Foscarnet Versus Ganciclovir for Severe Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Short- and Long-Term Follow-Up
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
Statistical Analysis
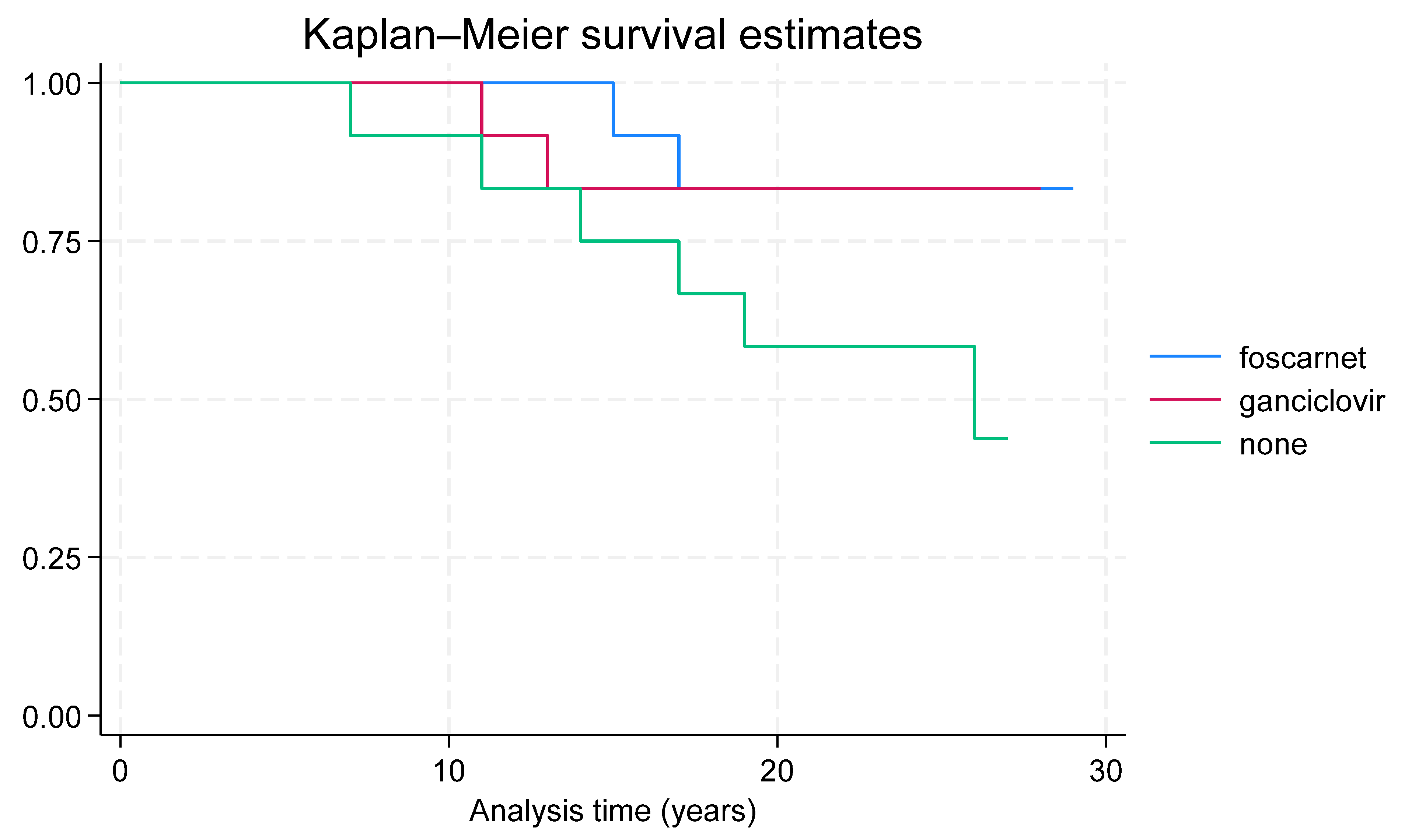
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Congenital CMV Infection: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Centers for Disease Control: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cytomegalovirus/hcp/clinical-overview/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/cmv/clinical/congenital-cmv.html (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Boppana, S.B.; Pass, R.F.; Britt, W.J.; Stagno, S.; Alford, C.A. Symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Neonatal morbidity and mortality. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1992, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, W.J. Maternal immunity and the natural history of congenital human cytomegalovirus infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaunt, G.; Ramin, K. Immunological tolerance of the human fetus. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 2, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, M.; Gallo, V.; Batshaw, M.L. Brain development and the ontogeny of developmental disabilities. Adv. Pediatr. 2002, 49, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pass, R.F.; Fowler, K.B.; Boppana, S.B.; Britt, W.J.; Stagno, S. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection following first trimester maternal infection: Symptoms at birth and outcome. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 35, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, S.P.; Finney, J.W.; Manganello, A.M.; Best, A.M. Prevention of child-to-mother transmission of cytomegalovirus among pregnant women. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, J.; Wolf, D.G.; Levy, I. Treatment of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection with intravenous ganciclovir followed by long-term oral valganciclovir. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Jester, P.M.; Sánchez, P.J.; Ahmed, A.; Arav-Boger, R.; Michaels, M.G.; Ashouri, N.; Englund, J.A.; Estrada, B.; Jacobs, R.F.; et al. for the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. Valganciclovir for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, J.G.; Englund, J.A.; Garcia-Prats, J.A.; Demmler, G.J. Ganciclovir treatment of steroid-associated cytomegalovirus disease in a congenitally infected neonate. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1994, 13, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitley, R.J.; Cloud, G.; Gruber, W.; Storch, G.A.; Demmler, G.J.; Jacobs, R.F.; Dankner, W.; Spector, S.A.; Starr, S.; Pass, R.F.; et al. Ganciclovir treatment of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Results of a phase II study. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, M.M.; Read, S.E.; Benson, M.; Vas, S.; Rachlis, A.; Kozousek, V.; Mortimer, C.; Harvey, P.; Schwartz, E.; Chew, E.; et al. Foscarnet therapy of cytomegalovirus retinitis in AIDS. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1990, 3, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palestine, A.G.; Polis, M.A.; De Smet, M.D.; Baird, B.F.; Falloon, J.; Kovacs, J.A.; Davey, R.T.; Zurlo, J.J.; Zunich, K.M.; Davis, M.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of foscarnet in the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis in patients with AIDS. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 115, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulds, D.; Heel, R.C. Ganciclovir: A review of its antiviral activity, pharmacockinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy in cytomegalovirus infections. Drugs 1990, 39, 597–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrisp, P.; Clissold, S.P. Foscarnet. A review of its antiviral activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in immunocompromised patients with cytomegalovirus retinitis. Drugs 1991, 41, 104–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, G.; Scholz, H.; Bartmann, U. Ganciclovir therapy for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection in infants: A two-regimen experience. J. Pediatr. 1994, 124, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, R.C.; Whitcup, S.M.; Mueller, B.U.; Lewis, L.L.; Pizzo, P.A.; Nussenblatt, R.B. Combined intravenous ganciclovir and foscarnet for children with recurrent cytomegalovirus retinitis. Ophtalmology 1995, 102, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, G.; Sali, E.; Anceschi, M.M.; Mazzocco, M.; Maranghi, L.; Clerico, A.; Castello, M.A. Foscarnet therapy for congenital cytomegalovirus hepatic fibrosis following prenatal ascites. J. Mat. Fet. Neon. Med. 2004, 15, 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, G. Hyperimmune globulin in pregnancy for prevention of congenital cytomegalovirus disease. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2017, 15, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, J.; Chodick, G.; Pardo, J. Revised protocol for secondary prevention of congenital cytomegalovirus infection with valaciclovir following infection in early pregnancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 77, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Sex Maternal Infection Birth Date | Main Neurological Abnormalities | Hearing | Short-Term Outcomes (2 Years) | Long-Term Outcomes (Years of Follow-Up) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. M Primary 13.03.99 | Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Right deafness | Right deafness Left hypoacusia | Mental retardation Bilateral deafness (23) |
| 2. M Non-primary 19.03.97 | Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Normal | Normal | Normal (26) |
| 3. F Primary 13.02.96 | Microcephaly Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Right hypoacusia | Mental motor retardation Right hypoacusia | Mental motor retardation Right deafness (28) |
| 4. F Non-primary 29.09.95 | Microcephaly Calcifications Lissencephaly Ventriculomegaly | Left hypoacusia | Mental retardation Tetraparesis Left hypoacusia | Severe mental retardation Tetraparesis Left deafness (27) |
| 5. M Primary 12.09.95 | Microcephaly Ventriculomegaly Cerebral and cerebellar hypoplasia | Left deafness | Mental retardation Bilateral deafness | Mental retardation Bilateral deafness (28) |
| 6. M Primary 20.04.96 | Microcephaly Ventriculomegaly Calcifications Schizencephaly | Bilateral deafness | Severe mental retardation Tetraplegia Bilateral deafness | Severe mental retardation Tetraplegia Bilateral deafness Death (15) |
| 7. M Non-primary 14.11.95 | Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Right hypoacusia | Normal | Normal (29) |
| 8. M Non-primary 31.09.96 | Microcephaly Calcification Leukoencephalopathy | Normal | Mental retardation | Mental retardation Bilateral hypoacusis (27) |
