Complete Sequence, Analysis and Organization of the Orgyia leucostigma Nucleopolyhedrovirus Genome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nucleotide Sequence Analysis
2.2. Gene Homology
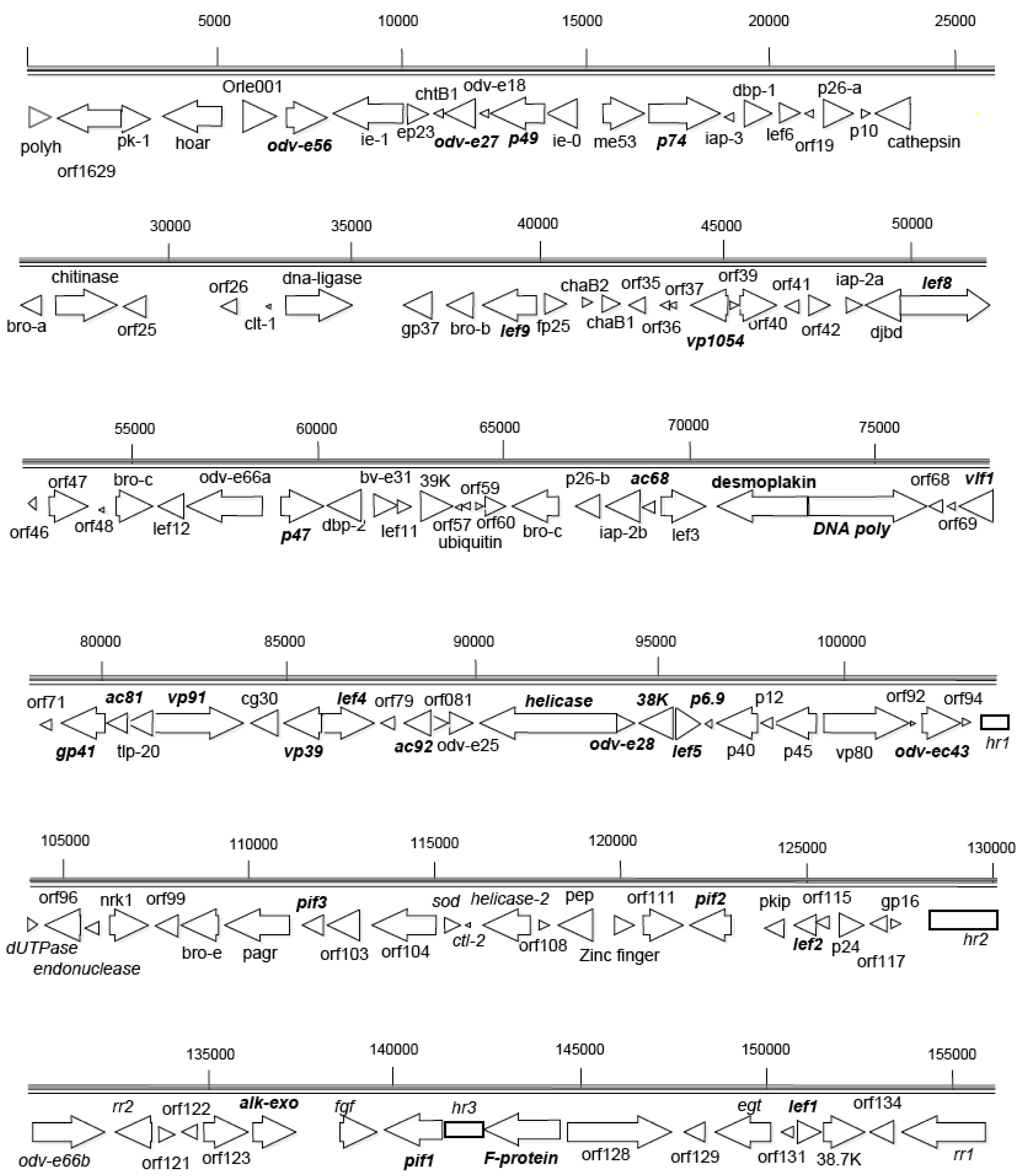
2.3. Gene Organization
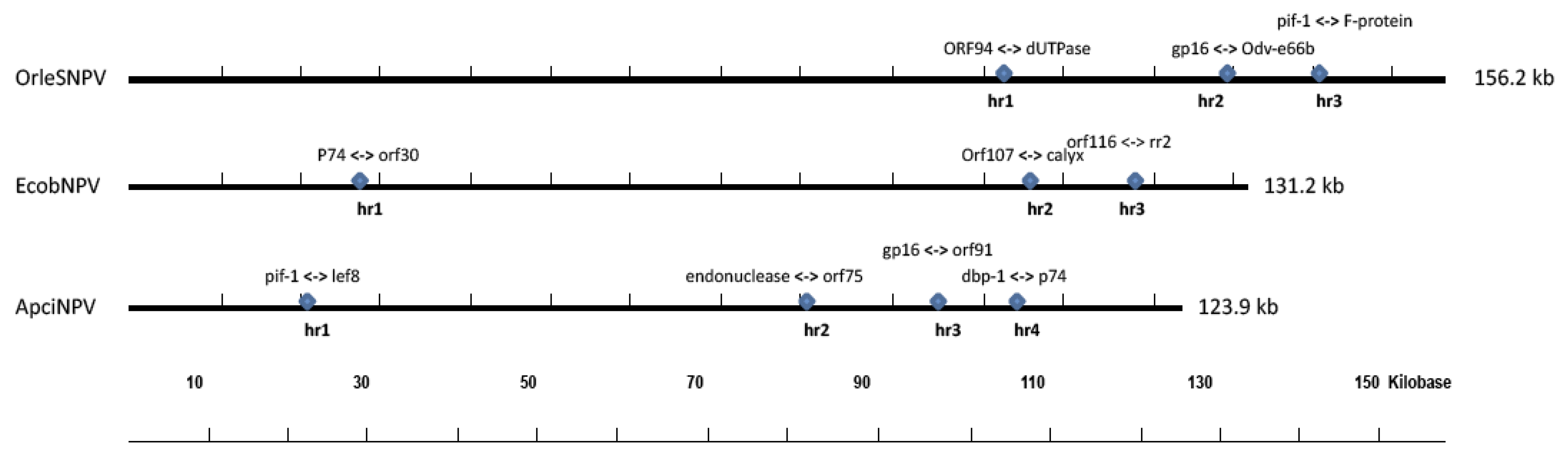
2.4. Homologous Regions and Direct Repeats
2.5. Baculovirus-Repeated ORFs
2.6. Genes with Two Homologues
2.7. Inhibitors of Apoptosis (iap)
2.8. Auxiliary Genes
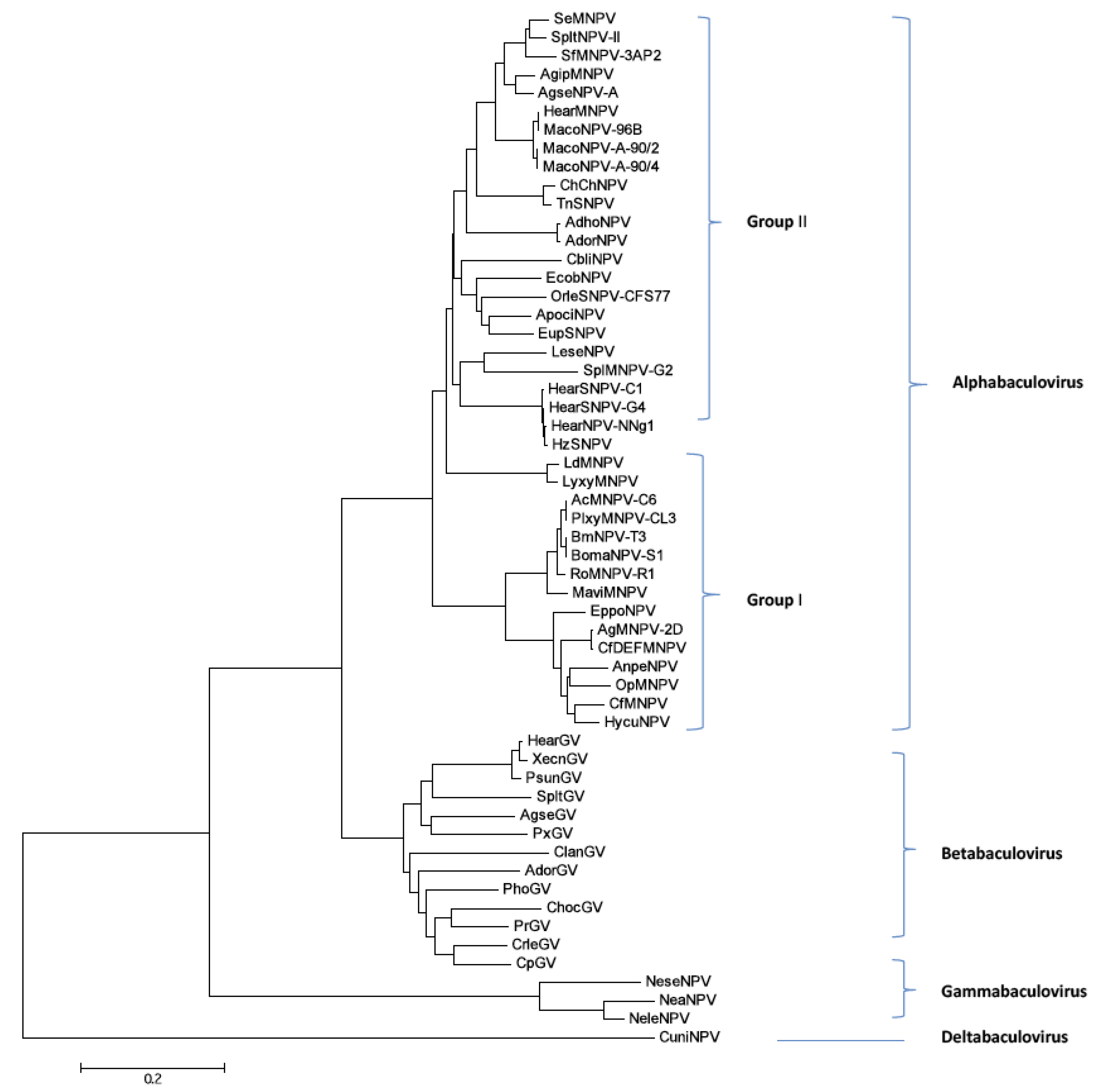
2.9. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Virus Propagation, DNA Extraction and Purification
3.2. DNA Sequencing and Analysis
3.3. Gene homology and Phylogenetic Analysis
| Genus (Group) | Virus name | Abbreviation | Length (bp) | G+C (%) | No. of ORFs | 1 No. of hrs | 2 No. of bro | GenBank accession | 3 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphabaculovirus (Group I) | Antheraea pernyi NPV | AnpeNPV | 126,629 | 53 | 147 | 3 | 2 | DQ486030 | [69] |
| Antheraea pernyi MNPV-L2 | AnpeMNPV-L2 | 126,246 | 53 | 145 | 6 | 2 | EF207986 | [70] | |
| Anticarsia gemmatalis MNPV-2D | AgMNPV-2D | 132,239 | 44 | 152 | 9 | 8 | DQ813662 | [71] | |
| Autographa californica MNPV-C6 | AcMNPV-C6 | 133,894 | 40 | 156 | 9 | 1 | L22858 | [17] | |
| Bombyx mori NPV-T3 | BmNPV-T3 | 128,413 | 40 | 143 | 7 | 5 | L33180 | [72] | |
| Bombyx mandarina NPV-S1 | BomaNPV-S1 | 126,770 | 40 | 141 | 7 | 3 | FJ882854 | [73] | |
| Choristoneura fumiferana MNPV | CfMNPV | 129,593 | 50 | 146 | 5 | 1 | AF512031 | [30] | |
| Choristoneura fumiferana DEF MNPV | CfDEFMNPV | 131,160 | 45 | 149 | 13 | 2 | AY327402 | [74] | |
| Epiphyas postivittana NPV | EppoNPV | 118,584 | 40 | 136 | 5 | 1 | AY043265 | [75] | |
| Hyphantria cunea NPV | HycuNPV | 132,959 | 45 | 148 | 6 | 5 | AP009046 | [76] | |
| Maruca vitrata NPV | MaviNPV | 111,953 | 39 | 126 | 5 | 0 | EF125867 | [77] | |
| Orgyia pseudotsugata MNPV | OpMNPV | 131,990 | 55 | 152 | 5 | 3 | U75930 | [29] | |
| Plutella xylostella MNPV (CL3) | PlxyMNPV | 134,417 | 40 | 153 | 9 | 2 | DQ457003 | [78] | |
| Rachiplusia ou MNPV-R1 | RoMNPV-R1 | 131,526 | 39 | 149 | 9 | 0 | AY145471 | [79] | |
| Alphabaculovirus (Group II) | Adoxophyes honmai NPV | AdhoNPV | 113,220 | 35 | 125 | 4 | 4 | AP006270 | [80] |
| Adoxophyes orana NPV | AdorNPV | 111,724 | 35 | 121 | 4 | 3 | EU591746 | [81] | |
| Agrotis ipsilon MNPV | AgipMNPV | 155,122 | 48 | 163 | 7 | 5 | EU839994 | [82] | |
| Agrotis segetum NPV-A | AgseNPV-A | 147,544 | 45 | 153 | 5 | 4 | DQ123841 | [83] | |
| Apocheima cinerarium NPV | ApciNPV | 123,876 | 45 | 118 | 4 | 0 | FJ914221 | NP | |
| Chrysodeixis chalcites NPV | ChchNPV | 149,622 | 39 | 151 | 0 | 4 | AY864330 | [57] | |
| Clanis bilineata NPV | ClbiNPV | 135,454 | 37 | 139 | 0 | 3 | DQ504428 | [21] | |
| Ectropis obliqua NPV | EcobNPV | 131,204 | 37 | 126 | 3 | 2 | DQ837165 | [28] | |
| Euproctis pseudoconspersa NPV | EupsNPV | 141,291 | 40 | 139 | 4 | 2 | FJ227128 | [84] | |
| Helicoverpa armigera SNPV-G4 | HearSNPV-G4 | 131,405 | 39 | 135 | 5 | 3 | AF271059 | [85] | |
| Helicoverpa armigera SNPV-C1 | HearSNPV-C1 | 130,759 | 38 | 137 | 5 | 3 | AF30304 | [86] | |
| Helicoverpa armigera MNPV | HearMNPV | 154,196 | 40 | 162 | 4 | 6 | EU730893 | NP | |
| Helicoverpa armigera SNPV NNg1 | HearSNPV-NNg1 | 132,425 | 39 | 143 | 5 | 4 | AP010907 | [87] | |
| Helicoverpa zea SNPV | HzSNPV | 130,869 | 39 | 139 | 5 | 2 | AF334030 | [88] | |
| Leucania separata NPV | LeseNPV | 168,041 | 48 | 169 | 8 | 10 | AY394490 | [89] | |
| Lymantria dispar MNPV | LdMNPV | 161,046 | 57 | 164 | 13 | 16 | AF081810 | [43] | |
| Lymantria xylina MNPV | LyxyMNPV | 156,344 | 53 | 157 | 13 | 14 | GQ202541 | [48] | |
| Mamestra configurata NPV-A (90/2) | MacoNPV-A (90/2) | 155,060 | 41 | 169 | 4 | 8 | U59461 | [46] | |
| Mamestra configurata NPV-A (90/4) | MacoNPV-A (90/4) | 153,656 | 168 | 4 | 7 | AF539999 | [90] | ||
| Mamestra configurata NPV-96B | MacoNPV-B | 158,482 | 40 | 169 | 4 | 7 | AYI26275 | [47] | |
| Orgyia leucostigma NPV | OrleNPV | 156,179 | 39 | 135 | 3 | 5 | EU309041 | TP | |
| Spodoptera exigua MNPV | SeMNPV | 135,611 | 43 | 139 | 6 | 0 | AF169823 | [45] | |
| Spodoptera frugiperda MNPV-3AP2 | SfMNPV-3AP2 | 131,330 | 40 | 143 | 8 | 1 | EF035042 | [91] | |
| Spodoptera frugiperda MNPV-19 | SfMNPV-19 | 132,565 | 40 | 141 | 8 | 1 | EU258200 | [92] | |
| Spodoptera litura MNPV-G2 | SpltMNPV-G2 | 139,342 | 42 | 141 | 17 | 2 | AF325155 | [22] | |
| Spodoptera litura MNPV- II | SpltMNPV- II | 148,634 | 44 | 147 | 7 | 2 | EU780426 | NP | |
| Trichoplusia ni SNPV | TnSNPV | 134,394 | 39 | 144 | 0 | 2 | DQ017380 | [93] | |
| Betabaculovirus | Adoxophyles orona GV | AdorGV | 99,657 | 34 | 119 | 0 | 0 | AF547984 | [94] |
| Agrotis segetum GV | AgseGV | 131,680 | 37 | 132 | 0 | 0 | AY522332 | NP | |
| Choristoneura occidentalis GV | ChocGV | 104,710 | 32 | 116 | 5 | 0 | DQ333351 | [61] | |
| Clostera anachoreta GV | ClanGV | 101,487 | 44 | 123 | 4 | 0 | HQ116624 | [95] | |
| Cryptophlebia leucotreta GV | CrleGV | 110,907 | 32 | 128 | 3 | 0 | AY229987 | [96] | |
| Cydia pomonella GV | CpGV | 123,500 | 45 | 143 | 0 | 1 | U53466 | [97] | |
| Helicoverpa armigera GV | HearGV | 169,794 | 40 | 179 | 9 | 10 | EU255577 | [98] | |
| Phthorimaea operculella GV | PhoGV | 119,217 | 35 | 130 | 12 | 1 | AF499596 | NP | |
| Pieris rapae GV | PrGV | 108,592 | 33 | 120 | 0 | 0 | GQ884143 | [99] | |
