Transmission, Pathological and Clinical Manifestations of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A Virus in Mammals with Emphasis on H5N1 Clade 2.3.4.4b
Abstract
1. Introduction
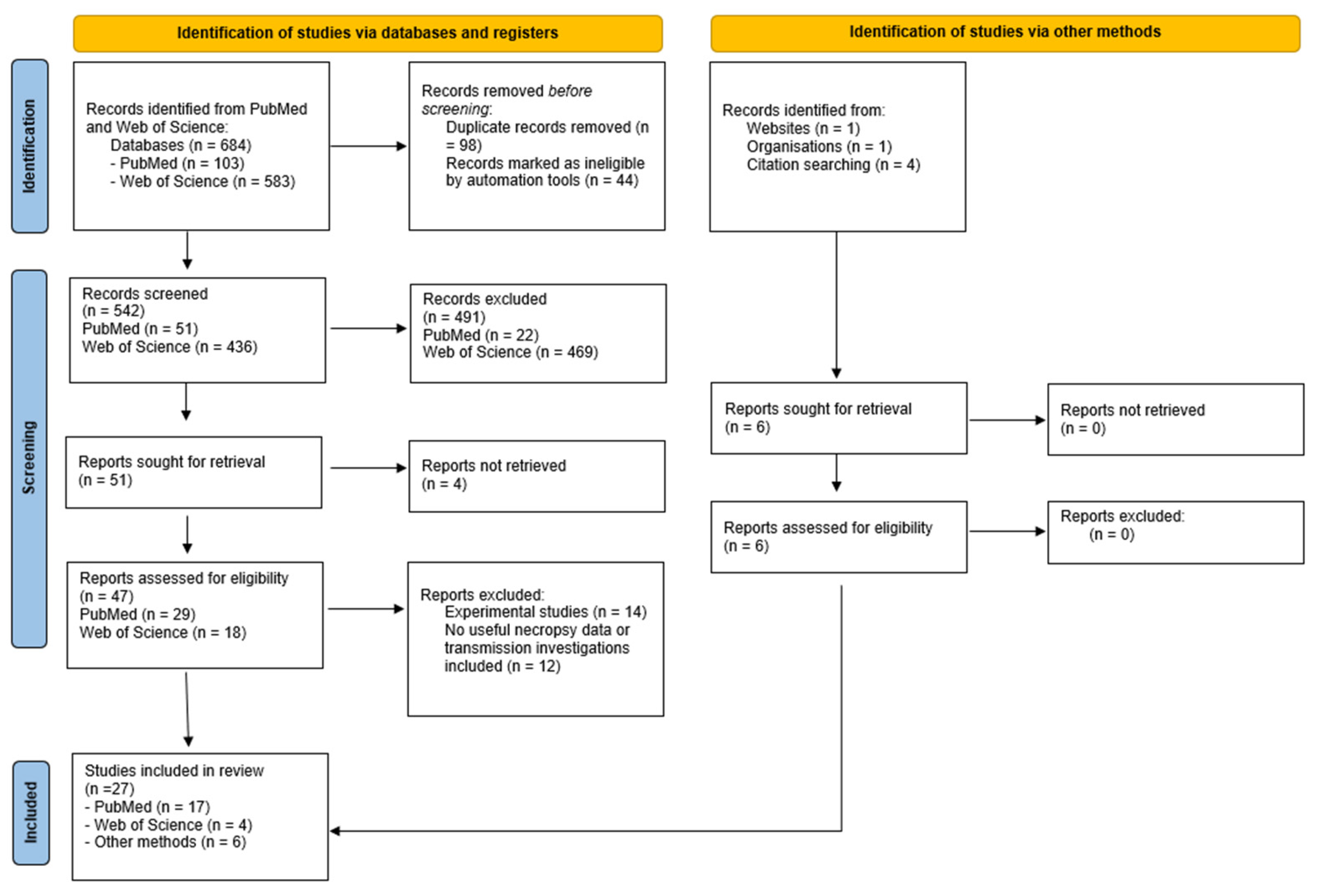
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Terrestrial mammals (including domesticated cats)
- -
- Marine mammals
- -
- Dairy cattle
3. Transmission, Clinical and Pathological Manifestations Among Mammals
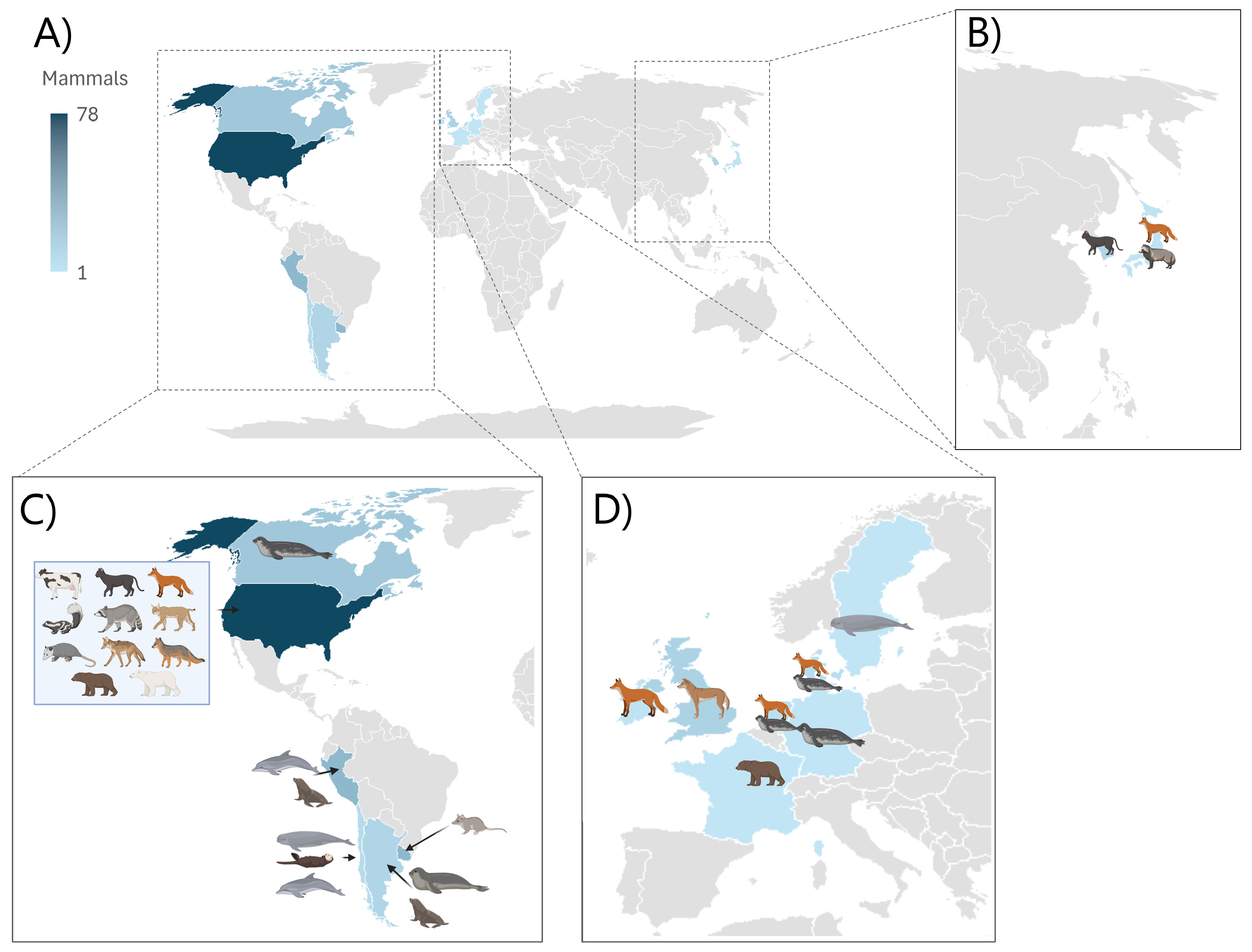
3.1. Introduction to Papers
3.2. Transmission Routes
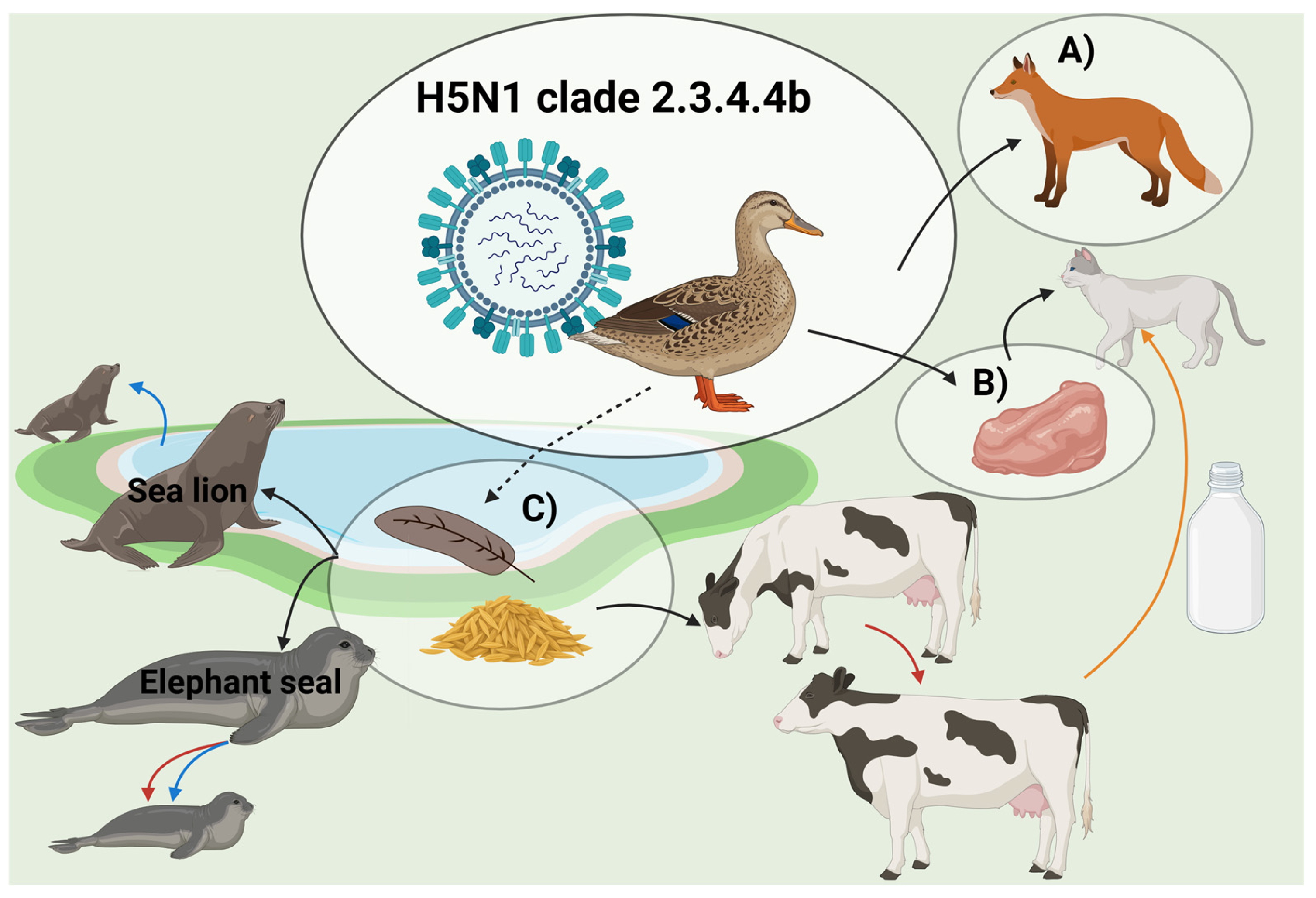
3.2.1. Spillover from Birds
3.2.2. Mammal-to-Mammal Transmission
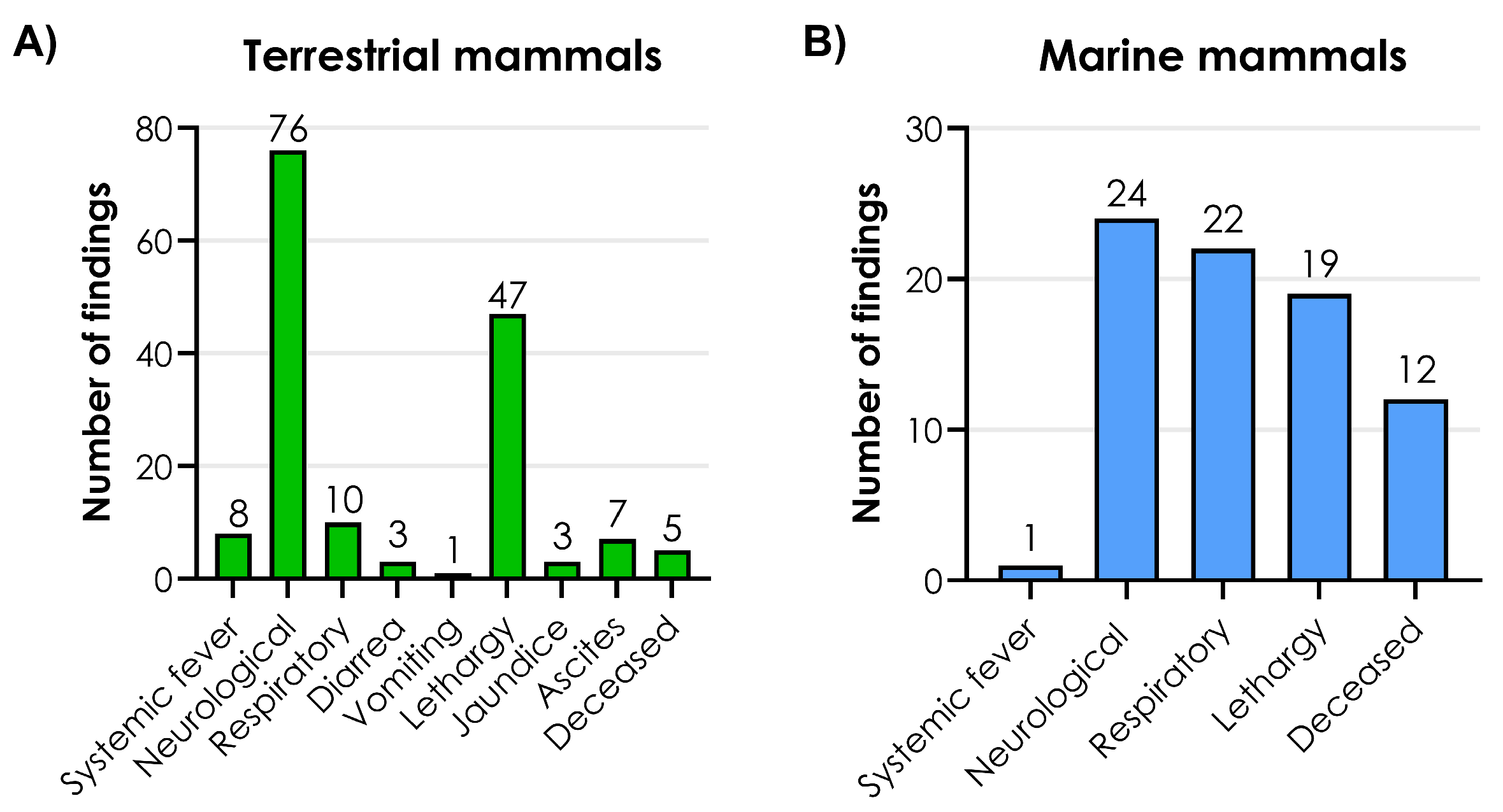
3.3. Clinical Signs
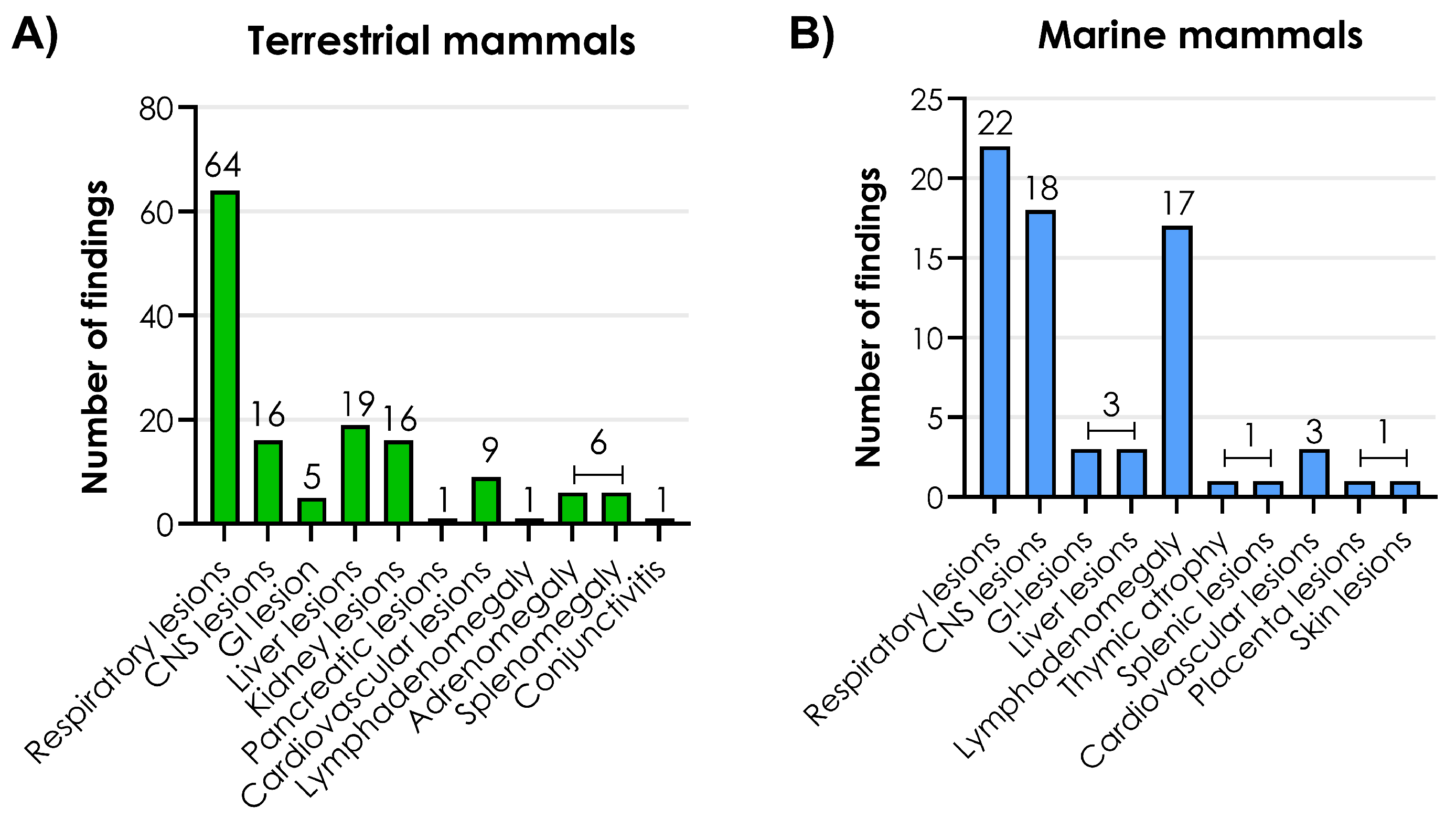
