Application of Bovine Nasal Epithelial Cells as an In Vitro Model for Studying Viral Infection in the Upper Respiratory Tract
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objective
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Viruses
2.2. Primary Cell Culture
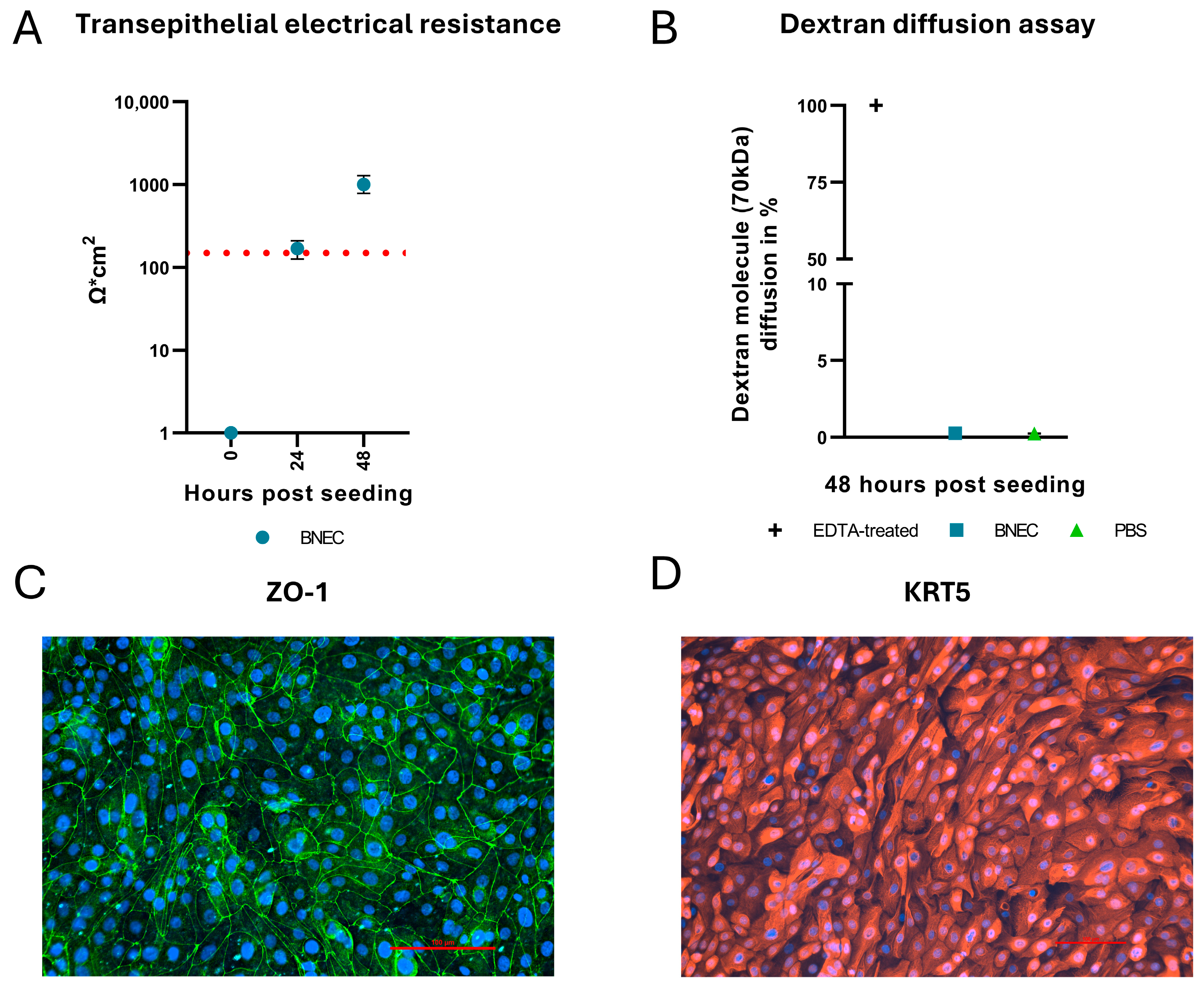
2.3. Epithelial Barrier Integrity
2.4. Infection of Primary Cell Cultures
2.5. Immunofluorescence and Brightfield Microscopy
2.6. Virus Titration
2.7. Nucleic Acid Preparation
2.8. Reverse Transcription-Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and qPCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Primary Cell Culture
3.2. BVDV Infection
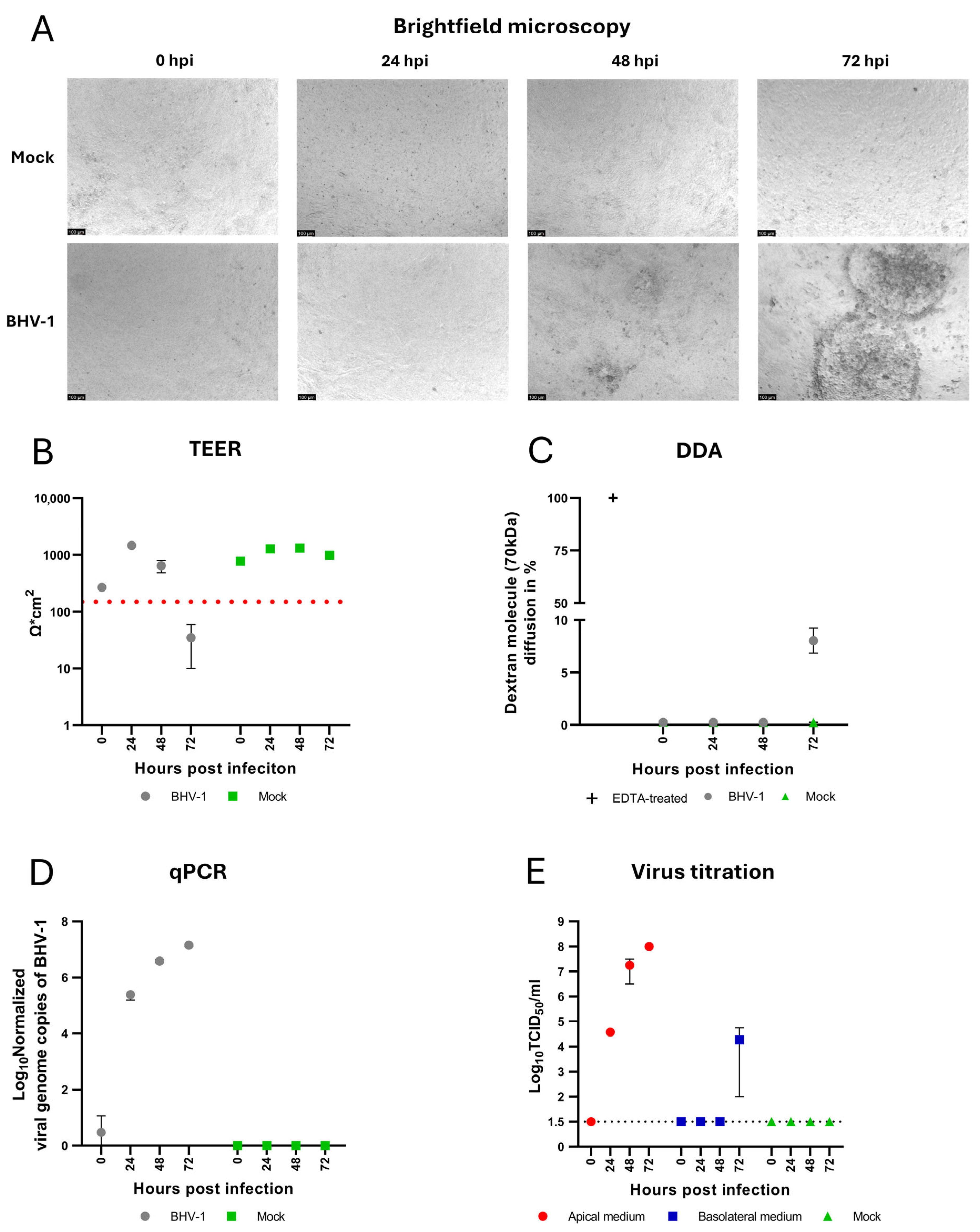
3.3. BHV-1 Infection
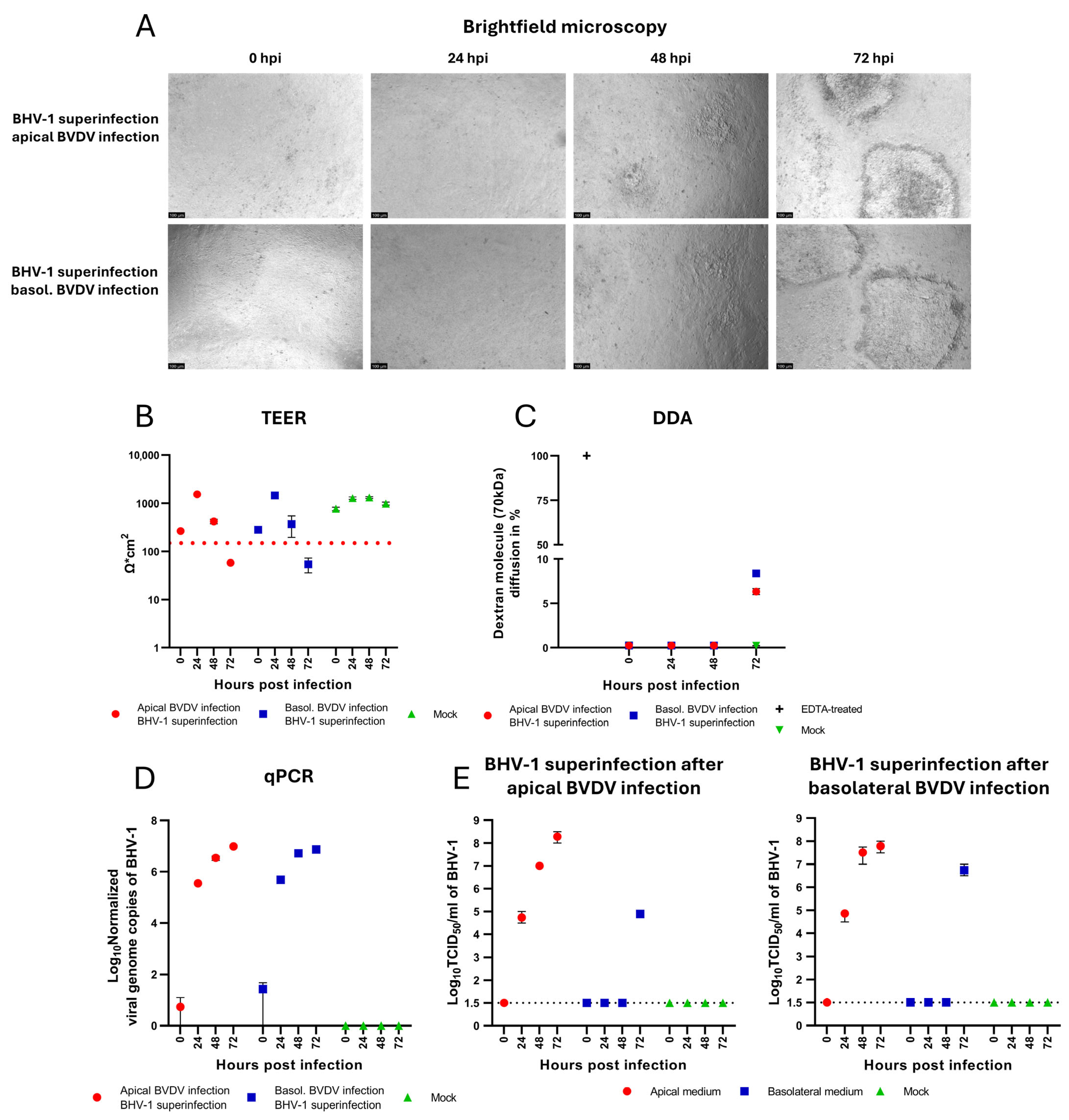
3.4. BHV-1 Superinfection of BVDV Infected Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurćubić, V.; Đoković, R.; Ilić, Z.; Petrović, M. Etiopathogenesis and Economic Significance of Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex (BRDC). Acta Agric. Serbica 2018, 23, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.A. Control Methods for Bovine Respiratory Disease for Feedlot Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loneragan, G.H.; Dargatz, D.A.; Morley, P.S.; Smith, M.A. Trends in Mortality Ratios among Cattle in US Feedlots. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 219, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.L.; Turkington, H.L.; Cosby, S.L. The Bacterial and Viral Agents of BRDC: Immune Evasion and Vaccine Developments. Vaccines 2021, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudino, M.; Nagamine, B.; Ducatez, M.F.; Meyer, G. Understanding the Mechanisms of Viral and Bacterial Coinfections in Bovine Respiratory Disease: A Comprehensive Literature Review of Experimental Evidence. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, M.; Lin, J.; Xue, F.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, X. Development of a One-Step Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection of Viral Pathogens Associated with the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 825257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.-Y.; Li, L.-M.; Tian, T.; Yin, J.-Y.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Q.-X.; Wang, T.-T.; Li, T.; et al. Prevalence of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus in Cattle between 2010 and 2021: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1086180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdawork, A.; Aklilu, H. Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis: Epidemiology, Control, and Impacts on Livestock Production and Genetic Resources. Vet. Res. Notes 2024, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postel, A.; Smith, D.B.; Becher, P. Proposed Update to the Taxonomy of Pestiviruses: Eight Additional Species within the Genus Pestivirus, Family Flaviviridae. Viruses 2021, 13, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, P.; Tautz, N. RNA Recombination in Pestiviruses: Cellular RNA Sequences in Viral Genomes Highlight the Role of Host Factors for Viral Persistence and Lethal Disease. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; García, M.L.; Curtis Hendrickson, R.; et al. Recent Changes to Virus Taxonomy Ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2022). Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnall, M.J.; Thrusfield, M.V. Engaging Veterinarians and Farmers in Eradicating Bovine Viral Diarrhoea: A Systematic Review of Economic Impact. Vet. Rec. 2017, 181, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Claassen, G.D.H.; Oude Lansink, A.G.J.M.; Loeffen, W.; Saatkamp, H.W. Economic Analysis of Classical Swine Fever Surveillance in the Netherlands. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moennig, V.; Becher, P. Control of Bovine Viral Diarrhea. Pathogens 2018, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, R.W.; Purdy, C.W.; Confer, A.W.; Saliki, J.T.; Loan, R.W.; Briggs, R.E.; Burge, L.J. Bovine Viral Diarrhea Viral Infections in Feeder Calves with Respiratory Disease: Interactions with Pasteurella spp., Parainfluenza-3 Virus, and Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 64, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Li, X.; Lv, X.; Liu, K.; Ren, J.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y. Current Progress on Innate Immune Evasion Mediated by Npro Protein of Pestiviruses. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1136051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Martin, E.; Schweizer, M. Fifty Shades of Erns: Innate Immune Evasion by the Viral Endonucleases of All Pestivirus Species. Viruses 2022, 14, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.; Chen, S.; Jia, W.; He, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, X. Non-Structural Proteins of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muylkens, B.; Thiry, J.; Kirten, P.; Schynts, F.; Thiry, E. Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Infection and Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 181–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Kumar, M.; Manohar, M.; Chauhan, R.S. Bovine Herpes Virus Infections in Cattle. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2009, 10, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Geiser, V.; Henderson, G.; Jiang, Y.; Meyer, F.; Perez, S.; Zhang, Y. Functional Analysis of Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) Genes Expressed during Latency. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 113, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostler, J.B.; Jones, C. The Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Latency-Reactivation Cycle, a Chronic Problem in the Cattle Industry. Viruses 2023, 15, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, L.N.D.; McCracken, M.D.; Hopkins, F.M.; Walker, R.D. Effect of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Infection on the Distribution of Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Virus in Calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1984, 45, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risalde, M.A.; Molina, V.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Pedrera, M.; Panadero, R.; Romero-Palomo, F.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C. Response of Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in Calves with Subclinical Bovine Viral Diarrhea Challenged with Bovine Herpesvirus-1. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 144, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risalde, M.A.; Molina, V.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Romero-Palomo, F.; Pedrera, M.; Garfia, B.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C. Pathogenic Mechanisms Implicated in the Intravascular Coagulation in the Lungs of BVDV-Infected Calves Challenged with BHV-1. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.; Chengappa, M.M.; Kuszak, J.; McVey, D.S. Bacterial Pathogens of the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.A.; Hendrick, S.; Janzen, E.; Pajor, E.A.; Orsel, K. Economic Impact of Digital Dermatitis, Foot Rot, and Bovine Respiratory Disease in Feedlot Cattle. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2021, 5, txab076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, T.; Sreenivasan, C.C.; Bhattarai, S.; Wang, D.; Kaushik, R.S.; Li, F. Isolation and Development of Bovine Primary Respiratory Cells as Model to Study Influenza D Virus Infection. Virology 2021, 559, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Fu, Y.; Meens, J.; Yang, W.; Meng, F.; Herrler, G.; Becher, P. Infection of Polarized Bovine Respiratory Epithelial Cells by Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV). Virulence 2021, 12, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Rivas, J.J.; Kisiela, D.; Czuprynski, C.J. Bovine Herpesvirus Type 1 Infection of Bovine Bronchial Epithelial Cells Increases Neutrophil Adhesion and Activation. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 131, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’jai, A.U.; Rivera, J.; Atapattu, D.N.; Owusu-Ofori, K.; Czuprynski, C.J. Gene Expression Profiling of Bovine Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed In Vitro to Bovine Herpesvirus 1 and Mannheimia Haemolytica. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 155, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, J.; Uhlenbruck, S.; Goris, K.; Keil, G.M.; Herrler, G. Three Viruses of the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex Apply Different Strategies to Initiate Infection. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, E.F.; Donis, R.O. Isolation of a Mutant MDBK Cell Line Resistant to Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Infection Due to a Block in Viral Entry. Virology 1995, 208, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, G.M.; Engelhardt, T.; Karger, A.; Enz, M. Bovine Herpesvirus 1 U(s) Open Reading Frame 4 Encodes a Glycoproteoglycan. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 3032–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, T.; Keil, G.M. Identification and Characterization of the Bovine Herpesvirus 5 US4 Gene and Gene Products. Virology 1996, 225, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tautz, N.; Meyers, G.; Stark, R.; Dubovi, E.J.; Thiel, H.J. Cytopathogenicity of a Pestivirus Correlates with a 27-Nucleotide Insertion. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7851–7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niesalla, H.S.; Dale, A.; Slater, J.D.; Scholes, S.F.E.; Archer, J.; Maskell, D.J.; Tucker, A.W. Critical Assessment of an In Vitro Bovine Respiratory Organ Culture System: A Model of Bovine Herpesvirus-1 Infection. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 158, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Wu, N.-H.; Seitz, M.; Herrler, G.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Efficient Suilysin-Mediated Invasion and Apoptosis in Porcine Respiratory Epithelial Cells after Streptococcal Infection under Air-Liquid Interface Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moennig, V.; Bolin, S.R.; Coulibaly, C.O.Z.; Kelso Gourley, N.E.; Liess, B.; Mateo, A.; Peters, W.; Greiser-Wilke, I. Untersuchungen Zur Antigenstruktur von Pestiviren Mit Hilfe Monoklonaler Antikörper. Dtsch. Tierärztliche Wochenschr. 1987, 94, 572–576. [Google Scholar]
