From Viral Infection to Malignancy: The Dual Threat of EBV and COVID-19 in Cancer Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
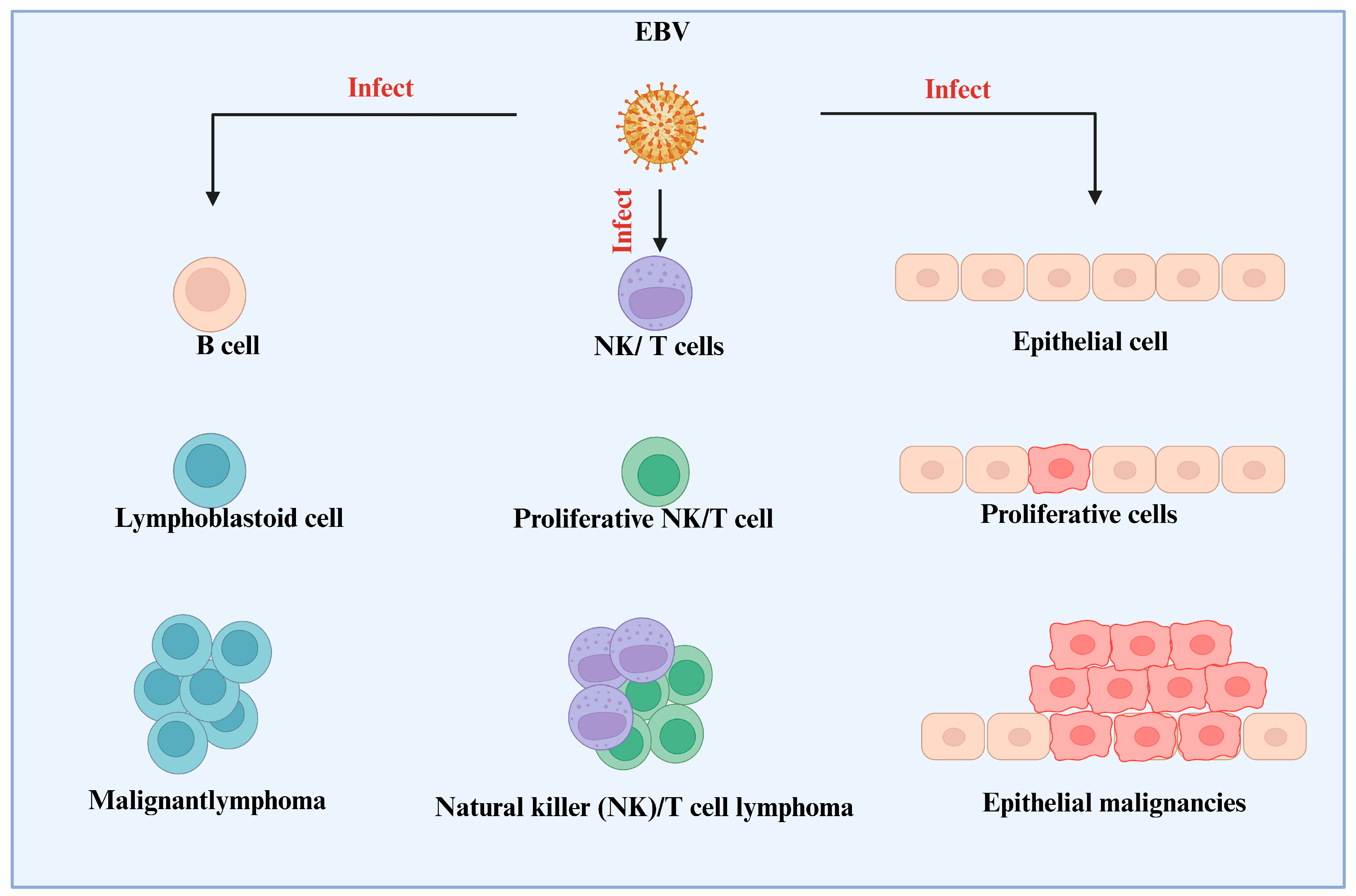
2. EBV and Cancer
Immunotherapeutic Advances in EBV-Associated Cancers
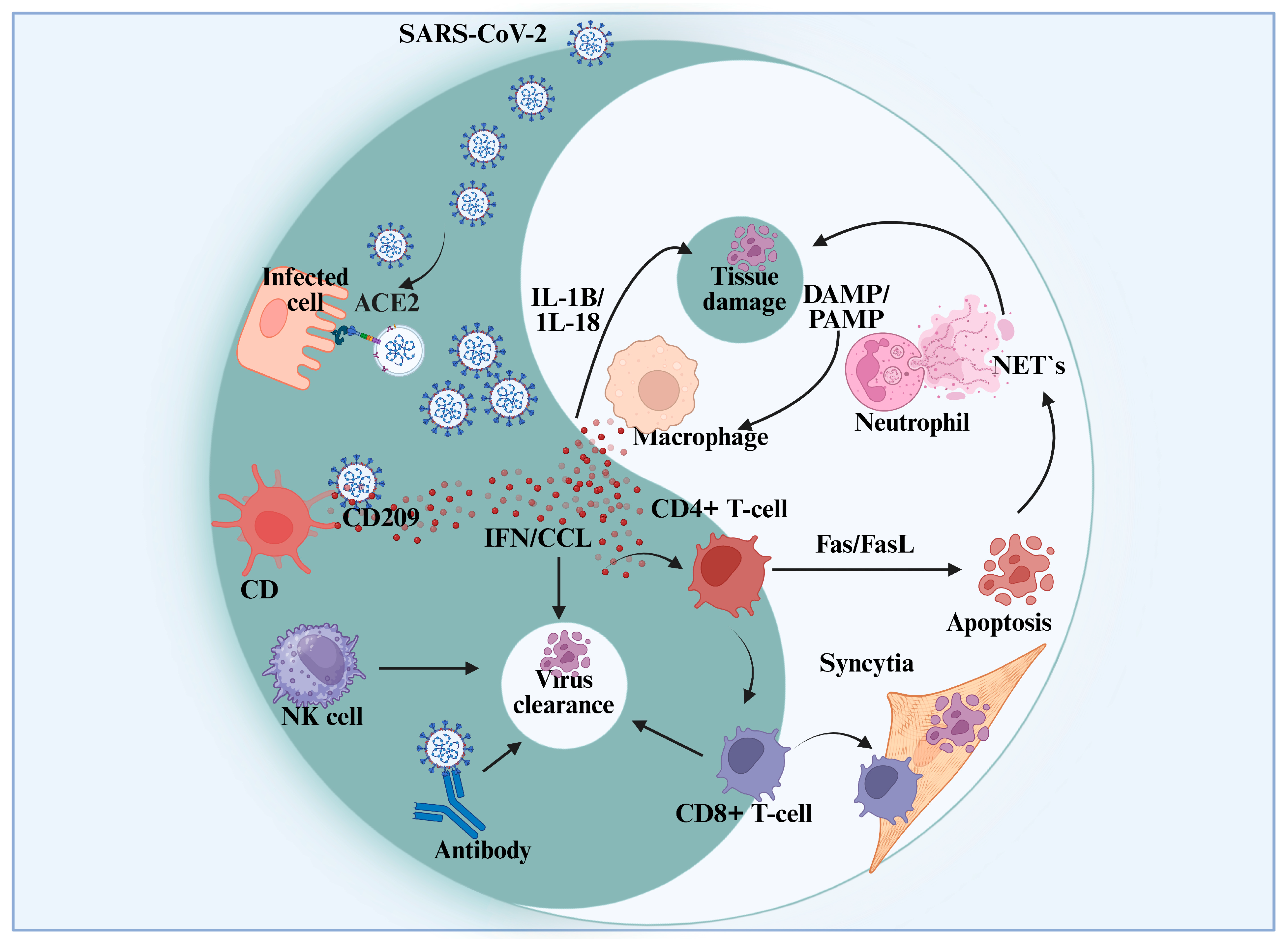
3. SARS-CoV-2 Entry Mechanisms and Their Effect on Host Cell Functions in COVID-19
4. Potential Cancer Links of COVID-19
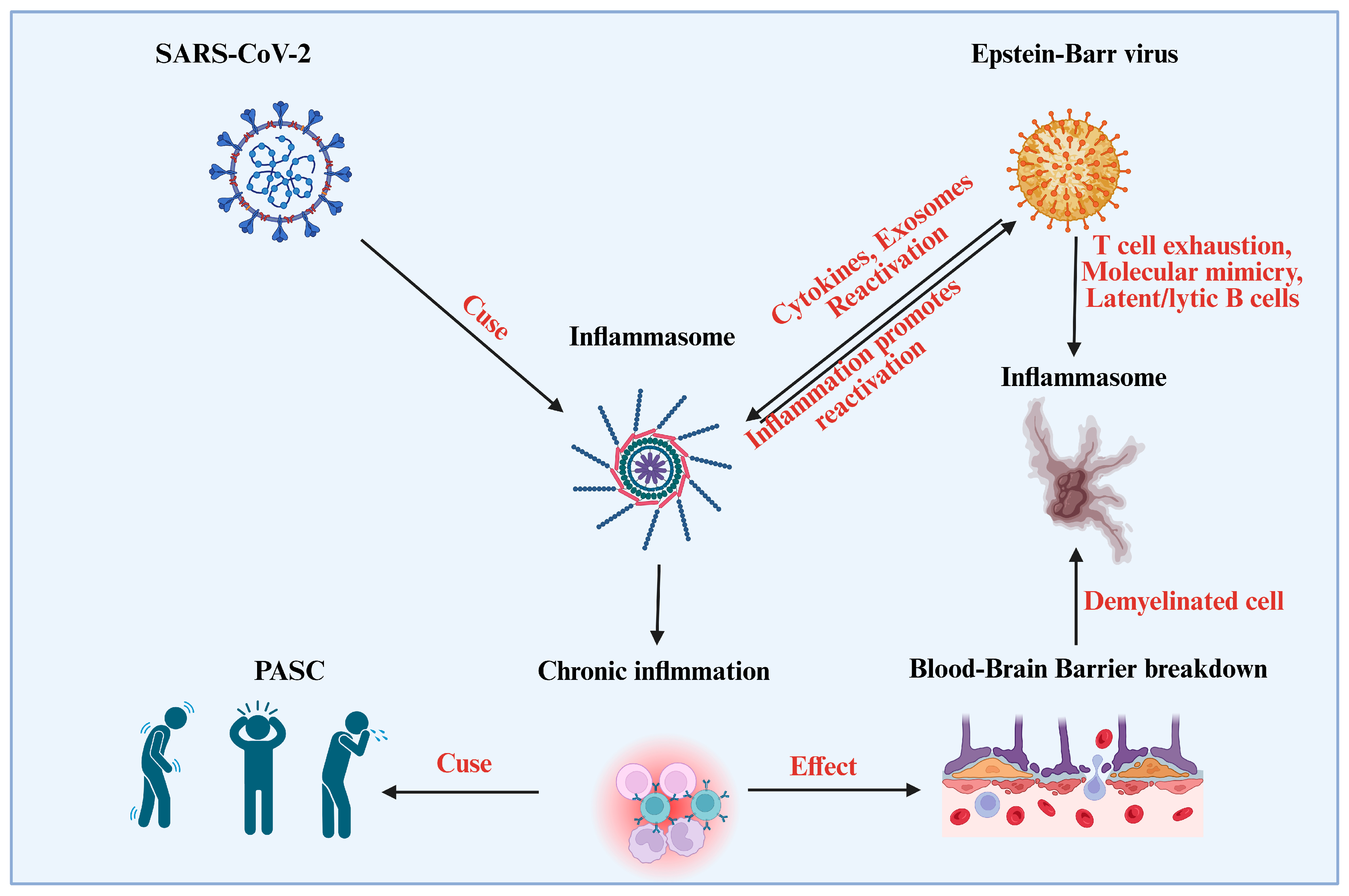
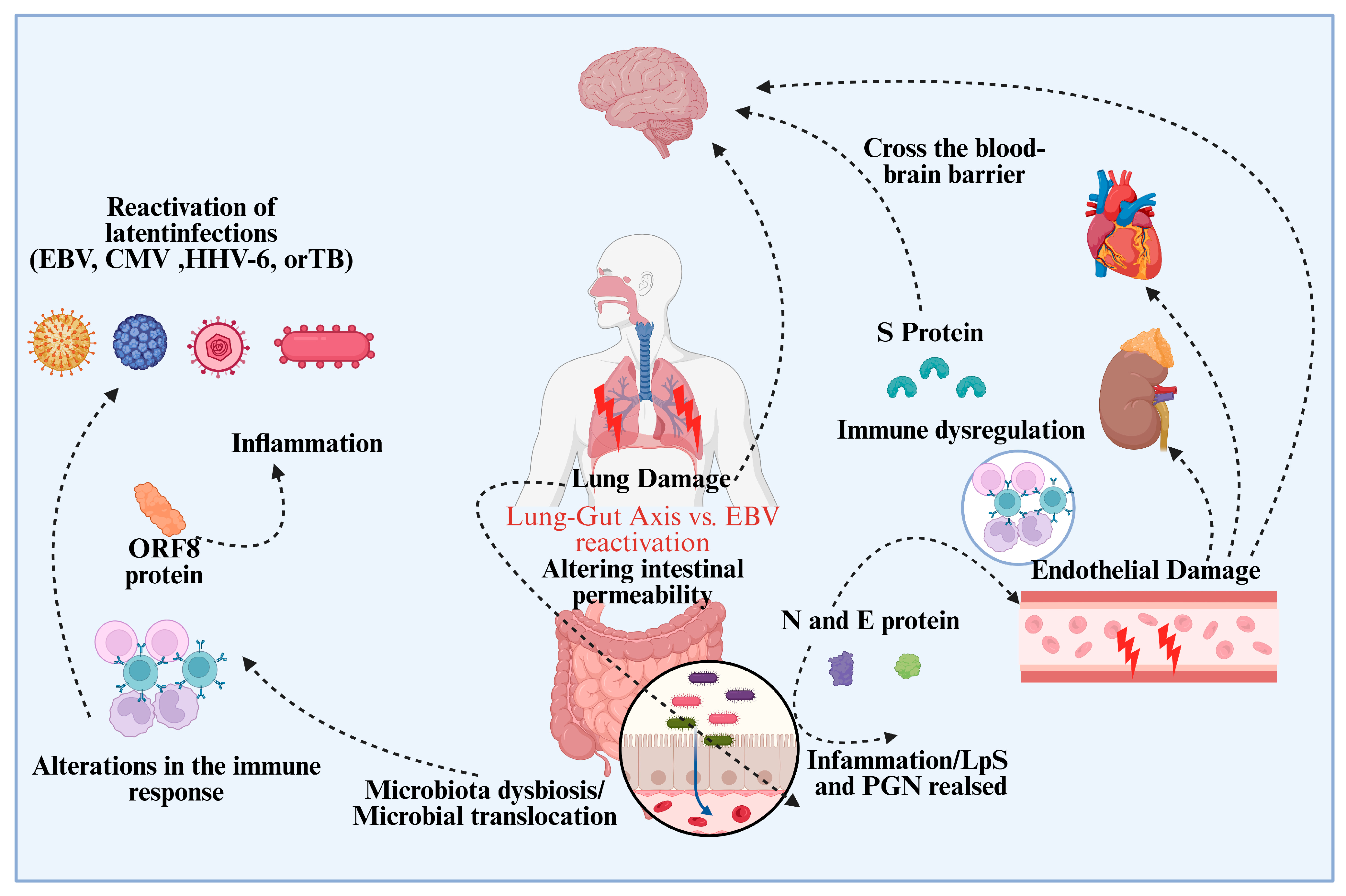
5. Dual Threat of EBV and COVID-19 in Cancer Development: The Synergistic Effects
6. Clinical Implications, Impact on Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment:
7. Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EBV | Epstein-Barr Virus |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| HHV-4 | Human Herpesvirus 4 |
| EBNA1 | Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 |
| LMP1 | Latent Membrane Protein 1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| HV-4 | Human Herpesvirus 4 |
| JAK/STAT | Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| PASC | Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (Long COVID) |
| DAMPs | Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| AK/STAT | Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| NETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 Beta |
| IL-18 | Interleukin 18 |
| ETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
| NK Cells | Natural Killer Cells |
| IFN | Interferon |
| CCL | Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand |
| Fas/FasL | Fas Receptor/Fas Ligand |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| HHV-6 | Human Herpesvirus 6 |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| PGN | Peptidoglycan |
| ORF8 | Open Reading Frame 8 (SARS-CoV-2 protein) |
| S Protein | Spike Protein (SARS-CoV-2) |
| N Protein | Nucleocapsid Protein (SARS-CoV-2) |
| E Protein | Envelope Protein (SARS-CoV-2) |
| BBB | Blood-Brain Barrier |
| GN | Peptidoglycan |
References
- Ye, R.; Wang, A.; Bu, B.; Luo, P.; Deng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yin, S. Viral oncogenes, viruses, and cancer: A third-generation sequencing perspective on viral integration into the human genome. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1333812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhalifa, A.M.E.; Nabi, S.U.; Shah, O.S.; Bashir, S.M.; Muzaffer, U.; Ali, S.I.; Wani, I.A.; Alzerwi, N.A.N.; Elderdery, A.Y.; Alanazi, A.; et al. Insight into Oncogenic Viral Pathways as Drivers of Viral Cancers: Implication for Effective Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1924–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeel, M. Oncogenic viruses-encoded microRNAs and their role in the progression of cancer: Emerging targets for antiviral and anticancer therapies. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Tay, J.K.; Loh, C.J.L.; Chu, A.J.M.; Yeong, J.P.S.; Lim, C.M.; Toh, H.C. Epstein–Barr virus epithelial cancers—A comprehensive understanding to drive novel therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, G.; Aneja, R. Cancer as a prospective sequela of long COVID-19. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 43, e2000331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, K.; Higginbotham, K. Epstein-Barr Virus; Philadelphia College: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Indari, O.; Ghosh, S.; Bal, A.S.; James, A.; Garg, M.; Mishra, A.; Karmodiya, K.; Jha, H.C. Awakening the sleeping giant: Epstein–Barr virus reactivation by biological agents. Pathog. Dis. 2024, 82, ftae002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Naghavi, M.; Ahmed, L.A. Global and regional incidence, mortality and disability-adjusted life-years for Epstein-Barr virus-attributable malignancies, 1990–2017. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.J.; Pachnio, A.; Pedroza-Pacheco, I.; Leese, A.M.; Begum, J.; Long, H.M.; Croom-Carter, D.; Stacey, A.; Moss, P.A.H.; Hislop, A.D.; et al. Asymptomatic Primary Infection with Epstein-Barr Virus: Observations on Young Adult Cases. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00382-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavifar, N.; Ghoncheh, M.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A.; Khosravi, B.; Salehiniya, H. Epidemiology and Inequality in the Incidence and Mortality of Nasopharynx Cancer in Asia. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2016, 7, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, R.L.; Chakravorty, A.; Sugden, B. Burkitt lymphomas evolve to escape dependencies on Epstein-Barr virus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 606412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, M.; Georges, D.; Clifford, G.M.; de Martel, C. Estimating the Global Burden of Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 922–930.e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smatti, M.K.