Abstract
In 2011–2013, we isolated and characterized small ruminant lentiviruses (SRLVs) from two flocks, one of goats and the other of sheep, that had never been in direct contact. Phylogenetic analysis of these viruses indicated a common origin, which led us to hypothesize indirect transmission of these viruses between the two flocks. Since, to our knowledge, there are no published data on the tenacity of these viruses, we started this work. In the first part, we monitored the loss of infectivity of two prototypic SRLV strains, MVV 1514 and CAEV-CO, over time, in liquid suspension. As expected, the suspensions stored at 4 °C better preserved the infectivity of the viruses. Additionally, viruses resuspended in milk, the medium mirroring the in vivo situation, proved more tenacious than those maintained in a cell culture medium. These viruses, subjected to harsh treatments such as drying and resuspending, partially maintained their replication capacity. After an immediate loss of nearly 1 log10 TCID50 immediately after desiccation, the viruses maintained their replication capacity for at least three weeks when desiccated in milk. These results suggest that fomites, clothing, or pastures contaminated with secretions or milk from infected animals might mediate the infection of animals independently of direct contact.
Keywords:
small ruminant lentiviruses; CAEV; MVV; VMV; tenacity; stability; replication capacity; transmission; fomites 1. Introduction
Maedi-visna virus (MVV) and caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus (CAEV) belong to the genus Lentivirus of the Retroviridae family. Due to their seemingly different hosts and discovery times, these viruses were long thought to be species-specific to sheep and goats, respectively. Further investigation has revealed that most small ruminant lentivirus (SRLV) genotypes are promiscuous and are now assigned to the group of SRLV. SRLVs are geographically widely distributed and consist of the following five different genotypes: A (prototypical MVV), B (prototypical CAE), and the more recently discovered C, D, and E genotypes, with each genotype further divided into subtypes [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Trading is considered the principal factor in the worldwide dissemination of these viruses, the most prominent example being the importation of infected sheep to Iceland in the year 1933, which led to the infection of the local sheep and the first description of the pathological signs induced by SRLVs such as Maedi (dyspnea) and Visna (wasting) [14,15]. Recently, however, a study failed to detect the Icelandic subtype (A1) in German sheep, questioning the introduction of the virus into Iceland through the importation of Karakul sheep from Germany [16]. This notwithstanding, MVV caused substantial economic losses in Iceland, being responsible for the death of approximately 100,000 sheep [17,18].
The pathogenesis of these viruses is similar and influenced by factors such as the virus’s genotype and subtype, the infected host’s genetics, and the management of the flock. Except for rare acute manifestations, such as myeloencephalitis in young kids, SRLVs have common pathogenic traits, such as a long clinical latency of months to years, a subtle development of pathologic lesions, and a slow clinical evolution. The organs affected are similar in the two species, but the lesions and, thus, the clinical manifestations are distributed differently. Interstitial pneumonia with progressive respiratory failure and wasting predominate in sheep, while multifocal arthritis, involving, in particular, the carpal joint, prevails in goats [19,20,21]. The mammary gland is affected in both species, with interstitial, indurative mastitis being the cause of important economic losses and epidemiologic consequences by reducing the quantity and quality of milk and mediating an efficient vertical transmission of the infection [22,23,24]. The abundance of macrophages in colostrum and the pronounced tropism of SRLVs for these cells ensure the efficient infection of kids via colostrum intake [25]. Horizontal transmission is a proven way of transmission, especially in young animals, and plays a prominent role in sheep, where vertical transmission may be less important [26,27].
Several routes of virus transmission are described in the literature, which, in addition to the colostral and respiratory routes, also contemplates venereal transmission, embryo transfer, iatrogenic transmission, and, more controversially, intrauterine transmission [25,28]. Transmission via fomites is described, but its importance is considered minor, although difficult to assess, mainly because of the lack of information on the tenacity of these viruses when exposed to environmental factors [29].
In 2011–2013, we analyzed a case of virus transmission from a flock of sheep to goats in an epidemiological context that tended to rule out any direct contact, suggesting possible transmission of infection via fomites [30]. To confirm or refute the plausibility of this hypothesis, in this work, we set out to characterize the tenacity of the virus when exposed to conditions similar to those potentially present in the field. Milk was used as the vehicle for the virus because lactogenic infection is considered one of the most efficient mediators of infection, and aerosols generated during milking could also transmit the infection [31]. SRLVs can be isolated from cell-free milk and milk cells, and the viral load in milk-associated cells is much higher than that observed in other tissues [32,33]. In analogy to experiments performed with HIV, where the virus showed a surprising sturdiness in dry blood [34,35], we tested the tenacity of SRLVs in wet and dry conditions using milk or tissue culture medium spiked with the virus.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus
Caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus (CAEV-CO), accession number M33677 (CEAVCG), was selected for our experiments. This virus is the prototypical representative of SRLV subtype B1. The virus was generated by transfecting goat synovial membrane (GSM) cells with a molecular clone of the virus with restored dUTPase activity, generously provided by Yahia Chebloune [36,37,38]. A viral stock of 6.125 log10 TCID50 was used for all of the experiments. Maedi-visna virus (MVV 1514: Visna virus Icelandic strain 1514), accession number M60609 [39], was a generous gift from Prof. Sergio Rosati, Università degli Studi di Torino. This virus belongs to the A1 subtype of SRLVs. It was first isolated from a sheep and is the prototypical virus causing maedi-visna in sheep. A viral stock of 5.8 log10 TCID50 was used for all of the experiments.
2.2. Nutrient Medium
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM—Seraglob, Switzerland, lot 410/631450), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (PAAN Biotech, Aidenbach, Germany, lot 190902), 1% Non-Essential Amino Acid (Seraglob, Switzerland, lot 410/821695), 0.5% of Penicillin–Streptomycin (Seraglob, Switzerland, lot 610/134072), and 1% of Amphotericin B (Seraglob, Switzerland, lot 610/763549) was used.
