Abstract
The cell lines of the NCI-60 panel represent different cancer types and have been widely utilized for drug screening and molecular target identification. Screening these cell lines for envelope proteins or gene sequences related to xenotropic murine leukemia viruses (X-MLVs) revealed that one cell line, EKVX, was a candidate for production of an infectious gammaretrovirus. The presence of a retrovirus infectious to human cells was confirmed by the cell-free transmission of infection to the human prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Amplification and sequencing of additional proviral sequences from EKVX confirmed a high degree of similarity to X-MLV. The cell line EKVX was established following passage of the original tumor cells through nude mice, providing a possible source of the X-MLV found in the EKVX cells.
1. Introduction
Continuous cell lines established from human cancer specimens are critical to cancer research. Biosafety guidelines have been established for handling these cell lines because of the potential presence of infectious agents. The NCI-60 panel comprises cell lines derived from human tumors from various organs (Table 1). The panel was developed by the Developmental Therapeutics Program (DTP) of the National Cancer Institute (NCI) as an in vitro drug screening tool [1], and at the time of its establishment, all cell lines were tested for known pathogens [2]. The NCI-60 panel is currently used to screen up to 3000 synthetic compounds or natural products per year for potential anticancer activity and is also frequently used for molecular target identification (dtp.nci.nih.gov/branches/btb/ivclsp.html). The DTP has supplied the cell lines of the panel to a large number of other research laboratories. Because of their widespread use, the discovery of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV) prompted us to screen the NCI-60 cell lines for previously undetected infectious retroviruses.

Table 1.
Derivation of the cell lines of the NCI-60 panel and results of virus screening.
| Cell line name | Tumor type | Immuno-blotting for Env | PCR for enva | PCR for gaga | Passaged through miceb | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT-549 | Breast | - | - | - | Nc | |
| Hs-578T | Breast | - | - | - | N | [3] |
| MCF-7 | Breast | - | - | - | N | [4] |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast | - | - | - | N | [5] |
| T-47D | Breast | - | - | - | N | [6] |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast | - | - | - | N | [7] |
| SF-268 | CNS | - | - | - | N | [8] |
| SF-295 | CNS | - | - | - | N | [8] |
| SF-539 | CNS | - | - | - | N | [9] |
| SNB-19d | CNS | - | - | - | N | [10,11,12] |
| SNB-75 | CNS | - | - | - | N | [10,11] |
| U251d | CNS | - | - | - | N | [12,13] |
| COLO-205 | Colon | - | - | - | N | [14] |
| HCC-2998 | Colon | - | - | - | Ye | |
| HCT-116 | Colon | - | - | - | N | [15] |
| HCT-15 | Colon | - | - | - | N | [16] |
| HT29 | Colon | - | - | - | N | [17] |
| KM12f | Colon | - | - | - | N | [18] |
| SW-620 | Colon | - | - | - | N | [19] |
| CCRF-CEM | Leukemia | - | - | - | N | [20] |
| HL-60 | Leukemia | - | - | - | N | [21] |
| K562 | Leukemia | - | - | - | N | [22] |
| MOLT-4 | Leukemia | - | - | - | N | [23] |
| RPMI-8226 | Leukemia | - | - | - | N | [24] |
| SR | Leukemia | - | - | - | N | [25] |
| LOX IMVI | Melanoma | - | - | - | Y | [26,27] |
| M14g | Melanoma | - | - | - | N | [28,29] |
| MALME-3M | Melanoma | - | - | - | N | [17] |
| MDA-MB-435g | Melanoma | - | - | - | N | [7,29,30,31] |
| SK-MEL-2 | Melanoma | - | - | - | N | [17] |
| SK-MEL-28 | Melanoma | - | - | - | N | [32] |
| SK-MEL-5 | Melanoma | - | - | - | N | [32] |
| UACC-257 | Melanoma | - | - | - | Ne | |
| UACC-62 | Melanoma | - | - | - | Ne | |
| A549 ATCC | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | N | [33] |
| EKVX | Non-Small Cell Lung | + | + | + | Y | [26] |
| HOP-62 | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | Ye | [34,35] |
| HOP-92 | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | Ne | [34,35] |
| NCI-H226 | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | N | [36,37] |
| NCI-H23 | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | N | [36,37] |
| NCI-H322M | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | N | [37,38,39] |
| NCI-H460 | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | N | [36,37] |
| NCI-H522 | Non-Small Cell Lung | - | - | - | N | [36,37] |
| IGR-OV1 | Ovarian | - | - | - | N | [40] |
| NCI/ADR-RESh | Ovarian | - | - | - | N | [41,42,43] |
| OVCAR-3 | Ovarian | - | - | - | N | [44] |
| OVCAR-4 | Ovarian | - | - | - | N | [45] |
| OVCAR-5 | Ovarian | - | - | - | N | [45] |
| OVCAR-8 | Ovarian | - | - | - | N | [45,46] |
| SK-0V-3 | Ovarian | - | - | - | N | [17] |
| DU145 | Prostate | - | - | - | N | [47] |
| PC-3 | Prostate | - | - | - | N | [48] |
| A498 | Renal | - | - | - | N | [33] |
| ACHN | Renal | - | - | - | N | [49] |
| CAKI-1 | Renal | - | - | - | N | [17] |
| RXF-393 | Renal | - | - | - | Y | [50] |
| SN12C | Renal | - | - | - | N | [51] |
| TK-10 | Renal | - | - | - | N | [52] |
| UO-31 | Renal | - | - | - | Ui | |
| 786-0 | Renal | - | - | - | N | [53] |
a “+”indicates a definitive band of the expected size was observed.
b Y=Yes. N=No. U=Unknown; no information was available from literature references.
c This cell line was obtained from ATCC. According to the ATCC description: “The BT-549 line was isolated in 1978 by W.G. Coutinho and E. Y. Lasfargues. Source tissue consisted of a papillary, invasive ductal tumor which had metastasized to 3 of 7 regional lymph nodes.” The establishment of other breast cancer cell lines by the same group has been described [54].
d SNB-19 and U251 are derived from the same individual [12].
e Michael Alley, NCI, personal communication.
f The KM12 cell line is the same as KM12C in Morikawa et al. [18] (Michael Alley, NCI, personal communication).
g Current samples of M14 and MDA-MB-435 are related [29]. MDA-MB-435 was originally isolated as a breast cancer cell line.
h NCI/ADR-RES was originally described as a breast cancer cell line, but is related to the ovarian cancer cell line OVCAR-8 [41].
i Highly unlikely to have been passaged through mice (W. Marston Linehan, NCI, personal communication).