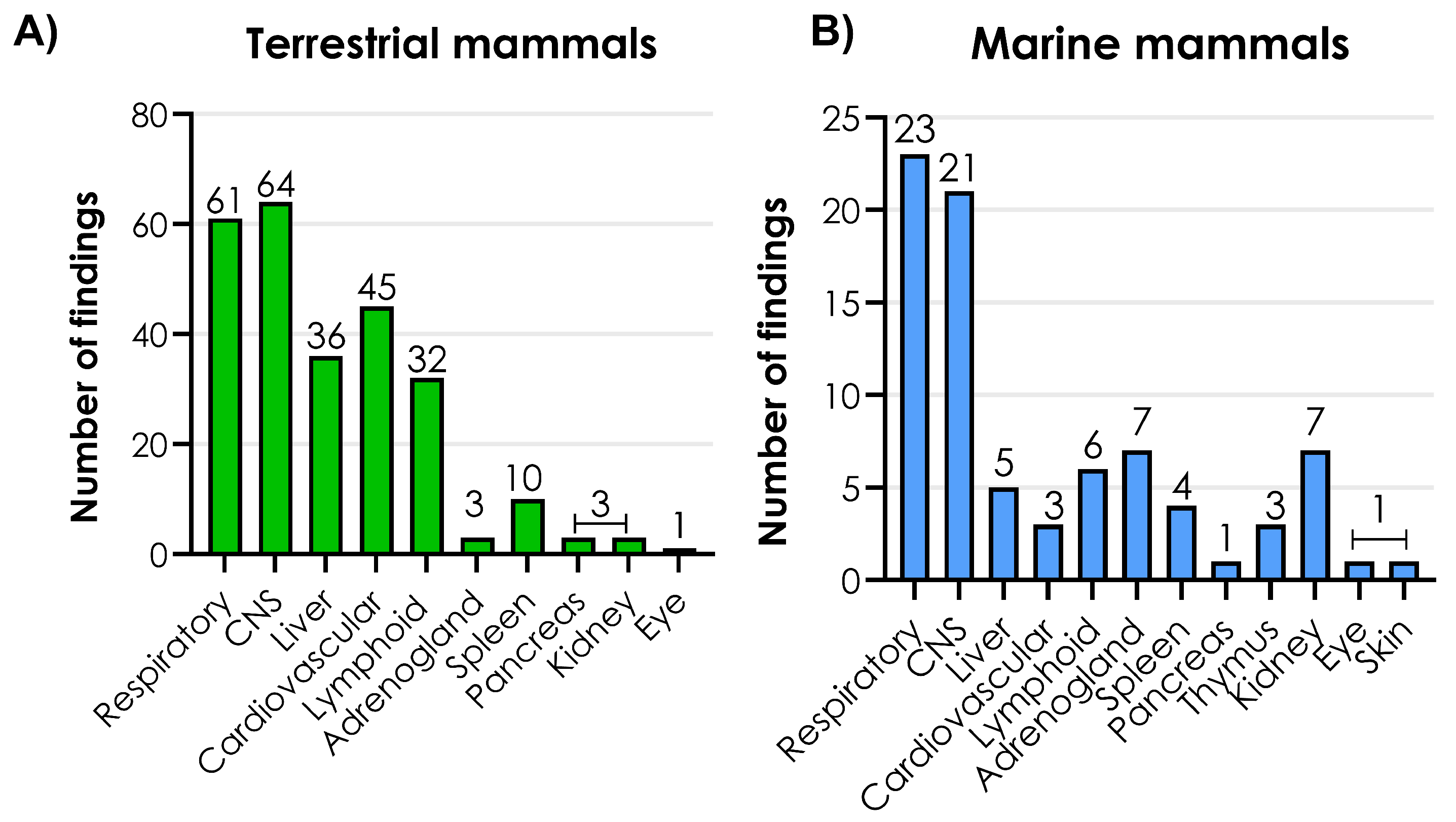
3.4. Macroscopic Lesions
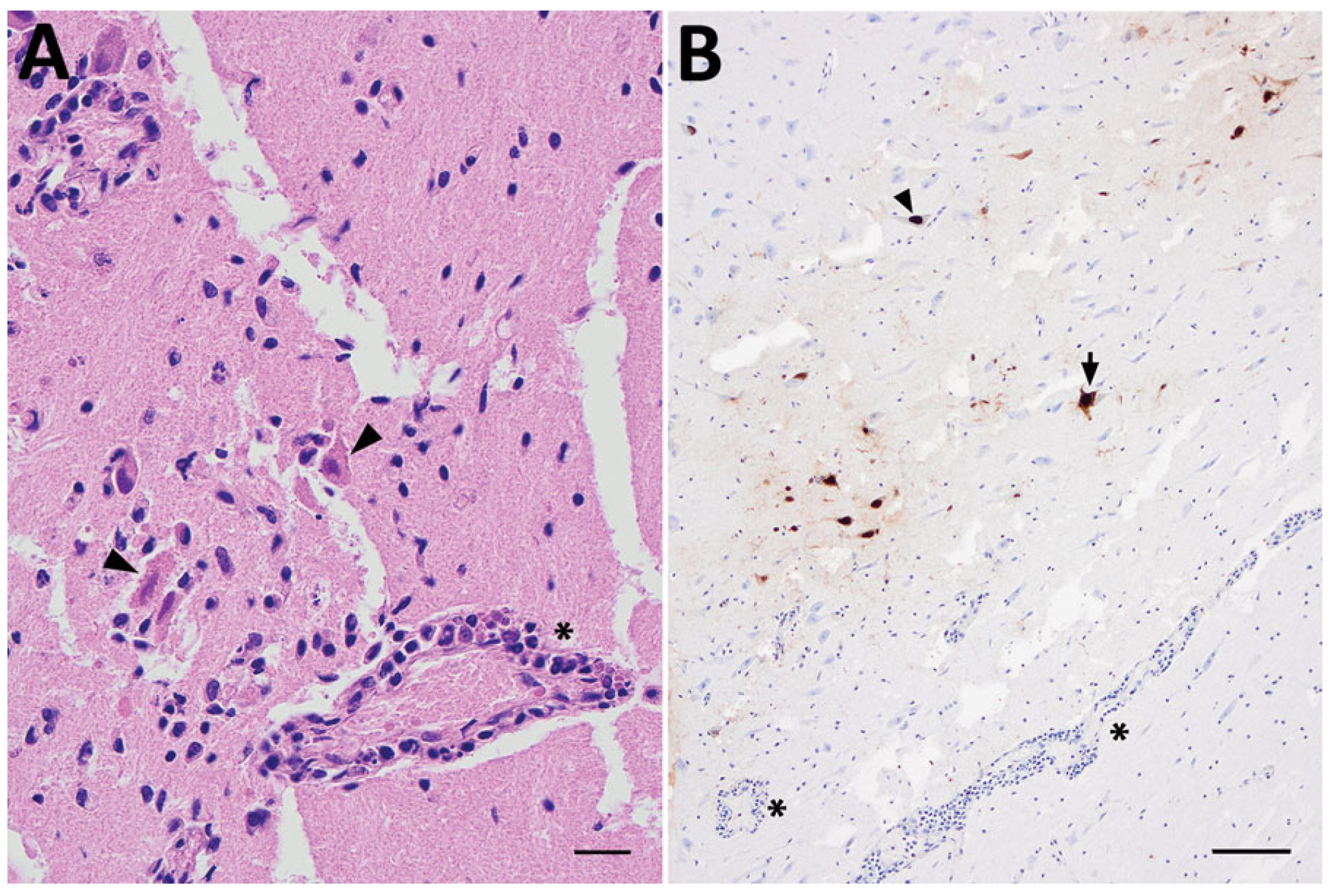
3.5. Histopathological Changes
3.6. Tissue Localization and Viral Quantification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webster, R.G.; Bean, W.J.; Gorman, O.T.; Chambers, T.M.; Kawaoka, Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 152–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. History of the Taxon: Genus Alphainfluenzavirus. Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy/taxondetails?taxnode_id=202303955&taxon_name=Alphainfluenzavirus (accessed on 14 October 2025).
- Chauhan, R.P.; Gordon, M.L. An overview of influenza A virus genes, protein functions, and replication cycle highlighting important updates. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elena, S.F.; Sanjuán, R. Adaptive Value of High Mutation Rates of RNA Viruses: Separating Causes from Consequences. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11555–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, M.O.; Angeletti, D.; Yewdell, J.W. Antibody Immunodominance: The Key to Understanding Influenza Virus Antigenic Drift. Viral Immunol. 2018, 31, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Blixt, O.; Stevens, J.; Lipatov, A.S.; Davis, C.T.; Collins, B.E.; Cox, N.J.; Paulson, J.C.; Donis, R.O. In vitro evolution of H5N1 avian influenza virus toward human-type receptor specificity. Virology 2012, 22, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Swayne, D.E. Pathogenesis and pathobiology of avian influenza virus infection in birds. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2009, 28, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo-Roa, C.; Nelson, M.I.; Ariyama, N.; Aguayo, C.; Almonacid, L.I.; Gonzalez-Reiche, A.S.; Muñoz, G.; Ulloa, M.; Ávila, C.; Navarro, C.; et al. Cross-species and mammal-to-mammal transmission of clade 2.3.4.4b highly pathogenic avian influenza A/H5N1 with PB2 adaptations. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieneke-Gröber, A.; Vey, M.; Angliker, H.; Shaw, E.; Thomas, G.; Roberts, C.; Klenk, H.; Garten, W. Influenza virus hemagglutinin with multibasic cleavage site is activated by furin, a subtilisin-like endoprotease. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 2407–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwhab, E.-S.M.; Veits, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Genetic changes that accompanied shifts of low pathogenic avian influenza viruses toward higher pathogenicity in poultry. Virulence 2013, 4, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charostad, J.; Rukerd, M.R.Z.; Mahmoudvand, S.; Bashash, D.; Hashemi, S.M.A.; Nakhaie, M.; Zandi, K. A comprehensive review of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1: An imminent threat at doorstep. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 55, 102638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrough, E.R.; Magstadt, D.R.; Petersen, B.; Timmermans, S.J.; Gauger, P.C.; Zhang, J.; Siepker, C.; Mainenti, M.; Li, G.; Thompson, A.C.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Virus Infection in Domestic Dairy Cattle and Cats, United States, 2024. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhart, M.M.; Vanstreels, R.E.T.; Nelson, M.I.; Olivera, V.; Campagna, J.; Zavattieri, V.; Lemey, P.; Campagna, C.; Falabella, V.; Rimondi, A. Epidemiological data of an influenza A/H5N1 outbreak in elephant seals in Argentina indicates mammal-to-mammal transmission. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Results of Influenza Risk Assessment Tool. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/pandemic-flu/php/monitoring/irat-virus-summaries.html (accessed on 14 October 2025).