- Cay, B.; Chappuis, G.; Coulibaly, C.; Dinter, Z.; Edwards, S.; Greiser-Wilke, I.; Gunn, M.; Have, P.; Hess, G.; Juntti, N.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Monoclonal Antibodies against Pertiviruses: Report of an International Workshop. Vet. Microbiol. 1989, 20, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.; Greiser-Wilke, I.; Moennig, V.; Liess, B. Preliminary Serological Characterization of Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus Strains Using Monoclonal Antibodies. Vet. Microbiol. 1986, 12, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveringhaus, E.; Cagatay, G.N.; Hardt, J.; Becher, P.; Postel, A. Different Impact of Bovine Complement Regulatory Protein 46 (CD46bov) as a Cellular Receptor for Members of the Species Pestivirus H and Pestivirus G. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärber, G. Beitrag zur kollektiven Behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Für Exp. Pathol. Und Pharmakol. 1931, 162, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schang, L.M.; Jones, C. Analysis of Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Transcripts during a Primary Infection of Trigeminal Ganglia of Cattle. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6786–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, E.; Bertoni, G.; Candrian, U. Detection and Characterization of Pestivirus Contaminations in Human Live Viral Vaccines. Biologicals 2002, 30, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marley, M.S.D.; Givens, M.D.; Galik, P.K.; Riddell, K.P.; Stringfellow, D.A. Development of a Duplex Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Detection of Bovine Herpesvirus 1 and Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus in Bovine Follicular Fluid. Theriogenology 2008, 70, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Xie, J.; Van Cleemput, J.; Wei, R.; Opsomer, G.; Nauwynck, H.J. Gammaherpesvirus BoHV-4 Infects Bovine Respiratory Epithelial Cells Mainly at the Basolateral Side. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steukers, L.; Vandekerckhove, A.P.; Van den Broeck, W.; Glorieux, S.; Nauwynck, H.J. Kinetics of BoHV-1 Dissemination in an In Vitro Culture of Bovine Upper Respiratory Tract Mucosa Explants. ILAR J. 2012, 53, E43–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.; Ramke, M.; Groos, S.; Warnecke, G.; Heim, A. A Differentiated Porcine Bronchial Epithelial Cell Culture Model for Studying Human Adenovirus Tropism and Virulence. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 178, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B.; Kolli, A.R.; Esch, M.B.; Abaci, H.E.; Shuler, M.L.; Hickman, J.J. TEER Measurement Techniques for In Vitro Barrier Model Systems. SLAS Technol. 2015, 20, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geys, J.; Nemery, B.; Hoet, P.H.M. Optimisation of Culture Conditions to Develop an In Vitro Pulmonary Permeability Model. Toxicol. Vitr. 2007, 21, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Einspanier, R.; Schoen, J. Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER): A Functional Parameter to Monitor the Quality of Oviduct Epithelial Cells Cultured on Filter Supports. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 144, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, K.; Tobias, S.; Jan, H.; Nicolas, S.; Michael, M. Measurements of Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) Are Affected by Junctional Length in Immature Epithelial Monolayers. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 156, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, R.; La Rocca, S.A.; Paton, D.; Bensaude, E.; Sandvik, T.; Davis, L.; Turner, J.; Drew, T.; Raue, R.; Vangeel, I.; et al. Viral Dose and Immunosuppression Modulate the Progression of Acute BVDV-1 Infection in Calves: Evidence of Long Term Persistence after Intra-Nasal Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; He, H. Detection of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Genotype 1 in Aerosol by a Real Time RT-PCR Assay. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilleau, G.; Stalder, H.; Almeida, L.; Oliveira Esteves, B.I.; Alves, M.P.; Schweizer, M. The Pestivirus RNase Erns Tames the Interferon Response of the Respiratory Epithelium. Viruses 2024, 16, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galen, B.; Cheshenko, N.; Tuyama, A.; Ramratnam, B.; Herold, B.C. Access to Nectin Favors Herpes Simplex Virus Infection at the Apical Surface of Polarized Human Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12209–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelhaas, M.; Jansen, M.; Haase, I.; Knebel-Mörsdorf, D. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Exhibits a Tropism for Basal Entry in Polarized Epithelial Cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2473–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozin, S.; Prank, U.; Sodeik, B. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Infection of Polarized Epithelial Cells Requires Microtubules and Access to Receptors Present at Cell–Cell Contact Sites. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, A.E.; McGwire, B.S.; Roizman, B. Infection of Polarized MDCK Cells with Herpes Simplex Virus 1: Two Asymmetrically Distributed Cell Receptors Interact with Different Viral Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5087–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, M.H.; Hage, J.J.; van Oirschot, J.T. Airborne Transmission of Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Infections in Calves under Field Conditions. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 76, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steukers, L.; Vandekerckhove, A.P.; Van den Broeck, W.; Glorieux, S.; Nauwynck, H.J. Comparative Analysis of Replication Characteristics of BoHV-1 Subtypes in Bovine Respiratory and Genital Mucosa Explants: A Phylogenetic Enlightenment. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 and Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Latency. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.N.; Inzana, T.J.; Rajagopalan, P. Bovine Airway Models: Approaches for Investigating Bovine Respiratory Disease. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 9, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C. Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Counteracts Immune Responses and Immune-Surveillance to Enhance Pathogenesis and Virus Transmission. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddawi, M.; Mitchell, G.B.; Clark, M.E.; Wood, R.D.; Caswell, J.L. Impairment of Innate Immune Responses of Airway Epithelium by Infection with Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 116, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moerman, A.; Straver, P.J.; de Jong, M.C.M.; Quak, J.; Baanvinger, T.; van Oirschot, J.T. Clinical Consequences of a Bovine Virus Diarrhoea Virus Infection in a Dairy Herd: A Longitudinal Study. Vet. Q. 1994, 16, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutumbetov, L.; Ragatova, A.; Azanbekova, M.; Myrzakhmetova, B.; Aldayarov, N.; Zhugunissov, K.; Abduraimov, Y.; Nissanova, R.; Sarzhigitova, A.; Kemalova, N.; et al. Investigation of the Pathogenesis of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus in Indigenous Cattle in Kazakhstan. Pathogens 2025, 14, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitters, M.; Fritsch, H.; Su, A.; Jung, K.; Becher, P. Application of Bovine Nasal Epithelial Cells as an In Vitro Model for Studying Viral Infection in the Upper Respiratory Tract. Viruses 2025, 17, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091188
Pitters M, Fritsch H, Su A, Jung K, Becher P. Application of Bovine Nasal Epithelial Cells as an In Vitro Model for Studying Viral Infection in the Upper Respiratory Tract. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091188
Chicago/Turabian StylePitters, Malte, Henrik Fritsch, Ang Su, Klaus Jung, and Paul Becher. 2025. "Application of Bovine Nasal Epithelial Cells as an In Vitro Model for Studying Viral Infection in the Upper Respiratory Tract" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091188
APA StylePitters, M., Fritsch, H., Su, A., Jung, K., & Becher, P. (2025). Application of Bovine Nasal Epithelial Cells as an In Vitro Model for Studying Viral Infection in the Upper Respiratory Tract. Viruses, 17(9), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091188






