Hepatitis C Virus Evasion Mechanisms from Neutralizing Antibodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Viral Evasion Mechanisms from Neutralizing Antibodies
2.1. Lipoproteins
2.2. Glycans
2.3. Interfering Antibodies
2.4. Cell-to-Cell Transmission
2.5. Quasispecies
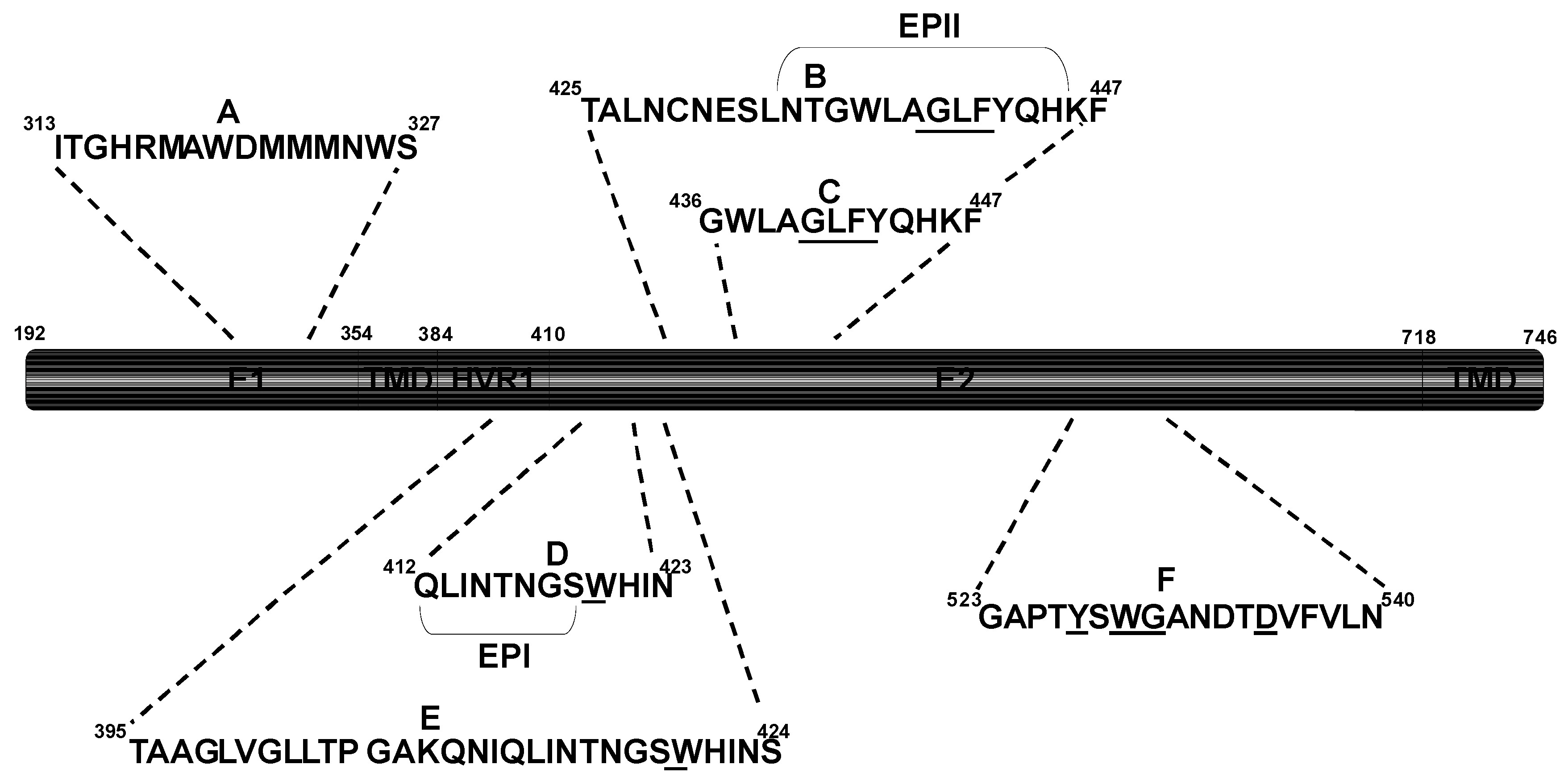
3. Implications for Passive Immunotherapy
Acknowledgement
References and Notes
- Global Burden of Hepatitis C Working Group. Global burden of disease (gbd) for hepatitis C. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 44, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavanchy, D. The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, C.W.; Finelli, L.; Alter, M.J. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, B.; Myers, G.; Howard, C.; Brettin, T.; Bukh, J.; Gaschen, B.; Gojobori, T.; Maertens, G.; Mizokami, M.; Nainan, O.; et al. Classification, nomenclature, and database development for hepatitis C virus (HCV) and related viruses: Proposals for standardization. International committee on virus taxonomy. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, Q.L.; Richman, K.H.; Han, J.H.; Berger, K.; Lee, C.; Dong, C.; Gallegos, C.; Coit, D.; Medina-Selby, R.; Barr, P.J.; et al. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1991, 88, 2451–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwein, J.M.; Scheel, T.K.; Jensen, T.B.; Lademann, J.B.; Prentoe, J.C.; Knudsen, M.L.; Hoegh, A.M.; Bukh, J. Development and characterization of hepatitis C virus genotype 1–7 cell culture systems: Role of CD81 and scavenger receptor class B type i and effect of antiviral drugs. Hepatology 2009, 49, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Bukh, J.; Combet, C.; Deleage, G.; Enomoto, N.; Feinstone, S.; Halfon, P.; Inchauspe, G.; Kuiken, C.; Maertens, G.; et al. Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2005, 42, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P. Genetic diversity and evolution of hepatitis C virus—15 years on. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, F.; Dubuisson, J. Hepatitis C virus entry into host cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health. NIH consensus statement on management of hepatitis C: 2002. NIH Consens. State Sci. Statements 2002, 19, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.L.; Morgan, T.R. The natural history of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 3, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, V.; Peters, M.G.; Zeuzem, S. New therapies for hepatitis C virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, V.; Vispo, E.; Poveda, E.; Labarga, P.; Martin-Carbonero, L.; Fernandez-Montero, J.V.; Barreiro, P. Directly acting antivirals against hepatitis C virus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermehren, J.; Sarrazin, C. New hepatitis C therapies in clinical development. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2011, 16, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.J.; Roberts, S.K.; Stedman, C.A.; Angus, P.W.; Ritchie, B.; Elston, R.; Ipe, D.; Morcos, P.N.; Baher, L.; Najera, I.; et al. Oral combination therapy with a nucleoside polymerase inhibitor (rg7128) and danoprevir for chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infection (inform-1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, M.B.; Cosset, F.L.; Baumert, T.F. Host neutralizing responses and pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2008, 48, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, A.G.; Patel, A.H. Immunotherapeutic potential of neutralizing antibodies targeting conserved regions of the hcv envelope glycoprotein e2. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.G.; Walker, C.M. Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature 2005, 436, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.M. Adaptive immunity to the hepatitis C virus. Adv. Virus Res. 2010, 78, 43–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, S.; Erickson, A.L.; Adams, E.J.; Kansopon, J.; Weiner, A.J.; Chien, D.Y.; Houghton, M.; Parham, P.; Walker, C.M. Analysis of a successful immune response against hepatitis C virus. Immunity 1999, 10, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, J.M.; Healey, C.J.; Watson, J.; Wong, V.S.; Duddridge, M.; Snowden, N.; Rosenberg, W.M.; Fleming, K.A.; Chapel, H.; Chapman, R.W. Clinical outcome of hypogammaglobulinaemic patients following outbreak of acute hepatitis c: 2 year follow up. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 110, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, J.J.; Pan, Y.; Freeman, A.J.; Harvey, C.E.; White, P.A.; Palladinetti, P.; Haber, P.S.; Marinos, G.; Levy, M.H.; Kaldor, J.M.; et al. Clearance of hepatitis C viremia associated with cellular immunity in the absence of seroconversion in the hepatitis C incidence and transmission in prisons study cohort. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.K.; Hijikata, M.; Iwamoto, A.; Alter, H.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Yoshikura, H. Neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis C virus and the emergence of neutralization escape mutant viruses. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.K.; Igarashi, H.; Kiyohara, T.; Cabezon, T.; Farci, P.; Purcell, R.H.; Yoshikura, H. A hyperimmune serum against a synthetic peptide corresponding to the hypervariable region 1 of hepatitis C virus can prevent viral infection in cell cultures. Virology 1996, 223, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farci, P.; Alter, H.J.; Wong, D.C.; Miller, R.H.; Govindarajan, S.; Engle, R.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.H. Prevention of hepatitis C virus infection in chimpanzees after antibody-mediated in vitro neutralization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1994, 91, 7792–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, K.; Alter, M.J.; Tankersley, D.L.; Beach, M.; Robertson, B.H.; Lambert, S.; Kuo, G.; Spelbring, J.E.; Meeks, E.; Sinha, S.; et al. Effect of immune globulin on the prevention of experimental hepatitis C virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, S.; Roggendorf, M.; Durkop, J.; Wiese, M.; Lorbeer, B.; Deinhardt, F. Long-term persistence of hepatitis C virus antibodies in a single source outbreak. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibert, A.; Meisel, H.; Kraas, W.; Schulz, A.; Jung, G.; Roggendorf, M. Early antibody response against hypervariable region 1 is associated with acute self-limiting infections of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 1997, 25, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.M.; Zeisel, M.B.; Blaser, E.; Schurmann, P.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.L.; Patel, A.H.; Meisel, H.; Baumert, J.; Viazov, S.; et al. Rapid induction of virus-neutralizing antibodies and viral clearance in a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 6025–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrick, R.J.; Schlauder, G.G.; Peterson, D.A.; Mushahwar, I.K. Examination of the buoyant density of hepatitis C virus by the polymerase chain reaction. J. Virol. Meth. 1992, 39, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijikata, M.; Shimizu, Y.K.; Kato, H.; Iwamoto, A.; Shih, J.W.; Alter, H.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Yoshikura, H. Equilibrium centrifugation studies of hepatitis C virus: Evidence for circulating immune complexes. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sato, K.; Tanaka, T.; Mishiro, S. Extraordinarily low density of hepatitis C virus estimated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation and the polymerase chain reaction. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomssen, R.; Bonk, S.; Thiele, A. Density heterogeneities of hepatitis C virus in human sera due to the binding of beta-lipoproteins and immunoglobulins. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1993, 182, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, D.; McCaustland, K.; Krawczynski, K.; Spelbring, J.; Humphrey, C.; Cook, E.H. Hepatitis C virus: Buoyant density of the factor viii-derived isolate in sucrose. J. Med. Virol. 1991, 34, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, S.; Castet, V.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Pichard-Garcia, L.; Avner, R.; Harats, D.; Roitelman, J.; Barbaras, R.; Graber, P.; Ghersa, P.; et al. The low-density lipoprotein receptor plays a role in the infection of primary human hepatocytes by hepatitis C virus. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, A.M.; Huima-Byron, T.; Parker, T.S.; Levine, D.M. Visualization of hepatitis C virions and putative defective interfering particles isolated from low-density lipoproteins. J. Viral Hepat. 1996, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomssen, R.; Bonk, S.; Propfe, C.; Heermann, K.H.; Kochel, H.G.; Uy, A. Association of hepatitis C virus in human sera with beta-lipoprotein. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1992, 181, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, P.; Komurian-Pradel, F.; Deforges, S.; Perret, M.; Berland, J.L.; Sodoyer, M.; Pol, S.; Brechot, C.; Paranhos-Baccala, G.; Lotteau, V. Characterization of low- and very-low-density hepatitis C virus rna-containing particles. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6919–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.S.; Jiang, J.; Cai, Z.; Luo, G. Human apolipoprotein e is required for infectivity and production of hepatitis C virus in cell culture. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13783–13793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaminza, P.; Dryden, K.A.; Boyd, B.; Wood, M.R.; Law, M.; Yeager, M.; Chisari, F.V. Ultrastructural and biophysical characterization of hepatitis C virus particles produced in cell culture. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10999–11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, G. Apolipoprotein e but not b is required for the formation of infectious hepatitis C virus particles. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12680–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, J.C.; Russell, R.S.