| Plutella xylostella GV | PxGV | 100,999 | 40 | 120 | 4 | 0 | AF270937 | [100] | |
| Pseudaletia unipuncta GV | PsunGV | 176,677 | 39 | 183 | 9 | 7 | EU678671 | NP | |
| Spodoptera litura GV | SpltGV | 124,121 | 38 | 136 | 0 | 6 | DQ288858 | [101] | |
| Xestia c-nigrum GV | XecnGV | 178,733 | 40 | 181 | 9 | 7 | AF162221 | [15] | |
| Gammabaculovirus | Neodiprion abietis NPV | NeabNPV | 84,264 | 33 | 93 | 5 | 0 | DQ317692 | [102] |
| Neodiprion lecontei NPV | NeleNPV | 81,755 | 33 | 89 | 0 | 0 | AY349019 | [12] | |
| Neodiprion sertifer NPV | NeseNPV | 86,462 | 33 | 90 | 6 | 0 | AY430810 | [11] | |
| Deltabaculovirus | Culex nigripalpus NPV | CuniNPV | 108,252 | 109 | 50 | 4 | 6 | AF403738 | [56] |
| ORF Name 1 | Position 2 | Intergenic Length Prom | Homologues (% aa identity) 4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Dir | Right | (bp) | (aa) | motifs 3 | EcobNPV | ChchNPV | OpMNPV | AcMNPV | ||
| 1 | polyhedrin | 1 | > | 738 | 51 | 246 | L | 1(95) | 1(94) | 3(86) | 8(89) |
| 2 | orf1629 | 789 | < | 2531 | −7 | 581 | ? | 2(26) | 2(28) | - | 9(25) |
| 3 | pk1 | 2524 | > | 3327 | 293 | 268 | L | 3(61) | 3(49) | 1(34) | 10(37) |
| 4 | hoar | 3620 | < | 5245 | 523 | 542 | E | 4(28) | 4(23) | - | - |
| rep1 | 4273 | 4348 | |||||||||
| 5 | orle001 | 5768 | > | 6715 | 232 | 316 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| rep2 | 6725 | 6809 | |||||||||
| 6 | odv-e56 | 6947 | > | 8080 | 124 | 378 | L | 5(71) | 7(39) | 146(59) | 148(59) |
| 7 | ie-1 | 8204 | < | 10120 | 70 | 639 | E | 6(52) | 16(31) | 145(30) | 147(33) |
| 8 | ep23 | 10190 | > | 10792 | 118 | 201 | ? | 7(36) | 15(36) | 144(38) | 146(30) |
| 9 | chtB1 | 10910 | < | 11185 | 17 | 92 | L | 8(64) | 14(53) | 142(44) | 145(52) |
| 10 | odv-e27 | 11202 | < | 12062 | 89 | 287 | L | 9(64) | 13(62) | 141(47) | 144(51) |
| 11 | odv-e18 | 12151 | < | 12420 | 14 | 90 | L | 10(42) | - | - | - |
| 12 | p49 | 12434 | < | 13921 | 22 | 496 | L | 11(57) | 11(57) | 139(44) | 142(47) |
| 13 | ie-0 | 13943 | < | 14794 | 665 | 284 | L | 12(49) | 10(39) | 138(27) | 141(31) |
| rep3 | 15148 | 15218 | |||||||||
| 14 | me53 | 15459 | > | 16604 | 90 | 382 | E,L | 13(43) | 8(34) | 137(23) | 139(23) |
| 15 | p74 | 16694 | > | 18649 | 119 | 652 | L | 14(71) | 17(57) | 134(59) | 138(58) |
| 16 | iap-3 | 18768 | < | 19052 | 208 | 95 | E,L | - | - | 35(52) | - |
| 17 | dbp-1 | 19260 | > | 20042 | 28 | 261 | E | 27(23) | 22(20) | 43(28) | 25(27) |
| 18 | lef6 | 20070 | > | 20666 | 253 | 199 | L | 16(23) | 21(34) | 40(35) | 28(38) |
| 19 | unknown | 20919 | < | 21179 | 212 | 87 | ? | 17(39)- | 20(40)- | 39(34)- | 29(28)- |
| 20 | p26-a | 21391 | > | 22224 | 45 | 278 | L | 18(45) | 19(44) | 132(31) | 136(31) |
| 21 | p10 | 22269 | > | 22544 | 233 | 92 | L | 19(83) | 18(68) | - | - |
| 22 | cathepsin | 22777 | < | 23760 | 2298 | 328 | E,L | 51(79) | 64(56) | 125(64) | 127(70) |
| rep4 | 25452 | 25626 | |||||||||
| 23 | bro-a | 26058 | < | 26651 | 345 | 198 | ? | - | 114(27) | - | - |
| 24 | chitinase | 26996 | > | 28690 | 130 | 565 | L | 50(72) | 65(68) | 124(70) | 126(69) |
| 25 | unknown | 28820 | < | 29464 | 1924 | 215 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 26 | unknown | 31388 | < | 31858 | 1052 | 157 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 27 | ctl-1 | 32910 | < | 33068 | 123 | 53 | E, L | 47(62) | 74(86) | 136(63) | 3(41) |
| 28 | dna-ligase | 33191 | > | 35014 | 1335 | 608 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| rep5 | 35314 | 36297 | |||||||||
| 29 | gp37 | 36349 | < | 37152 | 358 | 268 | L | 49(57) | 67(64) | 69(57) | 64(58) |
| 30 | bro-b | 37510 | < | 38265 | 213 | 252 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 31 | lef9 | 38478 | < | 39959 | 103 | 494 | ? | 46(78) | 52(74) | 65(63) | 62(68) |
| 32 | fp25 | 40062 | > | 40685 | 506 | 208 | E, L | 45(70) | 51(68) | 64(55) | 61(54) |
| 33 | chaB2 | 41191 | > | 41502 | 308 | 104 | ? | 44(46) | 50(48) | 63(48) | 60(46) |
| 34 | chaB1 | 41810 | > | 42331 | 72 | 174 | ? | 43(46) | 49(64) | 62(49) | 59(54) |
| 35 | unknown | 42403 | < | 42891 | 365 | 163 | ? | 42(58) | 48(43) | 61(35) | 57(40) |
| 36 | unknown | 43256 | < | 43543 | −55 | 96 | ? | 41(38) | 47(51) | - | - |
| 37 | unknown | 43488 | < | 43724 | 354 | 79 | ? | 40(46) | - | - | - |
| 38 | vp1054 | 44078 | < | 45112 | 18 | 345 | E | 39(50) | 45(51) | 58(35) | 54(38) |
| 39 | unknown | 45130 | > | 45396 | 6 | 89 | ? | - | 43(42) | - | - |
| 40 | unknown | 45402 | > | 46421 | 361 | 340 | ? | 36(24) | 42(31) | - | - |
| 41 | unknown | 46782 | < | 47198 | 54 | 139 | ? | 35(63) | 41(55) | 56(47) | 53(50) |
| 42 | unknown | 47252 | > | 47863 | 392 | 204 | ? | 34(26) | 40(32) | - | - |
| 43 | iap-2 | 48255 | > | 48728 | 43 | 158 | E | 54(29) | 62(38) | 74(29) | 71(28) |
| 44 | djbd | 48771 | < | 49754 | −42 | 328 | E,L | 33(27) | 38(23) | - | - |
| 45 | lef8 | 49712 | > | 52450 | −563 | 913 | E | 32(72) | 37(62) | 54(59) | 50(63) |
| 46 | unknown | 51887 | < | 52279 | 491 | 131 | ? | - | - | - | 17(60) |
| 47 | unknown | 52770 | > | 53852 | 219 | 361 | ? | - | - | 11(26) | 11(25) |
| 48 | unknown | 54071 | < | 54250 | 317 | 60 | ? | 30(46) | 35(38) | - | - |
| 49 | bro-c | 54567 | > | 55595 | 103 | 343 | ? | 76(56) | 69(45) | - | 2(21) |
| 50 | lef12 | 55698 | < | 56429 | 42 | 244 | ? | - | - | 46(38) | 41(48) |