| 9. M Primary 15.03.98 | Microcephaly Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Bilateral hypoacusia | Bilateral hypoacusia | Mental retardation Bilateral deafness (21) |
| 10. M Primary 06.09.98 | Microcephaly Calcifications Lissencephaly Ventriculomegaly | Normal | Mental retardation Paraparesis | Tetraparesis Bilateral hypoacusia Death (17) |
| 11. F Primary 25-11-97 | Calcifications Ventriculomegaly Chorioretinitis | Right hypoacusia | Motor retardation Right hypoacusia Visual impairment | Mental motor retardation Bilateral hypoacusia Visual impairment (21) |
| 12. M Non-primary 21.05.97 | Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Left hypoacusia | Left hypoacusia | Left deafness (28) |
| Patient Sex Maternal Infection Birth Date | Main Neurological Abnormalities | Hearing | Short-Term Outcomes (2 Years) | Long-Term Outcomes (Years of Follow-Up) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. M Non-primary 2-02-98 | Microcephaly Polymicroyria Ventriculomegaly | Bilateral hypoacusia | Mental retardation Bilateral hypoacusia | Mental retardation Bilateral hypoacusia (26) |
| 2. M Primary 27-06-99 | Calcifications Microcephaly Leukoencephalopathy | Normal | Mental retardation | Mental retardation Left hypoacusia (25) |
| 3. M Primary 03-08-97 | Microcephaly Calcifications Cerebral aplasia | Left deafness | Severe mental retardation Tetraparesis Left deafness | Severe mental retardation Tetraplegia Bilateral deafness Death (13) |
| 4. M Non-primary 17-09-95 | Microcephaly Calcifications Lissencephaly Hydrocephalus | Bilateral deafness | Severe mental retardation Tetraparesis Bilateral deafness | Tetraplegia Bilateral deafness Death (11) |
| 5. F Primary 29.12.95 | Microcephaly Calcifications Cerebral hypoplasia | Right hypoacusia | Mental motor retardation Right hypoacusia | Mental motor retardation Right deafness (28) |
| 6. F Non-primary 30.03.97 | Microcephaly Ventriculomegaly Cerebral hypoplasia | Normal | Normal | Normal (27) |
| 7. M Non-primary 06.05.96 | Microcephaly Calcifications Leukoencephalopathy | Normal | Mental motor retardation | Mental motor retardation (24) |
| 8. M Non-primary 31-06-98 | Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Bilateral deafness | Bilateral deafness | Mental retardation Bilateral deafness (25) |
| 9. M Primary 13.11.95 | Ventriculomegaly Cerebral hypoplasia Chorioretinitis | Normal | Visual impairment | Mental retardation Visual impairment (26) |
| 10. M Primary 26-03-96 | Microcephaly Calcifications Ventriculomegaly | Normal | Mental motor retardation | Mental retardation Paraparesis (28) |
| 11. F Primary 24-01-97 | Cerebral hypoplasia Ventriculomegaly Hemiplegia | Normal | Right hemiparesis | Right hemiparesis (27) |
| 12. M Primary 12-01-99 | Microcephaly Calcifications Ventriculomegaly | Normal | Mental motor retardation | Mental motor retardation (24) |
| Patient Sex Maternal Infection Birth Date | Main Neurological Abnormalities | Hearing | Short-Term Outcomes (2 Years) | Long-Term Outcomes (Years of Follow-Up) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. F Primary 10.07.98 | Leukoencephalopathy Ventriculomegaly Paraplegia | Normal | Mental retardation Right hypoacusia Paraplegia | Mental retardation Bilateral hypoacusia Tetraparesis (24) |
| 2. M Non-primary 19-11-97 | Microcephaly Cerebral and cerebellar hypoplasia | Bilateral hypoacusia | Mental motor retardation Bilateral deafness | Mental retardation Bilateral deafness (26) |