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Ali, N.H.; Pintus, G.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K. Epstein-Barr Virus Epidemiology, Serology, and Genetic Variability of LMP-1 Oncogene Among Healthy Population: An Update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.d.M.; Alves, C.E.d.C.; Pontes, G.S. Epstein-Barr virus: The mastermind of immune chaos. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1297994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.Y.; Siak, P.Y.; Leong, C.-O.; Cheah, S.-C. The role of Epstein–Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, J.T.; Lowy, D.R. An Introduction to Virus Infections and Human Cancer. In Recent Results in Cancer Research. Fortschritte der Krebsforschung. Progrès dans les Recherches sur le Cancer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 217, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.J.; Hsu, W.L.; Yang, H.I.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, H.C.; Chien, Y.C.; You, S.L. Epidemiology of virus infection and human cancer. In Recent Results in Cancer Research. Fortschritte der Krebsforschung. Progrès dans les Recherches sur le Cancer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 193, pp. 11–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bakouny, Z.; Labaki, C.; Grover, P.; Awosika, J.; Gulati, S.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Alimohamed, S.I.; Bashir, B.; Berg, S.; Bilen, M.A. Interplay of immunosuppression and immunotherapy among patients with cancer and COVID-19. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugl, A.; Andersen, C.L. Epstein-Barr virus and its association with disease-a review of relevance to general practice. BMC Fam. Pract. 2019, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahankhani, K.; Ahangari, F.; Adcock, I.M.; Mortaz, E. Possible cancer-causing capacity of COVID-19: Is SARS-CoV-2 an oncogenic agent? Biochimie 2023, 213, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.; Meehan, M.T.; Burrows, S.R.; Doolan, D.L.; Miles, J. Estimating the global burden of Epstein–Barr virus-related cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19 Epidemiological Update, Edition 177. Published 12 March 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Sullivan, J.L.; Kaplan, S.L.; Bond, S. Clinical manifestations and treatment of Epstein-Barr virus infection. Virol 2016, 2, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cascella, M. Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls Publishing; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vetsika, E.-K.; Callan, M. Infectious mononucleosis and Epstein-Barr virus. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2004, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Xia, J.; Duan, J.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Lan, W.; Ma, Q.; Wu, X.; Yuan, Y. Asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with non-severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19) have similar clinical features and virological courses: A retrospective single center study. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yayan, J.; Saleh, D.; Franke, K.J. Potential association between COVID-19 infections and the declining incidence of lung cancers. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, A.; Al Zaidan, L.; Malki, A. Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Malignancies: Roles of Viral Oncoproteins in Carcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.J.; Lui, A.J.; Hollern, D.P. The Evolving Landscape of B Cells in Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 3835–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, K.D.E.; Whitehurst, C.B. Incidence of Epstein-Barr virus reactivation is elevated in COVID-19 patients. Virus Res. 2023, 334, 199157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschos, K.; Smith, P.; Anderton, E.; Middeldorp, J.M.; White, R.E.; Allday, M.J. Epstein-barr virus latency in B cells leads to epigenetic repression and CpG methylation of the tumour suppressor gene Bim. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houen, G.; Trier, N.H. Epstein-Barr Virus and Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, R.; Kumar, R.R.; Thomas, K.C.; Rafi, M.; Reddiar, K.S.; George, P.S.; Ramadas, K. Epstein-Barr virus dynamics and its prognostic impact on nasopharyngeal cancers in a non-endemic region. Ecancermedicalscience 2022, 16, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucinska, M.; Nawrocki, S. COVID-19 Pandemic: Impact on Cancer Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harhaj, E.W.; Shembade, N. Lymphotropic Viruses: Chronic Inflammation and Induction of Cancers. Biology 2020, 9, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanrıverdi, Ö.; Alkan, A.; Karaoglu, T.; Kitaplı, S.; Yildiz, A. COVID-19 and Carcinogenesis: Exploring the Hidden Links. Cureus 2024, 16, e68303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diarimalala, R.O.; Wei, Y.; Hu, D.; Hu, K. Inflammasomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection and development of their corresponding inhibitors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1218039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaivola, J.; Nyman, T.A.; Matikainen, S. Inflammasomes and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, B.A.; Bhaduri-McIntosh, S. Inflammation and Epstein-Barr Virus at the Crossroads of Multiple Sclerosis and Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.J.; Deveau, T.M.; Munter, S.E.; Ryder, D.; Buck, A.; Beck-Engeser, G.; Chan, F.; Lu, S.; Goldberg, S.A.; Hoh, R.; et al. Impact of Pre-Existing Chronic Viral Infection and Reactivation on the Development of Long COVID. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Abrams, N.D.; Avula, L.R.; Carrick, D.M.; Chander, P.; Divi, R.L.; Dwyer, J.T.; Gannot, G.; Gordiyenko, N.; Liu, Q.; et al. Unraveling Links between Chronic Inflammation and Long COVID: Workshop Report. J. Immunol. 2024, 212, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani, A.; Vojdani, E.; Saidara, E.; Maes, M. Persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection, EBV, HHV-6 and other factors may contribute to inflammation and autoimmunity in long COVID. Viruses 2023, 15, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.Z.; Abbasi, A.; Kim, D.H.; Lippman, S.M.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Cleveland, D.W. Chromosomal fragile site breakage by EBV-encoded EBNA1 at clustered repeats. Nature 2023, 616, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQarni, S.; Al-Sheikh, Y.; Campbell, D.; Drotar, M.; Hannigan, A.; Boyle, S.; Herzyk, P.; Kossenkov, A.; Armfield, K.; Jamieson, L. Lymphomas driven by Epstein–Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA1) are dependant upon Mdm2. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3998–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, R.; Dawson, C.W.; Hu, C.; Shah, K.M.; Owen, T.J.; Date, K.L.; Maia, S.P.; Shao, J.; Arrand, J.R.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 inhibits the canonical NF-κB pathway in carcinoma cells by inhibiting IKK phosphorylation. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, M.; Pei, R.; Du, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, H.; He, M. In-cell infection: A novel pathway for Epstein-Barr virus infection mediated by cell-in-cell structures. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, D.; Migita, N.; Ishizawa, S.; Sato, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Kiyokawa, E. Co-occurrence of Epstein–Barr virus-positive nodal T/NK-cell lymphoma and nodal T-follicular helper cell lymphoma of different clonal origins: An autopsy case report. Pathol. Int. 2024, 74, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontzek, F.; Staiger, A.M.; Wullenkord, R.; Grau, M.; Zapukhlyak, M.; Kurz, K.S.; Horn, H.; Erdmann, T.; Fend, F.; Richter, J. Molecular profiling of EBV associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2023, 37, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, K.L.; Eich, C.R.; de Fariña, L.O.; Kadowaki, M.K.; da Conceição Silva, J.L.; Maller, A.; Simão, R.C.G. Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 variants: A brief review and practical implications. Braz. J. Microbiol. [Publ. Braz. Soc. Microbiol.] 2022, 53, 1133–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. Domains and Functions of Spike Protein in Sars-Cov-2 in the Context of Vaccine Design. Viruses 2021, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Yang, X.; Yang, D.; Bao, J.; Li, R.; Xiao, Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, D. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvamsi, P.V.; Tulsian, N.K.; Samsudin, F.; Qian, X.; Purushotorman, K.; Yue, G.; Kozma, M.M.; Hwa, W.Y.; Lescar, J.; Bond, P.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 S protein:ACE2 interaction reveals novel allosteric targets. eLife 2021, 10, e63646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Yu, M. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-induced neurological complications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 605972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Smajlović, S.; Tombuloglu, H.; Ćordić, S.; Hajdarević, A.; Kudić, N.; Al Mutai, A.; Turkistani, S.A.; Al-Ahmed, S.H.; Al-Zaki, N.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and multi-organ system damage: A review. Biomol. Biomed. 