| 51 | odv-e66a | 56471 | < | 58537 | 462 | 689 | ? | 31(29) | 101(39) | 50(29) | 46(30) |
| 52 | p47 | 58999 | > | 60183 | 290 | 395 | E | 29(63) | 33(61) | 45(49) | 40(52) |
| 53 | dbp-2 | 60473 | < | 61420 | 386 | 316 | E | 15(24) | 22(32) | 43(24) | 25(28) |
| 54 | bv-e31 | 61806 | > | 62489 | −66 | 228 | ? | 26(63) | 30(51) | 22(57) | 38(57) |
| 55 | lef11 | 62423 | > | 62839 | −76 | 139 | ? | 25(58) | 29(51) | 23(34) | 37(37) |
| 56 | 39K/pp31 | 62763 | > | 63659 | 277 | 299 | E | 24(51) | 28(33) | 24(34) | 36(34) |
| 57 | unknown | 63936 | < | 64151 | 47 | 72 | ? | 22(45) | - | - | - |
| 58 | ubiquitin | 64195 | < | 64443 | −203 | 83 | L | 21(83) | - | - | - |
| 59 | unknown | 64240 | > | 64479 | 13 | 80 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 60 | unknown | 64492 | > | 65079 | 144 | 196 | ? | 20(50) | 25(31) | 26(37) | 34(30) |
| 61 | bro-d | 65223 | < | 66503 | 419 | 427 | E | 89(25) | - | - | 2(28) |
| 62 | p26-b | 66922 | < | 67611 | 124 | 230 | ? | 18(28) | 19(30) | - | 136(27) |
| 63 | iap-2 | 67735 | < | 68691 | 150 | 319 | E | 54(33) | 62(32) | - | 71(27) |
| 64 | unknown | 68841 | < | 69230 | −1 | 130 | ? | 55(65) | 61(52) | 73(41) | 68(43) |
| 65 | lef3 | 69229 | > | 70461 | 278 | 411 | L | 56(41) | 60(32) | 72(28) | 67(26) |
| 66 | desmoplakin | 70739 | < | 73192 | −1 | 818 | L | 57(40) | 59(26) | 66(20) | |
| 67 | DNA-poly | 73191 | > | 76406 | 68 | 1072 | E | 58(57) | 58(55) | 70(41) | 65(42) |
| 68 | unknown | 76474 | < | 76863 | 7 | 130 | ? | 59(57) | 57(42) | 78(26) | - |
| 69 | unknown | 76870 | < | 77124 | 114 | 85 | ? | 60(88) | 56(83) | 79(40) | 76(41) |
| 70 | vlf1 | 77238 | < | 78404 | 153 | 389 | L | 61(84) | 76(75) | 80(70) | 77(74) |
| 71 | unknown | 78557 | < | 78901 | 41 | 115 | ? | 62(38) | - | - | - |
| 72 | gp41 | 78942 | < | 80156 | 5 | 405 | L | 63(68) | 78(49) | 83(45) | 80(55) |
| 73 | unknown | 80161 | < | 80754 | −67 | 198 | ? | 64(65) | 79(69) | 84(50) | 81(52) |
| 74 | tlp-20 | 80687 | < | 81430 | −31 | 248 | L | 65(42) | 80(47) | - | 82(34) |
| 75 | vp91 | 81399 | > | 83870 | 167 | 824 | L | 66(45) | 81(42) | 86(39) | 83(39) |
| 76 | cg30 | 84037 | < | 84801 | 129 | 255 | ? | 67(26) | - | 89(25) | 88(21) |
| 77 | vp39 | 84930 | < | 85961 | −1 | 344 | L | 68(51) | 82(47) | 90(46) | 89(41) |
| 78 | lef4 | 85960 | > | 87393 | 162 | 478 | E | 69(53) | 83(51) | 91(42) | 90(46) |
| 79 | unknown | 87555 | < | 87962 | 196 | 136 | ? | 70(49) | - | - | - |
| 80 | unknown | 88158 | < | 88913 | −1 | 252 | ? | 71(57) | 84(55) | 93(38) | 92(42) |
| 81 | unknown | 88912 | > | 89382 | 0 | 157 | ? | 72(69) | 85(63) | 94(40) | 93(46) |
| 82 | odv-e25 | 89382 | > | 90047 | 152 | 222 | E,L | 73(68) | 86(64) | 95(39) | 94(43) |
| 83 | helicase | 90199 | < | 93912 | −43 | 1238 | E,L | 74(61) | 87(52) | 96(35) | 95(43) |
| 84 | odv-e28 | 93869 | > | 94384 | 93 | 172 | ? | 75(69) | 88(65) | 97(50) | 96(54) |
| 85 | 38K | 94477 | < | 95424 | −140 | 316 | L | 77(60) | 91(55) | 99(43) | 98(44) |
| 86 | lef5 | 95284 | > | 96198 | 26 | 305 | ? | 78(61) | 92(59) | 100(44) | 99(46) |
| 87 | p6.9 | 96224 | < | 96499 | 68 | 92 | L | 79(57) | 93(69) | 101(62) | 100(60) |
| rep6 | 96350 | 96431 | |||||||||
| 88 | p40 | 96567 | < | 97697 | 55 | 377 | E,L | 80(59) | 94(50) | 102(41) | 101(38) |
| 89 | p12 | 97752 | < | 98105 | −4 | 118 | E,L | 81(56) | 95(34) | 103(30) | 102(31) |
| 90 | p45 | 98101 | < | 99282 | 164 | 394 | E, L | 82(67) | 96(54) | 104(39) | 103(41) |
| 91 | vp80 | 99446 | > | 101776 | 107 | 777 | ? | 83(67) | 97(32) | 105(27) | 104(26) |
| 92 | unknown | 101883 | > | 102047 | 41 | 55 | ? | 84(69) | - | - | - |
| 93 | odv-ec43 | 102088 | > | 103161 | 38 | 358 | L | 85(69) | 99(53) | 109(46) | 109(47) |
| 94 | unknown | 103199 | > | 103453 | 527 | 85 | ? | 86(54) | 100(39) | - | - |
| hr1 | 103528 | 103833 | |||||||||
| 95 | dUTPase | 103980 | > | 104399 | 110 | 140 | E | - | 119(49) | - | - |
| 96 | unknown | 104509 | < | 105501 | 118 | 331 | ? | 90(40) | - | - | 112(45) |
| 97 | endonuclease | 105619 | < | 106029 | 216 | 137 | ? | 88(40) | - | - | - |
| 98 | nrk1 | 106245 | > | 107324 | 101 | 360 | ? | 114(42) | 106(33) | 31(28) | 33(30) |
| 99 | unknown | 107425 | < | 108075 | 93 | 217 | ? | 116(64) | 107(62) | 107(58) | 106(55) |
| 100 | bro-e | 108168 | < | 109211 | 129 | 348 | ? | 76(59) | 69(47) | - | - |
| 101 | pagr | 109340 | < | 111118 | 307 | 593 | ? | 113(23) | - | - | - |
| 102 | pif3 | 111425 | < | 112030 | 66 | 202 | ? | 111(23) | 110(50) | 115(52) | 115(54) |
| 103 | unknown | 112096 | < | 112998 | 302 | 301 | ? | 110(28) | - | - | - |
| 104 | unknown | 113300 | < | 115057 | 193 | 586 | ? | - | 113(27) | - | - |
| 105 | sod | 115250 | > | 115720 | 95 | 157 | L | 109(61) | 115(71) | 29(47) | 31(75) |
| 106 | ctl-2 | 115815 | < | 115973 | 311 | 53 | ? | 47(47) | 74(50) | 30(50) | 3(77) |
| 107 | helicase-2 | 116284 | < | 117591 | 192 | 436 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 108 | unknown | 117783 | > | 118103 | 205 | 107 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 109 | calyx/pep | 118308 | < | 119270 | 545 | 321 | L | 108(63) | 121(50) | 129(31) | 131(30) |
| 110 | orle002 | 119815 | > | 120387 | 202 | 191 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 111 | unknown | 120589 | > | 121710 | 135 | 374 | ? | 107(52) | 124(44) | 113(62) | - |
| 112 | pif2 | 121845 | < | 122999 | 977 | 385 | L | 106(81) | 148(68) | 20(63) | 22(66) |