XMRV is a type C gammaretrovirus first identified in human prostate tumors [55], although considerable controversy surrounds the detection of XMRV in human samples [56,57]. The prostate cancer cell line 22Rv1 produces infectious XMRV [58], but other prostate cancer cell lines, e.g., DU145 and LNCaP, do not [59]. Hue et al. [60] recently reported that 2.2% of a large number of cell lines tested by PCR were positive for xenotropic murine leukemia virus (X-MLV) gag sequence. We used immunoblotting and PCR assays capable of detecting XMRV and other X-MLVs to screen the NCI-60 panel of tumor cell lines.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Lung Cancer Cell Line EKVX Tested Positive by Both Immunoblotting for Viral Envelope Protein and by PCR for gag and env Viral Gene Sequences
Total protein lysates were prepared from all 60 cell lines. Viral envelope protein (Env, also known as gp70) was detected by immunoblotting with monoclonal antibody 7C10 [61], which was raised against the envelope protein of Friend spleen focus-forming virus and which cross-reacts with XMRV and other X-MLV envelope proteins. A positive signal was detected in the lysate of only 1 cell line, EKVX (Table 1 and Figure 1A), a lung adenocarcinoma– derived cell line [26]. As a second means of screening for virus, PCR for XMRV and X-MLV– related gag and env sequences was performed. In concordance with the immunoblotting results, only EKVX yielded prominent bands of the expected size with both the env and gag primers, 533 bp and 731 bp, respectively (Table 1 and Figures 1B and 1C). This result is consistent with Hue et al. [60], who detected MLV-like sequences in EKVX by PCR. To rule out the possibility that EKVX cultures or derived materials were contaminated with mouse cells or DNA containing endogenous X-MLVs that could give rise to the env and gag products, we used nested PCR as described by Ono et al. [62] to test for the presence of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Although we could reliably detect 1/106 equivalents of mouse genomic DNA spiked into human genomic DNA, no mouse mitochondrial PCR products were observed with up to 250 ng of EKVX genomic DNA (data not shown). We were also unable to detect mouse DNA contamination using a single-round (45 cycles) PCR assay for intracisternal A particles (IAP) [63] on up to 600 ng of EKVX genomic DNA (Figure 1D). The mouse IAP products are ~200-300 bp; the ~100 bp band in the HCT-116 lane may be a primer dimer product, as it was observed frequently in no template controls in additional experiments.
We observed a faint ladder of background bands in all cell lines with the env primers. Therefore, we tested a subset of first round env products with nested primers, and a band of the appropriate size was only detected with EKVX (data not shown). The first round background bands were not observed in two representative cell line DNA samples (HCT-116 and DU145) spiked with a small amount (1/106) of genomic DNA containing the target DNA sequence (data not shown). Because no mouse DNA was detected in HCT-116 or DU145 genomic DNA using the IAP assay (Figure 1D), the background bands may have been the result of mispriming on human DNA sequences. A few cell lines gave rise to products of incorrect size with the gag primers (e.g., HCT-116 in Figure 1C), but no corresponding envelope PCR product was observed, and no product was detected using nested primers for gag (data not shown).
Lung can serve as a point of entry for virus infection. A search of the GEO database [64] reveals numerous examples of expression of the X-MLV/XMRV receptor XPR1 [65] in human lung cells. Although potential contamination with mouse sequences was not ruled out, XMRV sequences were reported in human respiratory secretions [66], suggesting that lung could be a target for MLV-like viruses. However, all 8 of the other lung cancer cell lines in the NCI-60 panel and 4 additional lung cancer cell lines [NCI-H1666, NCI-H650, NCI-H2122, NCI-H358; obtained from M. Lerman, NCI (data not shown)] that we tested by immunoblotting were negative for MLV-like virus.
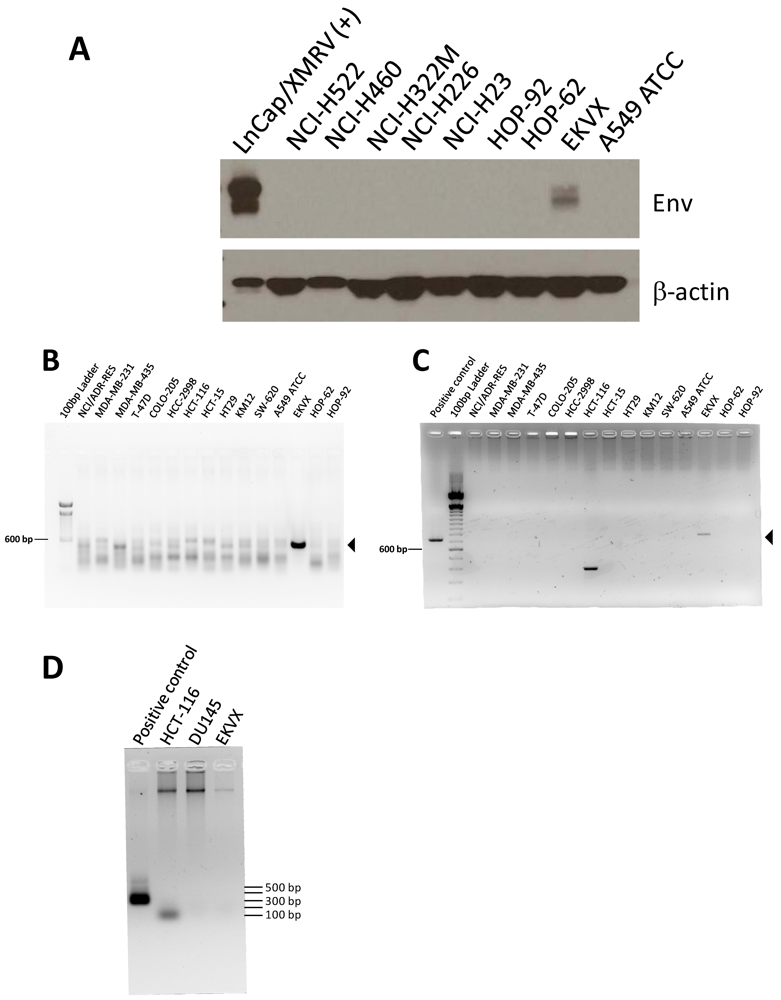
Figure 1.
