The Infectivity and Pathogenicity Characteristics of a Recombinant Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus, CHFJFQ
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses, and Antibodies
2.2. Isolation and Genome Sequencing of PEDV CHFJFQ
2.3. Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscope Assay
2.5. PEDV Amplification and Titer Assays
2.6. Construction of the Recombinant Vector
2.7. Generation of PEDV CHFJFQ Pseudovirus
2.8. Cell Adsorption, Infection, and Proliferation Assays
2.9. Western Blotting and Reverse Transcription–Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
2.10. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.11. Animal Experimental Challenge and Ethical Statement
2.12. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining and Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Bioinformatics
2.14. Statistical Analysis and Image Processing
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of the PEDV CHFJFQ
3.2. Biological Characteristics of the PEDV CHFJFQ Strain in Vitro
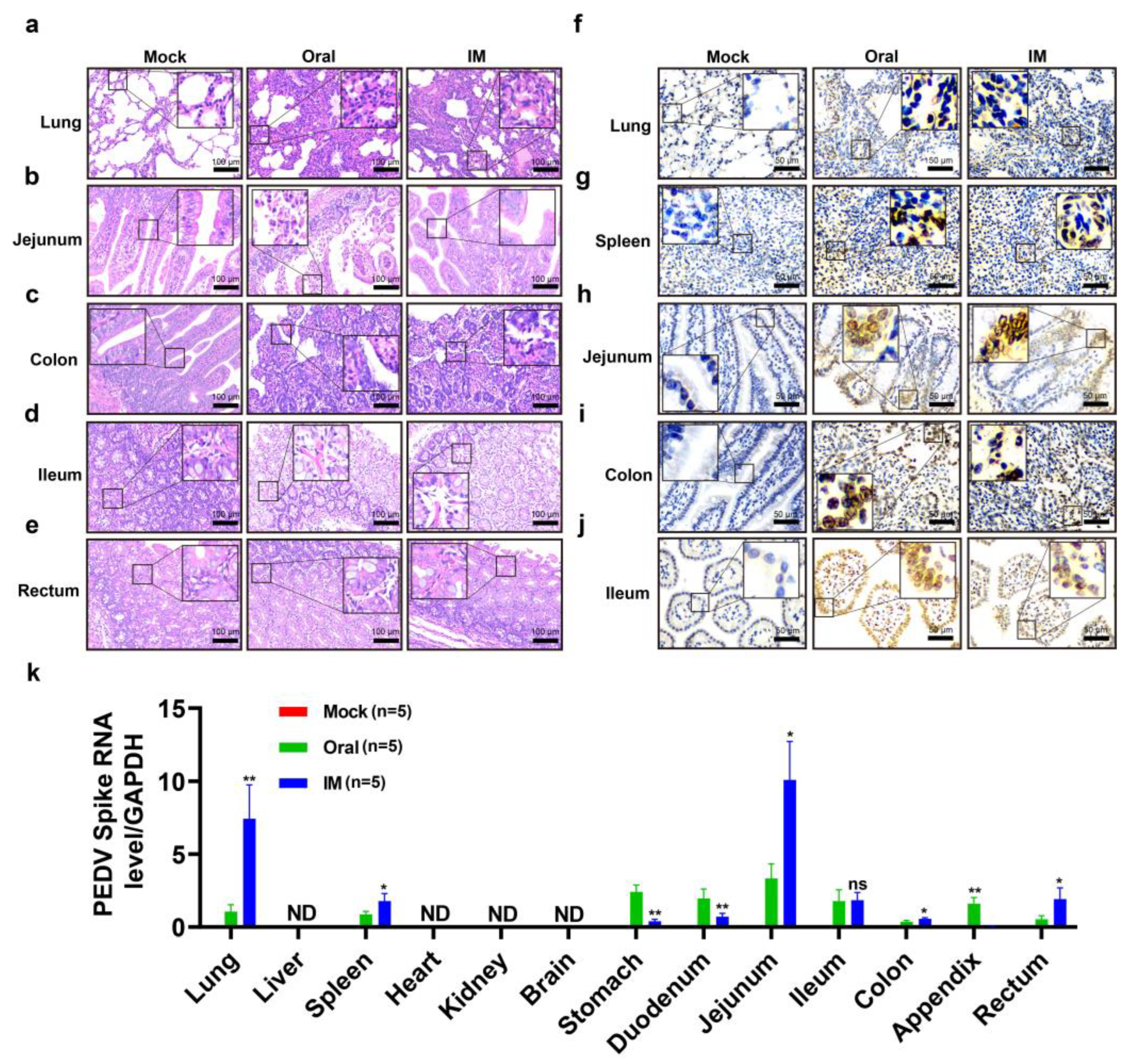
3.3. Pathogenicity of the PEDV CHFJFQ Strain in Piglets
3.4. Pathogenicity of the PEDV CHFJFQ Strain in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEDV | Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus |
| SADS | Porcine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus |
| TGEV | Transmissible gastroenteritis virus |
| PRRSV | Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus |
| PRV | Pseudorabies virus |
| PCV | Porcine circovirus |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| HEK | Human embryonic kidney |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| hpi | Hour post-infection |
| dpi | Day post-infection |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription–quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| TCID50 | 50% tissue culture infectious dose |
| F | Forward |
| R | Reverse |
References
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Dong, L.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Jiao, D.; Han, W.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, S. Molecular Mechanism of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Cell Tropism. mBio 2022, 13, e0373921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brian, D.A.; Baric, R.S. Coronavirus genome structure and replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 287, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Kong, F.; Hou, Y.J.; Wang, Q. Crucial mutation in the exoribonuclease domain of nsp14 of PEDV leads to high genetic instability during viral replication. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ge, X.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhou, L.; Guo, X.; Han, J.; Yang, H. The S Gene Is Necessary but Not Sufficient for the Virulence of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Novel Variant Strain BJ2011C. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00603-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Xiao, S. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: Molecular mechanisms of attenuation and vaccines. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Deng, F.; Shi, K.; Ye, G.; Wang, G.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S.; Fu, Z.; Peng, G. Dimerization of Coronavirus nsp9 with Diverse Modes Enhances Its Nucleic Acid Binding Affinity. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00692-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Foda, M.F.; Xiao, S. Porcine deltacoronavirus nsp5 inhibits interferon-β production through the cleavage of NEMO. Virology 2017, 502, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Xu, J.; Duan, X.; Xu, X.; Li, P.