2023, 23, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Meher, N.; Mohammed, A.; Razab, M.; Bhaskar, L.; Nawi, N.M. Neurological infection and complications of SARS-CoV-2: A review. Medicine 2023, 102, e30284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.; Huang, C.; Allen, C.; Ireland, J.; Roth, G.; Zou, Z.; Lu, J.; Lafont, B.A.; Garza, N.L.; Brumbaugh, B. SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung epithelial cells induces TMPRSS-mediated acute fibrin deposition. Nat. Cancer 2023, 14, 6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkotoky, S.; Dey, D.; Hazarika, Z. Interactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD): A structural perspective. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 2713–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahmeier, F.; Lavacca, T.M.; Goellner, S.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Prasad, V.; Cerikan, B.; Rajasekharan, S.; Mizzon, G.; Haselmann, U.; Funaya, C.; et al. Identification of host dependency factors involved in SARS-CoV-2 replication organelle formation through proteomics and ultrastructural analysis. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0087823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.; Goodyear, C.S.; Willicombe, M.; Gaskell, C.; Siebert, S.; Ide Silva, T.; Murray, S.M.; Rea, D.; Snowden, J.A.; Carroll, M. SARS-CoV-2-specific immune responses and clinical outcomes after COVID-19 vaccination in patients with immune-suppressive disease. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; Cortese, M.; Frankish, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Plociennikowska, A.; Heigwer, F.; Prasad, V.; Joecks, S.; Burkart, S.S. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a pro-inflammatory cytokine response through cGAS-STING and NF-κB. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassen, N.C.; Papies, J.; Bajaj, T.; Emanuel, J.; Dethloff, F.; Chua, R.L.; Trimpert, J.; Heinemann, N.; Niemeyer, C.; Weege, F. SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piracha, Z.; Tahir, R.; Noor-Ul-Ain, F.M.; Fatima, R.; Uppal, R. SARS-CoV-2 infection-associated detrimental effects on the various human organs. Int. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 5, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Z. Consequences of COVID-19 on the cardiovascular and renal systems. Sleep Med. 2022, 100, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kombe Kombe, A.J.; Biteghe, F.A.N.; Ndoutoume, Z.N.; Jin, T. CD8+ T-cell immune escape by SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 962079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-S.; Shin, E.-C. The activation of bystander CD8+ T cells and their roles in viral infection. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagher, H.; Chaftari, A.-M.; Subbiah, I.M.; Malek, A.E.; Jiang, Y.; Lamie, P.; Granwehr, B.; John, T.; Yepez, E.; Borjan, J.; et al. Long COVID in cancer patients: Preponderance of symptoms in majority of patients over long time period. eLife 2023, 12, e81182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahan, A.Z.; Hazra, T.K.; Das, S. The pivotal role of DNA repair in infection mediated-inflammation and cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, I.; Rubinstein, A.; Golovkin, A.; Kalinina, O.; Vasilyev, K.; Rudenko, L.; Isakova-Sivak, I. Dysregulated Immune Responses in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients: A Comprehensive Overview. Viruses 2022, 14, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, F.J.; Hope, C.M.; Masavuli, M.G.; Lynn, M.A.; Mekonnen, Z.A.; Yeow, A.E.L.; Garcia-Valtanen, P.; Al-Delfi, Z.; Gummow, J.; Ferguson, C. Long-term perturbation of the peripheral immune system months after SARS-CoV-2 infection. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.-Y.R.; Perlman, S. Immune dysregulation and immunopathology induced by SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses—Are we our own worst enemy? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davitt, E.; Davitt, C.; Mazer, M.B.; Areti, S.S.; Hotchkiss, R.S.; Remy, K.E. COVID-19 disease and immune dysregulation. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2022, 35, 101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaret, J.; Corroyer-Simovic, B.; Alidjinou, E.K.; Goffard, A.; Trauet, J.; Miczek, S.; Vuotto, F.; Dendooven, A.; Huvent-Grelle, D.; Podvin, J.; et al. Impaired Functional T-Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 After Two Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in Older People. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 778679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Manetti, A.C.; Franceschi, F.; La Russa, R.; Bertozzi, G.; Maiese, A.; Savioli, G.; Volonnino, G.; Longhitano, Y. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and Therapy. Medicina 2022, 58, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Luo, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Features of cytokine storm identified by distinguishing clinical manifestations in COVID-19. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 671788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Ren, H.C.; Cao, J.H. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 to cancer: Carcinogenic or anticancer? (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.H.; Ragusa, M.; Tortosa, F.; Torres, A.; Gresh, L.; Méndez-Rico, J.A.; Alvarez-Moreno, C.A.; Lisboa, T.C.; Valderrama-Beltrán, S.L.; Aldighieri, S.; et al. Viral reactivations and co-infections in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, A.; Amini, M.J.; Arabzadeh Bahri, R.; Jafarabady, K.; Salehi, S.A.; Hajishah, H.; Mozhgani, S.-H. Herpesviruses reactivation following COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinna, P.; Bratl, K.; Lambarey, H.; Blumenthal, M.J.; Schäfer, G. The impact of Co-infections for human gammaherpesvirus infection and associated pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maison, D.P.; Deng, Y.; Gerschenson, M. SARS-CoV-2 and the host-immune response. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1195871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Hall, D.; Omoru, O.B.; Gill, H.M.; Smith, S.; Janga, S.C. Mutational Landscape and Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 with Host Cellular Components. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, D.J.W.; Lew, Z.Z.R.; Chu, J.J.H.; Tan, K.S. Uncovering novel viral innate immune evasion strategies: What has SARS-CoV-2 taught us? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 844447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, B.L.; Cheng, M.T.; Csiba, K.; Meng, B.; Gupta, R.K. SARS-CoV-2 and innate immunity: The good, the bad, and the “goldilocks”. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.; Hilliam, Y.; Bomberger, J.M. Microbial and Immune Regulation of the Gut-Lung Axis during Viral-Bacterial Coinfection. J. Bacteriol. 2023, 205, e0029522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, C.; Chen, J.; Rouphael, N.; Pickering, H.; Phan, H.V.; Glascock, A.; Chu, V.; Dandekar, R.; Corry, D.; Kheradmand, F. Chronic Viral Reactivation and Associated Host Immune Response and Clinical Outcomes in Acute COVID-19 and Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonsenso, D.; Tantisira, K.G. Long COVID and SARS-CoV-2 persistence: New answers, more questions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Julg, B.; Mohandas, S.; Bradfute, S.B. Viral persistence, reactivation, and mechanisms of long COVID. Elife 2023, 12, e86015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Gandhi, S.; Mebane, A., 3rd; Singh, A.; Vishnuvardhan, N.; Patel, E. Cancer patients and COVID-19: Mortality, serious complications, biomarkers, and ways forward. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 26, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaeddini, M.; Etemad-Moghadam, S. SARS-Cov-2 infection in cancer patients, susceptibility, outcome and care. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 364, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slimano, F.; Baudouin, A.; Zerbit, J.; Toulemonde-Deldicque, A.; Thomas-Schoemann, A.; Chevrier, R.; Daouphars, M.; Madelaine, I.; Pourroy, B.; Tournamille, J.F.; et al. Cancer, immune suppression and Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Need to manage drug safety (French Society for Oncology Pharmacy [SFPO] guidelines). Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 88, 102063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wei, P. Infection with COVID-19 promotes the progression of pancreatic cancer through the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Discov. Oncol. 2023, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; De Giglio, M.A.R.; Roviello, G.N. Deciphering the Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, L.; Melenotte, C.; Griscelli, F.; Gachot, B.; Marabelle, A.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. The immuno-oncological challenge of COVID-19. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 946–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, H.; Xu, L.P.; Mo, X.D.; Liu, R.; Liang, S.; Wu, N.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Chang, Y.J.; et al. Immunosuppressant indulges EBV reactivation and related lymphoproliferative disease by inhibiting Vδ2(+) T cells activities after hematopoietic transplantation for blood malignancies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Song, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C. Positive Epstein–Barr virus detection in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, B.; Deng, Y.; Holler, A.; Nunez, N.; Azzi, T.; Vanoaica, L.D.; Müller, A.; Zdimerova, H.; Antsiferova, O.; Zbinden, A.; et al. CD8+ T cells retain protective functions despite sustained inhibitory receptor expression during Epstein-Barr virus infection in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, A.; Zhang, Z. Exploring common pathogenic association between Epstein Barr virus infection and long-COVID by integrating RNA-Seq and molecular dynamics simulations. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1435170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-L.; Fang, X.-L.; Mao, Y.-P.; Guo, R.; Li, W.-F.; Xu, S.-S.; Ma, J.; Chen, L.; Tang, L.-L. Association of delayed chemoradiotherapy with elevated Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and adverse clinical outcome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic: A retrospective study. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwaa, A.; Oyawoye, F.; Owusu, I.A.; Dosoo, D.; Manu, A.A.; Sobo, A.K.; Fosu, K.; Olwal, C.O.; Quashie, P.K.; Aikins, A.R. In vitro analysis suggests that SARS-CoV-2 infection differentially modulates cancer-like phenotypes and cytokine expression in colorectal and prostate cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, N.W.; Lau, C.Y.; Che, C.M.; Lee, V.H. Nasopharynx Battlefield: Cellular Immune Responses Mediated by Midkine in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and COVID-19. Cancers 2023, 15, 4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafi, A.R.; Motlagh, A.G.; Azadeh, P. The impact of COVID-19 on cancer recurrence: A narrative review. Arch. Iran. Med. 2022, 25, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganelli, R. Resurrecting Epstein-Barr Virus. Pathogens 2022, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Foo, C.; Zheng, G.; Huang, R.; Li, Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Insight into the mechanisms of coronaviruses evading host innate immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taefehshokr, N.; Taefehshokr, S.; Hemmat, N.; Heit, B. Covid-19: Perspectives on innate immune evasion. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 580641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, D.K.; Forero, A. Mechanisms of Antiviral Immune Evasion of SARS-CoV-2. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, C.; Wang, C.; Ramasamy, A.; Fonken, C.; Morse, B.; Lopez, N.; Wylie, D.; Melamed, E. Molecular Mimicry as a Mechanism of Viral Immune Evasion and Autoimmunity. Boxiv 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chijioke, O.; Azzi, T.; Nadal, D.; Münz, C. Innate immune responses against Epstein Barr virus infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, K.; Luo, R.; Cai, M.; Yun, J. Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapy of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Malignancies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münz, C. Epstein–Barr virus-specific immune control by innate lymphocytes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Liu, B.; Tang, G.; Jiao, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Gao, L.; Ni, X. B2M mutation paves the way for immune tolerance in pathogenesis of Epstein-Barr virus positive diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sausen, D.; Poirier, M.; Spiers, L.; Smith, E. Mechanisms of T cell evasion by Epstein-Barr virus and implications for tumor survival. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1289313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocherie, T.; Zafilaza, K.; Leducq, V.; Marot, S.; Calvez, V.; Marcelin, A.G.; Todesco, E. Epidemiology and Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern: The Impacts of the Spike Mutations. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severin, R.; Franz, C.K.; Farr, E.; Meirelles, C.; Arena, R.; Phillips, S.A.; Bond, S.; Ferraro, F.; Faghy, M. The effects of COVID-19 on respiratory muscle performance: Making the case for respiratory muscle testing and training. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, S.; Ying, L.Y. Epstein Barr Virus Reactivation during COVID-19 Hospitalization Significantly Increased Mortality/Death in SARS-CoV-2(+)/EBV(+) than SARS-CoV-2(+)/EBV(−) Patients: A Comparative Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2023, 2023, 1068000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, F.; De Angelis, M.L.; Baiocchi, M.; Rossi, R.; Biffoni, M.; Zeuner, A. COVID-19-Induced Modifications in the Tumor Microenvironment: Do They Affect Cancer Reawakening and Metastatic Relapse? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 592891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetsouphanh, C.; Darley, D.R.; Wilson, D.B.; Howe, A.; Munier, C.; Patel, S.K.; Juno, J.A.; Burrell, L.M.; Kent, S.J.; Dore, G. Immunological dysfunction persists for 8 months following initial mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Tizian, C.; Ferreira-Gomes, M.