Detection of viral protein and DNA in the human lung adenocarcinoma cell line EKVX. Immunoblotting and PCR were carried out on all 60 cell lines of the panel; a subset are shown. Immunoblotting of total protein lysates from lung cancer cell lines for Env with monoclonal antibody 7C10 (A). XMRV-infected LNCaP cell lysate [LNCaP/XMRV(+)] is included as a positive control. Env is present as both a precursor form (upper band) and a processed surface unit (lower band). Immunoblotting with β-actin antibody was used to confirm equal loading. Single-round PCR of genomic DNA for env (B) and gag (C) sequences. Template is genomic DNA from cell lines of the NCI-60 panel. Arrowheads indicate the expected fragment sizes: 533 bp for env and 731 bp for gag. Negative (no template) controls were run on separate gels and no products of the expected size were observed (data not shown). (D) EKVX and other representative cell lines, DU145 and HCT-116, were tested for mouse contamination by PCR for IAP using 600 ng genomic DNA as template. The positive control is genomic DNA from a mouse cell line diluted 1/105 in human cell line genomic DNA.
2.2. EKVX Produces Virus Capable of Infecting Human Cells
Cell-free supernatants were prepared from cultures of EKVX cells. Reverse transcriptase activity was detected in the EKVX supernatant using manganese, but not magnesium (data not shown), indicative of a mammalian type C retrovirus reverse transcriptase [67]. The ability of the EKVX viral supernatant to infect and spread in human cells was assessed using the human prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. LNCaP cells pretreated with polybrene were incubated with cell-free EKVX supernatant or fresh media (negative control). Cells were subcultured and total protein lysates were prepared at 10 and 16 days post-infection. Analysis by immunoblotting with monoclonal antibody 7C10 and with goat anti-Rauscher MLV p30 indicated the presence of capsid and envelope viral proteins in the lysate (Figure 2), indicating the establishment and spread of infection from the EKVX supernatant.
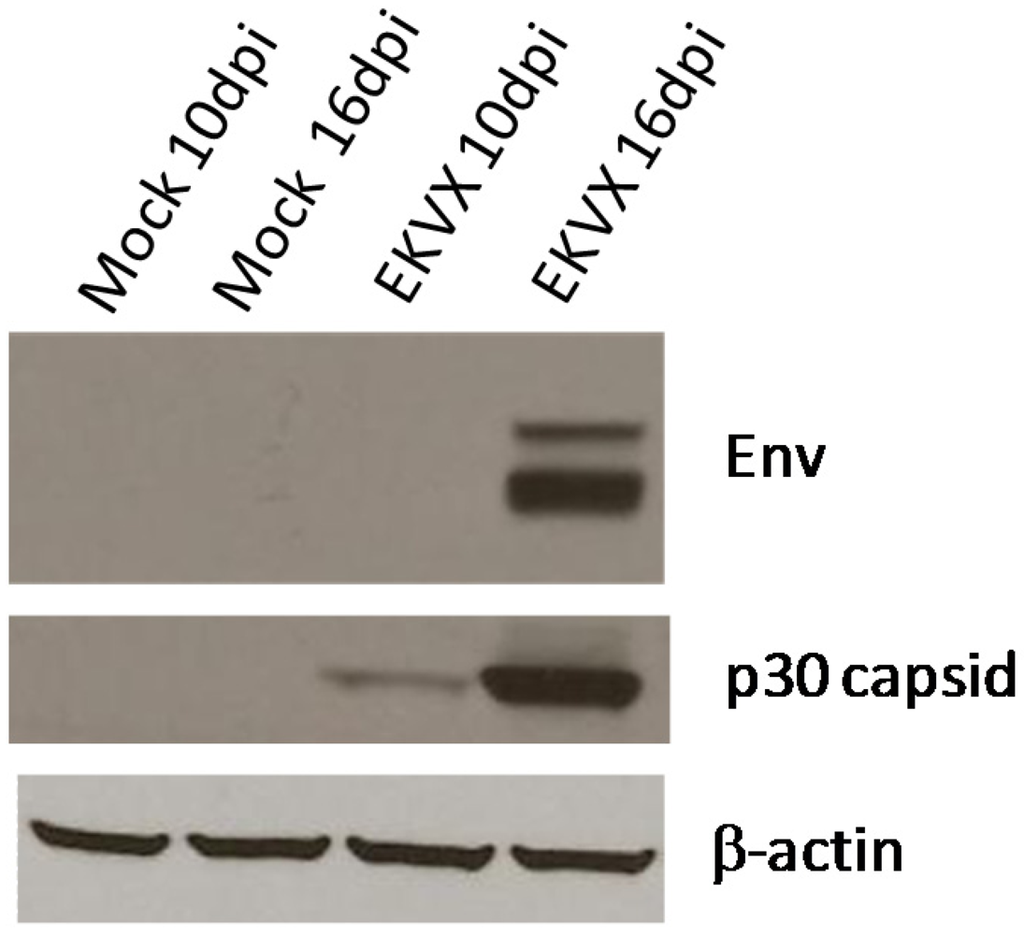
Figure 2.
Transmission of infection by a cell-free EKVX supernatant. Subconfluent LNCaP cells were infected with filtered supernatant from EKVX cells (EKVX) or with cell culture medium as a negative control (Mock) in the presence of polybrene. Total protein lysates were prepared at 10 and 16 days post-infection (dpi). Lysates were subjected to electrophoresis and immunoblotting with monoclonal antibody 7C10 for Env and with goat anti-RLV p30 capsid. Immunoblotting with β-actin antibody was used to confirm equal loading.
2.3. The EKVX Virus Is a Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus
The nucleotide sequences of the gag and env PCR fragments amplified from EKVX genomic DNA were determined. Sequences of the EKVX gag and env fragments were more closely related to X-MLVs than to XMRV (98% vs. 87% identity for gag; 99% vs. 92% identity for env). Based on these results, primers were designed to amplify additional regions in the LTR, gag, and env based on the sequence of DG-75 X-MLV. The sequences of these PCR products were determined and are aligned with representative XMRV and X-MLV sequences in Figure 3. The LTR-gag region of the EKVX virus lacks several of the defining characteristics of XMRV while aligning with 99% identity with the X-MLV sequence; most notably, it lacks the 14 bp deletion found in U3 and the short additions and 24 bp deletion found in the gag-leader of XMRV (Figure 3A). The primer binding sites for the EKVX sequence and the X-MLV sequence shown in Figure 3A are complementary to Gln-tRNAs, whereas that for XMRV is complementary to Pro-tRNA [68]. Gln-tRNA binding sites have been reported for numerous endogenous MLVs [69,70,71]. Also of note within the gag-leader region, MLV sequences contain an alternative (CTG) start codon, upstream of the ATG start codon, that yields a glycosylated precursor (glyco-Gag) [72]. In contrast to XMRV, which has an in-frame stop codon that precludes glyco-Gag synthesis [55], there is no stop codon between the CTG and ATG gag start codons and they are in frame with each other, suggesting that the EKVX virus should produce glyco-Gag. The env region (Figure 3B) lacks the trinucleotide G insertion found in XMRV, and the env-LTR region (Figure 3C) is missing the same 14 bp deletion in U3 as noted in Figure 3A. Together, these sequence data confirm that the EKVX virus is more closely related to X-MLVs than to the reported sequences of XMRV.
