The Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 Effectively Attenuates the In Vitro Replication of Multiple Lineages of Circulating Canine Distemper Viruses Isolated from Wild North American Carnivores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and CDV Isolates
2.2. Antivirals
2.3. Antiviral Screening
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
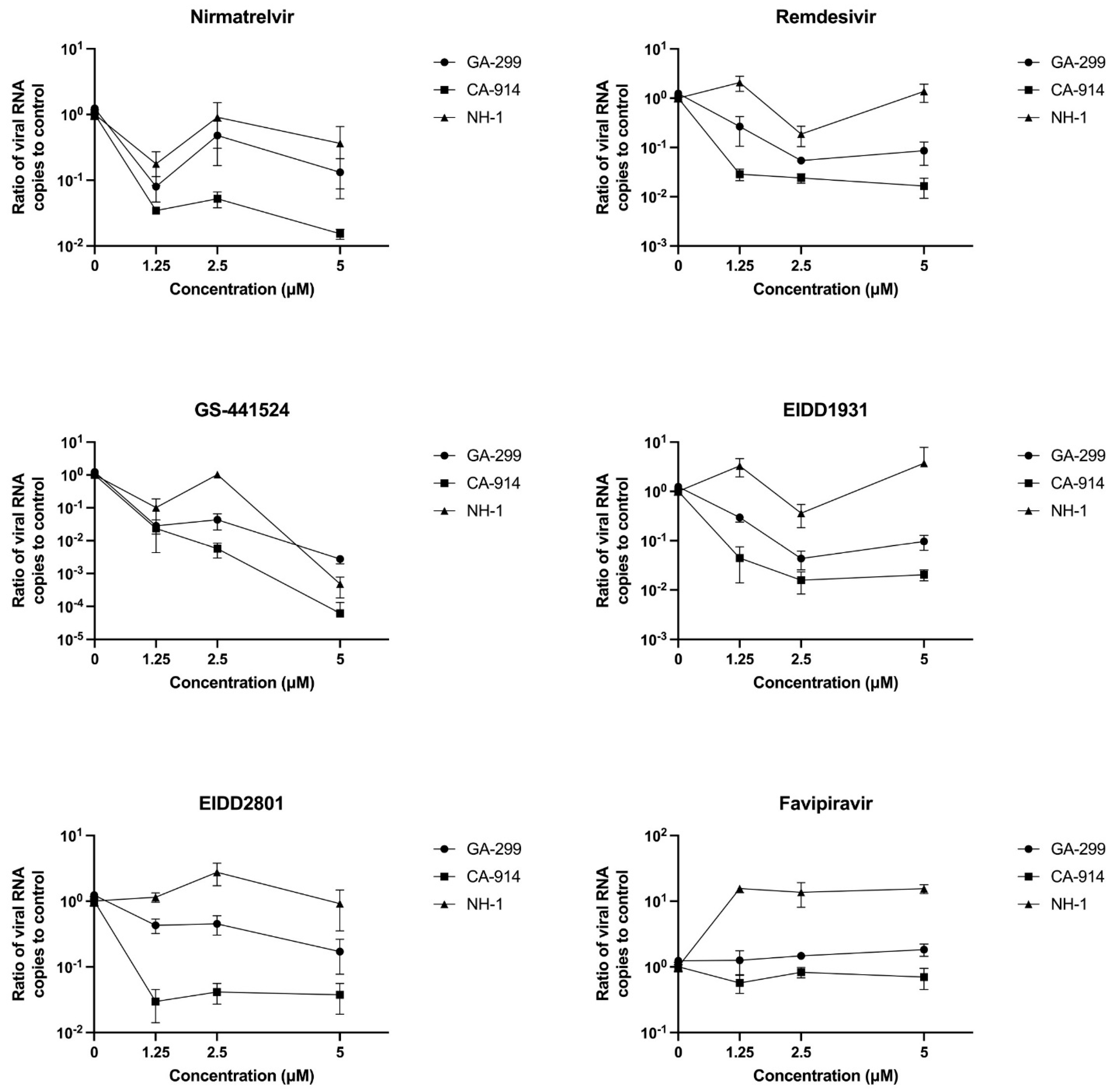
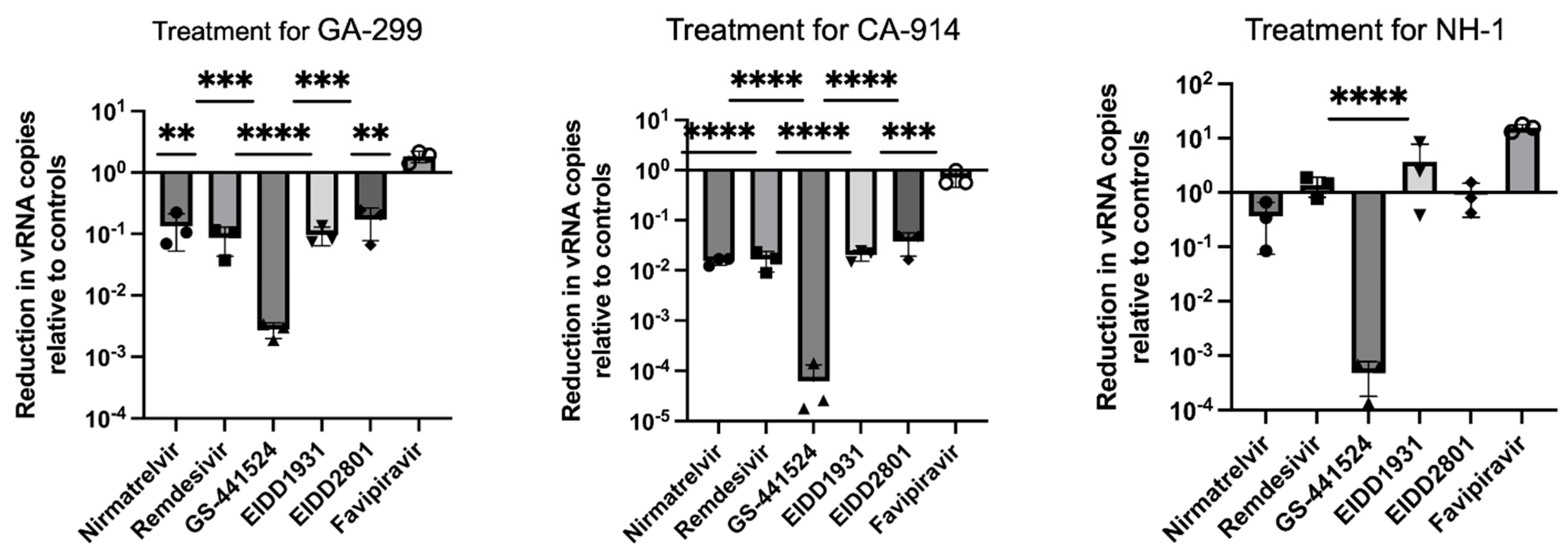
3. Results
3.1. Antivirals and Cytopathic Effect
3.2. Antivirals and CDV Replication
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapter 17—Paramyxoviridae and Pneumoviridae. In Fenner’s Veterinary Virology, 5th ed.; MacLachlan, N.J., Dubovi, E.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 327–356. ISBN 978-0-12-800946-8. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Gutierrez, M.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Diversity of Susceptible Hosts in Canine Distemper Virus Infection: A Systematic Review and Data Synthesis. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, G.E.; Appel, M.J. Canine Distemper. In Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 226–241. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.E.; Swift, P.; Fleer, K.A.; Torres, S.; Girard, Y.A.; Johnson, C.K. Risk Factors for Exposure to Feline Pathogens in California Mountain Lions (Puma Concolor). J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, L.E. Canine Viral Vaccines at a Turning Point—A Personal Perspective. In Advances in Veterinary Medicine; Schultz, R.D., Ed.; Veterinary Vaccines and Diagnostics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 41, pp. 289–307. [Google Scholar]
- Pesavento, P.A.; Murphy, B.G. Common and Emerging Infectious Diseases in the Animal Shelter. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceicao, C.; Bailey, D. Animal Morbilliviruses (Paramyxoviridae). In Encyclopedia of Virology, 4th ed.; Bamford, D.H., Zuckerman, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 68–78. ISBN 978-0-12-814516-6. [Google Scholar]
- Caswell, J.L.; Williams, K.J. Chapter 5—Respiratory System. In Jubb, Kennedy & Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals: Volume 2, 6th ed.; Maxie, M.G., Ed.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 465–591.e4. ISBN 978-0-7020-5318-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cantile, C.; Youssef, S. Chapter 4—Nervous System. In Jubb, Kennedy & Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals: Volume 1, 6th ed.; Maxie, M.G., Ed.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 250–406. ISBN 978-0-7020-5317-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, C.A. Retinal and Retinochoroidal Lesions in Early Neuropathic Canine Distemper. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1971, 158, 740–752. [Google Scholar]
- Martella, V.; Cirone, F.; Elia, G.; Lorusso, E.; Decaro, N.; Campolo, M.; Desario, C.; Lucente, M.S.; Bellacicco, A.L.; Blixenkrone-Møller, M.; et al. Heterogeneity within the Hemagglutinin Genes of Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) Strains Detected in Italy. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 116, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, G.; Jensen, T.D.; Gottschalck, E.; Arctander, P.; Appel, M.J.G.; Buckland, R.; Blixenkrone, M. Genetic Diversity of the Attachment (H) Protein Gene of Current Field Isolates of Canine Distemper Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Hagiwara, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Ishiguro, S. Genotypes of Canine Distemper Virus Determined by Analysis of the Hemagglutinin Genes of Recent Isolates from Dogs in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2936–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacinti, J.A.; Pearl, D.L.; Ojkic, D.; Campbell, G.D.; Jardine, C.M. Genetic Characterization of Canine Distemper Virus from Wild and Domestic Animal Submissions to Diagnostic Facilities in Canada. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 198, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, P.; Irwin, D.M.; Shen, X.; Chen, W.; Shen, Y. A New Canine Distemper Virus Lineage Identified from Red Pandas in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, e944–e952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, E.; Newell, T.K.; Dyer, N.; Wilkes, R.P. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Wild-Type Strains of Canine Distemper Virus Circulating in the United States. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Allison, R.W.; Johnston, L.; Murray, B.L.; Holland, S.; Meinkoth, J.; Johnson, B. Canine Distemper Virus Strains Circulating among North American Dogs. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, E.; Needle, D.B.; Stevens, B.; Yan, L.; Wilkes, R.P. Genetic Characteristics of Canine Distemper Viruses Circulating in Wildlife in the United States. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2020, 50, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xin, T.; Hou, S.; Lin, W.; Song, W.; Zhu, H.; Huang, K.; Jia, H. Genotyping and Pathogenic Characterization of Canine Distemper Virus Based on Mutations in the Hemagglutinin Gene in Chinese Domestic Dogs. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 21, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednicky, J.A.; Dubach, J.; Kinsel, M.J.; Meehan, T.P.; Bocchetta, M.; Hungerford, L.L.; Sarich, N.A.; Witecki, K.E.; Braid, M.D.; Pedrak, C.; et al. Genetically Distant American Canine Distemper Virus Lineages Have Recently Caused Epizootics with Somewhat Different Characteristics in Raccoons Living around a Large Suburban Zoo in the USA. Virol. J. 2004, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martella, V.; Elia, G.; Buonavoglia, C. Canine Distemper Virus. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2008, 38, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraghty, R.J.; Aliota, M.T.; Bonnac, L.F. Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Strategies and Nucleoside Analogues. Viruses 2021, 13, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.S.; Moore, K.H. Phosphorylation of Nucleoside Analog Antiretrovirals: A Review for Clinicians. Pharmacotherapy 2001, 21, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.K.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. Remdesivir Is a Direct-Acting Antiviral That Inhibits RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 with High Potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.; Hui, H.C.; Doerffler, E.; Clarke, M.O.; Chun, K.; Zhang, L.; Neville, S.; Carra, E.; Lew, W.; Ross, B.; et al. Discovery and Synthesis of a Phosphoramidate Prodrug of a Pyrrolo[2,1-f][Triazin-4-Amino] Adenine C-Nucleoside (GS-5734) for the Treatment of Ebola and Emerging Viruses. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Kothadia, J.P. Remdesivir. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.E.; Vogel, H.; Castillo, D.; Olsen, M.; Pedersen, N.; Murphy, B.G. Investigation of Monotherapy and Combined Anticoronaviral Therapies against Feline Coronavirus Serotype II in Vitro. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Wittenburg, L.; Yan, V.C.; Theil, J.H.; Castillo, D.; Reagan, K.L.; Williams, S.; Pham, C.