2.3. Drying Medium
As described above, DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS was used as a standard drying medium. To mimic natural conditions, commercially available pasteurized goat milk (milk), with a fat content of 3.5% (Molkerei Biedermann AG, Bischofszell, Switzerland), was also used.
2.4. Cells
GSM cells were used for the cultivation and titration of CAEV, while primary lamb synovial membrane (LSM) cells were used for the cultivation and titration of MVV. GSM and LSM cells were obtained as described previously [40].
2.5. Virus Stored in Liquid
Nutrient medium and milk were supplemented with 2.5% Penicillin–Streptomycin (Seraglob, Switzerland, lot 610/134072) and 1% of Amphotericin B (Seraglob, Switzerland, lot 610/763549) to prevent possible bacterial or fungal contamination. A working dilution of viruses was prepared by resuspending viral stocks in a nutrient medium or milk. The dilutions were prepared in a volume of 3 mL for every condition and every foreseeable timepoint and then aliquoted (1 mL into 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes) and stored under the following conditions:
Room temperature (RT)—tubes were stored at ambient room temperature (18–25 °C) and were shielded from direct sunlight. At 4 °C—tubes were stored in a refrigerator in the dark at a stable temperature of 4 °C. At the control time points (7, 14, and 21 days), three tubes for each condition were taken and titrated by limiting the endpoint dilution. In our Institute’s accreditation frame, the temperatures in the laboratories and refrigerators where the viruses were stored were monitored daily. To assess the tenacity of the viruses, 3 tubes for both milk and the nutrient medium and at each temperature were taken and titrated via 10-fold dilution in quadruplicates on 96-well tissue culture plates that were previously seeded with primary cells (LSM for MVV and GSM for CAEV) at 50% confluency.
The plates were incubated for 12 days and stained using the Hemacolor® staining kit (Hemacolor®, Merck, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. At this point, the plates were scored under a brightfield microscope for the presence of syncytia. The Spearman–Kärber method was used to calculate the titers [41].
2.6. Virus Dried, Stored, and Resuspended
