska, E.; Pejchal, R.; Julien, J.P.; Wang, S.K.; Ramos, A.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Moyle, M.; et al. Broad neutralization coverage of HIV by multiple highly potent antibodies. Nature 2011, 477, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejchal, R.; Doores, K.J.; Walker, L.M.; Khayat, R.; Huang, P.S.; Wang, S.K.; Stanfield, R.L.; Julien, J.P.; Ramos, A.; Crispin, M.; et al. A potent and broad neutralizing antibody recognizes and penetrates the HIV glycan shield. Science 2011, 334, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowska, E.; Ramos, A.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, T.Q.; Moquin, S.; Walker, L.M.; Wu, X.L.; Seaman, M.S.; Wrin, T.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. PGV04, an HIV-1 gp120 CD4 binding site antibody, is broad and potent in neutralization but does not induce conformational changes characteristic of CD4. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4394–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, J.F.; Mouquet, H.; Ueberheide, B.; Diskin, R.; Klein, F.; Oliveira, T.Y.K.; Pietzsch, J.; Fenyo, D.; Abadir, A.; Velinzon, K.; et al. Sequence and structural convergence of broad and potent HIV antibodies that mimic CD4 binding. Science 2011, 333, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, R.; Scheid, J.F.; Marcovecchio, P.M.; West, A.P.; Klein, F.; Gao, H.; Gnanapragasam, P.N.P.; Abadir, A.; Seaman, M.S.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; et al. Increasing the potency and breadth of an HIV antibody by using structure-based rational design. Science 2011, 334, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, R.; Klein, F.; Horwitz, J.A.; Halper-Stromberg, A.; Sather, D.N.; Marcovecchio, P.M.; Lee, T.; West, A.P., Jr.; Gao, H.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Restricting HIV-1 pathways for escape using rationally designed anti–HIV-1 antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ofek, G.; Laub, L.; Louder, M.K.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Longo, N.S.; Imamichi, H.; Bailer, R.T.; Chakrabarti, B.; Sharma, S.K.; et al. Broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by a gp41-specific human antibody. Nature 2012, 491, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R.; Weiss, R.A. AIDS/HIV. A boost for HIV vaccine design. Science 2010, 329, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zufferey, R.; Donello, J.E.; Trono, D.; Hope, T.J. Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element enhances expression of transgenes delivered by retroviral vectors. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2886–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Reese, M.G.; Eeckman, F.H.; Kulp, D.; Haussler, D. Improved splice site detection in genie. J. Comput. Biol. 1997, 4, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shattock, R.J.; Moore, J.P. Inhibiting sexual transmission of HIV-1 infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 1, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keele, B.F.; Giorgi, E.E.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Decker, J.M.; Pham, K.T.; Salazar, M.G.; Sun, C.; Grayson, T.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; et al. Identification and characterization of transmitted and early founder virus envelopes in primary HIV-1 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilen, C.B.; Parrish, N.F.; Pfaff, J.M.; Decker, J.M.; Henning, E.A.; Haim, H.; Petersen, J.E.; Wojcechowskyj, J.A.; Sodroski, J.; Haynes, B.F.; et al. Phenotypic and immunologic comparison of clade b transmitted/founder and chronic HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8514–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Bailes, E.; Pham, K.T.; Salazar, M.G.; Guffey, M.B.; Keele, B.F.; Derdeyn, C.A.; Farmer, P.; Hunter, E.; Allen, S.; et al. Deciphering human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmission and early envelope diversification by single-genome amplification and sequencing. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3952–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, D.M. Self-complementary AAV vectors: Advances and applications. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, V.M.; Gao, G.P.; Grant, R.L.; Schnell, M.A.; Zoltick, P.W.; Rozamus, L.W.; Clackson, T.; Wilson, J.M. Long-term pharmacologically regulated expression of erythropoietin in, primates following AAV-mediated gene transfer. Blood 2005, 105, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.P.; Galimidi, R.P.; Gnanapragasam, P.N.P.; Bjorkman, P.J. Single-chain Fv-based anti-HIV proteins: Potential and limitations. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.T.; Silvestri, G. Nonhuman primate models in AIDS research. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, K.A.; Li, J.T.; Veazey, R.; Halloran, M.; Park, I.W.; Karlsson, G.B.; Sodroski, J.; Letvin, N.L. A chimeric simian/human immunodeficiency virus expressing a primary patient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate env causes an AIDS-like disease after in vivo passage in rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6922–6928. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, K.A.; Li, J.T.; Voss, G.; Lekutis, C.; Tenner-Racz, K.; Racz, P.; Lin, W.; Montefiori, D.C.; Lee-Parritz, D.E.; Lu, Y.; et al. An env gene derived from a primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate confers high in vivo replicative capacity to a chimeric simian/human immunodeficiency virus in rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 3198–3206. [Google Scholar]
- Deyle, D.R.; Russell, D.W. Adeno-associated virus vector integration. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2009, 11, 442–447. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.; Huan-Tu, G.; Gonzalez-Edick, M.; Rivera, V.M.; Clackson, T.; Jooss, K.U.; Harding, T.C. Rapamycin-regulated control of antiangiogenic tumor therapy following raav-mediated gene transfer. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yi, S.; Simmons, A.; Tu, G.H.; Nguyen, M.; Harding, T.C.; VanRoey, M.; Jooss, K. An antibody delivery system for regulated expression of therapeutic levels of monoclonal antibodies in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Wang, P. Passive Immunization against HIV/AIDS by Antibody Gene Transfer. Viruses 2014, 6, 428-447. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6020428
Yang L, Wang P. Passive Immunization against HIV/AIDS by Antibody Gene Transfer. Viruses. 2014; 6(2):428-447. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6020428
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lili, and Pin Wang. 2014. "Passive Immunization against HIV/AIDS by Antibody Gene Transfer" Viruses 6, no. 2: 428-447. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6020428
APA StyleYang, L., & Wang, P. (2014). Passive Immunization against HIV/AIDS by Antibody Gene Transfer. Viruses, 6(2), 428-447. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6020428