-D.; Li, C.; Muller, F.L.; et al. An Optimized Bioassay for Screening Combined Anticoronaviral Compounds for Efficacy against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus with Pharmacokinetic Analyses of GS-441524, Remdesivir, and Molnupiravir in Cats. Viruses 2022, 14, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coggins, S.J.; Norris, J.M.; Malik, R.; Govendir, M.; Hall, E.J.; Kimble, B.; Thompson, M.F. Outcomes of Treatment of Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Using Parenterally Administered Remdesivir, with or without Transition to Orally Administered GS-441524. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.G.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N.C. The Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 Strongly Inhibits Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) Virus in Tissue Culture and Experimental Cat Infection Studies. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Perron, M.; Bannasch, M.; Montgomery, E.; Murakami, E.; Liepnieks, M.; Liu, H. Efficacy and Safety of the Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 for Treatment of Cats with Naturally Occurring Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.S.; Coggins, S.; Barker, E.N.; Gunn-Moore, D.; Jeevaratnam, K.; Norris, J.M.; Hughes, D.; Stacey, E.; MacFarlane, L.; O’Brien, C.; et al. Retrospective Study and Outcome of 307 Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Treated with Legally Sourced Veterinary Compounded Preparations of Remdesivir and GS-441524 (2020–2022). J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X231194460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyssen, P.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E.; Neyts, J. The Predominant Mechanism by Which Ribavirin Exerts Its Antiviral Activity in Vitro against Flaviviruses and Paramyxoviruses Is Mediated by Inhibition of IMP Dehydrogenase. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.T.; Balaban, H.Y. Hepatitis E Virus: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Clinical Manifestations, and Treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5543–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, K.; Daikoku, T. Favipiravir, an Anti-Influenza Drug against Life-Threatening RNA Virus Infections. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 209, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, T.; Sada, M.; Saraya, T.; Kurai, D.; Sunagawa, S.; Ishii, H.; Kimura, H. Detailed Analyses of Molecular Interactions between Favipiravir and RNA Viruses In Silico. Viruses 2022, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochmans, D.; van Nieuwkoop, S.; Smits, S.L.; Neyts, J.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; van den Hoogen, B.G. Antiviral Activity of Favipiravir (T-705) against a Broad Range of Paramyxoviruses In Vitro and against Human Metapneumovirus in Hamsters. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4620–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Narayanan, S.; Chang, K.-O. Inhibition of Influenza Virus Replication by Plant-Derived Isoquercetin. Antivir. Res. 2010, 88, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.K.; Agrawal, C.; Blunden, G. Rutin: A Potential Antiviral for Repurposing as a SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro) Inhibitor. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X21991723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.K.; Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, T. Glucosyl Hesperidin Prevents Influenza A Virus Replication in Vitro by Inhibition of Viral Sialidase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Lamb, A.J. Antimicrobial Activity of Flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 26, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, P.; Nolkemper, S.; Stintzing, F.C.; Reichling, J. Comparative in Vitro Study on the Anti-Herpetic Effect of Phytochemically Characterized Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Salvia Officinalis Grown at Two Different Locations. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, O.V.; Botelho, C.V.; Ferreira, C.G.T.; Ferreira, H.C.C.; Santos, M.R.; Diaz, M.A.N.; Oliveira, T.T.; Soares-Martins, J.A.P.; Almeida, M.R.; Silva, A. In Vitro Inhibition of Canine Distemper Virus by Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids: Implications of Structural Differences for Antiviral Design. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.K.; Shrivastava-Ranjan, P.; Chatterjee, P.; Flint, M.; Beadle, J.R.; Valiaeva, N.; Murphy, J.; Schooley, R.T.; Hostetler, K.Y.; Montgomery, J.M.; et al. Broad-Spectrum In Vitro Antiviral Activity of ODBG-P-RVn: An Orally-Available, Lipid-Modified Monophosphate Prodrug of Remdesivir Parent Nucleoside (GS-441524). Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01537-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, E.M.; Monreal, I.A.; Ruvalcaba, M.; Ortega, V.; Aguilar, H.C. Antivirals Targeting Paramyxovirus Membrane Fusion. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 51, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hidan, M.A.; Laaradia, M.A.; El Hiba, O.; Draoui, A.; Aimrane, A.; Kahime, K. Scorpion-Derived Antiviral Peptides with a Special Focus on Medically Important Viruses: An Update. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9998420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.K.; Jordan, R.; Arvey, A.; Sudhamsu, J.; Shrivastava-Ranjan, P.; Hotard, A.L.; Flint, M.; McMullan, L.K.; Siegel, D.; Clarke, M.O.; et al. GS-5734 and Its Parent Nucleoside Analog Inhibit Filo-, Pneumo-, and Paramyxoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyde, P.R.; Moore-Poveda, D.K.; De Clercq, E.; Neyts, J.; Matsuda, A.; Minakawa, N.; Guzman, E.; Gilbert, B.E. Use of Cotton Rats to Evaluate the Efficacy of Antivirals in Treatment of Measles Virus Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Deng, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Antiviral Effectivity of Favipiravir Against Peste Des Petits Ruminants Virus Is Mediated by the JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT Pathways. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 722840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-J.; Toots, M.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.-E.; Ludeke, B.; Luczo, J.M.; Ganti, K.; Cox, R.M.; Sticher, Z.M.; Edpuganti, V.; et al. Orally Efficacious Broad-Spectrum Ribonucleoside Analog Inhibitor of Influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Viruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00766-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Nam, H.H.; Adams, P.L.; Krafft, A.; Ince, W.L.; El-Kamary, S.S.; Sims, A.C. Advances in Respiratory Virus Therapeutics—A Meeting Report from the 6th Isirv Antiviral Group Conference. Antivir. Res. 2019, 167, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G.; Belloli, C.; Cirone, F.; Lucente, M.S.; Caruso, M.; Martella, V.; Decaro, N.; Buonavoglia, C.; Ormas, P. In Vitro Efficacy of Ribavirin against Canine Distemper Virus. Antivir. Res. 2008, 77, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, L.; Wong, G.; Sun, P.; Zheng, X.; Xia, X. Antiviral Efficacy of Favipiravir against Canine Distemper Virus Infection in Vitro. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.-Q.; Huang, W.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Tan, M.-J.; Liu, J.; Wei, H.-J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, D.