| 3. M Non-primary 04.11.95 | Hydrocephalus Cerebral hypoplasia Chorioretinitis | Normal | Severe mental motor retardation Left hypoacusia Visual impairment | Tetraplegia Blindness Bilateral hypoacusia Death (26) |
| 4. M Primary 21.11.06 | Cerebral and cerebellar hypoplasia Calcifications Hydrocephalus | Bilateral hypoacusia | Severe mental motor retardation Bilateral hypoacusia | Severe mental retardation Tetraparesis Bilateral deafness Death (14) |
| 5. M Primary 12.05.97 | Cerebral and cerebellar hypoplasia Calcifications Lissencephaly | Bilateral deafness | Severe mental motor retardation Bilateral deafness | Severe mental retardation Tetraplegia Bilateral deafness Death (7) |
| 6. M Non-primary 12.05.98 | Microcephaly Ventriculomegaly Tetraparesis | Normal | Mental retardation Tetraparesis | Severe mental retardation Tetraplegia Bilateral hypoacusia Death (11) |
| 7. M Non-primary 21.09.97 | Microcephaly Cerebral hypoplasia Calcifications Leukoencephalopathy | Bilateral hypoacusia | Severe mental motor retardation Bilateral hypoacusia | Tetraplegia Bilateral deafness Death (19) |
| 8. F Primary 10.01.99 | Microcephaly Calcifications Ventriculomegaly | Normal | Mental motor retardation Left hypoacusia | Bilateral hypoacusia Mental motor retardation (24) |
| 9. M Primary 19.02.97 | Microcephaly Cerebral atrophy Leukoencephalopathy | Bilateral hypoacusia | Mental motor retardation Bilateral deafness | Severe mental motor retardation Bilateral deafness (26) |
| 10. F Primary 27-2-98 | Cerebral atrophy Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy | Normal | Mental motor retardation | Mental retardation Paraparesis (25) |
| 11. M Primary 27.02.96 | Microcephaly Ventriculomegaly Leukoencephalopathy Chorioretinitis | Bilateral hypoacusia | Mental motor retardation Bilateral deafness Visual impairment | Mental retardation Bilateral deafness Blindness (27) |
| 12. M Non-primary 11.06.96 | Microcephaly Calcifications Paraplegia | Bilateral hypoacusia | Severe mental motor retardation Bilateral hypoacusia | Tetraparesis Bilateral deafness Death (17) |
| Foscarnet n = 12 | Ganciclovir n = 12 | No Therapy n = 12 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At birth | ||||
| Neurological abnormalities | 12 (100.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | - |
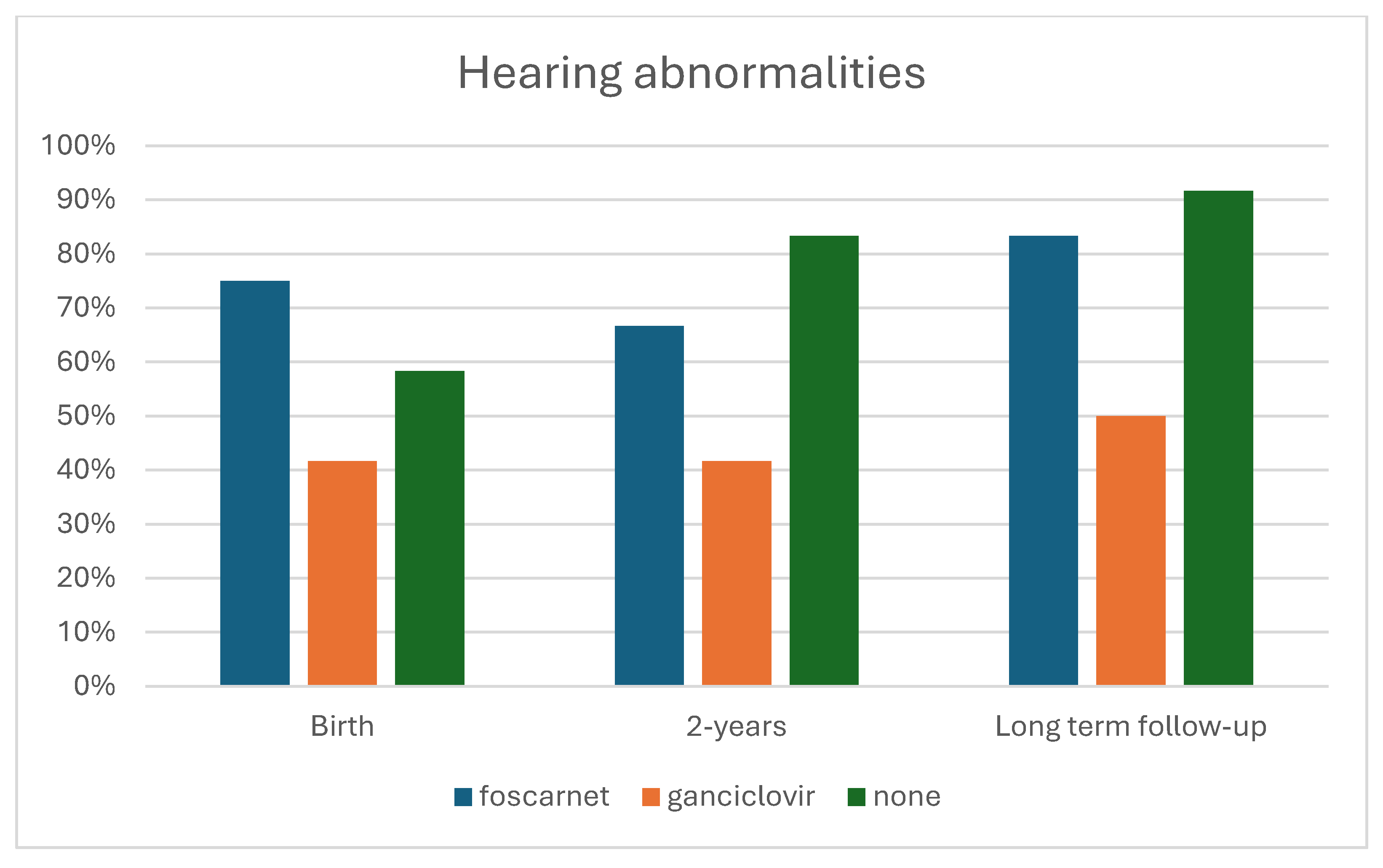
| Hearing abnormalities | 9 (75.0%) | 5 (41.7%) | 7 (58.3%) | 0.254 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Short-term outcomes (2 years) | ||||
| Neurological abnormalities | 7 (58.3%) | 9 (75.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.047 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 8 (66.7%) | 5 (41.7%) | 10 (88.9%) | 0.102 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Long-term outcomes (24 years) | ||||
| Neurological abnormalities | 9 (75.0%) | 10 (88.9%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.197 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 10 (88.9%) | 6 (50.0%) | 11 (91.7%) | 0.045 |
| Death | 2 (16.7%) | 2 (16.7%) | 6 (50.0%) | 0.109 |
| Therapy n = 24 | No Therapy n = 12 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At birth | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 24 (100.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | - |
| Hearing abnormalities | 14 (58.3%) | 7 (58.3%) | 1.000 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Short-term outcomes (2 years) | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 16 (66.7%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.023 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 13 (54.2%) | 10 (88.9%) | 0.086 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Long-term outcomes (24 years) | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 19 (79.2%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.088 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 16 (66.7%) | 11 (91.7%) | 0.102 |
| Death | 4 (16.7%) | 6 (50.0%) | 0.035 |
| Foscarnet n = 12 | No Therapy n = 12 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At birth | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 12 (100.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | - |
| Hearing abnormalities | 9 (75.0%) | 7 (58.3%) | 0.386 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Short-term outcomes (2 years) | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 7 (58.3%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.012 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 8 (66.7%) | 10 (88.9%) | 0.346 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Long-term outcomes (24 years) | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 9 (75.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.064 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 10 (88.9%) | 11 (91.7%) | 0.537 |
| Death | 2 (16.7%) | 6 (50.0%) | 0.083 |
| Ganciclovir n = 12 | No Therapy n = 12 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At birth | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 12 (100.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | - |
| Hearing abnormalities | 5 (41.7%) | 7 (58.3%) | 0.414 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Short-term outcomes (2 years) | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 9 (75.0%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.064 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 5 (41.7%) | 10 (88.9%) | 0.035 |
| Death | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | - |
| Long-term outcomes (24 years) | |||
| Neurological abnormalities | 10 (88.9%) | 12 (100.0%) | 0.140 |
| Hearing abnormalities | 6 (50.0%) | 11 (91.7%) | 0.025 |
| Death | 2 (16.7%) | 6 (50.0%) | 0.083 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nigro, G.; Buzzi, M.; Catenaro, M.; Coclite, E.; Muselli, M. Foscarnet Versus Ganciclovir for Severe Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Short- and Long-Term Follow-Up. Viruses 2025, 17, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050720
Nigro G, Buzzi M, Catenaro M, Coclite E, Muselli M. Foscarnet Versus Ganciclovir for Severe Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Short- and Long-Term Follow-Up. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050720
Chicago/Turabian StyleNigro, Giovanni, Marta Buzzi, Milena Catenaro, Eleonora Coclite, and Mario Muselli. 2025. "Foscarnet Versus Ganciclovir for Severe Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Short- and Long-Term Follow-Up" Viruses 17, no. 5: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050720
APA StyleNigro, G., Buzzi, M., Catenaro, M., Coclite, E., & Muselli, M. (2025). Foscarnet Versus Ganciclovir for Severe Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Short- and Long-Term Follow-Up. Viruses, 17(5), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050720