The virus stock dilutions were prepared as outlined in the preceding section, and the drying process was carried out in standard cell-culture 6-well plates (TPP AG, Trasadingen, Switzerland). The virus-containing milk or medium was inoculated into the empty wells of the 6-well plate, which was then placed into a biosafety laminar-flow cabinet with an open lid and left to dry at room temperature for 8 h. The day on which the plates were prepared and dried was designated as day 0.
The plates containing the dried viruses were then stored at room temperature (18–25 °C) or in a refrigerator at 4 °C, shielded from direct sunlight. At each control point (0, 7, 14, and 21 days), three plates from both RT and 4 °C for each virus and the two drying media were tested for replication-competent viruses.
The dried residue in each well was resuspended by adding 1 mL of DMEM+FBS, and 100 µL of the resuspended material was transferred into an Eppendorf tube containing 900 µL of fresh cell culture medium. A 10-fold dilution of the material was performed and finally transferred in quadruplicates to 96-well tissue culture plates seeded with primary cells (LSM for MVV and GSM for CAEV) at 50% confluency. The plates were incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere for 8 h, after which the supernatant was substituted with 100 μL of fresh DMEM + FBS medium.
Incubation, staining, and readout were performed as outlined in Section 2.6.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses and visualizations were performed using GraphPad Prism version 10.1.2 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to assess the normality of the data distribution. Two-way ANOVA was performed to analyze group differences in the time-course experiments. A Student’s t-test was used to evaluate the immediate effect of drying on virus infectivity. A p-value of less than 0.05 (p < 0.05) was considered statistically significant for all analyses.
3. Results
3.1. Virus Stored in Liquid
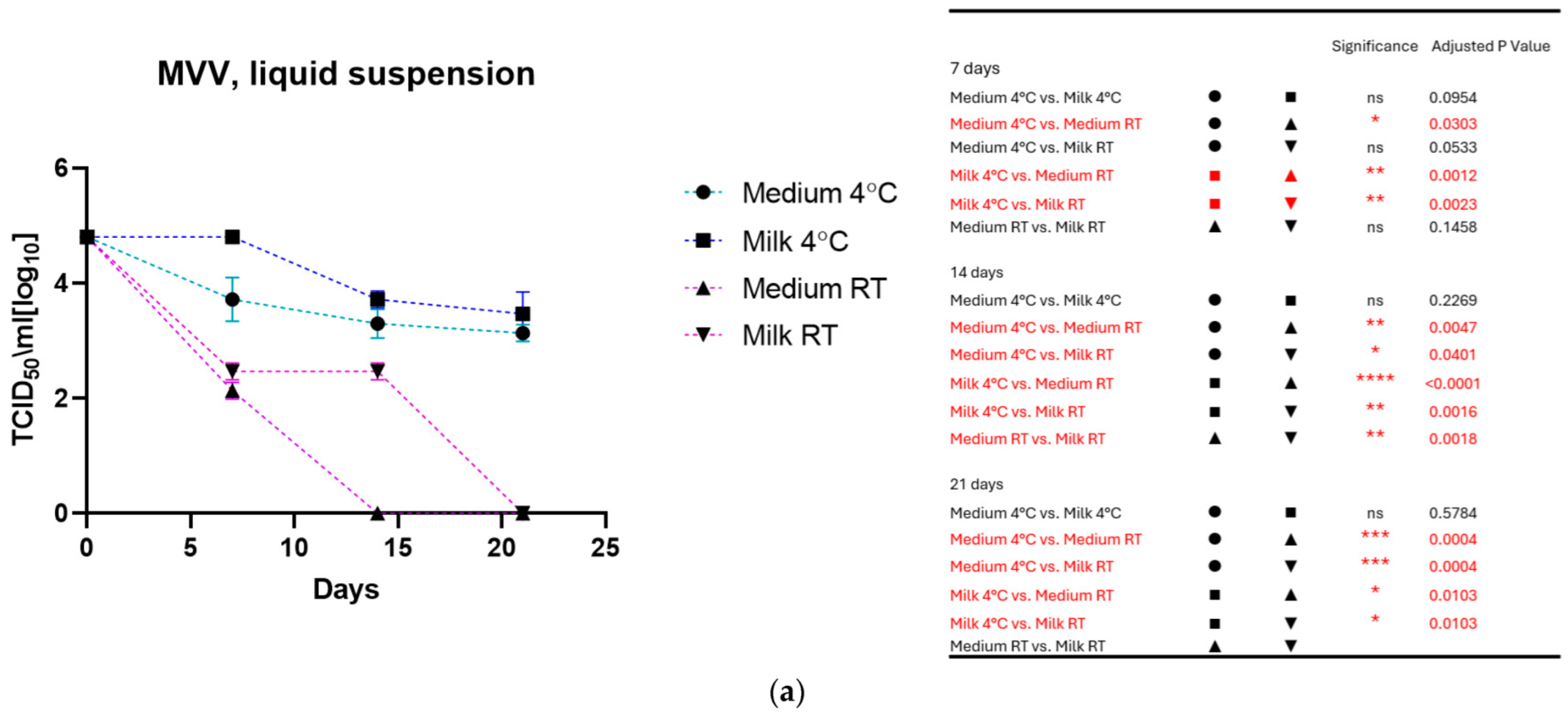
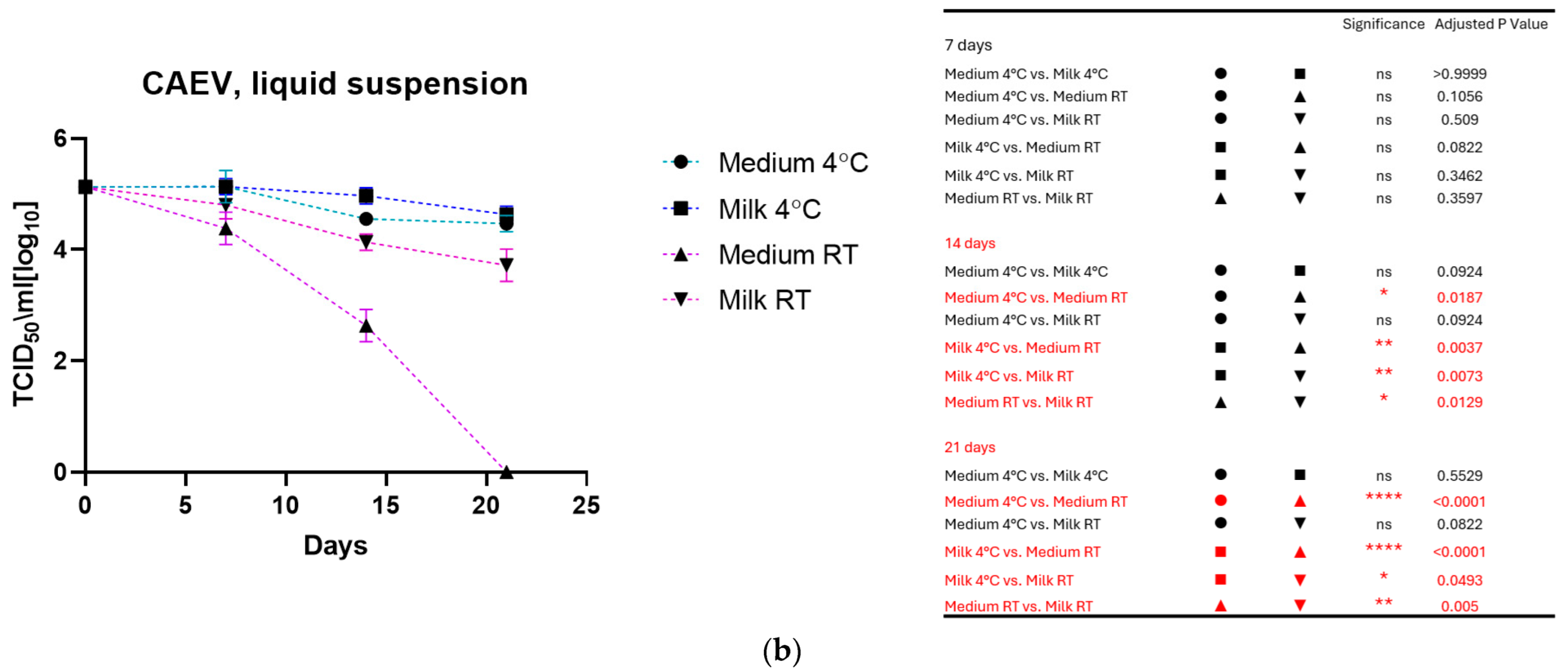
As shown in Figure 1a for MVV and Figure 1b for CAEV, the viruses incubated in the medium and milk at 4 °C were still infectious after three weeks, losing about 1 log10 TCID50. In contrast, storage at room temperature dramatically impacted infectivity. MVV lost its replication capacity after 2 weeks in the medium and about 2 log10 TCID50 in the milk. After three weeks, no infectious MVV could be recovered. CAEV was no longer infectious after 3 weeks of incubation at RT in the medium, but infectious viruses could be recovered when incubated in milk.