-Y. Effectiveness of Favipiravir (T-705) against Wild-Type and Oseltamivir-Resistant Influenza B Virus in Mice. Virology 2020, 545, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łagocka, R.; Dziedziejko, V.; Kłos, P.; Pawlik, A. Favipiravir in Therapy of Viral Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgess, K. Diagnosis and Management of Chylothorax in Dogs and Cats. Practice 2001, 23, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylothorax|American College of Veterinary Surgeons—ACVS. Available online: https://www.acvs.org/small-animal/chylothorax/ (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- El-Mal, E.O.A.; Abu-Seida, A.M.; Ashry, S.H.E. Biological Evaluation of Hesperidin for Direct Pulp Capping in Dogs’ Teeth. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 102, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodniewicz, T.; Grynkiewicz, G. Preclinical Drug Development. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 578–585. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, A.; Saville, B.R.; Marsh, J.A.; Snelling, T.L. An Introduction to Clinical Trial Design. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2019, 32, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.; Grootendorst, P.; Lexchin, J.; Cunningham, C.; Greyson, D. The Cost of Drug Development: A Systematic Review. Health Policy 2011, 100, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gukasyan, H.J.; Hailu, S.; Karami, T.K. Ophthalmic Drug Discovery and Development. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanekata, T.; Fukuda, T.; Miura, T.; Morino, H.; Lee, C.; Maeda, K.; Araki, K.; Otake, T.; Kawahata, T.; Shibata, T. Evaluation of the Antiviral Activity of Chlorine Dioxide and Sodium Hypochlorite against Feline Calicivirus, Human Influenza Virus, Measles Virus, Canine Distemper Virus, Human Herpesvirus, Human Adenovirus, Canine Adenovirus and Canine Parvovirus. Biocontrol. Sci. 2010, 15, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Gall, F.M.; Vesin, J.; Chambon, M.; Turcatti, G.; Fotiadis, D.; Riedl, R.; Plattet, P. Antiviral Screen against Canine Distemper Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion Activity. Viruses 2021, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yi, L.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X. Inhibition of Canine Distemper Virus Replication by Blocking Pyrimidine Nucleotide Synthesis with A77 1726, the Active Metabolite of the Anti-Inflammatory Drug Leflunomide. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravolatz, L.D.; Depcinski, S.; Sharma, M. Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Oral COVID Antiviral Drugs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 76, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, J.J.; Suárez, I.; Priesner, V.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Rybniker, J. Remdesivir against COVID-19 and Other Viral Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 34, e00162-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, H.B.; Thomsen, R.; Hansen, P.R. Nucleoside Analog GS-441524: Pharmacokinetics in Different Species, Safety, and Potential Effectiveness against COVID-19. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect 2022, 10, e00945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GS-441524 Studies. Available online: https://opendata.ncats.nih.gov/covid19/GS-441524 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Yan, V.C.; Pham, C.-D.; Yan, M.J.; Yan, A.J.; Khadka, S.; Arthur, K.; Ackroyd, J.J.; Georgiou, D.K.; Roon, L.E.; Bushman, L.R.