| 113 | pkip | 123976 | < | 124533 | 113 | 186 | L | 104(40) | 146(29) | - | - |
| 114 | lef2 | 124646 | < | 125275 | −43 | 210 | L | 103(50) | 136(46) | 6(38) | 6(40) |
| 115 | unknown | 125232 | < | 125630 | 232 | 133 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 116 | p24 | 125862 | > | 126572 | 21 | 237 | L | 101(57) | 134(55) | 127(36) | 129(37) |
| 117 | unknown | 126593 | < | 127081 | 75 | 163 | ? | 100(38) | - | - | - |
| 118 | gp16 | 127156 | > | 127458 | 2813 | 101 | L | 99(48) | 133(49) | 128(36) | 130(40) |
| hr2 | 127459 | 130270 | |||||||||
| 119 | odv-e66b | 130271 | > | 132241 | 250 | 657 | E, L | 31(41) | 101(62) | 50(44) | 46(30) |
| 120 | rr2 | 132491 | < | 133507 | 189 | 339 | E | 117(76) | 122(61) | - | - |
| 121 | unknown | 133696 | > | 134166 | 244 | 157 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 122 | unknown | 134410 | < | 134859 | 9 | 150 | ? | 91(76) | 126(28) | - | - |
| 123 | unknown | 134868 | > | 136097 | 90 | 410 | ? | 92(34) | 125(29) | - | - |
| 124 | alk-exo | 136187 | > | 137380 | 1145 | 398 | E | 93(48) | 127(44) | 131(37) | 133(39) |
| 125 | fgf | 138525 | > | 139562 | 432 | 346 | L | 95(36) | 130(31) | 27(27) | 32(30) |
| 126 | pif1 | 139994 | < | 141586 | 600 | 531 | L | 98(66) | 131(54) | 119(53) | 119(54) |
| hr3 | 141587 | 142185 | |||||||||
| 127 | f-protein | 142186 | < | 144276 | 368 | 697 | E,L | 118(55) | 150(42) | 21(23) | 23(21) |
| 128 | unknown | 144644 | > | 147478 | 308 | 945 | ? | 119(40) | 143(28) | - | - |
| 129 | unknown | 147786 | < | 148379 | 241 | 198 | ? | 121(40) | 142(28) | - | - |
| 130 | egt | 148620 | < | 150149 | 250 | 510 | E | 122(61) | 141(63) | 14(45) | 15(46) |
| 131 | unknown | 150399 | < | 150758 | 61 | 120 | ? | 123(44) | 139(49) | - | - |
| 132 | lef1 | 150819 | > | 151508 | 28 | 230 | E | 124(53) | 138(50) | 13(43) | 14(46) |
| 133 | 38.7K | 151536 | > | 152678 | 104 | 381 | ? | 125(38) | 137(29) | 12(24) | 13(25) |
| 134 | unknown | 152782 | < | 153459 | 182 | 226 | ? | - | - | - | - |
| 135 | rr1 | 153641 | < | 155923 | 257 | 761 | E | 126(66) | - | - | - |
| ORF | Name | Position | Homologue (% aa identity) 1 | Virus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | orle001 | 5768–6715 | unique | OrleNPV |
| 25 | unknown | 28820–29464 | APNV_p040 (25%) | AnpeNPV |
| 26 | unknown | 31388–31858 | McAVgp043 (31%) | MacoNPV-A |
| 28 | dna ligase | 33191–35014 | LyxMNPV_gp020 (32%) | LyxMNPV |
| 59 | unknown | 64240–64479 | APNV-p121 (43%) | AnpeNPV |
| 107 | helicase-2 | 116284–117591 | Ld-helicase-2 (60%) | LdMNPV |
| 108 | unknown | 117783–118103 | EupsNPV_gp105 (48%) | EupsNPV |
| 110 | orle002 | 119815–120387 | Agip90 (30%) | AgipMNPV |
| 115 | unknown | 125232–125630 | ORF88_ ApciNPV (41%) | ApciNPV |
| 121 | unknown | 133696–134166 | ORF84_AgseGV (55%) | AgseGV |
| 134 | unknown | 152782–153459 | LdOrf-24_LdMNPV (23%) | LdMNPV |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Theilmann, D.A.; Blissard, G.W.; Bonning, B.; Jehle, J.; O’Reilly, D.R.; Rohrman, G.F.; Thiem, S.; Vlak, J.M. Baculoviridae. In Virus Taxonomy, VIIIth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Fauquet, C.M., Mayo, M.A., Maniloff, J., Desselberger, U., Ball., L.A., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: London, UK, 2005; pp. 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lucarotti, C.J.; Morin, B.; Graham, R.I.; Lapointe, R. Production, application and field performance of AbietivTM the balsam fir sawfly nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virologica Sinica 2007, 22, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscardi, F. Assessment of the application of baculovirus for control of Lepidoptera. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandson, M. Insect pest control by viruses. In Encyclopedia of Virology; Mahy, B.W.J., van Regenmortel, M.H.V., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: London, UK, 2008; pp. 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Aucoin, M.G.; Mena, J.A.; Kamen, A.A. Bioprocessing of baculovirus vectors: A review. Curr. Gene Ther. 2010, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.F.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H.F.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.F. Baculovirus vector-mediated transfer of NIS gene into colon tumor cells for radionuclide therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5367–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehle, J.A.; Blissard, G.W.; Bonning, B.C.; Cory, J.S.; Herniou, E.A.; Rohrmann, G.F.; Theilmann, D.A.; Thiem, S.M.; Vlak, J.M. On the classification and nomenclature of baculoviruses: A proposal for revision. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissard, G.W.; Wenz, J.R. Baculovirus gp64 envelope glycoprotein is sufficient to mediate pH-dependent membrane fusion. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6829–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulach, D.M.; Kumar, C.A.; Zaia, A.; Liang, B.; Tribe, D.E. Group II nucleopolyhedrovirus subgroups revealed by phylogenetic analysis of polyhedrin and DNA polymerase gene sequences. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1999, 73, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Deng, F.; Rayner, S.; Wang, H.; HU, Z.; Evidence of major role of GP64 in group I alphabaculovirus evolution. Virus Resear. 