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus ORF3 protein causes endoplasmic reticulum stress to facilitate autophagy. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 235, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, R.; Dong, S.; Yu, R.; Li, Z. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) ORF3 Enhances Viral Proliferation by Inhibiting Apoptosis of Infected Cells. Viruses 2020, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.S.; Yang, J.S.; Oh, J.S.; Han, J.H.; Park, B.K. Differentiation of a Vero cell adapted porcine epidemic diarrhea virus from Korean field strains by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of ORF 3. Vaccine 2003, 21, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Moon, H.J.; Luo, Y.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, E.M.; Yang, J.S.; Song, D.S.; Kang, B.K.; Lee, C.S.; Park, B.K. Cloning and further sequence analysis of the ORF3 gene of wild- and attenuated-type porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses. Virus Genes 2008, 36, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, F.; Chen, B.; Hu, X.; Yu, R.; Dong, S.; Wang, R.; Li, Z. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus ORF3 Protein Is Transported through the Exocytic Pathway. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00808-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wicht, O.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; He, Q.; Rottier, P.J.; Bosch, B.J. A Single Point Mutation Creating a Furin Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein Renders Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Coronavirus Trypsin Independent for Cell Entry and Fusion. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8077–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Terada, Y.; Enjuanes, L.; Ohashi, S.; Kamitani, W. S1 Subunit of Spike Protein from a Current Highly Virulent Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Is an Important Determinant of Virulence in Piglets. Viruses 2018, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Li, C.; Qi, S.; Yang, D.; Jiang, N.; Yin, B.; Guo, D.; Kong, F.; Yuan, D.; Feng, L.; et al. A molecular epidemiological investigation of PEDV in China: Characterization of co-infection and genetic diversity of S1-based genes. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, D.; Cao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Zou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus E protein suppresses RIG-I signaling-mediated interferon-β production. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 254, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Enríquez, A.; Herrera-Camacho, I.; Millán-Pérez-Peña, L.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Santos-López, G.; Rivera-Benítez, J.F.; Rosas-Murrieta, N.H. Predicted 3D model of the M protein of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and analysis of its immunogenic potential. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, F.; Cao, W.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; et al. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Membrane Protein Interacted with IRF7 to Inhibit Type I IFN Production during Viral Infection. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Dong, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Tong, D. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus N protein prolongs S-phase cell cycle, induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, and up-regulates interleukin-8 expression. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Kong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Qin, W.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Ye, M.; Tong, W.; Liu, C.; et al. N protein of PEDV plays chess game with host proteins by selective autophagy. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2338–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication in Human Intestinal Cells Reveals Potential Susceptibility to Cross-Species Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Qiu, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, L. Molecular epidemiology of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in China. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S. Porcine epidemic diarrhea in China. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.; Yao, H. Genomic and epidemiological characteristics provide new insights into the phylogeographical and spatiotemporal spread of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in Asia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV): An update on etiology, transmission, pathogenesis, and prevention and control. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.I.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, E.H.; Park, S.J.; Yu, K.M.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, S.; Casel, M.A.B.; et al. Infection and Rapid Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Ferrets. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 704–709.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infectivity in human embryonic kidney cells. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2415–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simas, P.V.; Barnabé, A.C.; Durães-Carvalho, R.; Neto, D.F.; Caserta, L.C.; Artacho, L.; Jacomassa, F.A.; Martini, M.C.; Bianchi Dos Santos, M.M.; Felippe, P.A.; et al. Bat coronavirus in Brazil related to appalachian ridge and porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Peng, G.; Qi, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Du, L.; et al. Receptor usage and cell entry of porcine epidemic diarrhea coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6121–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The method of right and wrong cases (constant stimuli) without Gauss’s formulae. Br. J. Psychol. 1908, 2, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärber, G. Beitrag zur kollektiven Behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Für Exp. Pathol. Und Pharmakol. 1931, 162, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Varsani, A.; Roumagnac, P.; Botha, G.; Maslamoney, S.; Schwab, T.; Kelz, Z.; Kumar, V.; Murrell, B. RDP5: A computer program for analyzing recombination in, and removing signals of recombination from, nucleotide sequence datasets. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veaa087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspermeyer, J. MEGA Software Celebrates Silver Anniversary. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1558–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccoli Asabella, A.; Antonica, F.; Renna, M.A.; Rubini, D.; Notaristefano, A.; Nicoletti, A.; Rubini, G. Radio-guided sentinel lymph node identification by lymphoscintigraphy fused with an anatomical vector profile: Clinical applications. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2013, 27, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippmann, H.F. Analysis for free: Comparing programs for sequence analysis. Brief. Bioinform. 2004, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Shin, H.J. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infects and replicates in porcine alveolar macrophages. Virus Res. 2014, 191, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Yount, B.L., Jr.; Debbink, K.; Agnihothram, S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Plante, J.A.; Graham, R.L.; Scobey, T.; Ge, X.Y.; Donaldson, E.F.; et al. A SARS-like cluster of circulating bat coronaviruses shows potential for human emergence. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, C.; Peng, O.; Ashraf, U.; Xu, Q.; Gong, L.; Fan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xue, C.; et al. Global Dynamics of Porcine Enteric Coronavirus PEDV Epidemiology, Evolution, and Transmission. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniotti, M.B.; Papetti, A.; Bertasio, C.; Giacomini, E.; Lazzaro, M.; Cerioli, M.; Faccini, S.; Bonilauri, P.; Vezzoli, F.; Lavazza, A.; et al. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus in Italy: Disease spread and the role of transportation. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Yin, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; et al. A novel recombination porcine epidemic diarrhea virus isolated from Gansu, China: Genetic characterization and pathogenicity. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 290, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Gong, L.; Xue, C.; Cao, Y. Genetic epidemiology of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus circulating in China in 2012–2017 based on spike gene. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Marthaler, D.; Wang, Q.; Culhane, M.R.; Rossow, K.D.; Rovira, A.; Collins, J.; Saif, L.J. Distinct characteristics and complex evolution of PEDV strains, North America, May 2013–February 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, C.; Pan, H.; Fu, S.; Xu, W.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Liu, X. Characterization and evolution of the coronavirus porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus HLJBY isolated in China. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Shen, X.; Liu, H. Attenuated porcine-derived type 2 bovine viral diarrhea virus as vector stably expressing viral gene. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 279, 113842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C. Isolation and characterization of a Korean porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain KNU-141112. Virus Res. 2015, 208, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Guo, R.; Hu, M.; Sun, M.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; et al. Efficacy evaluation of a bivalent subunit vaccine against epidemic PEDV heterologous strains with low cross-protection. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0130924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Huang, L.; Yuan, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q. An alternative pathway of enteric PEDV dissemination from nasal cavity to intestinal mucosa in swine. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Wang, Q.; Scheuer, K.A.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Saif, L.J. Pathology of US porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain PC21A in gnotobiotic pigs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, L.; Krog, J.S.; Strandbygaard, B.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Kjaer, J.; Belsham, G.J.; Bøtner, A. Experimental Infection of Young Pigs with an Early European Strain of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus and a Recent US Strain. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Reilly, B.; Ma, G.; Murao, A.; Jha, A.; Aziz, M.; Wang, P. Neutrophils disrupt B-1a cell homeostasis by targeting Siglec-G to exacerbate sepsis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Dong, S.; Yu, L.; Si, F.; Li, C.; Xie, C.; Yu, R.; Li, Z. Three Amino Acid Substitutions in the Spike Protein Enable the Coronavirus Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus to Infect Vero Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0387222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewborisuth, C.; He, Q.; Jongkaewwattana, A. The Accessory Protein ORF3 Contributes to Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Direct Binding to the Spike Protein. Viruses 2018, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongthida, P.; Liwnaree, B.; Wanasen, N.; Narkpuk, J.; Jongkaewwattana, A. The role of ORF3 accessory protein in replication of cell-adapted porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV). Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Hu, H.; He, Q. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus ORF3 gene prolongs S-phase, facilitates formation of vesicles and promotes the proliferation of attenuated PEDV. Virus Genes 2015, 51, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, T.; Song, H.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; et al. Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses. Cell 2021, 184, 4380–4391.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirato, K.; Maejima, M.; Hirai, A.; Ami, Y.; Takeyama, N.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kusanagi, K.; Nunoya, T.; Taguchi, F. Enhanced cell fusion activity in porcine epidemic diarrhea virus adapted to suckling mice. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
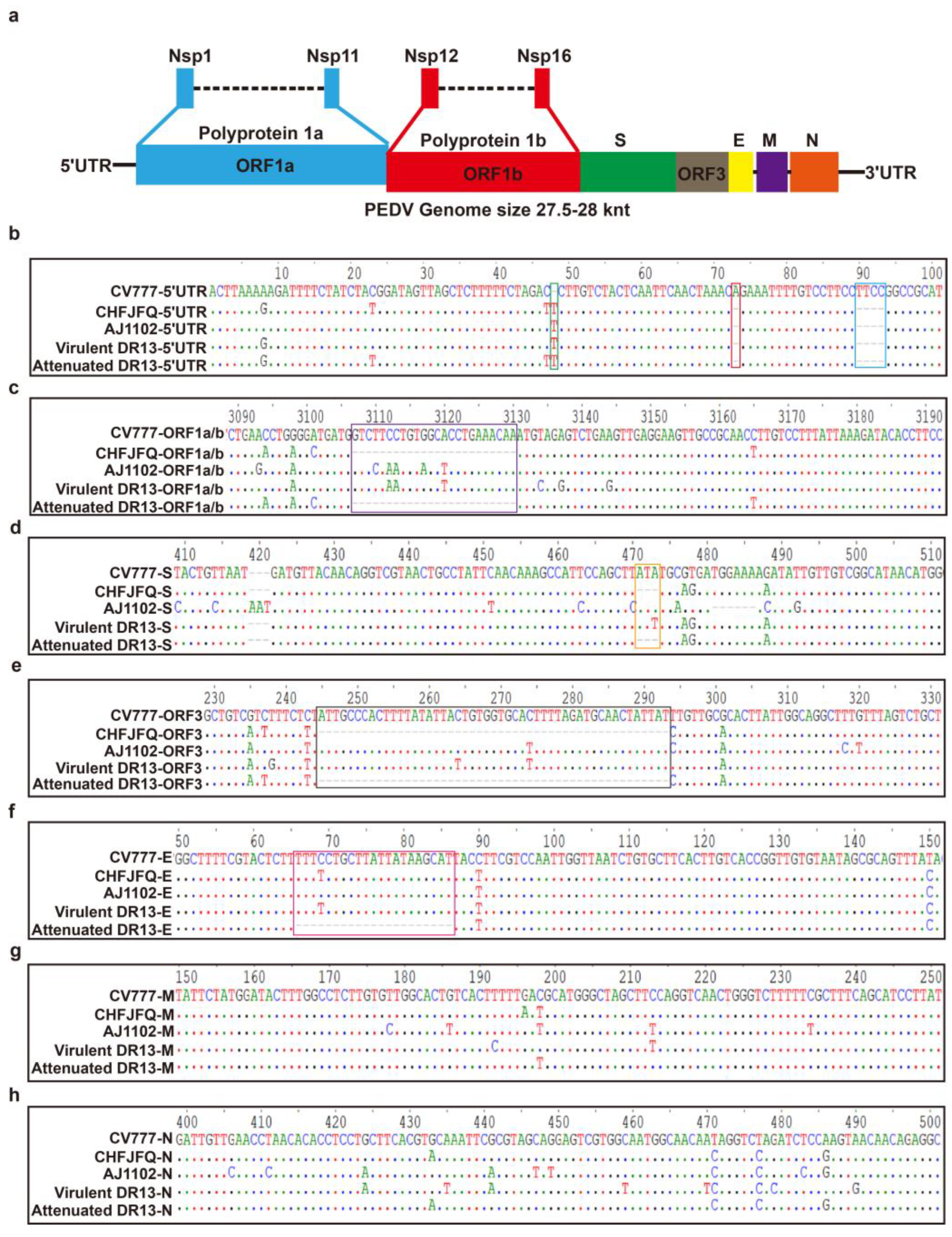


| Gene | PEDV CHFJFQ Strain | PREDICT/GCS-011 Strain (Myotis Bat) | Identity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nt) | Size (aa) | Size (nt) | Size (aa) | nt% | aa% | |
| 5′UTR | 292 | - | 292 | - | 96.58 | - |
| ORF1a/b | 20,321 | 6773 | 20,339 | 6779 | 92.02 | 96.55 |
| S | 4149 | 1382 | 4128 | 1357 | 87.40 | 90.6 |
| ORF3/NS3 | 276 | 91 | 675 | 224 | 93.44 | 92.59 |
| E | 231 | 76 | 231 | 76 | 93.07 | 93.42 |
| M | 681 | 226 | 681 | 226 | 93.83 | 92.92 |
| N | 1326 | 441 | 1335 | 444 | 93.25 | 94.33 |
| NS7 | - | - | 390 | 129 | - | - |
| 3′UTR | 334 | - | 248 | - | 99.55 | - |
| Total | 27,953 | 8989 | 28,320 | 9213 | 91.26 | 95.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Lin, M.; Huang, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Q. The Infectivity and Pathogenicity Characteristics of a Recombinant Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus, CHFJFQ. Viruses 2025, 17, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030401
Feng Z, Zhao H, Li Z, Lin M, Huang W, Liu C, Shen Y, Chen Q. The Infectivity and Pathogenicity Characteristics of a Recombinant Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus, CHFJFQ. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030401
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Zhihua, Heng Zhao, Zhaolong Li, Minhua Lin, Weili Huang, Chuancheng Liu, Yangkun Shen, and Qi Chen. 2025. "The Infectivity and Pathogenicity Characteristics of a Recombinant Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus, CHFJFQ" Viruses 17, no. 3: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030401
APA StyleFeng, Z., Zhao, H., Li, Z., Lin, M., Huang, W., Liu, C., Shen, Y., & Chen, Q. (2025). The Infectivity and Pathogenicity Characteristics of a Recombinant Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus, CHFJFQ. Viruses, 17(3), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030401