Xenotropic MLVs are so named because they can infect non-mouse species but cannot infect most laboratory strains of mice. X-MLV sequences are present as endogenous viruses in all laboratory and some house mouse strains [73,74,75,76,77], and endogenous viruses can be activated to produce infectious virus under certain conditions such as chemical or radiation exposure or immune induction [78,79,80,81,82]. Because EKVX was derived by passage through a nude mouse [26], the virus in the cell line may have been present in the original tumor or may have been acquired from nude mouse cells producing X-MLV. Several instances of human tumors and cell lines passed through nude mice having acquired viruses from the host have been reported [83,84,85,86,87,88,89]. However, not all cells passaged in mice acquire a virus. Indeed, four other cell lines of the NCI-60 panel are known to have been established after passage through mice (Table 1), and these tested negative for X-MLVs. The propensity for acquisition of a virus may depend on the strain of mouse, the means of immune suppression, the characteristics of the xenografted tumor, and whether the experimental protocol includes any additional factors (chemical exposure, radiation) that could promote the activation of an endogenous virus. Suzuki et al. [86] found that cells from 6/9 tumors transplanted into nude mice produced infectious murine type-C virus. Lusso et al. [85] found that cells recovered from all 6 human hematopoietic tumors studied that were transplanted into splenectomized, irradiated, and anti-asialo-GM1–treated nude mice acquired X-MLV infections. In other studies in which a variety of solid tumors were implanted as xenografts in nude mice or mice treated with mouse thymocyte antiserum, only 1/9 [87], 1/12 [84], and 2/11 [88] xenografts were associated with type C retroviruses. Intriguingly, Tralka et al. [88] reported IAP production in the human osteosarcoma cells that had acquired X-MLV infection. In a recent study, Zhang et al. [89] found evidence that 6/23 (mouse DNA-free) human cell lines established following passage through mice had been infected with X-MLV. Because of the possibility that the EKVX human lung cancer cell line acquired its X-MLV upon passage through nude mice, our study sheds no light on the controversy of whether X-MLV infections occur naturally in the human population.
The identification of a human infectious retrovirus in a commonly handled cell line is of concern on multiple counts: 1) unknown risk of infection and health risks to persons exposed to the virus, 2) unanticipated influence of infection and expression of viral proteins on experimental results [85,86], and 3) risk of spread of infectious virus to other cultured cell lines [89]. Infection of cells with X-MLV significantly altered the interactions of HIV-1 with those cells compared to their uninfected counterparts [85]. With respect to the potential for unintended spread of the virus among cultures, two reported examples of X-MLV in human cell lines that had not been transplanted into mice appear to have resulted from vertical transmission of virus from another infected cell line [90,91]. Zhang et al. [89] found that non-xenograft cell lines maintained in a xenograft-free facility showed no evidence of MLV infection, whereas 17% of non-xenograft cell lines cultured in laboratories that also maintained xenograft cultures became infected with MLV. Our study indicates that the X-MLV present in the EKVX cell line has not spread to other cell lines of the NCI-60 panel maintained by the DTP.
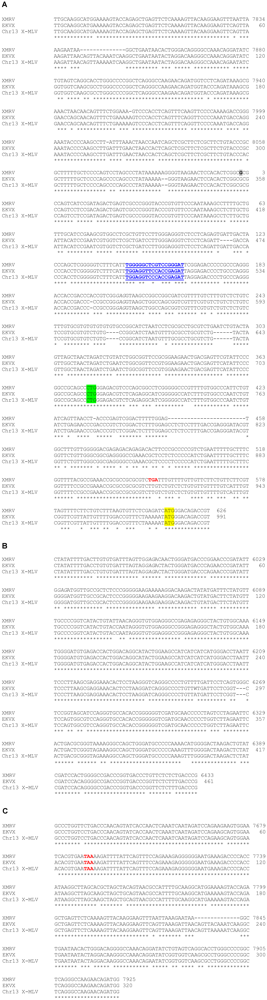
Figure 3.
Nucleotide sequence from the LTR, gag, and env regions of the EKVX virus. The sequences of regions of the EKVX virus are aligned with XMRV (VP62; accession no. DQ399707) and an endogenous X-MLV provirus from chromosome 13 (Chr13 X-MLV) of a C57BL/6 mouse (accession no. CT030655, nt 54,685-63,371). U3 sequence from the 3′ end of XMRV VP62 sequence was appended to the 5′ end in the figure to generate the predicted provirus sequence. Numbering for XMRV is according to XMRV VP62, with nt 1 (at the U3/R transition) highlighted in gray. Numbering for EKVX indicates the nucleotide number for each fragment shown. Conserved nucleotides are indicated by *. (A) LTR-gag leader region, compiled from PCR fragments generated with primers DG-75 7762F/DG-75 287R and DG-75 7945F/DG-75 664R. The primer binding site is underlined and shown in blue. The upstream glyco-Gag start is highlighted in green, and the in-frame stop codon in XMRV is shown in red. The start codon for the Gag polyprotein is highlighted in yellow. (B) env region, generated with primers VP62 5922F / VP62 6454R. (C) env-LTR region, generated with primers DG-75 7607F/DG-75 7968R. The stop codon for the Env polyprotein is shown in red.
Our results confirm the findings of Sfanos et al. [92], who published the results of a similar study while this manuscript was in preparation for publication. They tested 58 of the 60 cell lines of the NCI-60 panel, and like us, found EKVX to be the only one of these cell lines expressing an X-MLV. An important difference between their study and ours is that the cell lines tested by Sfanos et al. were obtained from the NCI and then cultured in their own laboratory, whereas our initial screen was conducted on materials (DNA and cell pellets) directly supplied by the DTP, providing an additional level of confidence that the virus is present in the source cell line maintained by the DTP. Additionally, we utilized a different envelope antibody and different PCR primers, further strengthening the validity of the findings of both papers.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Line Materials and Cell Culture
Frozen cell pellets and genomic DNA were obtained from the DTP. EKVX cells were obtained from the DTP, and LNCaP cells were obtained from the laboratory of F. Ruscetti, NCI. Both cell lines were cultured in RPMI supplemented with penicillin/streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum.