2009, 142, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Maruniak, A.; Maruniak, J.E.; Zanotto, P.M.A.; Doumbouya, A.E.; Liu, J-C.; Merritt, T.M.; Lanoie, J.S. Sequence analysis of the genome of the Neodiprion sertifer nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7036–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, H.A.M.; Lucarotti, C.J.; Krell, P.J.; Feng, Q.; Retnakaran, A.; Arif, B.M. Sequence and Organization of the Neodiprion lecontei nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7023–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Ebling, P.; Thurston, G.; Lucarotti, C.; Royama, T.; Goscott, R.; Georgeson, E.; Silver, J. Incidence and impact of Entomophaga aulicae (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) and a nucleopolyhedrovirus in an outbreak of the whitemarked tussock moth (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Can. Entomol. 2002, 134, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J.C.; Kaupp, W.J. Insect viruses. In Forest Pest Insects in Canada, Natural Resources Canada; Amstrong, J.A., Ives, W.G.H., Eds.; Natural Resources Canada: Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, 1995; pp. 327–340. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, T.; Ko, R.; Okano, K.; Seong, S.; Goto, C.; Maeda, S. Sequence analysis of the Xiestia c-nigrum granulovirus genome. Virology 1999, 262, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, S.A.B.; Garavaglia, M.J.; Belaich, M.N.; Ghiringhelli, P.D. Baculovirus: Molecular insights on their diversity and conservation. Int. J. Evol. Biol. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, M.D.; Howard, S.W.; Kuzio, J.; Ferber-Lopez, M.; Possee, R.D. The complete DNA sequence of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology 1994, 202, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herniou, E.A.; Oleszewski, J.A.; Cory, J.S.; O’Reilly, D.R. The genome sequence and evolution of baculoviruses. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herniou, E.A.; Luque, T.; Chen, X.; Vlak, J.M.; Winstanley, D.; Cory, J.; O’Reilly, D.R. Use of whole genome sequence data to infer baculovirus phylogeny. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8117–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.H.; Arif, B.M.; Jin, F.; Martens, W.M.; Chen, X.W.; Sun, J.S.; Zuidema, D.; Goldbach, R.W.; Vlak, J.M. Distinct gene arrangement in the Bazura suppressaria single-nucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 2841–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Yi, J.P.; Shen, W.D.; Wang, L.Q.; He, H.G.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, W.B.; Genomic sequence, organization and characteristic of a new nucleopolyhedrovirus isolated from Clanis bilineata larva. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; YU, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Bao, W.; Li, G.; Chen, C.; Han, H.; Hu, S.; Yan, H. Sequence analysis of the Spodoptera litura multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. Virology 2001, 287, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisy, D.J.; Rohrmann, G.F. Characterization of the replication of plasmids containing hr sequences in baculovirus-infected Spodoptera frugiperda cells. Virology 1993, 196, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, M.; Ahrens, CH.; Vlak, J.M.; Rohrmann, G.F. Replication of baculovirus DNA. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 2103–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theilmann, D.A.; Stewart, S. Tandemly repeated sequence at the 3′ end of the baculovirus Orygia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus is an enhancer element. Virology 1992, 187, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landais, I.; Vincet, R.; Bouton, M.; Devauchelle, G.; Duonor-Cerutti, M.; Ogliastro, M. Functional analysis of evolutionary conserved clusterinng of bZIP binding sites in the baculovirus homologous regions (hrs) suggests a cooperativity between host and viral transcriptional factors. Virology 2006, 334, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrmann, G.F. Early events in infection: Virus transcription. In Baculovirus Molecular Biology, 2nd ed.; National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.C.; Shang, J.Y.; Yang, Z.N.; Bao, Y.Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Genome sequence and organization of a nucleopolyhedrovirus that infects the tea looper caterpiller, Ectropis obliqua. Virology 2007, 360, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, C.H.; Russell, R.L.Q.; Funk, C.J.; Evans, J.T.; Harwood, S.H.; Rohrmann, G.F. The sequence of the Orygia pseudotsuguta multilcapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. Virology 1997, 229, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, J.G.; Lauzon, H.A.; Dominy, C.; Poloumienko, A.; Carstens, E.B.; Arif, B.M.; Krell, P.J. Analysis of the Choristoneura fumiferana nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Rohrmann, G.F.; Hashimoto, Y. Patterns of genome organization and content in lepidopteran baculoviruses. Virology 2000, 278, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Krell, P.J. Reiterated DNA fragments in defective genomes of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus are competent for AcMNPV-dependent