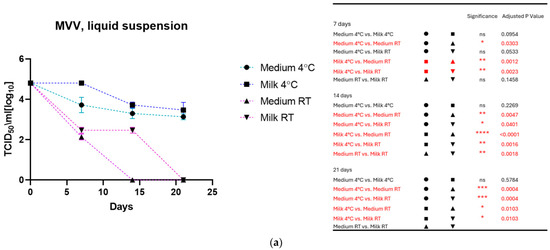
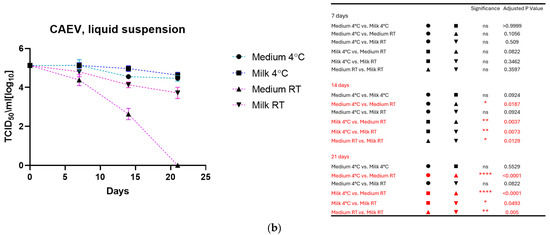
Figure 1.
(a) (MVV) and (b) (CAEV). The loss of infectivity of the virus suspensions over time is illustrated. Regardless of the storage liquid, the temperature of 4 °C has a noticeable protective effect. Remarkably, milk preserves the infectivity of virus suspensions better than the culture medium at room temperature. This was particularly evident for CAEV in Figure 1b. The table on the right shows the pairings with significant differences and the respective p-values, calculated by two-way ANOVA (ns: not significant, *—p-value < 0.05, **—p-value < 0.01, ***—p-value < 0.001, ****—p-value < 0.0001).
3.2. Virus: Dried, Stored, and Resuspended