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.N.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Apolipoprotein c1 association with hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9647–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.U.; Bassendine, M.F.; Burt, A.D.; Martin, C.; Pumeechockchai, W.; Toms, G.L. Association between hepatitis C virus and very-low-density lipoprotein (vldl)/ldl analyzed in iodixanol density gradients. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2418–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Dreux, M.; Cosset, F.L. Scavenger receptor class b type i and the hypervariable region-1 of hepatitis C virus in cell entry and neutralisation. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2011, 13, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnello, V.; Abel, G.; Elfahal, M.; Knight, G.B.; Zhang, Q.X. Hepatitis C virus and other flaviviridae viruses enter cells via low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1999, 96, 12766–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazahian, M.; Bohme, I.; Bonk, S.; Koch, A.; Scholz, C.; Grethe, S.; Thomssen, R. Low density lipoprotein receptor as a candidate receptor for hepatitis C virus. J. Med. Virol. 1999, 57, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, M.; Logvinoff, C.; Rice, C.M.; McKeating, J.A. Characterization of infectious retroviral pseudotype particles bearing hepatitis C virus glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6875–6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrin, V.; Boulanger, P.; Penin, F.; Granier, C.; Cosset, F.L.; Bartosch, B. Assembly of functional hepatitis C virus glycoproteins on infectious pseudoparticles occurs intracellularly and requires concomitant incorporation of e1 and e2 glycoproteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaminza, P.; Cheng, G.; Wieland, S.; Zhong, J.; Liao, W.; Chisari, F.V. Cellular determinants of hepatitis C virus assembly, maturation, degradation, and secretion. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sun, F.; Owen, D.M.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Gale, M., Jr.; Ye, J. Hepatitis C virus production by human hepatocytes dependent on assembly and secretion of very low-density lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 5848–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, A.; Long, G.; Hiet, M.S.; Brugger, B.; Chlanda, P.; Andre, P.; Wieland, F.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Bartenschlager, R. Biochemical and morphological properties of hepatitis C virus particles and determination of their lipidome. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3018–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Xu, C.; Ding, Q.; Li, R.; Xiang, Y.; Chung, J.; Zhong, J. A single point mutation in e2 enhances hepatitis C virus infectivity and alters lipoprotein association of viral particles. Virology 2009, 395, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, J.; Nielsen, S.; Zhong, J.; Bassendine, M.F.; Drummer, H.E.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A. Identification of a residue in hepatitis C virus e2 glycoprotein that determines scavenger receptor bi and cd81 receptor dependency and sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12020–12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Verney, G.; Dreux, M.; Donot, P.; Morice, Y.; Penin, F.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Lavillette, D.; Cosset, F.L. An interplay between hypervariable region 1 of the hepatitis C virus e2 glycoprotein, the scavenger receptor bi, and high-density lipoprotein promotes both enhancement of infection and protection against neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8217–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavillette, D.; Morice, Y.; Germanidis, G.; Donot, P.; Soulier, A.; Pagkalos, E.; Sakellariou, G.; Intrator, L.; Bartosch, B.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; et al. Human serum facilitates hepatitis C virus infection, and neutralizing responses inversely correlate with viral replication kinetics at the acute phase of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6023–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, J.C.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.; Zhao, M.; Bartosch, B.; Alter, H.; Emerson, S.U.; Cosset, F.L.; Purcell, R.H.; Bukh, J. Evidence for cross-genotype neutralization of hepatitis C virus pseudo-particles and enhancement of infectivity by apolipoprotein c1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005, 102, 4560–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisset, C.; Op de Beeck, A.; Horellou, P.; Dreux, M.; Gustot, T.; Duverlie, G.; Cosset, F.L.; Vu-Dac, N.; Dubuisson, J. High-density lipoproteins reduce the neutralizing effect of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected patient antibodies by promoting HCV entry. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2577–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreux, M.; Pietschmann, T.; Granier, C.; Voisset, C.