3.2. Immunoblotting
Total protein lysates were prepared as previously described [93], and 30 μg were subjected to electrophoresis on 4-12% Bis-Tris gels (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) with MOPS buffer and transferred to nitrocellulose. Monoclonal antibody 7C10 [61], polyclonal goat antisera against Rauscher MLV p30 (NCI, Bethesda, MD), and β-actin antibody (Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO) were used as primary antibodies. Detection was accomplished with horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibodies and enhanced chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL). XMRV-infected LNCaP cell lysate, provided by F. Ruscetti, was used as a positive control.
3.3. PCR
PCR for XMRV gag sequences was carried out on 75 ng of genomic DNA in a 25 μl reaction using primers 419F and 1154R and conditions as previously described [94] except the final concentration of each primer was 0.2 μM and the extension step was shortened to 45 s. PCR for XMRV env sequences was carried out similarly with primers 5922F (5′-GCTAATGCTACCTCCCTCCTGG) and 6454R (5′-GGCCCTACATTGAGGACCTGG) with an annealing temperature of 58°C. Hot-StartIt FideliTaq (USB, Cleveland, OH) was used for PCR. No template (water) controls and an XMRV-infected positive control (provided by F. Ruscetti) were included. In some cases, 150 ng genomic DNA was spiked with 1.5 pg or 0.15 pg (0.15 pg/150 ng approximates 1 provirus copy per cell) plasmid DNA containing the XMRV env sequence (provided by F. Ruscetti). Nested PCR was carried out on 1.5 µl of the first round product in a 25 μl reaction as previously described for gag [94] and at an annealing temperature of 58°C using primers 5942F (5′-GGGGACGATGACAGACACTTTCC) and 6271R (5′-GAGCCCACTGAGGAATCAAAACAG) for env. PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis on 1.5-2% agarose gels and staining with ethidium bromide.
Nested PCR was carried out as described [62] to test for the presence of mouse mitochondrial DNA in 250 ng EKVX genomic DNA. Single-round PCR for intracisternal A particles (IAP) for 45 cycles on up to 600 ng of EKVX genomic DNA was carried out as published [63].
Additional PCR products were generated for sequencing using Finnzyme Phusion polymerase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA) with up to 200 ng genomic DNA in 100 µl reactions containing the HF buffer supplied by the manufacturer, 200 μM dNTPs, and 0.5 μM each primer. Primers were designed to amplify regions in the LTR, gag, and env based on the sequence of DG-75 X-MLV (GenBank accession no. AF221065). Primers and conditions used were: DG-75 7762F (5′-CAAGCTAGCTGCAGTAACGCCATT) and DG-75 287R (5′-CAGACGCAGGCGCAAACATTAGAT) with initial denaturation for 30 s at 98°C followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 98°C for 8 s and annealing/extension at 72°C for 15 s, followed by a final extension at 72°C for 7 min; DG-75 7607F (5′-AAAGGCAGAATTTCGGTGGTGCAG) and DG-75 7968R (5′-TGCTGGTTCCGCTTTATCTGGGTA) with the same conditions; and DG-75 7945R (5′-TACCCAGATAAAGCGGAACCAGCA) and DG-75 664R (5′-AGGGTCAGACTCAAAGGAGTGGTT) with initial denaturation for 30 s at 98°C followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 98°C for 8 s, annealing at 70°C for 20 s, and extension at 72°C for 26 s, followed by a final extension at 72°C for 7 min. Products were separated on 2% agarose gels and extracted using a QiaexII Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA).
3.4. Sequencing and Alignment
Sanger sequencing was performed by the Laboratory of Molecular Technology, SAIC-Frederick. Sequences were assembled using Geneious v5.1.6 [95]. Sequences were aligned with representative XMRV and X-MLV sequences using Clustal W2 (www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2) [96,97]. Sequences have been deposited with GenBank with accession numbers JN861040, JN861041, and JN861042.
3.5. Cell-free Virus Transmission Assay
Supernatants were collected from cultures of EKVX cells 24 hours after a media change and were passed through 0.45 μm filters. For virus infection, subconfluent LNCaP cells in 6-well dishes were pretreated with polybrene (4 μg/ml), then the media was removed and replaced with cell-free EKVX supernatant or fresh media (negative control) containing polybrene (2 μg/ml). After 5 hours incubation, the media was changed in each well. Cells were subcultured and total protein lysates were prepared at 10 and 16 days post-infection. Analysis for viral proteins by immunoblotting was carried out.
4. Conclusions
The human lung adenocarcinoma cell line EKVX produces an X-MLV that is infectious to human cells. Because the EKVX cell line was established following the passage of the original tumor cells in nude mice, the source of the virus may be the activation of an endogenous virus in the mouse rather than the original human tumor. Regardless of the origin of the X-MLV in the cell line EKVX, its discovery serves as a reminder to handle all human-derived cell lines, even those tested for known human pathogens, with caution.
Acknowledgments
We thank Frank Ruscetti, Kathryn Jones, Ying Huang, John Coffin, and Michael Alley for helpful discussions. We appreciate the materials provided by the tumor repository of the NCI Developmental Therapeutics Program, Frank Ruscetti, and Michael Lerman, and are grateful for the technical assistance provided by Cari Sadowski and Dan Bertolette. This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Cancer Institute, Center for Cancer Research.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shoemaker, R.H. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Hackett, A.J.; Smith, H.S.; Springer, E.L.; Owens, R.B.; Nelson-Rees, W.A.; Riggs, J.L.; Gardner, M.B. Two syngeneic cell lines from human breast tissue: the aneuploid mammary epithelial (Hs578T) and the diploid myoepithelial (Hs578Bst) cell lines. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1977, 58, 1795–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Soule, H.D.; Vazguez, J.; Long, A.; Albert, S.; Brennan, M. A human cell line from a pleural effusion derived from a breast carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1973, 51, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Cailleau, R.; Young, R.; Olive, M.; Reeves, W.J., Jr. Breast tumor cell lines from pleural effusions. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1974, 53, 661–674. [Google Scholar]
- Keydar, I.; Chen, L.; Karby, S.; Weiss, F.R.; Delarea, J.; Radu, M.; Chaitcik, S.; Brenner, H.J. Establishment and characterization of a cell line of human breast carcinoma origin. Eur. J. Cancer 1979, 15, 659–670. [Google Scholar]
- Cailleau, R.; Olive, M.; Cruciger, Q.V. Long-term human breast carcinoma cell lines of metastatic origin: preliminary characterization. In Vitro 1978, 14, 911–915. [Google Scholar]
- Rutka, J.T.; Giblin, J.R.; Dougherty, D.Y.; Liu, H.C.; McCulloch, J.R.; Bell, C.W.; Stern, R.S.; Wilson, C.B.; Rosenblum, M.L. Establishment and characterization of five cell lines derived from human malignant gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 1987, 75, 92–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rutka, J.T.; Giblin, J.R.; Hoifodt, H.K.; Dougherty, D.V.; Bell, C.W.; McCulloch, J.R.; Davis, R.L.; Wilson, C.B.; Rosenblum, M.L. Establishment and characterization of a cell line from a human gliosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 5893–5902. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, J.L.; Behrens, D.L.; Mullins, D.E.; Kornblith, P.L.; Dexter, D.L. Plasminogen activator and inhibitor activity in human glioma cells and modulation by sodium butyrate. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kornblith, P.L.; Smith, B.H.; Leonard, L.A. Response of cultured human brain tumors to nitrosoureas: correlation with clinical data. Cancer 1981, 47, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- CNS cell lines SNB-19 and U251 are derived from the same individual. Available online: http://dtp.nci.nih.gov/docs/misc/common_files/U251_SNB-19.html.