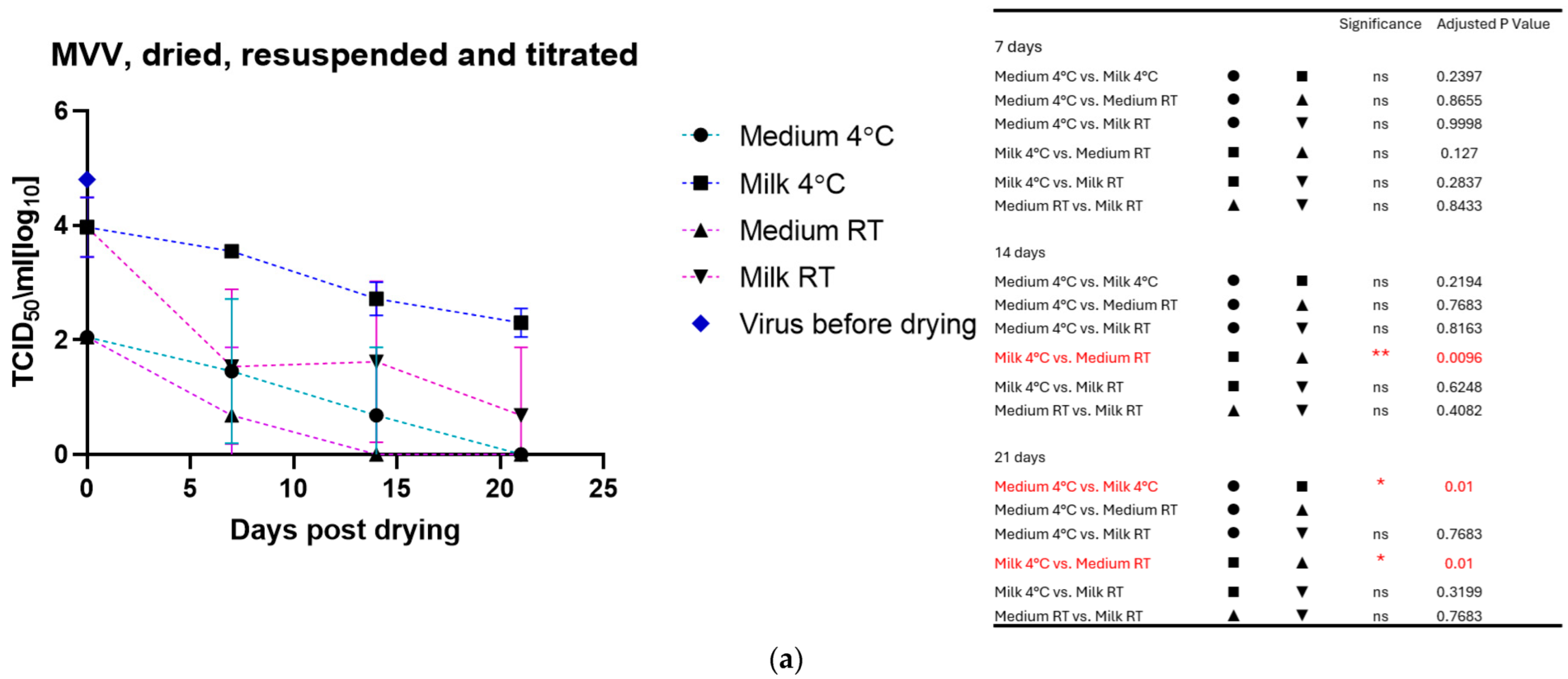
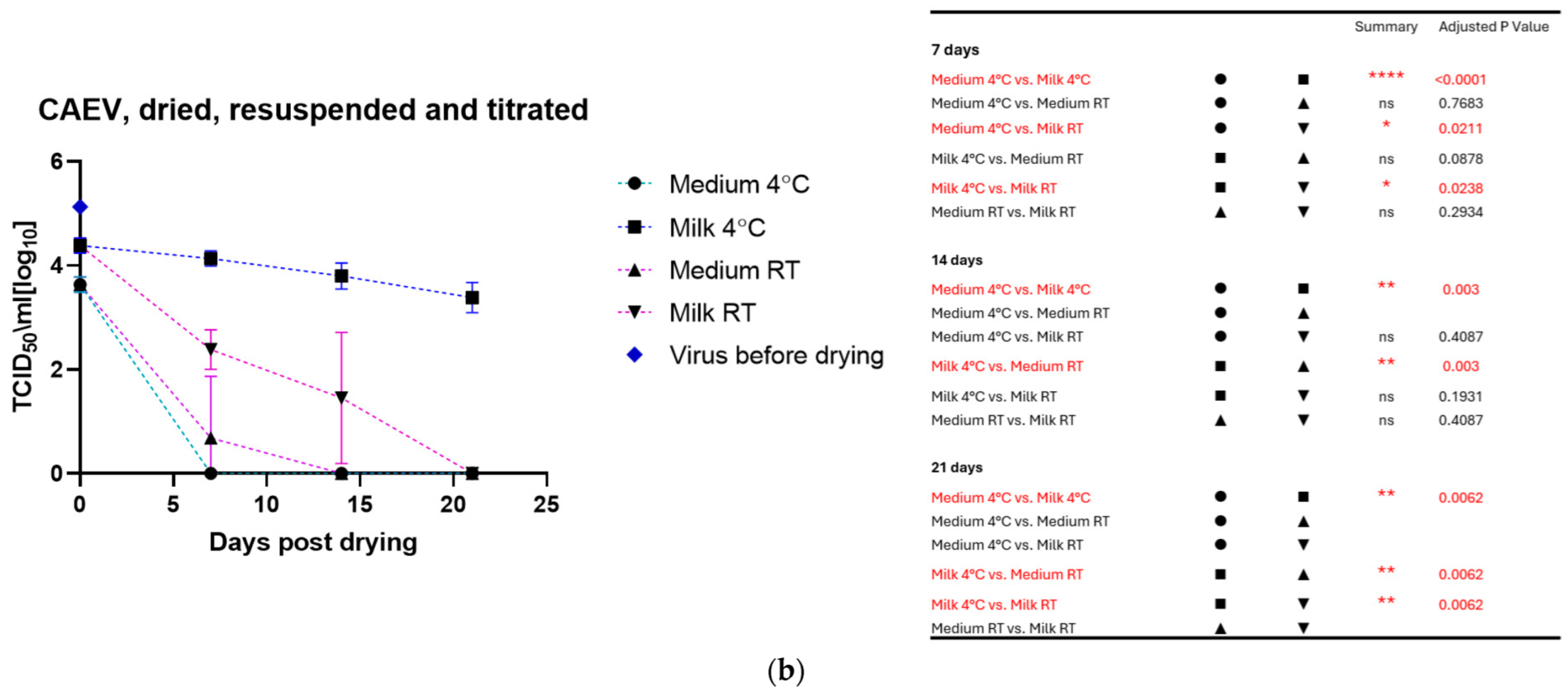
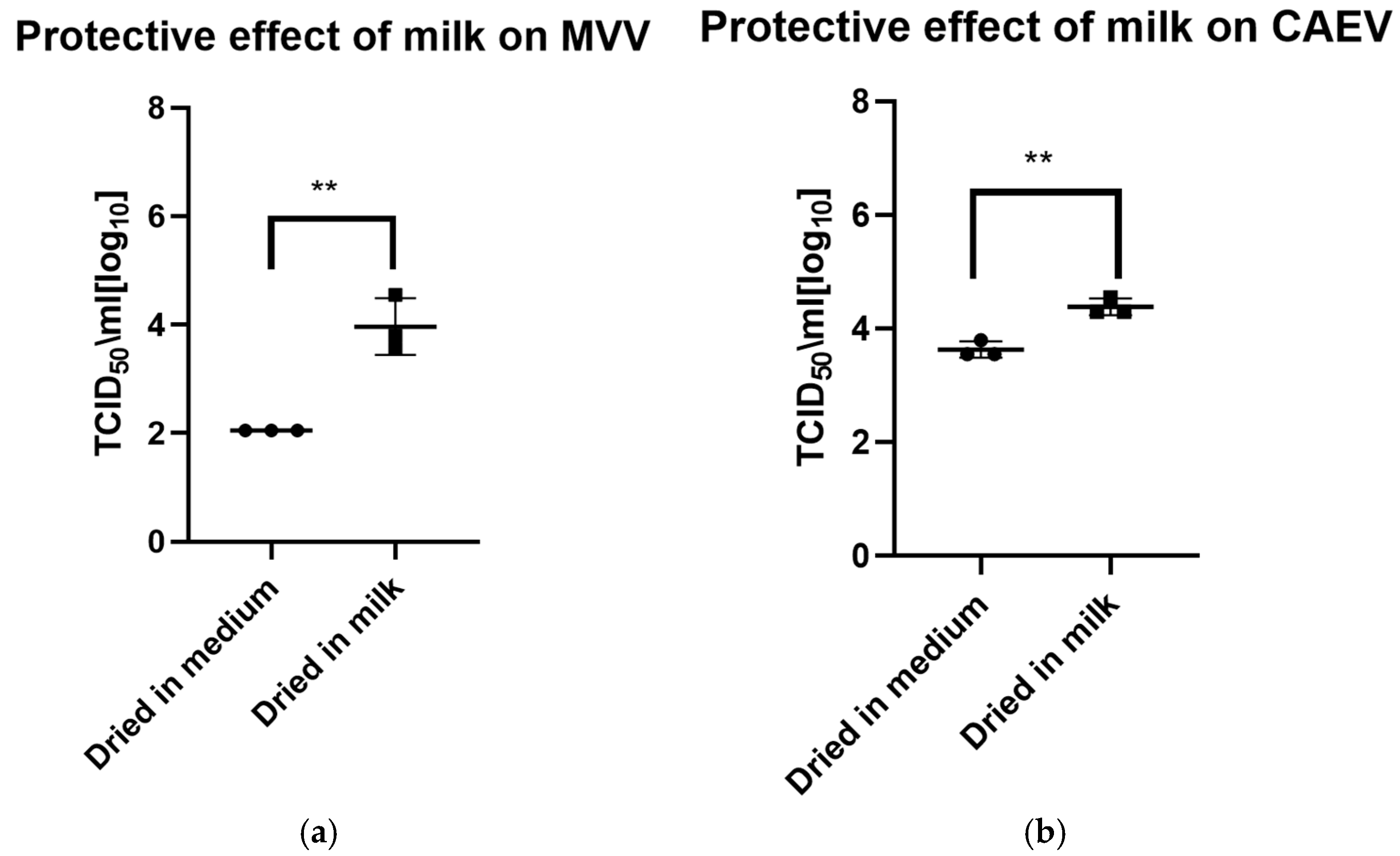
The drying process impacted the infectivity of both viruses, which lost about half to 1 log10 TCID50 immediately after drying. As for the viruses in liquid suspension, the storage temperature substantially impacted the tenacity of these viruses, as shown in Figure 2a for MVV and Figure 2b for CAEV. For both viruses, the presence of milk during the drying process showed a protective effect, permitting the recovery of infectious viruses for a more extended time period. This substantial protective role of milk is illustrated in Figure 3a for MVV and Figure 3b for CAEV.