- WHO Updated Joint FAO/WHO/WOAH Public Health Assessment of Recent Influenza A(H5) Virus Events in Animals and People. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/updated-joint-fao-who-woah-assessment-of-recent-influenza-a(h5n1)-virus-events-in-animals-and-people_dec2024 (accessed on 14 October 2025).
- CDC Technical Report: June 2024 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Viruses. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/php/technical-report/h5n1-06052024.html#cdc_research_or_data_summary_explore_more-human-cases-of-ah5n1 (accessed on 14 October 2025).
- CDC Global Summary of Recent Human Cases of H5N1 Bird Flu. Global Summary of Recent Human Cases of H5N1 Bird Flu. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/spotlights/h5n1-summary-08042025.html (accessed on 17 November 2025).
- Lagan, P.; McKenna, R.; Baleed, S.; Hanna, B.; Barley, J.; McConnell, S.; Georgaki, A.; Sironen, T.; Kauppinen, A.; Gadd, T.; et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus infection in foxes with PB2-M535I identified as a novel mammalian adaptation, Northern Ireland, July 2023. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2300526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsmo, E.J.; Wünschmann, A.; Beckmen, K.B.; Broughton-Neiswanger, L.E.; Buckles, E.L.; Ellis, J.; Fitzgerald, S.D.; Gerlach, R.; Hawkins, S.; Ip, H.S.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Clade 2.3.4.4b Infections in Wild Terrestrial Mammals, United States, 2022. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobek, B.T.; Berhane, Y.; Nadeau, M.-S.; Embury-Hyatt, C.; Lung, O.; Xu, W.; Lair, S. Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Infections in 2 Free-Ranging Black Bears (Ursus americanus), Quebec, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 2145–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchieri, M.; Reid, S.M.; Dastderji, A.; Cracknell, J.; Warren, C.J.; Mollett, B.C.; Peers-Dent, J.; Schlachter, A.-L.D.; Mcginn, N.; Hepple, R.; et al. Rapid mortality in captive bush dogs (Speothos venaticus) caused by influenza A of avian origin (H5N1) at a wildlife collection in the United Kingdom. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2361792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, L.; Vreman, S.; Heutink, R.; Roose, M.; Venema, S.; E Pritz-Verschuren, S.B.; Rijks, J.M.; Gonzales, J.L.; A Germeraad, E.; Engelsma, M.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 Virus Infections in Wild Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) Show Neurotropism and Adaptive Virus Mutations. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0286722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, S.; Marandino, A.; Tomás, G.; Panzera, Y.; Wallau, G.L.; Dezordi, F.Z.; Carrazco-Montalvo, A.; Cassarino, M.; Russi, V.; Pérez, R.; et al. Infection of South American coatis (Nasua nasua) with highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus displaying mammalian adaptive mutations. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 195, 106895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessière, P.; Gaide, N.; Croville, G.; Crispo, M.; Fusade-Boyer, M.; Monsef, Y.A.; Dirat, M.; Beltrame, M.; Dendauw, P.; Lemberger, K.; et al. High pathogenicity avian influenza A (H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in a captive Tibetan black bear (Ursus thibetanus): Investigations based on paraffin-embedded tissues, France, 2022. Microbiol Spectr. 2024, 12, e0373623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiono, T.; Kobayashi, D.; Kobayashi, A.; Suzuki, T.; Satake, Y.; Harada, R.; Matsuno, K.; Sashika, M.; Ban, H.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Virological, pathological, and glycovirological investigations of an Ezo red fox and a tanuki naturally infected with H5N1 high pathogenicity avian influenza viruses in Hokkaido, Japan. Virology 2023, 578, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-M.; Heo, G.-B.; An, S.-H.; Lee, H.; Park, E.; Cha, R.M.; Jang, Y.Y.; Sagong, M.; Kim, A.-Y.; Kim, J.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Infection in Cats, South Korea, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirolo, M.; Pohlmann, A.; Ahrens, A.K.; Kühl, B.; Rubio-Garcìa, A.; Kramer, K.; Meinfelder, U.; Rosenberger, T.; Morito, H.L.; Beer, M.; et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A virus (HPAIV) H5N1 infection in two European grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) with encephalitis. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, e2257810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lair, S.; Quesnel, L.; Signore, A.V.; Delnatte, P.; Embury-Hyatt, C.; Nadeau, M.-S.; Lung, O.; Ferrell, S.T.; Michaud, R.; Berhane, Y. Outbreak of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus in Seals, St. Lawrence Estuary, Quebec, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Jensen, T.K.; Hammer, A.S.V.; Ovesen, M.T.; Larsen, L.E. Characterization of high pathogenicity avian influenza H5Nx viruses from a wild harbor seal and red foxes in Denmark, 2021 and 2022. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsson, E.; Zohari, S.; Roos, A.; Banihashem, F.; Bröjer, C.; Neimanis, A. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus in a Harbor Porpoise, Sweden. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, L.; Fusaro, A.; Kuiken, T.; Mirinavičiūtė, G.; Ståhl, K.; Staubach, C.; Svartström, O.; Terregino, C.; Willgert, K.; Delacourt, R.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview March–June 2024. EFSA J. 2024, 22, 8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, M.; Fernández, A.; Ariyama, N.; Colom-Rivero, A.; Rivera, C.; Nuñez, P.; Sanhueza, P.; Johow, M.; Araya, H.; Torres, J.C.; et al. Mass mortality event in South American sea lions (Otaria flavescens) correlated to highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1 outbreak in Chile. Vet. Q. 2023, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, C.; Colom, A.; Fernández, A.; Alonso-Almorox, P.; Andrada, M.; Lombardo, D.; Sierra, E. Pathology of Influenza A (H5N1) infection in pinnipeds reveals novel tissue tropism and vertical transmission. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimmelmayr, R.; Rotstein, D.; Torchetti, M.K.; Gerlach, R. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Infection in Free-Ranging Polar Bear, Alaska, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauwen, E.J.A.; Herfst, S.; Leijten, L.M.; van Run, P.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Linster, M.; Bodewes, R.; Kreijtz, J.H.C.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; et al. The multibasic cleavage site in H5N1 virus is critical for systemic spread along the olfactory and hematogenous routes in ferrets. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3975–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Boltz, D.; Sturm-Ramirez, K.; Shepherd, K.R.; Jiao, Y.; Webster, R.; Smeyne, R.J. Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus can enter the central nervous system and induce neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14063–14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krassner, M.M.; Kauffman, J.; Sowa, A.; Cialowicz, K.; Walsh, S.; Farrell, K.; Crary, J.F.; McKenzie, A.T. Postmortem changes in brain cell structure: A review. Free Neuropathol. 2023, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.L.; Arruda, B.; Palmer, M.V.; Boggiatto, P.; Davila, K.S.; Buckley, A.; Zanella, G.C.; Snyder, C.A.; Anderson, T.K.; Hutter, C.R.; et al. Dairy cows inoculated with highly pathogenic avian influenza virus H5N1. Nature 2025, 637, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfes, M.A.; Kniss, K.; Kirby, M.K.; Garg, S.; Reinhart, K.; Davis, C.T.; Murray, E.L.; Wadford, D.A.; Harriman, K.; Zhu, S.; et al. Human infections with highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) viruses in the United States from March 2024 to May 2025. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 3889–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteranderl, C.; Herold, S.; Schmoldt, C. Human Influenza Virus Infections. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.; Smeyne, R.J.; Jang, H.; Miller, B.; Okun, M.S. Parkinsonism and neurological manifestations of influenza throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Park. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riel, D.; Leijten, L.M.; Verdijk, R.M.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.; van der Vries, E.; van Rossum, A.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Kuiken, T. Evidence for influenza virus CNS invasion along the olfactory route in an immunocompromised infant. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus: Interim Recommendations for Prevention, Monitoring, and Public Health Investigations. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/prevention/hpai-interim-recommendations.html (accessed on 17 November 2025).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larsen, S.V.; Israelson, R.; Torp, C.; Larsen, L.E.; Jensen, H.E.; Kristensen, C. Transmission, Pathological and Clinical Manifestations of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A Virus in Mammals with Emphasis on H5N1 Clade 2.3.4.4b. Viruses 2025, 17, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121548
Larsen SV, Israelson R, Torp C, Larsen LE, Jensen HE, Kristensen C. Transmission, Pathological and Clinical Manifestations of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A Virus in Mammals with Emphasis on H5N1 Clade 2.3.4.4b. Viruses. 2025; 17(12):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121548
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarsen, Sandra Vibeke, Rebekka Israelson, Charlotte Torp, Lars Erik Larsen, Henrik Elvang Jensen, and Charlotte Kristensen. 2025. "Transmission, Pathological and Clinical Manifestations of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A Virus in Mammals with Emphasis on H5N1 Clade 2.3.4.4b" Viruses 17, no. 12: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121548
APA StyleLarsen, S. V., Israelson, R., Torp, C., Larsen, L. E., Jensen, H. E., & Kristensen, C. (2025). Transmission, Pathological and Clinical Manifestations of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A Virus in Mammals with Emphasis on H5N1 Clade 2.3.4.4b. Viruses, 17(12), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121548