- Bigner, D.D.; Bigner, S.H.; Ponten, J.; Westermark, B.; Mahaley, M.S.; Ruoslahti, E.; Herschman, H.; Eng, L.F.; Wikstrand, C.J. Heterogeneity of genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of fifteen permanent cell lines derived from human gliomas. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1981, 40, 201–229. [Google Scholar]
- Semple, T.U.; Quinn, L.A.; Woods, L.K.; Moore, G.E. Tumor and lymphoid cell lines from a patient with carcinoma of the colon for a cytotoxicity model. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Brattain, M.G.; Fine, W.D.; Khaled, F.M.; Thompson, J.; Brattain, D.E. Heterogeneity of malignant cells from a human colonic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar]
- Dexter, D.L.; Barbosa, J.A.; Calabresi, P. N,N-dimethylformamide-induced alteration of cell culture characteristics and loss of tumorigenicity in cultured human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1979, 39, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Fogh, J.; Trempe, G. New human tumor cell lines. In Human Tumor Cells In Vitro; Fogh, J., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 115–159. [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa, K.; Walker, S.M.; Jessup, J.M.; Fidler, I.J. In vivo selection of highly metastatic cells from surgical specimens of different primary human colon carcinomas implanted into nude mice. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitz, A.; Stinson, J.C.; McCombs, W.B., 3rd; McCoy, C.E.; Mazur, K.C.; Mabry, N.D. Classification of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 4562–4569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foley, G.E.; Lazarus, H.; Farber, S.; Uzman, B.G.; Boone, B.A.; McCarthy, R.E. Continuous culture of human lymphoblasts from peripheral blood of a child with acute leukemia. Cancer 1965, 18, 522–529. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, S.J.; Gallo, R.C.; Gallagher, R.E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature 1977, 270, 347–349. [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio, C.B.; Lozzio, B.B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood 1975, 45, 321–334. [Google Scholar]
- Minowada, J.; Onuma, T.; Moore, G.E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1972, 49, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Moore, G.E.; Yagi, Y.; Pressman, D. Production of free light chains of immunoglobulin by a hematopoietic cell line derived from a patient with multiple myeloma. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1967, 125, 1246–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith, M.; Urba, W.J.; Longo, D.L. Growth inhibition of human lymphoma cell lines by the marine products, dolastatins 10 and 15. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Aamdal, S.; Fodstad, O.; Kaalhus, O.; Pihl, A. Chemosensitivity profiles of human cancers assessed by the 6-day SRC assay on serially xenografted tumors. Int. J. Cancer 1986, 37, 579–587. [Google Scholar]
- Fodstad, O.; Aamdal, S.; McMenamin, M.; Nesland, J.M.; Pihl, A. A new experimental metastasis model in athymic nude mice, the human malignant melanoma LOX. Int. J. Cancer 1988, 41, 442–449. [Google Scholar]
- Sulit, H.L.; Golub, S.H.; Irie, R.F.; Gupta, R.K.; Grooms, G.A.; Morton, D.L. Human tumor cells grown in fetal calf serum and human serum: influences on the tests for lymphocyte cytotoxicity, serum blocking and serum arming effects. Int. J. Cancer 1976, 17, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- MDA-MB-435 is a melanoma cell line, not a breast cancer cell line. Available online: http://dtp.nci.nih.gov/docs/misc/common_files/mda-mb-435-update.html.
- Brinkley, B.R.; Beall, P.T.; Wible, L.J.; Mace, M.L.; Turner, D.S.; Cailleau, R.M. Variations in cell form and cytoskeleton in human breast carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1980, 40, 3118–3129. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, J.M.; Creighton, C.J.; Meck, J.M.; Haddad, B.R.; Johnson, M.D. MDA-MB-435 cells are derived from M14 melanoma cells--a loss for breast cancer, but a boon for melanoma research. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 104, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, T.E.; Takahashi, T.; Resnick, L.A.; Oettgen, H.F.; Old, L.J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: mixed hemadsorption assays for humoral immunity to cultured autologous melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1976, 73, 3278–3282. [Google Scholar]
- Giard, D.J.; Aaronson, S.A.; Todaro, G.J.; Arnstein, P.; Kersey, J.H.; Dosik, H.; Parks, W.P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1973, 51, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar]
- McLemore, T.L.; Adelberg, S.; Czerwinski, M.; Hubbard, W.C.; Yu, S.J.; Storeng, R.; Wood, T.G.; Hines, R.N.; Boyd, M.R. Altered regulation of the cytochrome P4501A1 gene: novel inducer-independent gene expression in pulmonary carcinoma cell lines. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989, 81, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar]
- McLemore, T.; Alley, M.; Liu, W.; Hubbard, W.; Adelberg, S.; Czerwinski, M.; Yu, S.; Stinson, S.; Storeng, R.; Eggleston, J.; Boyd, M. Histopathologic, biochemical and molecular genetic characterization of four newly established human pulmonary carcinoma cell lines. In Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research, San Francisco, CA, USA, May 1989; p. 225.