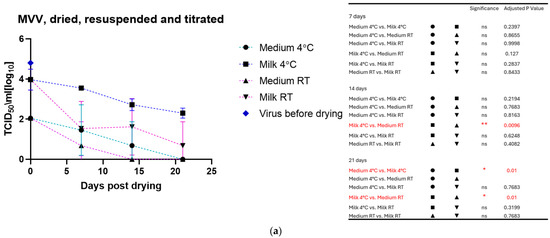
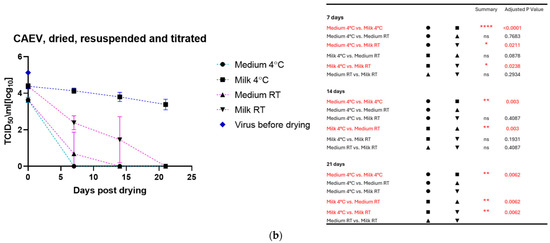
Figure 2.
(a) (MVV) and (b) (CAEV). Virus suspensions were dried, stored for different periods, and resuspended immediately before titration. The blue square shows the titer of the virus stock used. Storage in dry conditions induces a loss of infectivity over time, which is more pronounced at RT than at 4 °C. Independently of the storage temperature, milk shows an evident protective role in the infectivity of the stored virus preparations. The table on the right shows the pairings with significant differences and the respective p-values, calculated by two-way ANOVA (ns: not significant, *—p-value < 0.05, **—p-value < 0.01, ****—p-value < 0.0001).
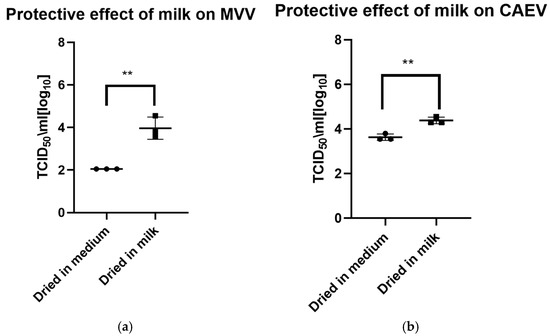
Figure 3.
(a) (MVV) and (b) (CAEV). Virus suspensions in tissue culture medium or milk were dried for 8 h. The following day, the dried material was rehydrated and resuspended in the same volume as before drying and immediately titrated. Milk showed a robust protective effect on the infectivity of MVV and CAEV, with a p-value of 0.0031 ** in both cases.
4. Discussion
In contrast to other viruses, to our knowledge, the tenacity of small ruminant lentiviruses has not yet been studied in detail [42]. The ability of these viruses to maintain their replication capacity (a term adopted from reference [42]) in the environment when exposed to a hostile milieu determines their potential ability to infect animals without direct contact, such as by grazing on a pasture previously used by infected animals or through contamination of caretakers’ clothing or fomites.
For our experiments, we chose two prototypic viruses for the two main genotypes, A (MVV 1514) and B (CAEV-CO), aware that this may limit the generalization of our results. Primary isolates would have been ideal, but these viruses often have a strict tropism for macrophages, making their titration extremely cumbersome.
Our experiments demonstrate the relative resilience of these viruses even under harsh conditions, such as drying and storage for several days before reconstitution and titration. For all conditions, milk appears to stabilize the viruses, and, not surprisingly, the lower storage temperature also positively affects the preservation of infectivity. This is in line with previously published observations of HIV, showing that the infectivity of the virus was preserved for a more extended period in blood or plasma compared to tissue culture medium [34].
The milk of SRLV-infected animals contains high titers of virus and numerous virus-infected cells, such as macrophages, that may contaminate the environment, pastures, fodder, and hands and clothes of people attending sheep and goats [32]. We also attempted to reproduce these results using infected cells instead of infectious virus in suspension.
The variability between the samples was too large to obtain significant results, but a clear trend mirrored the results obtained with viruses in suspension. The tenacity of these viruses, demonstrated in this work, makes their transmission from flock to flock by fomites or shared pastures plausible. This validates our original hypothesis that genetically very closely related viruses detected in two strictly separated flocks of sheep and goats may be a case of fomite-mediated transmission [30,43]. The application of strict biosafety rules will prevent such occurrences in the future. Similarly, circulating SRLVs in wild ruminants may originate from pasture contamination rather than direct contact between wild and farmed animals [44].
In conclusion, we must emphasize that our results do not yet allow us to determine the actual risk of SRLV transmission via fomites. Indeed, to answer this question, it will be necessary to establish the minimal infectious titer of these viruses in vivo, especially by the oral route. Indeed, the infectious titers required to infect an animal were shown to be very low for intratracheal infection but were estimated to be much higher for intranasal infection and the oral route [31,45].