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Mangeot, P.E.; Keck, Z.; Foung, S.; Vu-Dac, N.; Dubuisson, J.; et al. High density lipoprotein inhibits hepatitis C virus-neutralizing antibodies by stimulating cell entry via activation of the scavenger receptor bi. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18285–18295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarselli, E.; Ansuini, H.; Cerino, R.; Roccasecca, R.M.; Acali, S.; Filocamo, G.; Traboni, C.; Nicosia, A.; Cortese, R.; Vitelli, A. The human scavenger receptor class b type i is a novel candidate receptor for the hepatitis C virus. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5017–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreux, M.; Boson, B.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Molle, J.; Lavillette, D.; Bartosch, B.; Pecheur, E.I.; Cosset, F.L. The exchangeable apolipoprotein apoc-i promotes membrane fusion of hepatitis C virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 32357–32369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarini, J. Targeting the glycans of GP120: A novel approach aimed at the achilles heel of HIV. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffard, A.; Dubuisson, J. Glycosylation of hepatitis C virus envelope proteins. Biochimie 2003, 85, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gaschen, B.; Blay, W.; Foley, B.; Haigwood, N.; Kuiken, C.; Korber, B. Tracking global patterns of n-linked glycosylation site variation in highly variable viral glycoproteins: Hiv, siv, and hcv envelopes and influenza hemagglutinin. Glycobiology 2004, 14, 1229–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffard, A.; Callens, N.; Bartosch, B.; Wychowski, C.; Cosset, F.L.; Montpellier, C.; Dubuisson, J. Role of n-linked glycans in the functions of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8400–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkowska, E.; Kajumo, F.; Garcia, E.; Reinus, J.; Dragic, T. Hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein e2 glycans modulate entry, cd81 binding, and neutralization. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8072–8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, F.; Goffard, A.; Morel, V.; Duverlie, G.; McKeating, J.; Keck, Z.Y.; Foung, S.; Penin, F.; Dubuisson, J.; Voisset, C. The neutralizing activity of anti-hepatitis C virus antibodies is modulated by specific glycans on the e2 envelope protein. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8101–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helle, F.; Vieyres, G.; Elkrief, L.; Popescu, C.I.; Wychowski, C.; Descamps, V.; Castelain, S.; Roingeard, P.; Duverlie, G.; Dubuisson, J. Role of n-linked glycans in the functions of hepatitis C virus envelope proteins incorporated into infectious virions. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11905–11915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, F.; Duverlie, G.; Dubuisson, J. The hepatitis C virus glycan shield and evasion of the humoral immune response. Viruses 2011, 3, 1909–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, C.G.; Mihalik, K.; Virata-Theimer, M.L.; Yu, M.Y.; Alter, H.J.; Feinstone, S.M. Hepatitis C virus epitope-specific neutralizing antibodies in igs prepared from human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 8449–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhong, L.; Struble, E.B.; Watanabe, H.; Kachko, A.; Mihalik, K.; Virata-Theimer, M.L.; Alter, H.J.; Feinstone, S.; Major, M. Depletion of interfering antibodies in chronic hepatitis C patients and vaccinated chimpanzees reveals broad cross-genotype neutralizing activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.Y.; Bartosch, B.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Z.P.; Renzi, P.M.; Shen, L.M.; Granier, C.; Feinstone, S.M.; Cosset, F.L.; Purcell, R.H. Neutralizing antibodies to hepatitis C virus (HCV) in immune globulins derived from anti-hcv-positive plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 101, 7705–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.L.; Nelson, D.R.; Terrault, N.; Pruett, T.L.; Schiano, T.D.; Fletcher, C.V.; Sapan, C.V.; Riser, L.N.; Li, Y.; Whitley, R.J.; et al. A randomized, open-label study to evaluate the safety and pharmacokinetics of human hepatitis C immune globulin (civacir) in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2005, 11, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattentau, Q. Avoiding the void: Cell-to-cell spread of human viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, M.B.; Crema, A.; Lanzilli, G.; Serafino, A.; Bertolini, L.; Ravagnan, G.; Ponzetto, A.; Menzo, S.; Clementi, M.; Carloni, G. Molecular and cellular determinants of cell-to-cell transmission of hcv in vitro. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, M.B.; Serafino, A.; Crema, A.; Bertolini, L.; Manzin, A.; Lanzilli, G.; Bosman, C.; Iacovacci, S.; Giunta, S.; Ponzetto, A.; et al. Transmission in vitro of hepatitis C virus from persistently infected human b-cells to hepatoma cells by cell-to-cell contact. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe, C.L.; Grove, J.; Meredith, L.W.; Hu, K.; Syder, A.J.; Flores, M.V.; Timpe, J.M.; Krieger, S.E.; Baumert, T.F.; Tellinghuisen, T.L.; et al. Neutralizing antibody-resistant hepatitis C virus cell-to-cell transmission. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpe, J.M.; Stamataki, Z.; Jennings, A.; Hu, K.; Farquhar, M.J.; Harris, H.J.; Schwarz, A.; Desombere, I.; Roels, G.L.; Balfe, P.; et al. Hepatitis C virus cell-cell transmission in hepatoma cells in the presence of neutralizing antibodies. Hepatology 2008, 47, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witteveldt, J.; Evans, M.J.; Bitzegeio, J.; Koutsoudakis, G.; Owsianka, A.M.; Angus, A.G.; Keck, Z.Y.; Foung, S.K.; Pietschmann, T.; Rice, C.M.; et al. Cd81 is dispensable for hepatitis C virus cell-to-cell transmission in hepatoma cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedicto, I.; Molina-Jimenez, F.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.L.; Lavillette, D.; Prieto, J.; Moreno-Otero, R.; Valenzuela-Fernandez, A.; Aldabe, R.; Lopez-Cabrera, M.; et al. The tight junction-associated protein occludin is required for a postbinding step in hepatitis C virus entry and infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8012–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlone, M.E.; Budkowska, A. Hepatitis C virus cell entry: Role of lipoproteins and cellular receptors. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meertens, L.; Bertaux, C.; Cukierman, L.; Cormier, E.; Lavillette, D.; Cosset, F.L.; Dragic, T. The tight junction proteins claudin-1, -6, and -9 are entry cofactors for hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.T.; Catanese, M.T.; Law, L.M.; Khetani, S.R.; Syder, A.J.; Ploss, A.; Oh, T.S.; Schoggins, J.W.; MacDonald, M.R.; Bhatia, S.N.; et al. Real-time imaging of hepatitis C virus infection using a fluorescent cell-based reporter system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesek, S.; Westhaus, S.; Wicht, M.; Wappler, I.; Henschen, S.; Sarrazin, C.; Hamdi, N.; Abdelaziz, A.I.; Strassburg, C.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Impact of intra- and interspecies variation of occludin on its function as coreceptor for authentic hepatitis C virus particles. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7613–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukh, J.; Miller, R.H.; Purcell, R.H. Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis C virus: Quasispecies and genotypes. Semin. Liver Dis. 1995, 15, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, E.; Escarmis, C.; Sevilla, N.; Moya, A.; Elena, S.F.; Quer, J.; Novella, I.S.; Holland, J.J. Basic concepts in rna virus evolution. Faseb J. 1996, 10, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigen, M. On the nature of virus quasispecies. Trends Microbiol. 1996, 4, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.J.; De La Torre, J.C.; Steinhauer, D.A. Rna virus populations as quasispecies. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1992, 176, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Martell, M.; Esteban, J.I.; Quer, J.; Genesca, J.; Weiner, A.; Esteban, R.; Guardia, J.; Gomez, J. Hepatitis C virus (hcv) circulates as a population of different but closely related genomes: Quasispecies nature of hcv genome distribution. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 3225–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.U.; Lam, N.P.; Dahari, H.; Gretch, D.R.; Wiley, T.E.; Layden, T.J.; Perelson, A.S. Hepatitis C viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-alpha therapy. Science 1998, 282, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forns, X.; Purcell, R.H.; Bukh, J. Quasispecies in viral persistence and pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.C.; Mao, Q.; Lanford, R.E.; Bassett, S.; Laeyendecker, O.; Wang, Y.M.; Thomas, D.L. Hypervariable region 1 sequence stability during hepatitis C virus replication in chimpanzees. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3058–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, H.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Holland, P.V.; Popper, H. Transmissible agent in non-a, non-b hepatitis. Lancet 1978, 1, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, S.E.; Brasky, K.M.; Lanford, R.E. Analysis of hepatitis C virus-inoculated chimpanzees reveals unexpected clinical profiles. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinstone, S.M.; Alter, H.J.; Dienes, H.P.; Shimizu, Y.; Popper, H.; Blackmore, D.; Sly, D.; London, W.T.; Purcell, R.H. Non-a, non-b hepatitis in chimpanzees and marmosets. J. Infect. Dis. 1981, 144, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Taylor, D.; Morhardt, D.R.; Mihalik, K.; Puig, M.; Rice, C.M.; Feinstone, S.M.; Major, M.E. Long-term persistence of infection in chimpanzees inoculated with an infectious hepatitis C virus clone is associated with a decrease in the viral amino acid substitution rate and low levels of heterogeneity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9782–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, J.C.; Kumar, U.; Webster, D.; Monjardino, J.; Thomas, H.C. Comparison of the rate of sequence variation in the hypervariable region of e2/ns1 region of hepatitis C virus in normal and hypogammaglobulinemic patients. Hepatology 1998, 27, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, M.; Enomoto, N.; Marumo, F.; Sato, C. Rapid sequence variation of the hypervariable region of hepatitis C virus during the course of chronic infection. Hepatology 1993, 18, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Alter, H.J.; Miller, R.H.; Purcell, R.H. Nucleotide sequence and mutation rate of the h strain of hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1991, 88, 3392–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farci, P.; Shimoda, A.; Coiana, A.; Diaz, G.; Peddis, G.; Melpolder, J.C.; Strazzera, A.; Chien, D.Y.; Munoz, S.J.; Balestrieri, A.; et al. The outcome of acute hepatitis C predicted by the evolution of the viral quasispecies. Science 2000, 288, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Ootsuyama, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Nakazawa, T.; Muraiso, K.; Ohkoshi, S.; Hijikata, M.; Shimotohno, K. Marked sequence diversity in the putative envelope proteins of hepatitis C viruses. Virus Res 1992, 22, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Sekiya, H.; Ootsuyama, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Hijikata, M.; Ohkoshi, S.; Shimotohno, K. Humoral immune response to hypervariable region 1 of the putative envelope glycoprotein (gp70) of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Bukh, J.; Meunier, J.C.; Granier, C.; Engle, R.E.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Emerson, S.U.; Cosset, F.L.; Purcell, R.H. In vitro assay for neutralizing antibody to hepatitis C virus: Evidence for broadly conserved neutralization epitopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 14199–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Dubuisson, J.; Cosset, F.L. Infectious hepatitis C virus pseudo-particles containing functional e1-e2 envelope protein complexes. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Vitelli, A.; Granier, C.; Goujon, C.; Dubuisson, J.; Pascale, S.; Scarselli, E.; Cortese, R.; Nicosia, A.; Cosset, F.L. Cell entry of hepatitis C virus requires a set of co-receptors that include the CD81 tetraspanin and the sr-b1 scavenger receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41624–41630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farci, P.; Shimoda, A.; Wong, D.; Cabezon, T.; De Gioannis, D.; Strazzera, A.; Shimizu, Y.; Shapiro, M.; Alter, H.J.; Purcell, R.H. Prevention of hepatitis C virus infection in chimpanzees by hyperimmune serum against the hypervariable region 1 of the envelope 2 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996, 93, 15394–15399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieyres, G.; Dubuisson, J.; Patel, A.H. Characterization of antibody-mediated neutralization directed against the hypervariable region 1 of hepatitis C virus e2 glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 92, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hahn, T.; Yoon, J.C.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M.; Rehermann, B.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A. Hepatitis C virus continuously escapes from neutralizing antibody and t-cell responses during chronic infection in vivo. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.J.; Geysen, H.M.; Christopherson, C.; Hall, J.E.; Mason, T.J.; Saracco, G.; Bonino, F.; Crawford, K.; Marion, C.D.; Crawford, K.A.; et al. Evidence for immune selection of hepatitis C virus (hcv) putative envelope glycoprotein variants: Potential role in chronic hcv infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1992, 89, 3468–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.C.; Wang, Y.M.; Laeyendecker, O.; Ticehurst, J.R.; Villano, S.A.; Thomas, D.L. Acute hepatitis C virus structural gene sequences as predictors of persistent viremia: Hypervariable region 1 as a decoy. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2938–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankwitz, D.; Steinmann, E.; Bitzegeio, J.; Ciesek, S.; Friesland, M.; Herrmann, E.; Zeisel, M.B.; Baumert, T.F.; Keck, Z.Y.; Foung, S.K.; et al. Hepatitis C virus hypervariable region 1 modulates receptor interactions, conceals the cd81 binding site, and protects conserved neutralizing epitopes. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5751–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forns, X.; Thimme, R.; Govindarajan, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V.; Bukh, J. Hepatitis C virus lacking the hypervariable region 1 of the second envelope protein is infectious and causes acute resolving or persistent infection in chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2000, 97, 13318–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, P.; Huby, T.; Andreo, U.; Moreau, M.; Chapman, J.; Budkowska, A. The interaction of natural hepatitis C virus with human scavenger receptor sr-bi/cla1 is mediated by apob-containing lipoproteins. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentoe, J.; Jensen, T.B.; Meuleman, P.; Serre, S.B.; Scheel, T.K.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Gottwein, J.M.; Bukh, J. Hypervariable region 1 differentially impacts viability of hepatitis C virus strains of genotypes 1 to 6 and impairs virus neutralization. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondelli, M.U.; Cerino, A.; Segagni, L.; Meola, A.; Cividini, A.; Silini, E.; Nicosia, A. Hypervariable region 1 of hepatitis C virus: Immunological decoy or biologically relevant domain? Antivir. Res. 2001, 52, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.; Witteveldt, J.; Gatherer, D.; Owsianka, A.M.; Zeisel, M.B.; Zahid, M.N.; Rychlowska, M.; Foung, S.K.; Baumert, T.F.; Angus, A.G.; et al. Mutations within a conserved region of the hepatitis C virus e2 glycoprotein that influence virus-receptor interactions and sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5494–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Tanamy, M.; Keck, Z.Y.; Yi, M.; McKeating, J.A.; Patel, A.H.; Foung, S.K.; Lemon, S.M. In vitro selection of a neutralization-resistant hepatitis C virus escape mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 19450–19455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Saha, A.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Lau, P.; Krey, T.; Rey, F.A.; Foung, S.K. Mapping a region of hcv e2 that is responsible for escape from neutralizing antibodies and a core CD81-binding region that does not tolerate neutralization escape mutations. J. Virol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Li, S.H.; Xia, J.; von Hahn, T.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A.; Witteveldt, J.; Patel, A.H.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M.; et al. Mutations in hepatitis C virus e2 located outside the CD81 binding sites lead to escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies but compromise virus infectivity. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6149–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Struble, E.; Zhong, L.; Mihalik, K.; Major, M.; Zhang, P.; Feinstone, S.; Feigelstock, D. Hepatitis C virus with a naturally occurring single amino-acid substitution in the e2 envelope protein escapes neutralization by naturally-induced and vaccine-induced antibodies. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4138–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, J.C.; Russell, R.S.; Goossens, V.; Priem, S.; Walter, H.; Depla, E.; Union, A.; Faulk, K.N.; Bukh, J.; Emerson, S.U.; et al. Isolation and characterization of broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to the e1 glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broering, T.J.; Garrity, K.A.; Boatright, N.K.; Sloan, S.E.; Sandor, F.; Thomas, W.D., Jr.; Szabo, G.; Finberg, R.W.; Ambrosino, D.M.; Babcock, G.J. Identification and characterization of broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies directed against the e2 envelope glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12473–12482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owsianka, A.; Tarr, A.W.; Juttla, V.S.; Lavillette, D.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.L.; Ball, J.K.; Patel, A.H. Monoclonal antibody ap33 defines a broadly neutralizing epitope on the hepatitis C virus e2 envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11095–11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owsianka, A.M.; Timms, J.M.; Tarr, A.W.; Brown, R.J.; Hickling, T.P.; Szwejk, A.; Bienkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Thomson, B.J.; Patel, A.H.; Ball, J.K. Identification of conserved residues in the e2 envelope glycoprotein of the hepatitis C virus that are critical for CD81 binding. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8695–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, A.W.; Owsianka, A.M.; Timms, J.M.; McClure, C.P.; Brown, R.J.; Hickling, T.P.; Pietschmann, T.; Bartenschlager, R.; Patel, A.H.; Ball, J.K. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus e2 epitope defined by the broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody AP33. Hepatology 2006, 43, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Sung, V.M.; Perkins, S.; Rowe, J.; Paul, S.; Liang, T.J.; Lai, M.M.; Foung, S.K. Human monoclonal antibody to hepatitis C virus e1 glycoprotein that blocks virus attachment and viral infectivity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7257–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Xia, J.; Cai, Z.; Li, T.K.; Owsianka, A.M.; Patel, A.H.; Luo, G.; Foung, S.K. Immunogenic and functional organization of hepatitis C virus (HCV) glycoprotein e2 on infectious hcv virions. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, D.X.; Voisset, C.; Tarr, A.W.; Aung, M.; Ball, J.K.; Dubuisson, J.; Persson, M.A. Human combinatorial libraries yield rare antibodies that broadly neutralize hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 16269–16274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Maruyama, T.; Lewis, J.; Giang, E.; Tarr, A.W.; Stamataki, Z.; Gastaminza, P.