- Carney, D.N.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bepler, G.; Guccion, J.G.; Marangos, P.J.; Moody, T.W.; Zweig, M.H.; Minna, J.D. Establishment and identification of small cell lung cancer cell lines having classic and variant features. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 2913–2923. [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D. NCI series of cell lines: an historical perspective. J. Cell. Biochem. Suppl. 1996, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Falzon, M.; McMahon, J.B.; Gazdar, A.F.; Schuller, H.M. Preferential metabolism of N-nitrosodiethylamine by two cell lines derived from human pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Carcinogenesis 1986, 7, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar, A.F.; Linnoila, R.I.; Kurita, Y.; Oie, H.K.; Mulshine, J.L.; Clark, J.C.; Whitsett, J.A. Peripheral airway cell differentiation in human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar]
- Benard, J.; Da Silva, J.; De Blois, M.C.; Boyer, P.; Duvillard, P.; Chiric, E.; Riou, G. Characterization of a human ovarian adenocarcinoma line, IGROV1, in tissue culture and in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 4970–4979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cell Line NCI/ADR-RES is an ovarian tumor cell line, not a breast line. Available online: http://dtp.nci.nih.gov/docs/misc/common_files/NCI-ADRres.html.
- Batist, G.; Tulpule, A.; Sinha, B.K.; Katki, A.G.; Myers, C.E.; Cowan, K.H. Overexpression of a novel anionic glutathione transferase in multidrug-resistant human breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 15544–15549. [Google Scholar]
- Roschke, A.V.; Tonon, G.; Gehlhaus, K.S.; McTyre, N.; Bussey, K.J.; Lababidi, S.; Scudiero, D.A.; Weinstein, J.N.; Kirsch, I.R. Karyotypic complexity of the NCI-60 drug-screening panel. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8634–8647. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, T.C.; Young, R.C.; McKoy, W.M.; Grotzinger, K.R.; Green, J.A.; Chu, E.W.; Whang-Peng, J.; Rogan, A.M.; Green, W.R.; Ozols, R.F. Characterization of a human ovarian carcinoma cell line (NIH:OVCAR-3) with androgen and estrogen receptors. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 5379–5389. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, T.C.; Young, R.C.; Ozols, R.F. Experimental model systems of ovarian cancer: applications to the design and evaluation of new treatment approaches. Semin. Oncol. 1984, 11, 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Schilder, R.J.; Hall, L.; Monks, A.; Handel, L.M.; Fornace, A.J., Jr.; Ozols, R.F.; Fojo, A.T.; Hamilton, T.C. Metallothionein gene expression and resistance to cisplatin in human ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 45, 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, K.R.; Mickey, D.D.; Wunderli, H.; Mickey, G.H.; Paulson, D.F. Isolation of a human prostate carcinoma cell line (DU 145). Int. J. Cancer 1978, 21, 274–281. [Google Scholar]
- Kaighn, M.E.; Narayan, K.S.; Ohnuki, Y.; Lechner, J.F.; Jones, L.W. Establishment and characterization of a human prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC-3). Invest. Urol. 1979, 17, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Borden, E.C.; Hogan, T.F.; Voelkel, J.G. Comparative antiproliferative activity in vitro of natural interferons alpha and beta for diploid and transformed human cells. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 4948–4953. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, D.P.; Winterhalter, B.R.; Fiebig, H.H. Establishment and characterization of human tumor xenografts in thymus-aplastic nude mice. In Immunodeficient Mice in Oncology; Fiebig, H.H., Berger, D.P., Eds.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1992; Volume 42, pp. 23–46. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, S.; von Eschenbach, A.C.; Giavazzi, R.; Fidler, I.J. Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude mice. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 4109–4115. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, A.; Clayman, R.V.; Elbers, J.; Limas, C.; Wang, N.; Stone, K.; Gebhard, R.; Prigge, W.; Palmer, J. Characterization of two human cell lines (TK-10, TK-164) of renal cell cancer. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 3856–3862. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.D.; Elliott, A.Y.; Stein, N.; Fraley, E.E. In vitro cultivation of human renal cell cancer. I. Establishment of cells in culture. In Vitro 1976, 12, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasfargues, E.Y.; Coutinho, W.G.; Redfield, E.S. Isolation of two human tumor epithelial cell lines from solid breast carcinomas. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1978, 61, 967–978. [Google Scholar]
- Urisman, A.; Molinaro, R.J.; Fischer, N.; Plummer, S.J.; Casey, G.; Klein, E.A.; Malathi, K.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Tubbs, R.R.; Ganem, D.; et al. Identification of a novel Gammaretrovirus in prostate tumors of patients homozygous for R462Q RNASEL variant. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paprotka, T.; Delviks-Frankenberry, K.A.; Cingoz, O.; Martinez, A.; Kung, H.J.; Tepper, C.G.; Hu, W.S.; Fivash, M.J., Jr.; Coffin, J.M.; Pathak, V.K. Recombinant origin of the retrovirus XMRV. Science 2011, 333, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- van der Kuyl, A.C.; Berkhout, B. XMRV: not a mousy virus. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2011, 110, 273–274. [Google Scholar]
- Knouf, E.C.; Metzger, M.J.; Mitchell, P.S.; Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Tewari, M.; Miller, A.D. Multiple integrated copies and high-level production of the human retrovirus XMRV (xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus) from 22Rv1 prostate carcinoma cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7353–7356. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Kim, S.; Hong, S.; Das Gupta, J.; Malathi, K.; Klein, E.A.; Ganem, D.; Derisi, J.L.; Chow, S.A.; Silverman, R.H. An infectious retrovirus susceptible to an IFN antiviral pathway from human prostate tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007, 104, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Hue, S.; Gray, E.R.; Gall, A.; Katzourakis, A.; Tan, C.P.; Houldcroft, C.J.; McLaren, S.; Pillay, D.; Futreal, A.; Garson, J.A.; et al. Disease-associated XMRV sequences are consistent with laboratory contamination. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, L.; Koller, R.; Ruscetti, S. Monoclonal antibody to spleen focus-forming virus-encoded gp52 provides a probe for the amino-terminal region of retroviral envelope proteins that confers dual tropism and xenotropism. J. Virol. 1982, 43, 472–481. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, K.; Satoh, M.; Yoshida, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Kohara, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Mizusawa, H.; Sawada, H. Species identification of animal cells by nested PCR targeted to mitochondrial DNA. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 2007, 43, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Oakes, B.; Tai, A.K.; Cingoz, O.; Henefield, M.H.; Levine, S.; Coffin, J.M.; Huber, B.T. Contamination of human DNA samples with mouse DNA can lead to false detection of XMRV-like sequences. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, T.; Troup, D.B.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D1005–D1010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kozak, C.A. The mouse "xenotropic" gammaretroviruses and their XPR1 receptor. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, N.; Schulz, C.; Stieler, K.; Hohn, O.; Lange, C.; Drosten, C.; Aepfelbacher, M. Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related gammaretrovirus in respiratory tract. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Coffin, J.M. Retroviridae: The viruses and their replication. In Fundamental Virology, 3rd; Fields, B.N., Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 763–843. [Google Scholar]