Author Contributions
G.B. and M.S. conceived this work. M.S. and G.B. designed the experiments. M.S. generated the data. M.S., G.B. and V.N. analyzed these data. M.S. prepared the original draft. M.S., G.B. and V.N. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are indebted to the Federal Food Safety and Veterinary Office (FSVO) for financial support: Grant # 1.21.13.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data are available upon request at: maksym.samoilenko@unibe.ch.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Astrid Glück, Cristina Huber, and Marie-Luise Zahno, who conducted the preliminary experiments for this project. The technical support of Caroline Lehmann, Antoinette Golomingi, and Guadalupe Camina was highly appreciated. We are indebted to Sergio Rosati, Dipartimento di Scienze Veterinarie, University of Turin, Italy, and Yahia Chebloune, PAVAL Lab., Grenoble Alpes University, Grenoble, France, for providing the viruses used in this study (MVV 1514 and CAEV-CO, respectively).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SRLV | Small ruminant lentiviruses |
| MVV | Maedi-visna virus |
| CAEV | Caprine arthritis encephalitis virus |
| LSM | Lamb synovial membrane cells |
| GSM | Goat synovial membrane cells |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| RT | Room temperature |
References
- Olech, M.; Kuzmak, J.; Kycko, A.; Junkuszew, A. Phylogenetic analysis of small ruminant lentiviruses originating from naturally infected sheep and goats from poland based on the long terminal repeat sequences. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 66, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, R.; Adjadj, N.R.; De Regge, N. Phylogenetic analysis of belgian small ruminant lentiviruses supports cross species virus transmission and identifies new subtype b5 strains. Pathogens 2020, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhar, U.; Barlic-Maganja, D.; Zadnik, T.; Grom, J. Molecular and genetic characteristics of small ruminant lentiviruses in slovenia. Acta Vet. Hung. 2013, 61, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Homme, Y.; Ouardani, M.; Levesque, V.; Bertoni, G.; Simard, C.; Pisoni, G. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of small ruminant lentiviruses isolated from Canadian sheep and goats. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, C.; Cruz, J.C.; Mornex, J.F. Srlvs: A genetic continuum of lentiviral species in sheep and goats with cumulative evidence of cross species transmission. Curr. HIV Res. 2010, 8, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, R.; Mora, M.I.; Glaria, I.; Garcia, I.; Solano, C.; Lujan, L.; Badiola, J.J.; Contreras, A.; Berriatua, E.; Juste, R.; et al. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic study of Maedi visna and caprine arthritis encephalitis viral sequences in sheep and goats from spain. Virus Res. 2006, 121, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerset, B.; Storset, A.K.; Rimstad, E. Genetic diversity of small-ruminant lentiviruses: Characterization of norwegian isolates of caprine arthritis encephalitis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, R.G. Phylogenetic analysis of small ruminant lentiviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valas, S.; Benoit, C.; Guionaud, C.; Perrin, G.; Mamoun, R.Z. North american and french caprine arthritis-encephalitis viruses emerge from ovine maedi-visna viruses. Virology 1997, 237, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazit, A.; Yaniv, A.; Dvir, M.; Perk, K.; Irving, S.G.; Dahlberg, J.E. The caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus is a distinct virus within the lentivirus group. Virology 1983, 124, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, C.; Boni, J.; Huder, J.B.; Vogt, H.R.; Muhlherr, J.; Zanoni, R.; Miserez, R.; Lutz, H.; Schupbach, J. Phylogenetic analysis and reclassification of caprine and ovine lentiviruses based on 104 new isolates: Evidence for regular sheep-to-goat transmission and worldwide propagation through livestock trade. Virology 2004, 319, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogianni, A.I.; Bossis, I.; Ekateriniadou, L.V.; Gelasakis, A.I. Etiology, epizootiology and control of maedi-visna in dairy sheep: A review. Animals 2020, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miguel, R.; Arrieta, M.; Rodriguez-Largo, A.; Echeverria, I.; Resendiz, R.; Perez, E.; Ruiz, H.; Perez, M.; de Andres, D.; Reina, R.; et al. Worldwide prevalence of small ruminant lentiviruses in sheep: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Animals 2021, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdsson, B.; Grimsson, H.; Palsson, P.A. Maedi, a chronic, progressive infection of sheep’s lungs. J. Infect. Dis. 1952, 90, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrozza, M.L.; Niewiadomska, A.M.; Mazzei, M.; Abi-Said, M.R.; Hue, S.; Hughes, J.; Gatseva, A.; Gifford, R.J. Emergence and pandemic spread of small ruminant lentiviruses. Virus Evol. 2023, 9, vead005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaee, V.; Bazzucchi, M.; De Mia, G.M.; Otarod, V.; Abdollahi, D.; Rosati, S.; Luhken, G. Phylogenetic analysis of small ruminant lentiviruses in Germany and Iran suggests their expansion with domestic sheep. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pétursson, G. Experience with visna virus in Iceland. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 724, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson, P.A. Maedi-visna. J. Clin. Pathol. Suppl. (R Coll Pathol.) 1972, 6, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, M.C.; Johnson, L.K. Pathobiology of lentivirus infections of sheep and goats. Virus Res. 1994, 32, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacklaws, B.A. Small ruminant lentiviruses: Immunopathogenesis of visna-maedi and caprine arthritis and encephalitis virus. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguijon, E.; Reina, R.; Perez, M.; Polledo, L.; Villoria, M.; Ramirez, H.; Leginagoikoa, I.; Badiola, J.J.; Garcia-Marin, J.F.; de Andres, D.; et al. Small ruminant lentivirus infections and diseases. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel-Alne, G.E.; Krontveit, R.; Bohlin, J.; Valle, P.S.; Skjerve, E.; Solverod, L.S. The norwegian healthier goats program—Modeling lactation curves using a multilevel cubic spline regression model. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 4166–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, D.; Czopowicz, M.; Bagnicka, E.; Rzewuska, M.; Strzalkowska, N.; Kaba, J. Influence of small ruminant lentivirus infection on cheese yield in goats. J. Dairy Res. 2015, 82, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogianni, A.I.; Gelasakis, A.I. The impact of small ruminant lentiviruses infections on milk yield and milk quality traits in intensively reared dairy sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2025, 243, 107424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacklaws, B.A.; Berriatua, E.; Torsteinsdottir, S.; Watt, N.J.; de Andres, D.; Klein, D.; Harkiss, G.D. Transmission of small ruminant lentiviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 101, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.; Arranz, J.; Daltabuit-Test, M.; Leginagoikoa, I.; Juste, R.A.; Amorena, B.; de Andres, D.; Lujan, L.L.; Badiola, J.J.; Berriatua, E. Relative contribution of colostrum from maedi-visna virus (mvv) infected ewes to mvv-seroprevalence in lambs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2005, 78, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illius, A.W.; Savill, N.J. Maternal transmission of small ruminant lentivirus has no epidemiological importance. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 230, 106297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thormar, H. Maedi-visna virus and its relationship to human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Rev. 2005, 7, 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- Villoria, M.; Leginagoikoa, I.; Luján, L.; Pérez, M.; Salazar, E.; Berriatua, E.; Juste, R.A.; Minguijón, E. Detection of small ruminant lentivirus in environmental samples of air and water. Small Rumin. Res. 2013, 110, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinaux, L.; Zahno, M.L.; Deubelbeiss, M.; Zanoni, R.; Vogt, H.R.; Bertoni, G. Virological and phylogenetic characterization of attenuated small ruminant lentivirus isolates eluding efficient serological detection. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann-Hoesing, L.M.; White, S.N.; Broughton-Neiswanger, L.E.; Johnson, W.C.; Noh, S.M.; Schneider, D.A.; Li, H.; Taus, N.S.; Reynolds, J.; Truscott, T.; et al. Ovine progressive pneumonia virus is transmitted more effectively via aerosol nebulization than oral administration. Open J. Vet. Med. 2012, 2, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravazzolo, A.P.; Nenci, C.; Vogt, H.-R.; Waldvogel, A.; Obexer-Ruff, G.; Peterhans, E.; Bertoni, G. Viral load, organ distribution, histopathological lesions, and cytokine mrna expression in goats infected with a molecular clone of the caprine arthritis encephalitis virus. Virology 2006, 350, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.S.; Klevjer-Anderson, P.; Carlson, J.L.; McGuire, T.C. Transmission and control of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1983, 44, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, A.M.; Van Laethem, K.; Schmit, J.C.; Van Wijngaerden, E.; Reynders, M.; Debyser, Z.; Witvrouw, M.; Van Ranst, M.; De Clercq, E.; Desmyter, J. Long-term stability of human immunodeficiency virus viral load and infectivity in whole blood. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 29, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bueren, J.; Simpson, R.A.; Jacobs, P.; Cookson, B.D. Survival of human immunodeficiency virus in suspension and dried onto surfaces. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyper, J.M.; Clements, J.E.; Gonda, M.A.; Narayan, O. Sequence homology between cloned caprine arthritis encephalitis virus and visna virus, two neurotropic lentiviruses. J. Virol. 1986, 58, 665–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turelli, P.; Guiguen, F.; Mornex, J.F.; Vigne, R.; Querat, G. Dutpase-minus caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus is attenuated for pathogenesis and accumulates g-to-a substitutions. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4522–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltarelli, M.; Querat, G.; Konings, D.A.; Vigne, R.; Clements, J.E. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of molecular clones of caev which generate infectious virus. Virology 1990, 179, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staskus, K.A.; Retzel, E.F.; Lewis, E.D.; Silsby, J.L.; St Cyr, S.; Rank, J.M.; Wietgrefe, S.W.; Haase, A.T.; Cook, R.; Fast, D.; et al. Isolation of replication-competent molecular clones of visna virus. Virology 1991, 181, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martin, E.; Golomingi, A.; Zahno, M.; Cachim, J.; Di Labio, E.; Perler, L.; Abril, C.; Zanoni, R.; Bertoni, G. Diagnostic response to a cross-border challenge for the swiss caprine arthritis encephalitis virus eradication program. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2019, 161, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.A. Determination of 50% endpoint titer using a simple formula. World J. Virol. 2016, 5, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.; Lexow, F.; Bludau, A.; Koster, A.M.; Misailovski, M.; Seifert, U.; Eggers, M.; Rutala, W.; Dancer, S.J.; Scheithauer, S. How long do bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses retain their replication capacity on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review examining environmental resilience versus healthcare-associated infection risk by “fomite-borne risk assessment”. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0018623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatti-Cardinaux, L.; Pisoni, G.; Stoffel, M.H.; Zanoni, R.; Zahno, M.L.; Bertoni, G. Generation of a molecular clone of an attenuated lentivirus, a first step in understanding cytopathogenicity and virulence. Virology 2016, 487, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minardi da Cruz, J.C.; Singh, D.K.; Lamara, A.; Chebloune, Y. Small ruminant lentiviruses (srlvs) break the species barrier to acquire new host range. Viruses 2013, 5, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsteinsdottir, S.; Matthiasdottir, S.; Vidarsdottir, N.; Svansson, V.; Petursson, G. Intratracheal inoculation as an efficient route of experimental infection with maedi-visna virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2003, 75, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).