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Orally Administered GS-441524 in Dogs. bioRxiv 2021, 2021.02.04.429674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.; Allerton, C.M.N.; Anderson, A.S.; Aschenbrenner, L.; Avery, M.; Berritt, S.; Boras, B.; Cardin, R.D.; Carlo, A.; Coffman, K.J.; et al. An Oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of COVID-19. Science 2021, 374, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, J.; Leister-Tebbe, H.; Gardner, A.; Abreu, P.; Bao, W.; Wisemandle, W.; Baniecki, M.; Hendrick, V.M.; Damle, B.; Simón-Campos, A.; et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rima, B.; Collins, P.; Easton, A.; Fouchier, R.; Kurath, G.; Lamb, R.A.; Lee, B.; Maisner, A.; Rota, P.; Wang, L. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Pneumoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2912–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanave, G.; Cavalli, A.; Martella, V.; Fontana, T.; Losappio, R.; Tempesta, M.; Decaro, N.; Buonavoglia, D.; Camero, M. Ribavirin and Boceprevir Are Able to Reduce Canine Distemper Virus Growth in Vitro. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 248, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Valencia, J.; Forero-Muñoz, N.R.; Díaz, F.J.; Martins, E.; Barato, P.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Phylogenetic Evidence of the Intercontinental Circulation of a Canine Distemper Virus Lineage in the Americas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Isolate | Lineage | Origin Species | Organ | Geographical Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-299 | America-4 | (Raccoon, Procyon lotor) | Brain | Louisiana |
| CA-914 | America-3 | (Gray fox, Urocyon cinereoargenteus) | Brain | California |
| NH1 | Rhode Island | (Gray fox, Urocyon cinereoargenteus) | Lung | New Hampshire |
| Compound | Mechanism of Action | Chemical Formula | Structural Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| EIDD1931 | Nucleoside analog (cytosine) | C9H13N3O6 |  |
| EIDD2801 | Nucleoside analog (cytosine) | C13H19N3O7 |  |
| Favipiravir | Polymerase inhibitor | C5H4FN3O2 |  |
| GS-441524 | Nucleoside analog (adenosine) | C12H13N5O4 | 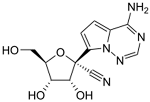 |
| Hesperidin | Flavonoid (specific mechanism unknown) | C28H34O15 |  |
| Nirmatrelvir | Protease inhibitor | C23H32F3N5O4 |  |
| Remdesivir | Nucleoside analog (adenosine) | C27H35N6O8P |  |
| Ribavirin | Nucleoside analogs (purine) | C8H12N4O5 |  |
| Rutin | Flavonoid (specific mechanism unknown) | C27H30O16 |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliver-Guimera, A.; Murphy, B.G.; Keel, M.K. The Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 Effectively Attenuates the In Vitro Replication of Multiple Lineages of Circulating Canine Distemper Viruses Isolated from Wild North American Carnivores. Viruses 2025, 17, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17020150
Oliver-Guimera A, Murphy BG, Keel MK. The Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 Effectively Attenuates the In Vitro Replication of Multiple Lineages of Circulating Canine Distemper Viruses Isolated from Wild North American Carnivores. Viruses. 2025; 17(2):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17020150
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliver-Guimera, Arturo, Brian G. Murphy, and M. Kevin Keel. 2025. "The Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 Effectively Attenuates the In Vitro Replication of Multiple Lineages of Circulating Canine Distemper Viruses Isolated from Wild North American Carnivores" Viruses 17, no. 2: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17020150
APA StyleOliver-Guimera, A., Murphy, B. G., & Keel, M. K. (2025). The Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 Effectively Attenuates the In Vitro Replication of Multiple Lineages of Circulating Canine Distemper Viruses Isolated from Wild North American Carnivores. Viruses, 17(2), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17020150