- Jühling, F.; Mörl, M.; Hartmann, R.K.; Sprinzl, M.; Stadler, P.F.; Pütz, J. tRNAdb 2009: compilation of tRNA sequences and tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D159–D162. [Google Scholar]
- Jern, P.; Stoye, J.P.; Coffin, J.M. Role of APOBEC3 in genetic diversity among endogenous murine leukemia viruses. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nikbakht, K.N.; Ou, C.Y.; Boone, L.R.; Glover, P.L.; Yang, W.K. Nucleotide sequence analysis of endogenous murine leukemia virus-related proviral clones reveals primer-binding sites for glutamine tRNA. J. Virol. 1985, 54, 889–893. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, C.Y.; Boone, L.R.; Yang, W.K. A novel sequence segment and other nucleotide structural features in the long terminal repeat of a BALB/c mouse genomic leukemia virus-related DNA clone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983, 11, 5603–5620. [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom, R.; Wills, J.W. Synthesis, Assembly, and Processing of Viral Proteins. In Retroviruses; Coffin J.M.;, Hughes, S.H.; Varmus, H.E., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 263–341. [Google Scholar]
- Frankel, W.N.; Stoye, J.P.; Taylor, B.A.; Coffin, J.M. Genetic analysis of endogenous xenotropic murine leukemia viruses: association with two common mouse mutations and the viral restriction locus Fv-1. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan, M.D.; Buckler, C.E.; Sears, J.F.; Rowe, W.P.; Martin, M.A. Organization and stability of endogenous xenotropic murine leukemia virus proviral DNA in mouse genomes. J. Virol. 1983, 45, 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Kozak, C.A.; O'Neill, R.R. Diverse wild mouse origins of xenotropic, mink cell focus-forming, and two types of ecotropic proviral genes. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O'Neill, R.R.; Khan, A.S.; Hoggan, M.D.; Hartley, J.W.; Martin, M.A.; Repaske, R. Specific hybridization probes demonstrate fewer xenotropic than mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus env-related sequences in DNAs from inbred laboratory mice. J. Virol. 1986, 58, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga, K.; Coffin, J.M. Structure and distribution of endogenous nonecotropic murine leukemia viruses in wild mice. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8289–8300. [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson, S.A.; Todaro, G.J.; Scolnick, E.M. Induction of murine C-type viruses from clonal lines of virus-free BALB-3T3 cells. Science 1971, 174, 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Haran-Ghera, N. Leukemogenic activity of centrifugates from irradiated mouse thymus and bone marrow. Int. J. Cancer 1966, 1, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, M.S.; Black, P.H.; Tracy, G.S.; Leibowitz, S.; Schwartz, R.S. Leukemia virus activation in chronic allogeneic disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1970, 67, 1914–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Igel, H.J.; Huebner, R.J.; Turner, H.C.; Kotin, P.; Falk, H.L. Mouse leukemia virus activation by chemical carcinogens. Science 1969, 166, 1624–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, M.; Kaplan, H.S. Leukemogenic activity of filtrates from radiation-induced lymphoid tumors of mice. Science 1959, 130, 387–388. [Google Scholar]
- Achong, B.G.; Trumper, P.A.; Giovanella, B.C. C-type virus particles in human tumours transplanted into nude mice. Br. J. Cancer 1976, 34, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Gautsch, J.W.; Knowles, A.F.; Jensen, F.C.; Kaplan, N.O. Highly efficient induction of type C retroviruses by a human tumor in athymic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1980, 77, 2247–2250. [Google Scholar]
- Lusso, P.; di Marzo Veronese, F.; Ensoli, B.; Franchini, G.; Jemma, C.; DeRocco, S.E.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Gallo, R.C. Expanded HIV-1 cellular tropism by phenotypic mixing with murine endogenous retroviruses. Science 1990, 247, 848–852. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Yanagihara, K.; Yoshida, K.; Seido, T.; Kuga, N. Infectious murine type-C viruses released from human cancer cells transplated into nude mice. Gann 1977, 68, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Todaro, G.J.; Arnstein, P.; Parks, W.P.; Lennette, E.H.; Huebner, R.J. A type-C virus in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells after inoculation into NIH Swiss mice treated with antithymocyte serum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1973, 70, 859–862. [Google Scholar]
- Tralka, T.S.; Yee, C.L.; Rabson, A.B.; Wivel, N.A.; Stromberg, K.J.; Rabson, A.S.; Costa, J.C. Murine type C retroviruses and intracisternal A-particles in human tumors serially passaged in nude mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1983, 71, 591–599. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.A.; Maitra, A.; Hsieh, J.T.; Rudin, C.M.; Peacock, C.; Karikari, C.; Brekken, R.A.; Stastny, V.; Gao, B.; Girard, L.; et al. Frequent detection of infectious xenotropic murine leukemia virus (XMLV) in human cultures established from mouse xenografts. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Antoine, M.; Wegmann, B.; Kiefer, P. Envelope and long terminal repeat sequences of an infectious murine leukemia virus from a human SCLC cell line: implications for gene transfer. Virus Genes 1998, 17, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Raisch, K.P.; Pizzato, M.; Sun, H.Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Cashdollar, L.W.; Grossberg, S.E. Molecular cloning, complete sequence, and biological characterization of a xenotropic murine leukemia virus constitutively released from the human B-lymphoblastoid cell line DG-75. Virology 2003, 308, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfanos, K.S.; Aloia, A.L.; Hicks, J.L.; Esopi, D.M.; Steranka, J.P.; Shao, W.; Sanchez-Martinez, S.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Burns, K.H.; Rein, A.; et al. Identification of replication competent murine gammaretroviruses in commonly used prostate cancer cell lines. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jelacic, T.M.; Thompson, D.; Hanson, C.; Cmarik, J.L.; Nishigaki, K.; Ruscetti, S. The tyrosine kinase sf-Stk and its downstream signals are required for maintenance of friend spleen focus-forming virus-induced fibroblast transformation. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, V.C.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Das Gupta, J.; Pfost, M.A.; Hagen, K.S.; Peterson, D.L.; Ruscetti, S.K.; Bagni, R.K.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Gold, B.; et al. Detection of an infectious retrovirus, XMRV, in blood cells of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Science 2009, 326, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ashton, B.; Buxton, S.; Cheung, M.; Cooper, A.; Heled, J.; Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Stones-Havas, S.; Sturrock, S.; et al. Geneious v5.1. 2010. Available online: http://www.geneious.com.
- Goujon, M.; McWilliam, H.; Li, W.; Valentin, F.; Squizzato, S.; Paern, J.; Lopez, R. A new bioinformatics analysis tools framework at EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W695–W699. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).