DNA replication. Virology 1994, 202, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Hasnain, S.E. Differential activity of two non-hr origins during replication of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5182–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.; Bjornson, R.; Pearson, G.; Rohrman, G. The Autographa californica baculovirus genome: evidence for multiple replication origins. Science 1992, 257, 1382–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, M.; Goldbach, R.W.; Vlak, J.M. A putative non-hr origin of DNA replication in the HindIII-K fragment of the Autographa californica multiple nucleocapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldens, J.G.; Broer, R.; Zuidema, D.; Goldbach, R.W.; Vlak, J.M. Identification and functional analysis of a non-hr origin of DNA replication in the genome of Spodoptera exigua multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Levin, D.B. Identification and functional analysis of a putative non-hr origin of DNA replication from the Spodoptera littorris type B multinucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, E.B.; Wu, Y. No single homologous repeat region is essential for DNA replication of the baculovirus Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen Virol. 2007, 88, 114–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bideshi, D.K.; Renault, S.; Stasiak, K.; Federici, B.A.; Bigot, Y. Phylogenetic analysis and possible functions of bro-like genes, a multigene family widespread among double-stranded DNA viruses of invertebrates and bacteria. J. Gen Virol. 2003, 84, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Pan, L.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Gong, Y.; Yang, K.; Pang, Y. Characterization of Spodoptera litura multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus 38.7 K protein, which contain a conserved BRO domain. Virus Res. 2006, 115, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskov, E.; Kang, W.; Maeda, S. Evidence for nucleic acid binding ability and nucleosome association of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus BRO proteins. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6784–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Kurihara, M.; Matsumoto, S. The BRO proteins of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus are nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins that utilize the CRM1-mediated nuclear export pathway. Virology 2006, 350, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzio, J.; Pearson, M.N.; Harwood, S.H.; Funk, C.J.; Evans, J.T.; Slavicek, J.M.; Rohrmann, G.F. Sequence and analysis of the genome of a baculovirus pathogenic for Lymantria dispar. Virology 1999, 253, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunagel, S.C.; Williamson, S.T.; Saksena, S.; Zhong, Z.; Russell, W.K.; Russell, D.H.; Summers, M.D. Trafficking of ODV-E66 is mediated via a sorting motif and other viral proteins: Facilitated trafficking to the inner nuclear membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 2004. 101, 8372–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijkel, W.F.J.; van Strien, E.A.; Heldens, J.G.M.; Broer, R.; Zuidema, D.; Golbach, R.W.; Vlak, J.M. Sequence and organization of the Spodoptera exigua multinucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 3289–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Donly, C.; Li, Q.; Willis, L.G.; Keddie, B.A.; Erlandson, M.A.; Theilmann, D.A. Identification and genomic analysis of a second species of nucleopolyhedrovirus isolated from Mamestra configurata. Virology 2002, 297, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Donly, C.; Li, L.; Willis, L.G.; Theilmann, D.A.; Erlandson, M. Sequence and organization of the Mamestra configurata nucleopolyhedro-virus genome. Virology 2002, 294, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nai, Y.S.; Wu, C.Y.; Wang, T.C.; Chen, Y.R.; Lau, W.H; Lo, C.F. Genomic sequencing and analysis of Lymantria xylina multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailov, V.S.; Vanarsdall, A.L.; Rohrmann, G.F. Isolation and characterization of the DNA-binding protein (DBP) of the Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virology 2008, 370, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanarsdall, A.L.; Mikhailov, V.S.; Rohrmann, G.F. Characterization of a baculovirus lacking the DBP (DNA-binding protein) gene. Virology 2007, 364, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.K.; Kaiser, W.J.; Seshagiri, S. Baculovirus regulation of apoptosis. Semin. Virol. 1998, 8, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Yanagimoto, K.; Kobayashi, M. Identification and functional analysis of Hyphantria cunea nucleopolyhedrovirus iap genes. Virology 2004, 321, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Deng, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, L.; Lu, S.; Qi, Y.; Xu, H. Functional analysis of the inhibitor of apoptosis genes in Antheraea pernyi nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Xiao, H.Z.; Du, E.Q.; Cai, G.S.; Lu, S.Y.; Qi, Y.P. Identification and functional analysis of LsMNPV Anti-apoptosis genes. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 40, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crook, N.E.; Clem, R.J.; Miller, L.K. An apoptosis inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Balinsky, C.A.; Moser, B.A.; Becnel, J.J.; Rock, D.L.; Kutish, G.F. Genome sequence of a baculovirus pathogenic for Culex nigripalpus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11157–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oers, M.M.; Abma-Henkens, M.H.C.; Herniou, E.A.; de Groot, J.C.W.; Peters, S.; Vlak, J.M. Genome sequence of Chrysodeixis chalcites nucleopolyhedrovirus, a baculovirus with two DNA photolyase genes. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2069–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herniou, E.A.; Olszewski, J.A.; O’Reilly, D.R.; Cory, J.S. Ancient coevolution of baculoviruses and their insects hosts. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3244–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Bonning, B.C. Evaluation of the insecticidal efficacy of wild-type and recombinant baculoviruses. In Methods in Molecular Biology. Baculovirus and Insect Cell Expression Protocols, 2nd ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 338. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, D.R.; Miller, L.K. Baculovirus Expression Vectors: A Laboratory Manual. XII; Freeman, W.H., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Escasa, S.R.; Lauzon, H.A.M.; Mathur, A.C.; Krell, P.J.; Arif, B.M. Sequence analysis of the Choristoneura occidentalis granulovirus genome. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonja, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.T.; Lui, J.S. BioOptimizer: A Bayesian scoring function approach to motif discovery. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.F.; Wang, D.; He, P.A.; Jiang, C.Y.; Song, L.; Chen, F.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Yu, L.; et al. Complete sequence and organization of Antheraea pernyi nucleopolyhedrovirus, a dr-rich baculovirus. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Ye, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, L. The genome sequence of the multinucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus of the Chinese oak silkworm Antheraea pernyi. Virology 2007, 366, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro Oliveira, J.V.; Wolff, J.L.C.; Garcia-Maruniak, A.; Ribeiro, B.M.; de Castro, M.E.B.; de Souza, M.L.; Moscardi, F.; Maruniak, J.E.; de Andrea Zanotto, P.M. Genome of the most widely used viral biopesticide: Anticarsia gemmatalis multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3233–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, S.; Majima, K.; Maeda, S. Sequence analysis of the genome of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.P.; Ye, Z.P.; Niu, C.Y.; Bao, Y.Y.; Wang, W.B.; Shen, W.D.; Zhang, C.X. Comparative analysis of the genomes of Bombyx mandarina and Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedroviruses. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, H.A.M.; Jamieson, P.B.; Krell, P.J.; Arif, B.M. Gene organization and sequencing of Choristoneura fumiferana defective nucleopolyhedrovirus genomes. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyink, O.; Dellow, R.A.; Olsen, M.J.; Caradoc-Davies, K.M.B.; Drake, K.; Herniou, E.A.; Cory, J.S.; O’Reilly, D.R.; Ward, V.K. Whole genome analysis of the Epiphyas postvittana nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Shikata, M.; Shirata, N.; Chaeychomsri, S.; Kobayashi, M. Gene organization and complete sequence of the Hyphantria cunea nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J. Gen Virol. 2006, 87, 2549–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Wu, C.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Wu, Y.J.; Lo, C.F.; Tsai, M.F.; Wang, C.H. Genomic and host range studies of Maruca vitrata nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2315–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.L; Lynn, D.E.; Genomic sequence analysis of a nucleopolyhedrovirus isolated from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.L.; Bonning, B.C. Comparative analysis of the genomes of Rachiplusia ou and Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1827–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, M.; Goto, C.; Kang, W.; Shikata, M.; Luque, T.; Kunimi, Y. Genome sequence and organization of a nucleopolyhedrovirus isolated from the smaller tea totrix, Adoxophyes honmai. Virology 2003, 316, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, S.; Winstanley, D. Genomic sequence and biological characterization of a nucleopolyhedrovirus isolated from the summer fruit tortrix, Adoxopheys orana. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2898–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.L. Genomic sequence analysis of the Illinois strain of the Agrotis ipsilon multiple nucelopolyhedrovirus. Virus Genes 2009, 38, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowska, A.K.; Peters, S.A.; Ziemnicka, J.; Vlak, J.M.; van Oers, M.M. Genome sequence of an enhancin gene-rich nucleopolyhedrovirus (NPV) from Agrotis segetum: Collinearity with Spodoptera exigua multiple NPV. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.D.