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Heinrich, F.; Frischbutter, S.; Angermair, S.; Hohnstein, T.; Mattiola, I. Untimely TGFβ responses in COVID-19 limit antiviral functions of NK cells. Nature 2021, 600, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J. NK cell dysfunction in patients with COVID-19. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, G.F.; Klein, S.J.; Zoller, H.; Peer, A.; Bellmann, R.; Joannidis, M. Correlation of interleukin-6 with Epstein–Barr virus levels in COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moppert, J.; Domagalski, K.; Wrotek, S.; Pawłowska, M. Are Selected Cytokines and Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Load Predictors of Hepatological Complications of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Children? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektaş, M.; Koca, N.; İnce, B. Higher Frequency and Poor Prognosis with COVID-19 Associated Cytokine Storm among Cancer Patients: Between Two Fires. J. Cancer Immunol. 2022, 4, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeggerl, A.D.; Nunhofer, V.; Lauth, W.; Badstuber, N.; Held, N.; Zimmermann, G.; Grabmer, C.; Weidner, L.; Jungbauer, C.; Lindlbauer, N. Epstein-Barr virus reactivation is not causative for post-COVID-19-syndrome in individuals with asymptomatic or mild SARS-CoV-2 disease course. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pablos, M.; Paiva, B.; Zabaleta, A. Epstein–Barr virus-acquired immunodeficiency in myalgic encephalomyelitis—Is it present in long COVID? J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, C.; Palma, G.; Bruzzese, F.; Budillon, A.; Napoli, C.; de Nigris, F. Spontaneous cancer remission after COVID-19: Insights from the pandemic and their relevance for cancer treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.Y.; Komarasamy, T.V.; Rmt Balasubramaniam, V. Hyperinflammatory immune response and COVID-19: A double edged sword. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 742941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.C.; Ramonell, R.P.; Haddad, N.S.; Anam, F.A.; Rudolph, M.E.; Walker, T.A.; Truong, A.D.; Dixit, A.N.; Han, J.E.; Cabrera-Mora, M.; et al. Dysregulated naive B cells and de novo autoreactivity in severe COVID-19. Nature 2022, 611, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczewski, L.M.; Cotler, J.; Merkow, R.P.; Palis, B.; Nelson, H.; Mullett, T.; Boffa, D.J. Alterations in Cancer Treatment During the First Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2340148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim-Malpass, J.; Vavolizza, R.D.; Cohn, W.F.; Kennedy, E.M.; Showalter, S.L. Cancer Screening and Treatment Delays During the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Role of Health Literacy in Care Re-engagement: Findings from an NCI-Designated Comprehensive Cancer Center sample. J. Cancer Educ. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Educ. 2023, 38, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infectious Mononucleosis. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/infections/herpesvirus-infections/infectious-mononucleosis (accessed on 11 August 2025).[Green Version]
- Li, Y.Q.; Khin, N.S.; Chua, M.L.K. The evolution of Epstein-Barr virus detection in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2018, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghupathy, R.; Hui, E.P.; Chan, A.T. Epstein-Barr virus as a paradigm in nasopharyngeal cancer: From lab to clinic. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Annu. Meet. 2014, 34, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.A.; Woo, J.K.; King, A.; Zee, B.C.; Lam, W.J.; Chan, S.L.; Chu, S.W.; Mak, C.; Tse, I.O.; Leung, S.Y.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus DNA to Screen for Nasopharyngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruffat, H.; Manet, E.; Rigolet, A.; Sergeant, A. The enhancer factor R of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6835–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fafi-Kremer, S.; Morand, P.; Barranger, C.; Barguès, G.; Magro, S.; Bés, J.; Bourgeois, P.; Joannes, M.; Seigneurin, J.-M. Evaluation of the Epstein-Barr virus R-gene quantification kit in whole blood with different extraction methods and PCR platforms. J. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 10, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Aspect | EBV | SARS-CoV-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Virus | Herpesvirus (HHV-4), oncogenic virus [20] | Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), recent viral infection [21] |
| Prevalence | Affects 90–95% of people worldwide [22] | Newer virus with widespread global impact [23] |
| Transmission | Primarily through saliva (“kissing disease”) [24] | Primarily through respiratory droplets, close contact [25] |