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, I.M.; Fox, R.I.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies protect against hepatitis C virus quasispecies challenge. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, M.; Mancini, N.; Diotti, R.A.; Tarr, A.W.; Ball, J.K.; Owsianka, A.; Adair, R.; Patel, A.H.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Identification of a broadly cross-reacting and neutralizing human monoclonal antibody directed against the hepatitis C virus e2 protein. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, N.; Diotti, R.A.; Perotti, M.; Sautto, G.; Clementi, N.; Nitti, G.; Patel, A.H.; Ball, J.K.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Hepatitis C virus (hcv) infection may elicit neutralizing antibodies targeting epitopes conserved in all viral genotypes. PLoS One 2009, 4, e8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiano, T.D.; Charlton, M.; Younossi, Z.; Galun, E.; Pruett, T.; Tur-Kaspa, R.; Eren, R.; Dagan, S.; Graham, N.; Williams, P.V.; et al. Monoclonal antibody hcv-abxtl68 in patients undergoing liver transplantation for HCV: Results of a phase 2 randomized study. Liver Transpl. 2006, 12, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galun, E.; Terrault, N.A.; Eren, R.; Zauberman, A.; Nussbaum, O.; Terkieltaub, D.; Zohar, M.; Buchnik, R.; Ackerman, Z.; Safadi, R.; et al. Clinical evaluation (phase i) of a human monoclonal antibody against hepatitis C virus: Safety and antiviral activity. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, R.; Landstein, D.; Terkieltaub, D.; Nussbaum, O.; Zauberman, A.; Ben-Porath, J.; Gopher, J.; Buchnick, R.; Kovjazin, R.; Rosenthal-Galili, Z.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of two neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis C virus (HCV): A potential treatment to prevent hcv reinfection in liver transplant patients. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, B.M.; Broering, T.J.; Babcock, G.J.; Szabo, G.; Finberg, R.W.; Cheslock, P.S.; Knauber, M.; Leav, B.A.; Lanford, R.; Purcell, R.H.; et al. A novel human monoclonal antibody directed against the e2 glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus (HCV) prevents infection in chimpanzees. Proceedings of The International Liver Congress, Copenhagen, Denmark, 22–26 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager, R. Hepatitis C virus molecular clones: From cdna to infectious virus particles in cell culture. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Keck, Z.Y.; Saha, A.; Xia, J.; Conrad, F.; Lou, J.; Eckart, M.; Marks, J.D.; Foung, S.K. Affinity maturation to improve human monoclonal antibody neutralization potency and breadth against hepatitis C virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, C.; Kashefi, K.; Hollinshead, M.; Sattentau, Q.J. Hiv-1 cell to cell transfer across an env-induced, actin-dependent synapse. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.; Welsch, S.; Jolly, C.; Briggs, J.A.; Vaux, D.; Sattentau, Q.J. Virological synapse-mediated spread of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 between t cells is sensitive to entry inhibition. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3516–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibody | Epitope | Escape Mutation(s) |
|---|---|---|
| IGH505 [120] | A (Linear) | - |
| IGH526 [120] | A (Linear) | - |
| 95-2 [121] | D (Linear) | - |
| HCV-1 [121] | D (Linear) | - |
| AP33 [122,123,124] | D (Linear) | N415Y§, N415D*, N417S*, G418D* |
| 3/11 [124] | D (Linear) | N415Y§, N415D*, N417S*, G418D* |
| CBH-5 [117,125,126] | F (Conformational) | - |
| A8 [127] | F (Conformational) | - |
| 1:7 [127] | F (Conformational) | - |
| AR3A-D [128] | E, C, F (Conformational) | - |
| e137 [129] | D, F (Conformational) | - |
| e20 [130] | F (Conformational) | - |
| CBH-2 [117,125,126] | B, F (Conformational) | D431G†, A439E† |
| HC-1 [117,118] | F (Conformational) | No escape |
| HC-11 [117,118] | B, F (Conformational) | L438F§ |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorenzo, C.D.; Angus, A.G.N.; Patel, A.H. Hepatitis C Virus Evasion Mechanisms from Neutralizing Antibodies. Viruses 2011, 3, 2280-2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112280
Lorenzo CD, Angus AGN, Patel AH. Hepatitis C Virus Evasion Mechanisms from Neutralizing Antibodies. Viruses. 2011; 3(11):2280-2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112280
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorenzo, Caterina Di, Allan G. N. Angus, and Arvind H. Patel. 2011. "Hepatitis C Virus Evasion Mechanisms from Neutralizing Antibodies" Viruses 3, no. 11: 2280-2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112280
APA StyleLorenzo, C. D., Angus, A. G. N., & Patel, A. H. (2011). Hepatitis C Virus Evasion Mechanisms from Neutralizing Antibodies. Viruses, 3(11), 2280-2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3112280