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, X.C.; Zhu, Z.R.; Zhang, C.X. Morphology and genome of Euproctis pseudoconspersa nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virus Genes 2009, 38, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ijkel, W.F.J.; Tarachini, R.; Wang, H.; Peters, S.; Zuidema, D.; Lankhorst, R.K.; Vlak, J.M.; Hu, Z. The sequence of the Helicoverpa armigera single nucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Ma, X.C.; Guo, Z.J. Comparison of the complete genome sequence between C1 and G4 isolates of the Helicoverpa armigera single nucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virology 2005, 333, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogembo, J.G.; Caoili, B.L.; Shikata, M.; Chaeychomsri, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Ikeda, M. Comparative genomic sequence analysis of novel Helicoverpa armigera nucleopolyhedrovris (NPV) isolated from Kenya and three other previously sequenced Helicoverpa spp. NPVs. Virus Genes 2009, 39, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, W.-J.; Wong, J.; Chun, G.; Lu, A.; McCutchen, B.F.; Presnail, J.K.; Herrmann, R.; Dolan, M.; Tingey, S.; et al. Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequences of Helicoverpa zea and Helicoverpa armigera single-nucleocapsid nucleopolyhedroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Qi, Y. Genome sequence of Leucania seperata nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, L.; Willis, G.; Erlandson, M.; Theilmann, D.A.; Donly, C. Complete comparative genomic analysis of two field isolates of Mamestra configurata nucleopolyhedrovirus-A. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harisson, R.L.; Puttler, B.; Popham, H.J.R. Genomic sequence analysis of a fast-killing isolate of Spodoptera frugiperda multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.L.C.; Valicente, F.H.; Martins, R.; Oliveira, J.V.; Zanotto, P.M. Analysis of the genome of Spodoptera frugiperda nucleopolyhedrovirus (SfMNPV-19) and of the high genomic heterogeneity in group II nucleopolyhedroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 89, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, L.G.; Siepp, R.; Stewart, T.M.; Erlandson, M.A.; Theilmann, D.A. Sequence analysis of the complete genome of Trichoplusia ni single nucleopolyhedrovirus and identification of of a baculoviral photolyase gene. Virology 2005, 338, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormleaton, S.; Kuzio, J.; Winstanley, D. The complete sequence of the Adoxophyes orana granulovirus genome. Virology 2003, 331, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yin, X. Genomic sequencing and analysis of Clostera anachoreta granuloviruses. Arch Virol. 2011, 156, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Jehle, J.A. The genome of the Cryptophlebia leucotreta granulovirus. Virology 2003, 317, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, T.; Finch, R.; Crook, N.; O’Reilly, D.R.; Winstanley, D. The complete sequence of the Cydia pomonella granulovirus genome. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2531–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.L.; Popham, H.J.R. Genomic sequence analysis of a granulovirus isolated from the Old World bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Virus Genes 2000, 21, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Zhang, B.Q.; Xu, H.J.; Cui, Y.J.; Xu, Y.P.; Zhang, M.J.; Han, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Bao, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.X. ODV-associated proteins of the Pieris rapae granulovirus. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Ueno, Y.; Fujita, T.; Sano, Y.; Matsumoto, T. Sequence analysis of the Plutella xylostella granulovirus genome. Virology 2000, 275, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Roh, J.Y.; Woo, S.D.; Jin, B.R.; Je, Y.H. Molecular and phylogenetic characterization of Spodoptera litura granulovirus. J. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.P.; Young, A.M.; Morin, B.; Lucarotti, C.J.; Koop, B.F.; Levin, D.B. Sequence analysis and organization of the Neodiprion abietis nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6952–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Thumbi, D.K.; Eveleigh, R.J.M.; Lucarotti, C.J.; Lapointe, R.; Graham, R.I.; Pavlik, L.; Lauzon, H.A.M.; Arif, B.M. Complete Sequence, Analysis and Organization of the Orgyia leucostigma Nucleopolyhedrovirus Genome. Viruses 2011, 3, 2301-2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112301
Thumbi DK, Eveleigh RJM, Lucarotti CJ, Lapointe R, Graham RI, Pavlik L, Lauzon HAM, Arif BM. Complete Sequence, Analysis and Organization of the Orgyia leucostigma Nucleopolyhedrovirus Genome. Viruses. 2011; 3(11):2301-2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112301
Chicago/Turabian StyleThumbi, David K., Robert J. M. Eveleigh, Christopher J. Lucarotti, Renée Lapointe, Robert I. Graham, Lillian Pavlik, Hilary A. M. Lauzon, and Basil M. Arif. 2011. "Complete Sequence, Analysis and Organization of the Orgyia leucostigma Nucleopolyhedrovirus Genome" Viruses 3, no. 11: 2301-2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112301
APA StyleThumbi, D. K., Eveleigh, R. J. M., Lucarotti, C. J., Lapointe, R., Graham, R. I., Pavlik, L., Lauzon, H. A. M., & Arif, B. M. (2011). Complete Sequence, Analysis and Organization of the Orgyia leucostigma Nucleopolyhedrovirus Genome. Viruses, 3(11), 2301-2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112301