| Common Infections | Frequently asymptomatic, can cause mononucleosis (“mono”) [26] | Can range from asymptomatic to severe respiratory illness [27] |
| Cancer Associations | Strongly associated with certain stomach malignancies, Burkitt lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma [4] | Not directly associated with cancer, but research into long-term cancer risks is ongoing [28] |
| Cancer Development Mechanism | Infects B-cells, promotes immune evasion, genetic instability, and cancer [29] | Immunosuppression and inflammation may increase cancer risk over time, particularly in high-risk individuals [19] |
| EBV Reactivation Risk | Reactivation in B-cells under specific conditions (immunosuppressive states) can lead to cancer [30] | May interact with latent infections like EBV, potentially leading to reactivation and cancer formation [31] |
| Immunological Impact | Latency in B-cells allows immune evasion [32] | Causes significant immune dysregulation, especially in severe cases or during treatment [33] |
| Impact on Cancer Care | Known viral oncogenic effects with established diagnostic protocols [34] | Delays in cancer care during the pandemic could affect cancer diagnosis and treatment, potentially worsening outcomes [35] |
| Chronic Inflammation | Can contribute to chronic inflammation in cancer types associated with EBV [36]. | Chronic inflammation in long COVID could contribute to increased cancer risk [37]. |
| Mechanism | Key Proteins | Pathways Affected | Associated Cancers | Therapeutic Approaches |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-cell immortalization | LMP1, EBNA2 | NF-κB, JAK/STAT | Burkitt lymphoma | CD19 CAR-T therapy |
| Immune evasion | EBNA1, BPLF1 | Antigen presentation | Hodgkin lymphoma | PD-1 inhibitors |
| Viral latency | EBERs, LMP2A | B-cell signaling | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | EBV-specific CTLs |
| Inflammation | LMP1 | Cytokine production | Gastric cancer | Anti-IL-6 therapies |
| Mechanism | Details |
|---|---|
| Virus Type and Characteristics | SARS-CoV-2 is an RNA virus with a spike protein that facilitates entry into cells via ACE2 receptors, primarily targeting respiratory epithelial cells [58,59,60]. |
| Viral Entry and Replication | The spike protein interacts with ACE2, enabling endocytosis and replication inside the host cell [60,61]. |
| Impact on Host Functions | SARS-CoV-2 affects immune responses, inflammatory signaling, and autophagy, contributing to disease severity and potentially long COVID [62,63,64]. |
| Target Organs | Primarily the lungs, but it can also affect the heart, kidneys, and intestines [65,66]. |
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
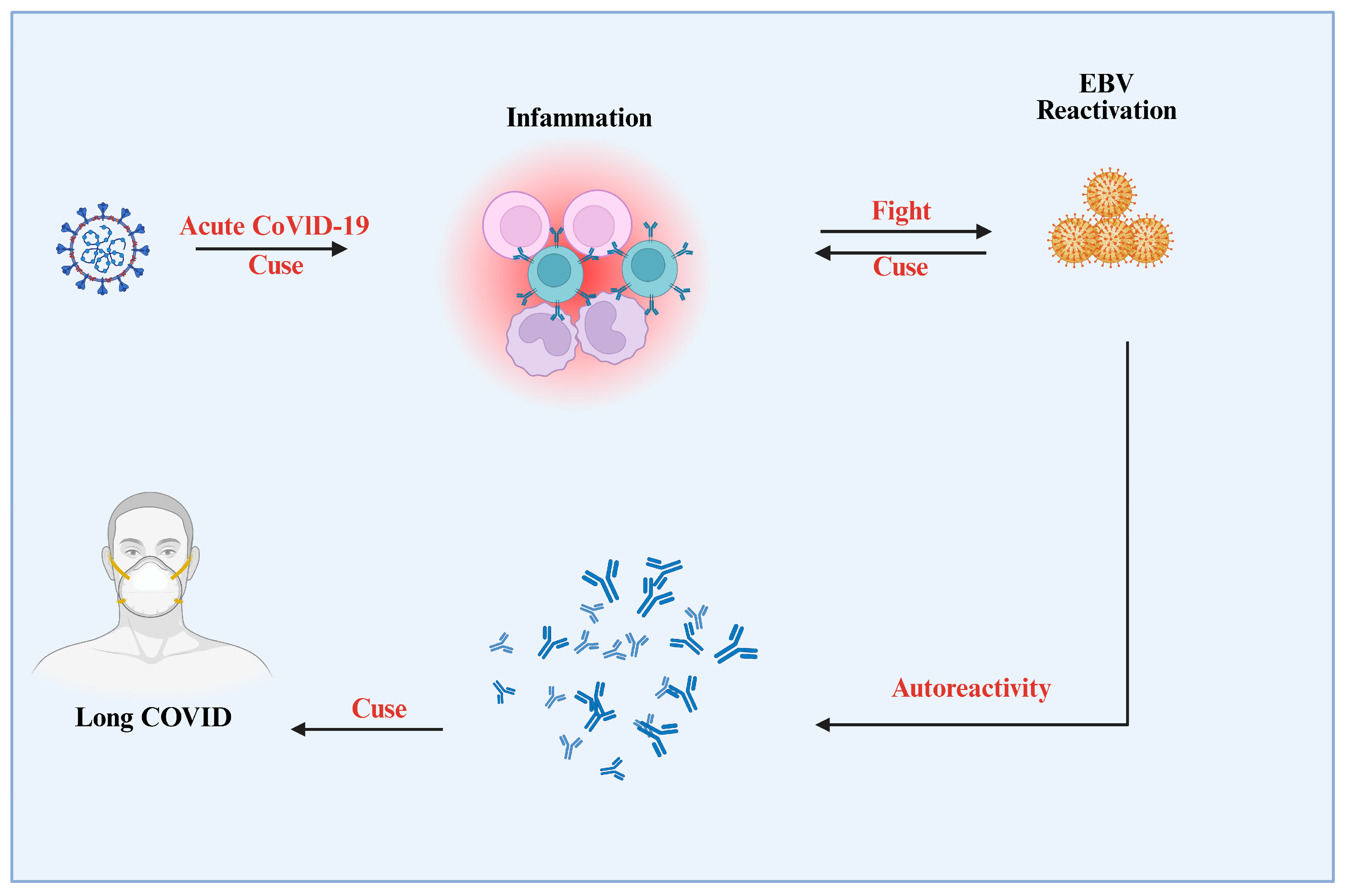
| EBV Reactivation Risk | Immunosuppression caused by COVID-19 may catalyze latent EBV reactivation, raising the risk of virally induced malignancies in immunocompromised patients [72,116,117]. |
| Impact on Immune Surveillance | COVID-19-induced dysregulation, including cytokine storms and T-cell depletion, compromises immune surveillance, enabling EBV to reactivate and promote carcinogenesis [118]. |
| Tumor Microenvironment Changes | COVID-19-induced inflammation may promote EBV replication and latency, creating a tumor-promoting microenvironment, especially for NPC [31,119]. |
| Immune Evasion by EBV | EBV can evade immune detection by inducing immune tolerance and latent infections in immune cells, which supports tumor growth [72,116]. |
| Impact on COVID-19 Immune Responses | COVID-19 impairs T-cells, B-cells, and NK-cells, reducing the ability to control latent EBV infections and promoting tumor development [76,120]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaadawe, M.; Radman, B.A.; Hu, L.; Long, J.; Luo, Q.; Tan, C.; Amirat, H.S.; Alsaadawi, M.; Lyu, X. From Viral Infection to Malignancy: The Dual Threat of EBV and COVID-19 in Cancer Development. Viruses 2025, 17, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091195
Alsaadawe M, Radman BA, Hu L, Long J, Luo Q, Tan C, Amirat HS, Alsaadawi M, Lyu X. From Viral Infection to Malignancy: The Dual Threat of EBV and COVID-19 in Cancer Development. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091195
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaadawe, Moyed, Bakeel A. Radman, Longtai Hu, Jingyi Long, Qingshuang Luo, Chushu Tan, Hadji Sitti Amirat, Mohenned Alsaadawi, and Xiaoming Lyu. 2025. "From Viral Infection to Malignancy: The Dual Threat of EBV and COVID-19 in Cancer Development" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091195
APA StyleAlsaadawe, M., Radman, B. A., Hu, L., Long, J., Luo, Q., Tan, C., Amirat, H. S., Alsaadawi, M., & Lyu, X. (2025). From Viral Infection to Malignancy: The Dual Threat of EBV and COVID-19 in Cancer Development. Viruses, 17(9), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091195








